Utilizing Immunocytokines for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
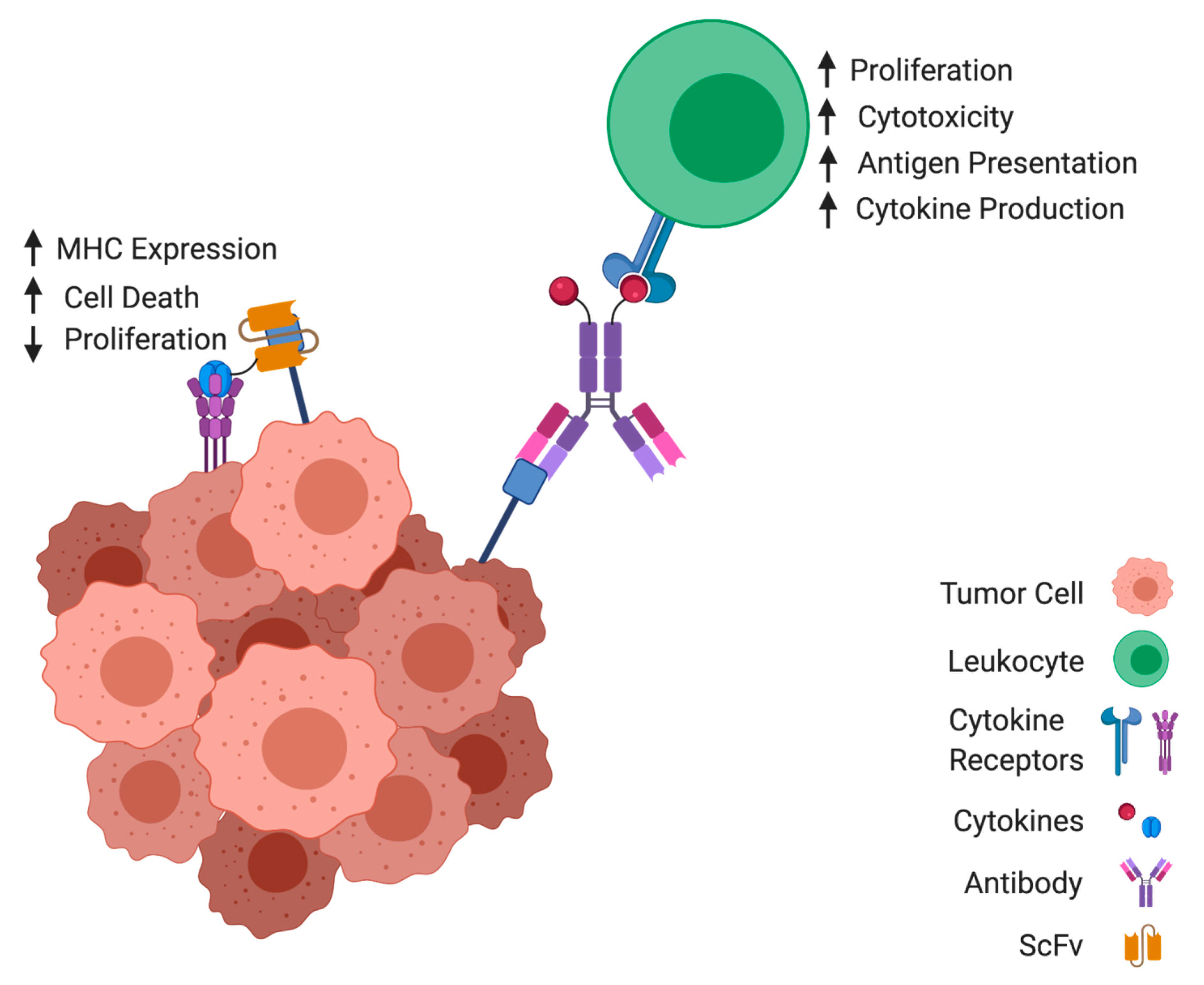
:1. Introduction
2. Immunocytokines in Pre-Clinical Models
2.1. Interleukin-2
2.2. Interferons
2.3. Tumor Necrosis Factor
2.4. Interleukin-12
2.5. Interleukin-15
2.6. Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
2.7. Additional Cytokines
2.8. Variants
3. Immunocytokines in Combination Therapeutic Approaches
3.1. Chemotherapy
3.2. Radiotherapy
3.3. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.4. Other Combinations
4. Clinical Investigations of Immunocytokines
5. Summary
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer Immunoediting: From Immunosurveillance to Tumor Escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, A.S.; Richards, E.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Enhanced in Vivo Growth and Resistance to Rejection of Tumor Cells Expressing Dominant Negative IFNγ Receptors. Immunity 1994, 1, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, D.Y.; Watson, J.; Gillis, S. Biochemical Separation of Interleukin 2. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 39, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.A.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gallo, R. Selective in Vitro Growth of T Lymphocytes from Normal Human Bone Marrows. Science 1976, 193, 1007–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.B.; Carlson, G.; Paetkau, V. Generation of Cytotoxic Lymphocytes to Syngeneic Tumors by Using Co-Stimulator (Interleukin 2): In Vivo Activity. J. Immunol. 1980, 125, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheever, M.A.; Greenberg, P.D.; Fefer, A.; Gillis, S. Augmentation of the Anti-Tumor Therapeutic Efficacy of Long-Term Cultured T Lymphocytes by in Vivo Administration of Purified Interleukin 2. J. Exp. Med. 1982, 155, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lienard, D.; Ewalenko, P.; Delmotte, J.J.; Renard, N.; Lejeune, F.J. High-Dose Recombinant Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Combination with Interferon Gamma and Melphalan in Isolation Perfusion of the Limbs for Melanoma and Sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, A.M.M.; Koops, H.S.; Klausner, J.M.; Kroon, B.B.R.; Schlag, P.M.; Liénard, D.; Van Geel, A.N.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Meller, I.; Nieweg, O.E.; et al. Isolated Limb Perfusion with Tumor Necrosis Factor and Melphalan for Limb Salvage in 186 Patients with Locally Advanced Soft Tissue Extremity Sarcomas: The Cumulative Multicenter European Experience. Ann. Surg. 1996, 224, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berraondo, P.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in Clinical Cancer Immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golomb, H.M.; Jacobs, A.; Fefer, A.; Ozer, H.; Thompson, J.; Portlock, C.; Ratain, M.; Golde, D.; Vardiman, J.; Burke, J.S. Alpha-2 Interferon Therapy of Hairy-Cell Leukemia: A Multicenter Study of 64 Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 1986, 4, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groopman, J.E.; Gottlieb, M.S.; Goodman, J.; Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Conant, M.A.; Prince, H.; Fahey, J.L.; Derezin, M.; Weinstein, W.M.; Casavante, C. Recombinant Alpha-2 Interferon Therapy for Kaposi’s Sarcoma Associated with the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 100, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volberding, P.A.; Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Golando, J.P.; Spiegel, R.J. Treatment of Kaposi’s Sarcoma with Interferon Alfa-2b (Intron A). Cancer 1987, 59, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, J.M.; Strawderman, M.H.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Smith, T.J.; Borden, E.C.; Blum, R.H. Interferon Alfa-2b Adjuvant Therapy of High-Risk Resected Cutaneous Melanoma: The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solal-Celigny, P.; Lepage, E.; Brousse, N.; Reyes, F.; Haioun, C.; Leporrier, M.; Peuchmaur, M.; Bosly, A.; Parlier, Y.; Brice, P.; et al. Recombinant Interferon Alfa-2b Combined with a Regimen Containing Doxorubicin in Patients with Advanced Follicular Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of Treatment of 255 Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Who Received High-Dose Recombinant Interleukin-2 Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.B.; Lotze, M.T.; Dutcher, J.P.; Fisher, R.I.; Weiss, G.; Margolin, K.; Abrams, J.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.; Hawkins, M.; et al. High-Dose Recombinant Interleukin 2 Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Melanoma: Analysis of 270 Patients Treated between 1985 and 1993. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Yang, J.C.; Topalian, S.L.; Chang, A.E.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Aebersold, P.; Leitman, S.; Linehan, W.M.; Seipp, C.A.; et al. Prospective Randomized Trial of High-Dose Interleukin-2 Alone or in Conjunction With Lymphokine-Activated Killer Cells for the Treatment of Patients With Advanced Cancer. JNCI 1993, 85, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, G.; Milstein, C. Continuous Cultures of Fused Cells Secreting Antibody of Predefined Specificity. Nature 1975, 256, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous Fusion Phage: Novel Expression Vectors That Display Cloned Antigens on the Virion Surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clackson, T.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G. Making Antibody Fragments Using Phage Display Libraries. Nature 1991, 352, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, C.F.; Kang, A.S.; Lerner, R.A.; Benkovic, S.J. Assembly of Combinatorial Antibody Libraries on Phage Surfaces: The Gene III Site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7978–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breitling, F.; Dübel, S.; Seehaus, T.; Klewinghaus, I.; Little, M. A Surface Expression Vector for Antibody Screening. Gene 1991, 104, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnemolla, B.; Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Castellani, P.; Meazza, R.; Berndt, A.; Ferrini, S.; Kosmehl, H.; Neri, D.; Zardi, L. Enhancement of the Antitumor Properties of Interleukin-2 by Its Targeted Delivery to the Tumor Blood Vessel Extracellular Matrix. Blood 2002, 99, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Carnemolla, B.; Sassi, F.; Castellani, P.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Birò, A.; Siri, A.; Orecchia, P.; et al. Selective Targeted Delivery of TNFα to Tumor Blood Vessels. Blood 2003, 102, 4384–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, H.R.; Volckaert, G.; Raus, J.C.M. Construction and Expression of Antibody-Tumor Necrosis Factor Fusion Proteins. Mol. Immunol. 1991, 28, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S.D.; Young, D.; Lo, K.M.; Foley, S.F.; Reisfeld, R.A. Expression of Genetically Engineered Immunoconjugates of Lymphotoxin and a Chimeric Anti-Ganglioside GD2 Antibody. Hybridoma 1991, 10, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S.D.; Reilly, E.B.; Lo, K.M.; Reisfeld, R.A. Antibody-Targeted Interleukin 2 Stimulates T-Cell Killing of Autologous Tumor Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fell, H.P.; Gayle, M.A.; Grosmaire, L.; Ledbetter, J.A. Genetic Construction and Characterization of a Fusion Protein Consisting of a Chimeric F(Ab’) with Specificity for Carcinomas and Human IL-2. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savage, P.; So, A.; Spooner, R.A.; Epenetos, A.A. A Recombinant Single Chain Antibody Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabzevari, H.; Gillies, S.D.; Mueller, B.M.; Pancook, J.D.; Reisfeld, R.A. A Recombinant Antibody-Interleukin 2 Fusion Protein Suppresses Growth of Hepatic Human Neuroblastoma Metastases in Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9626–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillies, S.D.; Lan, Y.; Williams, S.; Carr, F.; Forman, S.; Raubitschek, A.; Lo, K.M. An Anti-CD20-IL-2 Immunocytokine Is Highly Efficacious in a SCID Mouse Model of Established Human B Lymphoma. Blood 2005, 105, 3972–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keizer, R.J.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsi, L.; Balza, E.; Bestagno, M.; Castellani, P.; Carnemolla, B.; Biro, A.; Leprini, A.; Sepulveda, J.; Burrone, O.; Neri, D.; et al. Selective Targeting of Tumoral Vasculature: Comparison of Different Formats of an Antibody (L19) to the ED-B Domain of Fibronectin. