An Ecogeomorphological Approach to Land-Use Planning and Natural Hazard Risk Mitigation: A Literature Review
Abstract
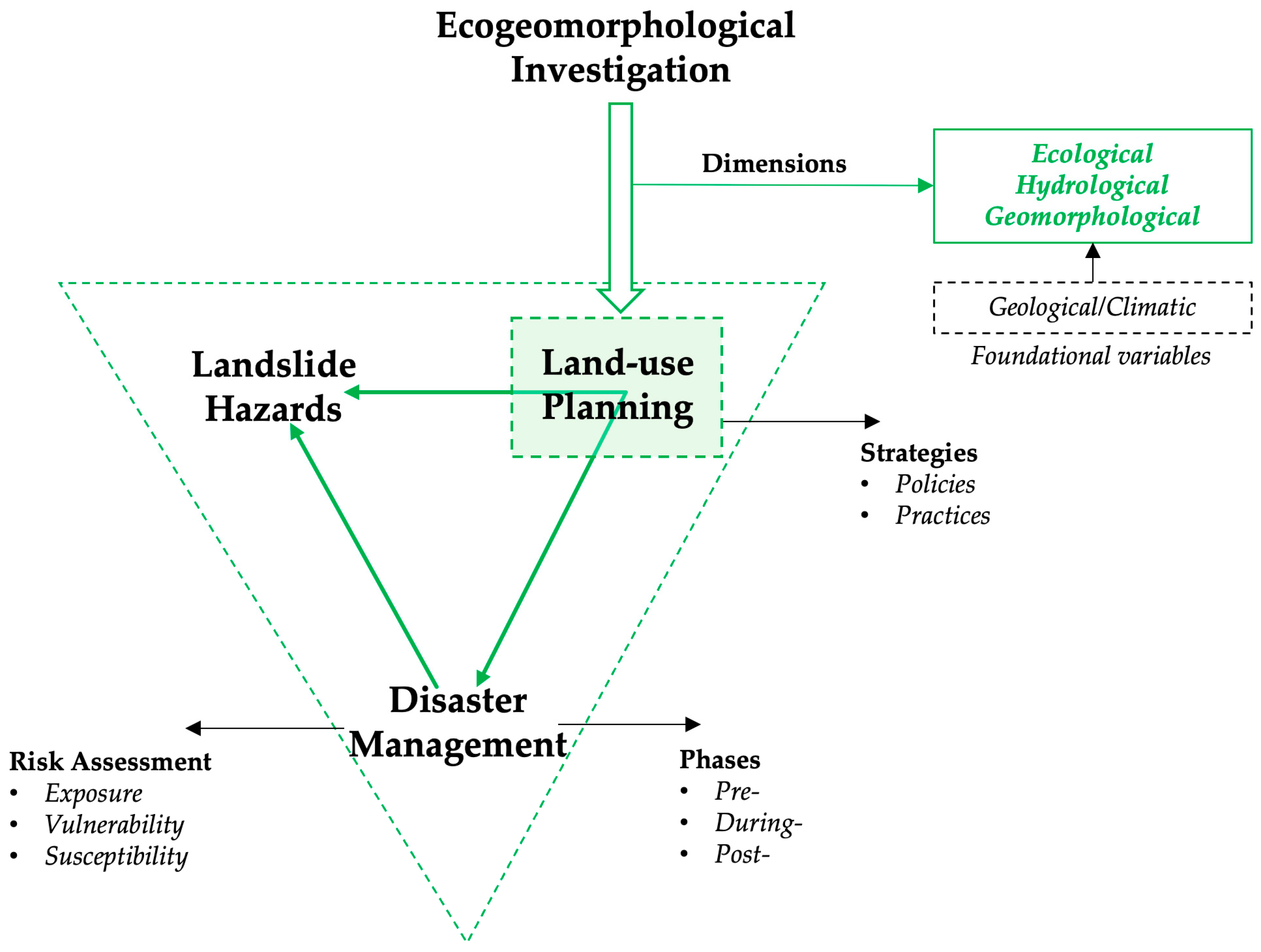
1. Introduction
- Can landslide research be applied in LUP to enhance broader DRM frameworks?
- Does ecogeomorphological research play a role in fostering the development of risk-aware LUP?
