Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Evaluation of Land Surface Thermal Contributions Based on Quality–Quantity Dimensions and Land Use–Geomorphology Coupling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval
2.3.2. Contribution of Heat Source and Sink Landscapes to LST
2.3.3. Contribution Index Calculation
3. Results
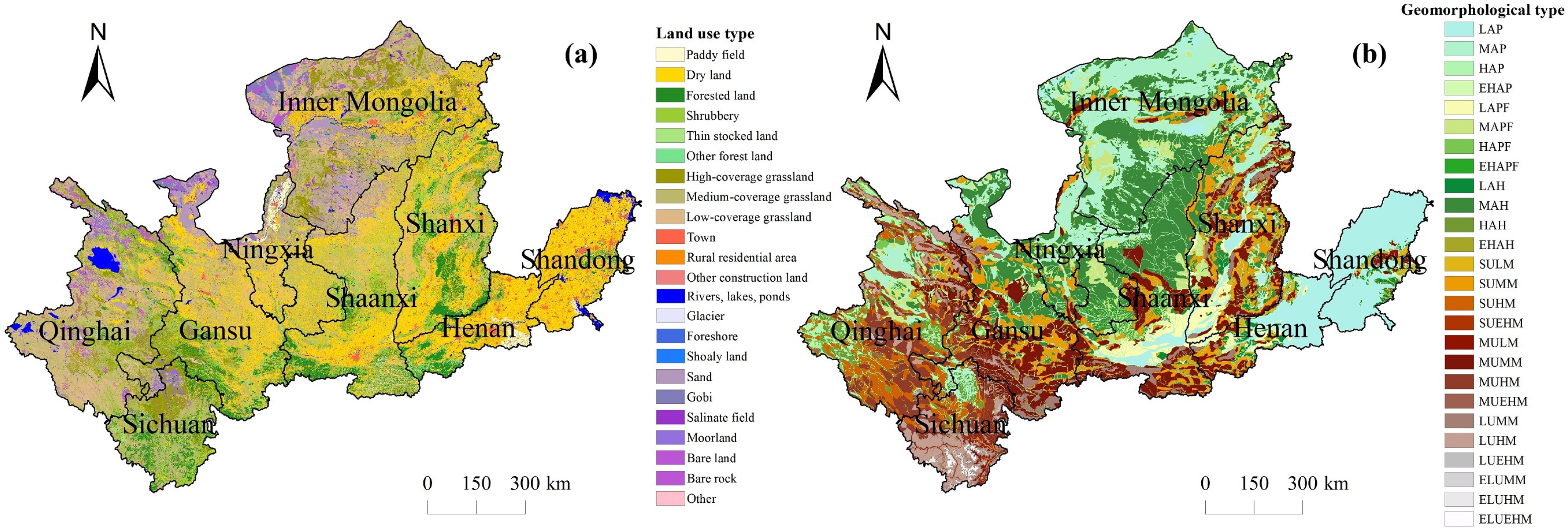
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Different Underlying Surface Types in the YRB
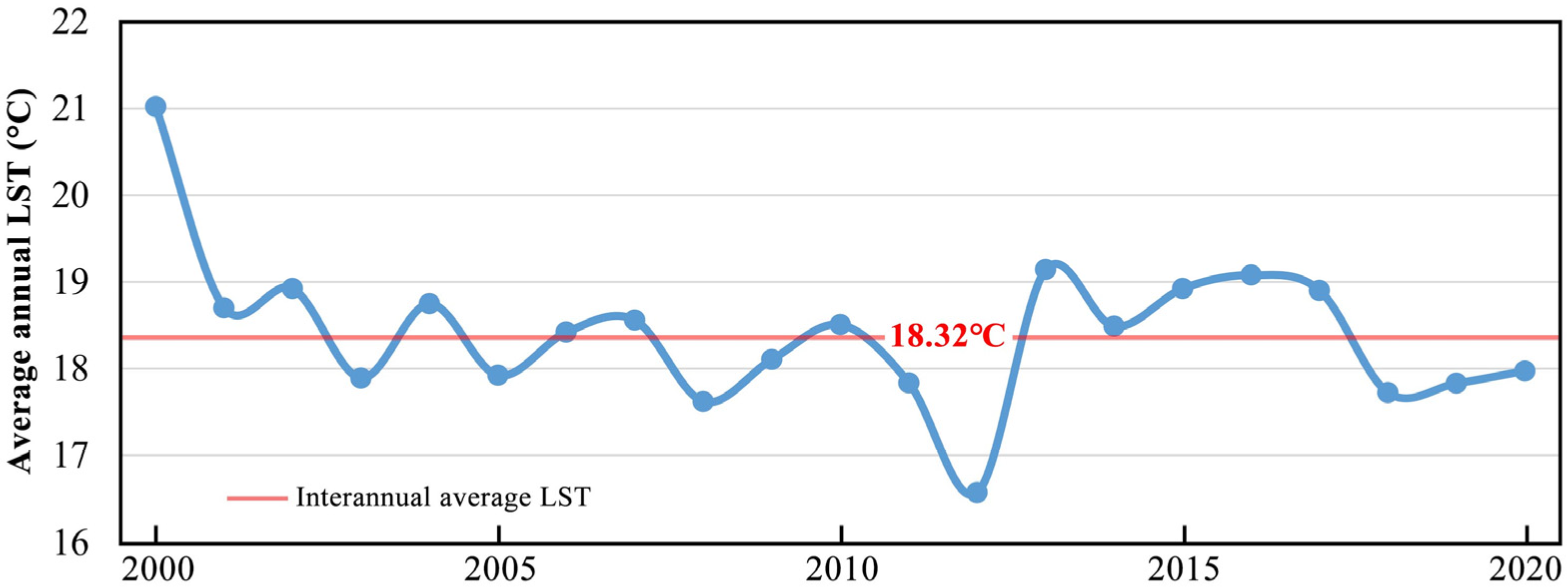
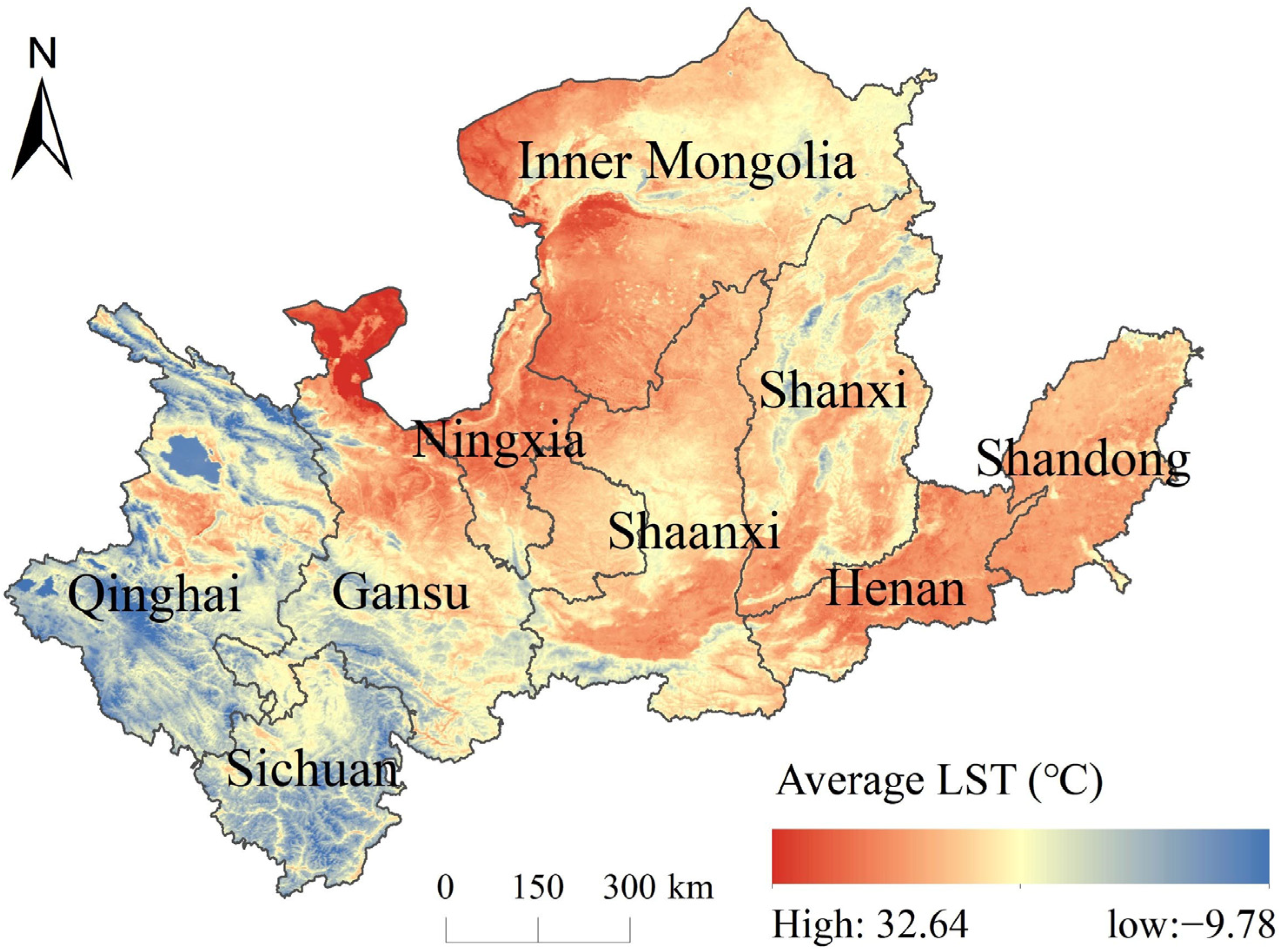
3.2. Spatial Distribution of LST Across Different Underlying Surface Types
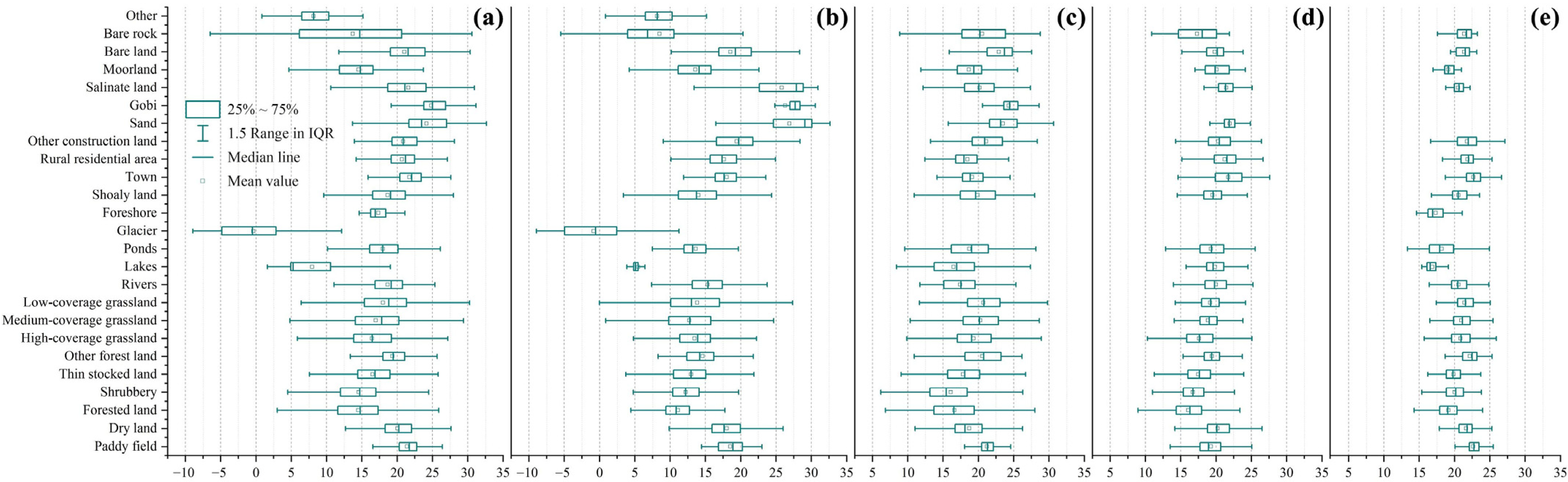
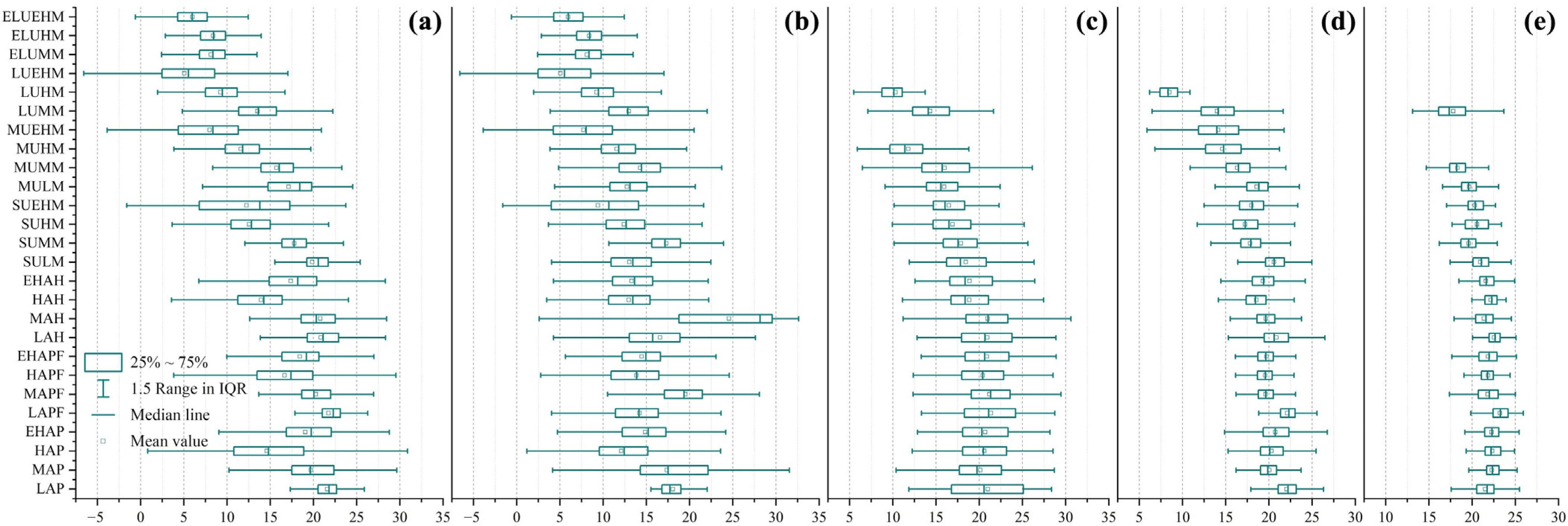
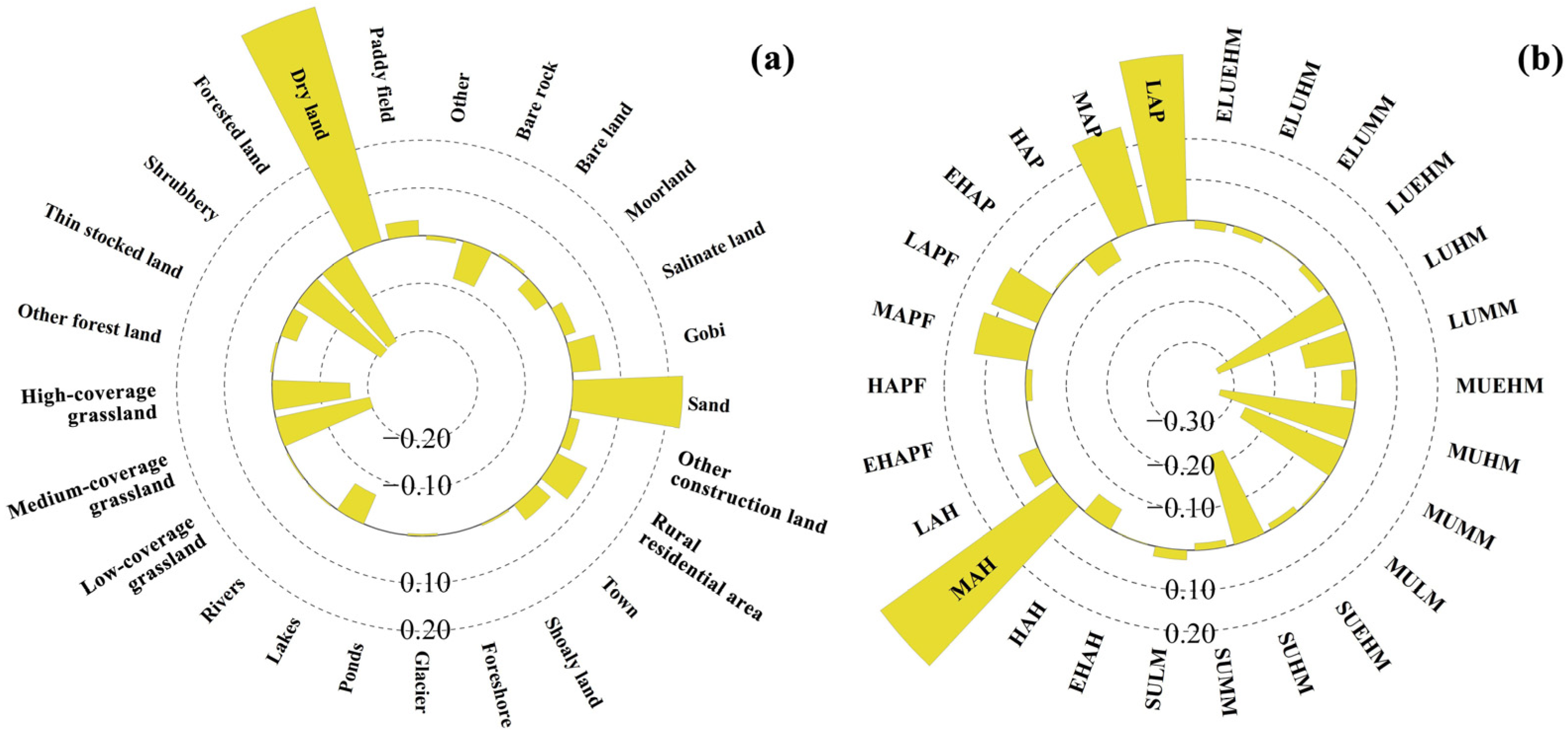
3.3. Contributions of Different Underlying Surface Types to the Thermal Environment of the YRB
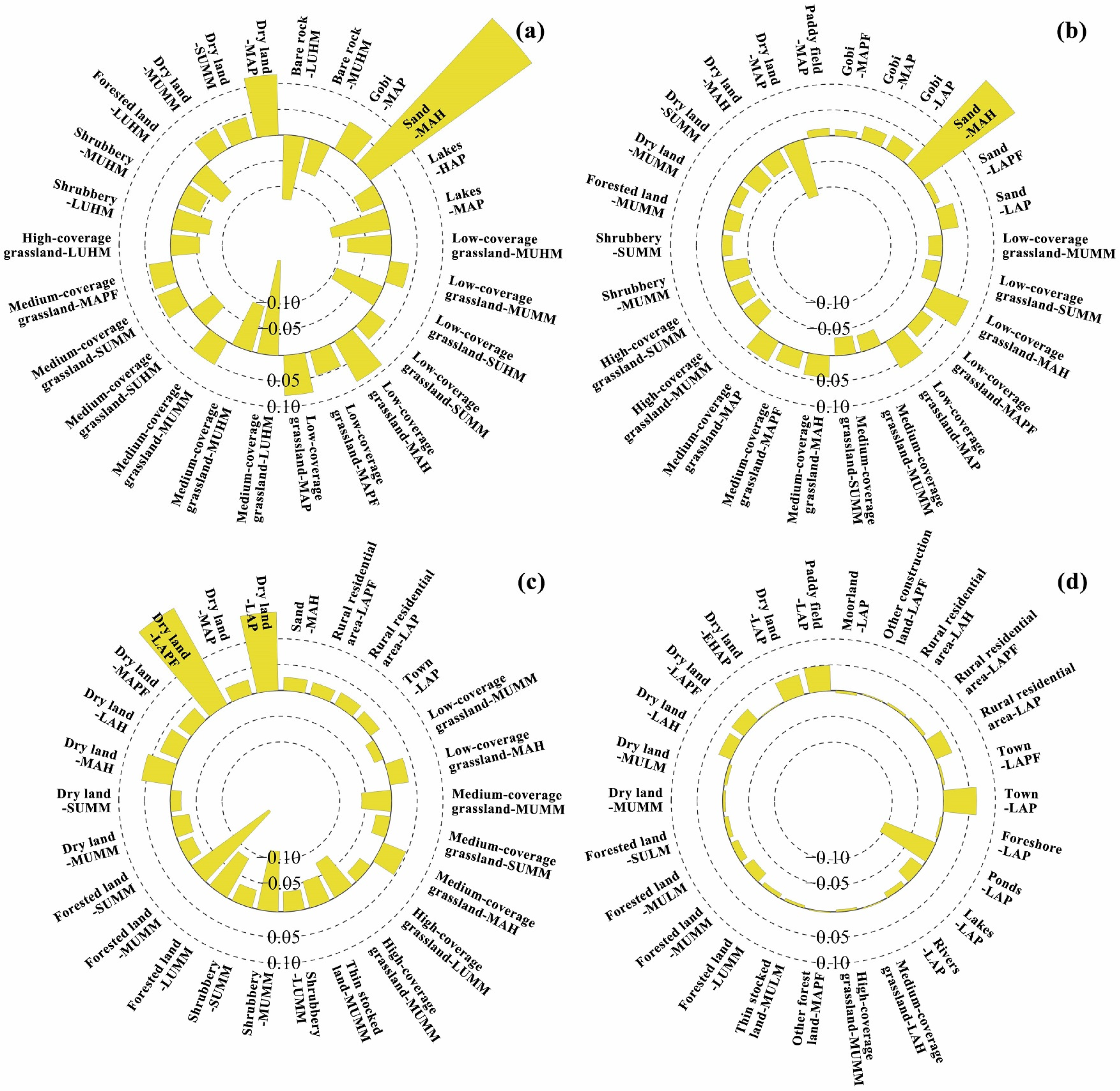
3.4. Combined Contributions of Land Use and Geomorphology to the Thermal Environment of the YRB
4. Discussion
4.1. Hierarchical Patterns of Integrated Thermal Contributions in the YRB
4.2. Policy Implications
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xuan, B.; Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Hu, Y. Spatiotemporal Relationship Between Human Activities and Urban Heat in Chinese Megacities Based on Multisource Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 17064–17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Sheffield, J.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Funk, C.; Miralles, D.G.; Peng, J.; Dyer, E.; Talib, J.; Beck, H.E.; Singer, M.B.; et al. Warming Accelerates Global Drought Severity. Nature 2025, 642, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Vohland, M. Downscaling Land Surface Temperatures at Regional Scales with Random Forest Regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia Cecilia, J.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Impact of Urban Morphology and Landscape Characteristics on Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Land Surface Temperature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wu, P.; Foody, G.M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Du, Y.; Ling, F. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Land Surface Temperature Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 1808–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Cai, X.; Li, C. Duration of Exposure to Compound Daytime-Nighttime High Temperatures and Changes in Population Exposure in China under Global Warming. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gong, J.; Cao, J.; Tian, Y.; Rao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Duman, I.; Kerimbaevich, E.F. Differential Spatiotemporal Patterns in Urban Thermal Environment Driven by Impervious Surface Trajectories: A Multi-Scale Assessment Framework. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2026, 117, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Creutzig, F.; Zhao, B.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C.; Ge, Q. Continuous Assessment of the Factors Driving the Urban Surface Thermal Environment in 1,469 Cities Worldwide. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2025, 2, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Feng, T. Driving Mechanism of Differentiation in Urban Thermal Environment during Rapid Urbanization. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Zhao, S. Intensifying Urban Imprint on Land Surface Warming: Insights from Local to Global Scale. iScience 2024, 27, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of Landscape Composition and Pattern on Land Surface Temperature: An Urban Heat Island Study in the Megacities of Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushore, T.D.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J. Estimating Urban LST Using Multiple Remotely Sensed Spectral Indices and Elevation Retrievals. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Ma, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Relationship between Night Time Light and Land Surface Temperature: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2022, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Aldosary, A.S.; Mortoja, M.G. Modeling Future Land Cover Changes and Their