Hydrophilic Auristatin Glycoside Payload Enables Improved Antibody-Drug Conjugate Efficacy and Biocompatibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Drug-Linker Compounds
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Antibody-Drug Conjugates
2.3. Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography
2.4. Aggregation Assay
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.6. In Vivo Xenograft Experiments
3. Results
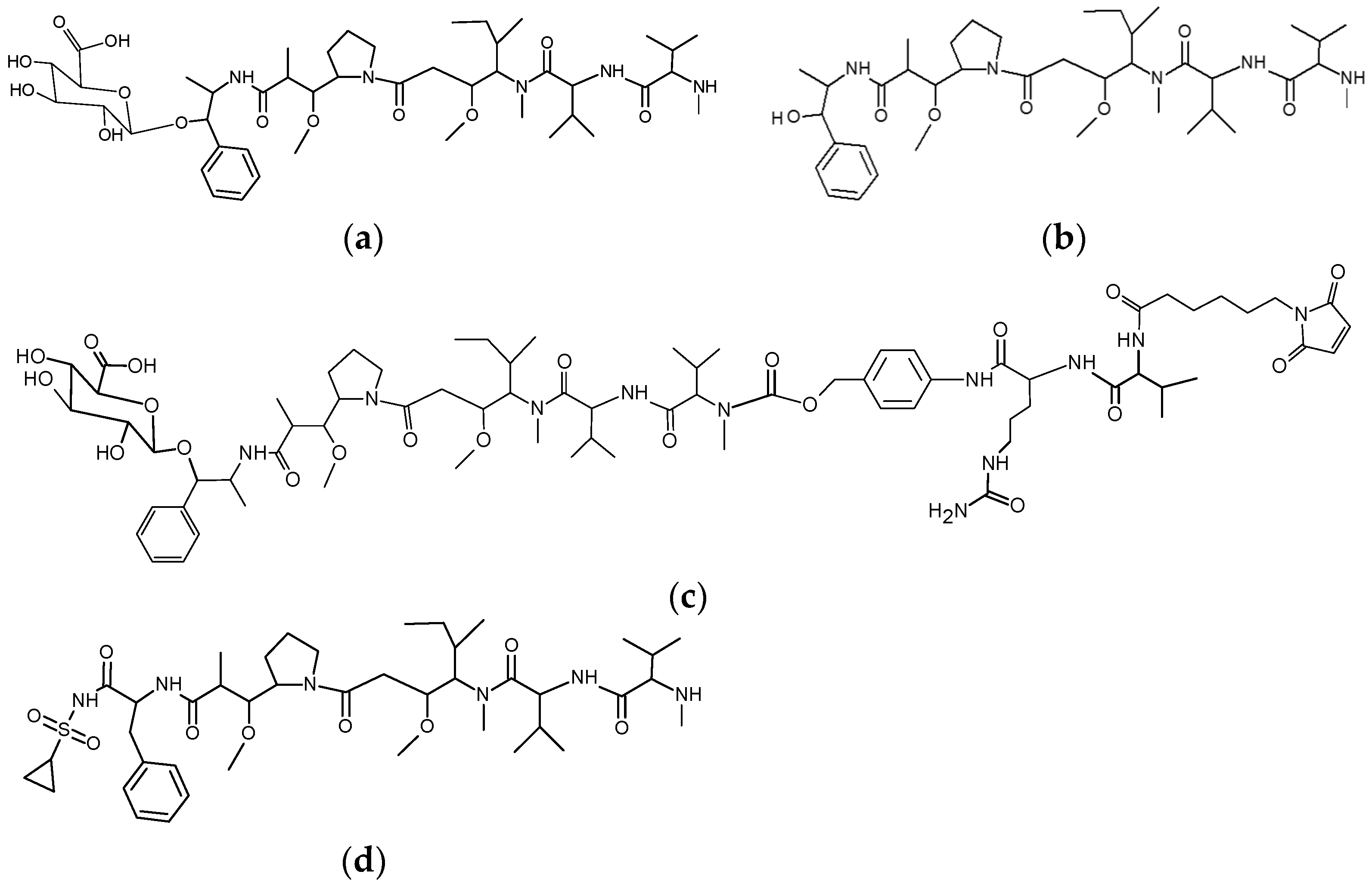
3.1. Glycoside-Modified Auristatin ADCs
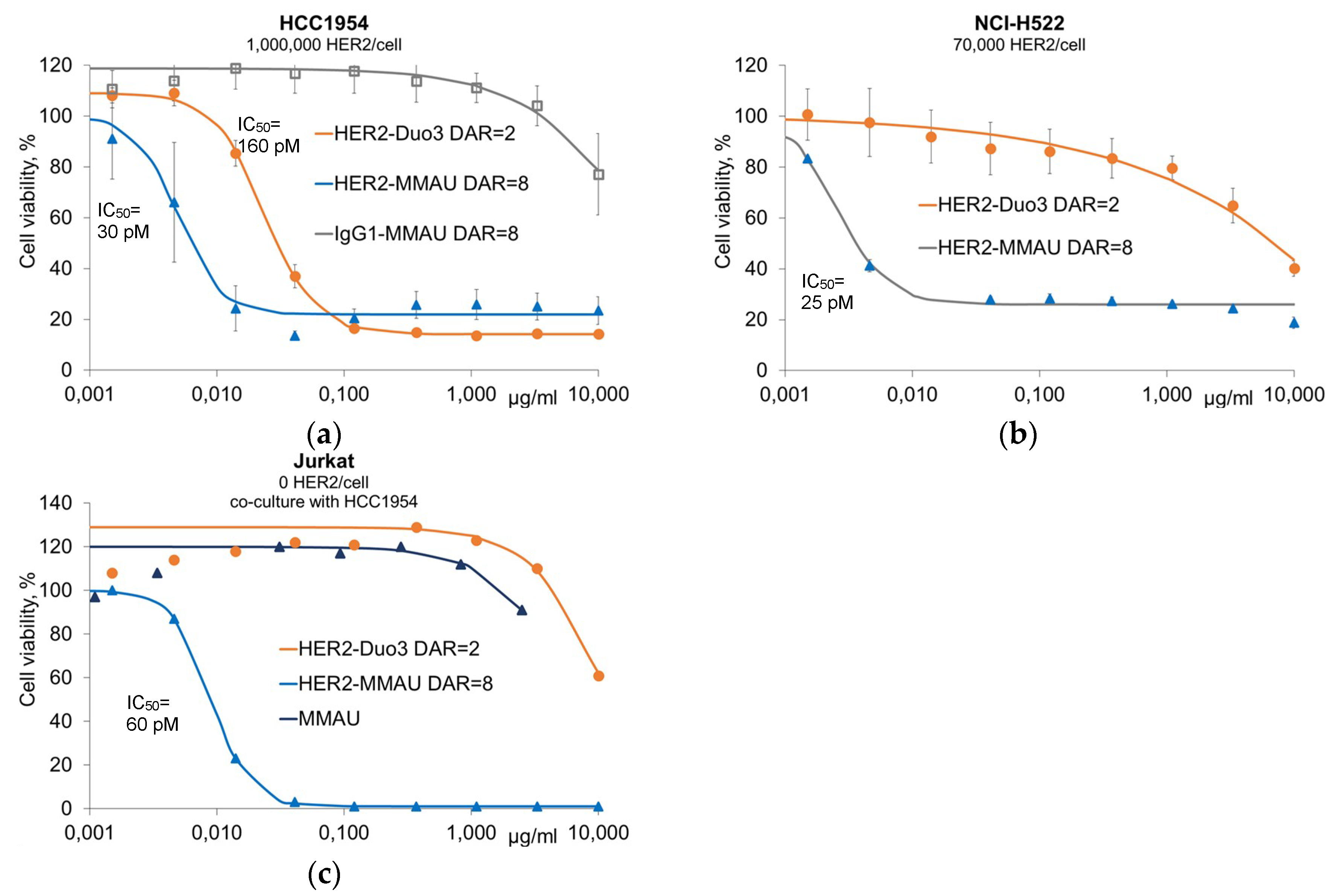
3.2. In Vitro Efficacy Evaluation
3.3. In Vivo Experiments
3.4. Efficacy in In Vitro 3D PDX Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, J.M.; Morris, C.Q. Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for personalized treatment of solid tumors: A review. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ponte, J.F.; Yoder, N.C.; Laleau, R.; Coccia, J.; Lanieri, L.; Qiu, Q.; Wu, R.; Hong, E.; Bogalhas, M.; et al. Effects of drug-antibody ratio on pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, efficacy, and tolerability of antibody-maytansinoid conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblett, K.J.; Senter, P.D.; Chace, D.F.; Sun, M.M.; Lenox, J.; Cerveny, C.G.; Kissler, K.M.; Bernhardt, S.X.; Kopcha, A.K.; Zabinski, R.F.; et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, R.P.; Bovee, T.D.; Doronina, S.O.; Burke, P.J.; Hunter, J.H.; Neff-LaFord, H.D.; Jonas, M.; Anderson, M.E.; Setter, J.R.; Senter, P.D. Reducing hydrophobicity of homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates improves pharmacokinetics and therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helin, J.; Saarinen, J.; Satomaa, T.; Ekholm, F.S. Saccharide Derivative of a Toxic Payload and Antibody Conjugates Thereof. International Patent Application No. PCT/FI2015/050471, 7 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De Goeij, B.E.C.G.; Satijn, D.; Freitag, C.M.; Wubbolts, R.; Bleeker, W.K.; Khasanov, A.; Zhu, T.; Chen, G.; Miao, D.; van Berkel, P.H.C.; et al. High turnover of tissue factor enables efficient intracellular delivery of antibody-drug conjugates. