Integration of Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction as Cell Harvest and Capture Operation in the Manufacturing Process of Monoclonal Antibodies
Abstract
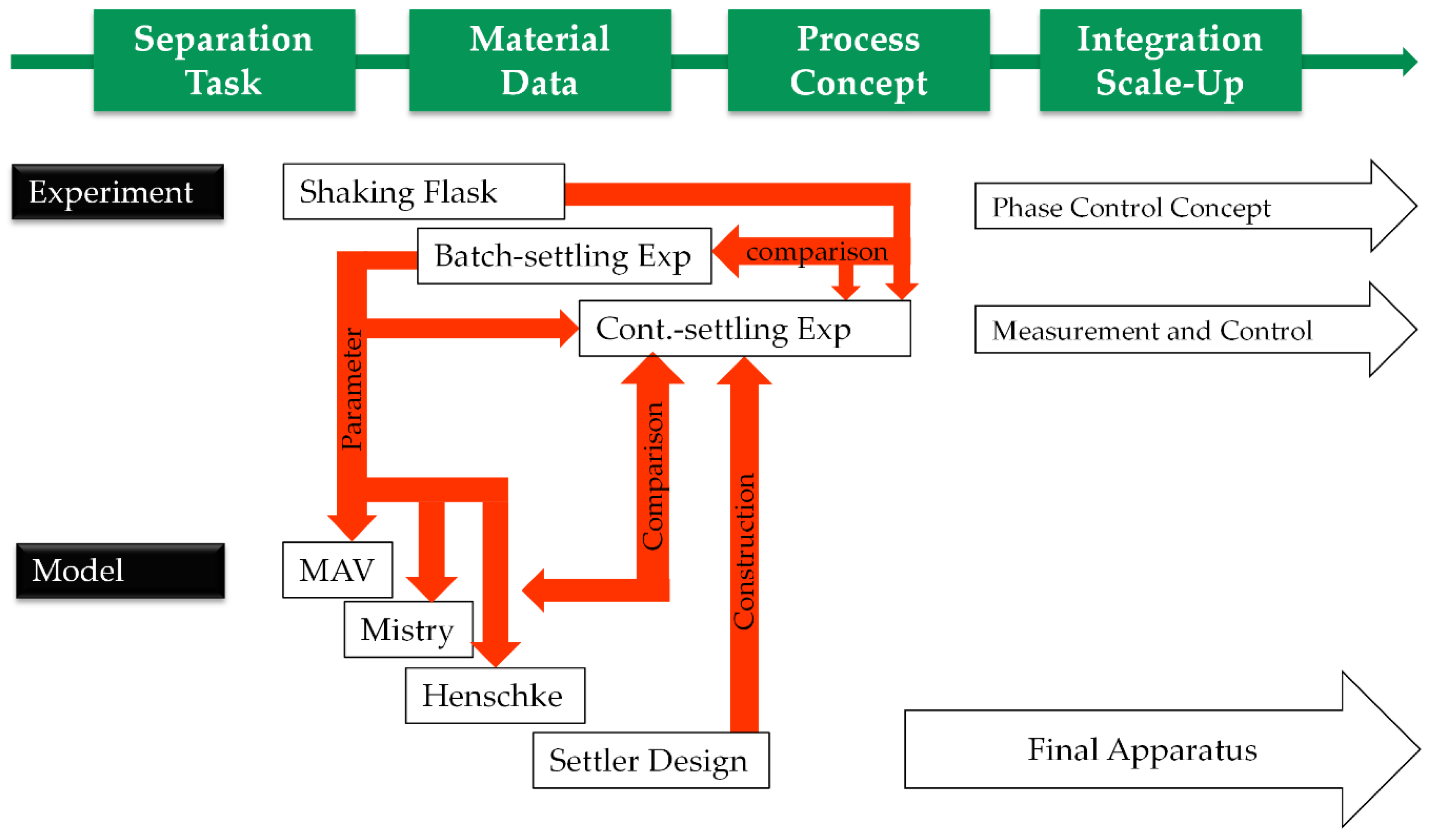
