Abstract
The Gully Land Consolidation Project (GLCP) was launched to create more arable land by excavating soil from the slopes on both sides of gullies, combined with simultaneous comprehensive gully prevention and control measures. The purpose of the GLCP is to increase crop production and reduce soil erosion to achieve ecological and agricultural sustainability. In this study, we assess the effects of the GLCP on soil erosion and crop production by studying the BaoChengGou Watershed in the Loess Plateau, primarily by means of high spatial-resolution satellite images (taken by the GF-1 and ZY-3 satellites) combined with the InVEST model and field investigations. Sloping cropland, sparse forestland, and natural grassland are the main land use types in the study area. After implementing the GLCP, consolidated land in the cropland increased by 7.35%, an increase that has come largely at the expense of grassland and forestland. The GLCP has markedly reduced soil erosion in the BaoChengGou Watershed, especially in the sense that soil erosion intensity was also reduced significantly in the project region on the whole, despite intensifying in certain places, such as excavated slopes; furthermore, it has improved crop yields in the study area by 10.9%. Comprehensive measurement shows the GLCP to be scientific, reasonable, and clearly efficacious. This study presents findings regarding the positive significance of the GLCP in promoting ecological and agricultural sustainability in the Loess Plateau.
1. Introduction
Ensuring global food security and environmental sustainability has been included in the United Nations Millennium Development Goals [1]. Food security is closely related to food availability, which not only emphasizes quality but also the quantity of the food supply. The sustainable availability of food is dependent on the degree of the food stability, which, in turn, is strongly affected by “food resilience and environmental sustainability” [2,3]. At present, on the one hand, the impact of ecosystem degradation on human well-being and economic development is increasing [4]. On the other hand, more reasonable management of the ecosystem has also provided a rare opportunity for mankind to eradicate poverty and realize sustainable development [5]. Therefore, the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment of the United Nations has put forward that, because of the great demand for natural resources, coordinating the advantages and disadvantages of various human activities has become an important principle of sustainability [6,7].
Land consolidation has a long history around the world, and it first appeared in Medieval Europe (Germany is the birthplace of modern land consolidation [8]). Later, land consolidation also occurred in The Netherlands, Russia, Canada, Japan, and Korea [9,10,11]. From the perspective of the development of land consolidation, it has gradually shifted from the traditional form of single goal, low-level rectification to multi-objective and high-level rectification. The goals and methods of land consolidation in different countries and regions vary in accordance with their specific conditions, states of political and social development, natural geography, and historical context [12]. However, so far, most scholars have generally conducted research on land remediation in plains. This study conducts research in the Loess Plateau, and it is of great significance for global land consolidation research.
The Loess Plateau has been paid special attention by Chinese government and academia, because of the considerable degree to which it has been affected by soil erosion [13,14,15]. Extensive soil erosion has depleted the amount of fertile land in the area, which means that a wider area needs to be reclaimed to support population growth; regional poverty has increased, as well as water scarcity, and still more serious land deterioration may result from inaction [16,17]. To cope with these worsening ecological problems, the Chinese Central Government has implemented the ‘Grain for Green’ (GFG) project in the Loess Plateau since 1999 [18,19], and the ecological environment of the Loess Plateau has recovered somewhat as a result [20,21]. Yan’an, as one of the first cities to participate in a national project for controlling soil erosion in China, converted more than 0.61 × 106 ha of farmland into grassland and forestland between 1992 and 2012, which resulted in a twofold the increase in forests and grassland coverage, from 30.9% to 67.0% [22,23]. However, in terms of the implementation of afforesting or restoring grassland of degraded farmland, the total area under cultivation has also been decreased by more than half of its original area by this project. Evidently, it remains uncertain whether the GFGP will benefit all peasants and universally improve local rural living conditions [24]. Furthermore, concerns that farmers may reclaim land again due to fewer subsides received have risen with the adjustment of the subsidies for the GFG project by the government [25,26]. The integrative approach taken to land rehabilitation on the Loess Plateau has efficiently achieved sustainable development. Thus, more time needs to be devoted to finding a solution to the conflicts between agricultural development and ecological protection in the Loess Plateau.
The “Gully Land Consolidation Project” is a project that was implemented initially by the Chinese governments in 2010, with the aim of finding an acceptable solution to the conflict between food security and ecological protection in the Loess Plateau, such as that arising from reducing the GFG subsidies. The GLCP was intended to create more land suitable for farming in gullies while restoring barren slope land to vegetation in its stead. Then, it spread and brought some benefits such as saving water, creating farmland for the sake of food security, and reducing flooding [27]. Shaanxi Province, a province in northern China that encompasses 12.68% of the Loess Plateau area, developed a program titled the “Plan for Filling Gullies to Create Farmland on the Loess Plateau” in 2010 [28]. The Ministry of Land and Resources and the Ministry of Finance ([2013] 914) have formally approved the implementation of this project, which covers an area of 33,700 ha, entails total investment of 4832 million Yuan, and will be implemented in the period between 2013 and 2020 [29]. The project has been underway in the “Red Capital of China”, Yan’an City, since 2013. The suggested approach taken by the project would be removing soil from the higher hills, flattening their ridges in the process, and then pushing the soil into the gullies and compacting it to reduce the possibility of it being affected by tunneling and subsidence until the resulting fields are flat or gently sloping. At the same time, rich topsoil is applied to make it suitable for crop growth [30]. Using the flat fields that are created in channels for cultivation will ultimately increase the cultivation land area in the Loess Plateau.
However, the GLCP requires excavation of the surrounding hills, which may destroy the stability of vegetation and slopes. The possibility that this process will destroy the environment or exacerbate soil erosion has even been raised [28].
