Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Flow Cytometry
3. Results
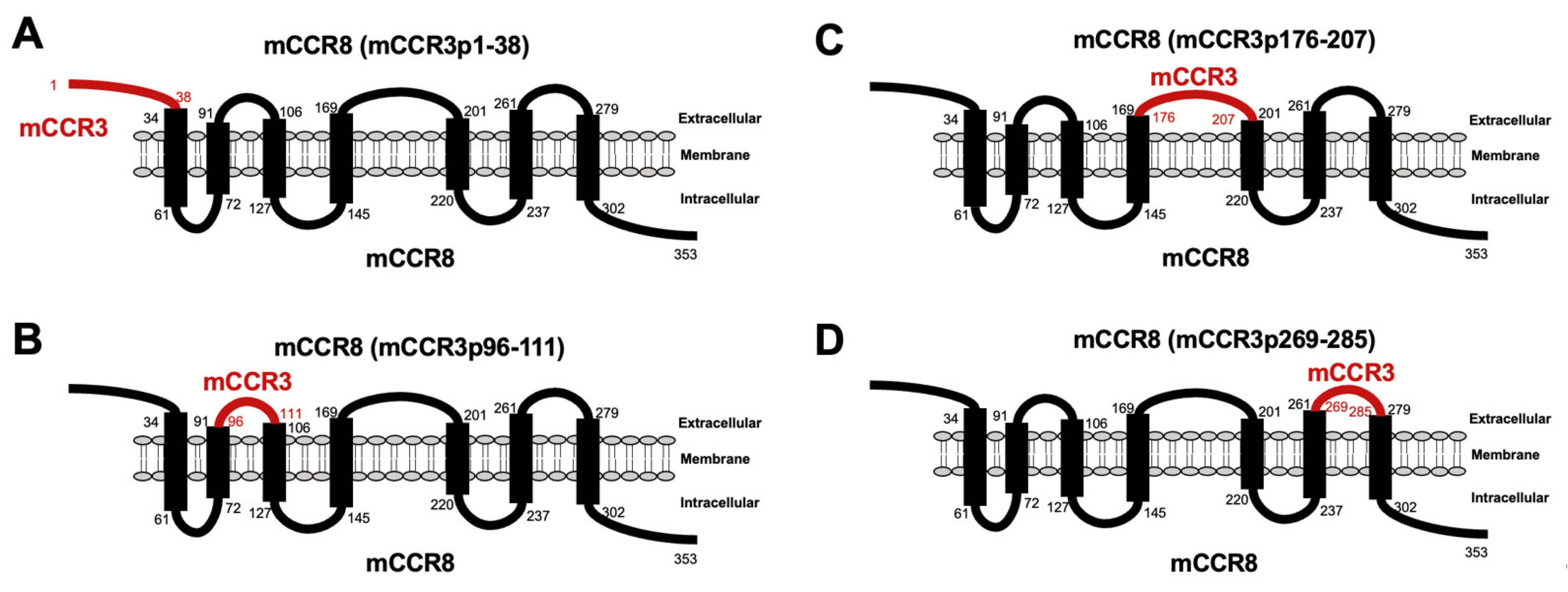
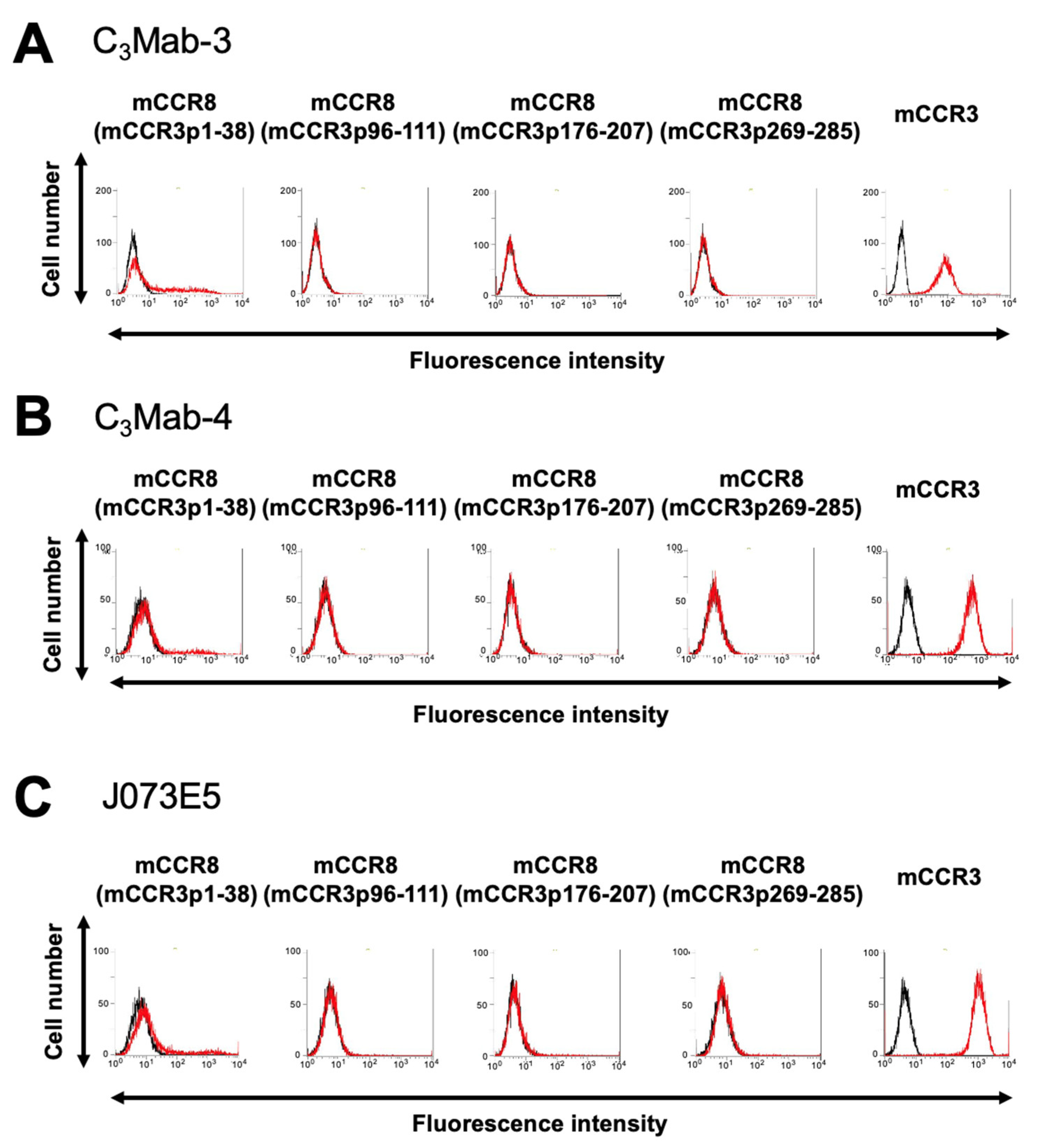
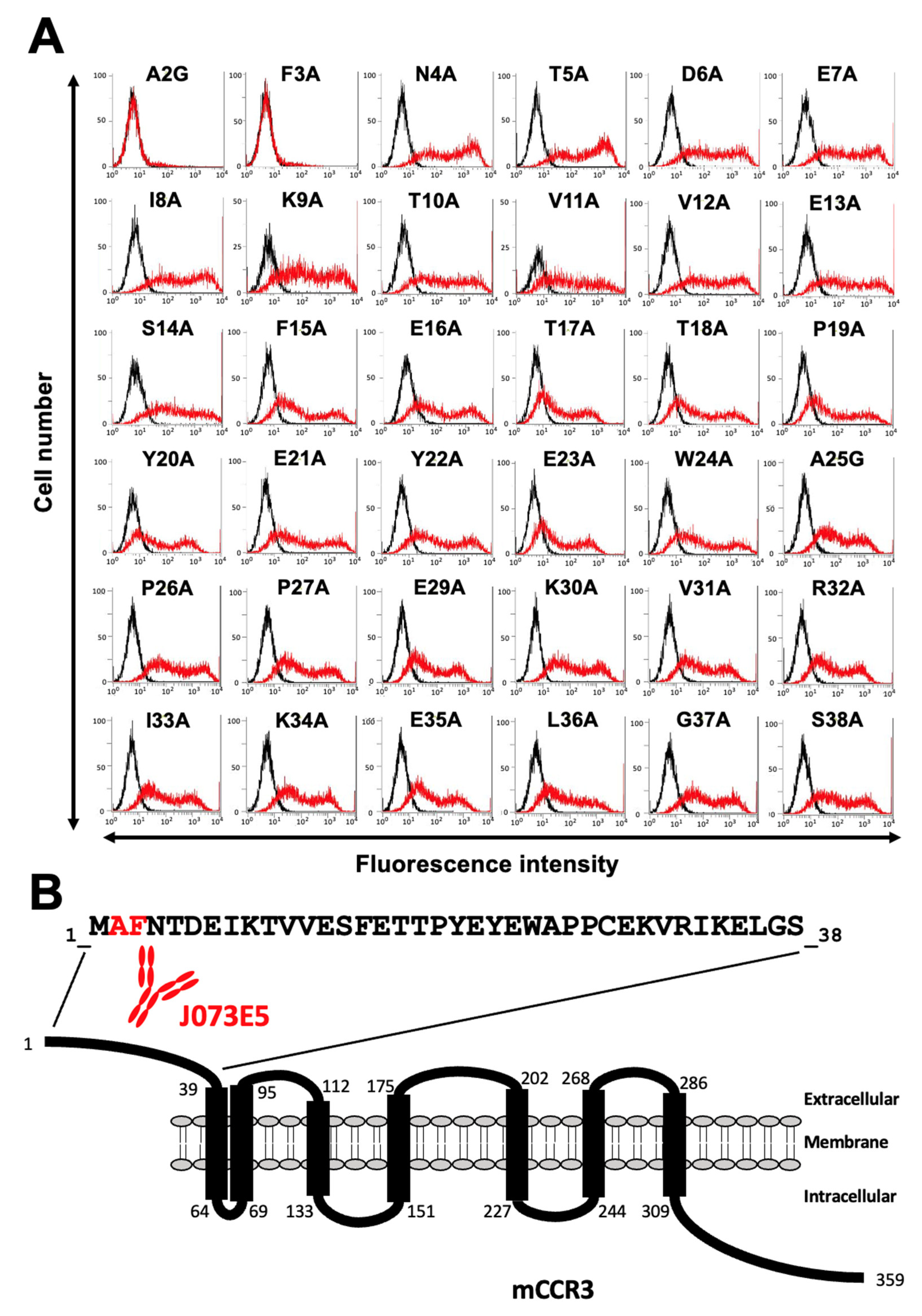
3.1. Determination of the Epitope of Anti-mCCR3 mAbs Using Flow Cytometry and Chimeric Proteins
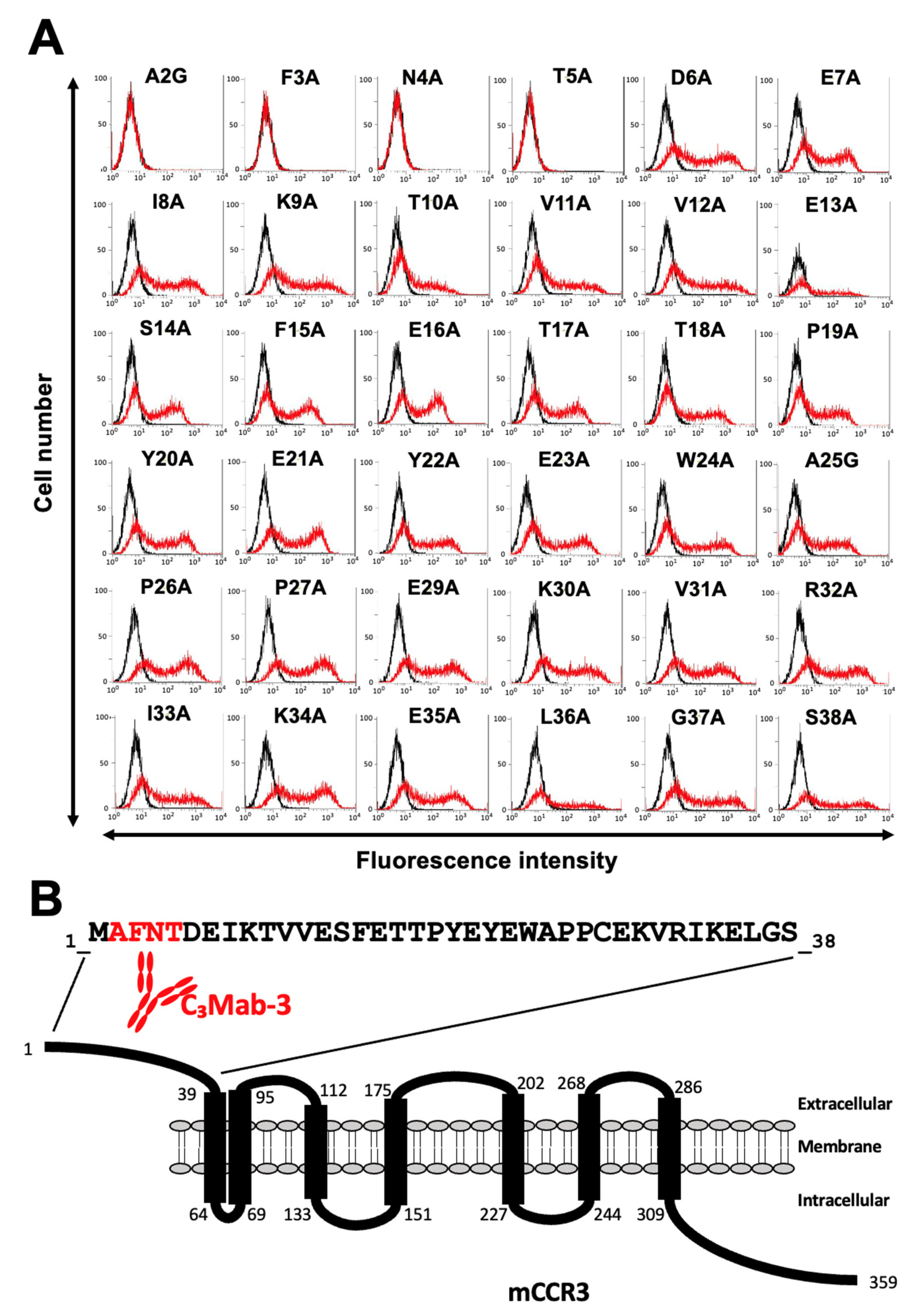
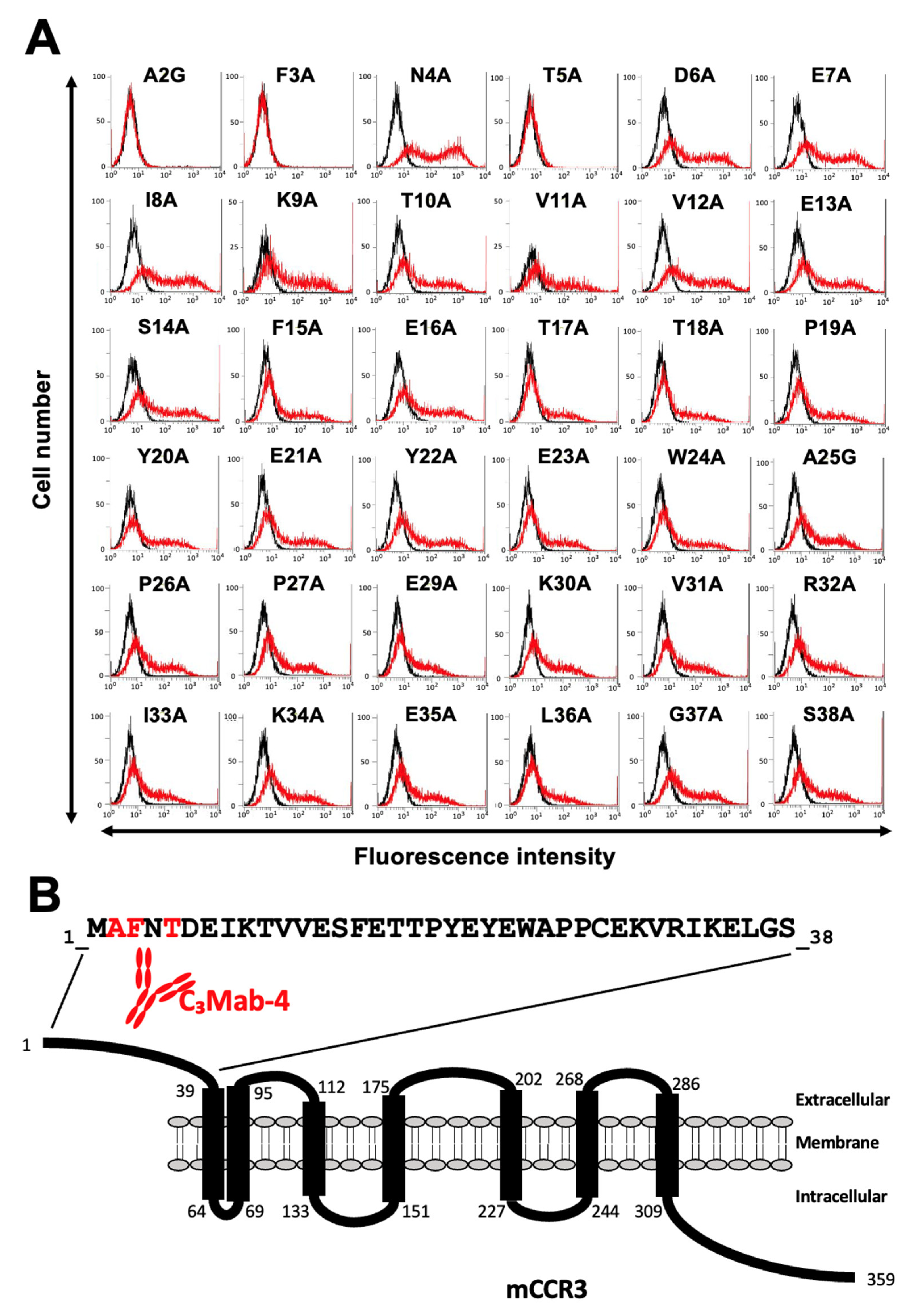
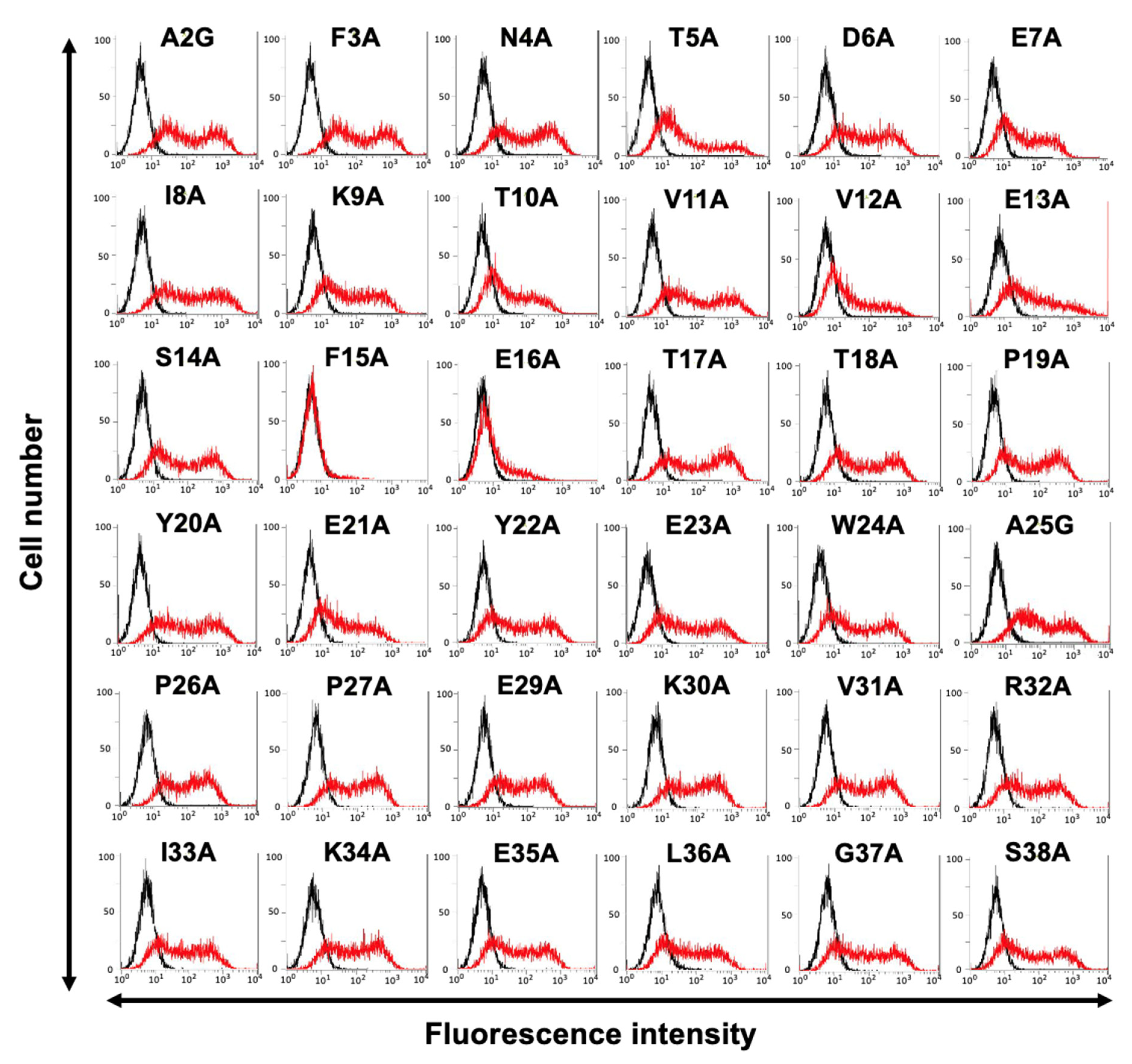
3.2. Determination of the C3Mab-3 Epitope Using Flow Cytometry and Alanine Scanning
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kufareva, I.; Salanga, C.L.; Handel, T.M. Chemokine and chemokine receptor structure and interactions: Implications for therapeutic strategies. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O. Chemokines: A New Classification System and Their Role in Immunity. Immunity 2000, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charo, I.F.; Ransohoff, R.M. The Many Roles of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, P.M.; Baggiolini, M.; Charo, I.F.; Hébert, C.A.; Horuk, R.; Matsushima, K.; Miller, L.H.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Power, C.A. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 145–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wise, E.L.; Duchesnes, C.; da Fonseca, P.; Allen, R.A.; Williams, T.J.; Pease, J.E. Small Molecule Receptor Agonists and Antagonists of CCR3 Provide Insight into Mechanisms of Chemokine Receptor Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27935–27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisset, L.R.