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. General Considerations
2.2. Process Development
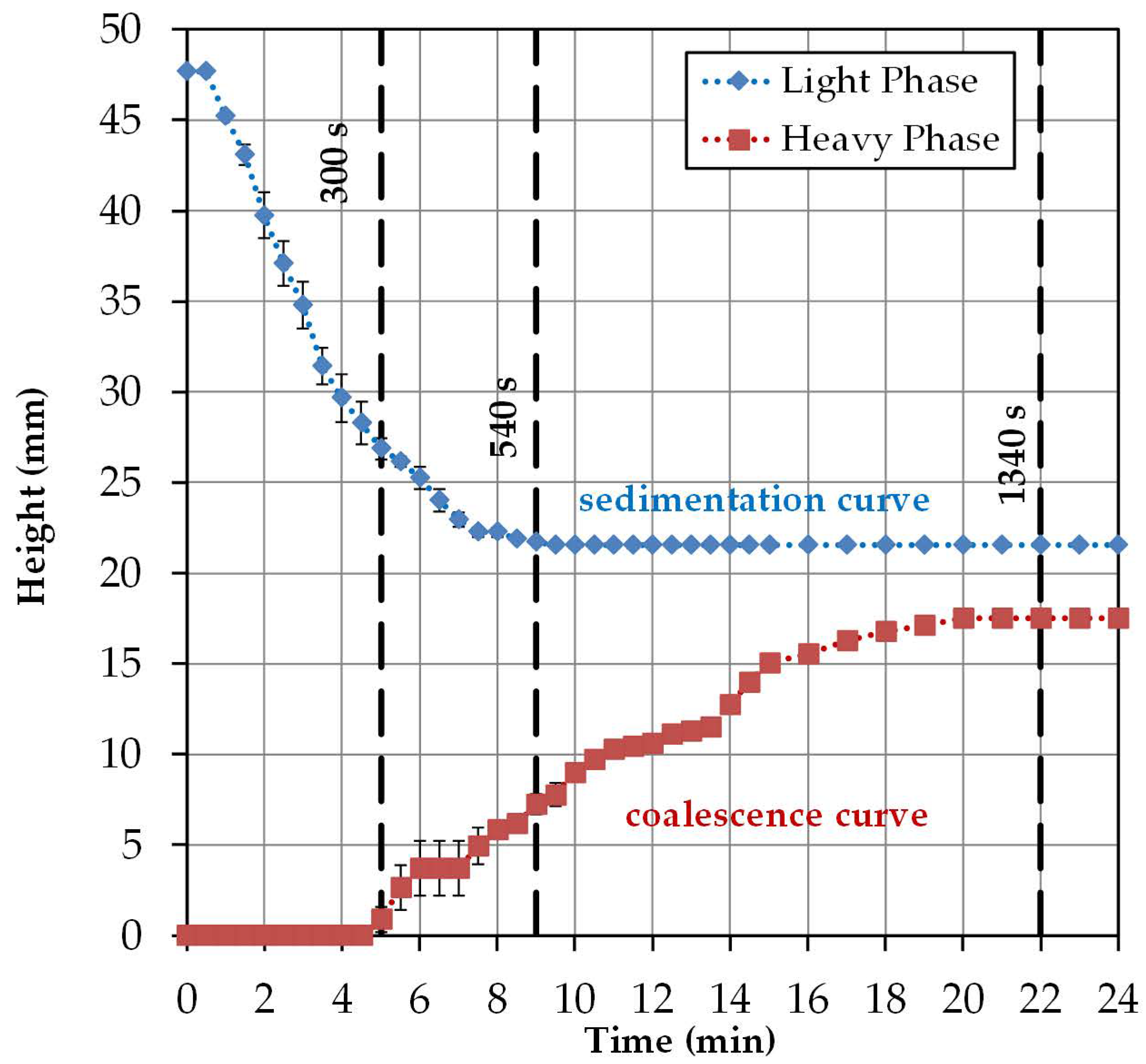
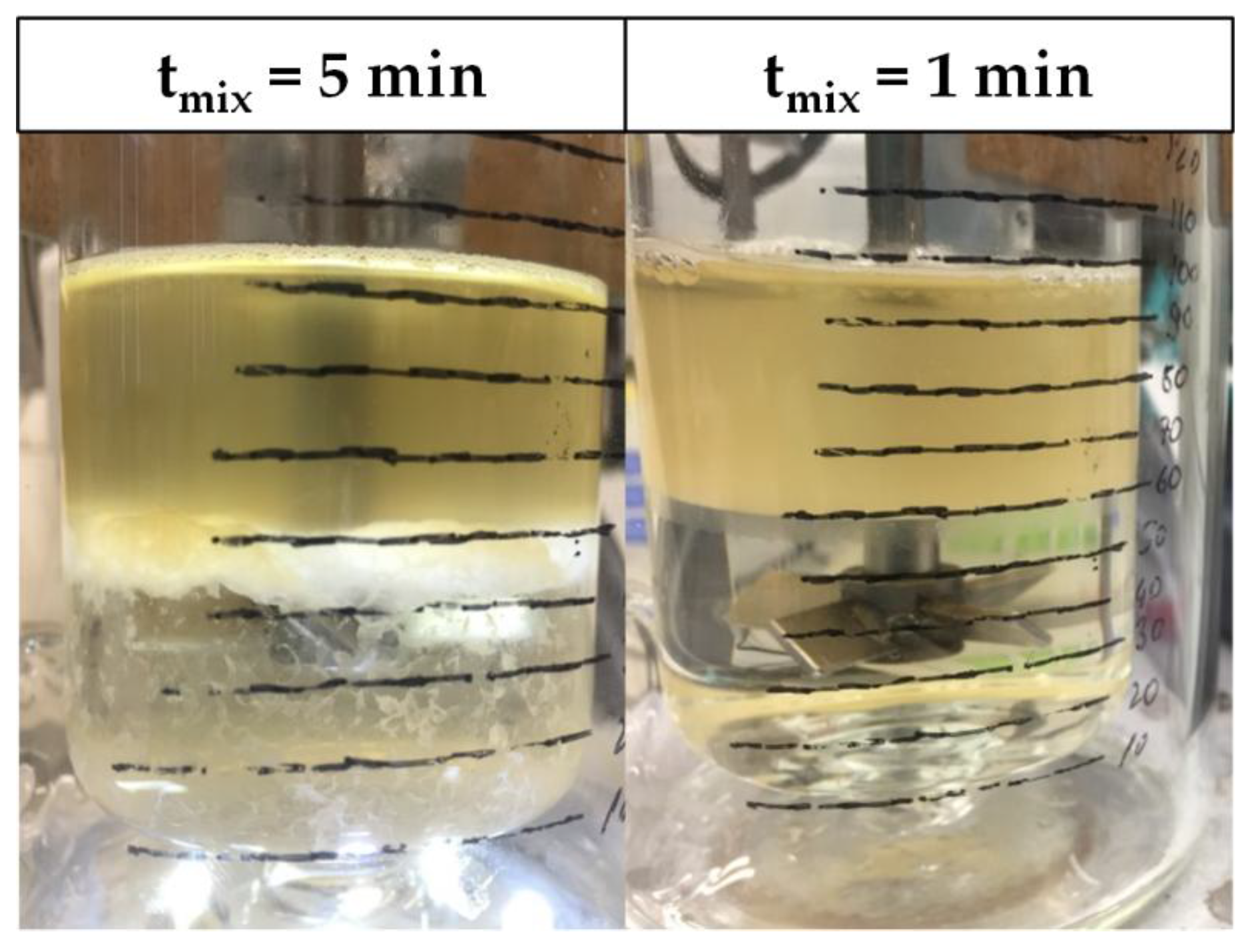
2.3. Batch-Settling Behavior
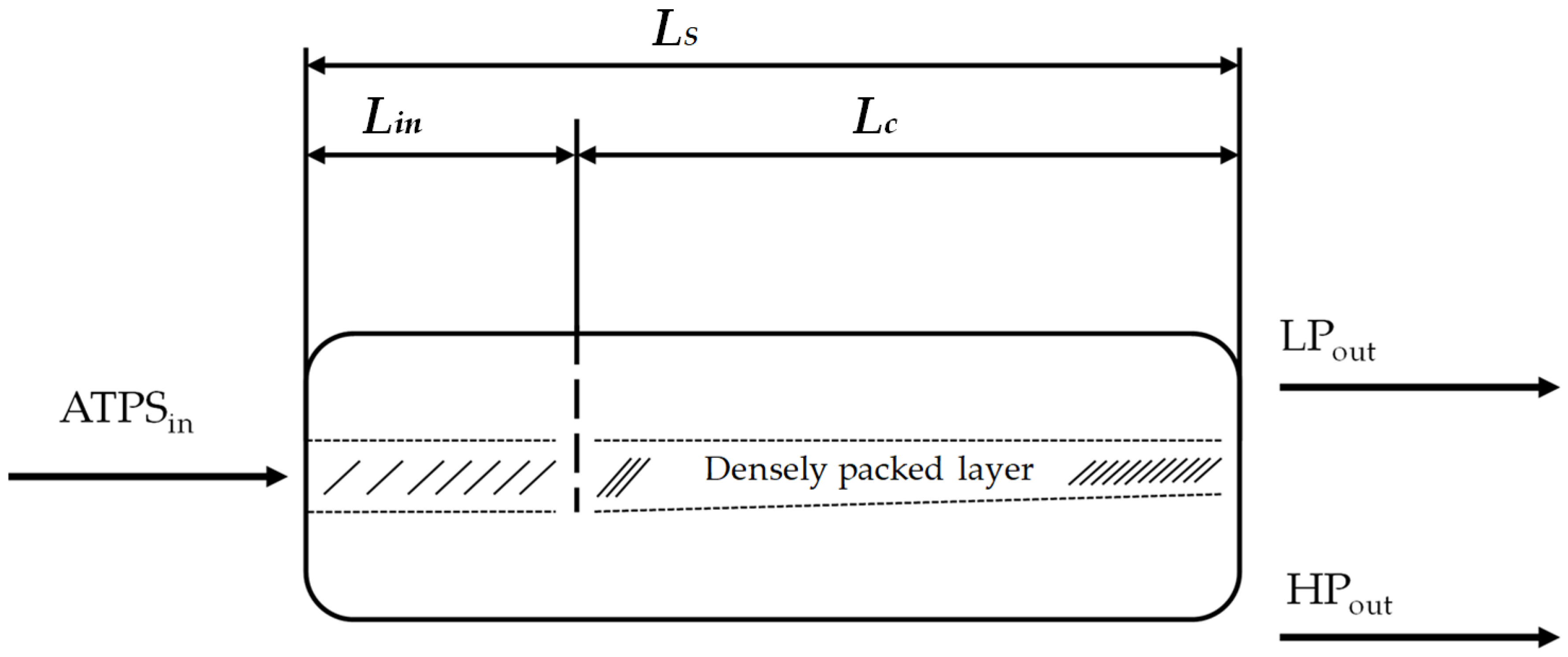