In this study, we quantitatively analyze the effects of the GLCP on the two aspects of ecological and agricultural development. The typical watershed selected in this research is representative of the entire GLCP. Taking the project of the BaoChengGou Watershed as an typical watershed, the impact of soil erosion and crop production before and after the implementation of GLCP is evaluated by the InVEST-sediment delivery model and field investigation, and we discuss whether it is feasible to turn the crisis of soil erosion into opportunities to increase the quantity of high standard cultivated land available on the Loess Plateau. This paper attempts to reveal how the GLCP helps to alleviate the contradiction between farmers’ well-being and ecological sustainability, benefitting both sides by both increasing local crop production and decreasing soil erosion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The BaoChengGou Watershed is situated between 36°56′35″ N and 37°4′52″ N latitude, and 107°54′18″ E to 107°58′48″ E longitude in the northwest of Wuqi County, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, China (Figure 1). The Baochenggou Watershed has typical climate and geomorphological characteristics of the Loess Plateau. Selecting such a typical Watershed as the study area can show the effect of the whole GLCP in the Loess Plateau to the greatest extent possible. The total area of the watershed is 5400 ha, and the length of its main channel is 15 km. The watershed belongs to the II area of the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau, with elevations ranging from 1309 to 1689 m above sea level. Over the long term, water and wind erosion has given rise to a hilly land fragmentation, gullies, hills, and gully landforms. It has a continental monsoon with four distinct seasons, namely, spring (March–May), summer (June–August), autumn (September–November), and winter (December–February). The annual average precipitation in the area is 483.4 mm, and precipitation in the flood season (June–September) constitutes 79.3% of the area’s total annual precipitation. The average annual temperature, evaporation capacity, solar radiation, and frost-free period are 7.8 °C, 891.23 mm, 117.24 kCal/cm2 and, 138 days, respectively.
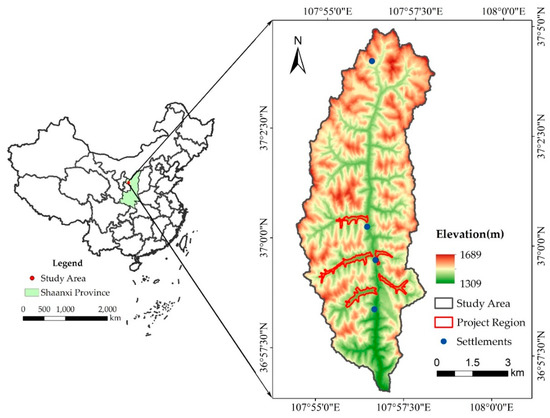
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and project region.
2.2. Project Introduction
The Gully Land Consolidation Project, located in the middle reaches of the BaoChengGou Watershed, was mainly funded by the central government and implemented by the local government. The project in the BaoChengGou watershed began in November 2014 and ended in June 2015. It consisted mainly of five sections, covering a total area of 90.18 ha.
The design of the project makes full use of the topography and geomorphology of the area. Numerous engineering disciplines were integrated in this project, including dam system engineering farmland and ecological environment protection engineering, rural roads engineering, irrigation and drainage engineering, and land consolidation engineering.
A dam system is considered the most effective way of conserving soil and water, because it can filter all floods and flows [31,32,33], while carrying the natural fertilizer and abundant silt that will be accumulated in the fields and in front of the dams [34]. Besides, water may also be accumulate in front of the dams [35], ensuring that plenty of natural fertilizer will gradually fill the dam lands in front of the dam, which may increase the fertility of nearby fields. Continuous flatlands were of course formed, which makes it possible to realize agricultural mechanization in the area [36,37]. Certain positive effects have been recognized: conserving water, and increasing the area of farmland that is available (thus improving food security and reducing disaster).
2.3. Data Sources
Land use data: Land use is a major factor influencing the ecosystem, and the accuracy of land-use data will greatly affect the findings of this study. The land-use data in this paper has been acquired by interpreting high-resolution No. 1 satellite (GF-1) images with a spatial resolution of 2 m.
The GF-1 is the first satellite of China’s high spatial resolution earth observation system, and its full-color band has a spatial resolution of 2 m [38]. The GF-1 multispectral data contain 4 spectral bands including blue, green, red, and near-infrared spectra, and it has the advantages of having high temporal resolution and wide coverage [39,40]. Because of the increasing spatial resolution of remote sensor data, modern remote sensing images contain more abundant spatial information than those previously available [41]. The remote sensing image data captured by GF-1 used in this paper comes from RSCloudMart (http://www.rscloudmart.com/en).
An image taken in July 2013 provides the most up-to-date land use data available before the project began and another image taken in June 2016 shows land use after the project ended. By using an object-based remote sensing image analysis algorithm in combination with field survey data, a precise land use map of the study area is obtained [42,43]. According to China’s current land use classification scheme, this paper divides the land use of BaoChengGou into 10 categories.
DEM: The digital elevation model (DEM) is derived from Resources No. 3 satellite (ZY-3), which can be used to create high-precision DEM data simply and quickly using The Environment for Visualizing Images (ENVI)’s DEM automatic extraction module [44].
The Resources No. 3 satellite (ZY-3) is a newly launched civilian high-resolution mapping satellite, occupying a station over China. The satellite carries with 4 cameras: 1 front-view full-color TDI CCD camera with ground resolution higher than 2.2 m and 2 front-view and rear-view full-color TDI CCD cameras with ground resolution higher than 3.5 m, in addition to a forward-looking multispectral camera with a resolution higher than 5.8 m, which is able to sense four bands of blue, green, red, and near-infrared spectra. The main imaging payload of ZY-3 for stereo mapping is a three-line camera, including a forward camera, a backward camera, and a nadir camera [45]. ZY-3 can acquire stereo full-color images, multi-spectral images, and ancillary data in a long-term, continuous, and stable manner [46].
The DEM data used in this study has been extracted from the stereo pair of nadir and forward-view images, which can achieve the most accurate results [47]. This study used satellite data collected between 2 July 2013 and 18 June 2016 with resolution of DEM equal to 2.38 m. The remote-sensing image data of Resources No. 3 satellite (ZY-3) used in this paper comes from RSCloudMart (http://www.rscloudmart.com/en).
Crop yield data: Crop yield and crop planting type data used in the study area were obtained through household surveys combined with interpretation of high spatial resolution remote-sensing images.
