Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Using Phenological Metrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Develop a framework to extract crop-specific phenological metrics from NDVI time-series data for major crops.
- (2)
- Map 1999–2022 spatiotemporal dynamics of farmland abandonment and recultivation, identify key temporal patterns and hotspots, and analyze policy and socio-economic drivers.
- (3)
- Evaluate vegetation recovery and degradation risks after land-use transitions. Monitor vegetation dynamics in transition zones to evaluate post-transition recovery trends and degradation risks
- (4)
- Explore trade-offs between ecological protection goals and food security implications and propose adaptive strategies for sustainable land management.
2. Materials and Methods
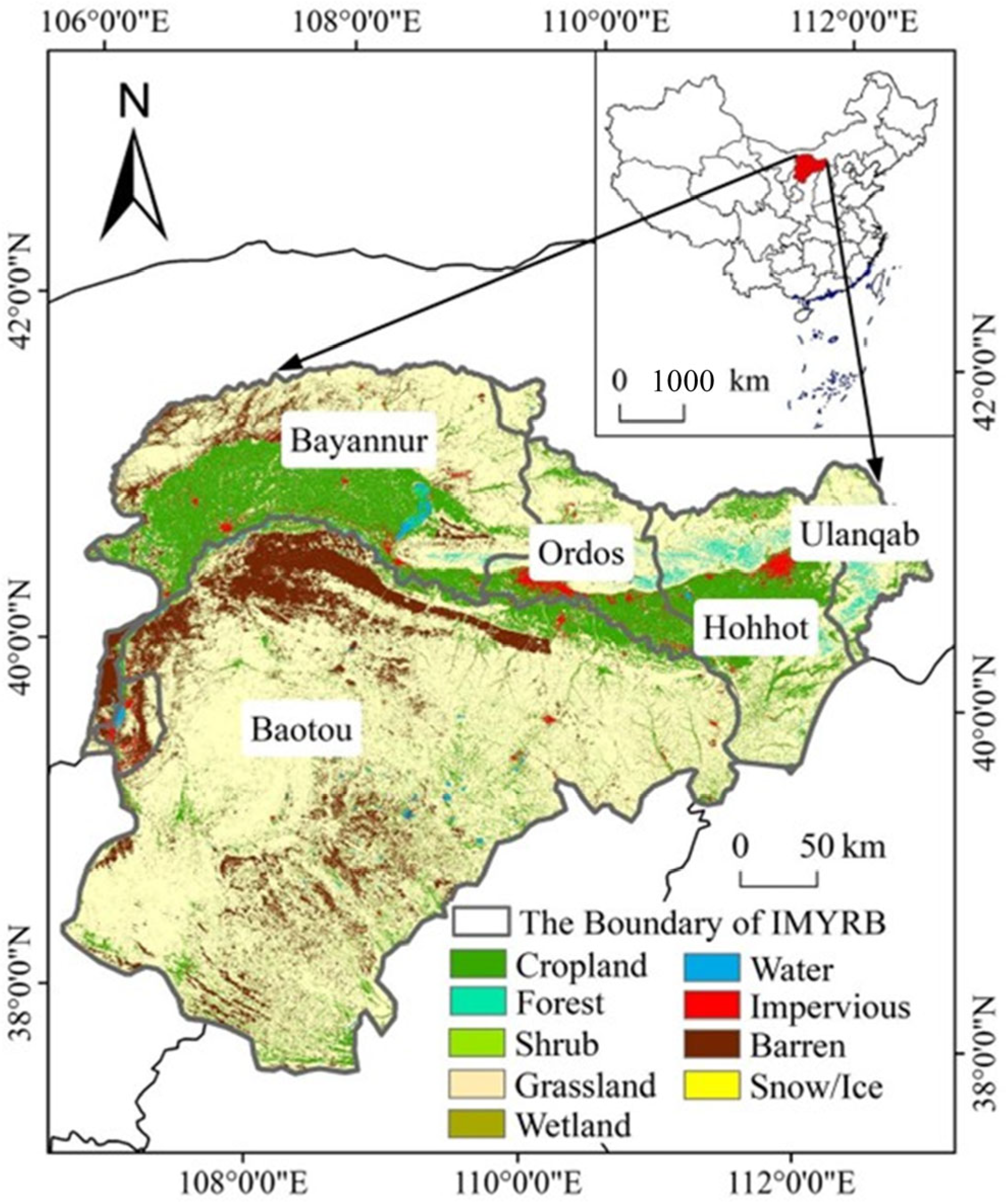
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. MODIS NDVI Product
2.2.2. Landsat Images
- (1)
- If the number of effective values was more than two, missing values were estimated using temporal linear interpolation.
