The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework on the Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions
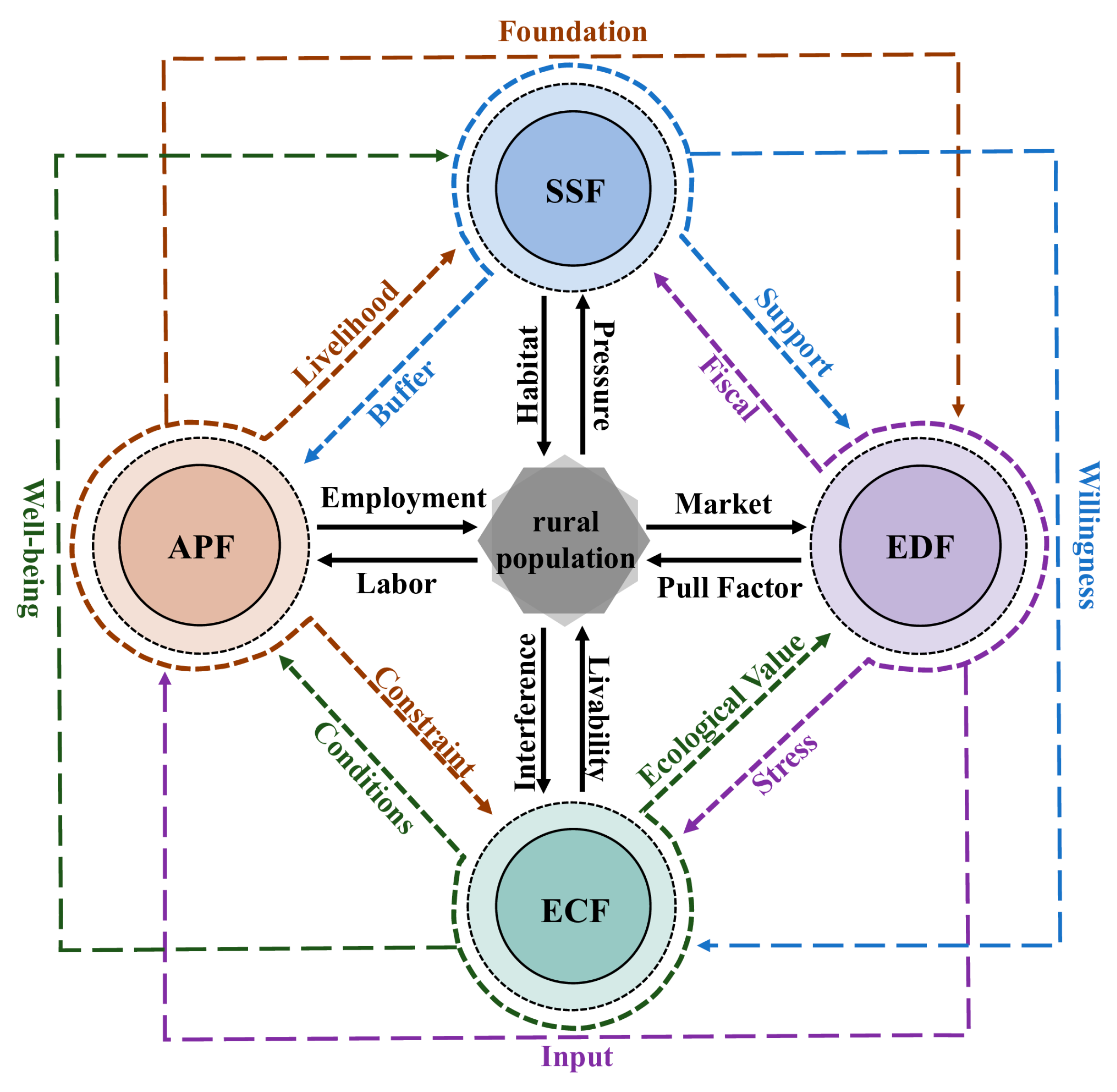
2.1. The Impact Path of Rural Population Decline on Rural Functions
2.2. Interactions Between Changes in Rural Functions
3. Materials and Methods
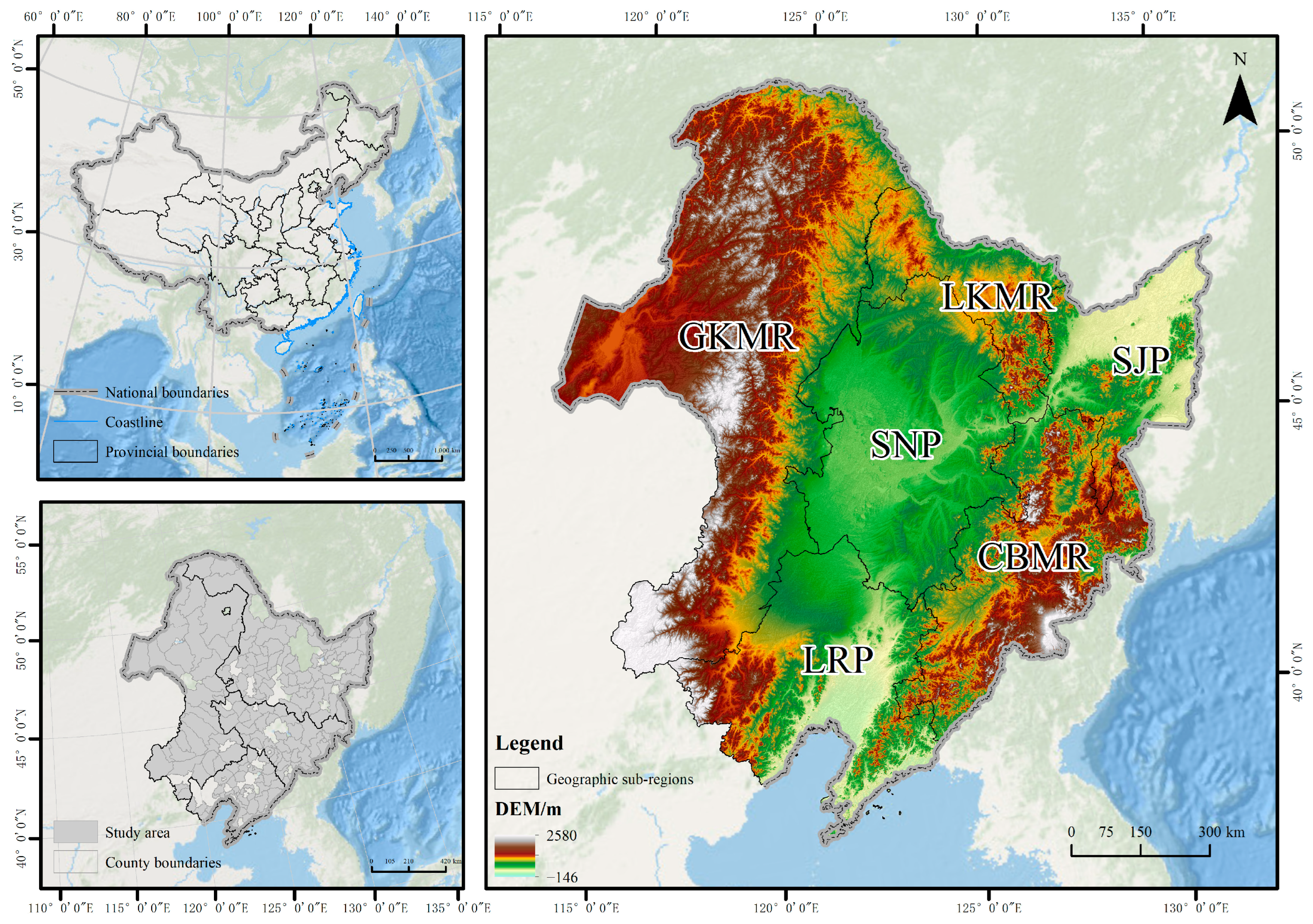
3.1. Overview of the Study Area and Data Sources
3.1.1. Overview of the Study Area
3.1.2. Data Sources
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Identification of the Extent and Types of Rural Population Shrinkage
3.2.2. Construction of Rural Function Evaluation Index System and Weight Calculation
3.2.3. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation
3.2.4. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression
4. Results
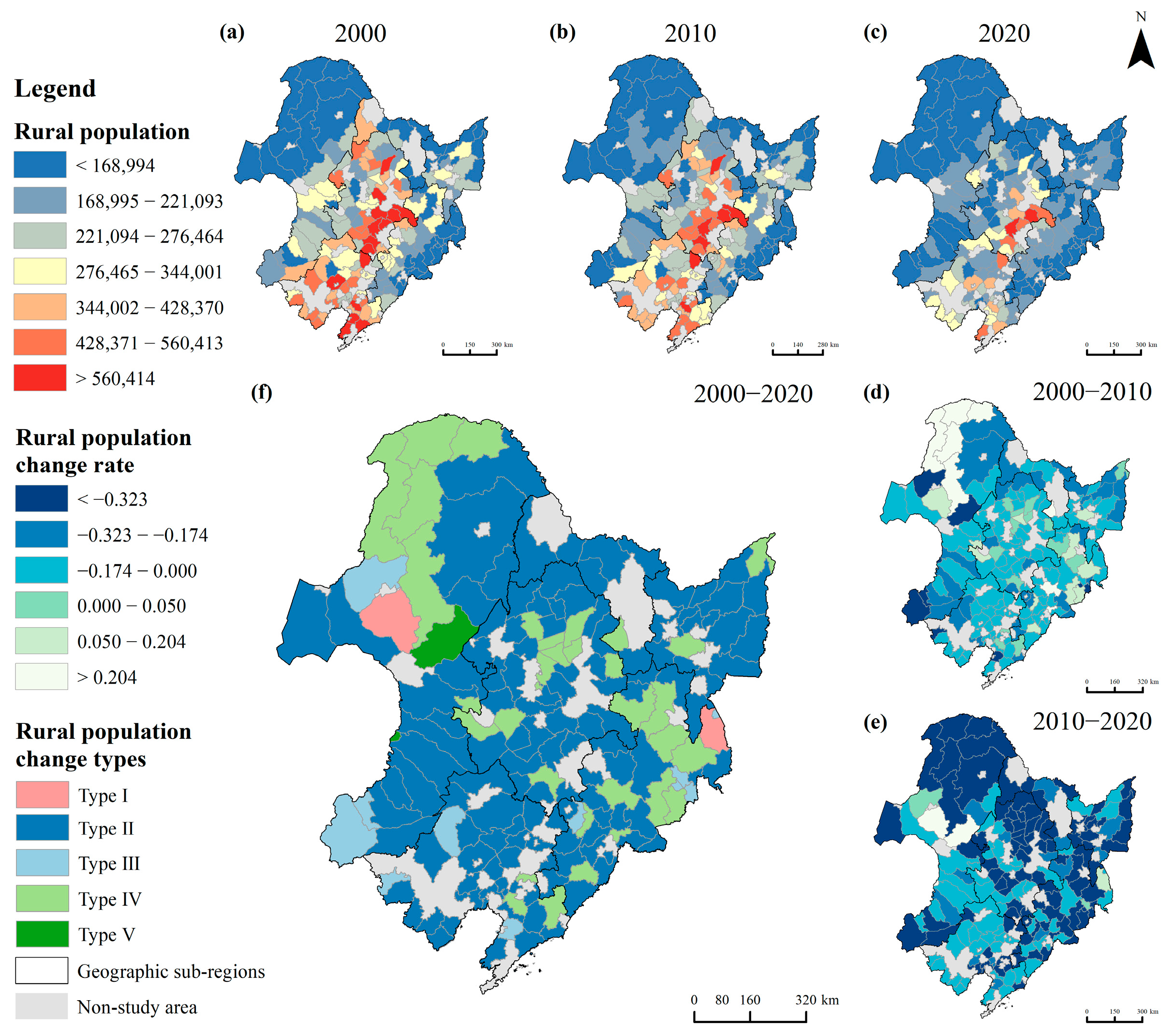
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Population Decline and Rural Functions in Northeast China
4.1.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Rural Population Shrinkage
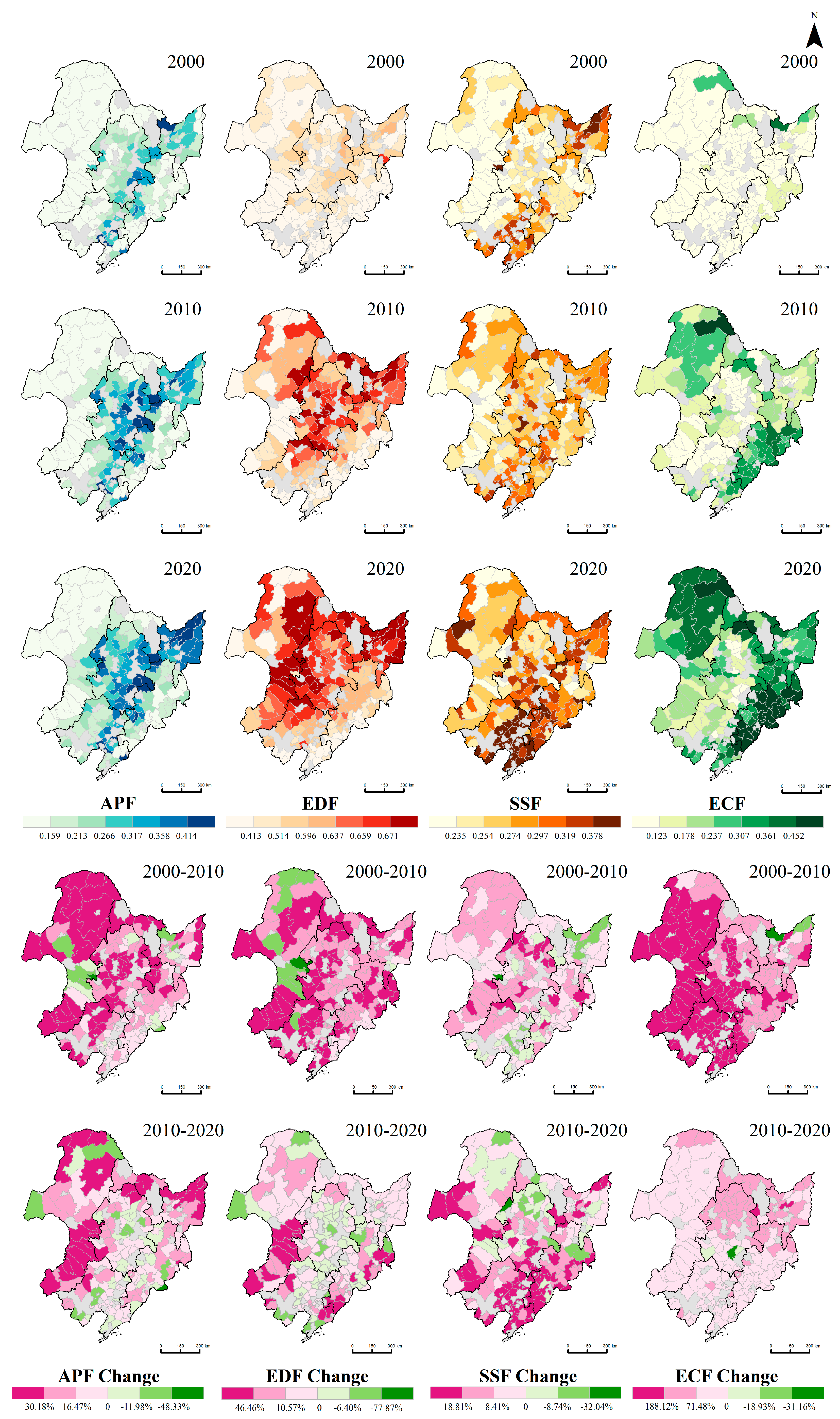
4.1.2. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Rural Functions Evolution
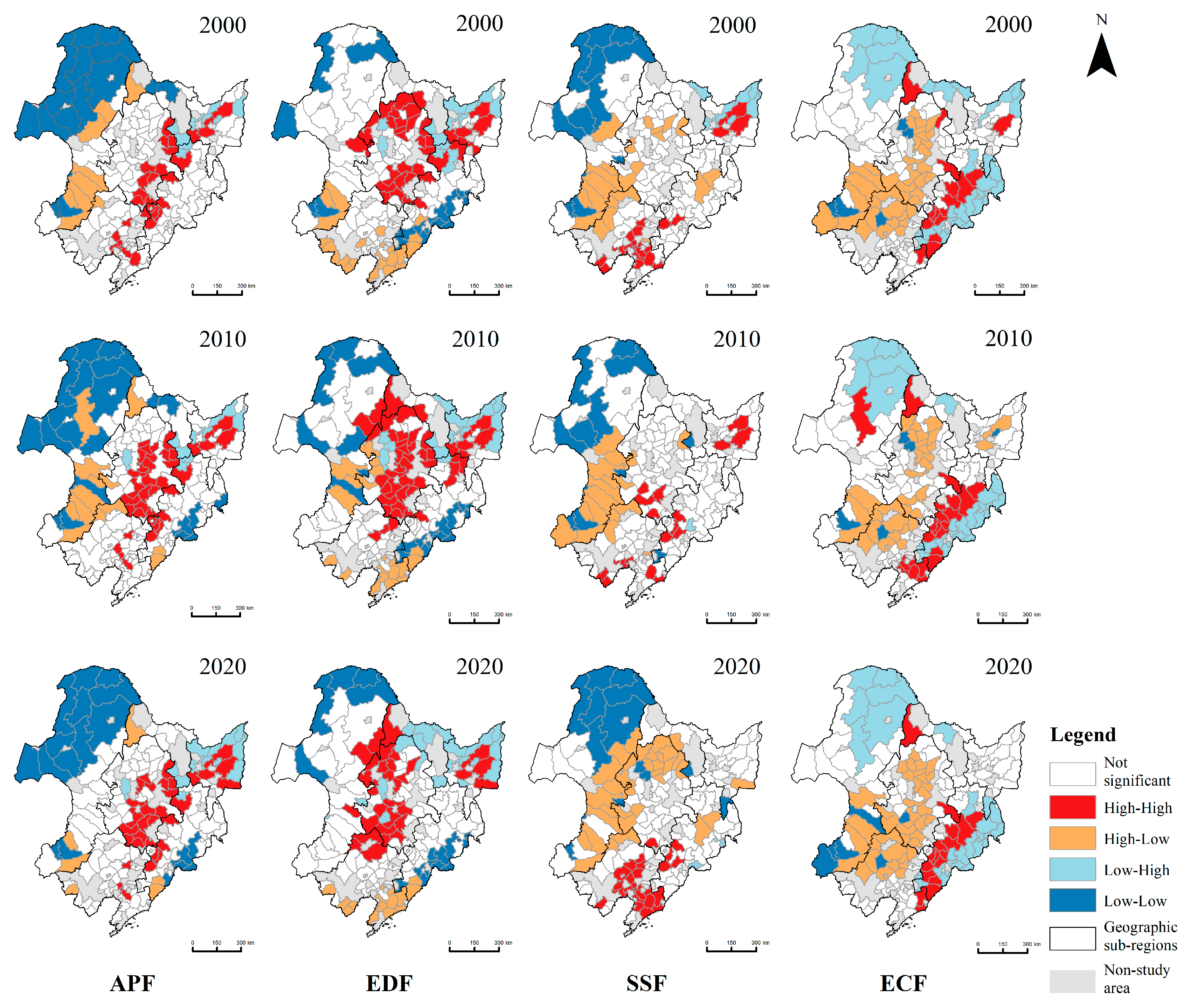
4.2. Spatial Correlation Between Rural Population and Rural Functions
4.3. GTWR Results Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions
5.2. Policy Recommendations
5.3. Research Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Woods, M.; Fois, F. Rural Decline or Restructuring? Implications for Sustainability Transitions in Rural China. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.M.; Lichter, D.T. Rural Depopulation: Growth and Decline Processes over the Past Century. Rural Sociol. 2019, 84, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dax, T.; Fischer, M. An Alternative Policy Approach to Rural Development in Regions Facing Population Decline. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2018, 26, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Lee, I.; Gkartzios, M. Overview of Social Policies for Town and Village Development in Response to Rural Shrinkage in East Asia: The Cases of Japan, South Korea and China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero, L.; Oliva, J. Thinking in Rural Gap: Mobility and Social Inequalities. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Long, H. The Economic and Environmental Effects of Land Use Transitions under Rapid Urbanization and the Implications for Land Use Management. Habitat Int. 2018, 82, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, T.; Qu, Y. Do Decaying Rural Communities Have an Incentive to Maintain Large-Scale Farming? A Comparative Analysis of Farming Systems for Peri-Urban Agriculture in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, F. Coupling Relationship between Agricultural Labor and Agricultural Production Against the Background of Rural Shrinkage: A Case Study of Songnen Plain, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y. Influences of population pressure change on vegetation greenness in China’s mountainous areas. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 9041–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission of the European Communities. The Future of Rural Society; Commission of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J. Impulses towards a Multifunctional Transition in Rural Australia: Gaps in the Research Agenda. J. Rural Stud. 2006, 22, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Territorial Multi-functionality Evaluation and Decision-making Mechanism at County Scale in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, G.; Ma, W.; Wu, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, T. Understanding the Relationship between Population–Land–Industry Element Inputs and Function Outputs of Rural Settlement: An Efficiency-Based Perspective. Habitat Int. 2025, 159, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, K. Influence of the Variation in Rural Population on Farmland Preservation in the Rapid Urbanization Area of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Empirical Examinations of Whether Rural Population Decline Improves the Rural Eco-Environmental Quality in a Chinese Context. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.; Plămădeală, O. Trends And Opportunities For The Young Human Factor In The Context Of International Migration Of The Workforce. In Proceedings of the Eurint International Conference, Iasi, Romania, 24–25 May 2024; pp. 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ștîrba, V.; Stratan, A.; Lucașenco, E. Migration, Remittances, And Local Development In Moldova. Econ. Sociol. 2023, 2, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Sorando, R.; Álvarez-Farizo, B.; Castellano, C.; Céspedes, V.; Gallardo, B.; Jiménez, J.J.; López, M.V.; López-Flores, R.; Moret-Fernández, D.; et al. Depopulation Impacts on Ecosystem Services in Mediterranean Rural Areas. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 52, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiviaho, A.; Einolander, J. Digital Transformation, Well-Being and Shrinking Communities: Narrowing the Divides between Urban and Rural. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wen, Q.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, P. Trade-off and Synergy of Rural Functions Under County Depopulation in the Typical Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wen, Q.; Qi, Y.; Du, G. Revealing the Rural Multifunctionality Declining and Its Causes in Depopulated Regions of Northeast China: A Case Study of Heilongjiang Province. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Modern Human-Earth Relationship and Human-Earth System Science. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 40, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Li, Y.; Zong, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Fu, B. The Modeling Framework of the Coupled Human and Natural Systems in the Yellow River Basin. Geogr. Sustain. 2025, 6, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H. The Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Mechanism of Rural Spatial Shrinkage in Local County, Southeast China. Buildings 2024, 14, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Measuring the Symbiotic Development of Rural Housing and Industry: A Case Study of Fuping County in the Taihang Mountains in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, G.; Ma, W.; Dong, X. How to Address “Population Decline and Land Expansion (PDLE)” of Rural Residential Areas in the Process of Urbanization:A Comparative Regional Analysis of Human-Land Interaction in Shandong Province. Habitat Int. 2021, 117, 102441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Jia, K. Multi-Dimensional Feature Recognition and Policy Implications of Rural Human–Land Relationships in China. Land 2021, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatial Coupling Relationship Between Rural Population and Economy Under the Background of Rural Shrinkage in Songnen Plain. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Qiao, J.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Pan, T. Spatial Coupling Relationship and Driving Mechanism of Population and Economy in Rural Areas in Qinling-Daba Mountains, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Integrated Urban–Rural Development in Northeast China under the Background of Population Shrinkage. Buildings 2023, 13, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, N. County-Rural Transformation Development from Viewpoint of “Population-Land-Industry” in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region under the Background of Rapid Urbanization. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, M.; Lu, D. Revisiting the Relationship Between Urbanization and Economic Development in China Since the Reform and Opening-Up. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Dong, L.; Yu, S. Research on Spatiotemporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of County-Level Urban Shrinkage in Urbanizing China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 109, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Jin, H.; Qi, W. Rural Population Change in China: Spatial Differences, Driving Forces and Policy Implications. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 51, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; Kang, C. The Evolution of China’s Rural Depopulation Pattern and Its Influencing Factors from 2000 to 2020. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 159, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, J. Understanding Urban Shrinkage from a Regional Perspective: Case Study of Northeast China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2020, 146, 05020025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, H.; Xu, X.; Huang, L.; Gu, Q.; Liu, H. County Zoning and Optimization Paths for Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 164, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, W.; Wang, L. How should rural development be chosen? The mechanism narration of rural regional function: A case study of Gansu Province, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Demographic Shifts and Agricultural Production Efficiency in the Context of Urban-Rural Transformation: Complex Networks and Geographic Differences. Glob. Food Secur. 2025, 45, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Luo, X. The Impact of Migration on Rural Poverty and Inequality: A Case Study in China. Agric. Econ. 2010, 41, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H. Land Use Policy in China: Introduction. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. Land Transfer in Rural China: Incentives, Influencing Factors and Income Effects. Appl. Econ. 2020, 52, 5477–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Koomen, E.; Ke, X. Determinants of Farmland Abandonment on the Urban–Rural Fringe. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, G.; Turner, R. Interrogating the Meaning of a Rural Business through a Rural Capitals Framework. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, D.; Smallbone, D. Developing Entrepreneurship and Enterprise in Europe’s Peripheral Rural Areas: Some Issues Facing Policy-Makers. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2006, 14, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Cui, J. Exploring Rural Decline with the Perspective of Demographics: Case Study of Hubei, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 120, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The Allocation and Management of Critical Resources in Rural China under Restructuring: Problems and Prospects. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Rural Well-Being: Geography of Opportunities. In OECD Rural Studies; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 978-92-64-42430-2. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez García, R.; García Marín, R. Servicios básicos y territorio: Limitaciones y éxodo rural en el cuadrante Sureste de España. An. geogr. Univ. Complut. 2024, 44, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haartsen, T.; Van Wissen, L. Causes And Consequences of Regional Population Decline for Primary Schools. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. En Soc. Geogr. 2012, 103, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaanse, S. Rural Facility Decline: A Longitudinal Accessibility Analysis Questioning the Focus of Dutch Depopulation-Policy. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 121, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, L.; Batáry, P.; Carmenta, R.; Gaston, K.J.; Gordon, R.; Macinnis-Ng, C.; Mori, A.S.; Nuñez, M.; Barlow, J. Ecology and Conservation under Ageing and Declining Human Populations. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 61, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Rural Population Decline, Cultivated Land Expansion, and the Role of Land Transfers in the Farming-Pastoral Ecotone: A Case Study of Taibus, China. Land 2022, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.L.; Vaccaro, I.; Sengupta, R.; Hartter, J.; Chapman, C.A. Integrating Landscapes That Have Experienced Rural Depopulation and Ecological Homogenization into Tropical Conservation Planning. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2008, 1, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenza-Peral, A.; Pérez-Ibarra, I.; Breceda, A.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Giménez, A. Can Local Policy Options Reverse the Decline Process of Small and Marginalized Rural Areas Influenced by Global Change? Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 127, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, X. Path of Rural Sustainable Development Based on the Evolution and Interaction of Rural Functions: A Case Study of Chongqing Municipality, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, L.; Herbohn, J.; Gregorio, N.; Harrison, S. Reforestation and Smallholder Livelihoods in the Humid Tropics. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, M. Combined Effects of Multi-Land Use Decisions and Climate Change on Water-Related Ecosystem Services in Northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Sustainability of Urban Development with Population Decline in Different Policy Scenarios: A Case Study of Northeast China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. On the rural revitalization taking county territory as the basic unit. Chongqing Soc. Sci. 2019, 6, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Evolution of Regional Population Decline and Its Driving Factors at the County Level in China. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 42–51+98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, K.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X. Spatial characteristics of population shrinkage and influencing factors detected by MGWR model in Guizhou County. World Reg. Stud. 2023, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Evolution and Influencing Factors of China’s Rural Population Distribution Patterns since 1990. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Gao, S.; Liu, Y. County Town Shrinkage in China: Identification, Spatiotemporal Variations and the Heterogeneity of Influencing Factors. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 95, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Feng, Z.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, A. Declining suitability for conversion of drylands to paddy fields in Northeast China: Impact of future climate and socio-economic changes. Geogr. Sustain. 2025, 6, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Fang, Y. Rural Multi-Function Evaluation and Evolution Characteristics in Liaoning Province. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, C. Evaluation and Pattern Optimization of Rural Production Space System Function: A Case Study of Banan District, Chongqing Municipality. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, L. Multifunctional Rural Development in China: Pattern, Process and Mechanism. Habitat Int. 2022, 121, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J. Rural Geography: Multifunctional Rural Geographies—Reactionary or Radical? Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2005, 29, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakoulaki, D.; Mavrotas, G.; Papayannakis, L. Determining Objective Weights in Multiple Criteria Problems: The Critic Method. Comput. Oper. Res. 1995, 22, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-I. Developing a Bivariate Spatial Association Measure: An Integration of Pearson’s r and Moran’s I. J. Geogr. Syst. 2001, 3, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression (GTWR): Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression. Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijker, D. Marginal Lands in Europe—Causes of Decline. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2005, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim LaFrombois, M.E.; Park, Y.; Yurcaba, D. How U.S. Shrinking Cities Plan for Change: Comparing Population Projections and Planning Strategies in Depopulating U.S. Cities. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2023, 43, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hediger, W.; Knickel, K. Multifunctionality and Sustainability of Agriculture and Rural Areas: A Welfare Economics Perspective. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2009, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loras-Gimeno, D.; Díaz-Lanchas, J.; Gómez-Bengoechea, G. Rural Depopulation in the 21st Century: A Systematic Review of Policy Assessments. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2025, 17, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Patterns in Chinese Black Soil Areas Considering Ecological Importance and Vulnerability. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Functions | Indexes/Unit | Effect | Index Connotation and Calculation Method | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural production function (APF) | Land reclamation rate/% | + | Farmland area/total land area | 0.297 |
| Per unit area grain yield/(t/ha) | + | Total grain output/farmland area | 0.254 | |
| Agricultural mechanization degree/(kW·h/ha) | + | Total power of agricultural machinery/farmland area | 0.143 | |
| Paddy field ratio/% | + | Paddy field area/total cultivated land area | 0.306 | |
| Economic development function (EDF) | Grain commodity rate/% | + | (Grain output − 400 kg × permanent population)/total grain output | 0.581 |
| Per unit area agricultural output/(104 yuan RMB/ha) | + | The output value of the primary industry/total land area | 0.091 | |
| Economic structure/% | + | The sum of the output value of secondary and tertiary industries/GDP | 0.161 | |
| Financial contribution rate/% | + | Financial revenue/GDP | 0.167 | |
| Social security function (SSF) | Healthcare/per 104 person | + | Number of beds in health institutions owned by 10,000 people | 0.137 |
| Road traffic density/(km/ha) | + | Road mileage/total land area | 0.45 | |
| Per capita housing area of rural residents/ha | + | Rural Settlement Area/number of the permanent population | 0.166 | |
| Per capita farmland area/ha | + | Farmland area/number of the permanent population | 0.247 | |
| Ecological Conservation function (ECF) | Climate regulation function/(yuan/ha) | + | Per unit area ecological service, the equivalence factor method of ecological service value | 0.228 |
| Environmental purification function/(yuan/ha) | + | Per unit area ecological service, the equivalence factor method of ecological service value | 0.209 | |
| Maintaining nutrient cycling function/(yuan/ha) | + | 0.243 | ||
| Biodiversity function/(yuan/ha) | + | 0.126 | ||
| Landscape aesthetics function/(yuan/ha) | + | 0.194 |
| APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
| Moran’s I | 0.495 | 0.486 | 0.445 | 0.122 | 0.205 | 0.153 | 0.122 | 0.180 | 0.232 | −0.341 | −0.221 | −0.365 |