Rainfall erosivity (R): R is the main factor causing soil erosion, which increases in direct proportion to rainstorm intensity and duration (InVEST_3.5.0_Documentation). The R is a GIS raster dataset, and it depends on the intensity and duration of rainfall in the area of interest. This study uses Wischmeier’s monthly scale calculation Equation (1) [48,49] using the inverse distance weight interpolation method, based on meteorological data such as rainfall
in which R is the rainfall erosivity factor; pi is average monthly rainfall; and p is annual rainfall. The rainfall data required to calculate p is taken from the National Meteorological Information Center (http://data.cma.cn/).
Soil erodibility (K): K is a measure of the susceptibility of soil particles to detachment and transport by rainfall and runoff [50]. This study uses the calculation method proposed by Williams [51,52]. According to Equation (2), soil type and soil texture data were used to calculate the K factor for the study area.
in which SAN, SIL, and CLA are sand fraction (%), silt fraction (%), and clay fraction (%), respectively. C is organic matter content in soil (%), and SN1 is equal to 1-SAN/100. The soil texture and soil organic matter in the formula are derived from the second national soil survey data and literature review.
Biophysical table: The biophysical table includes a Crop Management Factor (C) and Conservation Practice Factor (P), in which C reflects the extent to which the soil is protected by different types of vegetation cover. The latter is greatly affected by human activities, so different land use types have different C values. When the local surface is completely exposed, the C value is 1, and when the local surface is well protected, C = 0.001. C is calculated using Cai Chongfa’s C-factor research method [53,54]. P is the ratio of soil loss after taking measures to soil loss when no measures are taken [55]. When no soil conservation measures are taken in an area P is 1, and the minimum possible value of P is 0.01. The P value is obtained by combining the local soil and water conservation bulletin and land use types. In this study, previous research results and the status of local land use types are combined to determine the Crop Management Factor (C) and Conservation Practice Factor (P) [56,57].
2.4. Sediment Delivery Model
The InVEST model is a quantitative assessment of ecosystem services, which is made using land-use data. Beyond expressing the status of ecosystem services spatially, it can also be combined with scenario simulation software to evaluate the value of various ecosystem services in a future scenario. The InVEST model is simple and easy to operate, and yields comprehensive results. The InVEST model can flexibly adjust some parameters according to the actual situation of the study area, so it is suited to the assessment of ecosystem services in different areas. In addition, the final evaluation result of the model is expressed spatially in the form of a map, which can be compared with time and space analysis [58,59,60]. Researchers can choose specific-use modules, input corresponding data and parameters, and carry out multi-service and multi-target evaluation according to their own needs and the actual situation of the research area. The InVEST model is helpful to understand the spatial-temporal distribution and changes of ecosystem services in a specific region, and has important guiding significance for formulating relevant management policies [61,62].
The Sediment Delivery Model is a module of the InVEST model, which is able to calculate the actual soil erosion for each grid. Soil erosion in the study area is mainly determined by rainfall intensity, soil properties, topography, and vegetation. Change in land-use types and land-management practices may significantly alter the amount of sediment produced in a given area [63,64,65,66].
Soil erosion is calculated based on the universal soil loss equation (USLE), in which soil loss is related to vegetation cover, current land use, and soil conservation management. The information on land use patterns, rainfall, soil characteristics, and topography was prepared to estimate soil erosion on grid level i as follows:
in which R is the rainfall erosivity (MJ·mm (ha·h−1), K is the soil erodibility (ton·ha·h (MJ·ha·mm)−1), LS is the slope length–gradient factor, C is the cover-management factor, and P is the support practice factor [64].
The model-driven data includes land-use data, rainfall erosivity factor R, soil erodibility factor K, topographic factor LS, vegetation cover and management factor C, and soil conservation measure factor P. Its results are exported in the form of maps, which make the spatial distribution of soil erosion and soil conservation and their changes easy to read.
3. Results
3.1. Land Cover Change
Land cover types of the study area is mainly affected by topography, and climate characteristics such as rainfall and temperature [67,68]. Land cover types of the study watershed include grassland (43%), forestland (35%), cultivated land (16%), garden plots (4.6%), and built-up land (1.4%). An analysis of the land-cover types of the study area yields the following conclusions.
The vegetation in the project region is of the sparse forest shrub grass vegetation type, characterized by sparse forestland, shrub forestland, and natural grassland. Sparse forestland has been degraded by natural secondary forest; it is shrub-dominated and has few trees. It comprises mainly poplars and locusts planted artificially in recent years and distributed in blocks. Shrub forestland is mainly distributed in the valley and mountain ridges, and is the main achievement of returning farmland to forests, being populated by species such as Amorpha and sea buckthorn. The natural grassland within the project region is mainly distributed in the channels on both sides of gullies, on slopes of gradient greater than 25 degrees, and within channels abandoned by local people.
The main type of cultivated land in the study area is slope cropland. The cultivated land-use type indicates land used to cultivate drought-tolerant crops, including corn, buckwheat, millet, and sunflower, of which corn constitutes the largest proportion. Cultivated land is mainly distributed on gentle slopes and terraces on both sides of the trench. A classified land-use map and the percentage of the total area under all 10 land-use classes before and after consolidation are presented in Figure 2.
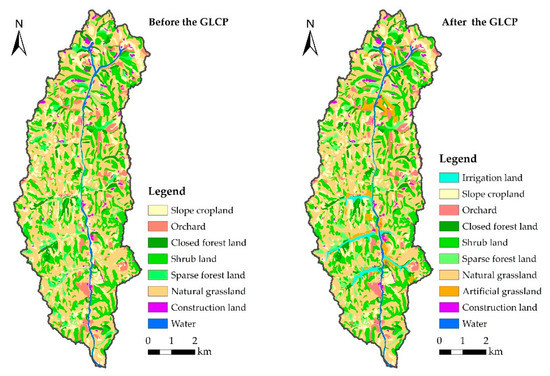
Figure 2.
Land cover type before and after GLCP (2013–2016).
