Using Remote Sensing to Quantify Vegetation Change and Ecological Resilience in a Semi-Arid System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Southern African Savannas and Resilience
| Indicator Measure | Definition |
|---|---|
| Elasticity | The period of restoration to a reference condition following a disturbance |
| Amplitude | Magnitude of change resulting from a disturbance |
| Malleability | Degree to which the state established after a disturbance differs from the original state |
| Damping | Pattern of oscillation in a system following disturbance |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
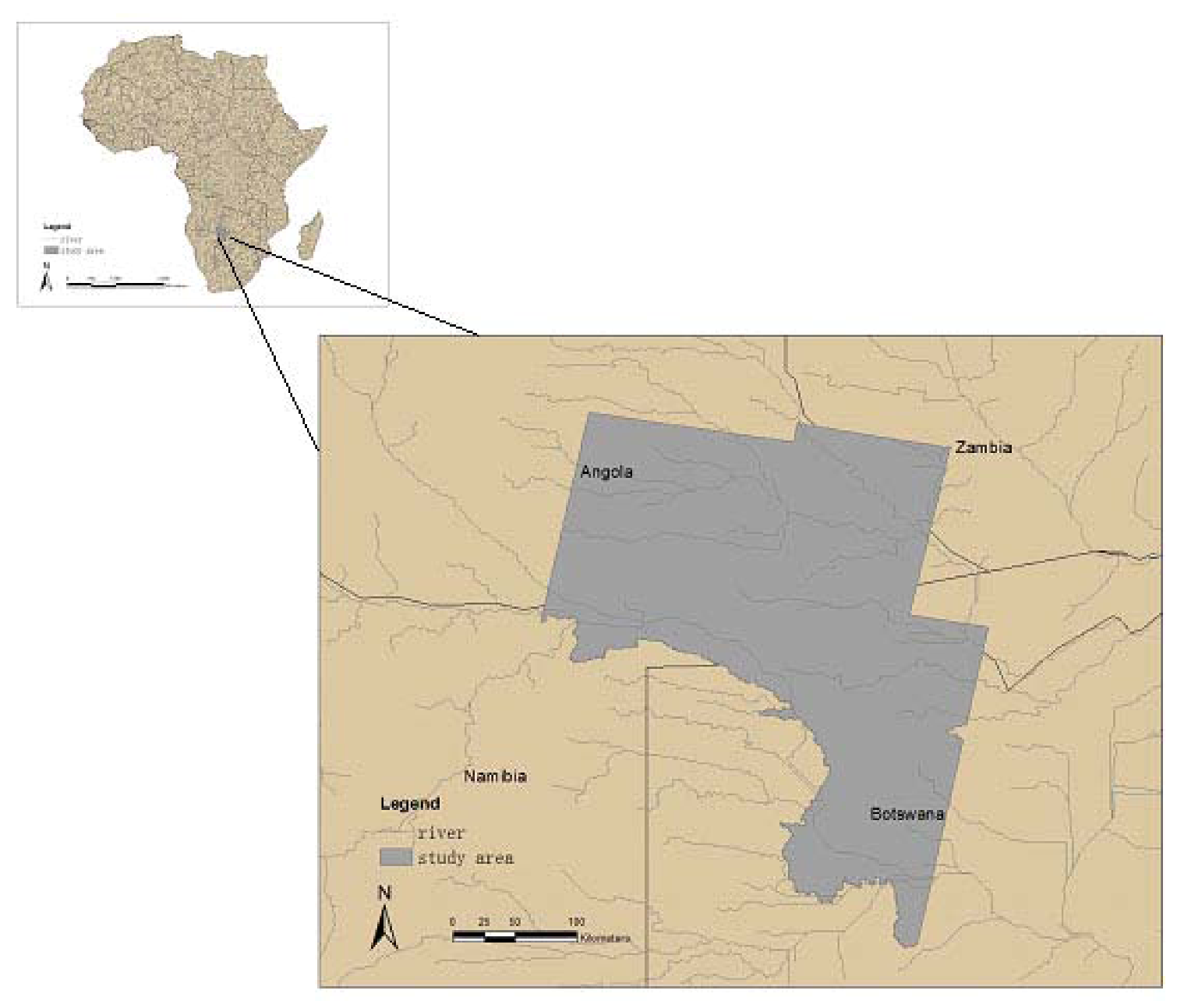
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Precipitation Data
2.2.2. Image Collection and Processing
| Image Footprint (path/row) | Image Date (mm-dd-yyyy) | Scanner | RMSE | Mosaic Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 187/73 | 06-08-1979 | Landsat MSS | 0.327 | 1970s |
| 187/74 | 05-18-1976 | Landsat MSS | 0.497 | 1970s |
| 188/72 | 06-30-1975 | Landsat MSS | 0.498 | 1970s |
| 188/73 | 06-18-1979 | Landsat MSS | 0.499 | 1970s |
| 188/74 | 06-12-1975 | Landsat MSS | 0.476 | 1970s |
| 189/72 | 05-27-1973 | Landsat MSS | 0.496 | 1970s |
| 189/73 | 05-27-1973 | Landsat MSS | 0.449 | 1970s |
| 175/72 | 06-09-1984 | Landsat TM | 0.426 | 1984 |
| 175/72 | 09-05-1990 | Landsat TM | --- | 1990 |
| 175/72 | 03-26-2009 | Landsat TM | 0.430 | 2009 |
| 175/73 | 06-09-1984 | Landsat TM | 0.389 | 1984 |
| 175/73 | 09-05-1990 | Landsat TM | --- | 1990 |
| 175/73 | 03-26-2009 | Landsat TM | 0.470 | 2009 |
| 175/74 | 06-09-1984 | Landsat TM | 0.386 | 1984 |
| 175/74 | 27-03-1992 | Landsat TM | --- | 1990 |
| 175/74 | 03-26-2009 | Landsat TM | 0.380 | 2009 |
| 176/72 | 07-02-1984 | Landsat TM | 0.362 | 1984 |
| 176/72 | 05-13-1989 | Landsat TM | --- | 1990 |
| 176/72 | 05-20-2009 | Landsat TM | 0.452 | 2009 |