Effects on the Land Surface Temperatures in the Saudi Arabian Eastern Coastal City of Dammam. Land 2017, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Mazzanti, P.; Bozzano, F.; Mugnozza, G.S. Trend Analysis of MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Land Cover in Central Italy. Land 2024, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aik, D.H.J.; Ismail, M.H.; Muharam, F.M. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and the Relationship with Land Surface Temperature Using Landsat and MODIS Imageries in Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Land 2020, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X.; Xin, J.; Kang, X.; Nie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, X.; et al. Systematic Overestimation of Urban Parks’ Cooling Effects May Mislead Heat-Governance-Oriented Park Planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 264, 105467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.H. Analysis and Precision of the Terrestrial Surface Temperature Using Landsat 8 and Sentinel 3 Images: Study Applied to the City of Granada (Spain). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Murayama, Y. Geo-Simulation of Land Use/Cover Scenarios and Impacts on Land Surface Temperature in Sapporo, Japan. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Haase, D.; Qureshi, S.; Firozjaei, M.K. Integrated Land Use and Urban Function Impacts on Land Surface Temperature: Implications on Urban Heat Mitigation in Berlin with Eight-Type Spaces. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 83, 103944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurduc, A.; Ermida, S.L.; DaCamara, C.C. On the Suitability of Different Satellite Land Surface Temperature Products to Study Surface Urban Heat Islands. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the Relationship between Land Use Land Cover Change and Land Surface Temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.A.; Kumar, P.; Gonencgil, B. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Land Use/Cover Change and Its Effect on Land Surface Temperature in Lahaul and Spiti, India. Land 2023, 12, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J. Characterizing, Monitoring, and Simulating Land Cover Dynamics Using GlobeLand30: A Case Study from 2000 to 2030. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Du, Z.; Dong, R.; Zheng, J.; Tu, Y.; Chen, X.; Hao, P.; Zhong, B.; Peng, D.; Zhao, J.; et al. FROM-GLC Plus: Toward near Real-Time and Multi-Resolution Land Cover Mapping. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1026–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, W.; Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. SinoLC-1: The First 1 m Resolution National-Scale Land-Cover Map of China Created with a Deep Learning Framework and Open-Access Data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 4749–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-L. Mapping Temporal and Spatial Changes in Land Use and Land Surface Temperature Based on MODIS Data. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Yao, X.; Li, M.; Yin, M.; Dong, F.; Yan, S.; Zhao, J. Exploring the main and interactive effects of urban morphology on land surface temperature across different functional zones: A local geoshapley analysis based on XAI. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 134, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Contribution of Urban Functional Zones to the Spatial Distribution of Urban Thermal Environment. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Meng, Q.; Qian, J.; Gao, J.; Li, T. Nonlinear Effects of Urban Multidimensional Characteristics on Daytime and Nighttime Land Surface Temperature in Highly Urbanized Regions: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Baklanov, A.; He, B.; Ge, Q. Mainstreaming the Local Climate Zone Framework for Climate-Resilient Cities. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Yu, B.; Li, P.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L. Understanding the Relationship between 2D/3D Variables and Land Surface Temperature in Plain and Mountainous Cities: Relative Importance and Interaction Effects. Build. Environ. 