- What are the main ecogeomorphological factors that affect landslides in LUP?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Screening
2.2. Data Interpretation and Descriptive Analysis
3. Research Trends and Scientific Mapping
3.1. Research Trends
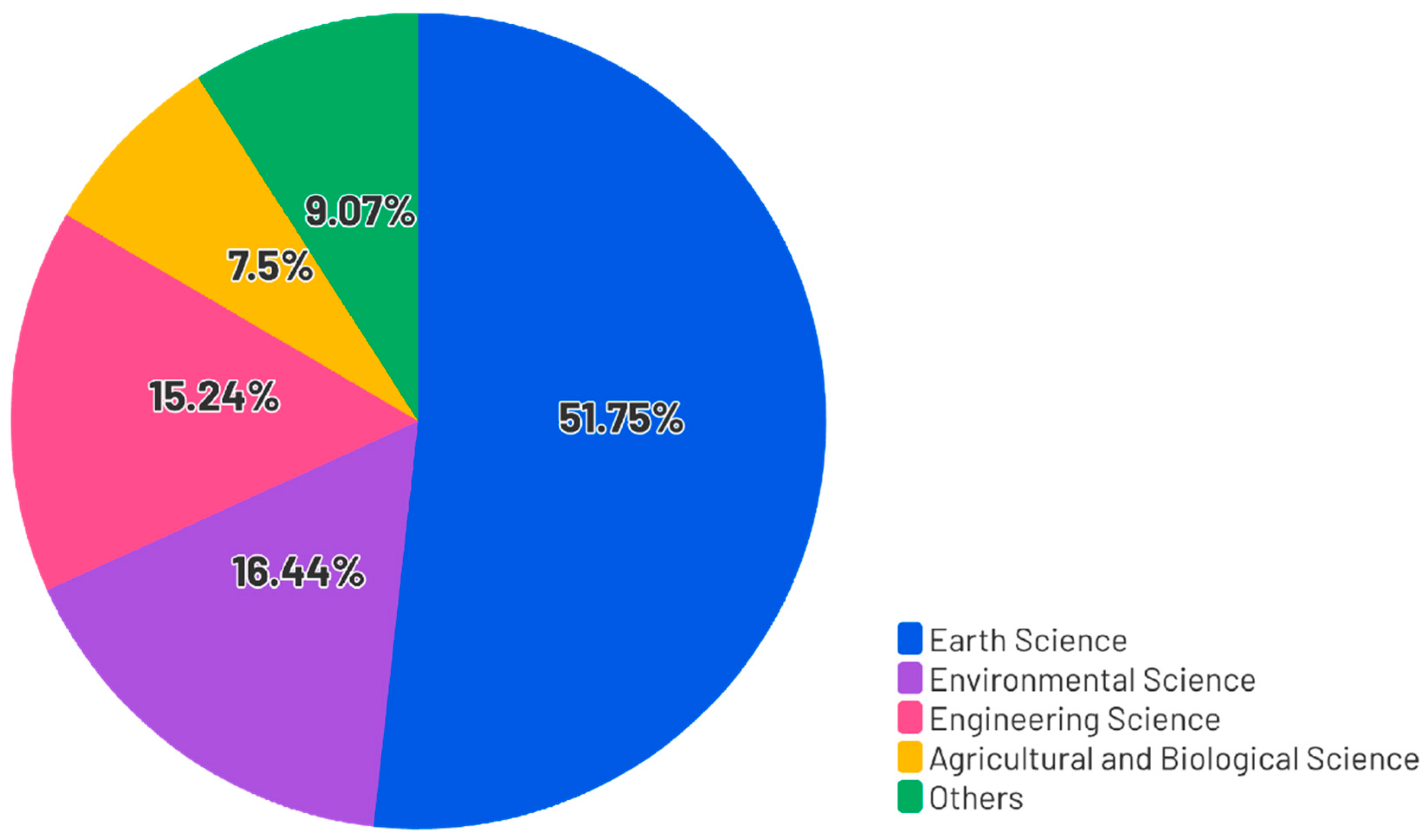
3.1.1. Research Domains
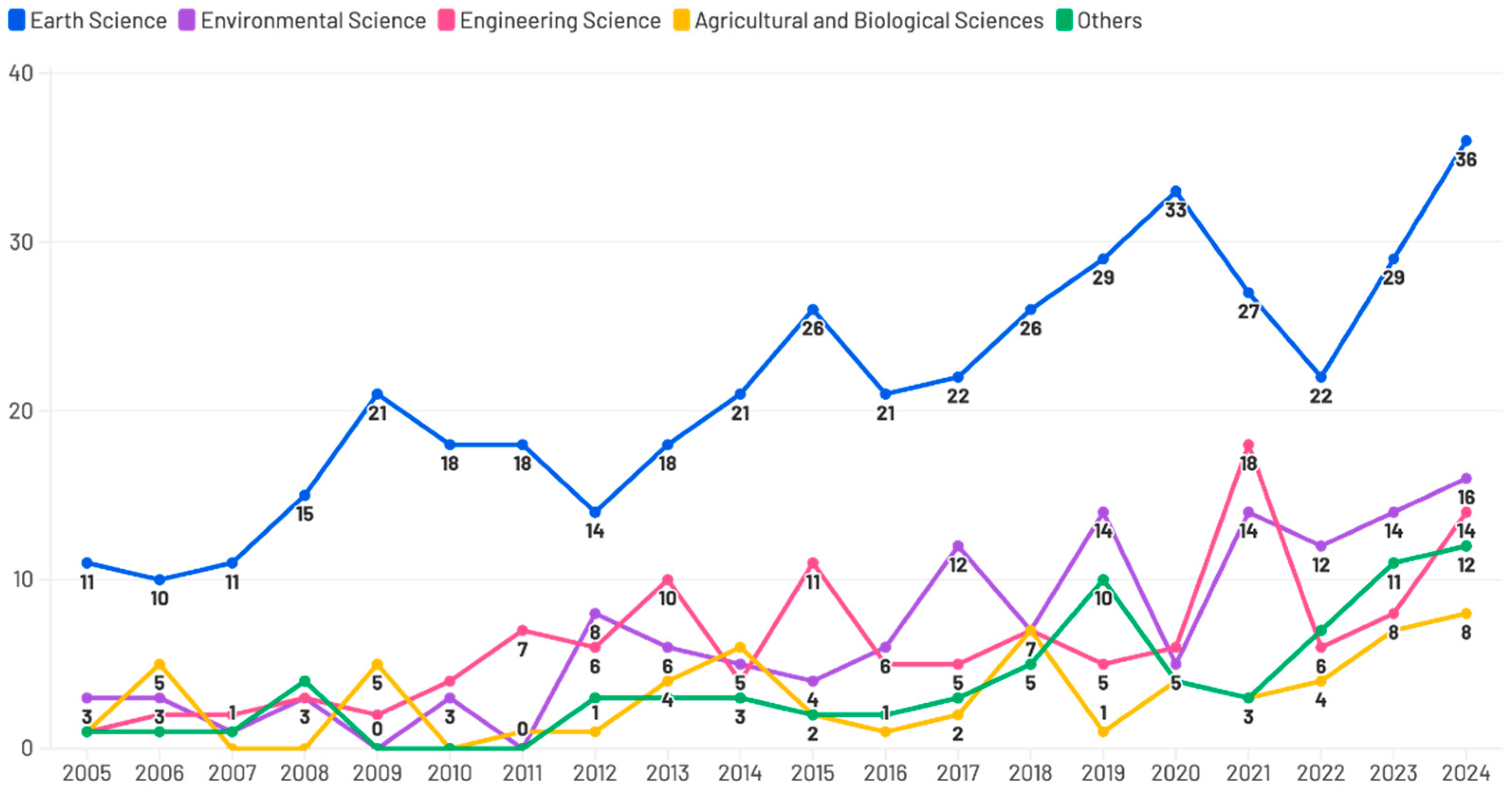
3.1.2. Publication Trends