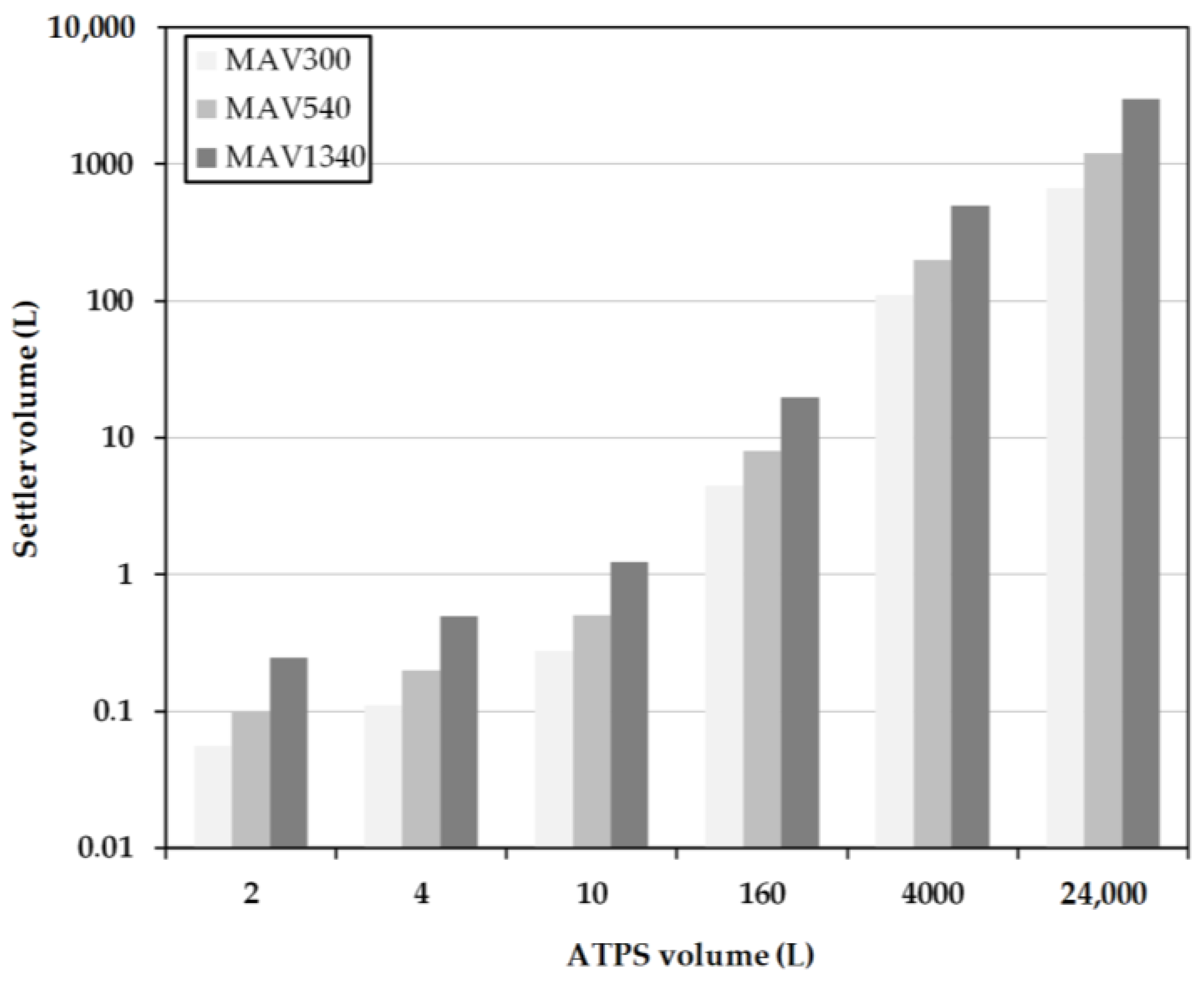
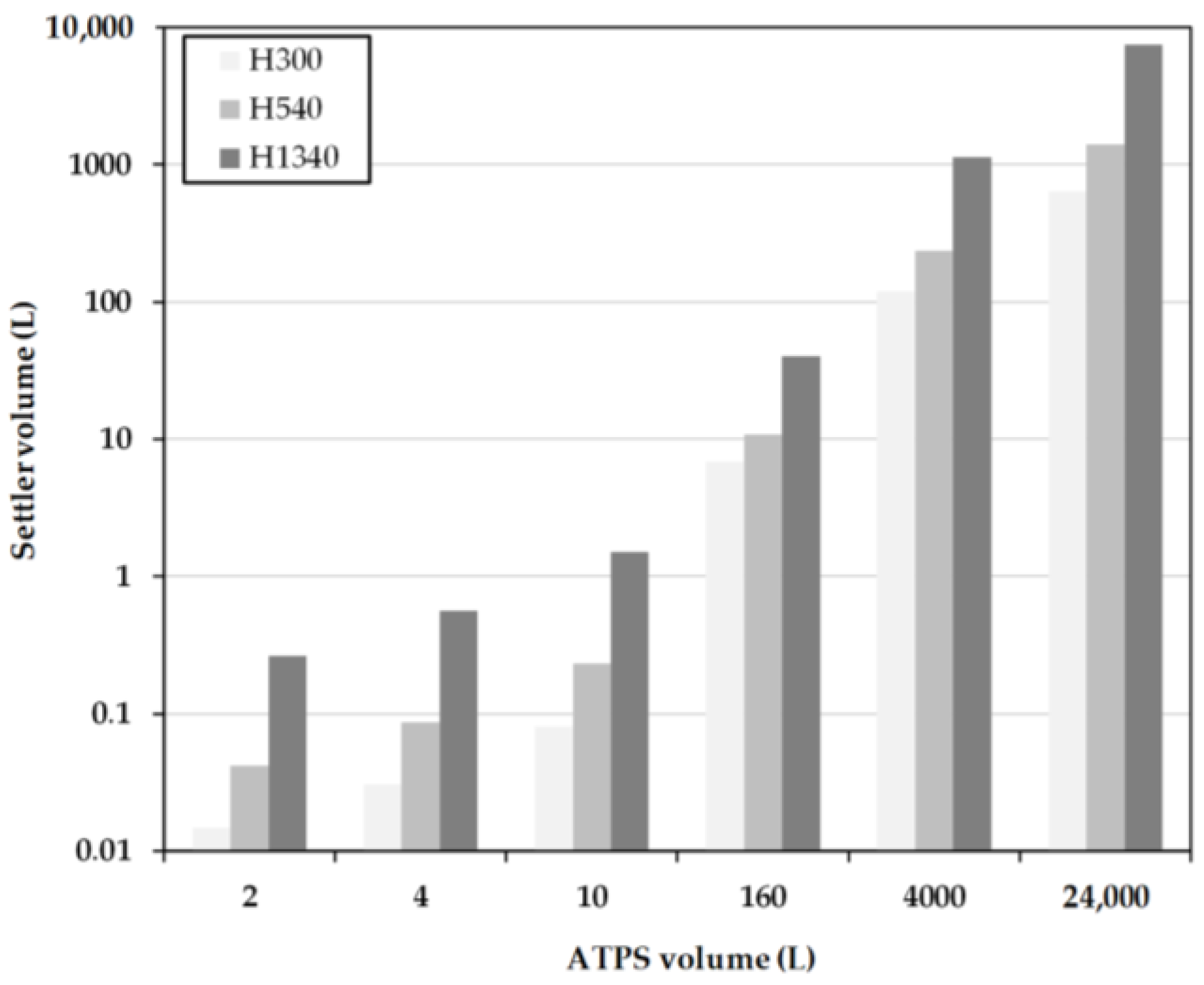
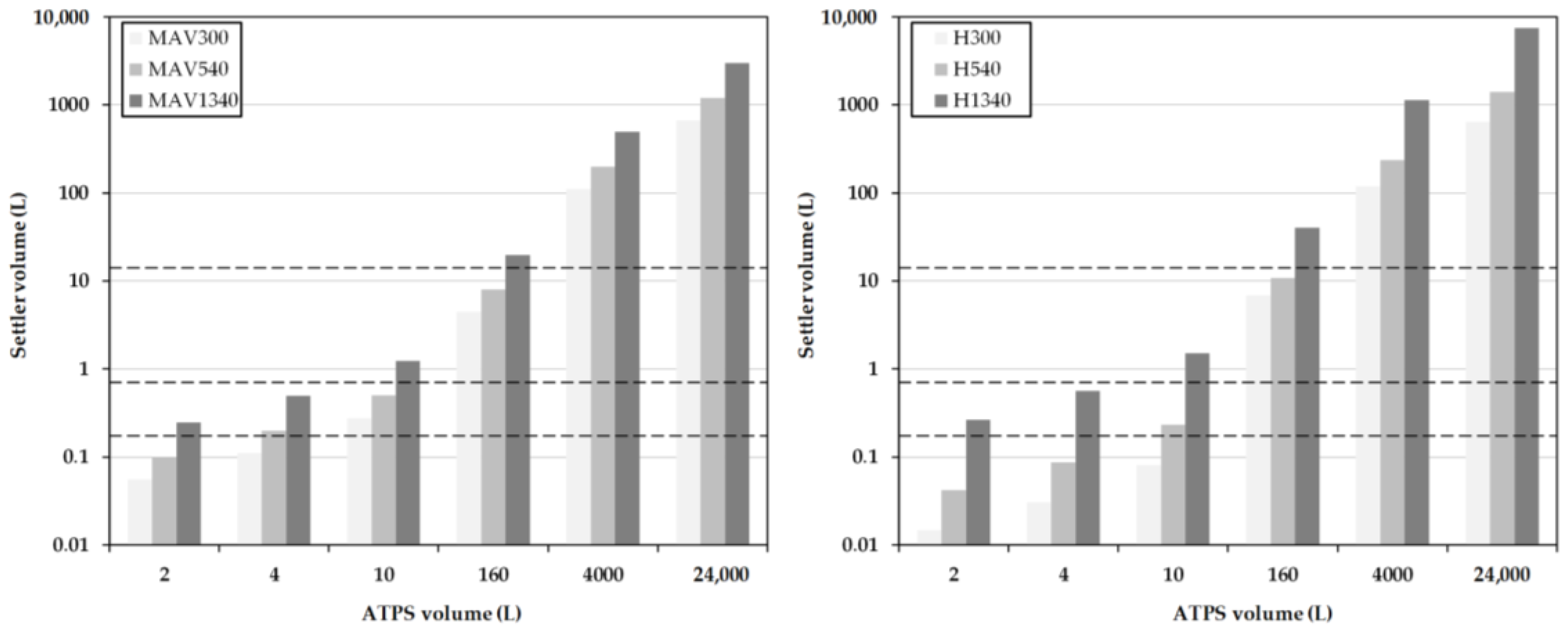
2.4. Early Prediction of Settler Dimensions
2.5. Henschke Method for Settler Dimensioning
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. System Selection and Batch-Settling Experiments
3.2. Model-Based Design
- Hp/DS = 0.54 at a cut-off time of 300 s,
- Hp/DS = 0.303 at a separation time of 540 s,
- Hp/DS = 0.1 with a separation time of 1340 s.