As shown in Table 1, new cultivated land within the project region has mainly come from grassland and forestland. Overall, cultivated land in the project region directly increased by 27.15 ha after the implementation of the project. Between 2013 and 2016, grassland was converted into cultivated land, resulting in an overall decrease of 30.7 ha. Forestland areas also decreased from 30.58% to 11.89%, representing an area of 16.86 ha with in the project region. At the same time, some of the new cultivated land was converted into artificial forest, artificial grassland, rural roads, and other soil and water conservation measures. The total area thus converted is about 25.46 ha. In general, almost all the lost forestland and grassland was converted to cultivated land; the reduced land was mainly converted into new cultivated land and the corresponding protective land, which increased by 52.61 ha. Therefore, including the original sloping land, the total area of consolidated land is 54 ha (7.35% in being cropland).

Table 1.
Temporal changes of land use in the project region (Unit: ha).
3.2. Estimating Soil Erosion by GLCP
The marked difference in spatial distribution of soil erosion is shown in Figure 3. In the watershed, soil erosion remains high in spite of the evident efficacy of the GFG [14,69], largely owing to the extensive degree of landform change within the area, the concentration of rainfall, and the high erodibility of loess. Soil erosion varies greatly between the bottom of the gully and the top of the slope (from the minimum of 5 ton/ha to the maximum of 382 ton/ha). Rainfall occurs intensively in the summer; therefore, sediment retention also decreases in this season and is directly correlated with precipitation in the summer. The characteristic soil composition of the Loess Plateau renders the loess vulnerable to rainfall.
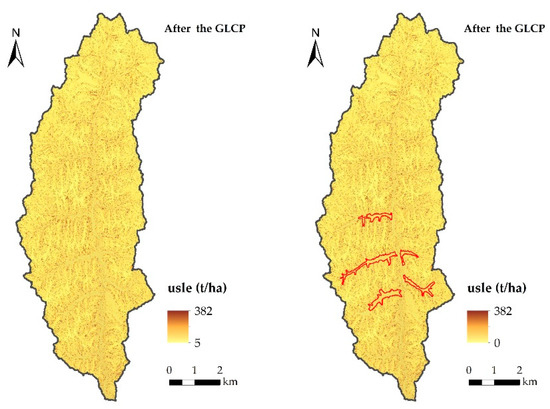
Figure 3.
Soil erosion in the study area before and after GLCP (2013, 2016).
Estimation of soil erosion before and after consolidation shows that the annual differences in soil erosion were very small, but the average annual soil erosion in the project region varied greatly. The average soil erosion of the entire watershed decreased slightly from 87 ton/ha in 2013 to 82 ton/ha in 2016, indicating that the GLCP had not exerted impact on sediment erosion in the whole watershed.
Changes in sediment erosion were analyzed at the regional scale throughout the BaoChengGou Watershed. Following this regional analysis, we then analyzed and compared sediment erosion in the project region in order to determine how the GLCP has affected sediment erosion. As shown in Figure 3, soil erosion of the project region decreased from 59 ton/ha in 2013 to 48 ton/ha in 2016; this marked decline indicates that the GLCP has significantly improved water and soil conservation ability. In order to better evaluate the effects of soil and water conservation, we categorize the observed sediment erosion (0–415 ton/ha/year) into six grades, including slight (0–10 ton/ha/year), mild (10–25), moderate (25–50), intense (50–80), extremely intense (80–150), and severe (>150). This classification is based on the Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion established by The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China [70].
Most of the area studied is classified as being subject to slight erosion is first, before the GLCP, accounting for 67.24% of the project region, and even increasing by up to 86.05%, retaining its position after the GLCP. The areas of mild, moderate, and severe erosion were characterized by reduced erosion, while erosion increased in areas of intense and extremely intense erosion. The spatial variation of sediment erosion intensity is presented in Figure 4. The slight erosion area expands dramatically in the project region. Another obvious change is the emergence of certain linear erosion zones, due to the excavation of slope forming new, steeper, slopes. It is obvious that the expansion of the slight erosion area was accompanied by a decrease in slope cropland and a resultant increase in new level land. Correspondingly, liner erosion emerged mainly in slop-excavated regions, which suffered intense, extremely intense, and even severe erosion.
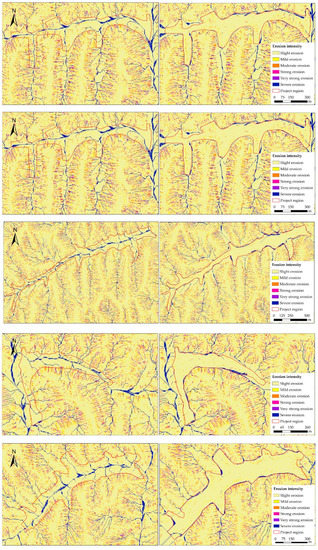
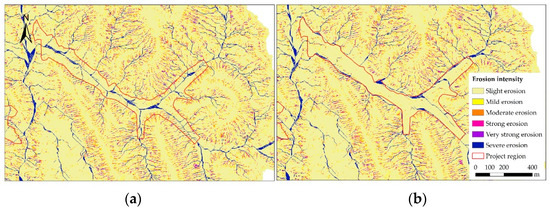
Figure 4.
Soil erosion intensity in the project region before and after GLCP (2013, 2016). (a) Before the GLCP and (b) after the GLCP.
3.3. Estimating Crop Production by GLCP
The marked difference in spatial distribution of crop production throughout the Watershed is shown in Figure 5. In the watershed, cropland was mainly distributed in areas of gentle slope (<25°); these cropland regions were of low quality because of their scattered fields, low soil fertility, and insufficient rainfall. There is almost no continuous smooth cropland, mainly due to the undulating topography of the area. Serious soil erosion and unreasonable farming management result in low soil fertility, exacerbated by low annual rainfall and inadequate irrigation, which further limit crop production in the study area.
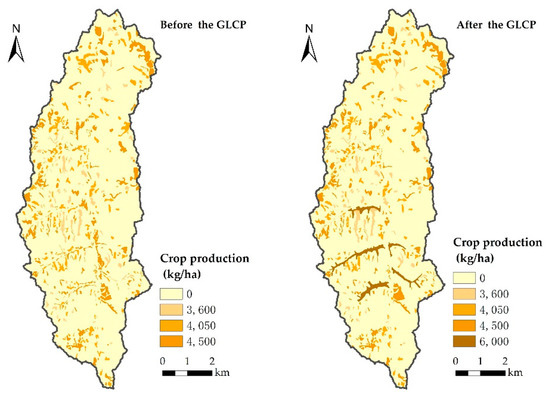
Figure 5.