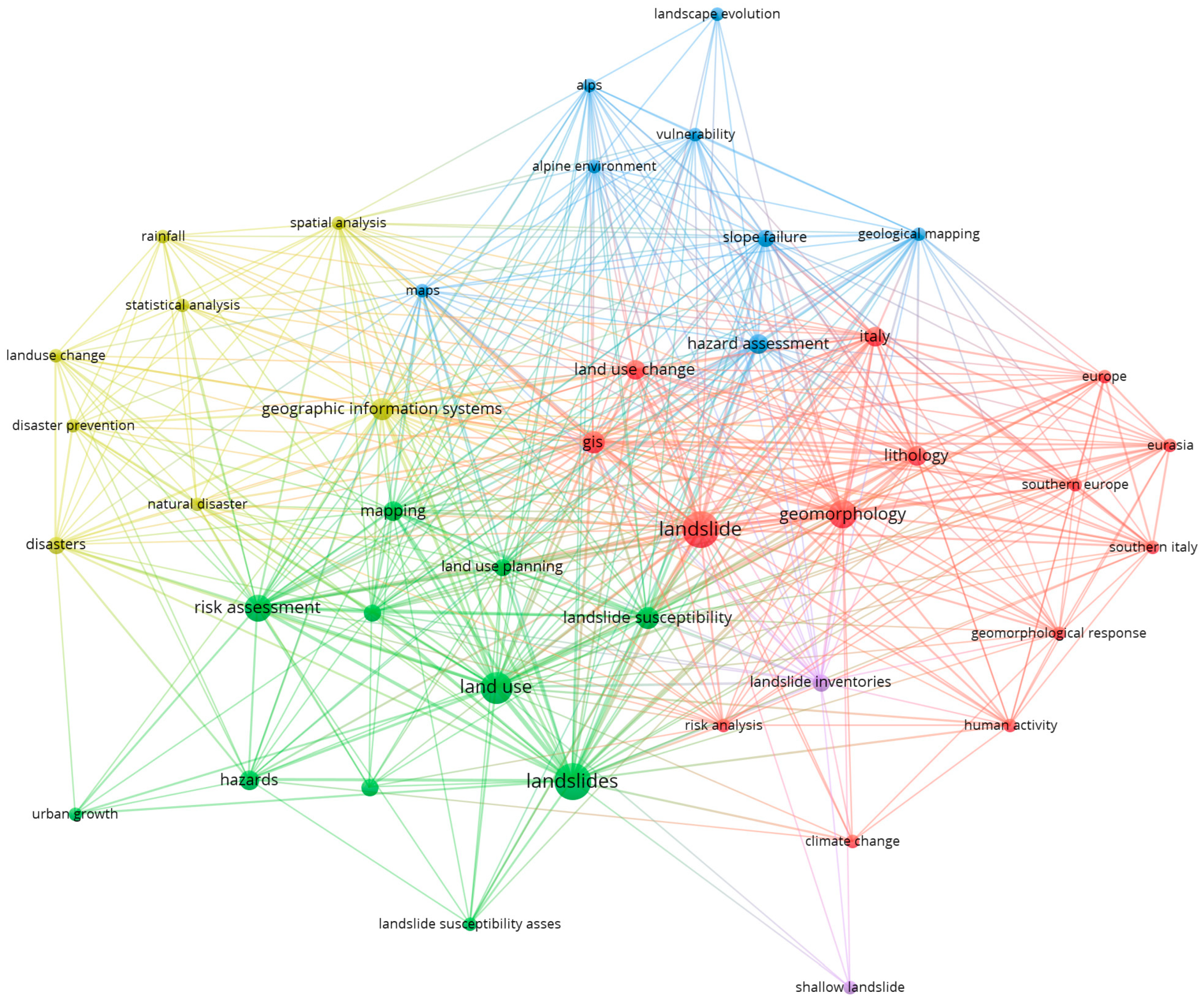
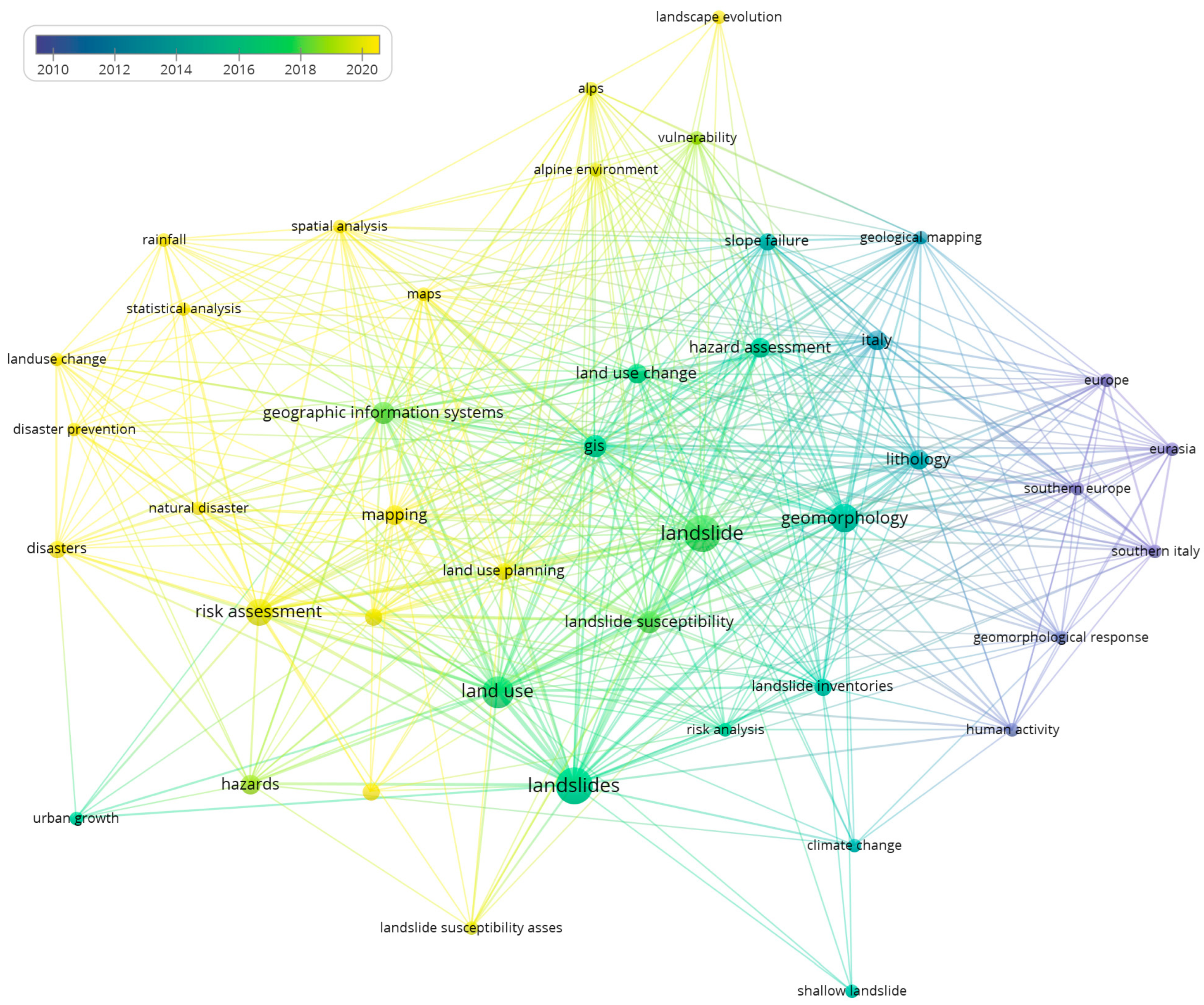
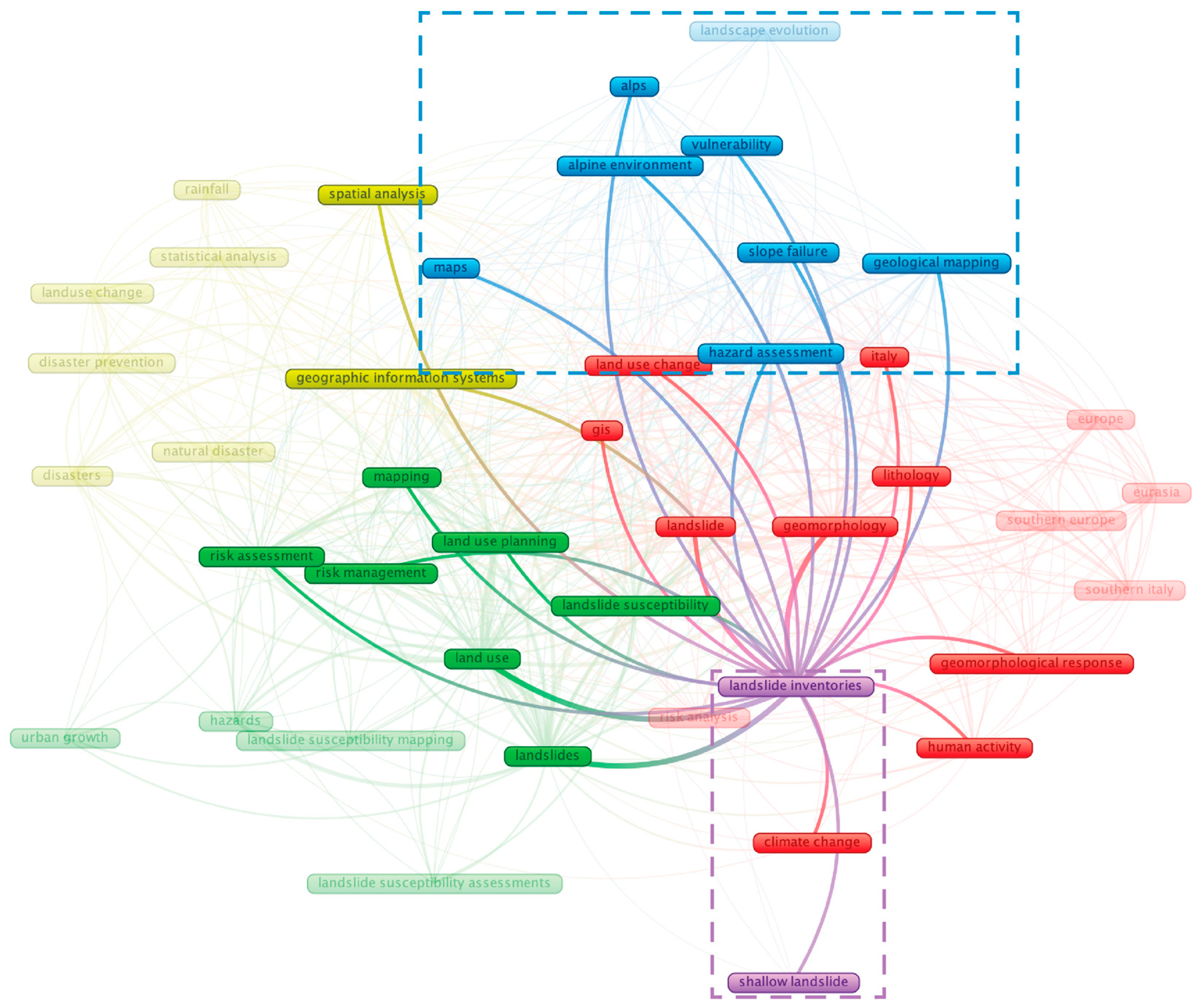
3.1.3. Keyword Co-Occurrence Network
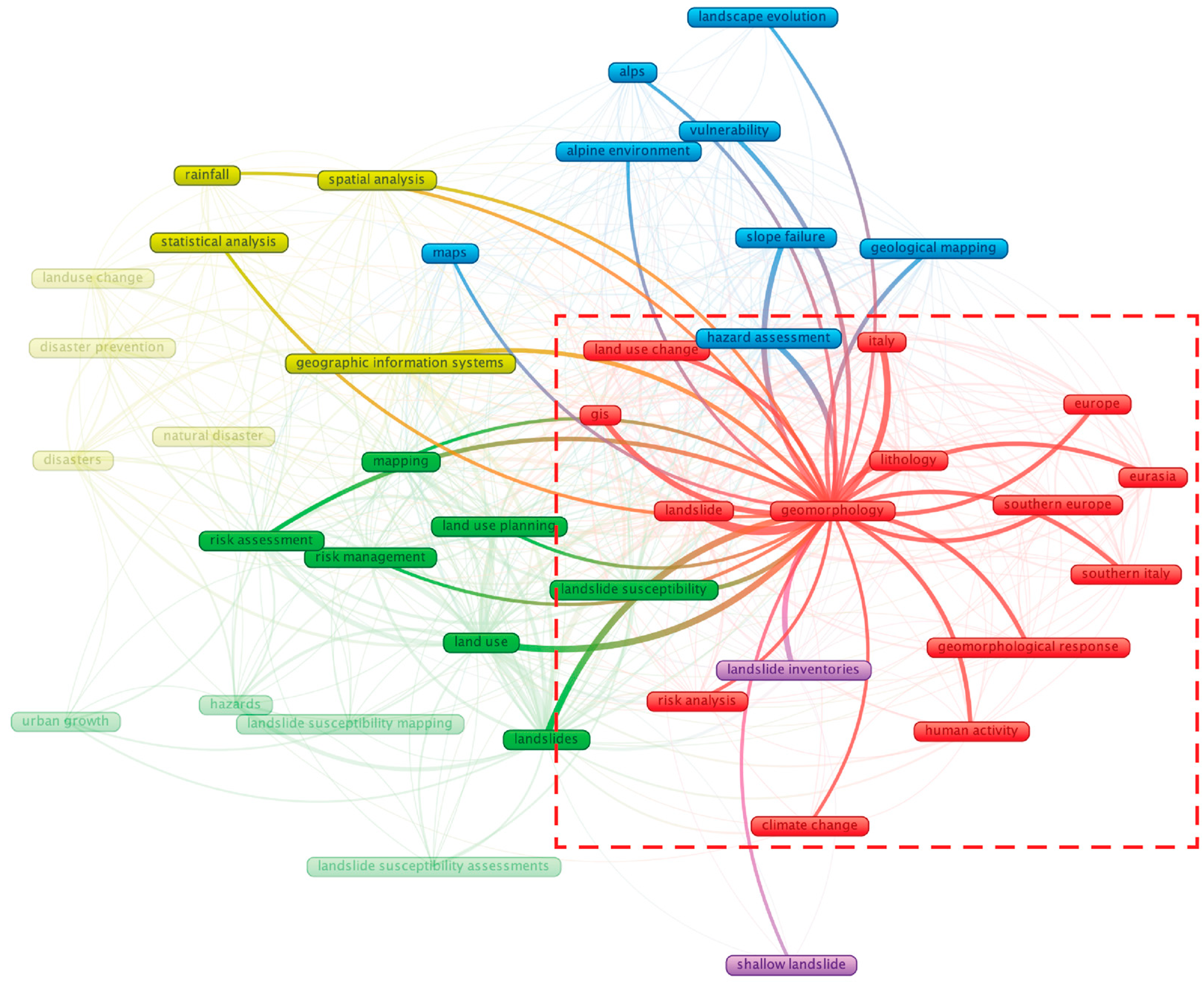
- First Cluster (Red) explores how geomorphology, lithology, and climatic factors interact with human activity to shape landslide dynamics, especially in Southern Europe and Eurasia.
