Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation in China’s Southern Hilly Area During 2000–2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
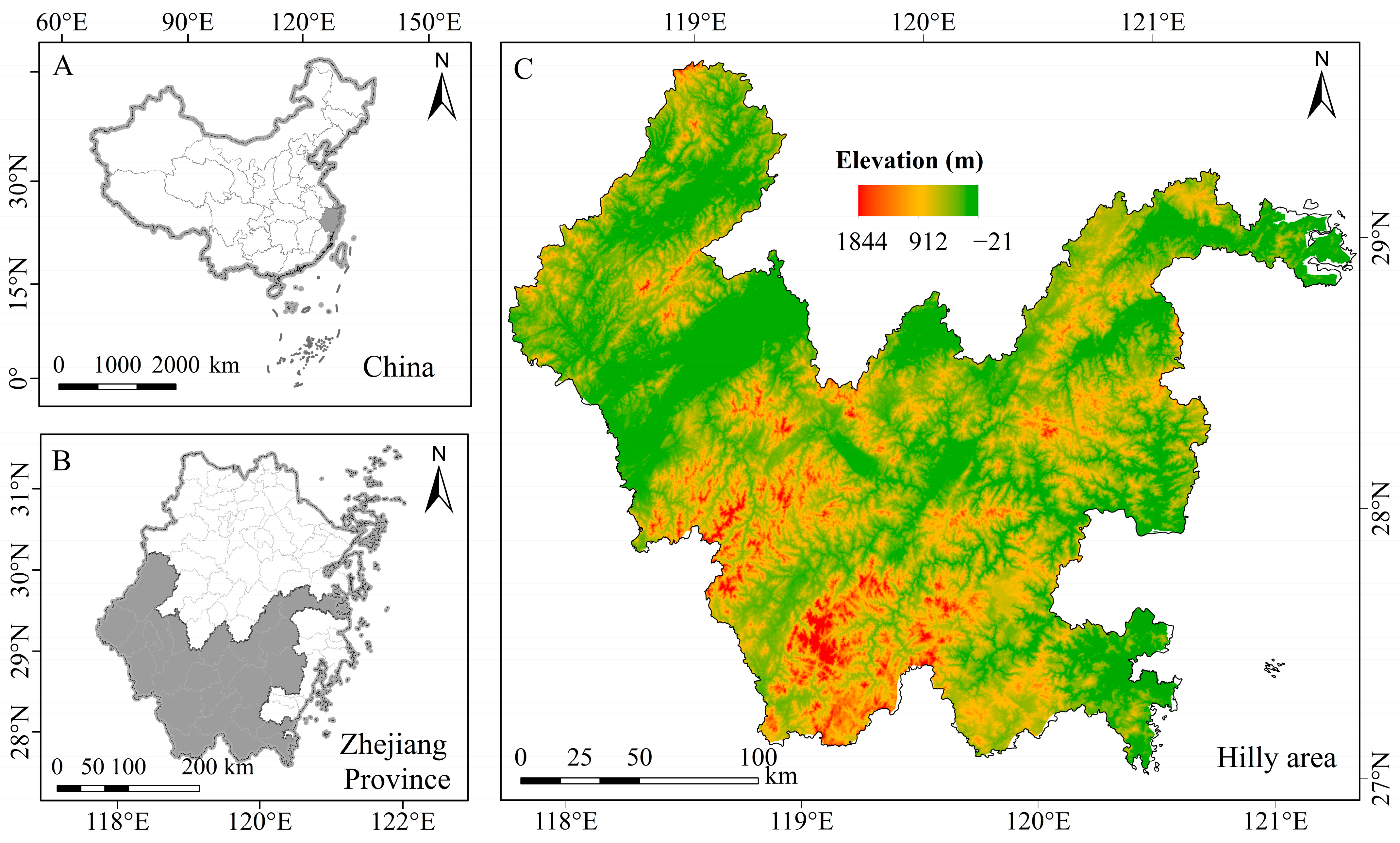
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Land Use Transformation
- (1)
- Land Use Transfer Matrix
- (2)
- Gravity Model
- (3)
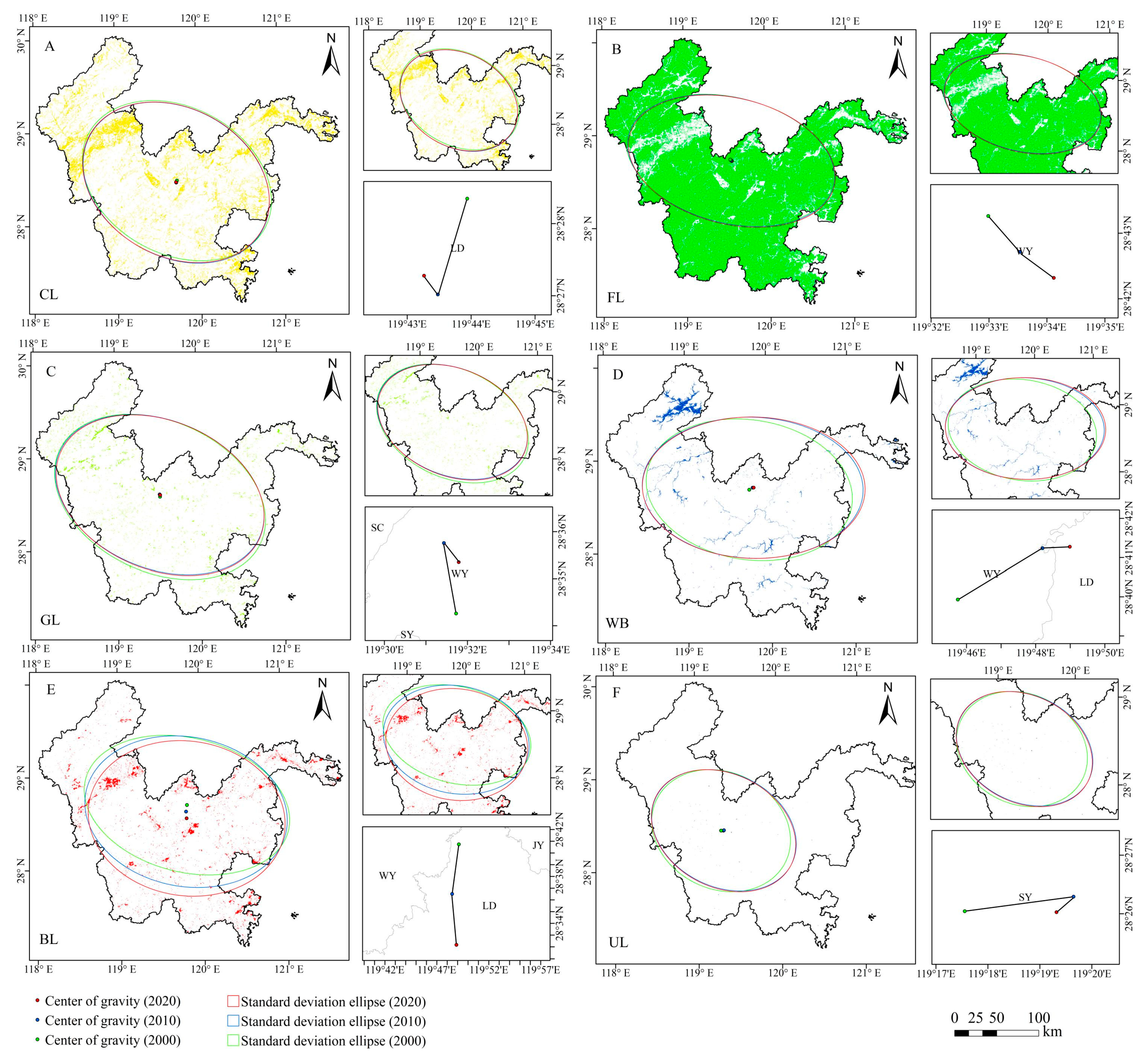
- Standard Deviational Ellipse (SDE)
2.3.2. Eco-Environmental Response
- (1)
- EEQI
- (2)
- Hot spot analysis
2.3.3. Driving Factors
- (1)
- Driving factors selection
- (2)
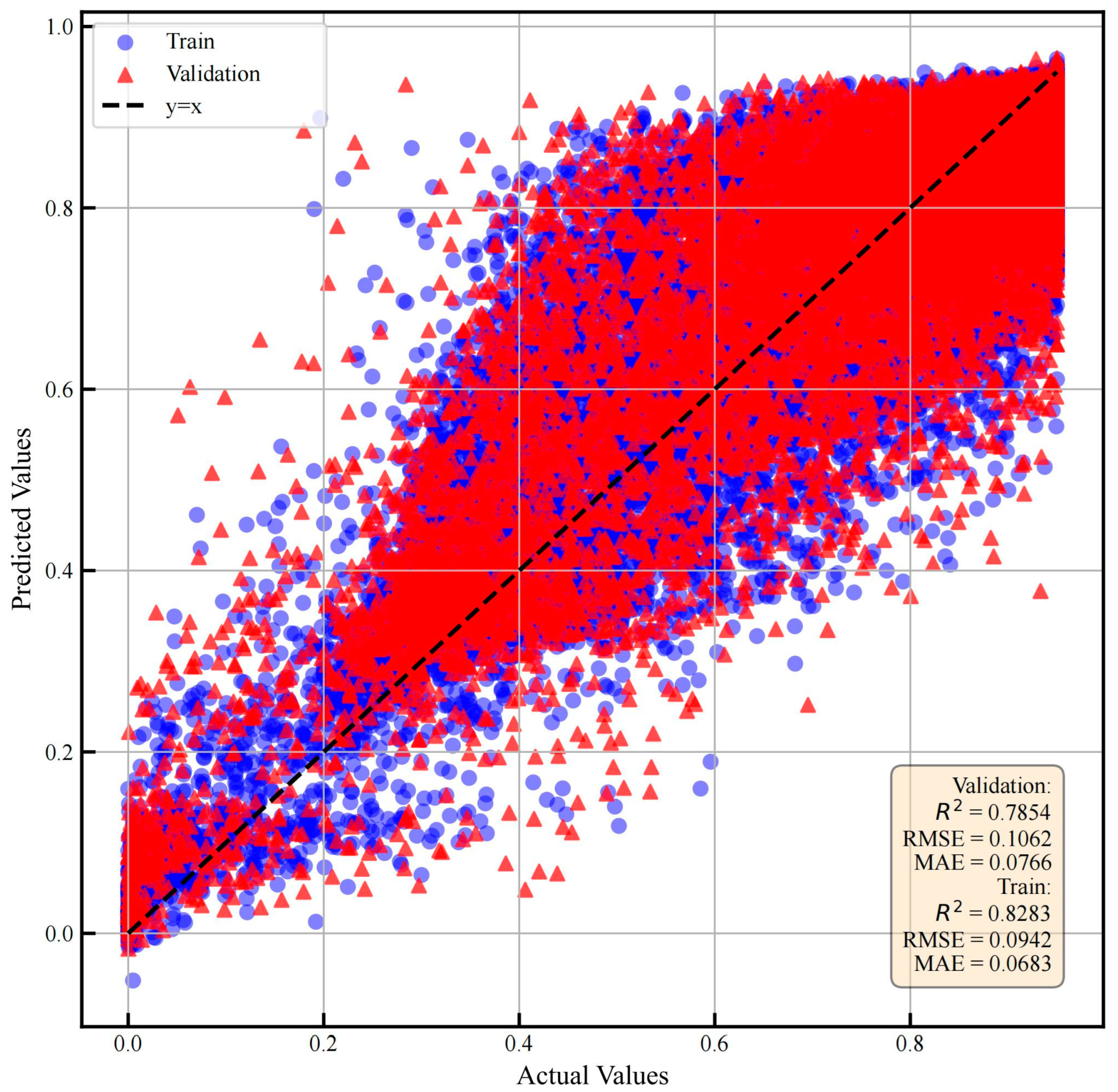
- XGBoost
- (3)
- SHAP
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Land Use Transformation
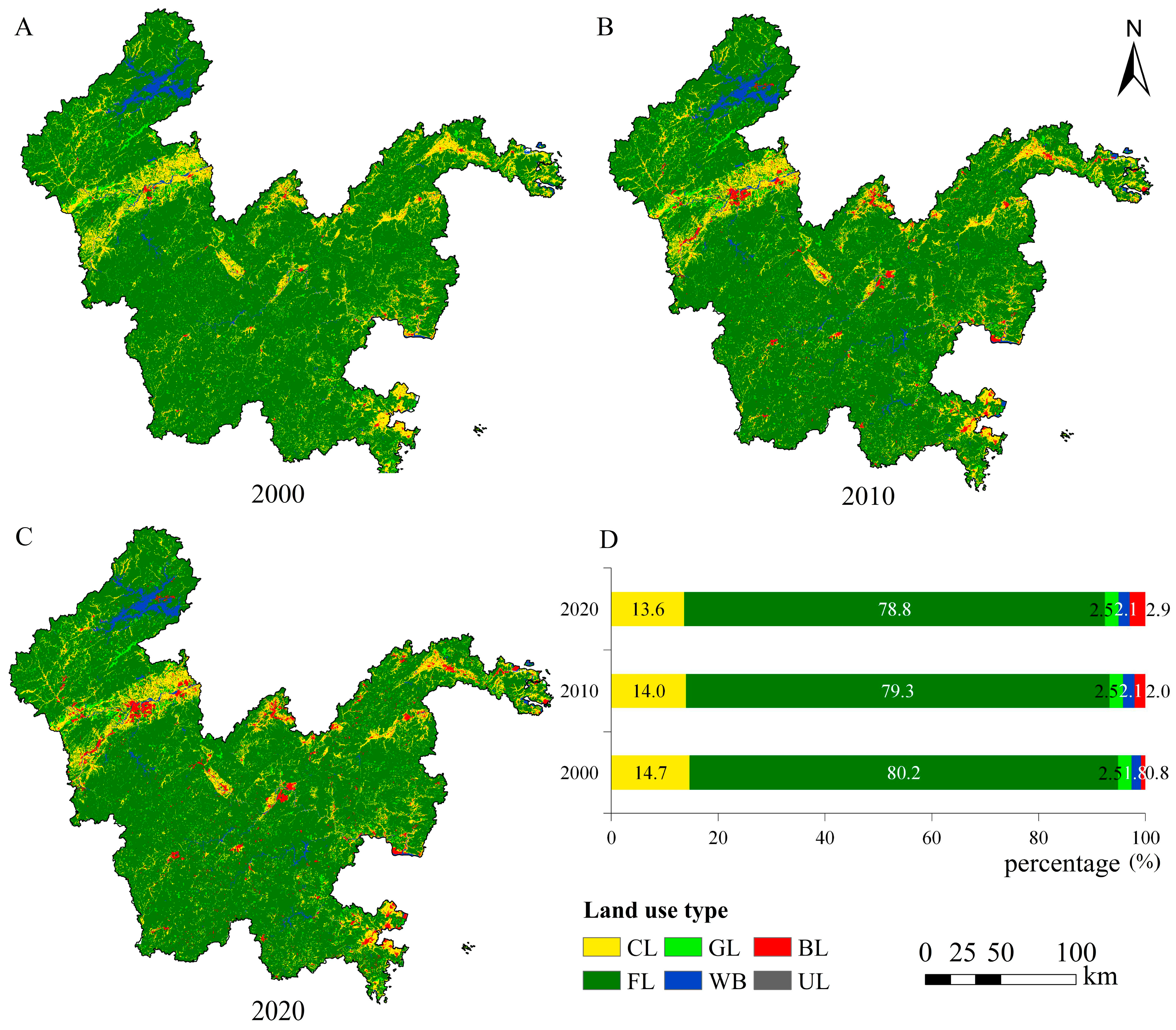
3.1.1. Changes in Land Use in Study Area
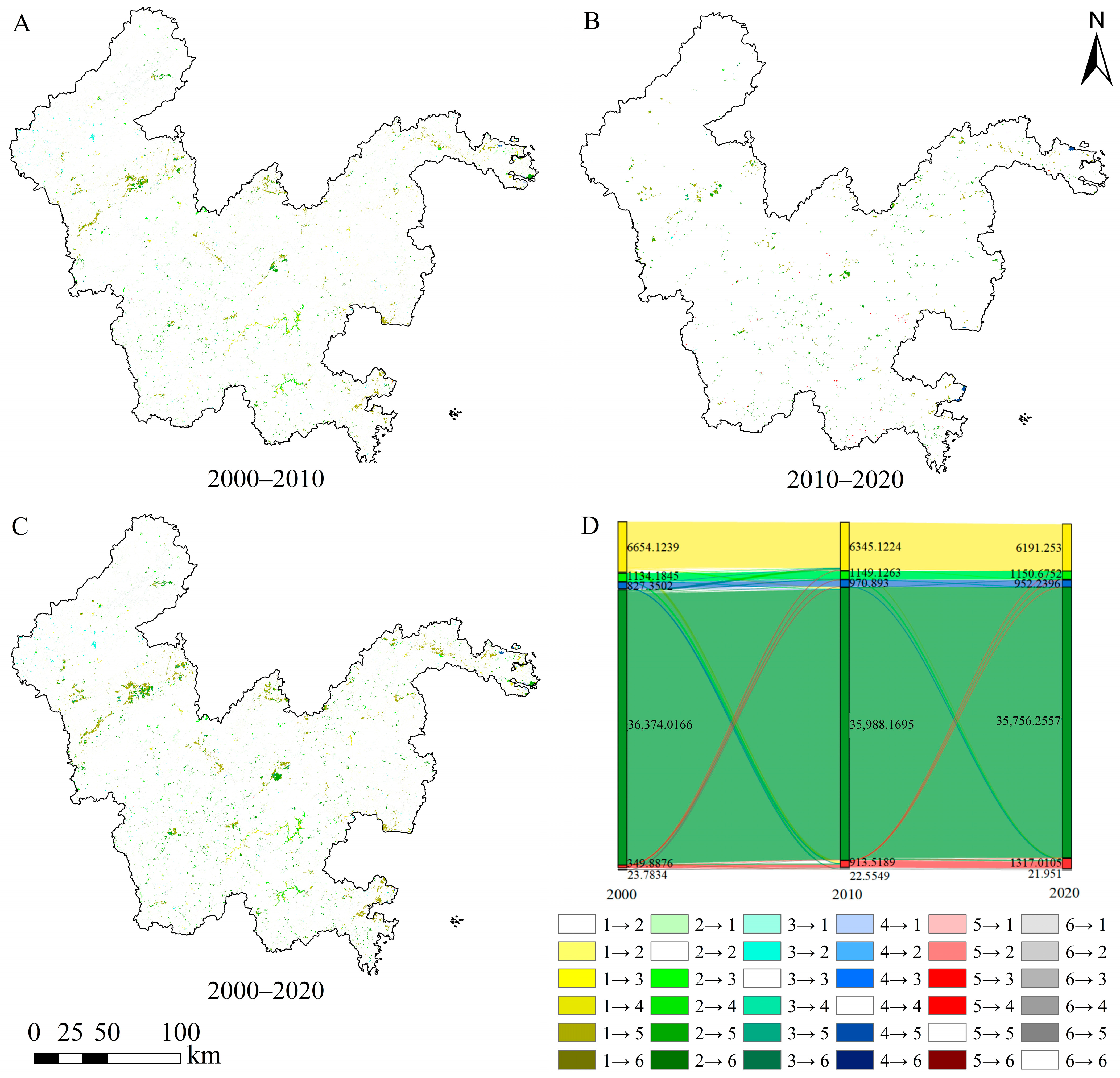
3.1.2. Characteristics of Land Use Transformation
3.2. Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation
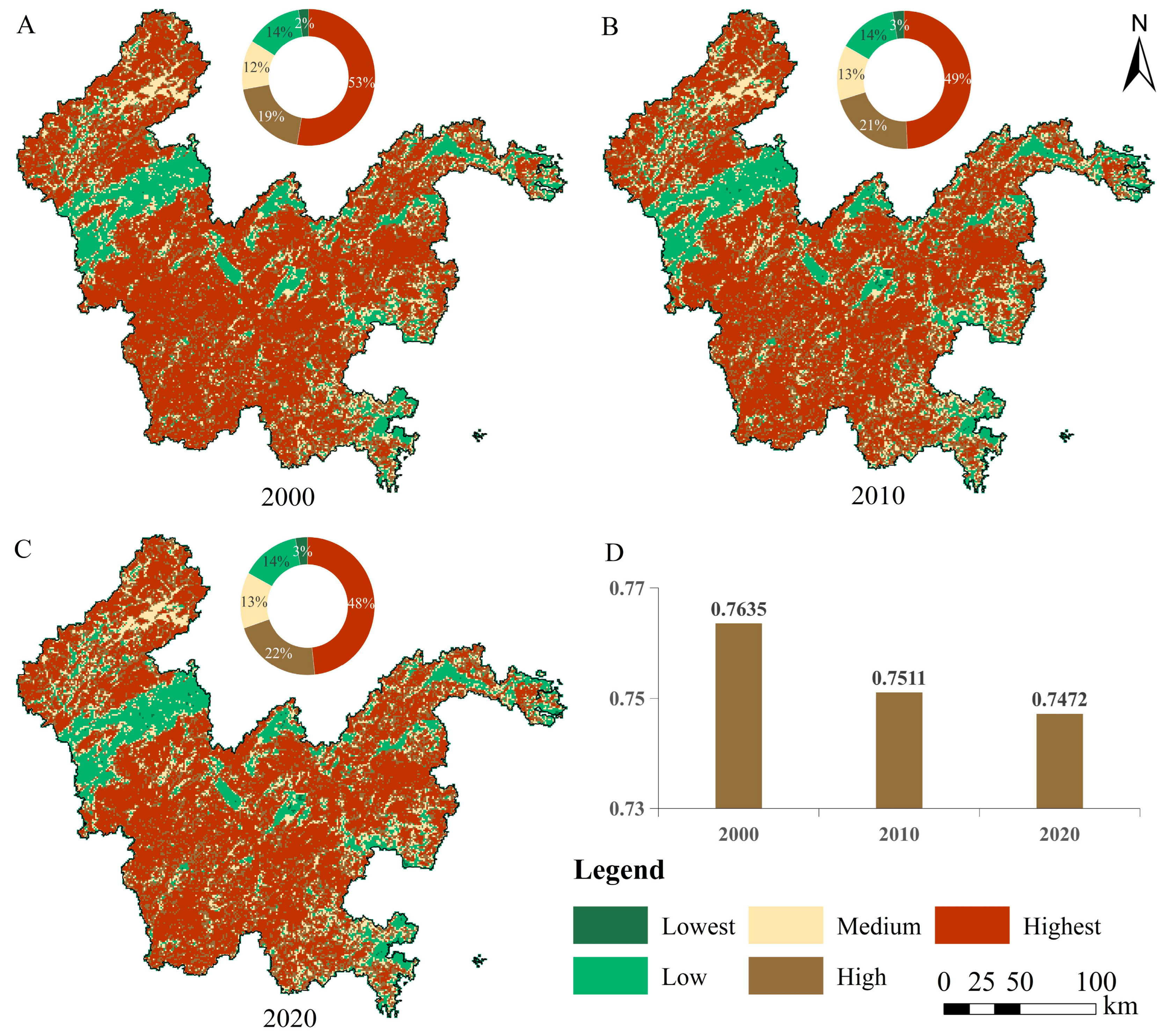
3.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of EEQI
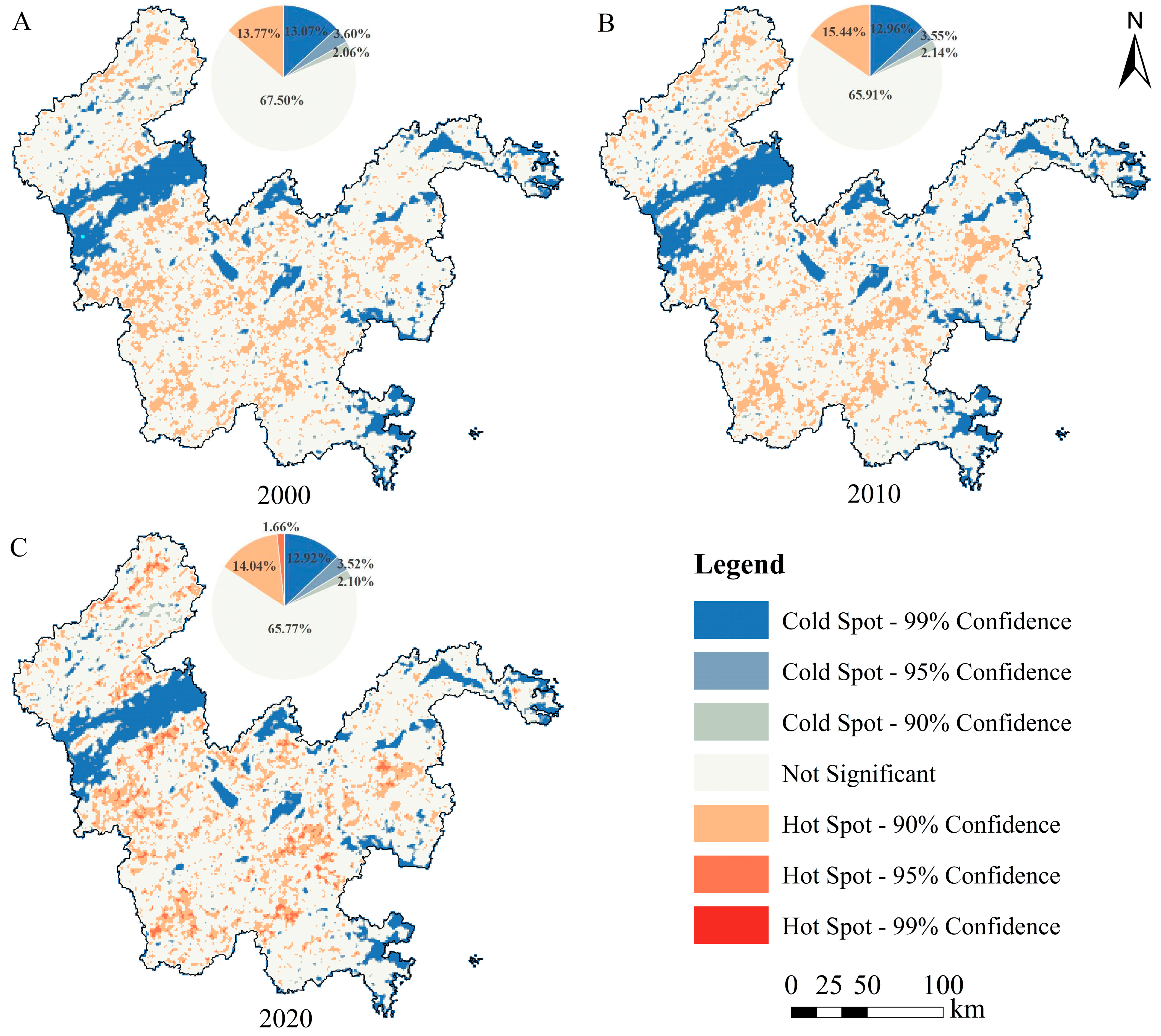
3.2.2. Hot Spots of EEQI
3.3. Driving Factors of EEQI
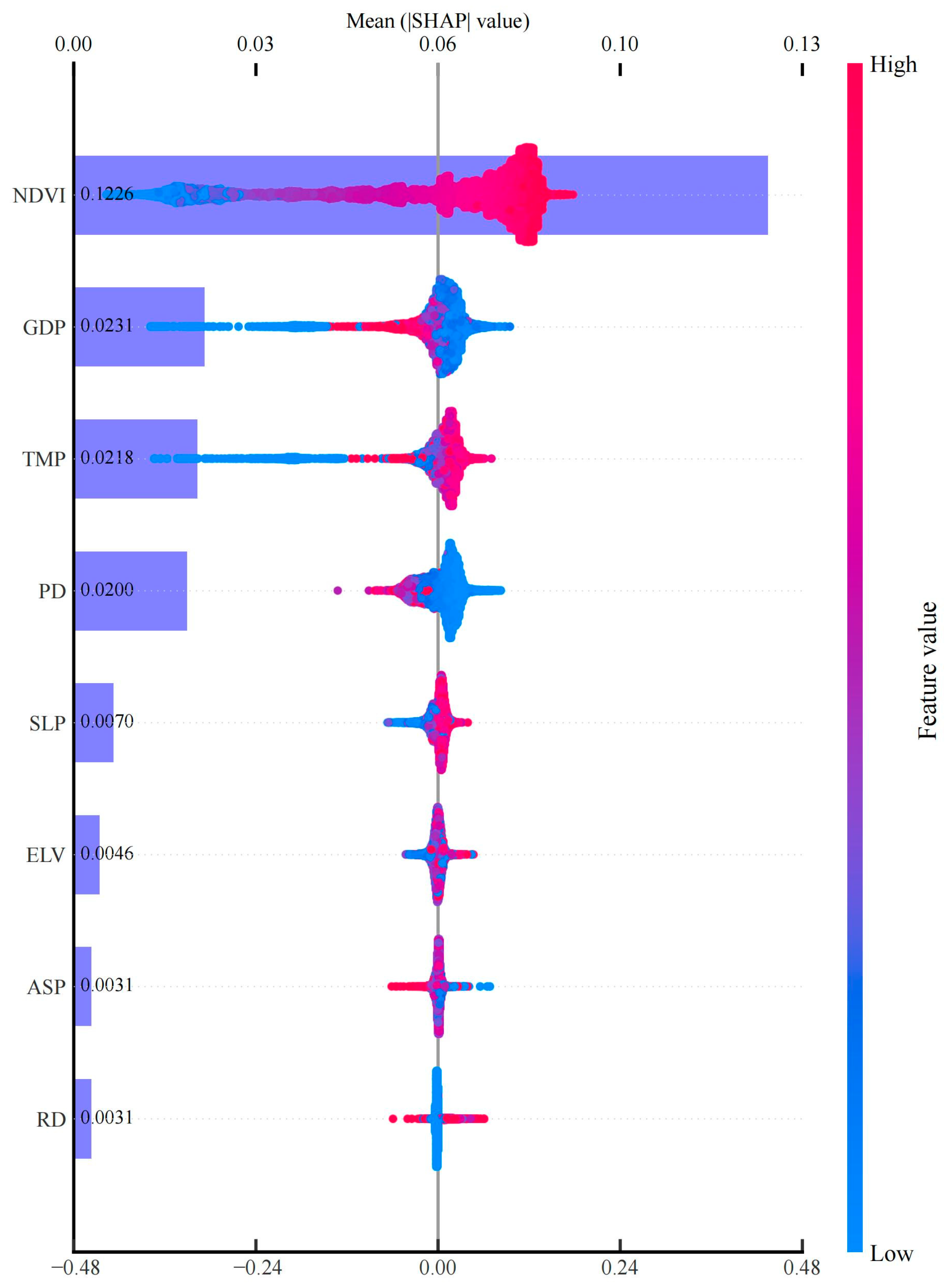
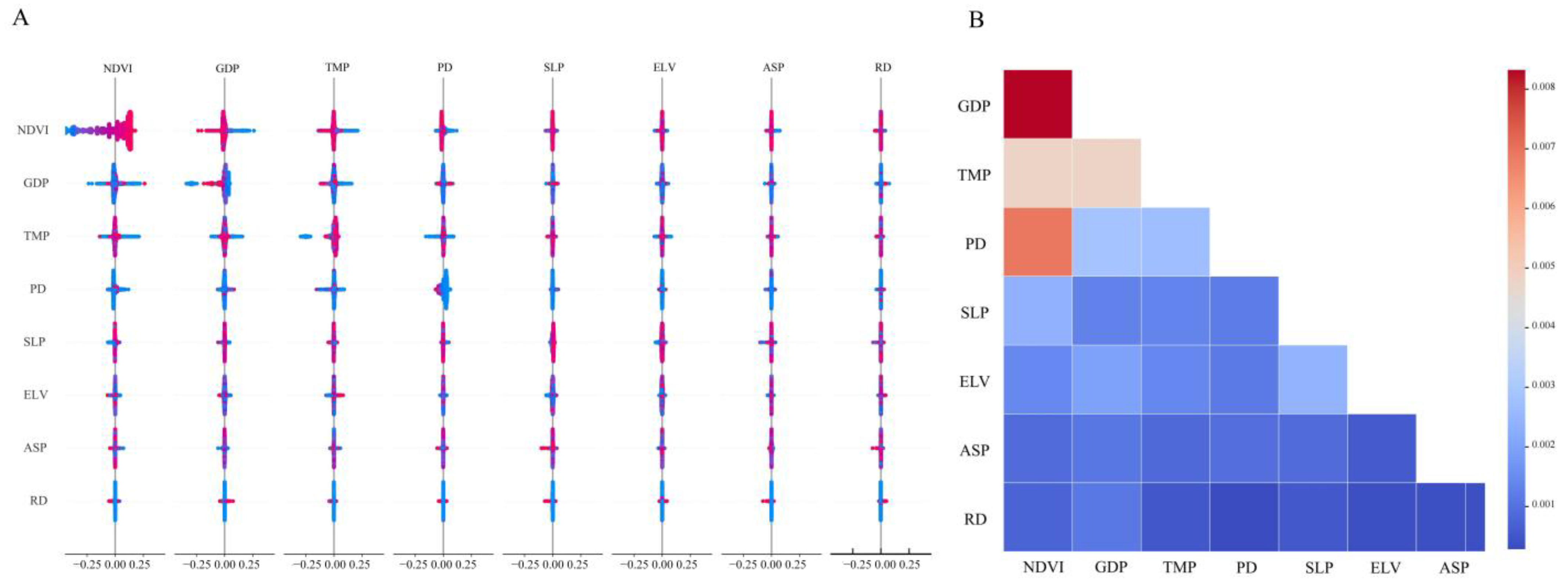
3.3.1. Relative Importance Analysis
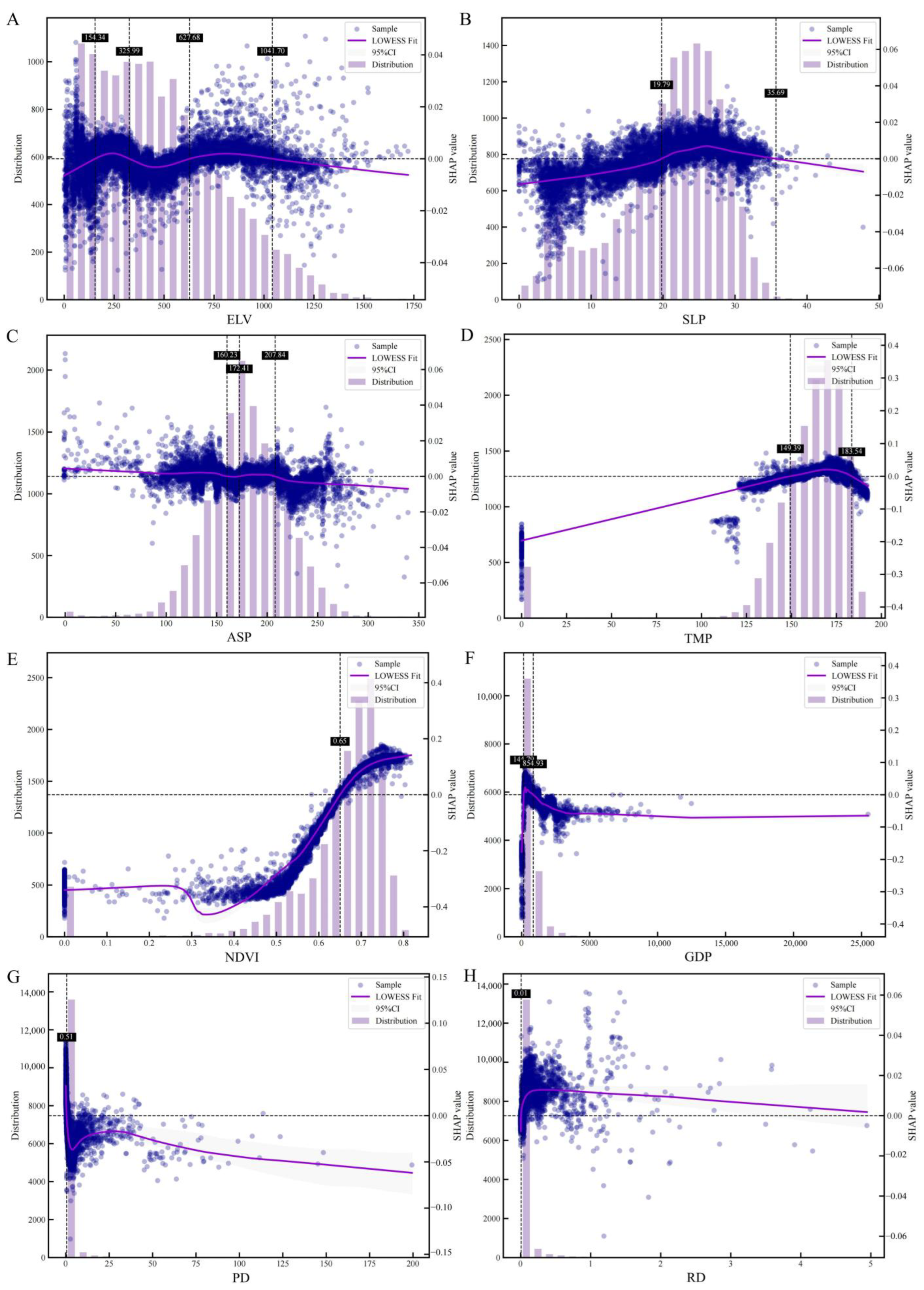
3.3.2. Partial Dependence Relationship Between Driving Factors and EEQI
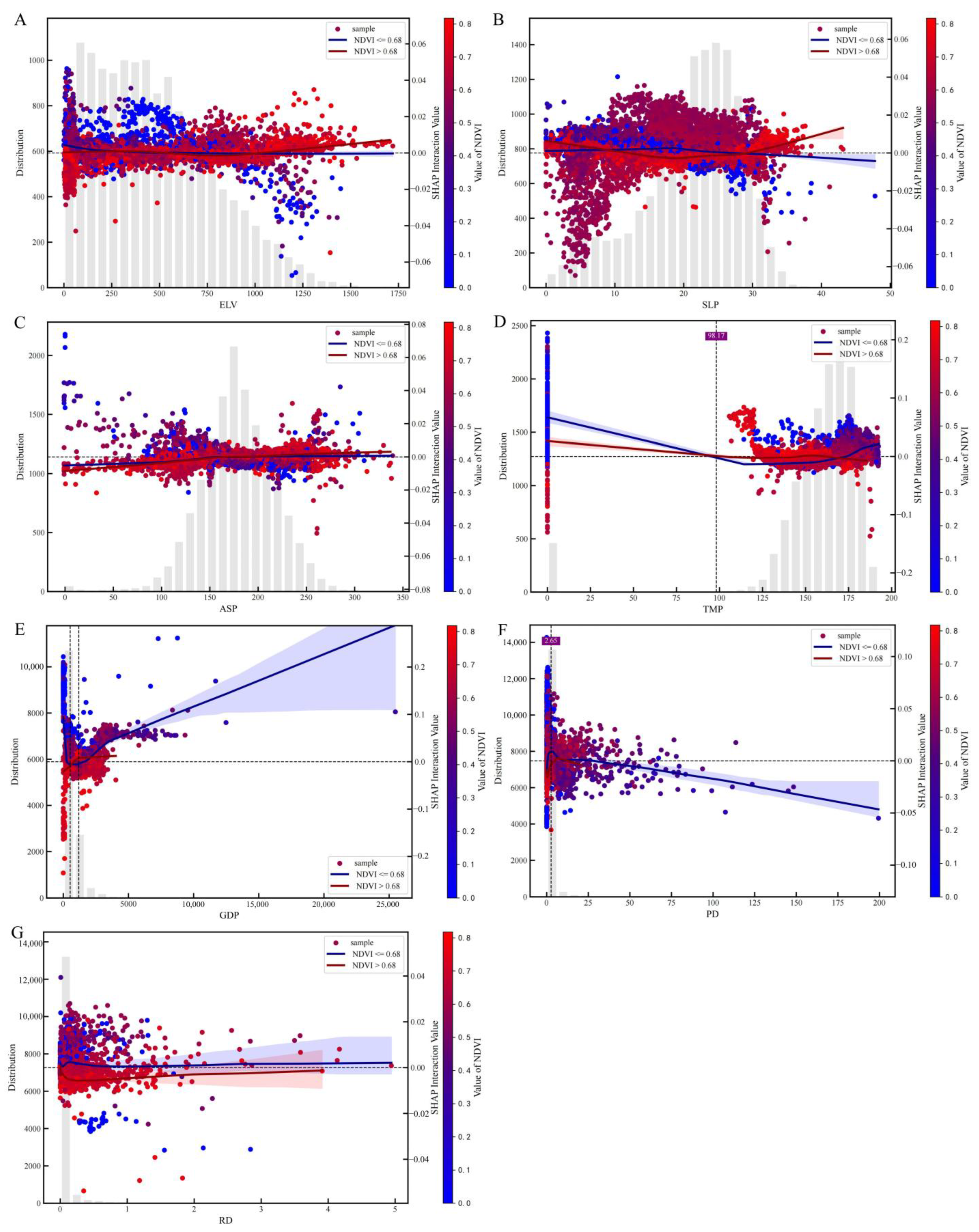
3.3.3. Interactions of Driving Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Results and Theoretical Contributions
4.2. Comparative Analysis
4.3. Policy Evolution and Phased Characteristics of EEQ Response
4.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEQ | Eco-environment quality |
| EEQI | Eco-environment quality index |
| CL | Cropland |
| FL | Forestland |
| GL | Grassland |
| WB | Water Bodies |
| BL | Built-up Land |
| UL | Unused Land |
| SDE | Standard Deviational Ellipse |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
References
- Zhou, G.; Long, H. Explanation of land-use system evolution: Modes, trends, and mechanisms. Land Use Policy 2025, 150, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Qin, X. Urbanization path: The fundamental problem of changes in land use patterns. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Zang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.Y. China’s rural revitalization and development: Theory, technology and management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1923–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Yang, G.S.; Tan, Y. Identifying ecological red lines in China’s yangtze river economic belt: A regional approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Lu, Y.; Ge, D.; Dong, P.; Gong, X.; Ma, X. The spatial pattern of agricultural ecosystem services from the production-living-ecology perspective: A case study of the huaihai economic zone, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 122, 106355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Kang, Z.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. The impact of land-use change on the ecological environment quality from the perspective of production-living-ecological space: A case study of the northern slope of tianshan mountains. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 83, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yong, Z.; Xiong, J.; Ma, G.; Li, J.; Liu, A. Spatiotemporal variation of ecological environment quality and extreme climate drivers on the qinghai-tibetan plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 2282–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, J. Land use/land cover change and its environmental effects in wuhan city. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 31, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Gari, S.R.; Newton, A.; Icely, J.D. A review of the application and evolution of the DPSIR framework with an emphasis on coastal social-ecological systems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 103, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, H.Q. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from fuzhou city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R. Spatial-temporal dynamics and drivers of ecosystem service interactions along the yellow river area in shaanxi province. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 496, 145095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2021, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Peng, J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Q. Significant trade-off for the impact of grain-for-green programme on ecosystem services in north-western yunnan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environment quality in arid areas based on the remote sensing ecological distance index: A case study of yuyang district in yulin city, China. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.H.; Li, W.Z.; Tian, L.X.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Chen, H.; Fang, X.Q.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, G.M.; Mu, X.M.; et al. Multiple afforestation programs accelerate the greenness in the ‘three north’ region of China from 1982 to 2013. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wu, W.; Tian, S.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y. Geographical feature and method factors significantly influence the reliability of ecological source information transmission at multi-scale. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Meng, R.; Li, S.; Zheng, L.; Song, M. Multi-scale matching and simulating flows of ecosystem service supply and demand in the wuhan metropolitan area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 476, 143648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Wen, C.H. Systematic coupling and multistage interactive response of the urban land use efficiency and ecological environment quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, C.C.; Shen, Y.J.; Wang, R.; Peng, J.B. Coupled mutual feedback and interaction mechanisms among the geological environment, ecological environment and human activities in the qinling mountains. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 2663–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Zhao, R.F.; Lu, H.T. Response of ecological environment quality to land use transition based on dryland oasis ecological index (DOEI) in dryland: A case study of oasis concentration area in middle heihe river, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ke, F.; Yu, J. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of rural production-living-ecological function: A case study of mountainous counties in zhejiang province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1495778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, S.W.; Yan, C.Z.; Li, R.D.; Wu, S.X.; Hu, Y.F.; Du, G.M.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. 1 km-Grid Dataset of Spatial Distribution of China’s GDP. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=33 (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2023); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Didan, K. MOD13a3 MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices Monthly l3 Global 1km SIN Grid v006; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Duan, X.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z. Land use transformation based on ecological-production-living spaces and associated eco-environment effects: A case study in the yangtze river delta. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, A. Dynamics of the eco-environmental quality in response to land use changes in rapidly urbanizing areas: A case study of wuhan, China from 2000 to 2018. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgard, J.E. The advance of population in the united states. Scribner’s Mon. 1872, 4, 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, N.; Liao, W. How do population and land urbanization affect CO2 emissions under gravity center change? A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, J.E.; Spencer, J.; Preisser, J.S.; Gesler, W.M.; Arcury, T.A. A suite of methods for representing activity space in a healthcare accessibility study. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2005, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachowicz, M.; Liu, T. Finding spatial outliers in collective mobility patterns coupled with social ties. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 30, 1806–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhou, J.; Pan, T.; Sun, Q.; Wu, M. Relationship of carbon emissions and economic growth in China’s construction industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, C.; Huang, J.; Mao, H. The urban land use transformations and associated effects on eco-environment in nothwest China arid region: A case study in hexi region, gansu province. Quat. Sci. 2003, 23, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, B.; Dai, L.; Chang, T.; Bao, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z. Land use transformation and its eco-environmental response in process of the regional development: A case study of jiangsu province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. Local spatial statistics: An overview. In Spatial Analysis: Modeling in a GIS Environment; Longley, P., Batty, M., Eds.; Geoinformation International: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 261–277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, C.; Guan, J. Spatial–temporal evolution and driving force analysis of eco-quality in urban agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Sun, W.; Li, M.Y.; Meng, L.L. Coupling coordination degree of production, living and ecological spaces and its influencing factors in the yellow river basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Qi, J.W.; Liu, P. Study on the ecological environment quality and its driving factors of the spatial transformation of production-living-ecological space in baishan city. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Cai, L. Using heteroskedasticity-consistent standard error estimators in OLS regression: An introduction and software implementation. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liao, W.; Qimuge, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Seasonal analysis of spatial and temporal variations in NDVI and its driving factors in inner mongolia during the vegetation growing season (1999–2019). Front. For. Glob. Change 2025, 8, 1555385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Zhao, G.; He, B.; Li, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. XGBoost-based method for flash flood risk assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, S.; Gong, H.; Zhang, C. Revealing the nonlinear impact of environmental regulation on ecological resilience using the XGBoost-SHAP model: Evidence from the yangtze river delta region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 514, 145700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; NIPS Foundation: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Xiong, W.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Hu, M. Investigating non-linear and synergistic effects of urban functional zone morphology on land surface temperature. Sust. Cities Soc. 2025, 130, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Extracting spatial effects from machine learning model using local interpretation method: An example of SHAP and XGBoost. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 96, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, E.S.; Tan, P.Y.; Qi, J.; Ho, R.; Sia, A.; Waykool, R.; Song, X.P.; Olszewska-Guizzo, A.; Meng, L.; et al. Beyond just green: Explaining and predicting restorative potential of urban landscapes using panorama-based metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 247, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Deng, X.Z.; Cheshmehzangi, A. The grain for green program enhanced synergies between ecosystem regulating services in loess plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Analyzing ecological environment change and associated driving factors in China based on NDVI time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Chen, B.Z.; Xia, Q.Q.; Zabi, G.; Li, G.F. Study on the complex relationship of tourism-economy-ecological environment in arid zones: The case of xinjiang, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1435660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Xie, T.; Lyu, D.; Cui, L.; Liu, Q.M. Analyzing the spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of ecological environment quality in the qinling mountains, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.Z.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.Y.; Ye, J.N.; Geng, J.W.; Ding, Z. Long-time series ecological environment quality monitoring and cause analysis in the dianchi lake basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; Zhao, F.; Teng, Y.; Teng, J.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Scale dependency of trade-offs/synergies analysis of ecosystem services based on bayesian belief networks: A case of the yellow river basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, C.; He, J.; Guo, Z.; Duan, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, R. NDVI based vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities at xinjiang from 2001 to 2020. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hang, N.T.; Ran, M.; Kong, J. Spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of vegetation carbon sinks in zhejiang province: A case study in rapidly urbanizing subtropical ecosystems. Plants 2025, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.H. Urbanization, economic development, and ecological environment: Evidence from provincial panel data in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.M.; Bai, X.Y.; Zhao, N. Explicating the responses of NDVI and GDP to the poverty alleviation policy in poverty areas of China in the 21st century. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.T.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.L.; Cheng, Z.Q. Attribution of climate change and human activities to vegetation NDVI in jilin province, China during 1998–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R. Coupling and coordination analysis of digital rural construction from the perspective of rural revitalization: A case study from zhejiang province of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, X.; Jia, H. Evaluate water yield and soil conservation and their environmental gradient effects in fujian province in south China based on InVEST and geodetector models. Water 2025, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Xiang, A.; Xiao, S.; Lin, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y. Terrain gradient response of landscape ecological environment to land use and land cover change in the hilly watershed in south China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Land Use Category | Secondary Classification | EEQI Weight |
|---|---|---|
| CL | Paddy field | 0.30 |
| Dry land | 0.25 | |
| FL | Forest | 0.95 |
| Scrubland | 0.65 | |
| Sparse forest | 0.45 | |
| Other forest | 0.40 | |
| GL | High coverage grassland | 0.75 |
| Medium coverage grassland | 0.45 | |
| Low coverage grassland | 0.20 | |
| WB | Inland waterway | 0.55 |
| Natural lake | 0.75 | |
| Artificial water | 0.55 | |
| Intertidal flat | 0.45 | |
| Floodplain | 0.55 | |
| BL | Urban land | 0.20 |
| Rural residential area | 0.20 | |
| Other construction land | 0.15 | |
| UL | Marshland | 0.65 |
| Bare soil | 0.05 | |
| Bare rock | 0.01 |
| Type | Factors | Abbreviation | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural factors | Elevation | ELV | 1.627 |
| Slope | SLP | 1.629 | |
| Aspect | ASP | 1.034 | |
| Temperature | TMP | 1.414 | |
| NDVI | NDVI | 1.449 | |
| Socioeconomic factors | Per capita GDP | GDP | 1.340 |
| Population density | PD | 1.323 | |
| Road density | RD | 1.021 |
| Years | Type | CL | FL | GL | WB | BL | UL | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2010 | CL | 6038.33 | 175.02 | 7.63 | 83.18 | 349.86 | 0.11 | 615.80 |