Crop yield in study area before and after GLCP (2013, 2016).
Estimation of crop production before and after consolidation showed that the annual differences in crop yield were very large; in particular, the crop yield in the project region increased significantly. Table 2 shows the crop yield change in the study area. The overall crop production of the entire watershed increased from 28.7 × 105 kg before consolidation to 32.1 × 105 kg after the GLCP, an increase of 10.9%, which indicated that the GLCP had significantly increased crop yields. As indicated in the table, consolidated land had been increased by 54 ha over the course of the project. Meanwhile, the crop production capacity of the project region had increased from 4500 kg/ha to 6600 kg/ha.

Table 2.
Crop yield change in the study area before and after the GLCP.
These results indicate that the effect of the GLCP on grain productive capacity has been substantial, resulting in an increase in unit yield of approximately 46.7%. In short, it has been found that the GLCP has not only significantly increased the area under cultivation but also increased the unit yield of cropland.
3.4. Estimating Comprehensive Measure System by GLCP
Due to the special landform and vegetation characteristics of the Loess Plateau, the GLCP of the BaoChengGou watershed is quite unlike a traditional land consolidation project. During the Gully Land Consolidation Project, managers implemented comprehensive measures adapted to this special situation (Figure 6).
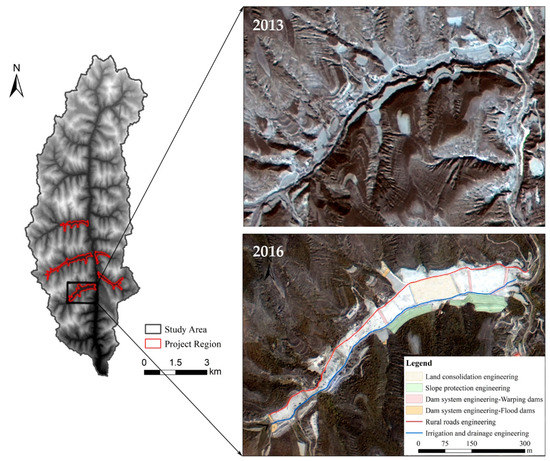
Figure 6.
Images (GF-1) of comprehensive measure system by GLCP in one of the project region (2013, 2016).
Dam system engineering, mainly including the construction and repair of large and medium-sized flood dams and warping dams, determined the possibility, feasibility, and reliability of the GLCP. The dam system of the GLCP could ensure that each dam will remains stable in a given rainstorm, and could also ensure that the growth of crops is not affected by flooding. Most importantly, the vast majority of the flood and sediment present in the area can be intercepted in the dam, so that the water and sand resources in the gully valley can be fully utilized.
Land consolidation engineering, also called land levelling engineering, refers to the use of digging machinery to excavate soil from the slope on both sides of gullies and fill them with excavated soil so as to increase the area of effective cultivated land available. The project adopted slope consolidation measures and ecological greening measures to ensure the stability of the excavated slopes.
Irrigation and drainage engineering, the establishment of various types of reservoirs and rain collecting cellars, could not only stop surface runoff and dissipate floods and flood pressure to a certain extent but also make full use of the soil flow of the loess layer and the channel water, develop water- saving irrigation, and play the dual role of stagnant water and water storage and increasing irrigation. Appropriate drainage channels were built in the farmland beside the dam to eliminate erosion and cutting of the dam and cultivated land.
Rural road engineering could be conducive to agricultural mechanization and facilitate transportation of agricultural products, thus greatly reducing farming costs and improving farming efficiency.
Farmland and ecological environment protection engineering work done in the GLCP involved establishing windbreak forests and taking ecological restoration measures to achieve sustainable development of farming and enhance the ability of the project region to withstand natural disasters. The project adopted the comprehensive plant protection measures including plant protection at the source of eroded gully, excavated slope, and dam slope ridge, in order to ensure the ecological safety of project area.
4. Discussion
Within the context of this research, sustainability is defined as the ability of land to provide a relatively consistent supply of ecological services and human well-being in the long term, without degrading the environment within which these services are provided [71]. The comprehensive measures of Nature-based solutions aim to enhance soil function and reduce connectivity of flows. Nature-based solutions can enhance the soil health and soil functions through which local eco-system services will be maintained or restored. Making the flows less connected, facilitating less rainfall to be transformed into runoff and therefore reducing flood risk, increasing soil moisture, and reducing droughts and soil erosion, we can achieve sustainability [72,73]. Enhanced ecosystem services contribute directly to the achievement of the United Nations sustainable development goals [74]. In conclusion, the Gully Land Consolidation Project demonstrates a method of balancing agricultural development and environment protection. Due to its integrated implementation, the GLCP tends to bring about varied favorable effects.
4.1. The Impact of the GLCP on the Ecological Environment
The uniform tendency towards slightly increased soil retention before and after consolidation indicates that the GLCP did not increase soil erosion intensity in the watershed. A relatively low intensity of soil erosion was observed in certain parts of the region, mostly in those areas characterized by relatively high levels of vegetation, such as sparse forestland and shrub forestland. High intensity of soil erosion was associated with cropland, especially unmanaged slope areas. An empirical investigation of soil erosion before and after the GLCP is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Comparative effects of ecological sustainability before and after the GLCP (a) Gully with intense soil erosion before the GLCP; (b) gully with slight soil erosion after the GLCP.
In the project region, total soil erosion was reduced by 18.6%, mainly due to topographic changes and soil and water conservation measures taken after consolidation. The area of slight and mild erosion intensity expanded by 18.18%, mainly at the expense of the area subject to intense and extremely intense erosion. However, the area of land subject to severe erosion has also increased, mainly on the excavated slopes on both sides of the gully due to a certain degree of slope stability degradation caused by extensive slope excavations, although fairly comprehensive slope protection measures have been taken. In general, the GLCP has improved the quality of the ecological environment, especially in terms of soil and water conversation in the watershed.
