Abstract
The human intestine is populated with an extremely dense and diverse bacterial community. Commensal bacteria act as an important antigenic stimulus producing the maturation of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). The production of immunoglobulin (Ig) A by B-cells in the GALT is one of the immune responses following intestinal colonization of bacteria. The switch of B-cells from IgM to IgA-producing cells in the Peyer’s patches and neighboring lamina propria proceeds by T-cell-dependent and T-cell-independent mechanisms. Several grams of secretory IgA (SIgA) are released into the intestine each day. SIgA serves as a first-line of defense in protecting the intestinal epithelium from enteric toxins and pathogenic microorganisms. SIgA has a capacity to directly quench bacterial virulence factors, influence the composition of the intestinal microbiota, and promote the transportation of antigens across the intestinal epithelium to GALT and down-regulate proinflammatory responses associated with the uptake of highly pathogenic bacteria and potentially allergenic antigens. This review summarizes the reciprocal interactions between intestinal B cells and bacteria, specifically, the formation of IgA in the gut, the role of intestinal IgA in the regulation of bacterial communities and the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis, and the effects of probiotics on IgA levels in the gastrointestinal tract.
1. Introduction
The gastrointestinal tract is populated with an extremely dense bacterial community (~1014 bacterial cells and 500–1,000 species) [1]. The host and commensal bacteria have established a symbiotic relationship that contributes to the development of the immune system and maintenance of our normal physiology. The host serves as a protective and nutrient-rich environment for the bacteria; while commensals, in turn, provide metabolic advantages, including the ability to break down indigestible food components, and serve as a natural defense against colonization with pathogens. In addition, the complex interplay between the microbiota and the host helps to shape the immune system throughout life [2,3]. A continuous dialogue between intestinal immune cells and bacteria ensures a homeostatic immune state, which includes hypo-responsiveness to environmental antigens (dietary antigens and commensals) and aggressive responsiveness to pathogens [4].
Gut epithelium plays a critical role in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis by recognition of commensal bacterial products through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as toll-like receptors (TLRs). Intestinal epithelial cells secrete cytokines that reinforce the epithelial barrier and regulate the local immune response [5]. Furthermore, the interaction of commensal bacteria with specialized cells located in intestinal crypts, called Paneth cells [6], leads to the secretion of antimicrobial products, including defensins, angiogenins, regenerating islet-derived 3γ (RegIIIγ) lectins and trefoil factors. These factors enhance the epithelial barrier, protect a stem cell niche, enhance systemic responses to infection and regulate the composition of luminal bacteria [7,8,9].
Gut microbiota promotes the development of immune system, which includes the activation and differentiation of B-cells. Although B-cells affect gut homeostasis by several mechanisms [10,11], the most likely is via antibody production. Maintenance of the homeostatic equilibrium between the intestinal microbiota and the plethora of luminal macromolecules and the human intestinal epithelial cell barrier requires the secretion of copious amounts of mucosal IgA into the gut lumen [12]. In humans, 40–60 mg/kg/day of IgA are produced daily by plasma cells located in the lamina propria (LP) of intestinal villi [13,14]. The IgA is transported across the epithelium and secreted into the gut lumen, where it is thought to provide protection against pathogens by multiple biological properties, which include blocking toxins and pathogens from adhering to the intestinal epithelium at the earliest steps of the infection process [15,16,17], and from directly recognizing receptor-binding domains to block bacterial attachment to intestinal epithelial cells [16,18]. Additionally, IgA mediates immune exclusion of pathogens and toxins, including a series of events of agglutination, entrapment and clearance [19,20,21]. Failure to generate and transport IgA into the lumen results in potentially pathogenic imbalance, leading to penetration of luminal antigens into the systemic compartment.
This review intends to summarize the reciprocal interactions between gut B-cells and intestinal bacteria and the role of IgA in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis.
2. Differentiation of B-Cells and Generation of IgA Induced by Gut Microbiota
The process of intestinal colonization starts at birth, when neonates are exposed to microorganisms from the maternal birth canal and the external environment. Bacterial colonization of the gut is a trigger for the induction of IgA production by B-cells. This process is characterized by class switching of B-cells from IgM to IgA production [22]. The early recognition of bacteria and the subsequent modulation of B-cell responses is an important process that promotes normal mucosal homeostasis.
2.1. Evidence of the Participation of Enteric Bacteria in the Differentiation and Activation of B-Cells in Animals and Humans
Studies of various animal models of impaired microbial control, including germ-free (GF), antibiotic-treated, restricted flora (RF) and activation-induced cytidine deaminase knockout (AID−/−) mice, have demonstrated that bacteria of the gastrointestinal tract participate in the differentiation and activation of B-cells. In GF animals, there are reduced numbers of lamina propria lymphocytes and IgA-producing plasma cells, as well as reduced systemic levels of serum immunoglobulin. Secondary lymphatic organs, such as the spleen and lymph nodes, are also underdeveloped [23,24]. In the presence of commensal bacteria, large quantities of IgA are secreted across the intestinal mucosa, accounting for >70% of total-body immunoglobulin production [25]. Because most of the antibodies in the gut are directed against resident microbiota, IgA deficiency can lead to a general overgrowth of microbes. This phenomenon has been demonstrated in B-lymphocyte knockout mice (BcKO) [26]. AID−/− mice lack the ability to switch from IgM- to IgA-producing B-cells, which similarly results in a large increase in the number of non-pathogenic, anaerobic bacteria residing throughout the small intestine, as well as a generalized hyperplasia of intestinal lymphoid follicles [27].
RF mice demonstrated a marked deficiency of innate-like B-cell subsets. However, the transfer of specific pathogen-free (SPF) luminal bacteria into RF pups immediately after birth led to significant expansion of the innate-like B-cell compartments. In contrast to RF mice, SPF mice harbor a wide variety of commensal microorganisms in their flora. SPF-exposed active IgA-producing intestinal B-cells were successfully restored in RF offspring, and these populations persisted into adulthood. Moreover, If RF females and males were treated with the antibiotic vancomycin and, subsequently, bred with an SPF male and female under SPF husbandry conditions, full restoration of functional B-cells was achieved in all offspring. Using a conventional bacterial culture and molecular phylotyping, innate-like B-cell restoration correlated with a shift from RF to SPF enteric microbiota. It was noted that post-weaning exposure to SPF microbiota resulted in no restoration of B-cells. These results suggested that a restricted population of gut microbiota adversely affects the development of B-cells and lead to the postulation of an early window of exposure to specific resident bacteria, which is crucial for the formation of B-cells [28].
The gut microbiota also has an impact on B-cell maturation in humans [29,30]. It has been shown that Pakistani infants living in impoverished areas have an accelerated maturation of the salivary IgA system compared with healthy Swedish infants [31]. In Swedish infants, the gut microbiota takes longer to establish and is characterized by a lower diversity than infants in developing countries [32,33,34]. A recent prospective newborn/infant cohort study examined, in 65 Swedish children, the correlation between B- or memory B-cells in blood and fecal bacteria at 1–8 weeks of life. The results suggested that the intestinal bacterial colonization pattern shaped B-cell maturation. The acquisition of specific early gut microbiota, especially E. coli and Bifidobacteria, promotes this maturation [29].