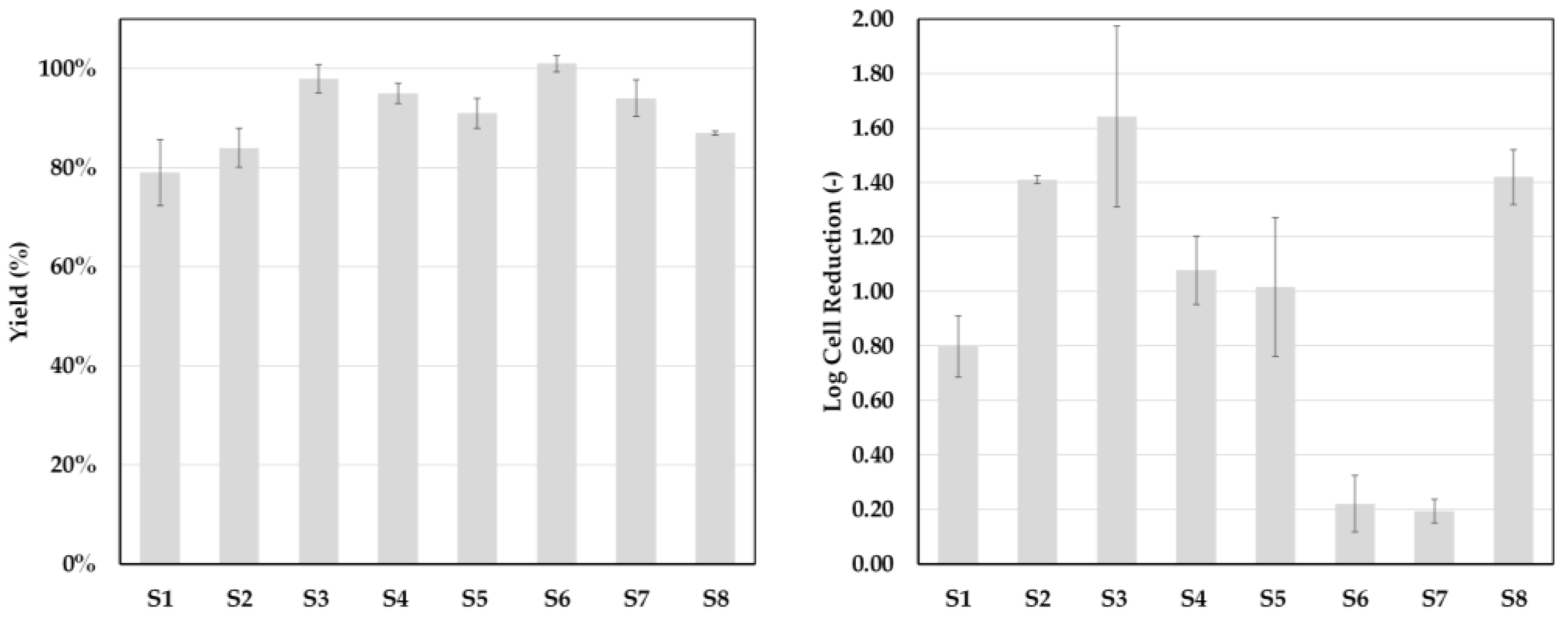
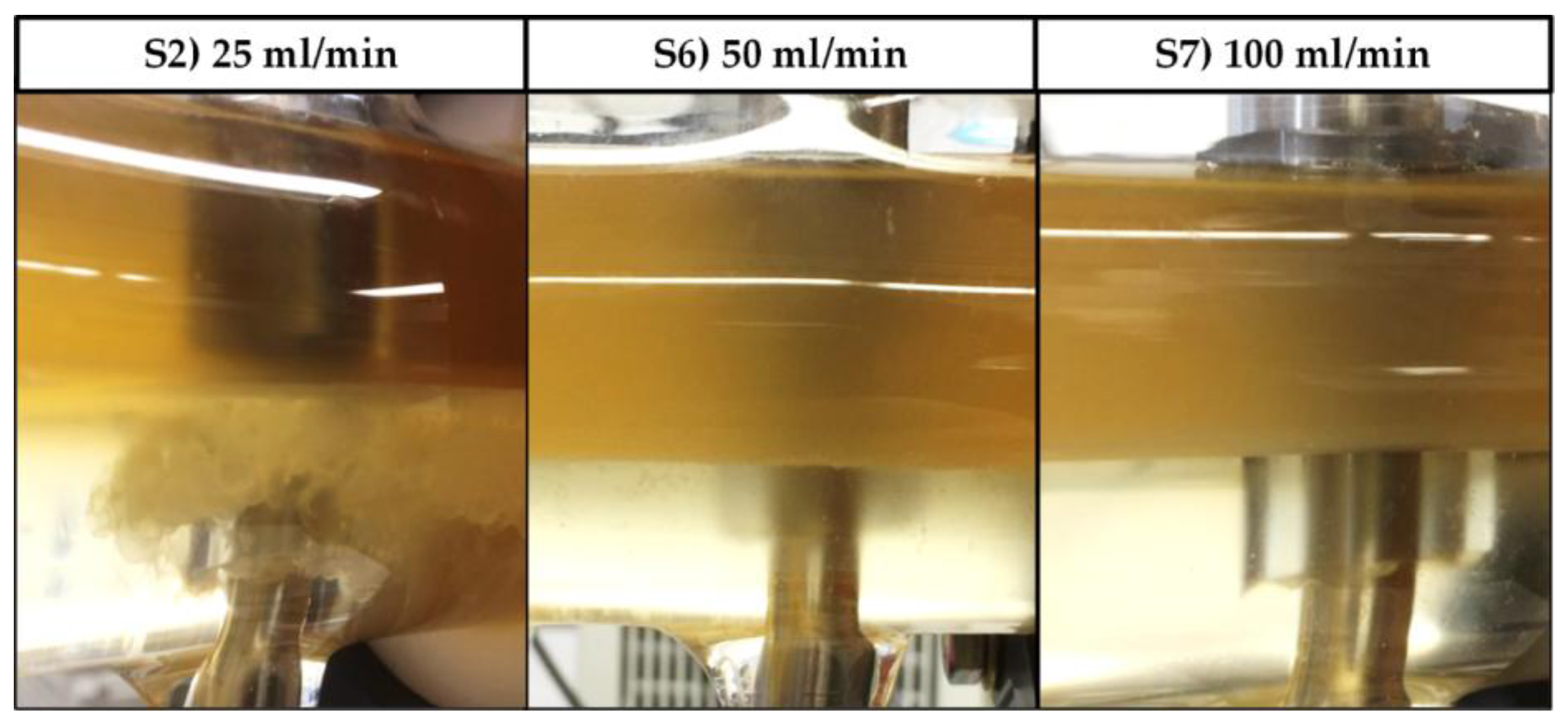
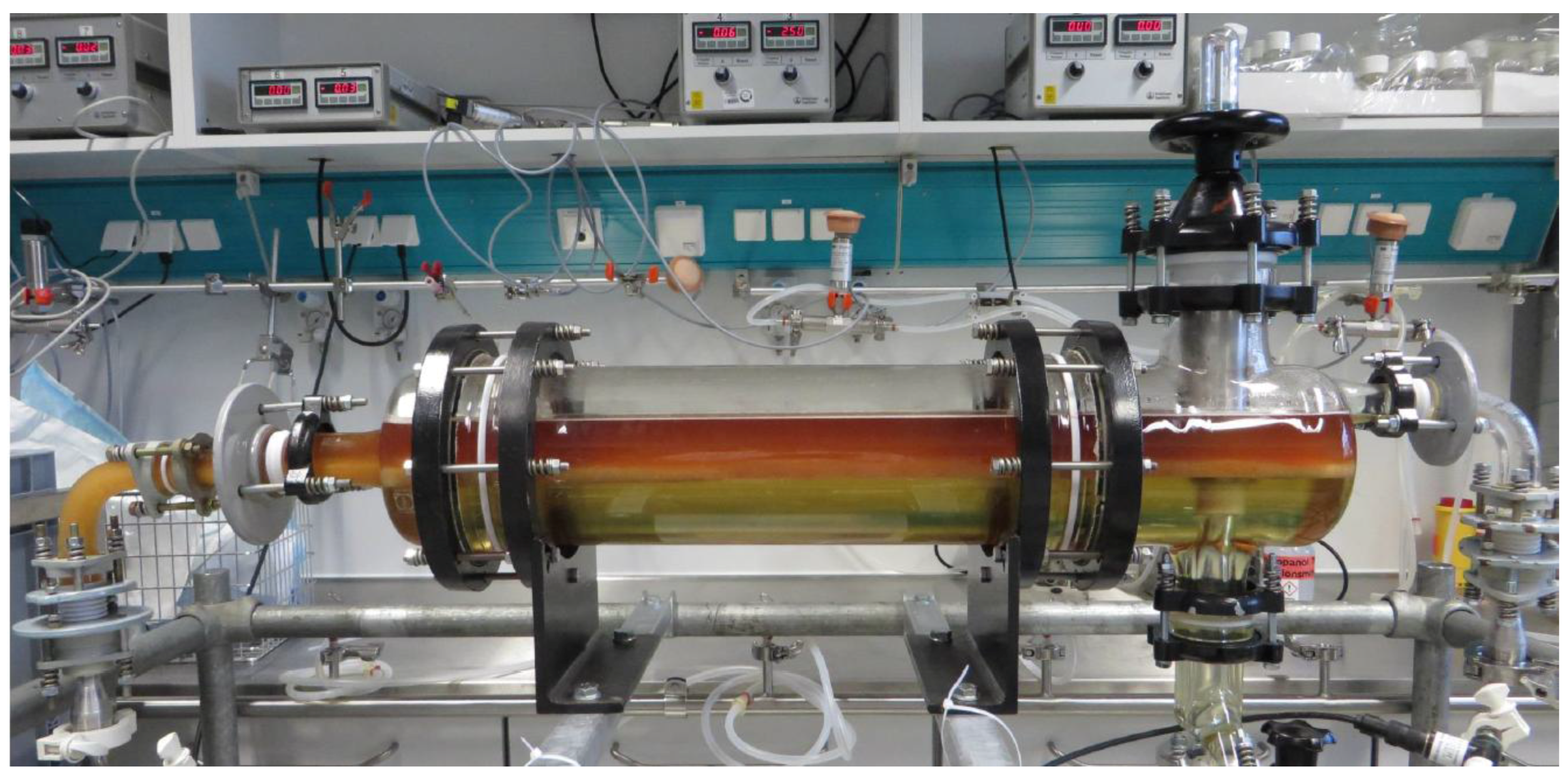
3.3. Process Performance
3.4. Comparison of Experiment and Model
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
4.2. Cultivation
4.3. Analytical Procedure
4.4. Procedures
4.4.1. Shaking Flask Experiments
4.4.2. Batch-Settling Experiments
4.4.3. Continuous-Settling Experiments
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Arunkumar, A.; Chollangi, S.; Tan, Z.G.; Borys, M.; Li, Z.J. Clarification technologies for monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes: Current state and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luechau, F.; Ling, T.C.; Lyddiatt, A. A descriptive model and methods for up-scaled process routes for interfacial partition of bioparticles in aqueous two-phase systems. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 50, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.-Å. Particle fractionation in liquid two-phase systems; the composition of some phase systems and the behaviour of some model particles in them; application to the isolation of cell walls from microorganisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1958, 27, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.-Å. Partition of Cell Particles and Macromolecules: Separation and Purification of Biomolecules, Cell Organelles, Membranes, and Cells in Aqueous Polymer Two-Phase Systems and Their Use in Biochemical Analysis and Biotechnology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jauregi, P.; Hoeben, M.A.; van der Lans, R.G.J.M.; Kwant, G.; van der Wielen, L.A.M. Recovery of small bioparticles by interfacial partitioning. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rito-Palomares, M.; Lyddiatt, A. Practical implementation of aqueous two-phase processes for protein recovery from yeast. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennison, C.; Lovrien, R. Three phase partitioning: Concentration and purification of proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 1997, 11, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Khoiroh, I.; Ling, T.C.; Show, P.L. Aqueous Two-Phase Flotation for the Recovery of Biomolecules. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 45, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, S.; Strube, J. Challenges in biotechnology production—Generic processes and process optimization for monoclonal antibodies. Chem. Eng. Process. 2005, 44, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.M.; Rosa, P.A.J.; Ferreira, I.F.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Chromatography-free recovery of biopharmaceuticals through aqueous two-phase processing. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobel, S.; Helling, C.