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafner, V.; Trachsel, E.; Neri, D. An Engineered Antibody-Interleukin-12 Fusion Protein with Enhanced Tumor Vascular Targeting Properties. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, T.R. The Biology of Interleukin-2. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.C.; Varki, N.; Gillies, S.D.; Furukawa, K.; Reisfeld, R.A. Long-Lived and Transferable Tumor Immunity in Mice after Targeted Interleukin-2 Therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 2801–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.C.; Pancook, J.D.; Gillies, S.D.; Mendelsohn, J.; Reisfeld, R.A. Eradication of Human Hepatic and Pulmonary Melanoma Metastases in SCID Mice by Antibody-Interleukin 2 Fusion Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, J.C.; Pancook, J.D.; Gillies, S.D.; Furukawa, K.; Reisfeld, R.A. T Cell-Mediated Eradication of Murine Metastatic Melanoma Induced by Targeted Interleukin 2 Therapy. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, J.C.; Varki, N.; Gillies, S.D.; Furukawa, K.; Reisfeld, R.A. An Antibody-Interleukin 2 Fusion Protein Overcomes Tumor Heterogeneity by Induction of a Cellular Immune Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7826–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lode, H.N.; Xiang, R.; Varki, N.M.; Dolman, C.S.; Gillies, S.D.; Reisfeld, R.A. Targeted Interleukin-2 Therapy for Spontaneous Neuroblastoma Metastases to Bone Marrow. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lode, H.N.; Xiang, R.; Pertl, U.; Förster, E.; Schoenberger, S.P.; Gillies, S.D.; Reisfeld, R.A. Melanoma Immunotherapy by Targeted IL-2 Depends on CD4+ T-Cell Help Mediated by CD40/CD40L Interaction. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lode, H.N.; Xiang, R.; Dreier, T.; Varki, N.M.; Gillies, S.D.; Reisfeld, R.A. Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Eradication of Neuroblastoma Metastases to Bone Marrow by Targeted Interleukin-2 Therapy. Blood 1998, 91, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, M.H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Bai, Q.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The Paradoxical Role of IL-10 in Immunity and Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.K.; Kalogriopoulos, N.A.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Ranheim, E.A.; Seo, S.; Kim, K.; Alderson, K.L.; Gan, J.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Intratumoral Hu14.18–IL-2 (IC) Induces Local and Systemic Antitumor Effects That Involve Both Activated T and NK Cells As Well As Enhanced IC Retention. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.K.; Kalogriopoulos, N.A.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Ranheim, E.A.; Seo, S.; Kim, K.; Alderson, K.L.; Gan, J.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Intratumoral Treatment of Smaller Mouse Neuroblastoma Tumors with a Recombinant Protein Consisting of IL-2 Linked to the Hu14.18 Antibody Increases Intratumoral CD8+ T and NK Cells and Improves Survival. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Neal, Z.C.; Gan, J.; Buhtoiarova, T.N.; Patankar, M.S.; Gubbels, J.A.A.; Hank, J.A.; Yamane, B.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Reisfeld, R.A.; et al. Differential Internalization of Hu14.18-IL2 Immunocytokine by NK and Tumor Cell: Impact on Conjugation, Cytotoxicity, and Targeting. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, E.E.; Lum, H.D.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Schmidt, B.E.; Furlong, M.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Hank, J.A.; Raubitschek, A.; Colcher, D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; et al. Intratumoral Immunocytokine Treatment Results in Enhanced Antitumor Effects. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gubbels, J.A.A.; Gadbaw, B.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Horibata, S.; Kapur, A.K.; Patel, D.; Hank, J.A.; Gillies, S.D.; Sondel, P.M.; Patankar, M.S.; et al. Ab-IL2 Fusion Proteins Mediate NK Cell Immune Synapse Formation by Polarizing CD25 to the Target Cell-Effector Cell Interface. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybak, J.N.; Roesli, C.; Kaspar, M.; Villa, A.; Neri, D. The Extra-Domain A of Fibronectin Is a Vascular Marker of Solid Tumors and Metastases. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10948–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zardi, L.; Carnemolla, B.; Siri, A.; Petersen, T.E.; Paolella, G.; Sebastio, G.; Baralle, F.E. Transformed Human Cells Produce a New Fibronectin Isoform by Preferential Alternative Splicing of a Previously Unobserved Exon. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsi, L.; Carnemolla, B.; Nicolò, G.; Spina, B.; Tanara, G.; Zardi, L. Expression of Different Tenascin Isoforms in Normal, Hyperplastic and Neoplastic Human Breast Tissues. Int. J. Cancer 1992, 52, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, S.S.; Silacci, M.; Birchler, M.; Neri, D. Tumor-Targeting Properties of Novel Antibodies Specific to the Large Isoform of Tenascin-C. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3200–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziffels, B.; Pretto, F.; Neri, D. Intratumoral Administration of IL2-and TNF-Based Fusion Proteins Cures Cancer without Establishing Protective Immunity. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutbrodt, K.L.; Schliemann, C.; Giovannoni, L.; Frey, K.; Pabst, T.; Klapper, W.; Berdel, W.E.; Neri, D. Antibody-Based Delivery of Interleukin-2 to Neovasculature Has Potent Activity against Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieckowski, S.; Hemmerle, T.; Prince, S.S.; Schlienger, B.D.; Hillinger, S.; Neri, D.; Zippelius, A. Therapeutic Efficacy of the F8-IL2 Immunocytokine in a Metastatic Mouse Model of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, Y.; Hirota, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Sumitomo, M.; Nakamura, K.; Ueda, R.; Niwa, R.; Suzawa, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Shitara, K.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of a Novel PSMA Antibody and Its IL-2 Conjugate in Prostate Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hornick, J.L.; Khawli, L.A.; Hu, P.; Sharifi, J.; Khanna, C.; Epstein, A.L. Pretreatment with a Monoclonal Antibody/Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Directed against DNA Enhances the Delivery of Therapeutic Molecules to Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Gu, N.; Zhang, D.; Qian, W.; Hou, S.; et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of an Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Based Immunocytokine in a Metastatic Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziffels, B.; Stringhini, M.; Probst, P.; Fugmann, T.; Sturm, T.; Neri, D. Antibody-Based Delivery of Cytokine Payloads to Carbonic Anhydrase IX Leads to Cancer Cures in Immunocompetent Tumor-Bearing Mice. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christ, O.; Seiter, S.; Matzku, S.; Burger, C.; Zöller, M. Efficacy of Local versus Systemic Application of Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Proteins in Tumor Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 985–998. [Google Scholar]
- Dougan, M.; Ingram, J.R.; Jeong, H.J.; Mosaheb, M.M.; Bruck, P.T.; Ali, L.; Pishesha, N.; Blomberg, O.; Tyler, P.M.; Servos, M.M.; et al. Targeting Cytokine Therapy to the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment Using PD-L1–Specific VHHs. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilcek, J. Fifty Years of Interferon Research: Aiming at a Moving Target. Immunity 2006, 25, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, E.A.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Cardillo, T.M.; Stein, R.; Chang, C.H. CD20-Targeted Tetrameric Interferon-α, a Novel and Potent Immunocytokine for the Therapy of B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2009, 114, 3864–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.A.; Rossi, D.L.; Cardillo, T.M.; Stein, R.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Chang, C.H. Preclinical Studies on Targeted Delivery of Multiple IFNα2b to HLA-DR in Diverse Hematologic Cancers. Blood 2011, 118, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.A.; Rossi, D.L.; Stein, R.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Chang, C.H. A Bispecific Antibody-IFNα2b Immunocytokine Targeting CD20 and HLA-DR Is Highly Toxic to Human Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7600–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Iyer, R.; Lu, X.; Lake, M.; Ladror, U.; Harlan, J.; Samanta, T.; Tomlinson, M.; Bukofzer, G.; et al. Empowering Therapeutic Antibodies with IFN-α for Cancer Immunotherapy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xuan, C.; Steward, K.K.; Timmerman, J.M.; Morrison, S.L. Targeted Delivery of Interferon-Alpha via Fusion to Anti-CD20 Results in Potent Antitumor Activity against B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2010, 115, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Tang, H.; Guo, J.