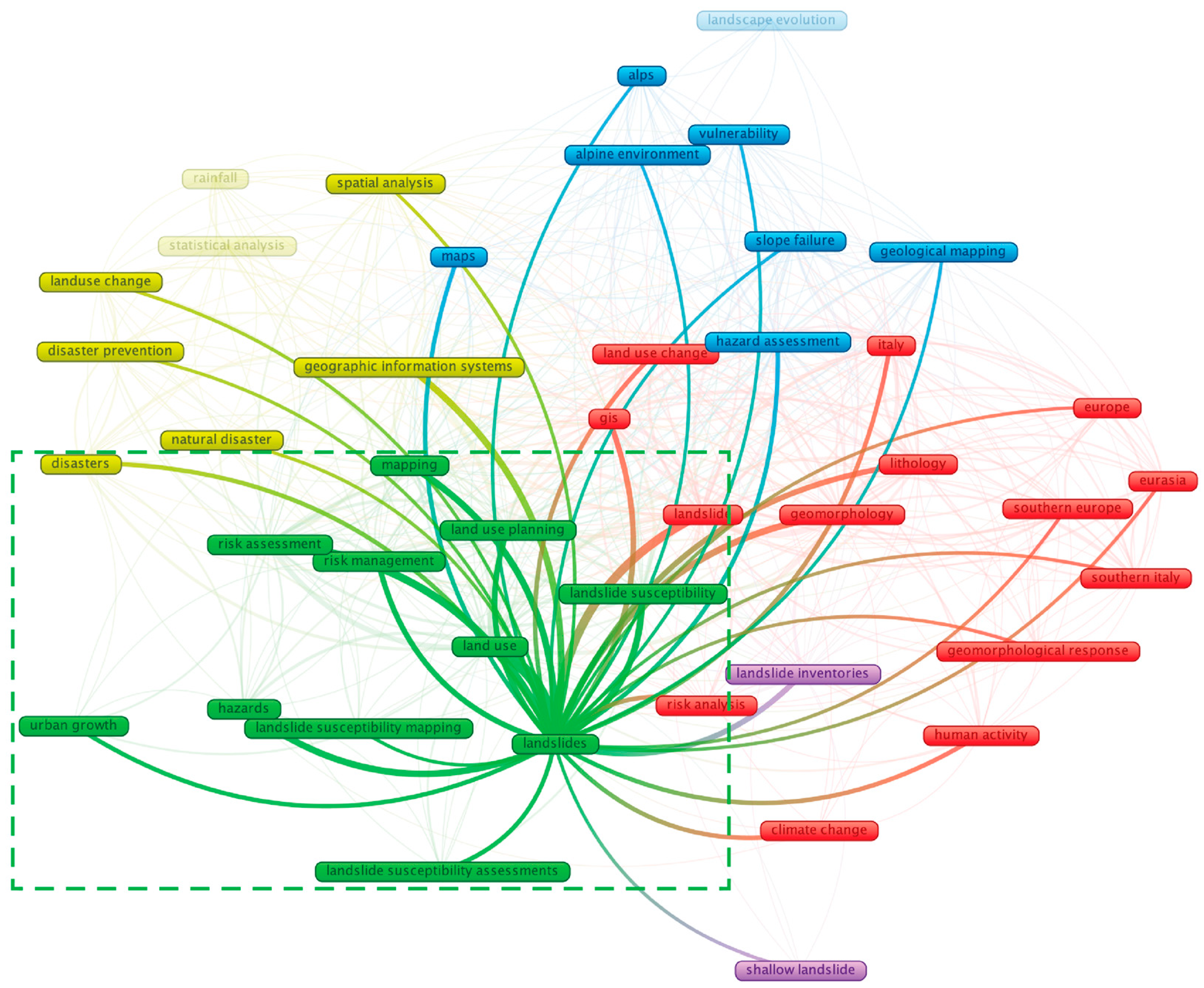
- Second Cluster (Green) focuses on evaluating landslide susceptibility in land-use change and urban development, emphasising risk management techniques.
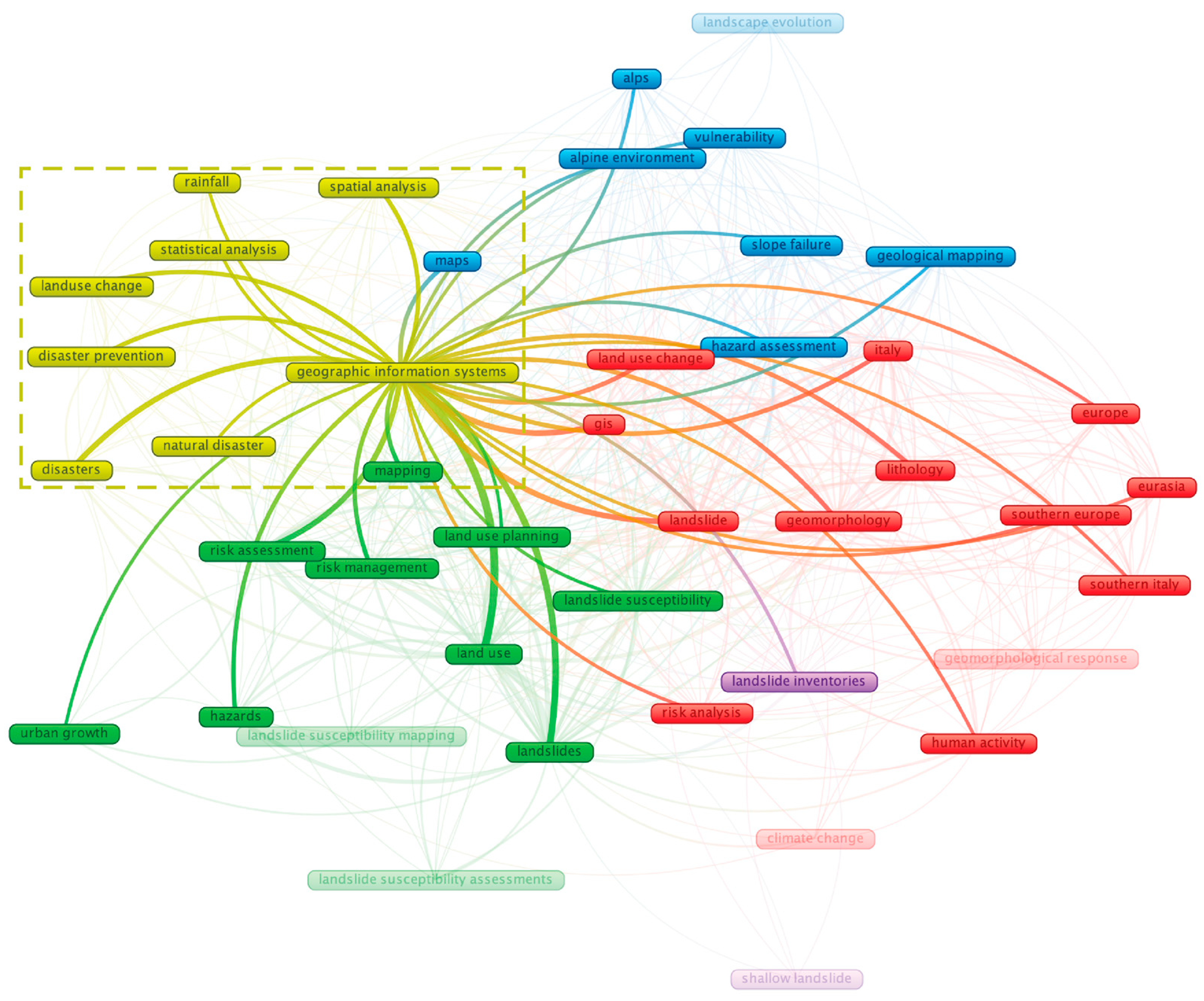
- Third Cluster (Yellow) examines geographic information systems, spatial analysis, statistical analysis, and disaster prevention, representing a methodological approach to landslide studies.