2023, 245, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liao, H.; Huang, B.; Peng, S.; Zhou, T. Spatial-Temporal Pattern of, and Driving Forces for, Urban Heat Island in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Indraganti, M.; Jawarneh, R.N. Land Surface Temperature Responses to Land Use Dynamics in Urban Areas of Doha, Qatar. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 104, 105273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, P.; Priya, R.S.; Sudha, G. Spatial Characteristics of Urban Heat Islands: Land Use-Based Assessment Using Chennai’s Second Master Plan. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 28, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Qiao, H.; Li, Q.; Song, M.; Yao, X.; Gao, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Qi, G.; Li, G. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment across Different Terrain Gradients in the Yellow River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 11, 1305282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Cui, X. Deciphering the Spatial Code of the Yellow River Basin: A Novel Framework for Optimizing Land Use Functions and Zoning Identification Strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Gao, B.; Gong, T.; Wang, B. Analyzing Changes in Frozen Soil in the Source Region of the Yellow River Using the MODIS Land Surface Temperature Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y. Multifractal Characteristics Analysis Based on Slope Distribution Probability in the Yellow River Basin, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Spatial Heterogeneity and Formation Mechanism of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of land surface temperature in Xinjiang based on MODIS. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhe, P.; Lucas, C.; Hawker, L.; Brine, M.; Wilkinson, H.; Cooper, A.; Saoulis, A.A.; Savage, J.; Sampson, C. FathomDEM: An Improved Global Terrain Map Using a Hybrid Vision Transformer Model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, B.; Cheng, W.; Han, J.; Qi, D.; Zhu, C. Research on geomorphological regionalization of China. Acta Geographica Sinica. 