| 176/73 | 07-02-1984 | Landsat TM | 0.447 | 1984 |
| 176/73 | 01-04-1991 | Landsat TM | --- | 1990 |
| 176/73 | 05-20-2009 | Landsat TM | 0.441 | 2009 |
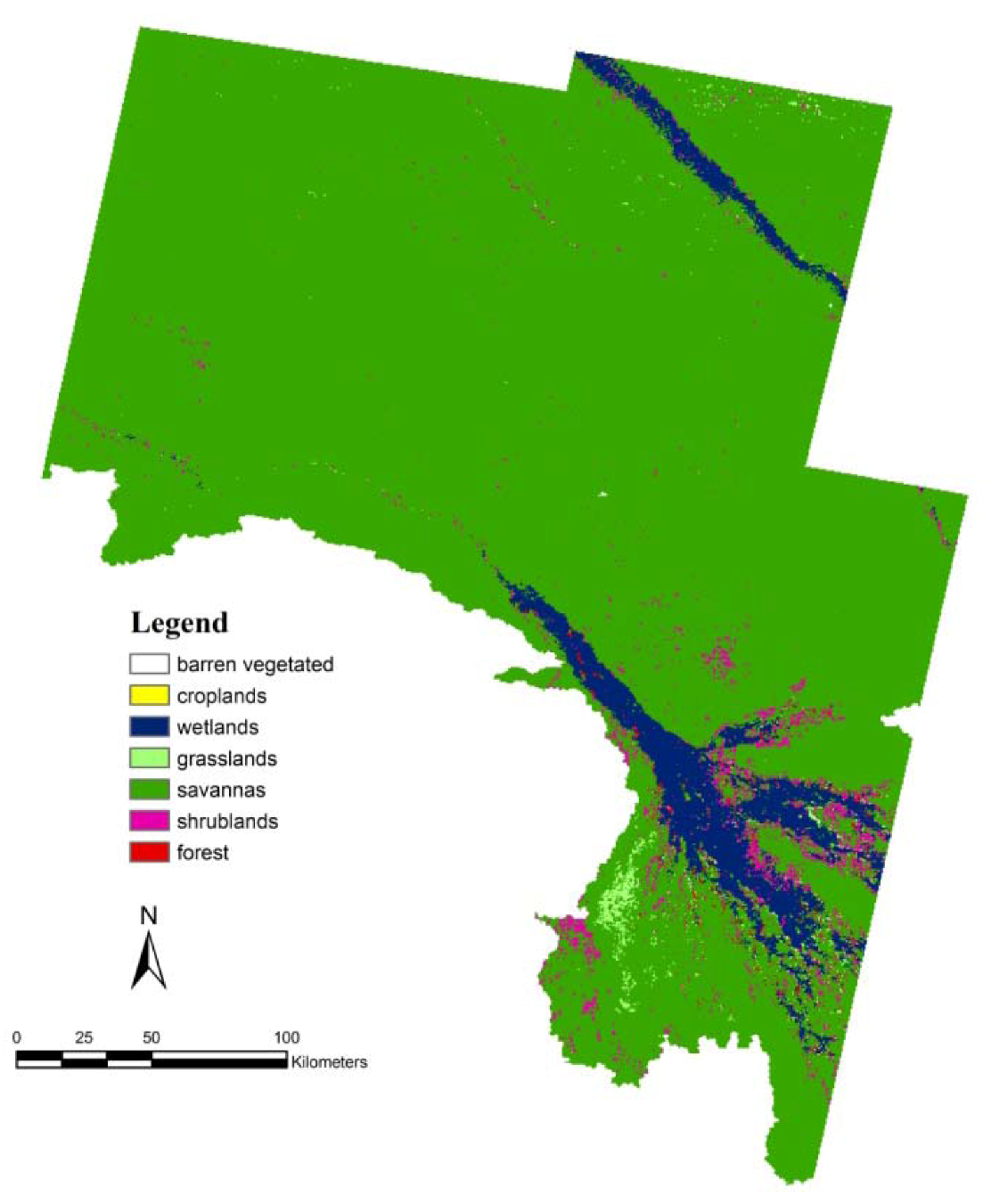
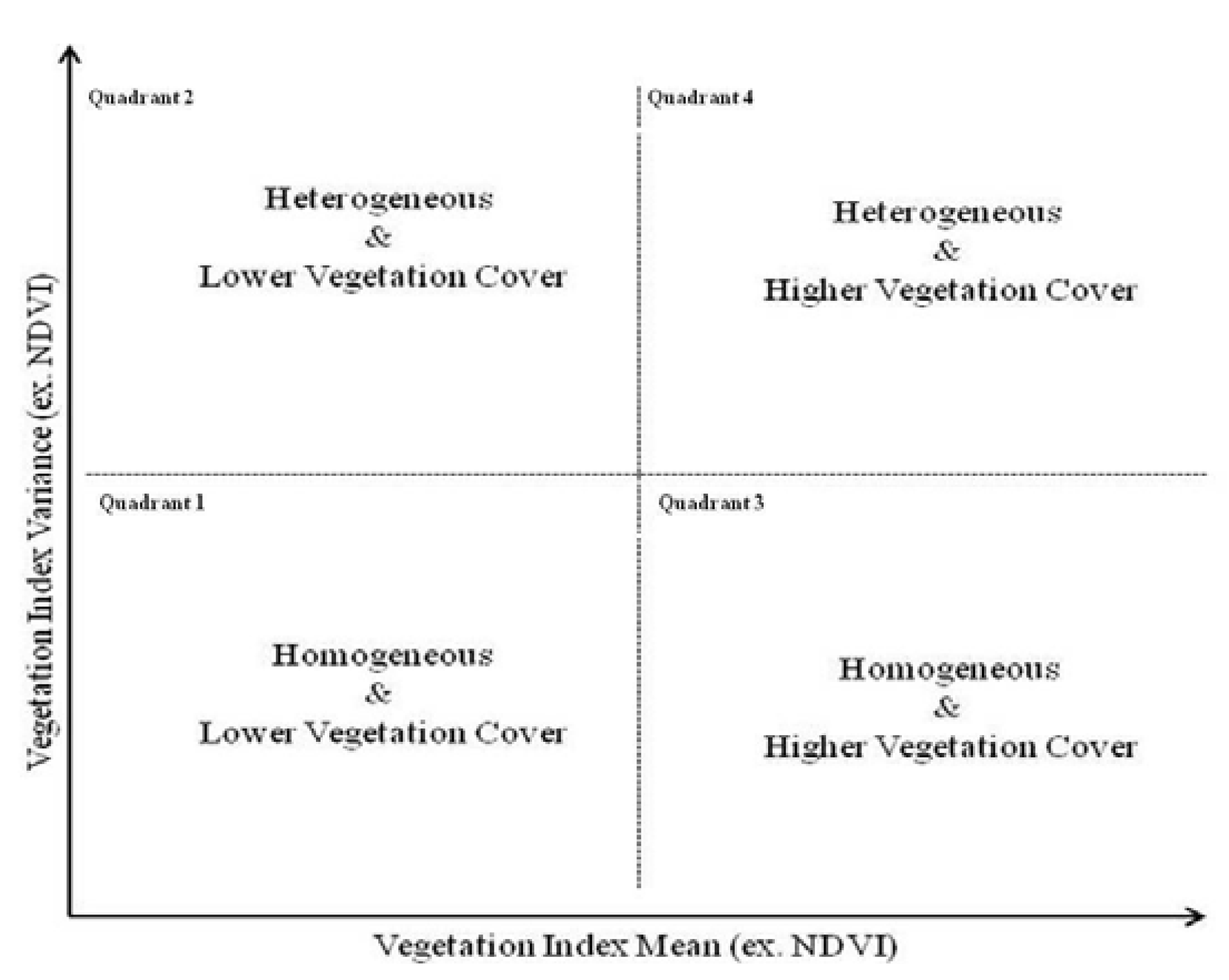
2.2.3. Mean-Variance Analysis
2.2.4. Persistence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Precipitation
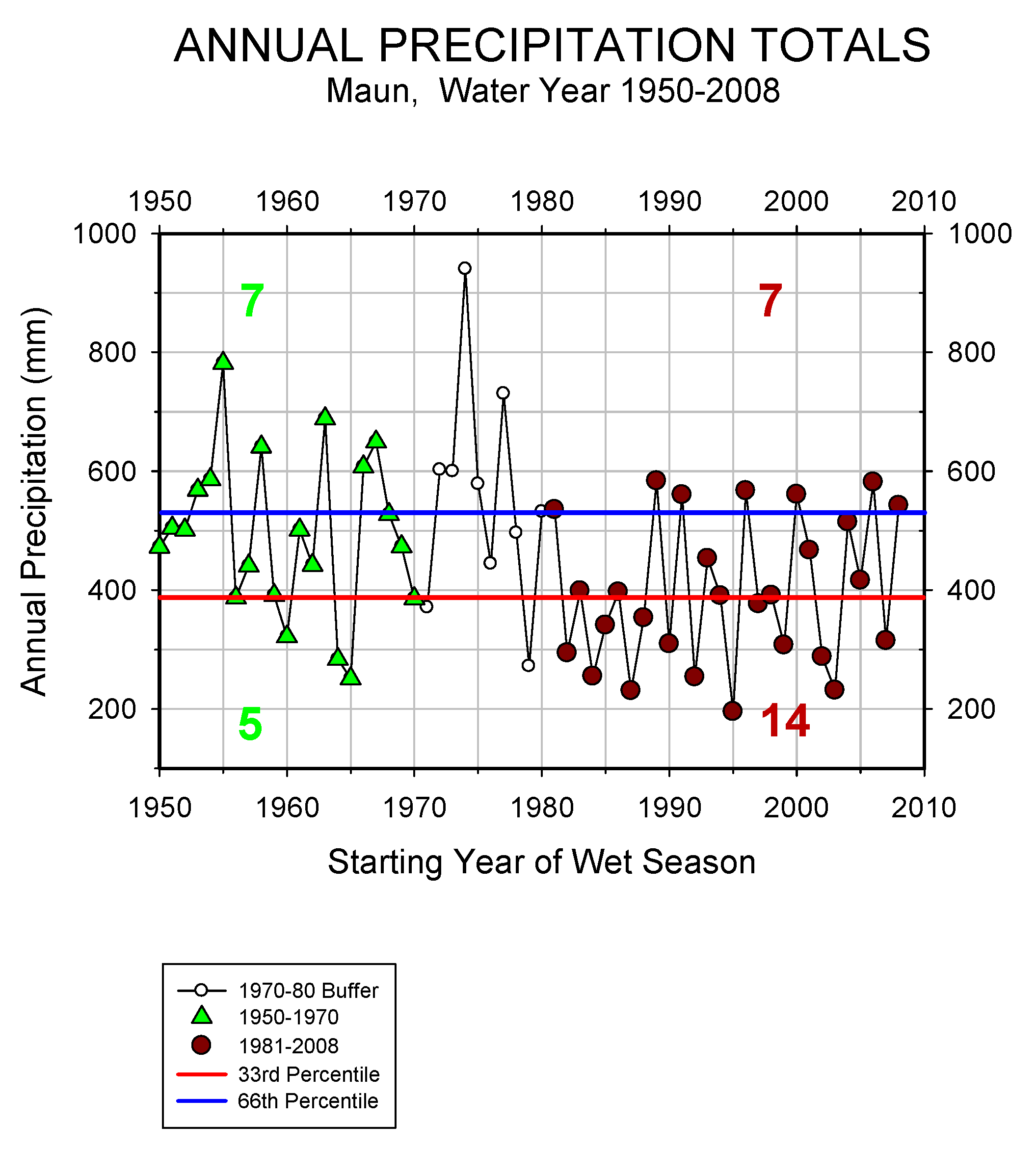
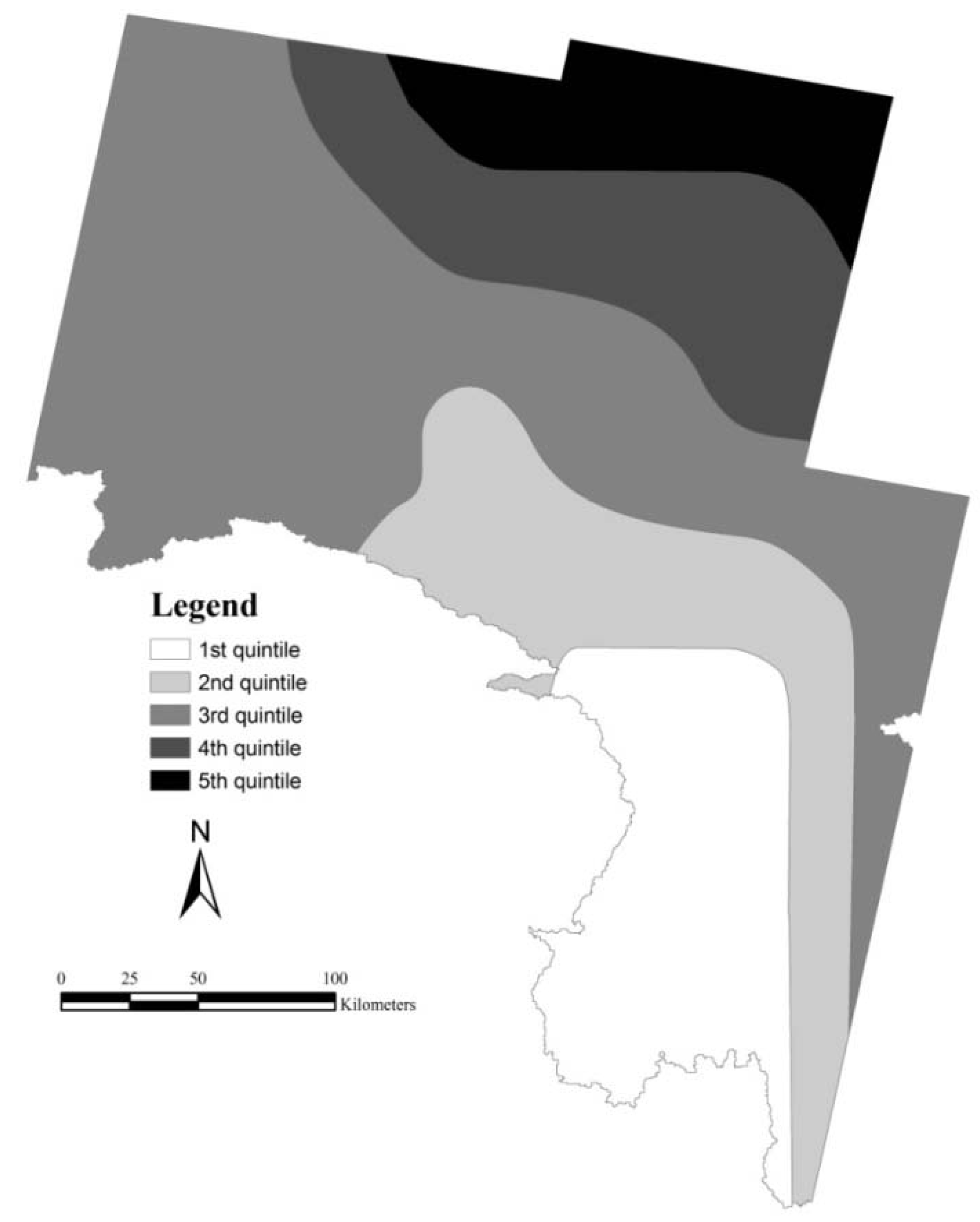
3.2. Mean-Variance Analysis
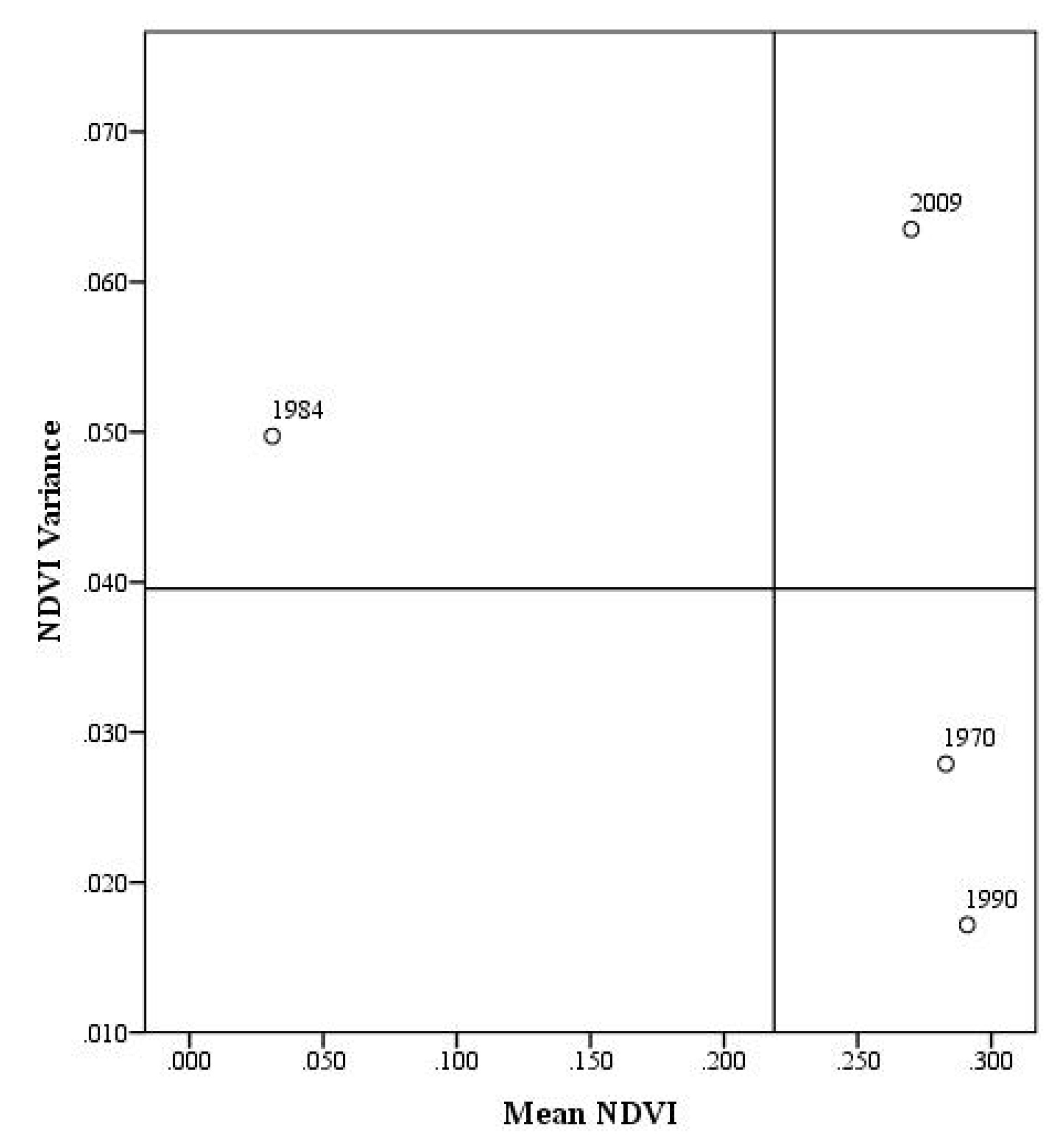
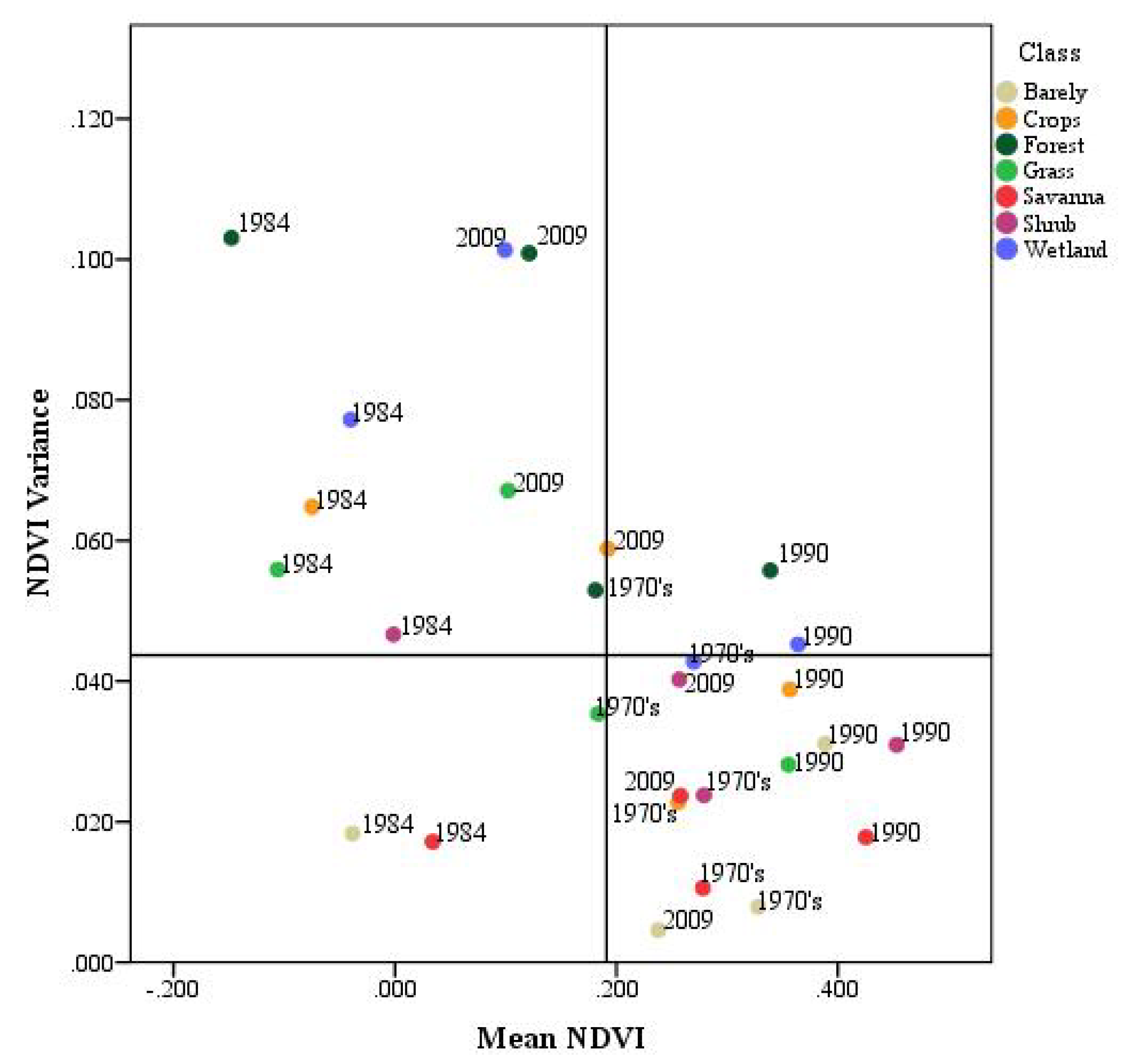
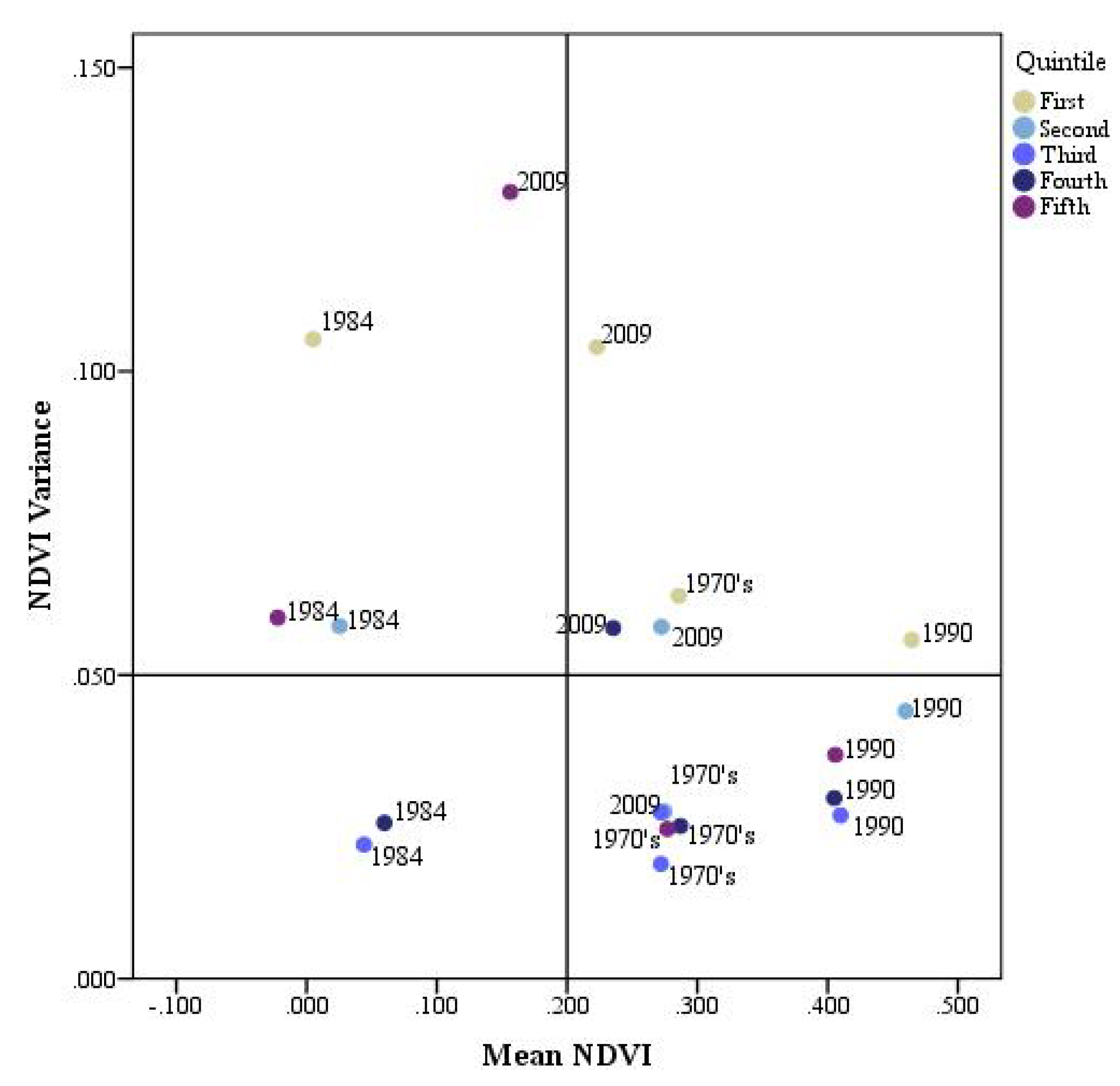
3.3. Persistence Analysis
3.4. Methodological Mean-Variance Framework for Resilience Context
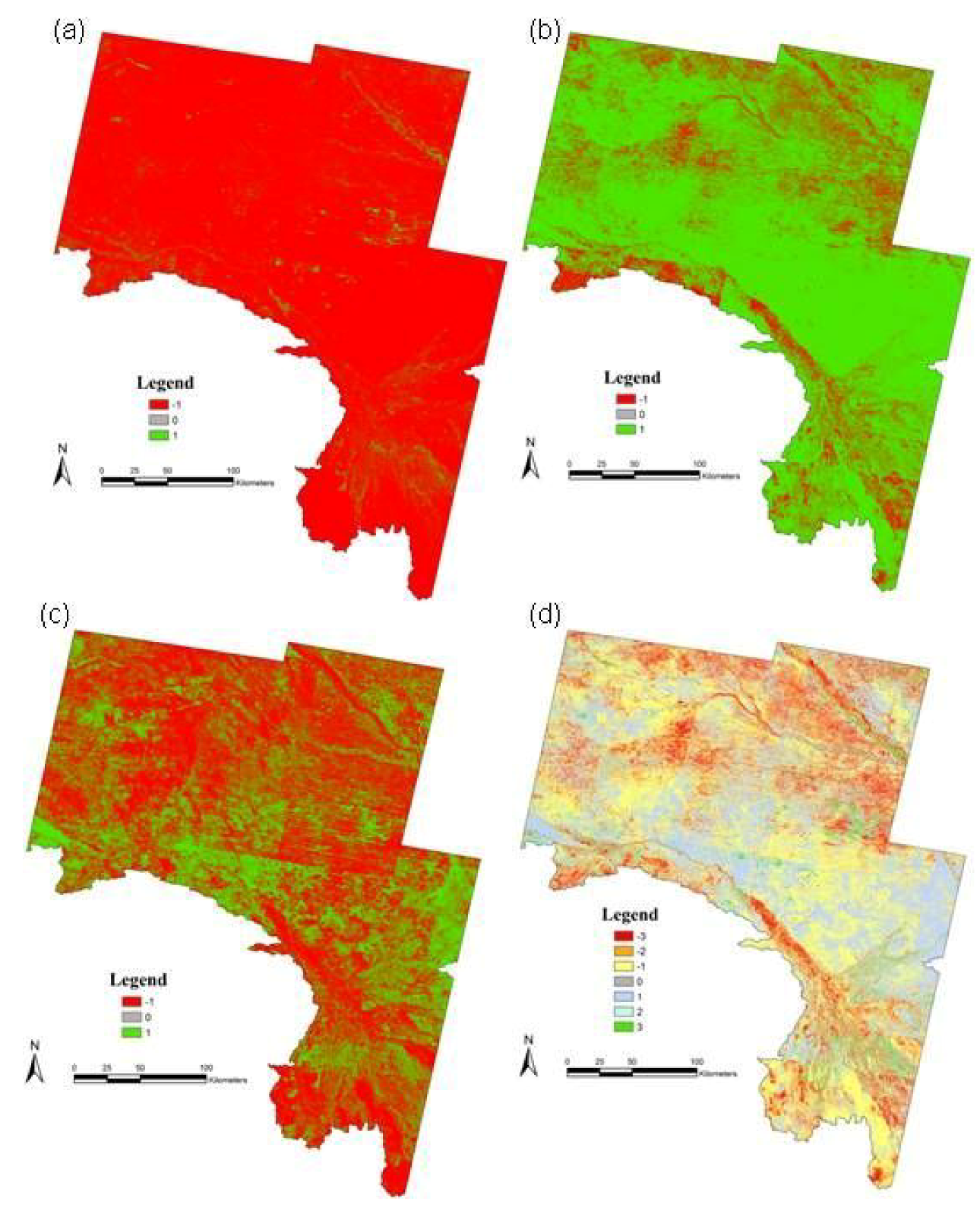
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Hill, M.J.; Hanan, N.P. Savannas: Biogeographical and Ecological Perspectives. In Ecosystem Function in Savannas: Measuring and Modeling at Landscape to Global Scales; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Scholes, R.J.; Archer, S.R. Tree-grass interactions in savanna. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Systemat. 1997, 28, 517–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.P.C.; Havstad, K.M. Nonlinear dynamics in arid and semi-arid systems: Interactions among drivers and processes across scales. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 65, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, R.J.; Walker, B.H. An African Savanna: Synthesis of the Nylsvley Study; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L., II; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernandez, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttich, C.; Herold, M.; Wegmann, M.; Cord, A.; Strohbach, B.; Schmullius, C.; Dech, S. Assessing effects of temporal compositing and varying observation periods for large-area land-cover mapping in semi-arid ecosystems: Implications