- (2)
- If only one valid observation was present, its value was directly assigned to the missing pixel.
- (3)
- If no valid observations existed, the missing value was filled in using MOD13Q1 NDVI data from the temporally and spatially closest date. To ensure compatibility, the MOD13Q1 product was resampled to 30 m using bilinear interpolation prior to gap filling.
2.2.3. Topography Information
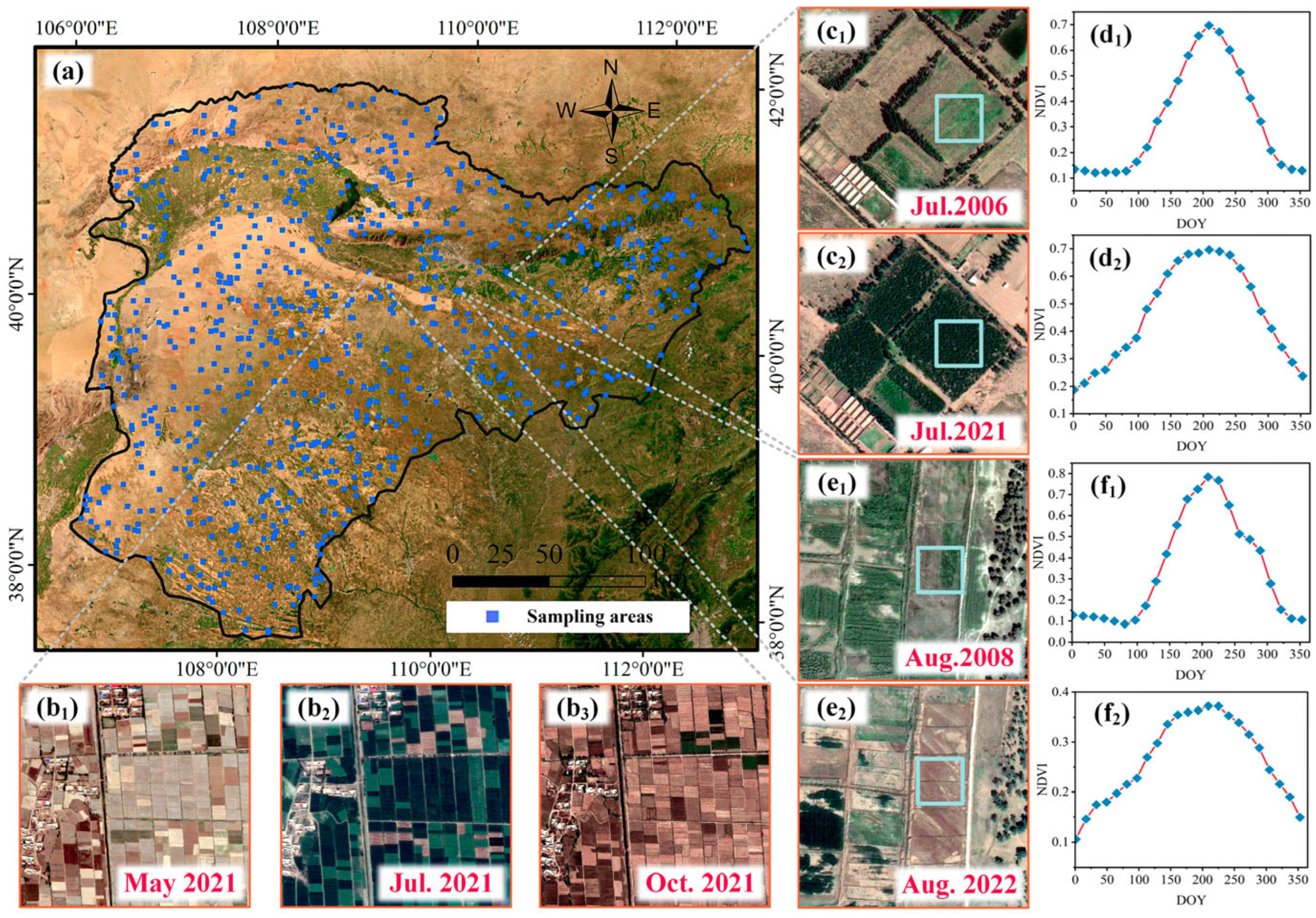
2.2.4. Sampling and Validation Data
2.3. Methods
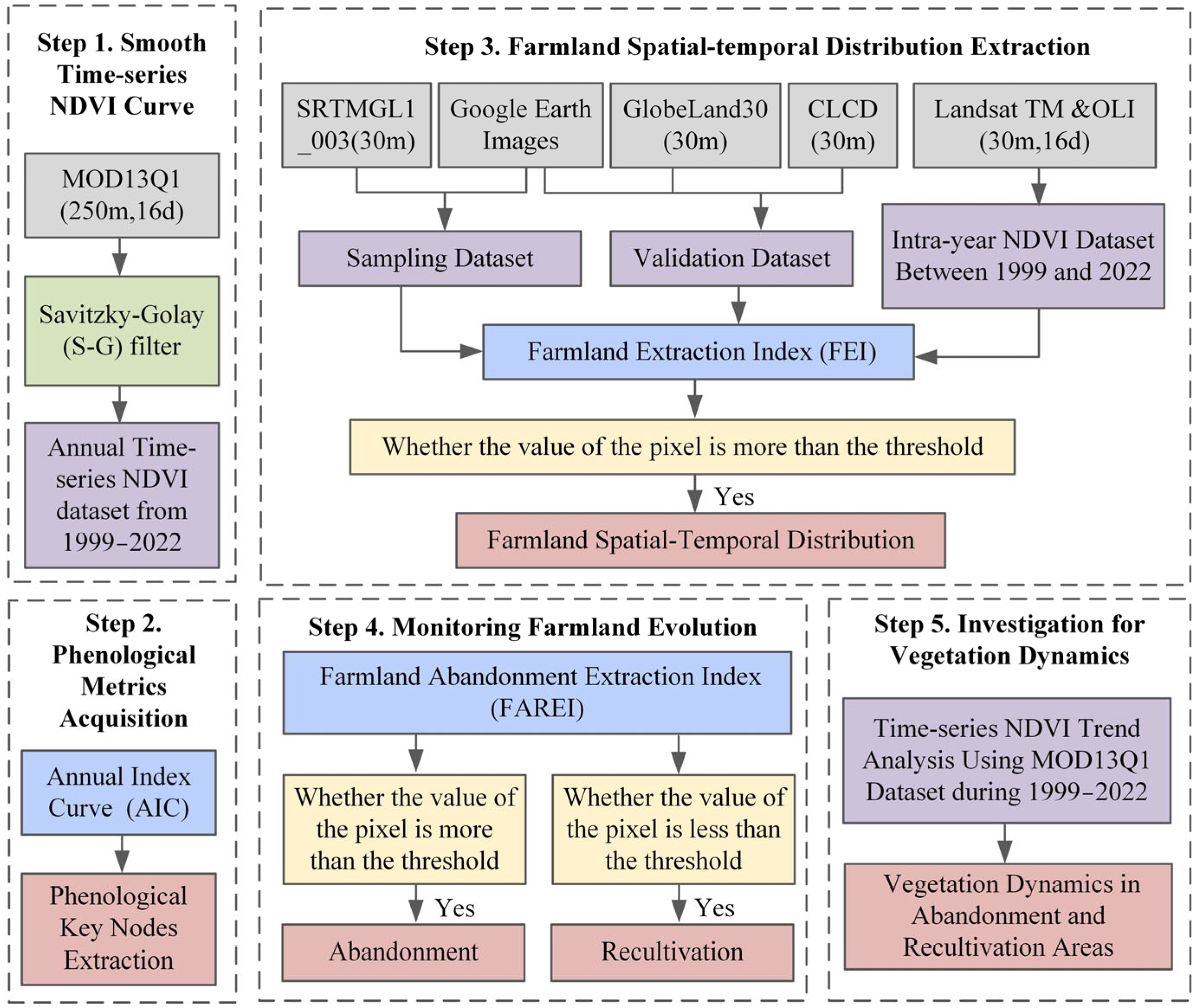
