Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Runoff and Sediment in the Dali River Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
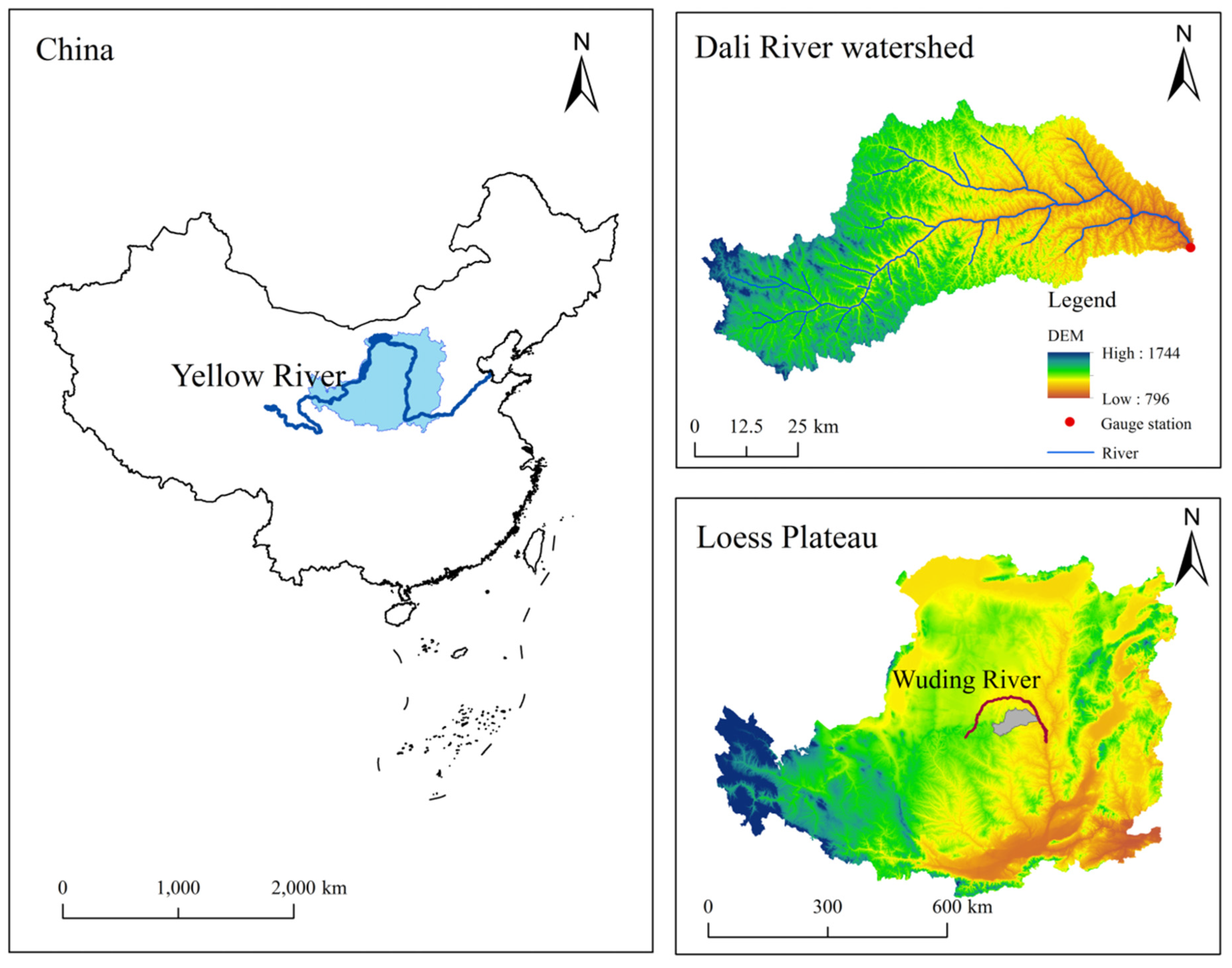
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. The Data Collected
2.3. Data Analysis
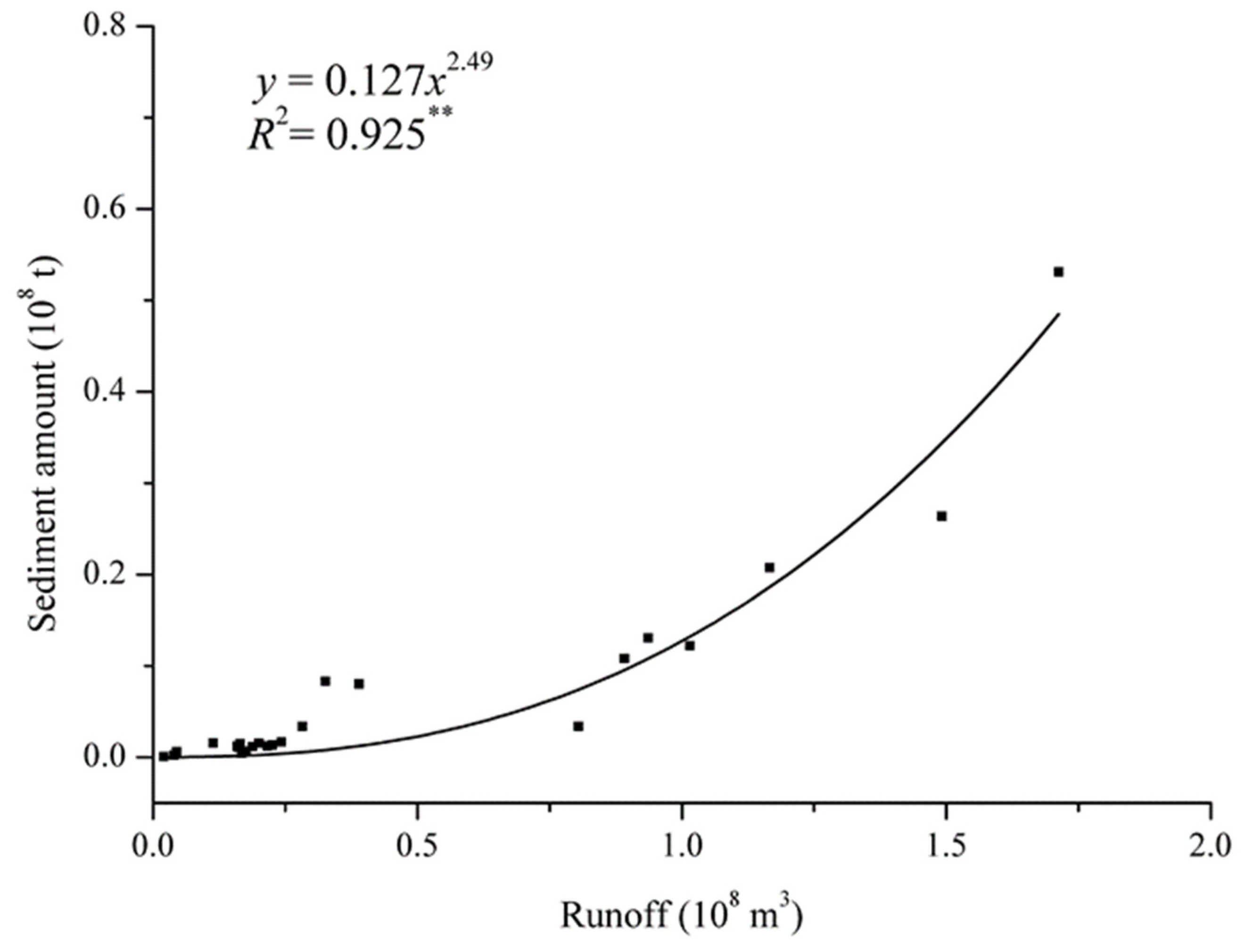
3. Results
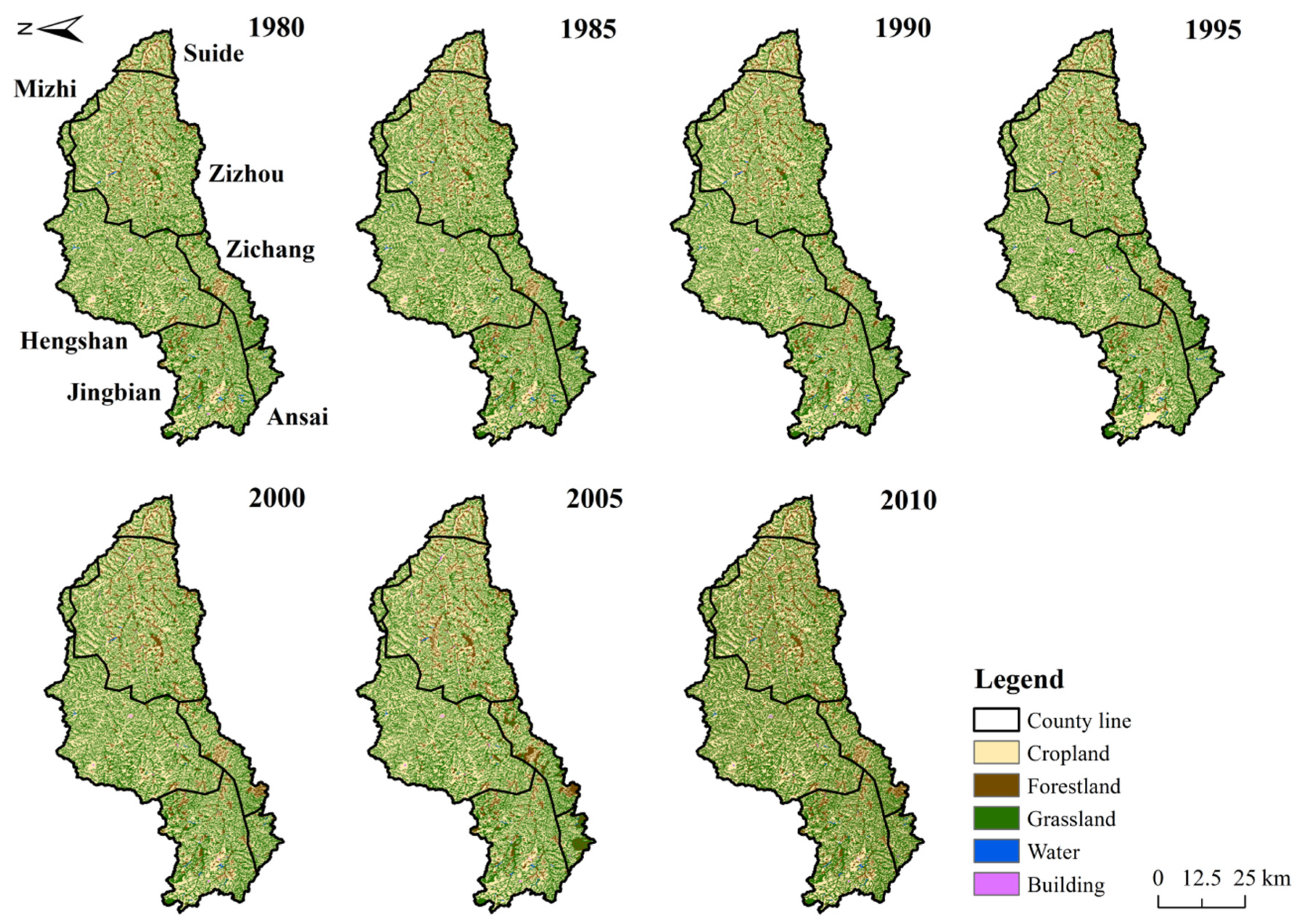
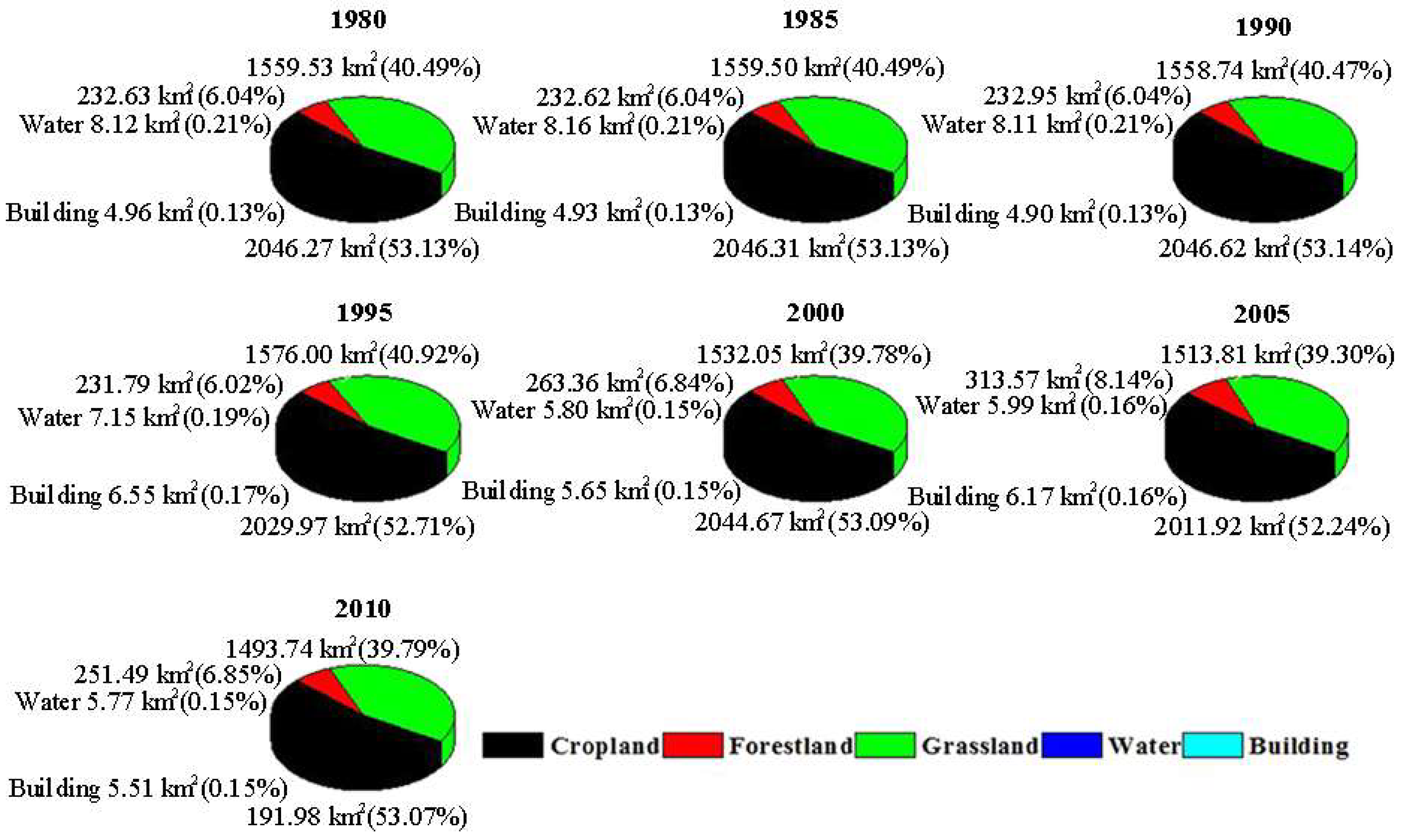
3.1. Changes of Land Uses and Landscape Pattern of the Watershed
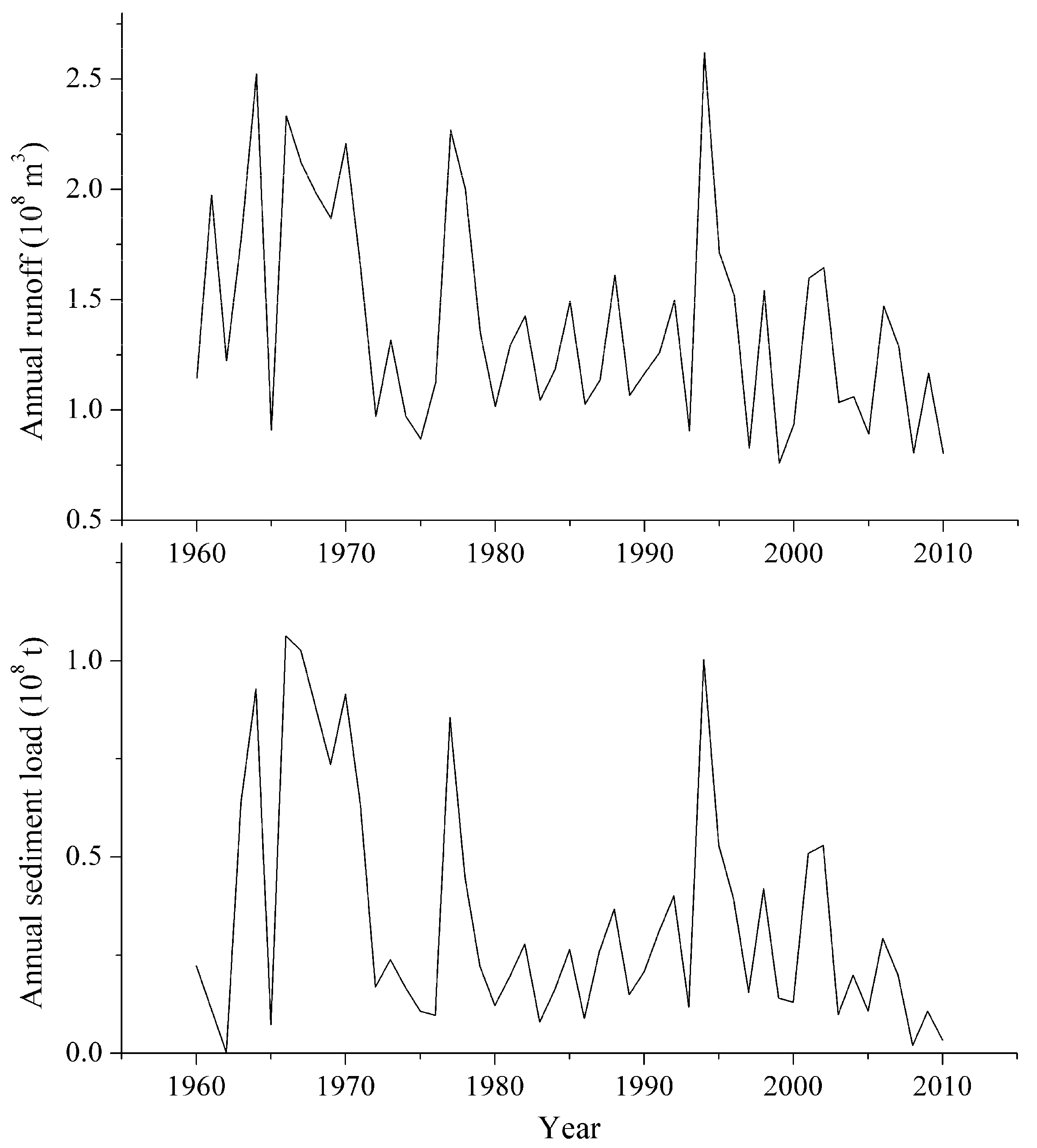
3.2. Changes of Runoff and Sediment in the Watershed
3.3. The Response Relationship Between Landscape Pattern Change and Runoff and Sediment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Daryanto, S. Quantifying the effects of precipitation, vegetation, and land preparation techniques on runoff and soil erosion in a Loess watershed of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, P.; Gong, J. Land-use changes and check dams reducing runoff and sediment yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Shi, W.; Song, Y.; He, X. Balancing green and grain trade. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, F. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Daryanto, S.; Wang, L. Land preparation and vegetation type jointly determine soil conditions after long-term land stabilization measures in a typical hilly catchment, Loess Plateau of