for global monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2445–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Mayaux, P.; Woodcock, C.E.; Baccini, A.; Schmullius, C. Some challenges in global land cover mapping: An assessment of agreement and accuracy in existing 1 km datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2538–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Henkel, K.; Herold, M.; Churkina, G. Exploiting synergies of global land cover products for carbon cycle modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J. Land Use and Land Cover Change: Local Processes and Global Impacts; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Monitoring the magnitude of land-cover change around the southern limits of the Sahara. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2001, 67, 841–847. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaille-Jammes, S.; Fritz, H.; Murindagomo, F. Spatial patterns of the NDVI-rainfall relationship at the seasonal and interannual time scales in an African savanna. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5185–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanacker, V.; Linderman, M.; Lupo, F.; Flasse, S.; Lambin, E. Impact of short term rainfall fluctuation on interannual land cover change in sub-Saharan Africa. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2005, 14, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, Y.; Poccard, I. A statistical study of NDVI sensitivity to seasonal and interannual rainfall variations in Southern Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2907–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.O.; Prince, S.D. Rainfall and foliar dynamics in tropical southern Africa: Potential impacts of global climatic change on savanna vegetation. Clim. Change 1996, 33, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C.O. Analysis of the dynamics of African vegetation using the normalized difference vegetation index. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, F.; Ryan, J.; Lluch-Cota, S.; Niquen, M. From anchovies to sardines and back: Multidecadal change in the Pacific ocean. Science 2003, 299, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E. The nature of rainfall variability over Africa on time scales of decades to millenia. Glob. Planet. Change 2000, 26, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, S.R.; Mantua, N.J. Empirical evidence for North Pacific regime shifts 1977 and 1989. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batisani, N.; Yarnal, B. Rainfall variability and trends in semi-arid Botswana: Implications for climate change adaptation policy. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Leposo, D.; Grist, J. The relationship between El Niño and drought over Botswana. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C.; Mulenga, H.M. Relationships between South African rainfall and SST anomalies in the southwest Indian Ocean. Int. J. Climatol. 1999, 19, 1651–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Ribbe, J.; Cai, W.; Cowan, T. Multidecadal variability in the transmission of ENSO signals to the Indian Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L10610. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S. El Niño, climate change, and Southern African climate. Environmetrics 2001, 12, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chown, S. Temporal biodiversity change in transformed landscapes: A southern African perspective. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2010, 365, 3729–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadza, C. Climate change: some likely multiple impacts in Southern Africa. Food Policy 1994, 19, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington-Allen, R.A.; Ramsey, R.; West, N.E. Spatiotemporal