Human IgA deficiency is commonly associated with a maturation defect in B-cells. IgA-deficient patients are generally asymptomatic, but exhibit a tendency to develop gastrointestinal disorders, e.g., celiac disease (CD) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), as well as allergies and mucosal infections [35,36,37].
2.2. Generation of IgA-Producing B-Cells in the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues
A prominent response of the immune system that follows microbial colonization of the gut is the generation of IgA-producing B-cells present in the gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) [4]. GALTs include organized lymphoid structure present in the wall of the small and large intestine-Peyer’s patches (PPs) and isolated lymphoid follicles (ILFs), and diffuse lymphoid tissue of the epithelium and the lamina propria (LP) [38,39].
2.2.1. Generation of IgA-Producing B-Cells in Peyer’s Patches
Peyer’s patches (PPs) are large structures built on a stromal cell (SC) scaffold, composed of several B-cell follicles separated by areas containing T-cells and dendritic cells (DCs). They are visible endoscopically, presenting in the colon and terminal ileum of normal humans. Formation of PPs requires multiple interactions between hematopoietic cells and SCs, in a precise time-window during embryogenesis [39,40]. Many of the PP lymphocytes reside in germinal centers (GCs). GCs are special microenvironments that allow interactions between B-cells, follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and follicular helper T-cells (TFH) [41]. The development of GCs is dependent on the presence of gut bacteria and helper T-cells. In conventionally reared mice with a complex gut microflora, GCs are present in PPs and in the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs), and the majority of the IgA-producing B-cells are generated in this environment [42]. However, GCs diminish with time in the PPs of germ-free mice that are colonized with a single defined microorganism [43]. In PPs, most of the GC B-cells are activated cells, expressing activation-induced cytiding deaminase (AID). AID is critical for class switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM) [44], which preferentially switches cells from IgM to IgA production. However, the cellular and molecular mechanism responsible for the predominance of IgA production is still unclear.
Studies indicate that PP DCs critically contribute to creating a special gut micro-environment. The unique function of DCs in PPs might be related to their location in the sub-epithelial dome (SED), where they directly access luminal bacteria. The epithelium that covers PPs contains M-cells, special cells that are considered to be the major site of antigen entry to the mucosa. Lamina propria DCs actively sample the small numbers of bacteria that are present at the apical surfaces of epithelial cells by extending their dendrites between the epithelial cells. The arms of DC extending between the intestinal epithelial cells reach the lumen, at which site “balloon bodies” pointing into the lumen are shown to engulf bacteria [45]. The bacteria-laden DCs migrate to PPs and MLNs to direct CSR to IgA, where they induce B-cells to differentiate into IgA-producing plasma cells. IgA-producing plasma cells are homing in the lamina propria and secrete dimeric IgA that is transcytosed across the epithelial cell layer, providing a defense against harmful gut microbiota, e.g., limiting bacterial association with the epithelium and preventing bacterial penetration of host tissue [46]. Commensal bacteria can normally persist in Peyer’s patch DCs in low quantities and contribute to the induction of local specific immune responses that limit dissemination beyond the MLNs, ultimately preventing systemic spread. The results of locally controlled IgA production are to create a simple feedback loop where DCs and epithelial cells drive IgA production until sufficient levels of IgA block microbial invasion [25].
T-cells in PPs are conditioned by gut DCs to produce cytokines, such as the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, which, together with interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10 produced by DCs, facilitate the preferential CSR of B-cells from IgM to IgA [25,47]. Fan et al. showed that B-cell stimulation leads to activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which depends on the combined effects of IL-6 and IL-10 [48]. IL-10 mediates the differentiation of germinal center B-cells into memory and plasma cells by inducing Janus kinase (JAK) proteins via the phosphorylation of STAT3 [49]. In addition, IL-10 by itself can also lead to significant AID transcription to facilitate IgA production [50]. Follicular helper T (TFH) cells also express high levels of molecules critically associated with helper functions, such as CD40L, inducible T-cell co-stimulator (ICOS) and IL21 [41]. Thus, activation of B-cells and class switching to IgA within the PP requires bacterial antigens and conventional B-T cell interactions. Alternatively, B cells can be activated in the absence of cognate B-T interactions, through TLR engagement by activated DCs. This might represent an evolutionarily primitive system for Ig production in which B-cells express AID upon stimulation through TLRs and undergo CSR to IgA-producing B-cells in the gut environment [51] (Figure 1, the left side).
2.2.2. Generation of IgA-Producing B-Cells in Isolated Lymphoid Follicles (ILFs) and IgA-Producing Plasma Cells in the Lamina Propria (LP)
Isolated lymphoid follicles develop only after birth, from small structures called crypto patches (CPs). ILFs are composed of a single discrete cluster of B-cells built around stromal cells, surrounded by a large number of DCs and a few T-cells interspersed between the B-cells [38,52]. The development of ILFs requires stimulation by commensal intestinal bacteria. The size and cellular composition of ILFs are highly variable and dependent on the bacterial load in the intestine. Hyperplasia of ILFs correlates with the expansion of anaerobic bacteria in the small intestine of mice that lack IgA. In addition to the presence of bacteria, formation of ILF depends on the presence of lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) helper T-cells, which play a critical role in the development of lymphoid tissue. RORγt+ LTi cells interact with SCs through the LTα1β2-LTβR axis [53] to produce matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs), subsequently activate TGFβ and facilitate the preferential CSR of B-cells to IgA. Mice that have impaired signaling downstream of the LTβR, such as RORγt−/−, LTα−/−, LTβ−/− and LTβR−/− mice, do not develop ILFs [53,54].
Similar to PPs, the epithelium that covers mature ILFs contains M-cells capable of taking up pathogens. Unlike the T-cell-dependent processes in the follicles of PPs, B-cell activation, induction of AID and generation of precursors for IgA plasma cells within ILFs are processes that do not require the help of T-cells. It is unique that IgA can be synthesized in the intestinal ILFs in the absence of T-cells and GCs [55]. Accumulating evidence indicates that ILF DCs alone appear to be sufficient for activation of B-cells [53]. Gut macrophage (Ф)-DCs, upon activation by intestinal bacteria, express many factors (e.g., tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)) that are required for IgA production [56]. This feature distinguishes gastrointestinal Ф-DCs from the DCs in spleen and lymph nodes. In addition, gut Ф-DCs secrete the B-cell activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL). These factors are known to enhance CSR to IgA independent of T-cell help [57] by interacting with the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R), B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and transmembrane activator, calcium-modulating and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI) expressed on IgM B-cells [58]. IgA-producing B-cells generated within ILFs then undergo differentiation to IgA plasma cells in the LP (Figure 1, the right side).