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Sun, Z.; Bian, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Targeting IFNα to Tumor by Anti-PD-L1 Creates Feedforward Antitumor Responses to Overcome Checkpoint Blockade Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, K.; Zivanovic, A.; Schwager, K.; Neri, D. Antibody-Based Targeting of Interferon-Alpha to the Tumor Neovasculature: A Critical Evaluation. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrar, M.A.; Schreiber, R.D. The Molecular Cell Biology of Interferon-γ and Its Receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 571–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, S.E.A.; Cretney, E.; Smyth, M.J. Perforin and Interferon-γ Activities Independently Control Tumor Initiation, Growth, and Metastasis. Blood 2001, 97, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Street, S.E.A.; Trapani, J.A.; MacGregor, D.; Smyth, M.J. Suppression of Lymphoma and Epithelial Malignancies Effected by Interferon γ. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebbinghaus, C.; Ronca, R.; Kaspar, M.; Grabulovski, D.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Engineered Vascular-Targeting Antibody-Interferon-γ Fusion Protein for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerle, T.; Neri, D. The Dose-Dependent Tumor Targeting of Antibody-IFNγ Fusion Proteins Reveals an Unexpected Receptor-Trapping Mechanism in Vivo. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Chang, C.H.; Rossi, E.A.; Cardillo, T.M.; Goldenberg, D.M. Interferon-Λ1 Linked to a Stabilized Dimer of Fab Potently Enhances Both Antitumor and Antiviral Activities in Targeted Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H. Historical Perspectives on Tumor Necrosis Factor and Its Superfamily: 25 Years Later, a Golden Journey. Blood 2012, 119, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Schwarz, L.; Hogan, M.E.; Rando, R.F. Triple Helix-Forming Oligodeoxyribonucleotides Targeted to the Human Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Gene Inhibit TNF Production and Block the TNF-Dependent Growth of Human Glioblastoma Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 5156–5164. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, D.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Constitutive Activation of NF-ΚB Causes Resistance to Apoptosis in Human Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma HuT-78 Cells: Autocrine Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Reactive Oxygen Intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14008–14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Grimshaw, M.J.; Kulbe, H.; Wilson, J.L.; Wilbanks, G.D.; Burke, F.; Balkwill, F.R. Expression and Regulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor α in Normal and Malignant Ovarian Epithelium. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zins, K.; Abraham, D.; Sioud, M.; Aharinejad, S. Colon Cancer Cell-Derived Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Mediates the Tumor Growth-Promoting Response in Macrophages by up-Regulating the Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 Pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogenboom, H.R.; Raus, J.C.M.; Volckaert, G. Targeting of Tumor Necrosis Factor to Tumor Cells: Secretion by Myeloma Cells of a Genetically Engineered Antibody-Tumor Necrosis Factor Hybrid Molecule. BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 1991, 1096, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S.D.; Young, D.; Lo, K.M.; Roberts, S. Biological Activity and in Vivo Clearance of Antitumor Antibody/Cytokine Fusion Proteins. Bioconjug. Chem. 1993, 4, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Adrian, N.; Williamson, B.; Panousis, C.; Fadle, N.; Smerd, J.; Fettah, I.; Scott, A.M.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Renner, C. Targeted Bioactivity of Membrane-Anchored TNF by an Antibody-Derived TNF Fusion Protein. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3930–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halin, C.; Gafner, V.; Villani, M.E.; Borsi, L.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of a Tumor Targeting Antibody Fragment, Fused to Interleukin 12 and to Tumor Necrosis Factor α. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3202. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, S.; Oosterwijk-Wakka, J.C.; Adrian, N.; Oosterwijk, E.; Fischer, E.; Wüest, T.; Stenner, F.; Perani, A.; Cohen, L.; Knuth, A.; et al. Targeted Therapy of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Synergistic Activity of CG250-TNF and IFNg. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, M.G.; Horn, S.A.; Cheung, L.H. A Novel Recombinant Fusion Toxin Targeting HER-2/NEU-over-Expressing Cells and Containing Human Tumor Necrosis Factor. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.A.; Rosenblum, M.G. The Immunocytokine ScFv23/TNF Sensitizes HER-2/Neu-Overexpressing SKBR-3 Cells to Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) via up-Regulation of TNF Receptor-1. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zundler, S.; Neurath, M.F. Interleukin-12: Functional Activities and Implications for Disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.B.; Robertson, M.J.; Gordon, M.; Lotze, M.T.; DeCoste, M.; DuBois, J.S.; Ritz, J.; Sandler, A.B.; Edington, H.D.; Garzone, P.D.; et al. Phase I Evaluation of Intravenous Recombinant Human Interleukin 12 in Patients with Advanced Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Halin, C.; Rondini, S.; Nilsson, F.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Enhancement of the Antitumor Activity of Interleukin-12 by Targeted Delivery to Neovasculature. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongaro, T.; Matasci, M.; Cazzamalli, S.; Gouyou, B.; De Luca, R.; Neri, D.; Villa, A. A Novel Anti-Cancer L19-Interleukin-12 Fusion Protein with an Optimized Peptide Linker Efficiently Localizes in Vivo at the Site of Tumors. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 291, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S.D.; Lo, K.M.; Lan, Y.; Dahl, T.; Wong, W.K.; Burger, C. Improved Circulating Half-Life and Efficacy of an Antibody-Interleukin 2 Immunocytokine Based on Reduced Intracellular Proteolysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.M.; Lan, Y.; Lauder, S.; Zhang, J.; Brunkhorst, B.; Qin, G.; Verma, R.; Courtenay-Luck, N.; Gillies, S.D. HuBC1-IL12, an Immunocytokine Which Targets EDB-Containing Oncofetal Fibronectin in Tumors and Tumor Vasculature, Shows Potent Anti-Tumor Activity in Human Tumor Models. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommavilla, R.; Pasche, N.; Trachsel, E.; Giovannoni, L.; Roesli, C.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Kaspar, M. Expression, Engineering and Characterization of the Tumor-Targeting Heterodimeric Immunocytokine F8-IL12. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2010, 23, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmerle, T.; Neri, D. The Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin-4 and 12 to the Tumor Neovasculature Eradicates Tumors in Three Mouse Models of Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, J.; Tighe, R.; Kradjian, G.; Guzman, W.; Bernhardt, A.; Neuteboom, B.; Lan, Y.; Sabzevari, H.; Schlom, J.; Greiner, J.W. The Immunocytokine NHS-IL12 as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1869–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morillon, Y.M.; Su, Z.; Schlom, J.; Greiner, J.W. Temporal Changes within the (Bladder) Tumor Microenvironment That Accompany the Therapeutic Effects of the Immunocytokine NHS-IL12. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paoloni, M.; Mazcko, C.; Selting, K.; Lana, S.; Barber, L.; Phillips, J.; Skorupski, K.; Vail, D.; Wilson, H.; Biller, B.; et al. Defining the Pharmacodynamic Profile and Therapeutic Index of NHS-IL12 Immunocytokine in Dogs with Malignant Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, J.C.; Waldmann, T.A.; Morris, J.C. Interleukin-15 Biology and Its Therapeutic Implications in Cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaspar, M.; Trachsel, E.; Neri, D. The Antibody-Mediated Targeted Delivery of Interleukin-15 and GM-CSF to the Tumor Neovasculature Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4940–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, S.; Mariner, J.; Waldmann, T.A.; Tagaya, Y. IL-15Rα Recycles and Presents IL-15 in Trans to Neighboring Cells. Immunity 2002, 17, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kermer, V.; Baum, V.; Hornig, N.; Kontermann, R.E.; Müller, D. An Antibody Fusion Protein for Cancer Immunotherapy Mimicking IL-15 Trans-Presentation at the Tumor Site. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, M.; Bessard, A.; Cochonneau, D.; Teppaz, G.; Solé, V.; Maillasson, M.; Birklé, S.; Garrigue-Antar, L.; Quéméner, A.; Jacques, Y. Tumor Targeting of the IL-15 Superagonist RLI by an Anti-GD2 Antibody Strongly Enhances Its Antitumor Potency. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Teppaz, G.; Lajoie, L.; Solé, V.; Bessard, A.; Maillasson, M.; Loisel, S.; Béchard, D.; Clémenceau, B.; Thibault, G.; et al. Highly Potent Anti-CD20-RLI Immunocytokine Targeting Established Human B Lymphoma in SCID Mouse. mAbs 2014, 6, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalf, D. The Colony-Stimulating Factors and Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantoff, P.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.D.; Berger, E.R.; Small, E.J.; Penson, D.F.; Redfern, C.H.; Ferrari, A.C.; Dreicer, R.; Sims, R.B.; et al. Sipuleucel-T Immunotherapy for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dreier, T.; Lode, H.N.; Xiang, R.; Dolman, C.S.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Kang, A.S. Recombinant Immunocytokines Targeting the Mouse Transferrin Receptor: Construction and Biological Activities. Bioconjug. Chem. 1998, 9, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelitsa, L.S.; Gillies, S.D.; Super, M.; Shimada, H.; Reynolds, C.P.; Seeger, R.C. Antidisialoganglioside/Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony-Stimulating Factor Fusion Protein Facilitates Neutrophil Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity and Depends on FcγRII (CD32) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) for Enhanced Effector Cell Adhesion and Azurophil Gr. Blood 2002, 99, 4166–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dela Cruz, J.S.; Trinh, K.R.; Morrison, S.L.; Penichet, M.L. Recombinant Anti-Human HER2/ Neu IgG3-(GM-CSF) Fusion Protein Retains Antigen Specificity and Cytokine Function and Demonstrates Antitumor Activity. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5112–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dela Cruz, J.S.; Trinh, K.R.; Chen, H.W.; Ribas, A.; Morrison, S.L.; Penichet, M.L. Anti-HER2/Neu IgG3-(IL-2) and Anti-HER2/Neu IgG3-(GM-CSF) Promote HER2/Neu Processing and Presentation by Dendritic Cells: Implications in Immunotherapy and Vaccination Strategies. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanzer, J.M.; Fichtner, I.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kufer, P. Antitumor Activity of a Dual Cytokine/Single-Chain Antibody Fusion Protein for Simultaneous Delivery of GM-CSF and IL-2 to Ep-CAM Expressing Tumor Cells. J. Immunother. 2006, 29, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Molema, G.; King, S.; Watkins, L.; Edgington, T.S.; Thorpe, P.E. Tumor Infarction in Mice by Antibody-Directed Targeting of Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature. Science 1997, 275, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, S.; Gao, B.; Duffy, S.; Watkins, L.; Rote, N.; Thorpe, P.E. Infarction of Solid Hodgkin’s Tumors in Mice by Antibody-Directed Targeting of Tissue Factor to Tumor Vasculature. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4646–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, F.; Kosmehl, H.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Targeted Delivery of Tissue Factor to the ED-B Domain of Fibronectin, a Marker of Angiogenesis, Mediates the Infarction of Solid Tumors in Mice. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, A.S.; Tintor, D.; Neri, D. Novel Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Proteins Featuring Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor, Interleukin-3 and Interleukin-4 as Payloads. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 271, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Neri, D. Tumor-Targeting Properties of Novel Immunocytokines Based on Murine IL1β and IL6. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, C.; Neri, D. The Antibody-Mediated Targeted Delivery of Interleukin-13 to Syngeneic Murine Tumors Mediates a Potent Anticancer Activity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasche, N.; Frey, K.; Neri, D. The Targeted Delivery of IL17 to the Mouse Tumor Neo-Vasculature Enhances Angiogenesis but Does Not Reduce Tumor Growth Rate. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halin, C.; Niesner, U.; Villani, M.E.; Zardi, L.; Neri, D. Tumor-Targeting Properties of Antibody-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Fusion Proteins. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, D.; Frey, K.; Kontermann, R.E. A Novel Antibody-4-1BBL Fusion Protein for Targeted Costimulation in Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Sadun, R.E.; Arias, R.S.; Flanagan, M.L.; Sachsman, S.M.; Nien, Y.C.; Khawli, L.A.; Hu, P.; Epstein, A.L. Targeted and Untargeted CD137L Fusion Proteins for the Immunotherapy of Experimental Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2758–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, T.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Cho, J.; Guzman, J.S.; Kamm, R.D.; Ploegh, H.L. Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment by a Chemokine/Anti-PD-L1 Nanobody Fusion Protein. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasche, N.; Woytschak, J.; Wulhfard, S.; Villa, A.; Frey, K.; Neri, D. Cloning and Characterization of Novel Tumor-Targeting Immunocytokines Based on Murine IL7. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 154, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, C.; Ferrara, C.; Xu, W.; Sam, J.; Lang, S.; Uhlenbrock, F.; Albrecht, R.; Herter, S.; Schlenker, R.; Hüsser, T.; et al. Tumor-Targeted 4-1BB Agonists for Combination with T Cell Bispecific Antibodies as off-the-Shelf Therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S.D.; Lan, Y.; Hettmann, T.; Brunkhorst, B.; Sun, Y.; Mueller, S.O.; Lo, K.M. A Low-Toxicity IL-2-Based Immunocytokine Retains Antitumor Activity despite Its High Degree of IL-2 Receptor Selectivity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, C.; Waldhauer, I.; Nicolini, V.G.; Freimoser-Grundschober, A.; Nayak, T.; Vugts, D.J.; Dunn, C.; Bolijn, M.; Benz, J.; Stihle, M.; et al. Cergutuzumab Amunaleukin (CEA-IL2v), a CEA-Targeted IL-2 Variant-Based Immunocytokine for Combination Cancer Immunotherapy: Overcoming Limitations of Aldesleukin and Conventional IL-2-Based Immunocytokines. OncoImmunology 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Codarri-Deak, L.; Nicolini, V.; Seeber, S.; Lauener, L.; Richard, M.; Bommer, E.; Karagianni, M.; Sam, J.; Schlenker, R.; et al. Abstract 1552: A Novel PD1-IL2v Immunocytokine for Preferential cis-Activation of IL-2R Signaling on PD-1 Expressing T Cell Subsets Strongly Potentiates Anti-Tumor T Cell Activity of PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibition and IL-2R-Beta-Gamma Agonism. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Cao, S.; Deng, S.; Xu, L.; Liang, Y.; Guo, J.; Bian, Y.; et al. A Next-Generation Tumor-Targeting IL-2 Preferentially Promotes Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T-Cell Response and Effective Tumor Control. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, T.; Casi, G.; Neri, D. A Chemically Defined Trifunctional Antibody-Cytokine-Drug Conjugate with Potent Antitumor Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, S.D. A New Platform for Constructing Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Proteins (Immunocytokines) with Improved Biological Properties and Adaptable Cytokine Activity. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2013, 26, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahin, D.; Arenas-Ramirez, N.; Rath, M.; Karakus, U.; Hümbelin, M.; van Gogh, M.; Borsig, L.; Boyman, O. An IL-2-Grafted Antibody Immunotherapy with Potent Efficacy against Metastatic Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Ramirez, N.; Zou, C.; Popp, S.; Zingg, D.; Brannetti, B.; Wirth, E.; Calzascia, T.; Kovarik, J.; Sommer, L.; Zenke, G.; et al. Improved Cancer Immunotherapy by a CD25-Mimobody Conferring Selectivity to Human Interleukin-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 367ra166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charych, D.H.; Hoch, U.; Langowski, J.L.; Lee, S.R.; Addepalli, M.K.; Kirk, P.B.; Sheng, D.; Liu, X.; Sims, P.W.; VanderVeen, L.A.; et al. NKTR-214, an Engineered Cytokine with Biased IL2 Receptor Binding, Increased Tumor Exposure, and Marked Efficacy in Mouse Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charych, D.; Khalili, S.; Dixit, V.; Kirk, P.; Chang, T.; Langowski, J.; Rubas, W.; Doberstein, S.K.; Eldon, M.; Hoch, U.; et al. Modeling the Receptor Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of NKTR-214, a Kinetically-Controlled Interleukin-2 (IL2) Receptor Agonist for Cancer Immunotherapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Khong, H.; Fa’ak, F.; Bentebibel, S.