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P. Chemokines and their receptors in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma: Progress and perspective. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, C.R. Moving targets: Cell migration inhibitors as new anti-inflammatory therapies. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, L.I.; Ijzerman, A.P. Small molecule antagonists for chemokine CCR3 receptors. Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 778–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellato, C.; Brummet, M.E.; Plitt, J.R.; Shahabuddin, S.; Baroody, F.M.; Liu, M.C.; Ponath, P.D.; Beck, L.A. Cutting Edge: Expression of the C-C Chemokine Receptor CCR3 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, Y.; Farzan, M.; Choe, H.; Ohagen, A.; Gartner, S.; Busciglio, J.; Yang, X.; Hofmann, W.; Newman, W.; et al. CCR3 and CCR5 are co-receptors for HIV-1 infection of microglia. Nature 1997, 385, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, H.; Qin, S.; Rao, P.; Wu, L.; LaRosa, G.; Kassam, N.; Ponath, P.D.; Mackay, C. Chemokine receptor usage by human eosinophils. The importance of CCR3 demonstrated using an antagonistic monoclonal antibody. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallusto, F.; Mackay, C.R.; Lanzavecchia, A. Selective Expression of the Eotaxin Receptor CCR3 by Human T Helper 2 Cells. Science 1997, 277, 2005–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, D.C.; Wong, Y.H. CC chemokine receptor-coupled signalling pathways. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao 2003, 35, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kroeze, W.K.; Sheffler, D.J.; Roth, B.L. G-protein-coupled receptors at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4867–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, G.T.; Stafford, S.; Adachi, T.; Jinquan, T.; Quan, S.; Grant, J.A.; Skov, P.S.; Poulsen, L.K.; Alam, R. Eotaxin induces degranulation and chemotaxis of eosinophils through the activation of ERK2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Blood 2000, 95, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Bertics, P.J. Chemoattractant-Induced Signaling via the Ras–ERK and PI3K–Akt Networks, along with Leukotriene C4 Release, Is Dependent on the Tyrosine Kinase Lyn in IL-5– and IL-3–Primed Human Blood Eosinophils. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, P.C.; Fischetti, C.A.; McBride, M.L.; Hassman, L.M.; Hogan, S.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. A central regulatory role for eosinophils and the eotaxin/CCR3 axis in chronic experimental allergic airway inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16418–16423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Kuo, C.