On the other hand, the GLCP has not only reduced soil erosion but also achieved the objectives of the GFGP: It has greatly increased the area of vegetation coverage while significantly reducing the area of slope farmland [18,27]. Although the local government has given some financial subsidies to farmers, it has still found itself unable to solve the local poverty problem. In the late stage of the GFGP, signs of lands unsuitable for planting being reclaimed again gradually appeared in a few areas. The GLCP’s work has greatly eliminated the need for ecologically fragile slopes by creating additional flat and productive farmland in the valleys. Therefore, the GLCP has also played a positive role in the sustainable development of ecology by ensuring the effectiveness of the GFGP.
4.2. The Impact of the GLCP on Agricultural Developemnt
A large quantity of high-yield flat farmland has been created to improve crop production and the efficiency of farming. The findings of this research show that there will be significant benefits arising from the development of areas previously unsuited to agriculture and degraded lands, and, if such areas are managed appropriately, a chance to transform a problem into an opportunity will appear. [75,76]. The undertaking of the GLCP is intended to provide as much land as farmers farmed before removing land from agricultural management by the GFGP. Additionally, relatively perfect conditions such as expansive levelling land and efficient irrigation and drainage facilities would promote agriculture and other related industries on a greater scale, raising the income of peasants through the gradual development of efficient agriculture.
Most importantly, the productivity of new cultivated land is much greater that the sloping farmland it has replaced. The continuous flat farmland created by the project has created a powerful condition for farmland mechanization and agricultural modernization. In particular, within the context of the current Chinese government’s strategy of precise poverty alleviation, the GLCP has greatly solved the problem of local poverty by improving the productivity of land and reducing the cost of production. In this way, agricultural sustainability could be realized while achieving the win-win benefits of ecological restoration and efficient use of land resources.
4.3. Evaluation of the Comprehensive Measures System
Overall, this project has formed a gully control system by establishing a dam system combined with warping dam and gully head protection, forming a plant protection system for slope and farmland through the artificial planting of “arbor shrub herb”, and forming slope- and farmland-flow grooming systems through the combination of reservoirs and drains, irrigation, and drainage measures. Through a series of omni-directional measures, the project will eventually achieve the goal of “harnessing the ditches to protect the ecology, levelling the land to achieve the benefits of the people’s livelihood” (Figure 8).
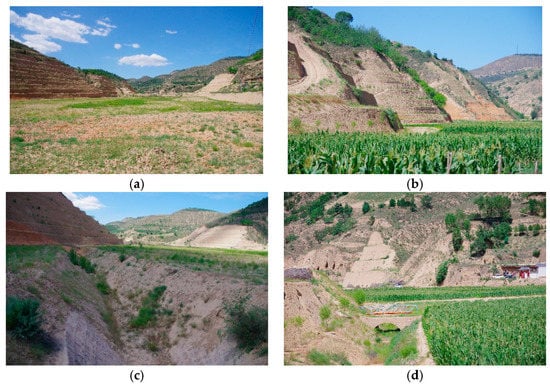
Figure 8.
Implementation effect of comprehensive measures (a) Continuous consolidated land, (b) excavated slope and protective measures, (c) drainage ditch, and (d) rural roads and plant protective measures.
Since 1978, the Chinese government has implemented 16 major sustainability programmes aimed at improving the ecological environment and sustainable development of people’s livelihood. This effort is unprecedented globally and has indeed brought great benefits to the natural environment and the people’s living environment around the country. The national land consolidation program is an important part of the 16 major sustainability programmes [77]. Since the GLCP in Yan’an was approved by the Chinese Government with an area of 33,733 ha in 2010, total investment in the project has reached to 4.83 billion Chinese Yuan.
The scope of the project is expected to be expanded to other suitable areas of the Loess Plateau in the future. It is estimated that by 2025, the Gully Land Consolidation Project may create 6.7 × 104 ha of basic farmland [78].
4.4. Methodological Limits and Future Research
In general, data of higher spatial resolution is more conducive to small-scale spatial variation studies [79]. In our research, we obtained land use and DEM data before and after consolidation, with spatial resolutions of 2 m and 4 m, respectively, through the high-resolution No. 1 (GF-1) satellite and the resources No. 3 (ZY-3) satellite. In future research, it is suggested to use UAV Low Altitude Surveying to acquire data of higher spatial resolution for the sake of greater accuracy [80,81].
Perhaps most importantly, our research only studied the situation before and after consolidation, and did not examine the process of consolidation itself. The process of the GLCP may cause considerable soil and water loss, due to the great surface soil disturbance it entails, to the extent of causing landslides in specific areas [28]. At the same time, it proved impossible to guarantee the incomes of local peasants during the GLCP process, which poses a great challenge to the sustainable development of the local ecology and agriculture. Therefore, the consolidation process itself could be examined in greater depth in future, affording a more comprehensive evaluation of the GLCP.
In addition, the evaluation of this study after consolidation was limited to 2 years after the end of the project. Due to the particularity of local site conditions, plant measures cannot exert their control effects in full over such a short period of time [82]. Therefore, the sustainable comprehensive impact of the project on the region could also benefit from examination over an extended period.
5. Conclusions
The Gully Land Consolidation Project is a very influential project in China, which has greatly affected the ecological sustainability and economic sustainability of the Loess Plateau.
Through high spatial resolution, remote-sensing image data, this paper analyses the effect of the GLCP on soil erosion and crop production in the BaoChengGou Watershed and evaluates its effects. The key findings of this study are summarized as follows:
Sloping cropland, sparse forestland, and natural grassland are the main land use types in the study area. After the GLCP, a large quantity of degraded sloping cropland and grassland has been converted into cultivated land. The proportion of consolidated land in the cropland increased by 7.35% and the flatness and continuity of the farmland in the project region showed clear improvement.
This study analyzed the effects of the GLCP on soil erosion using the InVEST-SD model. It is obvious that the GLCP has reduced soil erosion in the BaoChengGou Watershed, especially in that it also markedly reduced soil erosion intensity in the project region.
The effects of the GLCP on crop production have been analyzed by interpreting high-resolution images, combined with field research and questionnaires. The GLCP has improved crop production by 9.7% and has done much to ensure food security, promote precision poverty alleviation, and achieve sustainable development.