-E.; Janssen, L.M.E.; Chesson, B.C.; Creasy, C.A.; Forget, M.-A.; Kahn, L.M.S.; Pazdrak, B.; et al. Bempegaldesleukin Selectively Depletes Intratumoral Tregs and Potentiates T Cell-Mediated Cancer Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentebibel, S.-E.; Hurwitz, M.E.; Bernatchez, C.; Haymaker, C.; Hudgens, C.W.; Kluger, H.M.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Tagliaferri, M.A.; Zalevsky, J.; Hoch, U.; et al. A First-in-Human Study and Biomarker Analysis of NKTR-214, a Novel IL2Rβγ-Biased Cytokine, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diab, A.; Tannir, N.M.; Bentebibel, S.-E.; Hwu, P.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Haymaker, C.; Kluger, H.M.; Gettinger, S.N.; Sznol, M.; Tykodi, S.S.; et al. Bempegaldesleukin (NKTR-214) plus Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Safety, Efficacy, and Immune Activation (PIVOT-02). Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddart, R.A.; Siefker-Radtke, A.O.; Balar, A.V.; Bilen, M.A.; Powles, T.; Bamias, A.; Castellano, D.; Khalil, M.F.; Van Der Heijden, M.S.; Koshkin, V.S.; et al. PIVOT-10: Phase II Study of Bempegaldesleukin plus Nivolumab in Cisplatin-Ineligible Advanced Urothelial Cancer. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2021, 17, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khushalani, N.I.; Diab, A.; Ascierto, P.A.; Larkin, J.; Sandhu, S.; Sznol, M.; Koon, H.B.; Jarkowski, A.; Zhou, M.; Statkevich, P.; et al. Bempegaldesleukin plus Nivolumab in Untreated, Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma: Phase III PIVOT IO 001 Study Design. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2020, 16, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcin, G.; Paul, F.; Staufenbiel, M.; Bordat, Y.; Van der Heyden, J.; Wilmes, S.; Cartron, G.; Apparailly, F.; De Koker, S.; Piehler, J.; et al. High Efficiency Cell-Specific Targeting of Cytokine Activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pogue, S.L.; Taura, T.; Bi, M.; Yun, Y.; Sho, A.; Mikesell, G.; Behrens, C.; Sokolovsky, M.; Hallak, H.; Rosenstock, M.; et al. Targeting Attenuated Interferon-α to Myeloma Cells with a CD38 Antibody Induces Potent Tumor Regression with Reduced off-Target Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwels, A.; Van Lint, S.; Garcin, G.; Bultinck, J.; Paul, F.; Gerlo, S.; Van der Heyden, J.; Bordat, Y.; Catteeuw, D.; De Cauwer, L.; et al. A Safe and Highly Efficient Tumor-Targeted Type I Interferon Immunotherapy Depends on the Tumor Microenvironment. OncoImmunology 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghe, L.; Van Parys, A.; Cauwels, A.; Van Lint, S.; De Munter, S.; Bultinck, J.; Zabeau, L.; Hostens, J.; Goethals, A.; Vanderroost, N.; et al. Safe Eradication of Large Established Tumors Using Neovasculature-targeted Tumor Necrosis Factor-based Therapies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, R.; Neri, D. Potentiation of PD-L1 Blockade with a Potency-Matched Dual Cytokine–Antibody Fusion Protein Leads to Cancer Eradication in BALB/c-Derived Tumors but Not in Other Mouse Strains. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venetz, D.; Koovely, D.; Weder, B.; Neri, D. Targeted Reconstitution of Cytokine Activity upon Antigen Binding Using Split Cytokine Antibody Fusion Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18139–18147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holden, S.A.; Lan, Y.; Pardo, A.M.; Wesolowski, J.S.; Gillies, S.D.; Gillies, S.D. Augmentation of Antitumor Activity of an Antibody-Interleukin 2 Immunocytokine with Chemotherapeutic Agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Moschetta, M.; Pretto, F.; Berndt, A.; Galler, K.; Richter, P.; Bassi, A.; Oliva, P.; Micotti, E.; Valbusa, G.; Schwager, K.; et al. Paclitaxel Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy of the F8-IL2 Immunocytokine to EDA-Fibronectin-Positive Metastatic Human Melanoma Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pretto, F.; Elia, G.; Castioni, N.; Neri, D. Preclinical Evaluation of IL2-Based Immunocytokines Supports Their Use in Combination with Dacarbazine, Paclitaxel and TNF-Based Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mårlind, J.; Kaspar, M.; Trachsel, E.; Sommavilla, R.; Hindle, S.; Bacci, C.; Giovannon, L.; Neri, D. Antibody-Mediated Delivery of Interleukin-2 to the Stroma of Breast Cancer Strongly Enhances the Potency of Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6515–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedretti, M.; Verpelli, C.; Mårlind, J.; Bertani, G.; Sala, C.; Neri, D.; Bello, L. Combination of Temozolomide with Immunocytokine F16-IL2 for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyu, M.; Kurzrock, R.; Rosenblum, M.G. The Immunocytokine ScFv23/TNF Targeting HER-2/Neu Induces Synergistic Cytotoxic Effects with 5-Fluorouracil in TNF-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerle, T.; Probst, P.; Giovannoni, L.; Green, A.J.; Meyer, T.; Neri, D. The Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of TNF in Combination with Doxorubicin Eradicates Sarcomas in Mice and Confers Protective Immunity. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbellari, R.; Nadal, L.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Luca, R. De The Immunocytokine L19-TNF Eradicates Sarcomas in Combination with Chemotherapy Agents or with Immune Check-Point Inhibitors. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasche, N.; Wulhfard, S.; Pretto, F.; Carugati, E.; Neri, D. The Antibody-Based Delivery of Interleukin-12 to the Tumor Neovasculature Eradicates Murine Models of Cancer in Combination with Paclitaxel. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4092–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demaria, S.; Golden, E.B.; Formenti, S.C. Role of Local Radiation Therapy in Cancer Immunotherapy. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, Z.S.; Guy, E.I.; Francis, D.M.; Gressett, M.M.; Lauren, R.; Carmichael, L.L.; Yang, R.K.; Armstrong, E.A.; Navid, F.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. In Situ Tumor Vaccination by Combining Local Radiation and Tumor-Specific Antibody or Immunocytokine Treatments. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3929–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, P.A.; Sriramaneni, R.N.; Jin, W.J.; Jagodinsky, J.C.; Bates, A.M.; Jaquish, A.A.; Anderson, B.R.; Le, T.; Lubin, J.A.; Chakravarty, I.; et al. In Situ Vaccination at a Peripheral Tumor Site Augments Response against Melanoma Brain Metastases. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, Z.S.; Guy, E.I.; Werner, L.R.; Carlson, P.M.; Clinton, M.; Kler, J.S.; Busche, S.M.; Jaquish, A.A.; Sriramaneni, R.N.; Carmichael, L.L.; et al. Tumor-Specific Inhibition of in Situ Vaccination by Distant Untreated Tumor Sites. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rekers, N.H.; Olivo Pimentel, V.; Yaromina, A.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Biemans, R.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; Van Limbergen, E.J.; Neri, D.; Dubois, L.J.; et al. The Immunocytokine L19-IL2: An Interplay between Radiotherapy and Long-Lasting Systemic Anti-Tumour Immune Responses. OncoImmunology 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zegers, C.M.L.; Rekers, N.H.; Quaden, D.H.F.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Yaromina, A.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; Wieten, L.; Biessen, E.A.L.; Boon, L.; Neri, D.; et al. Radiotherapy Combined with the Immunocytokine L19-IL2 Provides Long-Lasting Antitumor Effects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rekers, N.H.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Yaromina, A.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Biemans, R.; Senden-Gijsbers, B.L.M.G.; Losen, M.; Van Limbergen, E.J.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; Neri, D.; et al. Combination of Radiotherapy with the Immunocytokine L19-IL2: Additive Effect in a NK Cell Dependent Tumour Model. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voeller, J.; Erbe, A.K.; Slowinski, J.; Rasmussen, K.; Carlson, P.M.; Hoefges, A.; Vandenheuvel, S.; Stuckwisch, A.; Wang, X.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Combined Innate and Adaptive Immunotherapy Overcomes Resistance of Immunologically Cold Syngeneic Murine Neuroblastoma to Checkpoint Inhibition. J. ImmunoTher. Cancer 2019, 6, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.E.; Yamane, B.H.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Lum, H.D.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Mahvi, D.M.; Gillies, S.D.; Sondel, P.M. Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with KS-IL2 Immunocytokine (EMD 273066) Results in an Enhanced Antitumor Effect against Murine Colon Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4875–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujawski, M.; Sherman, M.; Hui, S.; Zuro, D.; Lee, W.H.; Yazaki, P.; Sherman, A.; Szpikowska, B.; Chea, J.; Lasiewski, D.; et al. Potent Immunomodulatory Effects of an Anti-CEA-IL-2 Immunocytokine on Tumor Therapy and Effects of Stereotactic Radiation. OncoImmunology 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maria, N.S.S.; Barnes, S.R.; Weist, M.R.; Colcher, D.; Raubitschek, A.A.; Jacobs, R.E. Low Dose Focused Ultrasound Induces Enhanced Tumor Accumulation of Natural Killer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, F.; Schmitt, J.; Zips, D.; Krueger, M.A.; Pichler, B.J.; Gillies, S.D.; Strittmatter, W.; Handgretinger, R.; Schilbach, K. Enhanced Binding of Necrosis-Targeting Immunocytokine NHS-IL12 after Local Tumour Irradiation in Murine Xenograft Models. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, F.; Jelas, I.; Oehme, M.; Huber, S.M.; Sonntag, K.; Welker, C.; Gillies, S.D.; Strittmatter, W.; Zips, D.; Handgretinger, R.; et al. Tumor-Targeted IL-12 Combined with Local Irradiation Leads to Systemic Tumor Control via Abscopal Effects in Vivo. OncoImmunology 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maloney, D.G.; Grillo-López, A.J.; Bodkin, D.J.; White, C.A.; Liles, T.M.; Royston, I.; Varns, C.; Rosenberg, J.; Levy, R. Idec-C2b8: Results of a Phase I Multiple-Dose Trial in Patients with Relapsed Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 3266–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börschel, N.; Schwöppe, C.; Zerbst, C.; Angenendt, L.; Kessler, T.; Klapper, W.; Giovannoni, L.; Elia, G.; Neri, D.; Berdel, W.E.; et al. Potentiating the Activity of Rituximab against Mantle Cell Lymphoma in Mice by Targeting Interleukin-2 to the Neovasculature. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliemann, C.; Palumbo, A.; Zuberbühler, K.; Villa, A.; Kaspar, M.; Trachsel, E.; Klapper, W.; Menssen, H.D.; Neri, D. Complete Eradication of Human B-Cell Lymphoma Xenografts Using Rituximab in Combination with the Immunocytokine L19-IL2. Blood 2009, 113, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orecchia, P.; Conte, R.; Balza, E.; Pietra, G.; Mingari, M.C.; Carnemolla, B. Targeting Syndecan-1, a Molecule Implicated in the Process of Vasculogenic Mimicry, Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of the L19-IL2 Immunocytokine in Human Melanoma Xenografts. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37426–37442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orecchia, P.; Balza, E.; Pietra, G.; Conte, R.; Bizzarri, N.; Ferrero, S.; Mingari, M.C.; Carnemolla, B. L19-IL2 Immunocytokine in Combination with the Anti-Syndecan-1 46F2SIP Antibody Format: A New Targeted Treatment Approach in an Ovarian Carcinoma Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murer, P.; Kiefer, J.D.; Plüss, L.; Matasci, M.; Blümich, S.L.; Stringhini, M.; Neri, D. Targeted Delivery of TNF Potentiates the Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity of an Anti-Melanoma Immunoglobulin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, J.K.; Vandeveer, A.J.; Schlom, J.; Greiner, J.W. Enhanced Antitumor Effects by Combining an IL-12/Anti-DNA Fusion Protein with Avelumab, an Anti-PD-L1 Antibody. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20558–20571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Alexander Rolfe, P.; Hernández, V.M.; Guzman, W.; Kradjian, G.; Marelli, B.; Qin, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Combination Therapy with NHS-MuIL12 and Avelumab (Anti-PD-L1) Enhances Antitumor Efficacy in Preclinical Cancer Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5869–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Felder, M.; Lever, L.; Slowinski, J.; Rasmussen, K.; Hoefges, A.; Van De Voort, T.J.; Loibner, H.; Korman, A.J.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Effective Combination of Innate and Adaptive Immunotherapeutic Approaches in a Mouse Melanoma Model. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwager, K.; Hemmerle, T.; Aebischer, D.; Neri, D. The Immunocytokine L19-IL2 Eradicates Cancer When Used in Combination with CTLA-4 Blockade or with L19-TNF. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neal, Z.C.; Yang, J.C.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Lum, H.E.; Imboden, M.; Hank, J.A.; Lode, H.N.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Enhanced Activity of Hu14.18-IL2 Immunocytokine against Murine NXS2 Neuroblastoma When Combined with Interleukin 2 Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4839–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neal, Z.C.; Sondel, P.M.; Bates, M.K.; Gillies, S.D.; Herweijer, H. Flt3-L Gene Therapy Enhances Immunocytokine-Mediated Antitumor Effects and Induces Long-Term Memory. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilbach, K.; Alkhaled, M.; Welker, C.; Eckert, F.; Blank, G.; Ziegler, H.; Sterk, M.; Müller, F.; Sonntag, K.; Wieder, T.; et al. Cancer-Targeted IL-12 Controls Human Rhabdomyosarcoma by Senescence Induction and Myogenic Differentiation. OncoImmunology 2015, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Adrian, N.; Siebenborn, U.; Fadle, N.; Plesko, M.; Fischer, E.; Wüest, T.; Stenner, F.; Mertens, J.C.; Knuth, A.; et al. Sequential Cancer Immunotherapy: Targeted Activity of Dimeric TNF and IL-8. Cancer Immun. 2009, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menssen, H.D.; Harnack, U.; Erben, U.; Neri, D.; Hirsch, B.; Dürkop, H. Antibody-Based Delivery of Tumor Necrosis Factor (L19-TNFα) and Interleukin-2 (L19-IL2) to Tumor-Associated Blood Vessels Has Potent Immunological and Anticancer Activity in the Syngeneic J558L BALB/c Myeloma Model. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Nogusa, S.; Thapa, R.J.; Shaller, C.; Simmons, H.; Peri, S.; Adams, G.P.; Balachandran, S. Anti-CD70 Immunocytokines for Exploitation of Interferon-γ-Induced RIP1-Dependent Necrosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0061446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dakhel, S.; Ongaro, T.; Gouyou, B.; Matasci, M.; Villa, A.; Neri, D.; Cazzamalli, S. Targeted Enhancement of the Therapeutic Window of L19-TNF by Transient and Selective Inhibition of RIPK1-Signaling Cascade. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6678–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.; Schliemann, C.; Schwager, K.; Giavazzi, R.; Johannsen, M.; Neri, D. The Immunocytokine F8-IL2 Improves the Therapeutic Performance of Sunitinib in a Mouse Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, M.; Janke, M.; Lulei, M.; Beckhove, P.; Fournier, P.; Schirrmacher, V. An Effective Tumor Vaccine Optimized for Costimulation via Bispecific and Trispecific Fusion Proteins. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 777–789. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, P.; Aigner, M.; Schirrmacher, V. Transcriptome Analysis and Cytokine Profiling of Naive T Cells Stimulated by a Tumor Vaccine via CD3 and CD25. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, P.; Aigner, M.; Schirrmacher, V. Targeting of IL-2 and GM-CSF Immunocytokines to a Tumor Vaccine Leads to Increased Anti-Tumor Activity. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ye, D.; Thorpe, P.E. Enhancing the Potency of a Whole-Cell Breast Cancer Vaccine in Mice with an Antibody-IL-2 Immunocytokine That Targets Exposed Phosphatidylserine. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4785–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley Rumfield, C.; Pellom, S.T.; Morillon, Y.M.; Schlom, J.; Jochems, C. Immunomodulation to Enhance the Efficacy of an HPV Therapeutic Vaccine. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, G.; McCroskery, S.; Palese, P. Engineering Newcastle Disease Virus as an Oncolytic Vector for Intratumoral Delivery of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Immunocytokines. J. Virol. 