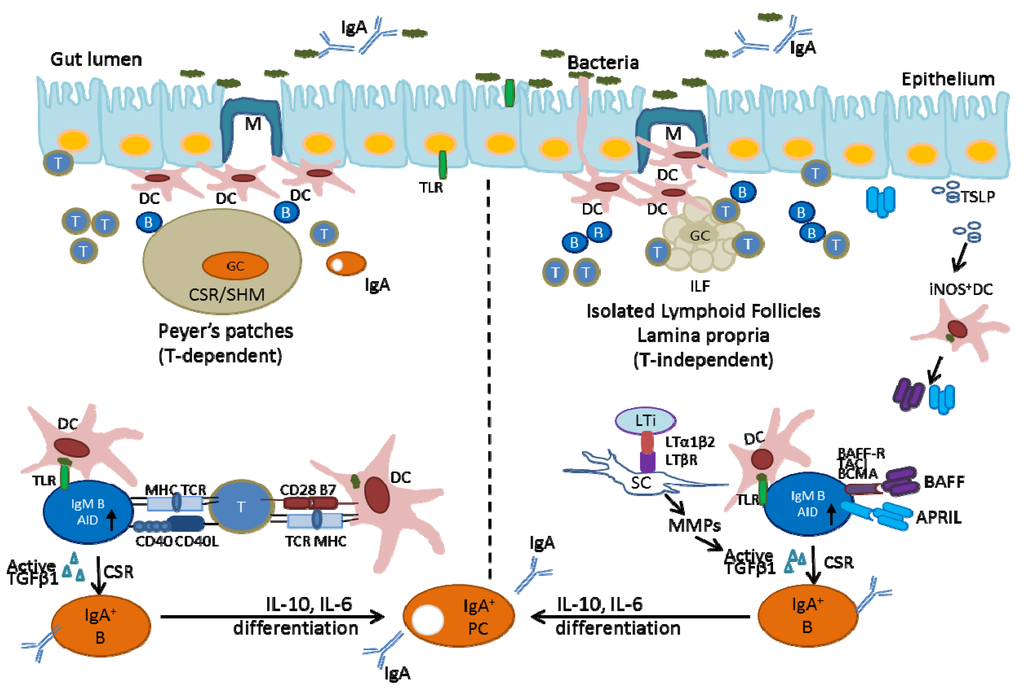
Figure 1.
Production of IgA in the intestine. The generation of IgA+ B-cells in the GCs of PPs is mainly T-cell dependent. Conventional B-T interactions through MHCII-TCR and CD40-CD40L induce AID in B-cells with subsequent class-switch recombination (CSR). The generation of IgA+ B-cells within ILFs and LP is T-cell independent. The interactions between BAFF/APRIL produced by activated DCs and their receptors on B-cells induce B-cell IgA class-switching and differentiation.
The LP is also a site where T-independent IgA responses are triggered by intestinal bacteria. Recent studies by using in situ staining of AID and AID reporter mice demonstrated that B-cells in the gut LP are activated AID-expressing cells which are undergoing CSR to IgA [57,59]. In humans, it was demonstrated that the interaction between bacteria, epithelial cells and DCs induces T-independent and CD40-independent CSR of LP B-cells through BAFF and APRIL produced by bacterial activated DCs and plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) [57,60]. Intestinal epithelial cells also produce BAFF, APRIL, IL6 and CXC-chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL 12) upon stimulation by bacteria through TLRs. In addition, activated gut epithelium secretes thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) to enhance the expression of APRIL and IL-10 by TNF-α and iNOS-producing DC. The resulting cytokine milieu might augment CSR [56,57] and create a survival niche for plasma cells in the intestinal LP [61]. Recent evidence indicated that mouse IgA-producing plasma cells also produce the antimicrobial mediators, TNFα and iNOS. Deletion of TNFα and iNOS in B-lineage cells resulted in a reduction in IgA production, altered diversification of the gut microbiota and poor clearance of a gut-tropic pathogen [62].
Finally, IgA-producing B-cells formed in PPs could represent cells that are homing to effector sites, such as LP. IgA-producing B-cells migrate from PPs to the draining MLNs and from there to the thoracic duct lymph and blood, to the LP of the gut. The final egress process from bloodstream to intestinal mucosa involves a α4β7 integrin, expressed by lymphocytes, and mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MADCAM-1), expressed by endothelial venules [63]. The preferential gut-homing of IgA-producing B-cells, but not IgM- or IgG-producing B-cells, can be explained by a response of the IgA-synthesizing B-cells to thymus-expressed chemokine (TECK; also called CCL25), which expressed within the small intestine, especially in epithelial crypts [64]. Further migration into the LP of the villi might depend on CXCL12 expressed in the gut [64].
3. Control of Gut Microbiota by Intestinal IgA
It has been shown that natural and specific IgA antibodies in breast milk are capable of binding commensal bacteria and may be involved in the progressive, controlled establishment of the newborn’s microbiota [65,66]. “Classical” IgA generated from T-cell-dependent processes with high affinity is essential to provide protection from more invasive commensal species, such as segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) and from true pathogens, such as Salmonella typhimurium. “Innate” IgA produced from T-independent processes with low affinity is sufficient to protect the host from excess mucosal immune activation induced by harmless commensal microbes [67]. A substantial fraction of the commensal bacteria is “coated” with IgA. This IgA can be identified as commensal-bound IgA detected by flow cytometry (high affinity) from T-dependent processes and commensal-reactive IgA detected by Western blot or ELISA (much lower affinity) from T-independent processes [67]. Classical IgA and innate IgA are thought to combine to build up the overall IgA repertoire in the intestine [61].
3.1. Limited Access of Bacteria in the Intestinal Lumen to Intestinal Tissues Mediated by IgA
Secretory IgA (SIgA) provides a defense against harmful gut microbiota by limiting bacterial association with the epithelium and preventing bacterial penetration of host tissue [46], which has been shown in the neonatal intestinal epithelium. Interestingly, this process did not require diversification of the natural antibody repertoire; for example, the nitrophenol-specific IgA produced in young quasi-monoclonal mice (engineered and almost monoclonal mice) was sufficient to limit the penetration of commensal Enterobacter cloacae [68]. Similarly, in adult mice, the presence of SIgA limits the translocation of aerobic bacteria from the intestinal lumen to the MLNs [25].
SIgA protects the intestinal epithelium against colonization and/or invasion by binding antigens on pathogens or commensals in the luminal mucous layer. The microorganism is surrounded by a hydrophilic shell and is repelled by the epithelial glycocalyx, thus providing immune exclusion of bacteria [13]. Immune exclusion not only protects the epithelium from invading pathogens, it is also important in maintaining gut homeostasis by preventing overgrowth of the enteric microflora [4,59,69]. Furthermore, IgA can protect against intracellular pathogens by binding and neutralizing viral or bacterial components during transcytosis of the epithelium. The immune complexes are then secreted apically, and invasion is inhibited [70].