This study analyzed the practical effect of the GLCP in the BaoChengGou Watershed. As a result, an integrated control system combining engineering measures with plant measures has been found to ensure ecological safety and increase crop production. The GLCP can make important contributions to promoting ecological and agricultural sustainability and achieving harmony in human, land, and natural relations.
Author Contributions
X.H. (Xiaoliang Han) and X.W. designed the paper. X.H. (Xiaoliang Han) collected the data and wrote the paper. P.L. contributed to the InVEST simulation data. Y.S., S.Y., and M.W. reviewed and edited the paper. S.Z. and X.H. (Xiaona Han) revised the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Ministry of Land and Resources Cooperation Project (200-661704104) and National Key Research and Development Project (2016YFC0502504).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Bardgett, R.D. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broeck, G.; Maertens, M. Horticultural exports and food security in developing countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2016, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Mertz, O.; Erb, K.H.; Haberl, H.; Wu, W. Land system change and food security: Towards multi-scale land system solutions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mooney, H.; Hull, V.; Davis, S.J.; Gaskell, J.; Hertel, T.; Lubchenco, J.; Seto, K.C.; Gleick, P.; Kremen, C.; et al. Systems integration for global sustainability. Science 2015, 347, 1258832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.M.A.; Lara, H.; Brian, K. Ecosystem Services in Conservation Planning: Targeted Benefits vs. Co-Benefits or Costs? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; Defries, R.S.; Diaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M.; et al. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, H.B.J.; Groot, R.S.D. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: A Framework for Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pašakarnis, G.; Maliene, V. Towards sustainable rural development in Central and Eastern Europe: Applying land consolidation. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, Z.; Shagaida, N. Land policies and agricultural land markets in Russia. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, A. The methods to consolidate scattered tenanted lots into large rice paddy lots by the land consolidation projects in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2005, 3, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, G.S.; Thapa, G.B. Impacts and causes of land fragmentation, and lessons learned from land consolidation in South Asia. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, F. Land Consolidation: An Approach for Sustainable Development in Rural China. Ambio 2010, 40, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, B.; Lu, Y. Soil and Water Conservation on the Loess Plateau in China: Review and Perspective. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 3547–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lü, Y.; He, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Hoag, D.; Keske, C.M.H.; Lu, C. Sustainable value of degraded soils in China’s Loess Plateau: An updated approach. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 97, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Shao, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Water use efficiency and sustainability of different long-term crop rotation systems in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 72, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.I.; Childress, W.M.; Li, Y.; Spence, R.D.; Ren, J. An integrated simulation model for a semi-arid agroecosystem in the Loess Plateau of northwestern China. Agric. Syst. 2007, 52, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatio-temporal patterns of cropland conversion in response to the “Grain for Green Project” in China’s loess hilly region of Yanchuan County. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5642–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Environment: China’s land creation project stands firm. Nature 2014, 511, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Rui, L.I. Effects of the grain-for-green program on soil erosion in China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2012, 27, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C. The Grain for Green Project induced land cover change in the Loess Plateau: A case study with Ansai County, Shanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gong, P. Forest Cover Dynamics from Landsat Time-Series Data over Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau during the Grain for Green Project; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2016; pp. 4101–4118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; He, C.; Chen, L.; Cao, S. Improving food security in China by taking advantage of marginal and degraded lands. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Feldman, M.W.; Daily, G.C. Does household composition matter? The impact of the Grain for Green Program on rural livelihoods in China. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 75, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.; King, B. Evaluating China’s Slope Land Conversion Program as sustainable management in Tianquan and Wuqi Counties. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.X.; Xu, C.G.; Li, C.; Wang, X.Q. Attitudes of farmers in China’s northern Shaanxi Province towards the land-use changes required under the Grain for Green Project, and implications for the project’s success. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Q.; Li, Y. The Transformation of Agricultural Development towards a Sustainable Future from an Evolutionary View on the Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study of Fuxian County. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3644–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. The creation of farmland by gully filling on the Loess Plateau: A double-edged sword. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Engineering philosophy and design scheme of gully land consolidation in Loess Plateau. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y. Filling gullies to create farmland on the loess plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7589–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, V.M.; Mosch, W.M.; García, C.C.; Barberá, G.G.; Cano, J.A.N.; López-Bermúdez, F. Effectiveness and geomorphological impacts of check dams for soil erosion control in a semiarid Mediterranean catchment: El Cárcavo (Murcia, Spain). Catena 2007, 70, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Lü, Y.; Gao, Y. Check Dam in the Loess Plateau of China: Engineering for Environmental Services and Food Security. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10298–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-Z.; Zhang, H.-W.; Zhang, O. Development of check-dam systems in gullies on the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Díaz, A.; Marín-Sanleandro, P.; Ortiz-Silla, R. Loss of soil fertility estimated from sediment trapped in check dams. South-eastern Spain. Catena 2012, 99, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Jin, Z. Gully land consolidation project in Yan’an is inheritance and development of wrap land dam project on the Loess Plateau. J. Earth Environ. 2015, 6, 261–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoffi, P.; Gardin, L. Effectiveness of the GAEC standard of cross compliance retain terraces on soil erosion control. Ital. J. Agron. 2011, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukamachi, K. Sustainability of terraced paddy fields in traditional satoyama landscapes of Japan. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Huang, J.; Feng, L. Improved capabilities of the Chinese high-resolution remote sensing satellite GF-1 for monitoring suspended particulate matter (SPM) in inland waters: Radiometric and spatial considerations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Campbell, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yin, S.; Xing, Z.; Jin, X. Comparison of object-based and pixel-based Random Forest algorithm for wetland vegetation mapping using high spatial resolution GF-1 and SAR data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Baret, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for Chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Tian, X. Vegetation change detection research of Dunhuang city based on GF-1 data. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.; Gutiérrez, P.; Hervás-Martínez, C.; Six, J.; Plant, R.; López-Granados, F. Object-Based Image Classification of Summer Crops with Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5019–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhou, Q.-B.; Wu, W.-B.; Hu, Q.; Lu, M.; Liu, S.-B. Mapping regional cropping patterns by using GF-1 WFV sensor data. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Sun, G.; Ranson, K.J.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W. Extraction of ground surface elevation from ZY-3 winter stereo imagery over deciduous forested areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, S.; Pan, J.; Zhu, Q. Correction of ZY-3 image distortion caused by satellite jitter via virtual steady reimaging using attitude data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fu, X.; Dou, X.; Liu, H.; Fang, Z. Comparison and Analysis of Accuracy of Elevation Extraction Based on the Zy-3 01 and 02 Satellites Stereoscopic Images. ISPRS-Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-3, 2379–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.Y.; Huan, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, M.Y. DEM Generation and Accuracy Assessment Using ZY-3 Stereo Image Pairs. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 738–739, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, S.; Xie, Y.; Leng, G.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Spatial-temporal changes of rainfall erosivity in the loess plateau, China: Changing patterns, causes and implications. Catena 2018, 166, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.-Y. Spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall erosivity in the Yanhe River watershed of hilly and gully region, Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, F.; Kumar, L.; Esmaeili, A. Improvement to the prediction of the USLE K factor. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Arnold, J.G. A system of erosion—Sediment yield models. Soil Technol. 1997, 11, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.L.; Shu, A.P.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Yu, B. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.L. Effect of Vegetation Changes on Soil Erosion on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbrodt, S.; Saumer, P.; Behrens, T.; Seeber, C.; Scholten, T. Assessing the USLE crop and management factor C for soil erosion modeling in a large mountainous watershed in Central China. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 21, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Chowdary, V.M.; Mal, B.C. Identification of critical erosion prone areas in the small agricultural watershed using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 21, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.X.; Xie, J.Q.; Shi, X.; Gen-Batu, G.E.; Dong, Z.; Cheng, Z.Q. Different Types of Vegetation Cover and Water Conservation Benefits. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 3, 12–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, Q.K.; Xie, H.X.; Wang, C.M.; Guo, W.L. GIS and CSLE Based Quantitative Assessment of Soil Erosion in Shaanxi, China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 23, 61–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, S.; Garnero, G.; Barbieri, C.; Giaimo, C. The Integration of Ecosystem Services in Planning: An Evaluation of the Nutrient Retention Model Using InVEST Software. Land 2017, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Nehren, U.; Rahman, S.; Meyer, M.; Rimal, B.; Aria Seta, G.; Baral, H. Modeling Land Use and Land Cover Changes and Their Effects on Biodiversity in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land 2018, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.; Quinn, J. Application of Anthromes to Frame Scenario Planning for Landscape-Scale Conservation Decision Making. Land 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, J.W.; May, L.; Oliver, T.H.; Hamel, P.; Sharp, R.; Bullock, J.M. National scale evaluation of the InVEST nutrient retention model in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redhead, J.W.; Stratford, C.; Sharps, K.; Jones, L.; Ziv, G.; Clarke, D.; Oliver, T.H.; Bullock, J.M. Empirical validation of the InVEST water yield ecosystem service model at a national scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, M.; Trevisani, S.; Comiti, F.; Marchi, L. Geomorphometric assessment of spatial sediment connectivity in small Alpine catchments. Geomorphology 2013, 188, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A new approach to modeling the sediment retention service (InVEST 3.0): Case study of the Cape Fear catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Vicente, M.; Poesen, J.; Navas, A.; Gaspar, L. Predicting runoff and sediment connectivity and soil erosion by water for different land use scenarios in the Spanish Pre-Pyrenees. Catena 2013, 102, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sougnez, N.; van Wesemael, B.; Vanacker, V. Low erosion rates measured for steep, sparsely vegetated catchments in southeast Spain. Catena 2011, 84, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Z.; Gong, J.; Fu, B.; Huang, Y. The effect of land cover/vegetation on soil water dynamic in the hilly area of the loess plateau, China. Catena 2007, 70, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Zheng, Z. Land use/land cover changes and regional climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part I: Observational evidence. Clim. Chang. 2014, 129, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuo, J. Quantitative Assessment of Soil Erosion in Areas Under Grain for Green Project in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi Province Based on GIS and RS. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 220–229. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gong, E.; Yao, Z. Characteristics of Sediment Yield and Its Relation to Land Use of Laohahe Drainage Basin in Liaoning Province, P.R. China. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation, Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China, 5–7 August 2011; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, T.; Jing, L.; Shi, J.L.; Han, X.L.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y. Benefit Analysis and Evaluation of the Key Land Consolidation and Readjustment Projects. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Nunes, J.; Novara, A.; Finger, D.; Avelar, D.; Kalantari, Z.; Cerdà, A. The superior effect of nature based solutions in land management for enhancing ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 610–611, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masselink, R.J.H.; Temme, A.J.A.M.; Díaz, R.G.; Sarasíbar, J.C.; Keesstra, S.D. Assessing hillslope-channel connectivity in an agricultural catchment using rare-earth oxide tracers and random forests models. Cuadernos De Investigación Geográfica 2017, 43, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, H.; Balian, E.; Azevedo, J.M.N.; Beumer, V.; Brodin, T.; Claudet, J.; Fady, B.; Grube, M.; Keune, H.; Lamarque, P.; et al. Nature-based solutions: New influence for environmental management and research in Europe. GAIA-Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2015, 24, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin Iii, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sietz, D.; Lüdeke, M.K.B.; Walther, C. Categorisation of typical vulnerability patterns in global drylands. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.; He, C.; Yu, D.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Du, G.; Li, Y. Transforming the Loess Plateau of China. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2016, 3, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Hall, R.J.; Coops, N.C.; Franklin, S.E. High Spatial Resolution Remotely Sensed Data for Ecosystem Characterization. BioScience 2004, 54, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, M.A.; Greenfield, R.; Tesfamichael, S. Wetland Assessment Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (uav) Photogrammetry. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B1, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ding, H.; Tang, G.; Na, J.; Huang, X.; Xue, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, F. Detection of Catchment-Scale Gully-Affected Areas Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) on the Chinese Loess Plateau. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, J. Evaluation on effect of land consolidation on habitat quality based on InVEST model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).