2019, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, B.L.; Hank, J.A.; Darjatmoko, S.R.; Polans, A.S.; Yanke, E.M.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Seo, S.; Kim, K.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Anti-Tumor and Immunomodulatory Activity of Resveratrol in Vitro and Its Potential for Combining with Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soto, B.L.; Hank, J.A.; Van De Voort, T.J.; Subramanian, L.; Polans, A.S.; Rakhmilevich, A.L.; Yang, R.K.; Seo, S.; Kim, K.; Reisfeld, R.A.; et al. The Anti-Tumor Effect of Resveratrol Alone or in Combination with Immunotherapy in a Neuroblastoma Model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 60, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, H.; Serrano, L.M.; Pfeiffer, T.; Olivares, S.; McNamara, G.; Smith, D.D.; Al-Kadhimi, Z.; Forman, S.J.; Gillies, S.D.; Jensen, M.C.; et al. Combining Adoptive Cellular and Immunocytokine Therapies to Improve Treatment of B-Lineage Malignancy. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, D.M.; Albertini, M.R.; Schalch, H.; Hank, J.A.; Gan, J.; Surfus, J.; Mahvi, D.; Schiller, J.H.; Warner, T.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Phase I Clinical Trial of the Immunocytokine EMD 273063 in Melanoma Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4463–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osenga, K.L.; Hank, J.A.; Albertini, M.R.; Gan, J.; Sternberg, A.G.; Eickhoff, J.; Seeger, R.C.; Matthay, K.K.; Reynolds, C.P.; Krailo, M.; et al. A Phase I Clinical Trial of the Hu14.18-IL2 (EMD 273063) as a Treatment for Children with Refractory or Recurrent Neuroblastoma and Melanoma: A Study of the Children’s Oncology Group. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribas, A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Atkins, M.B.; Whiteside, T.L.; Gooding, W.; Kovar, A.; Gillies, S.D.; Kashala, O.; Morse, M.A. Phase I/II Open-Label Study of the Biologic Effects of the Interleukin-2 Immunocytokine EMD 273063 (Hu14.18-IL2) in Patients with Metastatic Malignant Melanoma. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albertini, M.R.; Hank, J.A.; Gadbaw, B.; Kostlevy, J.; Haldeman, J.; Schalch, H.; Gan, J.; Kim, K.M.; Eickhoff, J.; Gillies, S.D.; et al. Phase II Trial of Hu14.18-IL2 for Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shusterman, S.; London, W.B.; Gillies, S.D.; Hank, J.A.; Voss, S.D.; Seeger, R.C.; Reynolds, C.P.; Kimball, J.; Albertini, M.R.; Wagner, B.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Hu14.18-IL2 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4969–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albertini, M.R.; Yang, R.K.; Ranheim, E.A.; Hank, J.A.; Zuleger, C.L.; Weber, S.; Neuman, H.; Hartig, G.; Weigel, T.; Mahvi, D.; et al. Pilot Trial of the Hu14.18-IL2 Immunocytokine in Patients with Completely Resectable Recurrent Stage III or Stage IV Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shusterman, S.; Naranjo, A.; van Ryn, C.; Hank, J.A.; Parisi, M.T.; Shulkin, B.L.; Servaes, S.; London, W.B.; Shimada, H.; Gan, J.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Tolerability of Hu14.18-IL2 with GMCSF and Isotretinoin in Recurrent or Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Children’s Oncology Group Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6044–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hank, J.A.; Gan, J.; Ryu, H.; Ostendorf, A.; Stauder, M.C.; Sternberg, A.; Albertini, M.; Lo, K.M.; Gillies, S.D.; Eickhoff, J.; et al. Immunogenicity of the Hu14.18-IL2 Immunocytokine Molecule in Adults with Melanoma and Children with Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, D.C.; Hank, J.A.; Kolesar, J.; Lorentzen, D.; Gan, J.; Seo, S.; Kim, K.M.; Shusterman, S.; Gillies, S.D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; et al. Genotypes of NK Cell KIR Receptors, Their Ligands, and Fcγ Receptors in the Response of Neuroblastoma Patients to Hu14.18-IL2 Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9554–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.K.; Kuznetsov, I.B.; Ranheim, E.A.; Wei, J.S.; Sindiri, S.; Gryder, B.E.; Gangalapudi, V.; Song, Y.K.; Patel, V.; Hank, J.A.; et al. Outcome-Related Signatures Identified by Whole Transcriptome Sequencing of Resectable Stage III/IV Melanoma Evaluated after Starting Hu14.18-IL2. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shusterman, S.; London, W.B.; Hank, J.A.; Parisi, M.T.; Shulkin, B.L.; Servaes, S.-E.-N.; Naranjo, A.; Shimada, H.; Gan, J.; Gillies, S.; et al. A Feasibility and Phase II Study of the Hu14.18-IL2 Immunocytokine in Combination with GM-CSF and Isotretinoin in Patients with Recurrent or Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, C.; Maur, M.; Berardi, R.; Rocca, A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Spitaleri, G.; Masini, C.; Pierantoni, C.; González-Iglesias, R.; Zigon, G.; et al. The Tumor-Targeting Immunocytokine F16-IL2 in Combination with Doxorubicin: Dose Escalation in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors and Expansion into Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schliemann, C.; Gutbrodt, K.L.; Kerkhoff, A.; Pohlen, M.; Wiebe, S.; Silling, G.; Angenendt, L.; Kessler, T.; Mesters, R.M.; Giovannoni, L.; et al. Targeting Interleukin-2 to the Bone Marrow Stroma for Therapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Relapsing after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Braud, F.G.; Catania, C.; Masini, C.; Maur, M.; Cascinu, S.; Berardi, R.; Giovannoni, L.; Spitaleri, G.; Boselli, S.; Neri, D. Combinations of the Immunocytokine F16-IL2 with Doxorubicin or with Paclitaxel Investigated in Phase Ib Studies in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Braud, F.G.; Catania, C.; Onofri, A.; Pierantoni, C.; Cascinu, S.; Maur, M.; Masini, C.; Conte, P.F.; Giovannoni, L.; Tasciotti, A.; et al. Combination of the Immunocytokine F16-IL2 with Doxorubicin or Paclitaxel in Patients with Solid Tumors: Results from Two Phase Ib Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.P.; Cristea, M.C.; Lewis, N.L.; Lewis, L.D.; Komarnitsky, P.B.; Mattiacci, M.R.; Felder, M.; Stewart, S.; Harter, J.; Henslee-Downey, J.; et al. A Phase 1b Study of Humanized KS-Interleukin-2 (HuKS-IL2) Immunocytokine with Cyclophosphamide in Patients with EpCAM-Positive Advanced Solid Tumors. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladkov, O.; Ramlau, R.; Serwatowski, P.; Milanowski, J.; Tomeczko, J.; Komarnitsky, P.B.; Kramer, D.; Krzakowski, M.J. Cyclophosphamide and Tucotuzumab (HuKS-IL2) Following First-Line Chemotherapy in Responding Patients with Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer. Drugs 2015, 26, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.-J.; Bubley, G.J.; Weber, R.; Redfern, C.; Gold, D.P.; Finke, L.; Kovar, A.; Dahl, T.; Gillies, S.D. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Biological Pharmacodynamics of the Immunocytokine EMD 273066 (HuKS-IL2). J. Immunother. 2004, 27, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitaleri, G.; Berardi, R.; Pierantoni, C.; De Pas, T.; Noberasco, C.; Libbra, C.; González-Iglesias, R.; Giovannoni, L.; Tasciotti, A.; Neri, D.; et al. Phase I/II Study of the Tumour-Targeting Human Monoclonal Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Protein L19-TNF in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weide, B.; Eigentler, T.K.; Pflugfelder, A.; Zelba, H.; Martens, A.; Pawelec, G.; Giovannoni, L.; Ruffini, P.A.d.; Elia, G.; Neri, D.; et al. Intralesional Treatment of Stage III Metastatic Melanoma Patients with L19-IL2 Results in Sustained Clinical and Systemic Immunologic Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danielli, R.; Patuzzo, R.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Gallino, G.; Maurichi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Cutaia, O.; Lazzeri, A.; Fazio, C.; Miracco, C.; et al. Intralesional Administration of L19-IL2/L19-TNF in Stage III or Stage IVM1a Melanoma Patients: Results of a Phase II Study. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigentler, T.K.; Weide, B.; De Braud, F.; Spitaleri, G.; Romanini, A.; Pflugfelder, A.; Gonzaĺez-Iglesias, R.; Tasciotti, A.; Giovannoni, L.; Schwager, K.; et al. A Dose-Escalation and Signal-Generating Study of the Immunocytokine L19-IL2 in Combination with Dacarbazine for the Therapy of Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7732–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weide, B.; Eigentler, T.; Catania, C.; Ascierto, P.A.; Cascinu, S.; Becker, J.C.; Hauschild, A.; Romanini, A.; Danielli, R.; Dummer, R.; et al. A Phase II Study of the L19IL2 Immunocytokine in Combination with Dacarbazine in Advanced Metastatic Melanoma Patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Spitaleri, G.; Curigliano, G.; Roigas, J.; Weikert, S.