3.2. Regulation of Bacterial Communities in the Gut Lumen by Secretory IgA
The AID-deficient mouse model demonstrated that SIgA is critical for regulating bacterial communities in the gut lumen. The absence of IgA in the lumen of AID−/− mice leads to an excessive anaerobic expansion in all segments of the small intestine [27]. Among the expanded anaerobes, segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB) are predominant, and they strongly stimulate the generation of gut IgA in germ-free mice. Most of the induced IgA is not specific to the SFB [71].
Recent studies indicated that SIgA promotes the establishment of host-microbial relationships by modulating bacterial epitopes and modifying bacterial metabolism, as demonstrated by down-regulation of bacterial genes involved in the metabolism of oxidative products [69]. Peterson et al. [69] used a germ-free mouse model to directly examine the impact of IgA on host-commensal interactions. They first established hybridoma cells producing IgA monoclonal antibody against the capsular polysaccharide (CPS4) of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (B.t.). Rag−/− mice, which lack mature B- and T-cells were made to harbor IgA-producing hybridoma cells; they were subsequently challenged with B.t, and the host’s response was analyzed. The authors found that B.t. elicited a robust oxidative stress response from the host in the absence of IgA. The presence of B.t.-specific IgA antibodies suppressed this response; thereby underscoring IgA’s potential to dampen injurious host responses to commensal microbiota. Interestingly, the specific anti-CPS4 IgA response induced an expression by bacteria of another capsular locus (CPS5). It is thus possible that the adaptive immune system through IgA maintains a dialog with gut microbiota by generating a selective response to bacteria that stimulate the immune system. Therefore, the adaptive immune system apparently drives diversification of bacterial surface structures by exposing the bacteria in the lumen to IgA [69].
Hapfelmeier et al. reported several important features of IgA responses by using a “reversible” germ-free mouse model. First, the intestinal-specific IgA response provoked by commensal bacteria requires a large dose of live bacteria for IgA production (109 bacteria). Furthermore, the response is characterized by a slow onset (≥14 days), a long half-life (>16 weeks) and an adaptability to the predominant commensal species in the intestinal lumen at a particular time [72]. The introduction of specific bacterial species and the associated generation of bacteria-specific IgA could serve to adjust a dynamic intestinal IgA repertoire to gradually changing microbiota composition.
3.3. IgA-Based Immune Complexes As Regulators of Intestinal Homeostasis
The interaction between the commensal microbiota and IgA is highly complex. Studies have indicated that between 25%–75% of the microbiota are interacted with IgA [73,74], attached as a dimer with bound secretory component (SC) in a Fab-specific or in a Fab-independent manner [75]. Proposed mechanisms of protection of SIgA-reactive bacteria and SIgA-based immune complexes in the intestinal mucosa have been demonstrated in Figure 2. IgA-reactive commensal bacteria enhances barrier function through multiple mechanisms, including reinforcement of tight junctions [76] and overproduction of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) [77], which helps to maintain mucosal barrier integrity and intestinal homeostasis by transporting polymeric IgA antibodies across intestinal epithelial cells into gut secretions. Proteolytic cleavage of pIgR at the apical surface of intestinal epithelial cells releases the extracellular domain of pIgR, known as the secretory component (SC), either in free form or as part of the SIgA complex. The SC enhances innate defense mechanisms by the prevention of bacterial adherence to the intestinal mucous layer and neutralization of potential proinflammatory factors [78] (Figure 2e). The IgA-based immune complex can also bind the human myeloid IgA Fc receptor Fc αRI (CD89), constitutively expressed on immune cells, such as neutrophils, interstitial dendritic cells, monocytes and some macrophages [12]. Receptor binding can initiate antimicrobial activity (including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, phagocytosis and generation of bactericidal superoxides) [79]. Most importantly, IgA may play an important role in controlling the sampling of commensal bacteria, which specifically targets them to pass across Peyer’s patch M-cells. Indeed, IgA-based immune complexes with commensal bacteria are taken up by M-cells, wherein they activate underlying tolerogenic myeloid DCs, resulting in the down-regulation of local proinflammatory responses [80,81] (Figure 2f). The process was demonstrated by a direct visualization of a fluorescently-labeled commensal bacterium administered in the form of an IgA-based complex into the intestine of mice [82]. The interaction of SIgA with DCs is dependent on the IgA moiety. SIgA is internalized into DCs, whereas the association with CD4+ T-cells is limited to cell surface. The surface interaction of SIgA with CD4+ T-helper cells might down-regulate T-cell activation by which decrease the production of inflammatory mediators (Figure 2g) [83].
Another role of SIgA in maintaining bacterial homeostasis is its contribution to microbial biofilm formation (Figure 2h). A biofilm is defined as a community of microorganisms attached to a living surface by a self-produced polymeric matrix. Biofilms have been shown to protect encased bacteria from natural immune defenses, such as antimicrobial compounds, due to the inability of these compounds to penetrate the complex biofilm architecture [84]. IgA may have a role in excluding pathogenic bacteria from the epithelial surface by trapping them within the biofilm or anchoring them within the mucus. On the other hand, the biofilm containing IgA and non-pathogenic bacteria may benefit colonization on the mucosal surface and ensure a steady-state growth rate of commensal microbiota in the intestinal lumen [85]. Bollinger et al. have shown the formation of biofilms containing IgA and non-pathogenic E. coli on epithelial cell monolayers grown in vitro [86,87]. The association of IgA with biofilm formation in the gut has been demonstrated using sections from animal and human tissues [88]. Bacteria that bind IgA may have a selective advantage in the gut biofilm [89]; for example, studies have indicated that SIgA possesses a broad reactivity with type 1 fimbriae specifically expressed on certain E. coli bacteria. The absence of SIgA, as seen in patients with IgA deficiency, might therefore alter the ability of type-1-fimbriated E. coli to colonize the large intestines of these individuals. The potential role of biofilms in the complex bacteria-bacteria or bacteria-host interactions that take place in the gut remains largely unexplored.