| Z score | 10.800 | 10.117 | 9.858 | 3.131 | 4.824 | 3.844 | 3.242 | 4.766 | 5.931 | −7.750 | −5.206 | −8.589 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| OLS | TWR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | |
| AICc | −177.805 | −61.329 | −1081.633 | 366.149 | −252.538 | −114.536 | −1171.370 | 9.348 |
| R2 | 0.507 | 0.161 | 0.200 | 0.241 | 0.591 | 0.273 | 0.356 | 0.640 |
| R2 Adjusted | 0.589 | 0.268 | 0.352 | 0.637 | ||||
| GWR | GTWR | |||||||
| APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | |
| AICc | −532.480 | −287.452 | −1331.130 | 153.944 | −555.980 | −336.568 | −1381.360 | −278.576 |
| R2 | 0.795 | 0.520 | 0.579 | 0.561 | 0.808 | 0.601 | 0.688 | 0.854 |
| R2 Adjusted | 0.794 | 0.518 | 0.576 | 0.558 | 0.806 | 0.598 | 0.686 | 0.853 |
| Variable | Year | APF | EDF | SSF | ECF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p ≤ 0.1 (%) | + | − | p ≤ 0.1 (%) | + | − | p ≤ 0.1 (%) | + | − | p ≤ 0.1 (%) | + | − | ||
| RPD | 2000 | 100.00% | 169 | 0 | 66.86% | 142 | 27 | 80.47% | 167 | 2 | 75.74% | 61 | 108 |
| 2010 | 100.00% | 169 | 0 | 76.92% | 72 | 97 | 65.09% | 159 | 10 | 92.31% | 41 | 128 | |
| 2020 | 95.86% | 166 | 3 | 98.22% | 1 | 168 | 75.74% | 162 | 7 | 86.98% | 36 | 133 | |
| 2000 | 79.29% | 57 | 112 | 88.17% | 141 | 28 | 69.23% | 18 | 151 | 71.60% | 9 | 160 | |
| 2010 | 87.57% | 94 | 75 | 100.00% | 169 | 0 | 59.17% | 48 | 121 | 73.96% | 89 | 80 | |
| 2020 | 81.07% | 102 | 67 | 100.00% | 169 | 0 | 64.50% | 31 | 138 | 43.79% | 80 | 89 | |
| RPc | 2000 | 100.00% | 0 | 169 | 66.86% | 86 | 83 | 47.34% | 18 | 151 | 69.23% | 42 | 127 |
| 2010 | 100.00% | 0 | 169 | 94.08% | 6 | 163 | 44.38% | 23 | 146 | 85.21% | 21 | 148 | |
| 2020 | 100.00% | 0 | 169 | 85.80% | 24 | 145 | 29.59% | 118 | 51 | 47.34% | 99 | 70 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; Wu, K. The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China. Land 2025, 14, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091772
Zhang Y, Dai Z, Chen Y, Li Z, Shan X, Wang X, Feng Z, Wu K. The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China. Land. 2025; 14(9):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091772
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yichi, Zihong Dai, Yirui Chen, Zihan Li, Xinyu Shan, Xinyi Wang, Zhe Feng, and Kening Wu. 2025. "The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China" Land 14, no. 9: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091772
APA StyleZhang, Y., Dai, Z., Chen, Y., Li, Z., Shan, X., Wang, X., Feng, Z., & Wu, K. (2025). The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China. Land, 14(9), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091772