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Roemer, A.; Kloeters, C.; Rogalla, P.; Pecher, G.; et al. The Tumour-Targeting Human L19-IL2 Immunocytokine: Preclinical Safety Studies, Phase i Clinical Trial in Patients with Solid Tumours and Expansion into Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2926–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudman, S.M.; Jameson, M.B.; Mckeage, M.J.; Savage, P.; Jodrell, D.I.; Harries, M.; Acton, G. A Phase 1 Study of AS1409, a Novel Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Protein, in Patients with Malignant Melanoma or Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papadia, F.; Basso, V.; Patuzzo, R.; Maurichi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Zardi, L.; Ventura, E.; González-Iglesias, R.; Lovato, V.; Giovannoni, L.; et al. Isolated Limb Perfusion with the Tumor-Targeting Human Monoclonal Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Protein L19-TNF plus Melphalan and Mild Hyperthermia in Patients with Locally Advanced Extremity Melanoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Van Limbergen, E.J.; Oberije, C.J.G.; Troost, E.G.C.; Hadrup, S.R.; Dingemans, A.M.C.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Eckert, F.; Hiley, C.; Dooms, C.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy (SABR) Combined with Immunotherapy (L19-IL2) versus Standard of Care in Stage IV NSCLC Patients, ImmunoSABR: A Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Open-Label Phase II Trial. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, J.F.; Jameson, M.B.; Savage, P.; Jodrell, D.; Rudman, S.M.; Erlandsson, F.; Acton, G.; McKeage, M. A Phase I Study of AS1409, a Novel Antibody-Cytokine Fusion Protein, in Patients with Malignant Melanoma (MM) or Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Gnad-Vogt, U.S.; Gallerani, E.; Beck, J.; Sessa, C.; Omlin, A.; Mattiacci, M.R.; Liedert, B.; Kramer, D.; Laurent, J.; et al. A Phase i Dose-Escalation Study of the Immunocytokine EMD 521873 (Selectikine) in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strauss, J.; Heery, C.R.; Kim, J.W.; Jochems, C.; Donahue, R.N.; Montgomery, A.S.; McMahon, S.; Lamping, E.; Marte, J.L.; Madan, R.A.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Trial of a Tumor-Targeted Cytokine (NHS-IL12) in Subjects with Metastatic Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Heuvel, M.M.; Verheij, M.; Boshuizen, R.; Belderbos, J.; Dingemans, A.M.C.; De Ruysscher, D.; Laurent, J.; Tighe, R.; Haanen, J.; Quaratino, S. NHS-IL2 Combined with Radiotherapy: Preclinical Rationale and Phase Ib Trial Results in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Following First-Line Chemotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Mehnert, J.M.; Cuillerot, J.-M.; von Heydebreck, A.; Ott, P.A.; Hodi, F.S. Targeted Modified IL-2 (NHS-IL2, MSB0010445) Combined with Stereotactic Body Radiation in Advanced Melanoma Patients after Progression on Ipilimumab: Assessment of Safety, Clinical, and Biologic Activity in a Phase 2a Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, TPS9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Heery, C.R.; Bilusic, M.; Singh, N.K.; Madan, R.A.; Sabzevari, H.; Schlom, J.; Gulley, J.L. First-in-Human Phase I Trial of NHS-IL12 in Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, TPS2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brummelen, E.M.J.; Huisman, M.C.; de Wit-van der Veen, L.J.; Nayak, T.K.; Stokkel, M.P.M.; Mulder, E.R.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Vugts, D.J.; Van Dongen, G.A.M.S.; Verheul, H.M.; et al. 89Zr-Labeled CEA-Targeted IL-2 Variant Immunocytokine in Patients with Solid Tumors: CEA-Mediated Tumor Accumulation and Role of IL-2 Receptor-Binding. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24737–24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellens, J.H.M.; Tabernero, J.; Lassen, U.N.; Melero, I.; Homicsko, K.; Argilés, G.; Perez Gracia, J.L.; Sorensen, M.; Coukos, G.; ANGEVIN, E.; et al. CEA-Targeted Engineered IL2: Clinical Confirmation of Tumor Targeting and Evidence of Intra-Tumoral Immune Activation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachanova, V.; Lansigan, F.; Quick, D.P.; Vlock, D.; Gillies, S.; Nakamura, R. Remission Induction in a Phase I/II Study of an Anti-CD20-Interleukin-2 Immunocytokine DI-Leu16-IL2 in Patients with Relapsed B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansigan, F.; Nakamura, R.; Quick, D.P.; Vlock, D.; Raubitschek, A.; Gillies, S.D.; Bachanova, V. DI-Leu16-IL2, an Anti-CD20-Interleukin-2 Immunocytokine, Is Safe and Active in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Report of Maximum Tolerated Dose, Optimal Biologic Dose, and Recommended Phase 2 Dose. Blood 2016, 128, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansigan, F.; Nakamura, R.; Quick, D.; Vlock, D.; Raubitschek, A.A.; Gillies, S.D.; Bachanova, V. Phase I/II Study of an Anti-CD20-Interleukin-2 Immunocytokine DI-Leu16-IL2 in Patients with Relapsed b-Cell Lymphoma (NHL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, e19046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerensen, M.M.; Ros, W.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Robbrecht, D.; Rohrberg, K.S.; Martin-Liberal, J.; Lassen, U.N.; Melero Bermejo, I.; Lolkema, M.P.; Tabernero, J.; et al. Safety, PK/PD, and Anti-Tumor Activity of RO6874281, an Engineered Variant of Interleukin-2 (IL-2v) Targeted to Tumor-Associated Fibroblasts via Binding to Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e15155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Antigen | Disease | Cytokine Delivered | Phase | Clinical Trial # | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD2 | Neuroblastoma Melanoma Sarcoma Solid childhood tumors | IL-2 | I and II | NCT00590824 NCT00082758 NCT03958383 NCT03209869 NCT01334515 NCT00003750 NCT00109863 | [195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205] |
| Tnc A1 | Breast carcinoma AML Solid tumors MCC | IL-2 | I and II | NCT01131364 NCT01134250 NCT02957032 NCT02054884 NCT03207191 | [206,207,208,209] |
| EpCAM | SCLC Prostate carcinoma Ovarian carcinoma Breast carcinoma Bladder carcinoma Kidney carcinoma Lung carcinoma Solid tumors | IL-2 | I and II | NCT00132522 NCT00016237 | [210,211,212] |
| EDB | Melanoma RCC NSCLC Solid tumors Pancreatic carcinoma Colorectal carcinoma DLBCL Glioblastoma Sarcoma Glioma | IL-2 IL-12 TNF | I, II, and III | NCT01058538 NCT02086721 NCT01198522 NCT01253837 NCT02076620 NCT02076646 NCT04471987 NCT02957019 NCT01213732 NCT01055522 NCT04443010 NCT04032964 NCT03420014 NCT03779230 NCT04573192 NCT03705403 NCT02938299 NCT03567889 NCT01253096 NCT00625768 NCT02076633 | [159,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222] |
| Histone/DNA structures | NSCLC Solid tumors Pancreatic carcinoma Urogenital carcinoma Bladder carcinoma NHL Kaposi sarcoma Melanoma | IL-2LT IL-12 | I and II | NCT04327986 NCT04235777 NCT00879866 NCT01032681 NCT04303117 NCT01973608 NCT01417546 NCT02994953 | [223,224,225,226,227] |
| CEA | Solid tumors | IL-2v | I | NCT02350673 NCT02004106 | [228,229] |
| CD20 | B cell lymphoma | IL-2 | I and II | NCT02151903 NCT01874288 NCT00720135 | [230,231,232] |
| FAP | Solid tumors RCC Melanoma Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Breast carcinoma HNC Esophageal carcinoma Cervical carcinoma | IL-2v | I and II | NCT03063762 NCT03875079 NCT03193190 NCT02627274 NCT03386721 | [233] |
| PD-1 | Solid tumors | IL-2v | I | NCT04303858 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Runbeck, E.; Crescioli, S.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Papa, S. Utilizing Immunocytokines for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies 2021, 10, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010010
Runbeck E, Crescioli S, Karagiannis SN, Papa S. Utilizing Immunocytokines for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies. 2021; 10(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleRunbeck, Erin, Silvia Crescioli, Sophia N. Karagiannis, and Sophie Papa. 2021. "Utilizing Immunocytokines for Cancer Therapy" Antibodies 10, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010010
APA StyleRunbeck, E., Crescioli, S., Karagiannis, S. N., & Papa, S. (2021). Utilizing Immunocytokines for Cancer Therapy. Antibodies, 10(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10010010