-H.; Morohoshi, K.; Liu, F.-T.; Ono, S.J. The murine CCR3 receptor regulates both eosinophilia and hyperresponsiveness in IgE-mediated allergic conjunctivitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantry, D.; Burgess, L.E. Chemokines in Allergy. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2002, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, J.E. Asthma, Allergy and Chemokines. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, D.; Nakamura, T.; Komatsu, N.; Nawata, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Higashi, H.; Ono, S.J. Roles of Chemokines in Ocular Allergy and Possible Therapeutic Strategies. Cornea 2004, 23, S48–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Lim, S.-J.; Won, K.Y.; Bae, G.; Kim, G.Y.; Min, J.W.; Noh, B.-J. Eosinophils in Colorectal Neoplasms Associated with Expression of CCL11 and CCL24. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.K.; Mir, H.; Kapur, N.; Bae, S.; Singh, S. CC chemokines are differentially expressed in Breast Cancer and are associated with disparity in overall survival. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorena, S.; Oliveira, D.; Dorta, R.; Landman, G.; Kowalski, L. Eotaxin expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas with and without tumour associated tissue eosinophilia. Oral Dis. 2003, 9, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, C.; Rollins, B.J. Chemokines and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Li, G.; Asano, T.; Saito, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-Mouse CCR2 Monoclonal Antibody (C2Mab-6) by N-Terminal Peptide Immunization. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Li, G.; Saito, M.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-human CCR2 Monoclonal Antibody (C2Mab-9) by N-Terminal Peptide Immunization. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 3 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Goto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of Novel Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies (C3Mab-6 and C3Mab-7) by N-terminal Peptide Immunization. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Saito, M.; Li, G.; Goto, N.; Nanamiya, R.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. C3Mab-3: A Monoclonal Antibody for Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 3 for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-Mouse CCR4 Monoclonal Antibody (C4Mab-1) by N-Terminal Peptide Immunization. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of an Anti-Mouse CCR8 Monoclonal Antibody (C8Mab-1) for Flow Cytometry and Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Saito, M.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kitamura, K.; Kudo, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. C8Mab-3: An Anti-Mouse CCR8 Monoclonal Antibody for Immunocytochemistry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 8 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Human CC Chemokine Receptor 9 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Cx6Mab-1: A Novel Anti-Mouse CXCR6 Monoclonal Antibody Established by N-Terminal Peptide Immunization. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Li, G.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of the Anti-Human CCR2 Monoclonal Antibody C2Mab-9. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Identification of the Binding Epitope of an Anti-mouse CCR4 Monoclonal Antibody, C4Mab-1. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2022, 41, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Li, G.; Saito, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of an Anti-Human CCR9 Monoclonal Antibody (C9Mab-1) Using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2021, 40, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-EpCAM Monoclonal Antibody for Various Applications. Antibodies 2022, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itai, S.; Fujii, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Chang, Y.-W.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Handa, S.; Suzuki, H.; Harada, H.; Yamada, S.; et al. Establishment of CMab-43, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-CD133 Monoclonal Antibody, for Immunohistochemistry. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2017, 36, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ogasawara, S.; Yamada, S.; Yanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Saidoh, N.; Yoshida, K.; Honma, R.; Kato, Y. Development of RAP Tag, a Novel Tagging System for Protein Detection and Purification. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2017, 36, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Yoshida, H.; Nosaki, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. RAP Tag and PMab-2 Antibody: A Tagging System for Detecting and Purifying Proteins in Plant Cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 510444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. MAP Tag: A Novel Tagging System for Protein Purification and Detection. Monoclon. Antibodies Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2016, 35, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakasa, A.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J.; Arimori, T. Site-specific epitope insertion into recombinant proteins using the MAP tag system. J. Biochem. 2020, 168, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Kohli, L.L.; Stone, M.J. Characterization of binding between the chemokine eotaxin and peptides derived from the chemokine receptor CCR3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27250–27257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, C.J.; Ludeman, J.P.; Canals, M.; Bridgford, J.L.; Hinds, M.G.; Clayton, D.J.; Christopoulos, A.; Payne, R.J.; Stone, M.J. Structural Basis of Receptor Sulfotyrosine Recognition by a CC Chemokine: The N-Terminal Region of CCR3 Bound to CCL11/Eotaxin-1. Structure 2014, 22, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, G.-S.; Wang, S.-B.; Xu, W.-H. CCR3 monoclonal antibody inhibits airway eosinophilic inflammation and mucus overproduction in a mouse model of asthma. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tateyama, N.; Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Li, G.; Yoshikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry. Antibodies 2022, 11, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11040075
Tateyama N, Asano T, Suzuki H, Li G, Yoshikawa T, Tanaka T, Kaneko MK, Kato Y. Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry. Antibodies. 2022; 11(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTateyama, Nami, Teizo Asano, Hiroyuki Suzuki, Guanjie Li, Takeo Yoshikawa, Tomohiro Tanaka, Mika K. Kaneko, and Yukinari Kato. 2022. "Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry" Antibodies 11, no. 4: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11040075
APA StyleTateyama, N., Asano, T., Suzuki, H., Li, G., Yoshikawa, T., Tanaka, T., Kaneko, M. K., & Kato, Y. (2022). Epitope Mapping of Anti-Mouse CCR3 Monoclonal Antibodies Using Flow Cytometry. Antibodies, 11(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib11040075