2013, 68, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, S.-B. Reconstruction of Daytime Land Surface Temperatures under Cloud-Covered Conditions Using Integrated MODIS/Terra Land Products and MSG Geostationary Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Vejre, H. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Characteristics of Remotely Sensed Region Heat Islands during the Rapid Urbanization (1995–2015) of Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freychet, N.; Hegerl, G.C.; Lord, N.S.; Lo, Y.T.E.; Mitchell, D.; Collins, M. Robust Increase in Population Exposure to Heat Stress with Increasing Global Warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 064049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, J.; Sun, D.; Ren, J.; Xue, B.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C.; Li, X. How Urban Heat Island Magnifies Hot Day Exposure: Global Unevenness Derived from Differences in Built Landscape. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M.; Yu, P. The Response of Land Surface Temperature Changes to the Vegetation Dynamics in the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, M.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Cao, W.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X. Human-Perceived Temperature Changes Linked to Local Climate Zones under Extreme Hot and Cold Weathers: A Study in the North China Plain. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 121, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, F. Effect of Human Settlements on Urban Thermal Environment and Factor Analysis Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Changsha City. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Peng, W. Quantifying the Spatial Differentiation Mechanism of Land Use Degree. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Tang, S.; Wu, X. Supply and Demand Analysis of Urban Thermal Environments Regulation Services from an Accessibility Perspective: A Coupled Thermal Risk and Green Space Cooling Assessment Model. Urban Clim. 2025, 60, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wu, C.; Yeh, P.J.-F.; Hu, B.X.