- Fourth Cluster (Blue) concentrates on landscape evolution, vulnerability, and geological mapping, which relate to hazard assessment in mountainous environments.
- Fifth Cluster (Purple) focuses on the development of landslide inventories and classification systems, indicating the impact of external factors on different landslide occurrences.
3.1.4. Keywords in Temporal Trends
4. Results
4.1. First Cluster (Red): Geomorphological Processes and Human Drivers of Landslides
4.1.1. First Cluster Key Literature Topic
4.1.2. First Cluster Key Literature Detailed Review
4.1.3. First Cluster Future Direction
4.2. Second Cluster (Green): LUP and Landslide Susceptibility Assessment
4.2.1. Second Cluster Key Literature Topic
4.2.2. Second Cluster Key Literature Detailed Review
4.2.3. Second Cluster Future Direction
4.3. Third Cluster (Yellow): Geospatial and Statistical Approach for Disaster Prevention
4.3.1. Third Cluster Key Literature Topic
4.3.2. Third Cluster Key Literature Detailed Review
4.3.3. Third Cluster Future Direction
4.4. Remaining Cluster
4.4.1. Remaining Cluster Key Literature Topic
4.4.2. Remaining Cluster Key Literature Detailed Review
4.4.3. Remaining Cluster Future Direction
5. Discussion
- Can landslide research be applied in LUP to enhance broader DRM frameworks?
- Does ecogeomorphological research play a role in fostering the development of risk-aware LUP?
- What are the main ecogeomorphological factors that affect landslides in LUP?
5.1. Land-Use Planning (LUP)
5.2. Ecogeomorphology
5.3. Research Gaps/Future Research Questions
- Identification of the different types of ecogeomorphological factors that shape LUP in each local context.
- Development of an integrated methodological framework that can capture synergies between ecological, hydrological, and geomorphological dimensions for DRM.
- Examination of how ecological, hydrological, and geomorphological data can be better integrated into a unified framework for LUP and hazard mitigation.
- Identification of the authorities and governance barriers that limit the implementation of ecogeomorphologically informed LUP.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tebbens, S.F. Landslide Scaling: A Review. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA000662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruden, D. A simple definition of a landslide. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. Bull. de L’association Int. de Géologie de L’ingénieur 1991, 43, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causes, L. Landslide Types and Processes; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Ngai, Y.Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2002, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoms, M.; Parsons, M. Eco-Geomorphology: An Interdisciplinary Approach to River Science; IAHS-AISH Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2002; Volume 276. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, N.; Bellot, J.; Couteron, P.; Parsons, A.; Paton Née Mueller, E. Short-Range Ecogeomorphic Processes in Dryland Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moeslund, J.E.; Arge, L.; Bøcher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Svenning, J.-C. Topography as a driver of local terrestrial vascular plant diversity patterns. Nord. J. Bot. 2013, 31, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Pu, R.; Liu, Y. A review on anthropogenic geomorphology. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K. Effects of watershed topography, soils, land use, and climate on baseflow hydrology in humid regions: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowles, H.C. The Ecological Relations of the Vegetation on the Sand Dunes of Lake Michigan. Part I.—Geographical Relations of the Dune Floras. Bot. Gaz. 1899, 27, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S. Lake Michigan Dune Development Plants as Agents and Tools in Geomorphology. J. Geol. 1958, 66, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterkamp, W.R.; Hupp, C.R.; Schening, M.R. Little River revisited—Thirty-five years after Hack and Goodlett. In Biogeomorphology, Terrestrial and Freshwater Systems; Hupp, C.R., Osterkamp, W.R., Howard, A.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wheaton, J.M.; Gibbins, C.; Wainwright, J.; Larsen, L.; McElroy, B. Preface: Multiscale Feedbacks in Ecogeomorphology. Geomorphology 2011, 126, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, L.; Jerolmack, D.; Cardinale, B.J.; Vanacker, V.; Wright, J. Dynamic interactions of life and its landscape: Feedbacks at the interface of geomorphology and ecology. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, L.A.; Viles, H.A.; Carter, N.E.A. Biogeomorphology revisited: Looking towards the future. Geomorphology 2002, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corenblit, D.; Corbara, B.; Steiger, J. Biogeomorphological eco-evolutionary feedback between life and geomorphology: A theoretical framework using fossorial mammals. Sci. Nat. 2021, 108, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichel, J.; Corenblit, D.; Dikau, R. Conditions for feedbacks between geomorphic and vegetation dynamics on lateral moraine slopes: A biogeomorphic feedback window. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.A. Biogeomorphology. In The History of the Study of Landforms or the Development of Geomorphology: Geomorphology in the Second Half of the Twentieth Century; Burt, T.P., Goudie, A.S., Viles, H.A., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2022; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, E.N.; Wainwright, J.; Parsons, A.J.; Turnbull, L. Land Degradation in Drylands: An Ecogeomorphological Approach. In Patterns of Land Degradation in Drylands: Understanding Self-Organised Ecogeomorphic Systems; Mueller, E.N., Wainwright, J., Parsons, A.J., Turnbull, L., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Hoque, M.; Saha, U.; Islam, A. Assessment of dam-induced changes in ecogeomorphological behaviour and fluvial functionality in the Damodar River, West Bengal, India. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2022, 71, 722–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Moghaddam, M.; Khezri, S. Ecogeomorphological Condition and Hydrological Indicators of the Self-Purification Capacity of Rivers: A Case Study of Siminehrood River in Northwestern Iran. Int. J. Environ. Health Eng. 2023, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Briain, R.; Corenblit, D.; Garófano Gómez, V.; O’Leary, C. Towards biogeomorphic river restoration: Vegetation as a critical driver of physical habitat. River Res. Appl. 2024, 40, 1087–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, A.; Erciyas Yavuz, K.; Karaer, F.; Polat, N.; Bakan, G.; Gürgöze, S. Ecogeomorphological Investigation of Anthropogenic Changes in the Kızılırmak River Mouth, Türkiye. Wetlands 2024, 44, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poufarashzadeh, F.; Madadi, A.; Gharachorlu, M.; Sareskanrood, S. Spatial-statistical modelling of deforestation from an ecogeomorphic perspective in typical Hyrcanian forests, northern Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimani, K.; Darvishi, S. Comparative analysis of land use changes modelling based-on new hybrid models and CA-Markov in the Urmia lake basin. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 3749–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, F.; Ferland, Y. Land-use planning for disaster risk management. Land. Tenure J. 2015, 2014, 70–103. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, W.; Beban, J.G.; Kilvington, M. Risk-based land use planning for natural hazard risk reduction. GNS Sci. Misc. Ser. 2013, 67, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Falasca, F.; Sette, C.; Montaldi, C. Addressing land use planning: A methodology for assessing pre- and post-landslide event urban configurations. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, H. Land use planning and health and well-being. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, S115–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G. Land Use and Spatial Planning: Enabling Sustainable Management of Land Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein, M.; Maser, C. Land-Use Planning for Sustainable Development; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann, B.; Renn, O. Risk perception research: An introduction. In Cross-Cultural Risk Perception: A Survey of Empirical Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 11–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wachinger, G.; Renn, O. Risk Perception and Natural Hazards. CapHaz-Net WP3 Report, DIALOGIK Non-Profit Institute for Communication and Cooperative Research, Stuttgart. 2010. Available online: https://giam.zrc-sazu.si/sites/default/files/caphaz-net_wp3_risk-perception2.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Sutanta, H.; Rajabifard, A.; Bishop, I.D. Disaster risk reduction using acceptable risk measures for spatial planning. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2013, 56, 761–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godber, A. Urban floodplain land-use–acceptable risk? Aust. J. Emerg. Manag. 2005, 20, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Renn, O.; Klinke, A. A framework of adaptive risk governance for urban planning. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2036–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, S.M.; Falcão, M.J.; Komljenovic, D.; de Almeida, N.M. A systematic literature review on urban resilience enabled with asset and disaster risk management approaches and GIS-based decision support tools. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burby, R.; Deyle, R.; Godschalk, D.; Olshansky, R. Creating Hazard Resilient Communities through Land-Use Planning. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2000, 1, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanashree, M.; Baskar, P.; Mohan, L.; Janani, N.; Kathirvel, L.; Ramachandiran, P.; Aakash, S. The Role of Google Earth Engine in Flood Disaster Management: A Review of Capabilities and Challenges. Adv. Environ. Res. 2025, 26, 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Waleed, M.; Sajjad, M. On the emergence of geospatial cloud-based platforms for disaster risk management: A global scientometric review of google earth engine applications. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 97, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Bo, M.; Ren, X.; Dai, K. Application and exploration of artificial intelligence technology in urban ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction: A scoping review. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bail, R.d.F.; Kovaleski, J.L.; da Silva, V.L.; Pagani, R.N.; Chiroli, D.M.d.G. Internet of things in disaster management: Technologies and uses. Environ. Hazards 2021, 20, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Aziz, A.; Ogunmola, G.A. Agricultural disaster risk management and capability assessment using big data analytics. Big Data 2022, 10, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.K.; Sulaiman, N.; Chan, S.W.; Nazir, U.; Abid, M.; Han, H.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Vega-Muñoz, A. Toward an Integrated Disaster Management Approach: How Artificial Intelligence Can Boost Disaster Management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, N.; Tokdemir, O.B.; Günaydın, H.M. Artificial Intelligence in Earthquake Disaster Risk Management: A Systematic Review of Applications, Challenges, and Research Gaps. In Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 791–807. [Google Scholar]
- Aljohani, F.H.; Abi Sen, A.A.; Ramazan, M.S.; Alzahrani, B.; Bahbouh, N.M. A Smart Framework for Managing Natural Disasters Based on the IoT and ML. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velev, D.; Zlateva, P. Challenges of artificial intelligence application for disaster risk management. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zêzere, J.; Reis, E.; Garcia, R.; Oliveira, S.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Vieira, G.; Ferreira, A. Integration of spatial and temporal data for the definition of different landslide hazard scenarios in the area north of Lisbon (Portugal). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsos, M.-C.; Vescoukis, V. Natural Hazards and Spatial Data Infrastructures (SDIs) for Disaster Risk Reduction. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X. Intelligent Map Reader: A Framework for Topographic Map Understanding with Deep Learning and Gazetteer. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25363–25376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, U.A.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zeeshan, Z.; Nawaz, S.A.; Bhatti, M.; Mehmood, A.; Ain, Q.U.; Wen, L. Geometric Algebra Applications in Geospatial Artificial Intelligence and Remote Sensing Image Processing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155783–155796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, Y.S.; Supangkat, S.H. Spatial Data Infrastructure Integrated with Geospatial Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS), Bandung, Indonesia, 2–4 August 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.; Greenhalgh, T.; Westhorp, G.; Buckingham, J.; Pawson, R. RAMESES publication standards: Meta-narrative reviews. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.; He, J. Understanding the Role and Methods of Meta-Analysis in IS Research. Commun. Ais CAIS 2006, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, A.; Tate, M.; Johnstone, D. Beyond synthesis: Re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behav. Inf. Technol. Behav. IT 2011, 32, 1199–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, J.; Nordhausen, T.; Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Ewald, H. Using citation tracking for systematic literature searching—Study protocol for a scoping review of methodological studies and a Delphi study [version 2; peer review: 2 approved with reservations]. F1000Research 2021, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pare, G.; Trudel, M.-C.; Jaana, M.; Kitsiou, S. Synthesizing Information Systems Knowledge: A Typology of Literature Reviews. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, Y.; Abu-Shanab, E. A descriptive framework for the field of knowledge management. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2020, 62, 4481–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukar, U.A.; Sayeed, M.S.; Razak, S.F.A.; Yogarayan, S.; Amodu, O.A.; Mahmood, R.A.R. A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, B. Risk perception, risk attitude, risk communication, risk management: A conceptual appraisal. In Proceedings of the 15th Internaional Emergency Management Society (TIEMS) Annual Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 17–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, D.A. Farmers’ motivations, risk perceptions and risk management strategies in a developing economy: Bangladesh experience. J. Risk Res. 2011, 14, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing Bibliometric Networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact: Methods and Practice; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 285–320. [Google Scholar]
- Stallins, J.A. Geomorphology and ecology: Unifying themes for complex systems in biogeomorphology. Geomorphology 2006, 77, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, E.; Adamaitis, C.; Alessio, P.; Anderson, S.; Goto, E.; Gray, S.; Gurrola, L.; Morell, K. Applications in geomorphology. Geomorphology 2020, 366, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, N.J. The landslide hazard map of bogota an updating. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences—ISPRS Archives, Karisruhe, Germany, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bozicek, B.; Koren, E. Management of Landslides in Small Settlements in Slovenia. In Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides; Advances in Landslide Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 989–998. [Google Scholar]
- Oppikofer, T.; Nordahl, B.; Bunkholt, H.; Nicolaisen, M.; Jarna, A.; Iversen, S.; Hermanns, R.L.; Böhme, M.; Molina, F.X.Y. Database and online map service on unstable rock slopes in Norway—From data perpetuation to public information. Geomorphology 2015, 249, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, V.M.; Bonachea, J.; Remondo, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Rivas, V.; Barbieri, M.; Capocchi, S.; Soldati, M.; Cendrero, A. Land management versus natural factors in land instability: Some examples in northern Spain. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 398–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.H. Geomorphology: Processes, Taxonomy and Applications; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–215. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, R.; Pacheco, J.; Wallenstein, N.; Pimentel, A.; Marques, R.; Silva, R. Integrating geological knowledge in planning methods for small islands coastal plans. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 2, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo, C.; Walker, L.R.; Shiels, A.B.; Bussmann, R.; Claessens, L.; Fisch, S.; Lozano, P.; Negi, G.; Paolini, L.; Poveda, G.; et al. Landsliding and Its Multiscale Influence on Mountainscapes. Bioscience 2009, 59, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolongo, D.; Pennetta, L.; Piccarreta, M.; Fallacara, G.; Boenzi, F. Spatial and temporal variations in soil erosion and deposition due to land-levelling in a semi-arid area of Basilicata (Southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, A.; Dondapati, A.; Gupta, S.; Raj, R. Leveraging artificial neural networks for robust landslide susceptibility mapping: A geospatial modelling approach in the ecologically sensitive Nilgiri District, Tamil Nadu. Geohazard Mech. 2024, 2, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyeltshen, S.; Chhetri, I.B.; Dema, K. Evaluation of statistical modelling (SM) approaches for landslide susceptibility mapping: Geospatial insights for Bhutan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, M.; Ghazifard, A.; Akgün, H.; Asghari-Kaljahi, E. Landslide susceptibility assessment of South Pars Special Zone, southwest Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.E.; Trandafir, A.C. Landslide risk assessment and mitigation. In Bridge Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; Substructure Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 315–359. [Google Scholar]