mapping of the dry season vegetation response of sagebrush steppe. Comm. Ecol. 2004, 5, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington-Allen, R.A.; Ramsey, R.; West, N.E.; Norton, B.E. Quantification of the ecological resilience of drylands using digital remote sensing. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Goheen, J.; Young, T.; Keesing, F.; Palmer, T. Consequences of herbivory by native ungulates for the reproduction of a savanna tree. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose, S.; Matheson, W.; Tempest, F.; Boyle, T. The development and causes of range degradation features in southeast Botswana using multi-temporal Landsat MSS imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 1990, 56, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Adger, W.N.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.; Rockstrom, J. Social-ecological resilience to coastal disasters. Science 2005, 309, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Walker, B.H.; Anderies, J.M.; Abel, N. From metaphor to measurement: Resilience of what to what? Ecosystems 2001, 4, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, W.E.; O’Leary, J. Measures of resilience: the response of coastal sage scrub to fire. Vegetatio 1986, 65, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoniello, T.; Lanfredi, M.; Liberti, M.; Coppola, R.; Macchiato, M. Estimation of vegetation cover resilience from satellite timer series. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2008, 5, 511–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougill, A.; Trodd, N. Monitoring and Modelling Open Savannas Using Multisource Information: Analyses of Kalahari Studies. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 1999, 8, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.G.H.; Robertson, F. Fire: The Ecological Effects of Fire in Savannas. In Determinants of Tropical Savannas; Walker, T.S., Walker, B.H., Eds.