China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Xiao, L.; Xu, G.; Zhu, T. Land-use types and slope topography affect the soil labile carbon fractions in the Loess hilly-gully area of Shaanxi, China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Jia, F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, T. Responses of vertical soil moisture to rainfall pulses and land uses in a typical loess hilly area, China. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Soil respiration and response of carbon source changes to vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. When and where did the Loess Plateau turn “green”? Analysis of the tendency and breakpoints of the normalized difference vegetation index. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sun, G.; Fu, B.; Su, C.; Liu, Y.; Lamparski, H. Regional effects of vegetation restoration on water yield across the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Lu, Y. A conceptual model for a process-oriented landscape pattern analysis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Metzger, M.J.; Maes, J.; Pinto-Correia, T. Policy impacts on regulating ecosystem services: Looking at the implications of 60 years of landscape change on soil erosion prevention in a Mediterranean silvo-pastoral system. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Skidmore, A.K.; Hao, F.H.; Wang, T. Soil erosion dynamics response to landscape pattern. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; van Doorn, A.; Quetier, F.; Chouvardas, D.; Rounsevell, M. The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: The importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Response of nitrogen pollution in surface water to land use and social-economic factors in the Weihe River watershed, northwest China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Cheng, X.; Chen, L. A precipitation-weighted landscape structure model to predict potential pollution contributions at watershed scales. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A.C.; Prinsen, H.A.M. Vegetation patterns as biological indicators for identifying runoff and sediment source and sink areas for semi-arid landscapes in Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yu, K.; Ren, Z.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. Distribution of soil organic carbon impacted by land-use changes in a hilly watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.Z.; Wang, T.; Han, Z.W.; Qie, Y.F. Surveying sandy deserts and desertified lands in north-western China by remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3603–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.; Billeter, R.; Aviron, S.; Schweiger, O.; Herzog, F. The influence of thematic resolution on metric selection for biodiversity monitoring in agricultural landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbin, L.; Wu, J.G. Use and misuse of landscape indices. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Effect of rainfall variation and landscape change on runoff and sediment yield from a loess hilly catchment in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Marter-Kenyon, J.; López-Carr, D.; Liang, X. Land cover and landscape changes in Shaanxi Province during China’s Grain for Green Program (2000–2010). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hobbs, R. Key issues and research priorities in landscape ecology: An idiosyncratic synthesis. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ai, L.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, G.; Liao, W. Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liang, D.; Lu, N. Landscape ecology: Coupling of pattern, process, and scale. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; He, X. Assessing effects of landscape pattern on sediment yield using sediment delivery distributed model and a landscape indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 22, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Li, Y.; Yi, Y. The influence of changes in land use and landscape patterns on soil erosion in a watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchamalo, M.; Hooke, J.M.; Sandercock, P.J. Flow and sediment connectivity in semi-arid landscapes in SE Spain: Patterns and controls. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Ren, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, T.; Xu, G.; Yu, K.; Shi, P.; Tang, S. Variations in runoff and sediment in watersheds in loess regions with different geomorphologies and their response to landscape patterns. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J. The correlation analysis on the landscape pattern index and hydrological processes in the Yanhe watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; He, C.; Chen, L.; Song, C. The effects of land-use combinations on soil erosion: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Nearing, M.A. Impact of climate change on soil erosion, runoff, and wheat productivity in central Oklahoma. Catena 2005, 61, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Landscape Pattern Metrics | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Patch | NP | The number of the patch |
| Patch Density | PD | Patch Density is the number of corresponding patches divided by the total landscape area |
| Largest Patch Index | LPI | The area of the largest patch of the corresponding patch type divided by the total landscape area |
| Landscape Shape Index | LSI | The area of the largest patch of the corresponding patch type divided by the total landscape area |
| Contagion Index | CONTAG | Extent to which patch types are aggregated or clumped as a percentage of the maximum possible |
