Characterization Analysis of Human Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Partially Purified Human FBPs as Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies
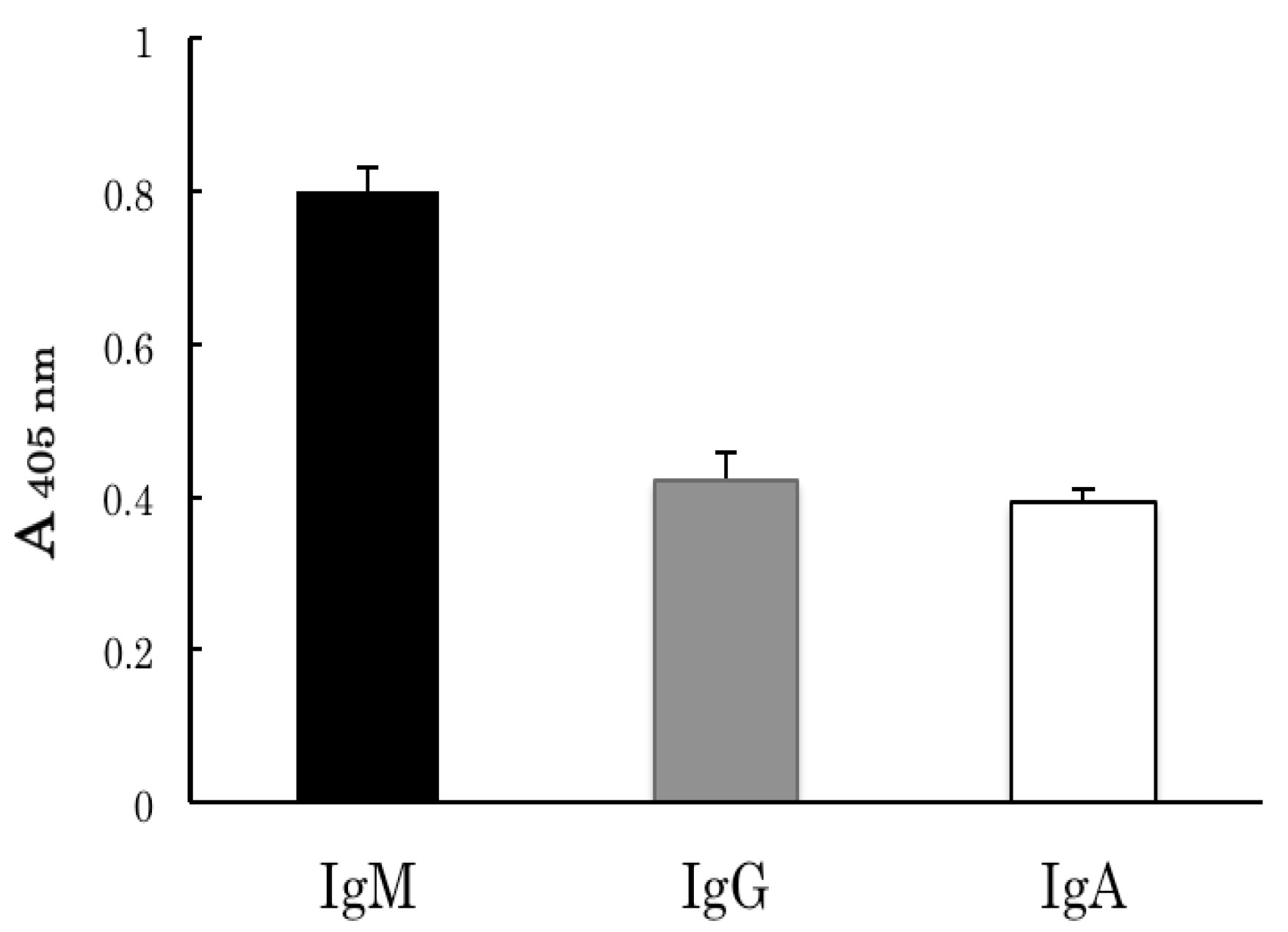

2.2. Binding Analyses of IgM Antibody Binding Ferritin


3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Ferritin and Antiserum to Ferritin
3.3. Preparation of Recombinant Human H and L Subunit Homopolymers
3.4. Protein Determination
3.5. Biotin Labeling of Peptide Fragment
3.6. Partial Purification of Human Serum FBPs
3.7. Identification of Human FBPs Using Immunocoprecipitation
3.8. Competitive Inhibition of Zinc Binding by Human Serum Zinc-Binding Proteins by Ferritin
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplemental Files
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, S.C.; Arosio, P.; Bottke, W.; Briat, J.F.; von Darl, M.; Harrison, P.M.; Laulhere, J.P.; Levi, S.; Lobreaux, S.; Yewdall, S.J. Structure, function, and evolution of ferritins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1992, 47, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Adelman, T.G.; Drysdale, J.W. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 4451–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.M.; Arosio, P. The ferritins: molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1275, 161–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orino, K.; Watanabe, K. Molecular, physiological and clinical aspects of the iron storage protein ferritin. Vet. J. 2008, 178, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, E.C. Ferritin: structure, gene regulation, and cellular function in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzago, A.; Arosio, P.; Iacobello, C.; Ruggeri, G.; Capucci, L.; Brocchi, E.; de Simone, F.; Gamba, D.; Gabri, E.; Levi, S.; Albertini, A. Immunochemical characterization of human liver and heart ferritins with monoclonal antibodies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 872, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, G.M.; Beamish, M.R.; Hales, C.N.; Hodgkins, M.; Jacobs, A.; Llewellin, P. An immunoradiometric assay for ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972, 25, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.A.; Chavey, P.S.; Smith, J.E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure serum ferritin and the relationship between serum ferritin and nonheme iron stores in cats. Vet. Pathol. 1994, 31, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.A.; Smith, J.E.; Gray, M.; Chavey, P.S.; Weeks, B.R. An improved ferritin assay for canine sera. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 1992, 21, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Furugouri, K. The relationship between serum ferritin concentrations and tissue non-heme iron or tissue ferritin in dairy cattle. Jpn. J. Vet. Sci. 1987, 49, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Moore, K.; Boyington, D.; Pollmann, D.S.; Schoneweis, D. Serum ferritin and total iron-binding capacity to estate iron storage in pigs. Vet. Pathol. 1984, 21, 597–600. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.E.; Moore, K.; Cipriano, J.E.; Morris, P.G. Serum ferritin as a measure of stored iron in horses. J. Nutr. 1984, 114, 677–681. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, G.O.; Miller, F.M.; Worwood, M. Serum ferritin concentration and iron stores in normal subjects. J. Clin. Pathol. 1973, 26, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Human H-kininogen is a ferritin-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13630–13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massover, W.H. α2-Macroglobulin: a ferritin-binding protein. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 737, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santambrogio, P.; Massover, W.H. Rabbit serum alpha-2-macroglobulin binds to liver ferritin: association causes a heterogeneity of ferritin molecules. Br. J. Haematol. 1989, 71, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orino, K.; Hamada, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Nambo, Y.; Kondo, T.; Watanabe, K. Identification of horse anti-ferritin autoantibody. J. Equine Sci. 2006, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orino, K.; Ishiji, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Watanabe, K. Characterization of bovine serum ferritin-binding proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2004, 137A, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Orino, K.; Uehara, M; Okano, S.; Watanabe, K. Purification and characterization of canine serum ferritin-binding proteins. Biometals 2006, 19, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Kuboi, T.; Nagakura, T.; Hayashi, S.; Hoshi, F.; Mutoh, K.; Watanabe, K.; Orino, K. Characterization of feline serum ferritin-binding proteins: the presence of a novel ferritin-binding protein as an inhibitory factor in feline ferritin immunoassay. Biometals 2009, 22, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Hayashi, K.; Miyamaoto, T.; Tanaka, M.; Okano, S.; Yamamoto, S. Characterization of ferritin and ferritin-binding proteins in canine serum. Biometals 2000, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Kunichika, T.; Watanabe, K.; Orino, K. Apolipoprotein B binds ferritin by hemin-mediated binding: evidence of direct binding of apolipoprotein B and ferritin to hemin. Biometals 2008, 21, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orino, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Watanabe, K. Fibrinogen as a ferritin-binding protein in horse plasma. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 785–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, N.; Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Ferritin binds to light chain of human H-kininogen and inhibits kallikrein-mediated bradykinin release. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Kondo, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Orino, K. The presence of heat-labile factors interfering with binding analysis of fibrinogen with ferritin in horse plasma. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, V.; Arosio, P.; Cazzola, M.; Cozzi, A.; Levi, S.; Meloni, F.; Zappone, E. Characterization of a ferritin-binding protein present in human serum. Br. J. Haematol. 1987, 65, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsu, Y.; Goto, Y.; Arisato, N.; Sasaki, K.; Kohgo, Y. Ferritin-binding proteins in serum. Br. J. Haematol. 1988, 68, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orino, K.; Saji, M.; Ozaki, M.; Ohya, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Watanabe, K. Inhibitory effects of horse serum on immunoassay of horse ferritin. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covell, A.M.; Jacobs, A.; Worwood, M. Interaction of ferritin with serum: implications for ferritin turnover. Clin. Chim. Acta 1984, 139, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesters, J.K.; Will, M. Zinc transport proteins in plasma. Br. J. Nutr. 1981, 46, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scot, B.J.; Bradwell, A.R. Identification of the serum binding proteins for iron, zinc, cadmium, nickel and calcium. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Arredondo, A.; Nunez, M.T. Iron and copper metabolism. Mol. Aspects Med. 2005, 26, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, J.M.; Treffry, A.; Harrison, P.M. The location of antigenic sites on ferritin molecules. FEBS Lett. 1984, 175, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeva, E.E.; Vorobyova, U.A.; Denisova, E.A.; Medvedeva, D.A.; Cheknev, S.B. Binding of zinc cations to human serum γ-globulin. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 141, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Muranishi, N.; Murata, Y.; Orino, K.; Okano, S.; Yamamoto, S. Biochemical properties of canine serum ferritin: iron content and nonbinding to concanavalin A. Biometals 2000, 13, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc: role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Cur. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.U.; Binder, C.J.; Kaveri, S. Naturally occurring auto-antibodies in homeostasis and disease. Trends Immunol. 2008, 30, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santambrogio, P.; Cozzi, A.; Levi, S.; Arosio, P. Human serum ferritin G-subunit is recognized by anti-L ferritin subunit antibodies and concanavalin-A. Br. J. Haematol. 1987, 65, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worwood, M.; Cragg, S.J.; Williams, A.M.; Wagstaff, M.W.; Jacobs, A. The clearance of 131I-human plasma ferritin in man. Blood 1982, 60, 827–833. [Google Scholar]
- Rucker, P.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Role of H and L subunits in mouse ferritin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 33352–33357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of protein in the rage from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Higashi, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Orino, K. Characterization Analysis of Human Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies. Antibodies 2014, 3, 169-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3010169
Higashi S, Nagasawa K, Yoshikawa Y, Watanabe K, Orino K. Characterization Analysis of Human Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies. Antibodies. 2014; 3(1):169-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3010169
Chicago/Turabian StyleHigashi, Shusaku, Kosei Nagasawa, Yasunaga Yoshikawa, Kiyotaka Watanabe, and Koichi Orino. 2014. "Characterization Analysis of Human Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies" Antibodies 3, no. 1: 169-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3010169
APA StyleHigashi, S., Nagasawa, K., Yoshikawa, Y., Watanabe, K., & Orino, K. (2014). Characterization Analysis of Human Anti-Ferritin Autoantibodies. Antibodies, 3(1), 169-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib3010169