- Sandric, I.; Chitu, Z. Landsat Time Series Analysis for Modelling Temporal Probability for Landslide Occurrences in Curvature Subcarpathians, Romania. In Proceedings of the GI_FORUM 2013: Creating the Gisociety, Salzburg, Austria, 2–5 July 2013; pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Z.; Xiaoyu, Z.; Hao, L.; Chenyi, Z.; Zhile, S.; Lijun, J.; Zelin, W.; Zheng, F.; Jiayang, Y.; Xin, Y.; et al. The relationship between geological disasters with land use change, meteorological and hydrological factors: A case study of Neijiang City in Sichuan Province. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanveer, C.T.A.; Mohammed, H.; Puthuvathara, A.I.; Dilruba, P.M.; Rajalakshmi, T.R. Landslide Hazard Zonation of Peerumedu Taluk Using ArcGIS. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1139–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Prawiradisastra, F.; Shomim, A.F.; Trisnafiah, S.; Khaerani, P.; Tejakusuma, I.G.; Zakaria, Z. Forensic assessment of landslides induced by environmental changes in Sumedang, Indonesia, an important step for the future disaster prevention. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Science: Bristol, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Quiquerez, A.; Gauthier, E.; Bichet, V.; Petit, C.; Murgia, L.; Richard, H. Reconstructing patterns of vegetation recovery and landscape evolution after a catastrophic landslide (Mont Granier, French Alps, 1248 CE). Anthropocene 2022, 40, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilopo, W.; Erzagian, E.; Ratri, D.; Fathani, T.F. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment in Trenggalek, East Java, Indonesia: A Geological Overview. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 873–883. [Google Scholar]
- Peruccacci, S.; Brunetti, M.T.; Gariano, S.L.; Melillo, M.; Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for possible landslide occurrence in Italy. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.S.; Adhikari, B.R.; Shaw, R.; Bhattarai, D.; Yanai, S. Geomorphological analysis and early warning systems for landslide risk mitigation in Nepalese mid-hills. Nat. Hazards 2023, 117, 1793–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audisio, C.; Nigrelli, G.; Pasculli, A.; Sciarra, N.; Turconi, L. A GIS spatial analysis model for landslide hazard mapping application in Alpine Area. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2017, 12, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P.; Di Lisio, A.; Russo, F.; Zelano, A. Geomorphology and landslide susceptibility assessment using GIS and bivariate statistics: A case study in southern Italy. Nat. Hazards 2008, 47, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.L.; Harrison, S.; Reinhardt, L. Landslide inventories for climate impacts research in the European Alps. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, L.; Cofone, G.; Coscarelli, R.; Gullà, G. Shallow landslides triggered by consecutive rainfall events at Catanzaro strait (Calabria–Southern Italy). J. Maps 2015, 11, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gares, P.A.; Sherman, D.J.; Nordstrom, K.F. Geomorphology and natural hazards. Geomorphology 1994, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervas-Mons, J.; Domínguez-Cuesta, M.J.; Jiménez-Sánchez, M. Potential and Limitations of the New European Ground Motion Service in Landslides at a Local Scale. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Nijhuis, S.; Bobbink, I. The Role of Spatial Planning in Landscape-Based Groundwater Recharge: A Systematic Literature Review. Water 2025, 17, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wei, Y. Landslide Geomorphology: Pattern, Process and Stability. J. Earth Sci. 2025, 36, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, N.R.; Walter, J.I. Detailed mapping of shallow landslides in eastern Oklahoma and western Arkansas and potential triggering by Oklahoma earthquakes. Geomorphology 2020, 366, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A. Utilizing Hybrid Machine Learning and Soft Computing Techniques for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in a Drainage Basin. Water 2024, 16, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa Priya, V.; Shah, S.; Praveen, L.; Rajesh, R.M. Deep Learning Model for Automated Landslide and Debris Flow Detection. Int. Res. J. Adv. Eng. Hub (IRJAEH) 2025, 3, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanehkaran, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Azarafza, M.; Yimin, M. Application of artificial neural networks and geographic information system to provide hazard susceptibility maps for rockfall failures. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Chen, J. A novel method based on deep learning model for national-scale landslide hazard assessment. Landslides 2023, 20, 2379–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirsyayu, T.; Soma, A.S.; Paembonan, S. Land use direction based on landslide susceptibility levels in the Rongkong Watershed, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Asian J. For. 2025, 9, r090106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel-Yorke, K.; Anim, M.; Nyarko, B.K. Sedimentation assessment using hydrological simulation and bathymetry survey: The case of river Amissa drainage basin, Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muladi, M.; Wirawan, I.M.; Lestari, D.; Choirul, S.; Raka, E.; Leksono, A.; Qodri, F.; Prasetyo, S. Chirpstack-Based LoRAWAN Platform for Land-Sliding Monitoring System. Instrum. Mes. Métrologie 2025, 24, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Martínez-Graña, A. Landslide Hazard Prediction Based on Small Baseline Subset–Interferometric Synthetic-Aperture Radar Technology Combined with Land-Use Dynamic Change and Hydrological Conditions (Sichuan, China). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoni, S.; Nocentini, N.; Barbadori, F.; Medici, C.; Gatto, A.; Rosi, A.; Casagli, N. A novel prototype national-scale landslide nowcasting system for Italy combining rainfall thresholds and risk indicators. Landslides 2025, 22, 1341–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, R.; Fey, C.; Kuschel, E.; Voit, K.; Zangerl, C.; Lehner, F.; Valentin, G. Insights into the evolution of a post-failure rock slope. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2025, 84, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Ao, Y.; Jia, X.; Peng, P.; Li, M.; Li, J. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of Geo-Disaster Resilience in China and the Impact Mechanism of Environmental Governance. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Nawazuzzoha, M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Ali, S.A.; Fnais, M.; Shamim, S.K.; Ahmad, A.; Andráš, P. Mapping landslide susceptibility and risk assessment on fragile ecosystem of Himalayan River basins. All Earth 2025, 37, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, L.; Li, H.; He, L.; Liu, S. Multi-Scale Debris Flow Warning Technology Combining GNSS and InSAR Technology. Water 2025, 17, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, B.K.; Gautam, P.; Adhikari, B.; Lamichhane, S. Dynamics of active landslide along central Himalayan route: A case study of Guthitar landslide, Dhankuta, Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2024, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustina, I.; Mutia, A.; Rochman, G.; Fardani, I.; Aji, R. STUDY Of SPATIAL CHANGE IN ASTANA VILLAGE HERITAGE AREA, CIREBON, INDONESIA. Plan. Malays. 2023, 21, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Bitar, J.; Morante, F.; Chávez-Moncayo, M.; Blanco-Torrens, R.; Carrión, P. Engineering Solutions for the Stabilisation of a Hill Located in an Urban Area. Case Study: Las Cabras Hill, Duran-Ecuador. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2022, 17, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnell, Y.; Blondeau, S.; Jarman, D. Rock slope failure in the Southern Carpathians (Romania): Range-wide inventory and links with long-term mountain landscape evolution. Geomorphology 2022, 418, 108433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, H. Enhancing Disaster Response Systems: Predicting and Mitigating the Impact of Natural Disasters Using AI. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 2, 501. [Google Scholar]
- Endla, P.; Bandlamudi, S.; Sasirekha, N.; Devi, S.S.; Pokhriyal, S.; Nandhini, P. Real Time Artificial Intelligence Powered Engagement Platforms for Proactive Disaster Management Emergency Response and Risk Mitigation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainability Innovation in Computing and Engineering (ICSICE 2024), Chennai, India, 30–31 December 2025; pp. 932–943. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, K.P.; Octavianti, T.; Dogulu, N.; Tyralis, H.; Papacharalampous, G.; Rowberry, R.; Fan, P.; Everard, M.; Francesch-Huidobro, M.; Migliari, W.; et al. Transforming Disaster Risk Reduction with AI and Big Data: Legal and Interdisciplinary Perspectives. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2025, 15, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, P.; Madhesh, C.; Mathew, A.; Shekar, P.R. Machine learning and deep learning-based landslide susceptibility mapping using geospatial techniques in Wayanad, Kerala state, India. HydroResearch 2025, 8, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilogallo, A.; Scorza, F.; Murgante, B. Ecosystem Services-Based City Ranking in Italy: A Tool to Enhance Sustainable Thinking in Regeneration Strategies. Land 2024, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, M.L.; Cavallero, L.; Easdale, M.; Tittonell, P.; López, D.R. Mapping Ecosystem Conservation Priority Based on Social Assessment, a Tool to Assist Land Use Planning. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 754–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, M.; Samuel, H.; Sunday, E.; Etim, E. Sustainable Smart Urban Form: Integration of Green Spaces and Ecosystem Services in Developing Cities of Nigeria. J. Eng. Ind. Res. 2025, 6, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenDor, T.; Danielle, S.; Woodruff, S.; Olander, L. A research agenda for ecosystem services in American environmental and land use planning. Cities 2017, 60, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.P.; Oscar, M.N. Land-use planning based on ecosystem service assessment: A case study in the Southeast Pampas of Argentina. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 154, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effiong, C. Climate justice in land use planning: Exploring the potential and challenges of nature-based solutions integration in Nigeria. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.; Bond, A. A Nature-based Solutions Framework for Embedding Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation into Urban Land Use Plans through Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA). Environ. Manag. 2024, 75, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Division on Earth and Lift Studies; Board on Earth Sciences and Resources; Committee on Challenges and Opportunities in Earth Surfaces Processes. Landscapes on the Edge: New Horizons for Research on Earth’s Surface; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Corenblit, D.; Steiger, J. Vegetation as a major conductor of geomorphic changes on the Earth surface: Toward evolutionary geomorphology. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, P.; Rodríguez, J. 2.14 Modelling Ecogeomorphic Systems. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saco, P.M.; Willgoose, G.R.; Hancock, G.R. Eco-geomorphology of banded vegetation patterns in arid and semi-arid regions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istanbulluoglu, E.; Yetemen, O.; Vivoni, E.; Gutiérrez-Jurado, H.; Bras, R. Eco-geomorphic implications of hillslope aspect: Inferences from analysis of landscape morphology in central New Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinchum, B.; Hagan, D.; Harman, C. Exploring the connection between critical zone structure and tree distribution in a semiarid eroding landscape with shallow seismic refraction. Vadose Zone J. 2025, 24, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Fierer, N.; Gabor, R.; Barnard, H.; Anderson, R.; Hoffman, B.; McKnight, D. Ecogeomorphology: Impressions of organisms in critical zone evolution. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. EP33C–08. [Google Scholar]
- Hensel, M.U. Geomorphic Tectonics. Technol.|Archit. + Des. 2023, 7, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente-Sotomayor, F.; Egas, A.; Teller, J. Land policies for landslide risk reduction in Andean cities. Habitat Int. 2021, 107, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.E.; Sasahara, K. Engineering Measures for Landslide Disaster Mitigation. In Landslides—Disaster Risk Reduction; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 609–631. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Ye, Y.; Su, D.; Yi, S.; Yang, R.; Haase, D.; Lausch, A. Adaptive ranking of specific tree species for targeted green infrastructure intervention in response to urban hazards. Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 107, 128776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, J.-E.; Allen, T.; Saitgalina, M.; Whytlaw, J.L.; Behr, J.; Anuar, K.A.; Hutton, N.; Nwandu-Vincent, O. Considering Equity in Green Infrastructure Using an Integrative Planning Framework for Green Infrastructure Implementation. Public Work. Manag. Policy 2025, 30, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Welden, N.A.; Renaud, F.G. Ecosystem-based adaptation strategies to multi-hazard risk reduction and policy implications in the Pearl River and Yangtze River deltas, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2025, 116, 105053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabral, A.; Ghosh, K.; Chatterjee, R.; Shaw, R. Progress in Ecosystem-Based Approach for Disaster Risk Reduction Over the Last 20 Years. In Two Decades from the Indian Ocean Tsunami: Key Challenges and Advancements; Shaw, R., Izumi, T., Djalante, R., Imamura, F., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Malecha Matthew, L.; Woodruff Sierra, C.; Berke Philip, R. Planning to Exacerbate Flooding: Evaluating a Houston, Texas, Network of Plans in Place during Hurricane Harvey Using a Plan Integration for Resilience Scorecard. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2021, 22, 04021030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Focus on landslide hazards | Did not focus on landslide hazards |
| Focus on ecology and geomorphology related Empirical studies Focus on land-use planning | Did not focus on ecology and not geomorphology related Literature reviews, commentaries, or meta-analysis Did not focus on land-use planning |
| Evidence of Ecogeomorphological Factor in Relation to Land Use | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Articles | Ecological | Hydrological | Geomorphological |
| First Cluster | |||
| Keller, E. et al. [67] | - | - | Topographic roughness |
| Zamora, N. J. [68] | - | Drainage | Relief |
| Bozicek, B. and Koren, E. [69] | - | Steam erosion | Surface weathering |
| Oppikofer, T. et al. [70] | - | - | Slope failures |
| Bruschi, V. M. et al. [71] | - | - | Sedimentation rate |
| Sanders, M. H. [72] | - | River morphology | Soil texture |
| Coutinho, R. et al. [73] | - | - | Geological characterisation |
| Restrepo, C. et al. [74] | Deforestation | - | Geological substrates |
| Capolongo, D. et al. [75] | - | - | Soil erosion |
| Second Cluster | |||
| Rahaman, A. et al. [76] | Elevation | Rainfall distribution | Slope direction |
| Gyeltshen, S. et al. [77] | Vegetation index | River distance | Lithological units |
| Azarafza, M. et al. [78] | - | - | Topographic contours |
| Popescu, M. E. and Trandafir, A. C. [79] | - | - | Tectonic uplift |
| Sandric, I. and Chitu, Z. [80] | Natural vegetation | Rainfall threshold | - |
| Third Cluster | |||
| Xin, Z. et al. [81] | Fractional vegetation cover | Annual rainfall | - |
| Thanveer, C. T. A. et al. [82] | Lineament density | Drainage density | Soil texture |
| Prawiradisastra, F. et al. [83] | - | Waterflow accumulation | Lithology thickness |
| Quiquerez, A. et al. [84] | Vegetation communities | Lacustrine sedimentation | - |
| Wilopo, W. et al. [85] | - | Seepages water | Geological structure |
| Peruccacci, S. et al. [86] | - | Cumulated rainfall | - |
| Fourth Cluster | |||
| Thapa, P. S. et al. [87] | - | Displacement, Soil moisture | - |
| Audisio, C. et al. [88] | Vegetation cover | Rainfall characteristics | - |
| Magliulo, P. et al. [89] | - | - | Slope angle |
| Fifth Cluster | |||
| Wood, J. L. et al. [90] | - | - | Topographies |
| Borrelli, L. et al. [91] | Elevation | Rainfall events | Soil erosion |
| Categorisation of LUP Approaches in Landslide-Related Studies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disaster Phases | Articles | Policy and Regulatory Framework | Statistics and Risk Modelling | Zoning and Land Classification | Ecosystem-Based Solution |
| Pre- Disaster | Rahaman, A. et al. [76] | - | yes | yes | - |
| Gyeltshen, S. et al. [77] | - | yes | yes | - | |
| Xin, Z. et al. [81] | - | yes | yes | - | |
| Thapa, P. S. et al. [87] | yes | - | - | yes | |
| Thanveer, C. T. A. et al. [82] | yes | - | yes | - | |
| Prawiradisastra, F. et al. [83] | yes | - | - | yes | |
| Keller, E. et al. [67] | yes | - | - | yes | |
| Azarafza, M. et al. [78] | yes | yes | - | - | |
| Bozicek, B. and Koren, E. [69] | - | - | yes | yes | |
| Audisio, C. et al. [88] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Wood, J. L. et al. [90] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Oppikofer, T. et al. [70] | yes | - | - | - | |
| Popescu, M. E. and Trandafir, A. C. [79] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Sanders, M. H. [72] | - | yes | - | yes | |
| Sandric, I. and Chitu, Z. [80] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Capolongo, D. et al. [75] | - | yes | - | - | |
| During Disaster | Zamora, N. J. [68] | - | yes | - | - |
| Peruccacci, S. et al. [86] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Borrelli, L. et al. [91] | - | - | yes | - | |
| Restrepo, C. et al. [74] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Post- Disaster | Quiquerez, A. et al. [84] | yes | - | yes | yes |
| Wilopo, W. et al. [85] | yes | yes | - | - | |
| Bruschi, V. M. et al. [71] | - | yes | - | - | |
| Coutinho, R. et al. [73] | - | - | yes | yes | |
| Magliulo, P. et al. [89] | yes | - | yes | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Tyc, J.; Hensel, M. An Ecogeomorphological Approach to Land-Use Planning and Natural Hazard Risk Mitigation: A Literature Review. Land 2025, 14, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091911
Zhang Z, Tyc J, Hensel M. An Ecogeomorphological Approach to Land-Use Planning and Natural Hazard Risk Mitigation: A Literature Review. Land. 2025; 14(9):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091911
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiyi, Jakub Tyc, and Michael Hensel. 2025. "An Ecogeomorphological Approach to Land-Use Planning and Natural Hazard Risk Mitigation: A Literature Review" Land 14, no. 9: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091911
APA StyleZhang, Z., Tyc, J., & Hensel, M. (2025). An Ecogeomorphological Approach to Land-Use Planning and Natural Hazard Risk Mitigation: A Literature Review. Land, 14(9), 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091911