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Design and Operation of Continuous Countercurrent Chromatography in Biotechnological Production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9169–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strube, J.; Grote, F.; Josch, J.P.; Ditz, R. Process Development and Design of Downstream Processes. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2011, 83, 1044–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesel, A.; Schmidt-Traub, H.; Lenz, J.; Strube, J. Modelling gradient elution of bioactive multicomponent systems in non-linear ion-exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1006, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, M.; Britsch, L.; Strube, J. Continuous preparative liquid chromatography in the downstrem processing of biotechnological products. Acta Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Trends in upstream and downstream process development for antibody manufacturing. Bioengineering 2014, 1, 188–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.-H.; Chang, W.-J.; Hong, H.; Lim, S.-M.; Kim, D.-I.; Koo, Y.-M. Continuous-flow fractionation of animal cells in microfluidic device using aqueous two-phase extraction. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, R.C.V.; Medronho, R.A.; Castilho, L.R. Separation of CHO cells using hydrocyclones. Cytotechnology 2008, 56, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Protein partitioning equilibrium between the aqueous poly(ethylene glycol) and salt phases and the solid protein phase in poly(ethylene glycol)-salt two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 685, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.A.J.; Azevedo, A.M.; Sommerfeld, S.; Mutter, M.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Bäcker, W. Application of aqueous two-phase systems to antibody purification: A multi-stage approach. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Theoretical and Experimental Evaluation of Hydrophobicity of Proteins to Predict their Partitioning Behavior in Aqueous Two Phase Systems: A Review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asenjo, J.A.; Andrews, B.A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: A perspective. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8826–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polson, A.; Potgieter, G.M.; Largier, J.F.; Mears, G.E.F.; Joubert, F.J. The fractionation of protein mixtures by linear polymers of high molecular weight. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1964, 82, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggersgluess, J.; Wellsandt, T.; Strube, J. Integration of aqueous two-phase extraction into downstream processing. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, A.L.; Raquel Aires-Barros, M.; Azevedo, A.M. Partitioning in Aqueous Two-Phase Systems: Fundamentals, Applications and Trends. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 45, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Sattar, A.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; et al. Aqueous two-phase system (ATPS): An overview and advances in its applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2016, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, D.P.C.; Campos, S.R.R.; Azevedo, A.M.; Baptista, A.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Predicting protein partition coefficients in aqueous two phase system. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.; Murty, V.R.; Thivaharan, V.; Rajasekar, V.; Ramesh, V. Aqueous Two Phase Systems for the Recovery of Biomolecules—A Review. SCIT 2011, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rito-Palomares, M. Practical application of aqueous two-phase partition to process development for the recovery of biological products. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 807, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. DoE based integration approach of upstream and downstream processing regarding HCP and ATPE as harvest operation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia-Saloma, E.; Vázquez-Villegas, P.; Aguilar, O.; Rito-Palomares, M. Continuous aqueous two-phase systems devices for the recovery of biological products. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, M.H.; Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. On the kinetics of phase separation in aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 711, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsson, P.-Å.; Tjerneld, F. [1] Phase diagrams. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 228, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T. Liquid-liquid partitioning methods for bioseparations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2000, 2, 329–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kula, M.-R. Extraction and Purification of Enzymes Using Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Appl. Biochem. Bioeng. Enzyme Technol. 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidhar, M.; Merchuk, J.C.; Sembira, A.N.; Wolf, D. Characteristics of a motionless mixer for dispersion of immiscible fluids—II. Phase inversion of liquid-liquid systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1986, 41, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 711, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, S.L.; Kaul, A.; Merchuk, J.C.; Asenjo, J.A. Mathematical modelling and computer simulation of aqueous two-phase continuous protein extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 741, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschke, M. Dimensionierung Liegender Flüssig-Flüssig-Abscheider Anhand Diskontinuierlicher Absetzversuche/Martin Henschke. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