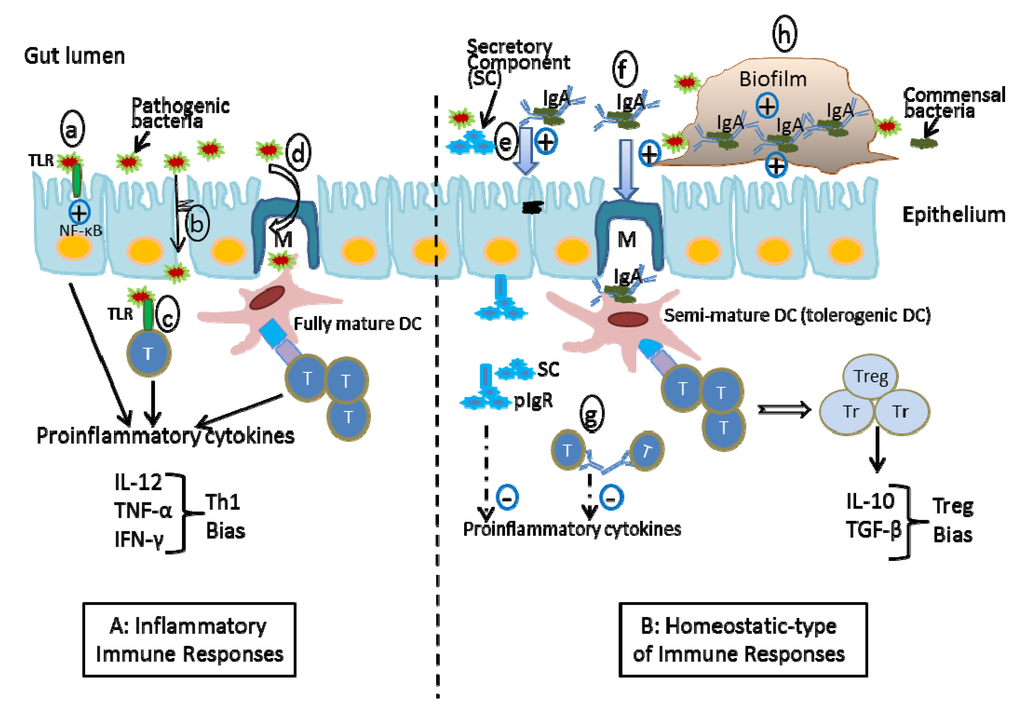
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of the protection of SIgA-coated bacteria and SIgA-based immune complexes in the intestinal mucosa A. Inflammatory immune responses: pathogens trigger inflammation by activating TLR signals (a), disrupting the intestinal barrier (b), and activating T-cells by pathogens (c) and by fully mature dendritic cells (DCs) (d). B. Homeostatic-type immune responses: Non-pathogenic bacteria coated by SIgA down-regulate local inflammation by reinforcing the barrier function (e), inducing regulatory T cells (f), directly interacting with T-helper cells (g), and biofilm formation (h). The combination of these events contributes to the maintenance of homeostasis.
4. The Effect of Probiotics on Intestinal IgA Levels
Probiotics are live, microbial food ingredients that are considered to be beneficial to health. Bacterial strains with the most convincing evidence of beneficial properties belong to the genera Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Probiotics have been demonstrated to be effective in reducing the incidence and severity of necrotizing enterocolitis in animal models [90] and babies [91], reducing the severity of acute diarrhea in children [92] and reducing recurrences of Clostridium difficile colitis in adults [93]. The beneficial effects of probiotics can be achieved through a variety of mechanisms. Probiotics can help fortify the gut’s barrier function [94] and modulate immune responses in the intestine, including promoting tolerogenic DC [95] and regulatory T-cell (Treg) [96] phenotypes, inhibiting inflammatory cytokine production [90,97] and enhancing natural killer cell activity [98]. Probiotics also stimulate systemic and mucosal IgA production in humans [99,100]. Clinical studies of both preterm infants treated with antibiotics and normal full-term infants have shown that supplementation with the probiotic, Bifidobacterium lactis, augments the IgA level in stools [101,102].
In animal models, probiotics have been shown to augment total and pathogen-specific IgA levels upon infection. Mice given L. casei displayed significantly increased IgA-producing cells in the LP of small intestine. Specific antibodies against L. casei were not produced, indicating the non-responsiveness of the gut immune system to the beneficial bacterium [103]. Pretreatment of mice with Bifidobacterium species (B. bifidum and B. infantis) also significantly reduced illness after challenge with rotavirus, while gut mucosal pathogen-specific IgA antibody titers were increased in animals given probiotic pretreatment [104,105]. In infant rabbits pretreated with L. casei, the morbidity resulting from enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) infection was reduced, attributed to increased mucosal levels of anti-EHEC and anti-Shiga toxin IgA antibodies compared with controls [106]. In gnotobiotic pigs, a probiotic combination of L. acidophilus strain NCFMTM and L. reuteri strain ATCC 23272 given prior to rotavirus infection significantly enhanced the responses of intestinal IgA secreting cells and total serum IgM and intestinal IgM and IgG titers [107]. However, not all probiotics are equivalent in terms of their effects on IgA production. A combination of L. rhamnosus and B. lactis did not increase IgA levels in rats [108]. Therefore, probiotics may modulate immune responses, leading to tolerance or IgA activation, but their impact appears to be highly dependent on the probiotic species and strain and on the animal model studied.
5. Summary
Intestinal microbiota drives the development of intestinal B-cell-derived, IgA-producing plasma cells residing in the lamina propria of intestine. There is a crucial window early in development when an as yet undefined small intestinal and colonic microbiota is essential for the B-cell system to develop. Secretory IgA reacts with the commensal organisms in the lumen of the intestine. These IgA-reactive commensals allow a controlled proliferation of resident luminal microorganisms, which, in turn, actually stimulate the host’s vigorous immune response to the occasional pathogenic invader. Probiotics have an enhancing effect on this protective mechanism. Even though recent findings revealed new complexities in the mechanisms and functions of IgA in the gut, more studies are still required to understand host-bacterial relationships in the gut. We still know very little about the composition of bacterial communities in the intestine, how these communities adapt to different environmental conditions in distinct segments of the intestine, their impact on host physiology and how the IgA diversity and quality impact on the composition of commensal bacteria. All these questions need to be addressed in order to fully understand the development and function of the immune system, to manipulate the system and reinforce its fitness and to develop novel approaches for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Acknowledgements
The research topics presented in this review are supported in part by Public Health Service Grant DK56338, which funds the Texas Medical Center Digestive Diseases Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Angenent, L.T.; Gordon, J.I. Getting a Grip on Things: How Do Communities of Bacterial Symbionts Become Established in Our Intestine? Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The Gut Flora As a Forgotten Organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ha, S.A.; Tsuji, M.; Fagarasan, S. Intestinal IgA Synthesis: A Primitive Form of Adaptive Immunity That Regulates Microbial Communities in the Gut. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Paglino, J.; Eslami-Varzaneh, F.; Edberg, S.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of Commensal Microflora by Toll-Like Receptors Is Required for Intestinal Homeostasis. Cell 2004, 118, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette, A.J. Paneth Cells and Innate Immunity in the Crypt Microenvironment. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, K.; Plitas, G.; Schnabl, B.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Pamer, E.G. MyD88-Mediated Signals Induce the Bactericidal Lectin RegIII Gamma and Protect Mice Against Intestinal Listeria Monocytogenes Infection. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, L.V.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Hong, C.V.; Gordon, J.I. Angiogenins: A New Class of Microbicidal Proteins Involved in Innate Immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Salzman, N.H.; Underwood, M.A.; Bevins, C.L. Paneth Cells, Defensins, and the Commensal Microbiota: A Hypothesis on Intimate Interplay at the Intestinal Mucosa. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- Golovkina, T.V.; Shlomchik, M.; Hannum, L.; Chervonsky, A. Organogenic Role of B Lymphocytes in Mucosal Immunity. Science 1999, 286, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Takedatsu, H.; Blumberg, R.S.; Bhan, A.K. Chronic Intestinal Inflammatory Condition Generates IL-10-Producing Regulatory B Cell Subset Characterized by CD1d Upregulation. Immunity 2002, 16, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti, A.; Chen, K.; Chorny, A. Immunoglobulin Responses at the Mucosal Interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 273–293. [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; Johansen, F.E.; Brandtzaeg, P. The Immune Geography of IgA Induction and Function. Mucosal. Immunol. 2008, 1, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden, P.J.; Stok, W.; Bianchi, A.T. Contribution of Immunoglobulin-Secreting Cells in the Murine Small Intestine to the Total 'Background' Immunoglobulin Production. Immunology 1987, 62, 551–555. [Google Scholar]