| Patch Cohesion Index | CONHESION | The physical connectedness of the corresponding patch type, which is an area-weighted mean perimeter-area ratio |
| Landscape Division Index | DIVSION | Reflect the degree of fragmentation of the landscape |
| Shannon’s Diversity Index | SHDI | The number of different patch types and the proportional area distribution among patch types |
| NP | PD | LPI | LSI | CONTAG | COHESION | DIVISION | SHDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff | −0.55 ** | −0.56 ** | −0.12 | −0.02 | 0.42 ** | −0.30 * | −0.19 * | −0.55 ** |
| Sediment | −0.54 ** | −0.53 ** | −0.10 | −0.08 | 0.50 ** | −0.41 ** | −0.20 * | −0.43 ** |
| Dependent Variables | Independent Variables | Landscape Pattern Metrics | Regression | R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff | x1 | NP | y = −48.326x1 + 2.908 | 0.489 | 0.007 |
| x2 | PD | y = −7.048x2 + 0.567 | 0.171 | 0.052 | |
| x3 | LPI | y = −0.051x3 + 1.503 | 0.014 | 0.114 | |
| x4 | LSI | y = −0.005x4 + 1.679 | 0.025 | 0.205 | |
| x5 | CONTAG | y = 0.111x5-5.663 | 0.422 | 0.008 | |
| x6 | COHESION | y = −1.503x6-148.619 | 0.304 | 0.013 | |
| x7 | DIVISION | y = −26.743x7 + 27.385 | 0.186 | 0.036 | |
| x8 | SHDI | y = −13.596x8 + 13.414 | 0.555 | 0.006 | |
| Sediment | x1 | NP | y = −20.241x1 + 1.435 | 0.591 | 0.005 |
| x2 | PD | y = −3.298x2 + 2.268 | 0.536 | 0.006 | |
| x3 | LPI | y = −0.02x3 + 0.341 | 0.097 | 0.184 | |
| x4 | LSI | y = −0.007x4 + 1.026 | 0.078 | 0.147 | |
| x5 | CONTAG | y = 0.064x5 − 3.696 | 0.498 | 0.007 | |
| x6 | COHESION | = −0.975x6 − 96.989 | 0.407 | 0.008 | |
| x7 | DIVISION | y = −14.073x7 + 14.008 | 0.202 | 0.033 | |
| x8 | SHDI | y = −5.115x8 + 4.815 | 0.431 | 0.008 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y. Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Runoff and Sediment in the Dali River Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Land 2019, 8, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8120180
Zhang Y, Bi Z, Zhang X, Yu Y. Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Runoff and Sediment in the Dali River Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Land. 2019; 8(12):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8120180
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Zhilei Bi, Xin Zhang, and Yang Yu. 2019. "Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Runoff and Sediment in the Dali River Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China" Land 8, no. 12: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8120180
APA StyleZhang, Y., Bi, Z., Zhang, X., & Yu, Y. (2019). Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Runoff and Sediment in the Dali River Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Land, 8(12), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8120180