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 93–140. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, B.H.; Noy-Meir, I. Aspects of the Stability and Resilience of Savanna Ecosystems. In Ecology of Tropical Savannas; Huntley, B.J., Walker, B.H., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany/New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 577–590. [Google Scholar]
- Martiny, N.; Camberlin, P.; Richard, Y.; Philippon, N. Compared regimes of NDVI and rainfall in semi-arid regions of Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5201–5223. [Google Scholar]
- Farrar, T.J.; Nicholson, S.E.; Lare, A.R. The influence of soil type on the relationships between NDVI, rainfall, and soil moisture in semiarid Botswan. II. NDVI response to soil moisture. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 50, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, T.M.; Caylor, K.K.; Manfreda, S.; Levin, S.A.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Dynamic response of grass cover to rainfall variability: implications for the function and persistence of savanna ecosystems. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stige, L.; Stave, J.; Chan, K.; Ciannelli, L.; Pettorelli, N.; Glantz, M.; Herren, H. The effect of climate variation on agro-pastoral production in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3049–3053. [Google Scholar]
- Area, Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation. Mitigation of Human-Elephant Conflict in the Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area through Community Based Problem Animal Control, with Particular Reference to the Use of Chilli Peppers. 2006. Available online: http://www.dlist-benguela.org/sites/default/files/doclib/human%20elephant%20conflict%20TFCA.pdf (Accessed on 3 August 2013).