- Apter, F.M.; Lencer, W.I.; Finkelstein, R.A.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Neutra, M.R. Monoclonal Immunoglobulin A Antibodies Directed Against Cholera Toxin Prevent the Toxin-Induced Chloride Secretory Response and Block Toxin Binding to Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Vitro. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 5271–5278. [Google Scholar]
- Helander, A.; Miller, C.L.; Myers, K.S.; Neutra, M.R.; Nibert, M.L. Protective Immunoglobulin A and G Antibodies Bind to Overlapping Intersubunit Epitopes in the Head Domain of Type 1 Reovirus Adhesin Sigma1. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10695–10705. [Google Scholar]
- Mantis, N.J.; McGuinness, C.R.; Sonuyi, O.; Edwards, G.; Farrant, S.A. Immunoglobulin A Antibodies Against Ricin A and B Subunits Protect Epithelial Cells From Ricin Intoxication. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, A.B.; Helander, A.; Silvey, K.J.; Chandran, K.; Lucas, W.T.; Nibert, M.L.; Neutra, M.R. Secretory Immunoglobulin A Antibodies Against the Sigma1 Outer Capsid Protein of Reovirus Type 1 Lang Prevent Infection of Mouse Peyer's Patches. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplancke, B.; Gaskins, H.R. Microbial Modulation of Innate Defense: Goblet Cells and the Intestinal Mucus Layer. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 1131S–1141S. [Google Scholar]
- Lievin-Le, M.V.; Servin, A.L. The Front Line of Enteric Host Defense Against Unwelcome Intrusion of Harmful Microorganisms: Mucins, Antimicrobial Peptides, and Microbiota. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantis, N.J.; Forbes, S.J. Secretory IgA: Arresting Microbial Pathogens at Epithelial Borders. Immunol. Invest 2010, 39, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikina, T.; Hiroi, T.; Iwatani, K.; Jang, M.H.; Fukuyama, S.; Tamura, M.; Kubo, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Kiyono, H. IgA Class Switch Occurs in the Organized Nasopharynx- and Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue, but Not in the Diffuse Lamina Propria of Airways and Gut. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6259–6264. [Google Scholar]
- Bealmear, P.M.; Mirand, E.A.; Holtermann, O.A. Miscellaneous Immune Defects in Gnotobiotic and SPF Mice. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1983, 132C, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ouwehand, A.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. The Role of the Intestinal Microflora for the Development of the Immune System in Early Childhood. Eur. J. Nutr. 2002, 41, I32–I37. [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Uhr, T. Induction of Protective IgA by Intestinal Dendritic Cells Carrying Commensal Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulzhenko, N.; Morgun, A.; Hsiao, W.; Battle, M.; Yao, M.; Gavrilova, O.; Orandle, M.; Mayer, L.; Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. Crosstalk Between B Lymphocytes, Microbiota and the Intestinal Epithelium Governs Immunity Versus Metabolism in the Gut. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagarasan, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Suzuki, K.; Nagaoka, H.; Hiai, H.; Honjo, T. Critical Roles of Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase in the Homeostasis of Gut Flora. Science 2002, 298, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Su, T.T.; Dalwadi, H.; Stephan, R.P.; Fujiwara, D.; Huang, T.T.; Brewer, S.; Chen, L.; Arditi, M.; Borneman, J.; et al. Resident Enteric Microbiota and CD8+ T Cells Shape the Abundance of Marginal Zone B Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3411–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, A.C.; Bjornsson, V.; Ljung, A.; Ceder, M.; Johansen, S.; Lindhagen, G.; Tornhage, C.J.; Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.E.; Rudin, A. Infant B Cell Memory Differentiation and Early Gut Bacterial Colonization. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4315–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, A.; Lundell, A.C. Infant B Cell Memory and Gut Bacterial Colonization. Gut Microbes. 2012, 3, 474–475. [Google Scholar]
- Mellander, L.; Carlsson, B.; Jalil, F.; Soderstrom, T.; Hanson, L.A. Secretory IgA Antibody Response Against Escherichia Coli Antigens in Infants in Relation to Exposure. J. Pediatr. 1985, 107, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlerberth, I.; Carlsson, B.; de, M.P.; Jalil, F.; Khan, S.R.; Larsson, P.; Mellander, L.; Svanborg, C.; Wold, A.E.; Hanson, L.A. Intestinal Colonization With Enterobacteriaceae in Pakistani and Swedish Hospital-Delivered Infants. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1991, 80, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlerberth, I.; Wold, A.E. Establishment of the Gut Microbiota in Western Infants. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowrouzian, F.; Hesselmar, B.; Saalman, R.; Strannegard, I.L.; Aberg, N.; Wold, A.E.; Adlerberth, I. Escherichia Coli in Infants' Intestinal Microflora: Colonization Rate, Strain Turnover, and Virulence Gene Carriage. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 54, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzi, M.; Kull, I.; Sjoberg, R.; Wan, J.; Melen, E.; Bayat, N.; Ostblom, E.; Pan-Hammarstrom, Q.; Nilsson, P.; Hammarstrom, L. Selective IgA Deficiency in Early Life: Association to Infections and Allergic Diseases During Childhood. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamut, G.; Verkarre, V.; Suarez, F.; Viallard, J.F.; Lascaux, A.S.; Cosnes, J.; Bouhnik, Y.; Lambotte, O.; Bechade, D.; Ziol, M.; et al. The Enteropathy Associated With Common Variable Immunodeficiency: the Delineated Frontiers With Celiac Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2262–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meini, A.; Pillan, N.M.; Villanacci, V.; Monafo, V.; Ugazio, A.G.; Plebani, A. Prevalence and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease in IgA-Deficient Children. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996, 77, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Hiroi, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Masunaga, Y.; Hachimura, S.; Kaminogawa, S.; Takahashi-Iwanaga, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Kiyono, H.; et al. Identification of Multiple Isolated Lymphoid Follicles on the Antimesenteric Wall of the Mouse Small Intestine. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, T.D.; Carragher, D.M.; Rangel-Moreno, J. Development of Secondary Lymphoid Organs. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Honda, K.; Vieira, P.; Yoshida, H. Organogenesis of Peripheral Lymphoid Organs. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 195, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.; Tangye, S.G.; Mackay, C.R. T Follicular Helper (TFH) Cells in Normal and Dysregulated Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casola, S.; Otipoby, K.L.; Alimzhanov, M.; Humme, S.; Uyttersprot, N.; Kutok, J.L.; Carroll, M.C.; Rajewsky, K. B Cell Receptor Signal Strength Determines B Cell Fate. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Cebra, J.J. Influences of Microbiota on Intestinal Immune System Development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1046S–1051S. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Fagarasan, S.; Yamada, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Honjo, T. Class Switch Recombination and Hypermutation Require Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID), a Potential RNA Editing Enzyme. Cell 2000, 102, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieppa, M.; Rescigno, M.; Huang, A.Y.; Germain, R.N. Dynamic Imaging of Dendritic Cell Extension into the Small Bowel Lumen in Response to Epithelial Cell TLR Engagement. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Macpherson, A.J. Immune Adaptations That Maintain Homeostasis With the Intestinal Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Hashiguchi, M.; Toda, E.; Iwasaki, A.; Hachimura, S.; Kaminogawa, S. CD11b+ Peyer's Patch Dendritic Cells Secrete IL-6 and Induce IgA Secretion From Naive B Cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Rothstein, T.L. Lymphokine Dependence of STAT3 Activation Produced by Surface Immunoglobulin Cross-Linking and by Phorbol Ester Plus Calcium Ionophore Treatment in B Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber-Nordt, R.M.; Riley, J.K.; Greenlund, A.C.; Moore, K.W.; Darnell, J.E.; Schreiber, R.D. Stat3 Recruitment by Two Distinct Ligand-Induced, Tyrosine-Phosphorylated Docking Sites in the Interleukin-10 Receptor Intracellular Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 27954–27961. [Google Scholar]