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Niu, J. Widespread Global Enhancement of Vegetation Resistance to Compound Dry-Hot Events Due to Anthropogenic Climate Change. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yao, Y.; Xiang, K.; Dai, X.; Li, W.; Dai, H.; Lu, K.; Li, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Spatial-Temporal Pattern of Ecosystem Services and Sustainable Development in Representative Mountainous Cities: A Case Study of Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fu, S.; Cui, H.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Qiao, J. Identifying the Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Drought Characteristics and Its Constraint Factors in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primary Type | Secondary Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Paddy field | Dry land | —— | —— |
| Forest land | Forested land | Shrubbery | Thin stocked land | Other forest land |
| Grassland | High-coverage grassland | Medium-coverage grassland | Low-coverage grassland | |
| Water body | Rivers | Lakes | Ponds | Glacier |
| Foreshore | Shoaly land | —— | —— | |
| Construction land | Town | Rural residential area | Other construction land | —— |
| Unused land | Sand | Gobi | Salinate land | Moorland |
| Bare land | Bare rock | Other | —— | |
| Relief Amplitude | Elevation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Altitude (<1000 m) | Medium Altitude (1000~3500 m) | High Altitude (3500~5000 m) | Extremely High Altitude (>5000 m) | |
| Plain (generally <30 m) | Low-altitude plain (LAP) | Medium-altitude plain (MAP) | High-altitude plain (HAP) | Extremely high-altitude plain (EHAP) |
| Platform (generally >30 m) | Low-altitude platform (LAPF) | Medium-altitude platform (MAPF) | High-altitude platform (HAPF) | Extremely high-altitude platform (EHAPF) |
| Hills (<200 m) | Low-altitude hills (LAH) | Medium-altitude hills (MAH) | High-altitude hills (HAH) | Extremely high-altitude hills (EHAH) |
| Small undulating mountains (200–500 m) | Small undulating low mountain (SULM) | Small undulating mid-mountain (SUMM) | Small undulating high mountain (SUHM) | Small undulating extremely high mountain (SUEHM) |