- Gaughan, A.E.; Waylen, P.R. Spatial and temporal precipitation variability in the Okavango-Kwando-Zambezi catchment, southern Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 82, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, S.; Scholes, R.J. Leaf green-up in a semi-arid African savanna—Separating tree and grass responses to environmental cues. J. Veg. Sci. 2007, 181, 583–594. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Green, G.M.; Schweik, C.M.; Randolf, J.C. Retrieving Land-Cover Change Information from Landsat Satellite Images by Minimizing Other Sources of Reflectance Variability. In Seeing the Forest and the Trees: Human–Environment Interactions in Forest Ecosystems; Moran, E.F., Ostrom, E., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, B.L.; Barker, J.L. Landsat MSS and TM post-calibration dynamic rangers, exoatmospheric reflectance and at-satellite temperatures. EOSAT Landsat Tech. Notes 1986, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J.; Renzullo, L.J.; Barrett, D.J.; Marks, A.S.; Botha, E.J. Estimating fractional cover of photosynthetic vegetation, non-photosynthetic vegetation and bare soil in the Australian tropical savanna region upscaling the EO-1 Hyperion and MODIS sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Karnieli, A. Remote Sensing of the seasonal variability of vegetation in a semi-arid environment. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 45, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.W.; Loveland, T.L.; Pierce, L. A vegetation classification logic based on remote sensing for use in global biogeochemical models. Ambio 1994, 23, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sedano, F.; Gong, P.; Ferrao, M. Land cover assessment with MODIS imagery in southern African Miombo ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Change, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.