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekholm, F.S.; Pynnönen, H.; Vilkman, A.; Pitkänen, V.; Helin, J.; Saarinen, J.; Satomaa, T. Introducing glycolinkers for the functionalization of cytotoxic drugs and applications in antibody-drug conjugation chemistry. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandercock, A.M.; Rust, S.; Guillard, S.; Sachsenmeier, K.; Holoweckyj, N.; Hay, C.; Flynn, M.; Huang, Q.; Yan, K.; Herpers, B.; et al. Identification of anti-tumour biologics using primary tumour models, 3-D phenotypic screening and image-based multi-parametric profiling. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruokonen, S.K.; Redón, M.; Pitkänen, V.; Helin, J.; Satomaa, T.; Wiedmer, S.K.; Ekholm, F.S. Capillary electrophoresis experiments. Unpublished work. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Gundersen, G.W.; Fernandez, N.F.; Wang, Z.; Monteiro, C.D.; McDermott, M.G.; Ma’ayan, A. The harmonizome: A collection of processed datasets gathered to serve and mine knowledge about genes and proteins. Database 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Marhoul, J.; Jacobson, F. Statistical modeling of the drug load distribution on trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), a lysine-linked antibody drug conjugate. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhospice, F.; Brégeon, D.; Belmant, C.; Dennler, P.; Chiotellis, A.; Fischer, E.; Gauthier, L.; Boëdec, A.; Rispaud, H.; Savard-Chambard, S.; et al. Site-specific conjugation of monomethyl auristatin E to anti-CD30 antibodies improves their pharmacokinetics and therapeutic index in rodent models. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokter, W.; Ubink, R.; van der Lee, M.; van der Vleuten, M.; van Achterberg, T.; Jacobs, D.; Loosveld, E.; van den Dobbelsteen, D.; Egging, D.; Mattaar, E.; et al. Preclinical profile of the HER2-targeting ADC SYD983/SYD985: Introduction of a new duocarmycin-based linker-drug platform. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Amphlett, G.; Blättler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Zhang, W. Structural characterization of the maytansinoid-monoclonal antibody immunoconjugate, huN901-DM1, by mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronina, S.O.; Mendelsohn, B.A.; Bovee, T.D.; Cerveny, C.G.; Alley, S.C.; Meyer, D.L.; Oflazoglu, E.; Toki, B.E.; Sanderson, R.J.; Zabinski, R.F.; et al. Enhanced activity of monomethylauristatin F through monoclonal antibody delivery: Effects of linker technology on efficacy and toxicity. Bioconjugate Chem. 2006, 17, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Emmerton, K.K.; Jonas, M.; Zhang, X.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Setter, J.R.; Nicholas, N.D.; Okeley, N.M.; Lyon, R.P.; Benjamin, D.R.; et al. Intracellular released payload influences potency and bystander-killing effects of antibody-drug conjugates in preclinical models. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2710–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Senter, P.D.; Lewis Phillips, G.D. Trastuzumab-auristatin immunoconjugates inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in human breast cancer cells in vitro. Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 46, 1456. [Google Scholar]
- Doronina, S.O.; Toki, B.E.; Torgov, M.Y.; Mendelsohn, B.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Chace, D.F.; DeBlanc, R.L.; Gearing, R.P.; Bovee, T.D.; Siegall, C.B.; et al. Development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorywalska, M.; Dushin, R.; Moine, L.; Farias, S.E.; Zhou, D.; Navaratnam, T.; Lui, V.; Hasa-Moreno, A.; Casas, M.G.; Tran, T.T.; et al. Molecular basis of valine-citrulline-PABC linker instability in site-specific ADCs and its mitigation by linker design. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, W.H.; Anlyan, A.J. Comparison of the β-glucuronidase activity of normal, tumor, and lymph node tissues of surgical patients. Science 1947, 106, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosslet, K.; Straub, R.; Blumrich, M.; Czech, J.; Gerken, M.; Sperker, B.; Kroemer, H.K.; Gesson, J.P.; Koch, M.; Monneret, C. Elucidation of the mechanism enabling tumor selective prodrug monotherapy. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maderna, A.; Doroski, M.D.; Chen, Z.; Risley, H.L.; Casavant, J.M.; O’Donnell, C.C.J.; Porte, A.M.; Subramanyam, C. Bifunctional Cytotoxic Agents. International Patent Application No. PCT/IB2015/050280, 30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.C.; Andreyka, J.B.; Bernhardt, S.X.; Kissler, K.M.; Kline, T.; Lenox, J.S.; Moser, R.F.; Nguyen, M.T.; Okeley, N.M.; Stone, I.J.; et al. Development and properties of β-glucuronide linkers for monoclonal antibody-drug conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 2006, 17, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño, A.M.; Lock-Hock, N.; Steiner, R.D.; Graham, B.H.; Szlago, M.; Greenstein, R.; Pineda, M.; Gonzalez-Meneses, A.; Çoker, M.; Bartholomew, D.; et al. Clinical course of sly syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type VII). J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satomaa, T.; Pynnönen, H.; Vilkman, A.; Kotiranta, T.; Pitkänen, V.; Heiskanen, A.; Herpers, B.; Price, L.S.; Helin, J.; Saarinen, J. Hydrophilic Auristatin Glycoside Payload Enables Improved Antibody-Drug Conjugate Efficacy and Biocompatibility. Antibodies 2018, 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7020015
Satomaa T, Pynnönen H, Vilkman A, Kotiranta T, Pitkänen V, Heiskanen A, Herpers B, Price LS, Helin J, Saarinen J. Hydrophilic Auristatin Glycoside Payload Enables Improved Antibody-Drug Conjugate Efficacy and Biocompatibility. Antibodies. 2018; 7(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatomaa, Tero, Henna Pynnönen, Anja Vilkman, Titta Kotiranta, Virve Pitkänen, Annamari Heiskanen, Bram Herpers, Leo S. Price, Jari Helin, and Juhani Saarinen. 2018. "Hydrophilic Auristatin Glycoside Payload Enables Improved Antibody-Drug Conjugate Efficacy and Biocompatibility" Antibodies 7, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7020015
APA StyleSatomaa, T., Pynnönen, H., Vilkman, A., Kotiranta, T., Pitkänen, V., Heiskanen, A., Herpers, B., Price, L. S., Helin, J., & Saarinen, J. (2018). Hydrophilic Auristatin Glycoside Payload Enables Improved Antibody-Drug Conjugate Efficacy and Biocompatibility. Antibodies, 7(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7020015