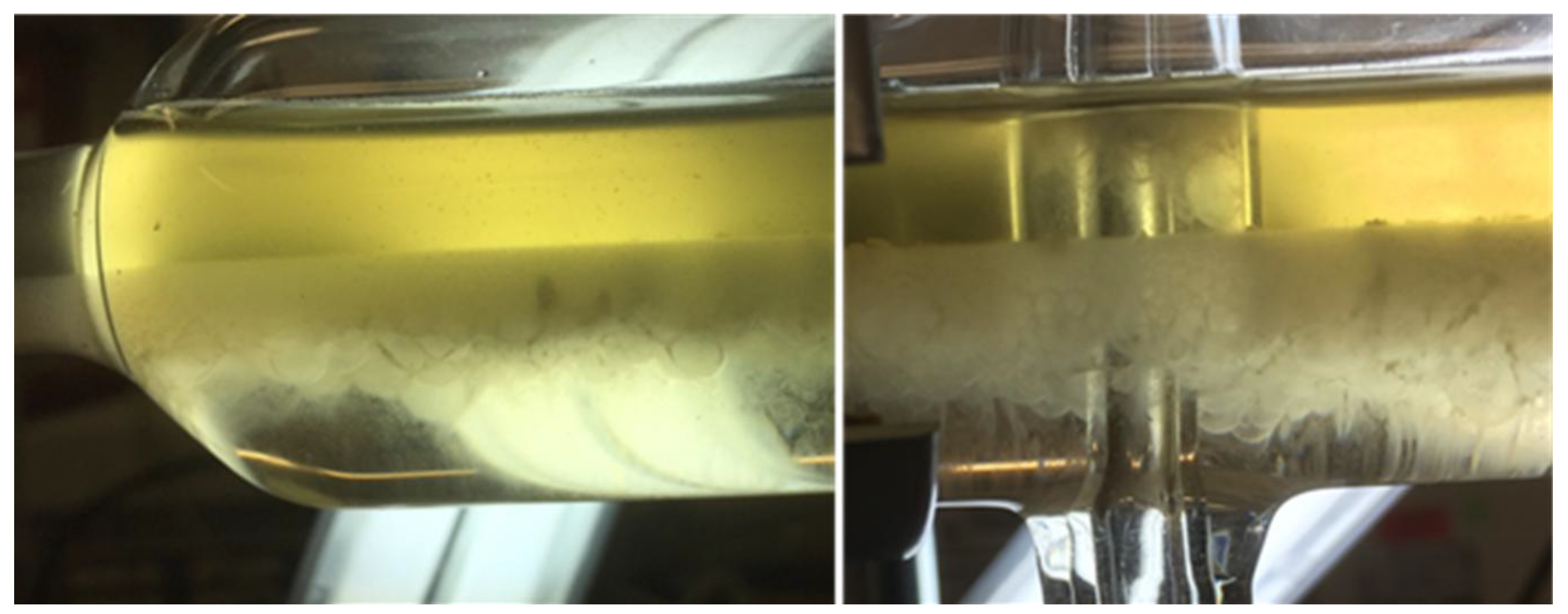
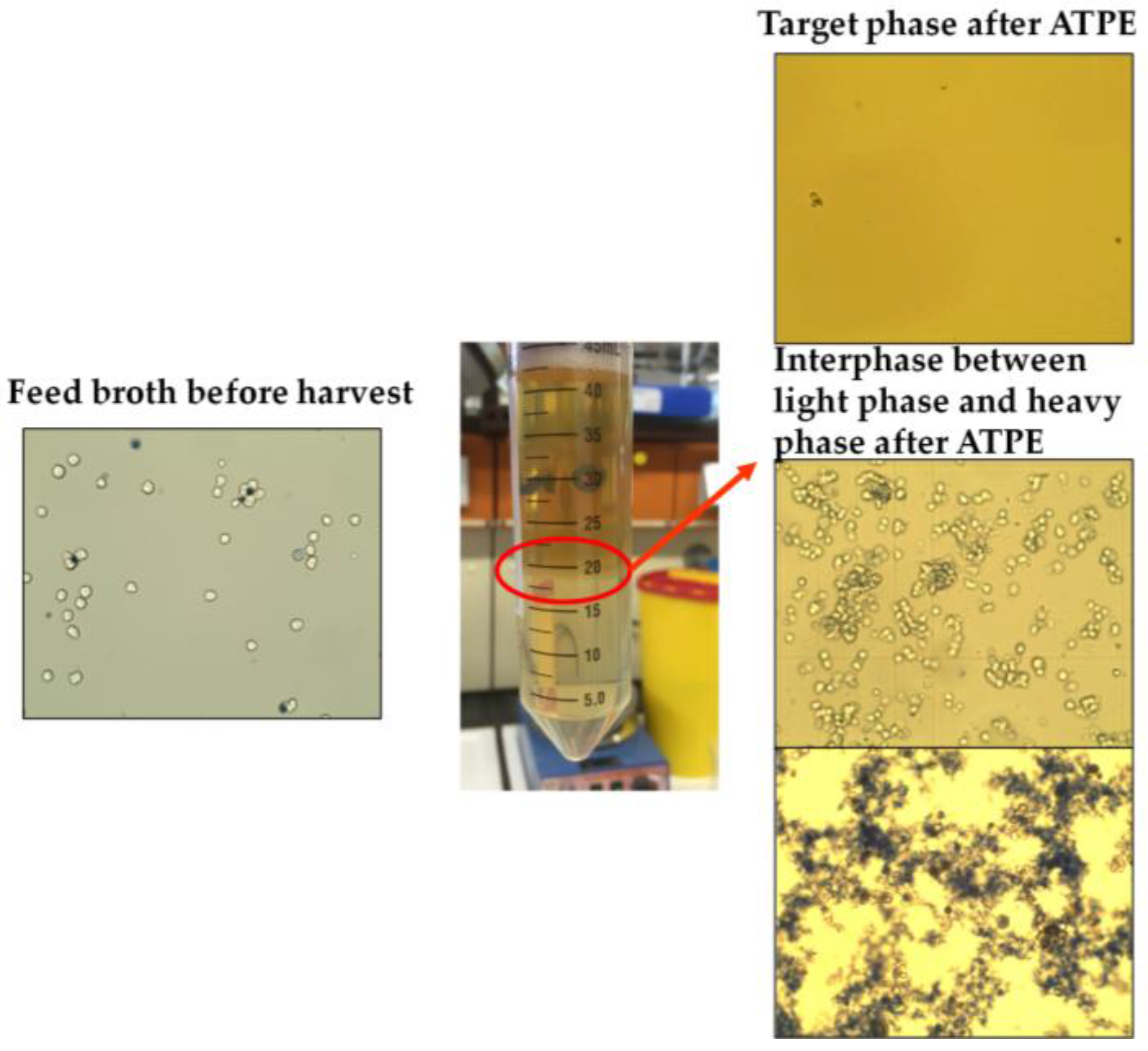
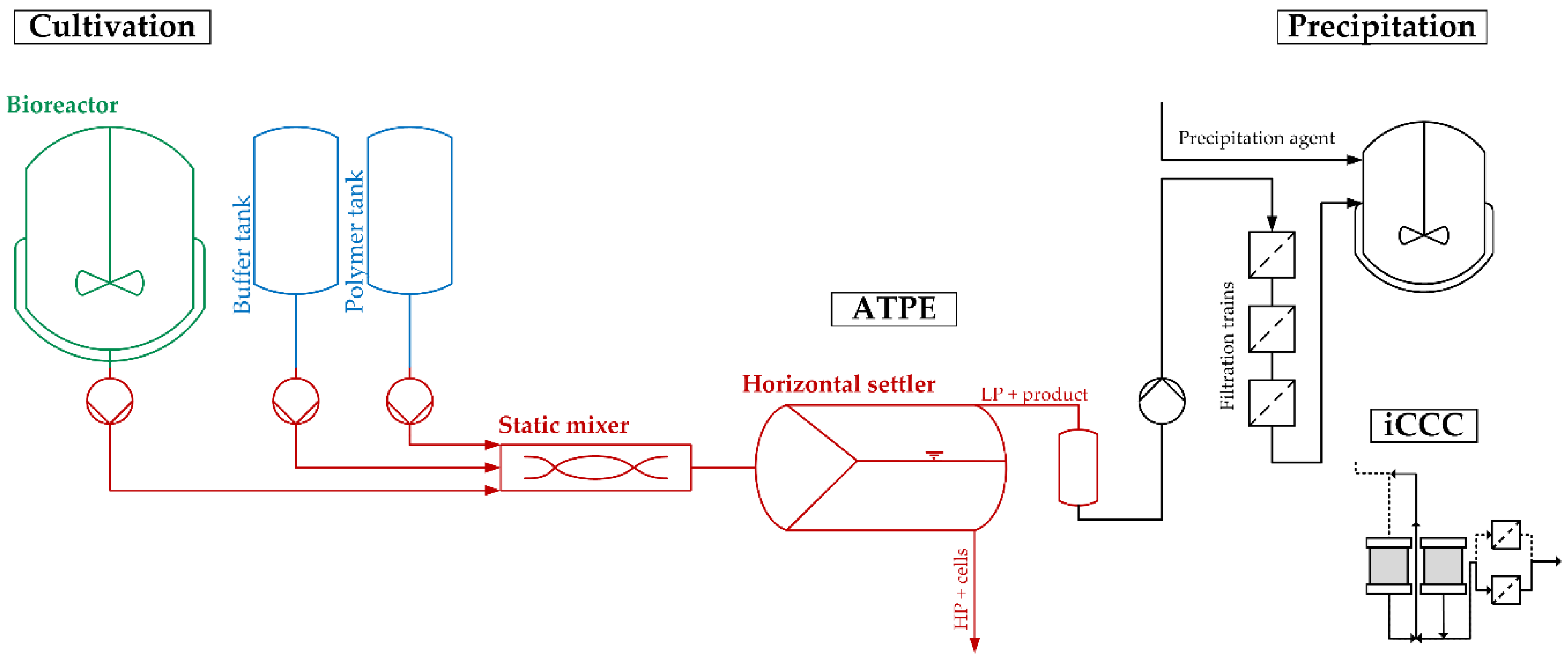




| System Point | Yield (%) | SEC-Purity (%) | Log Cell Reduction (−) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SP1 | 95 ± 2.33 | 80.93 ± 0.02 | 2.08 ± 0.1 |
| SP2 | 80 ± 0.39 | 81.97 ± 1.7 | 2.47 ± 0.02 |
| SP3 | 63 ± 3.00 | 67.98 ± 1.8 | 3.45 ± 0.2 |
| SP4 | 80 ± 1.62 | 80.98 ± 0.03 | 0.61 ± 0.02 |
| Time Interval | dhp/dt (mm/min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| 540 s | 3.8 | 3.87 | 3.62 |
| 1340 s | 2.09 | 2.07 | 2.17 |
| Time Interval | a | b | c |
|---|---|---|---|
| 540 s | 0.6230 | 0.1604 | 3.1096 |
| 1340 s | 0.6276 | 0.0824 | 3.1644 |
| σ (mN/m) | σw (mN/m) | (kg/m3) | (kg/m3) | (Pa⋅s) | (Pa⋅s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0702 | 72.75 | 1102.5 | 0.1337 | 0.0074 | 0.0048 |
| Mode | Yield IgG (%) | Log Cell Reduction (−) | Pressure Increase (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | 95 | 1.29 | 0.1 |
| Continuous | 80.4 | 0.44 | 0.9 |
| SP1 | SP2 | SP3 | SP4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG 400 (w%) | 15.5 | 17 | 20 | 9 |
| Buffer (w%) | 40 | 43.75 | 45 | 53 |
| Broth (w%) | 44.5 | 39.75 | 35 | 38 |
| Volume split LP/HP | 1:1 | 1:1 | 1:1 | 1:4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmidt, A.; Richter, M.; Rudolph, F.; Strube, J. Integration of Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction as Cell Harvest and Capture Operation in the Manufacturing Process of Monoclonal Antibodies. Antibodies 2017, 6, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6040021
Schmidt A, Richter M, Rudolph F, Strube J. Integration of Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction as Cell Harvest and Capture Operation in the Manufacturing Process of Monoclonal Antibodies. Antibodies. 2017; 6(4):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6040021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidt, Axel, Michael Richter, Frederik Rudolph, and Jochen Strube. 2017. "Integration of Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction as Cell Harvest and Capture Operation in the Manufacturing Process of Monoclonal Antibodies" Antibodies 6, no. 4: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6040021
APA StyleSchmidt, A., Richter, M., Rudolph, F., & Strube, J. (2017). Integration of Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction as Cell Harvest and Capture Operation in the Manufacturing Process of Monoclonal Antibodies. Antibodies, 6(4), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6040021