-P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, S.; Adler, R.F. ENSO indices based on patterns of satellite-derived precipitation. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, G.; Foran, B.D. The use of spectral and spatial variability to monitor cover change on inert landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 23, 361–363. [Google Scholar]
- Lanfredi, M.; Simoniello, T.; Macchiato, M. Temporal persistence in vegetation cover changes observed from satellite: Development of an estimation procedure in the test site of the Mediterranean Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.L.; Tsonis, A.A. Has the climate recently shifted? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Wiegand, K.; Wards, D.; Moustakas, A. The rhythm of savanna patch dynamics. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Gibbes, C.; Southworth, J.; Waylen, P. Using Remote Sensing to Quantify Vegetation Change and Ecological Resilience in a Semi-Arid System. Land 2013, 2, 108-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/land2020108
Cui X, Gibbes C, Southworth J, Waylen P. Using Remote Sensing to Quantify Vegetation Change and Ecological Resilience in a Semi-Arid System. Land. 2013; 2(2):108-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/land2020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xia, Cerian Gibbes, Jane Southworth, and Peter Waylen. 2013. "Using Remote Sensing to Quantify Vegetation Change and Ecological Resilience in a Semi-Arid System" Land 2, no. 2: 108-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/land2020108
APA StyleCui, X., Gibbes, C., Southworth, J., & Waylen, P. (2013). Using Remote Sensing to Quantify Vegetation Change and Ecological Resilience in a Semi-Arid System. Land, 2(2), 108-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/land2020108