- Lafarge, S.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Richard, Y.; Pozzetto, B.; Cogne, M.; Cognasse, F.; Garraud, O. Complexes Between Nuclear Factor-KappaB P65 and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Are Key Actors in Inducing Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase Expression and Immunoglobulin A Production in CD40L Plus Interleukin-10-Treated Human Blood B Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Lamarre, A.; McCoy, K.; Harriman, G.R.; Odermatt, B.; Dougan, G.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. IgA Production Without Mu or Delta Chain Expression in Developing B Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.T.; Patel, S.R.; Lin, E.; Butler, B.R.; Lake, J.G.; Newberry, R.D.; Williams, I.R. Lymphotoxin-Independent Expression of TNF-Related Activation-Induced Cytokine by Stromal Cells in Cryptopatches, Isolated Lymphoid Follicles, and Peyer's Patches. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kitamura, H.; Maruya, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Ivanov, I.I.; Itoh, K.; Littman, D.R.; Fagarasan, S. Requirement for Lymphoid Tissue-Inducer Cells in Isolated Follicle Formation and T Cell-Independent Immunoglobulin A Generation in the Gut. Immunity 2008, 29, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.G.; Chaplin, D.D.; McDonald, K.G.; McDonough, J.S.; Newberry, R.D. Isolated Lymphoid Follicle Formation Is Inducible and Dependent Upon Lymphotoxin-Sufficient B Lymphocytes, Lymphotoxin Beta Receptor, and TNF Receptor I Function. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar]
- Gardby, E.; Kagrdic, D.; Kjerrulf, M.; Bromander, A.; Vajdy, M.; Hornquist, E.; Lycke, N. The Influence of Costimulation and Regulatory CD4+ T Cells on Intestinal IgA Immune Responses. Dev. Immunol. 1998, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, H.; Abe, Y.; Iwata, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Matsushita, M.; Shiohara, T.; Akira, S.; Ohteki, T. Regulation of IgA Production by Naturally Occurring TNF/INOS-Producing Dendritic Cells. Nature 2007, 448, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xu, W.; Santini, P.A.; Polydorides, A.D.; Chiu, A.; Estrella, J.; Shan, M.; Chadburn, A.; Villanacci, V.; Plebani, A.; et al. Intestinal Bacteria Trigger T Cell-Independent Immunoglobulin A(2) Class Switching by Inducing Epithelial-Cell Secretion of the Cytokine APRIL. Immunity 2007, 26, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Schneider, P. TACI, an Enigmatic BAFF/APRIL Receptor, With New Unappreciated Biochemical and Biological Properties. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Fagarasan, S. Dynamic Interactions Between Bacteria and Immune Cells Leading to Intestinal IgA Synthesis. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Leung, H. The Role of the BAFF/APRIL System on T Cell Function. Semin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O. New Concepts in the Generation and Functions of IgA. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.H.; Rojas, O.L.; Simard, N.; McCarthy, D.D.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Rubino, S.; Robertson, S.J.; Larijani, M.; Gosselin, J.; Ivanov, I.I.; et al. Acquisition of a Multifunctional IgA+ Plasma Cell Phenotype in the Gut. Nature 2012, 481, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Berlin, C.; Berg, E.L.; Briskin, M.J.; Andrew, D.P.; Kilshaw, P.J.; Holzmann, B.; Weissman, I.L.; Hamann, A.; Butcher, E.C. Alpha 4 Beta 7 Integrin Mediates Lymphocyte Binding to the Mucosal Vascular Addressin MAdCAM-1. Cell 1993, 74, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, E.P.; Kuklin, N.A.; Youngman, K.R.; Lazarus, N.H.; Kunkel, E.J.; Pan, J.; Greenberg, H.B.; Butcher, E.C. The Intestinal Chemokine Thymus-Expressed Chemokine (CCL25) Attracts IgA Antibody-Secreting Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Ley, R. The Human Gut Microbiome: Ecology and Recent Evolutionary Changes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, E.; Balmer, M.L.; Fritz, J.H.; Hapfelmeier, S. Functional Flexibility of Intestinal IgA—Broadening the Fine Line. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N.L.; Spoerri, I.; Schopfer, J.F.; Nembrini, C.; Merky, P.; Massacand, J.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Lamarre, A.; Burki, K.; Odermatt, B.; et al. Mechanisms of Neonatal Mucosal Antibody Protection. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6256–6262. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, D.A.; McNulty, N.P.; Guruge, J.L.; Gordon, J.I. IgA Response to Symbiotic Bacteria As a Mediator of Gut Homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.I.; Pedron, T.; Tournebize, R.; Olivo-Marin, J.C.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Phalipon, A. Anti-Inflammatory Role for Intracellular Dimeric Immunoglobulin a by Neutralization of Lipopolysaccharide in Epithelial Cells. Immunity 2003, 18, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Meek, B.; Doi, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Chiba, T.; Honjo, T.; Fagarasan, S. Aberrant Expansion of Segmented Filamentous Bacteria in IgA-Deficient Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hapfelmeier, S.; Lawson, M.A.; Slack, E.; Kirundi, J.K.; Stoel, M.; Heikenwalder, M.; Cahenzli, J.; Velykoredko, Y.; Balmer, M.L.; Endt, K.; et al. Reversible Microbial Colonization of Germ-Free Mice Reveals the Dynamics of IgA Immune Responses. Science 2010, 328, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruta, T.; Inoue, R.; Nojima, I.; Tsukahara, T.; Hara, H.; Yajima, T. The Amount of Secreted IgA May Not Determine the Secretory IgA Coating Ratio of Gastrointestinal Bacteria. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Waaij, L.A.; Limburg, P.C.; Mesander, G.; van der Waaij, D. In Vivo IgA Coating of Anaerobic Bacteria in Human Faeces. Gut 1996, 38, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestecky, J.; Russell, M.W. Specific Antibody Activity, Glycan Heterogeneity and Polyreactivity Contribute to the Protective Activity of S-IgA at Mucosal Surfaces. Immunol. Lett. 2009, 124, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Homeostatic Impact of Indigenous Microbiota and Secretory Immunity. Benef. Microbes. 2010, 1, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, F.E.; Kaetzel, C.S. Regulation of the Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor and IgA Transport: New Advances in Environmental Factors That Stimulate PIgR Expression and Its Role in Mucosal Immunity. Mucosal. Immunol. 