| FL | 280.19 | 35,716.31 | 100.97 | 69.76 | 203.93 | 2.86 | 657.70 | |
| GL | 6.54 | 74.60 | 1035.91 | 2.17 | 14.45 | 0.51 | 98.28 | |
| WB | 10.65 | 10.64 | 1.97 | 796.51 | 7.52 | 0.07 | 30.84 | |
| BL | 8.34 | 3.80 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 336.23 | 0.00 | 13.65 | |
| UL | 0.04 | 2.10 | 1.54 | 0.42 | 0.68 | 18.99 | 4.79 | |
| Gain | 305.77 | 266.16 | 112.29 | 156.85 | 576.44 | 3.55 | 1421.06 | |
| 2010–2020 | CL | 6191.00 | 0.27 | 1.14 | 152.71 | 154.12 | ||
| FL | 35,748.60 | 6.36 | 0.74 | 232.47 | 239.57 | |||
| GL | 3.65 | 1130.49 | 14.98 | 18.63 | ||||
| WB | 949.90 | 20.99 | 20.99 | |||||
| BL | 0.25 | 4.01 | 13.55 | 0.46 | 895.25 | 18.26 | ||
| UL | 0.60 | 21.95 | 0.60 | |||||
| Gain | 0.25 | 7.66 | 20.18 | 2.34 | 421.76 | 0.00 | 452.18 | |
| 2000–2020 | CL | 5888.73 | 172.02 | 7.79 | 84.23 | 501.24 | 0.11 | 765.39 |
| FL | 276.80 | 35,488.81 | 114.57 | 70.50 | 420.50 | 2.84 | 885.20 | |
| GL | 6.30 | 74.13 | 1023.77 | 1.98 | 27.49 | 0.51 | 110.41 | |
| WB | 10.44 | 10.19 | 1.97 | 790.95 | 13.74 | 0.07 | 36.41 | |
| BL | 7.92 | 3.55 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 336.97 | 12.92 | ||
| UL | 0.04 | 2.09 | 1.54 | 0.42 | 1.28 | 18.42 | 5.37 | |
| Gain | 301.50 | 261.98 | 125.98 | 158.46 | 964.25 | 3.53 | 1815.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Ke, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation in China’s Southern Hilly Area During 2000–2020. Land 2025, 14, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091766
Xu Z, Ke F, Yu J, Zhang H. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation in China’s Southern Hilly Area During 2000–2020. Land. 2025; 14(9):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091766
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhiyuan, Fuyan Ke, Jiajie Yu, and Haotian Zhang. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation in China’s Southern Hilly Area During 2000–2020" Land 14, no. 9: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091766
APA StyleXu, Z., Ke, F., Yu, J., & Zhang, H. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Eco-Environmental Response to Land Use Transformation in China’s Southern Hilly Area During 2000–2020. Land, 14(9), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091766