| Medium undulating mountains (500–1000 m) | Medium undulating low mountain (MULM) | Medium undulating mid-mountain (MUMM) | Medium undulating high mountain (MUHM) | Medium undulating extremely high mountain (MUEHM) |
| Large undulating mountains (1000–2500 m) | —— | Large undulating mid-mountain (LUMM) | Large undulating high mountain (LUHM) | Large undulating extremely high mountain (LUEHM) |
| Extremely large undulating mountains (>2500 m) | —— | Extremely large undulating mid-mountain (ELUMM) | Extremely large undulating high mountain (ELUHM) | Extremely large undulating extremely high mountain (ELUEHM) |
| LST Grade | LST Region |
|---|---|
| High | T > u + 2 std |
| Relatively High | u + 0.5 std < T < u + 2 std |
| Medium | u − 0.5 std < T < u + 0.5 std |
| Relatively Low | u − 2 std < T < u − 0.5 std |
| Low | T < u − 2 std |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Xie, X. Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Evaluation of Land Surface Thermal Contributions Based on Quality–Quantity Dimensions and Land Use–Geomorphology Coupling. Land 2025, 14, 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122318
Li Z, Yang J, Liu H, Xie X. Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Evaluation of Land Surface Thermal Contributions Based on Quality–Quantity Dimensions and Land Use–Geomorphology Coupling. Land. 2025; 14(12):2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122318
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhe, Jun Yang, He Liu, and Xiao Xie. 2025. "Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Evaluation of Land Surface Thermal Contributions Based on Quality–Quantity Dimensions and Land Use–Geomorphology Coupling" Land 14, no. 12: 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122318
APA StyleLi, Z., Yang, J., Liu, H., & Xie, X. (2025). Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Evaluation of Land Surface Thermal Contributions Based on Quality–Quantity Dimensions and Land Use–Geomorphology Coupling. Land, 14(12), 2318. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122318