2011, 4, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.E.; Frantz, A.L.; Rogier, E.W.; Johansen, F.E.; Kaetzel, C.S. Regulation of the Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor by the Classical and Alternative NF-KappaB Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Mucosal. Immunol. 2011, 4, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopenian, D.C.; Akilesh, S. FcRn: the Neonatal Fc Receptor Comes of Age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hase, K.; Kawano, K.; Nochi, T.; Pontes, G.S.; Fukuda, S.; Ebisawa, M.; Kadokura, K.; Tobe, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Kawano, S.; et al. Uptake Through Glycoprotein 2 of FimH(+) Bacteria by M Cells Initiates Mucosal Immune Response. Nature 2009, 462, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neutra, M.R.; Kraehenbuhl, J.P. Transepithelial Transport and Mucosal Defence I: The Role of M Cells. Trends Cell Biol. 1992, 2, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantis, N.J.; Rol, N.; Corthesy, B. Secretory IgA's Complex Roles in Immunity and Mucosal Homeostasis in the Gut. Mucosal. Immunol. 2011, 4, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, J.; Garin, N.; Spertini, F.; Corthesy, B. Targeting of Secretory IgA to Peyer's Patch Dendritic and T Cells After Transport by Intestinal M Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial Biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, R.R.; Everett, M.L.; Palestrant, D.; Love, S.D.; Lin, S.S.; Parker, W. Human Secretory Immunoglobulin A May Contribute to Biofilm Formation in the Gut. Immunology 2003, 109, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, R.R.; Everett, M.L.; Wahl, S.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Orndorff, P.E.; Parker, W. Secretory IgA and Mucin-Mediated Biofilm Formation by Environmental Strains of Escherichia Coli: Role of Type 1 Pili. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestrant, D.; Holzknecht, Z.E.; Collins, B.H.; Parker, W.; Miller, S.E.; Bollinger, R.R. Microbial Biofilms in the Gut: Visualization by Electron Microscopy and by Acridine Orange Staining. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2004, 28, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Friman, V.; Adlerberth, I.; Connell, H.; Svanborg, C.; Hanson, L.A.; Wold, A.E. Decreased Expression of Mannose-Specific Adhesins by Escherichia Coli in the Colonic Microflora of Immunoglobulin A-Deficient Individuals. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2794–2798. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Mangalat, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Lactobacillus Reuteri Strains Reduce Incidence and Severity of Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis Via Modulation of TLR4 and NFkappaB Signaling in the Intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G608–G617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Walker, W.A. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Bousvaros, A.; Lee, J.W.; Diaz, A.; Davidson, E.J. Efficacy of Probiotic Use in Acute Diarrhea in Children: a Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002, 47, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, M.C.; Alemayehu, D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Gut Solutions to a Gut Problem: Bacteriocins, Probiotics and Bacteriophage for Control of Clostridium Difficile Infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohland, C.L.; MacNaughton, W.K. Probiotic Bacteria and Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G807–G819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.L.; Lammers, K.; Brigidi, P.; Vitali, B.; Rizzello, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Campieri, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Knight, S.C.; Stagg, A.J. Modulation of Human Dendritic Cell Phenotype and Function by Probiotic Bacteria. Gut 2004, 53, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Dingle, B.M.; Tran, D.Q.; Rhoads, M. Lactobacillus Reuteri DSM 17938 Changes the Frequency of Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells in the Intestine and Mesenteric Lymph Node in Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e56547. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Mangalat, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Human Derived Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri Strains Differentially Reduce Intestinal Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G1087–G1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Hart, A.L.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J.; Knight, S.C. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics: Recent Advances. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2009, 15, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, Y.; Kawata, Y.; Hara, H.; Terada, A.; Mitsuoka, T. Effect of a Probiotic Formula on Intestinal Immunoglobulin A Production in Healthy Children. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 42, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, M.; Isolauri, E.; Soppi, E.; Virtanen, E.; Laine, S.; Arvilommi, H. Enhancement of the Circulating Antibody Secreting Cell Response in Human Diarrhea by a Human Lactobacillus Strain. Pediatr. Res. 1992, 32, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D.; Czerkies, L.A.; Cekola, P.; Litov, R.; Benbow, M.; Santema, S.; Alexander, D.D.; Perez, V.; Sun, S.; Saavedra, J.M.; et al. Bifidobacterium Lactis Bb12 Enhances Intestinal Antibody Response in Formula-Fed Infants: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2012, 36, 106S–117S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Koebnick, C.; Schildt, J.; Mueller, M.; Radke, M.; Blaut, M. Effects of Bifidobacterium Lactis Bb12 Supplementation on Body Weight, Fecal PH, Acetate, Lactate, Calprotectin, and IgA in Preterm Infants. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, C.M.; Perdigon, G. The Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus Casei Induces Activation of the Gut Mucosal Immune System Through Innate Immunity. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Duffy, L.C.; Griffiths, E.; Dryja, D.; Leavens, A.; Rossman, J.; Rich, G.; Riepenhoff-Talty, M.; Locniskar, M. Immune Responses in Rhesus Rotavirus-Challenged BALB/c Mice Treated With Bifidobacteria and Prebiotic Supplements. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 51, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Gill, H.S. A Dietary Probiotic (Bifidobacterium Lactis HN019) Reduces the Severity of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Infection in Mice. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 189, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Shimizu, K.; Nomoto, K.; Takahashi, M.; Watanuki, M.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, T.; Hamabata, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Takeda, Y. Protective Effect of Lactobacillus Casei Strain Shirota on Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Infection in Infant Rabbits. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Azevedo, M.S.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Saif, L.J.; Van, N.T.; Wen, K.; Yousef, A.E.; Yuan, L. Influence of Probiotic Lactobacilli Colonization on Neonatal B Cell Responses in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 122, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, M.; Rechkemmer, G.; Watzl, B. Prebiotic Inulin Enriched With Oligofructose in Combination With the Probiotics Lactobacillus Rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium Lactis Modulates Intestinal Immune Functions in Rats. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).