2.3.1. Time-Series NDVI Curve Smoothing
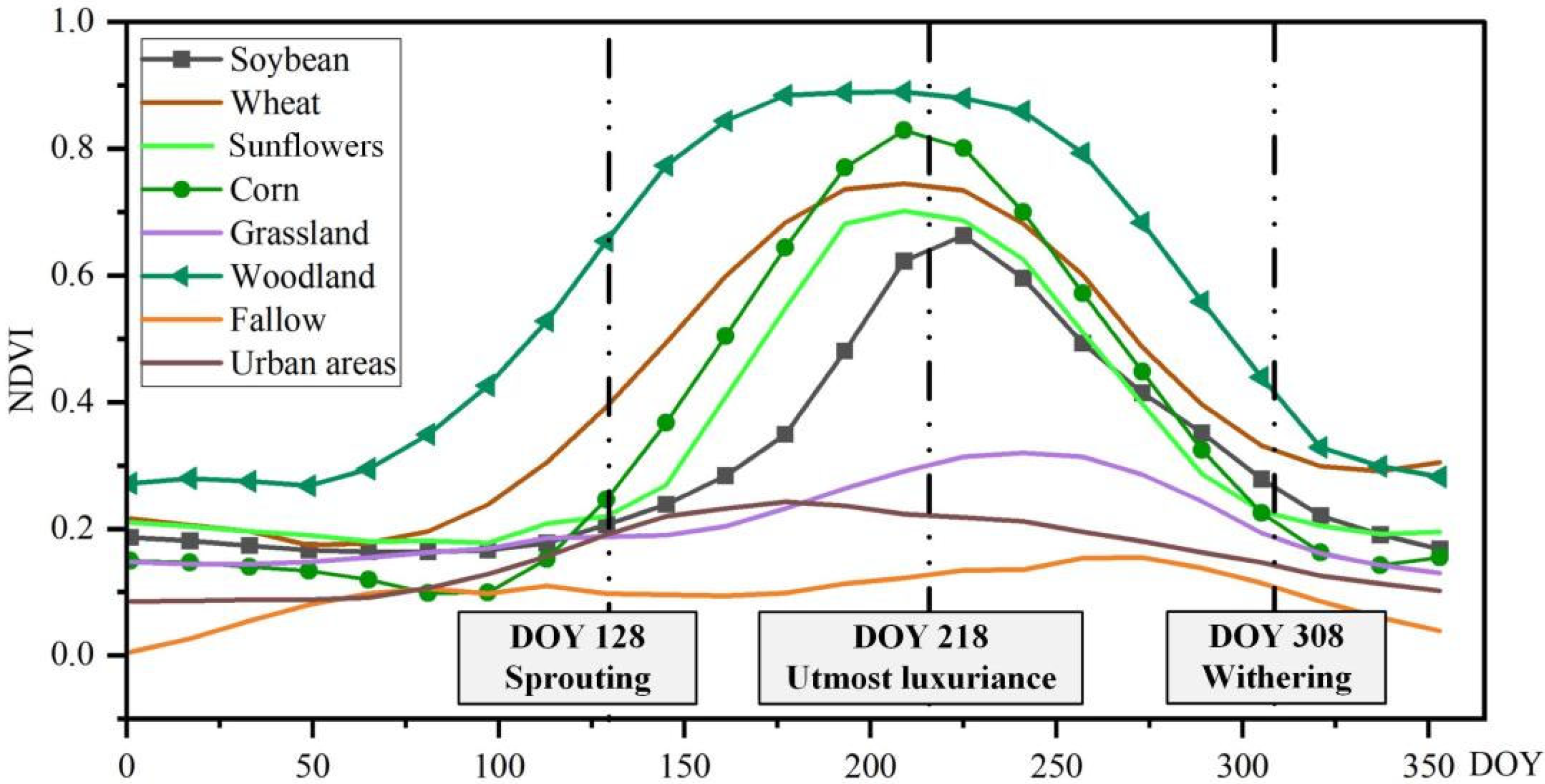
2.3.2. Phenological Metric Acquisition
2.3.3. Farmland Extraction and Abandonment/Recultivation Monitoring
2.3.4. Investigation for Vegetation Restoration
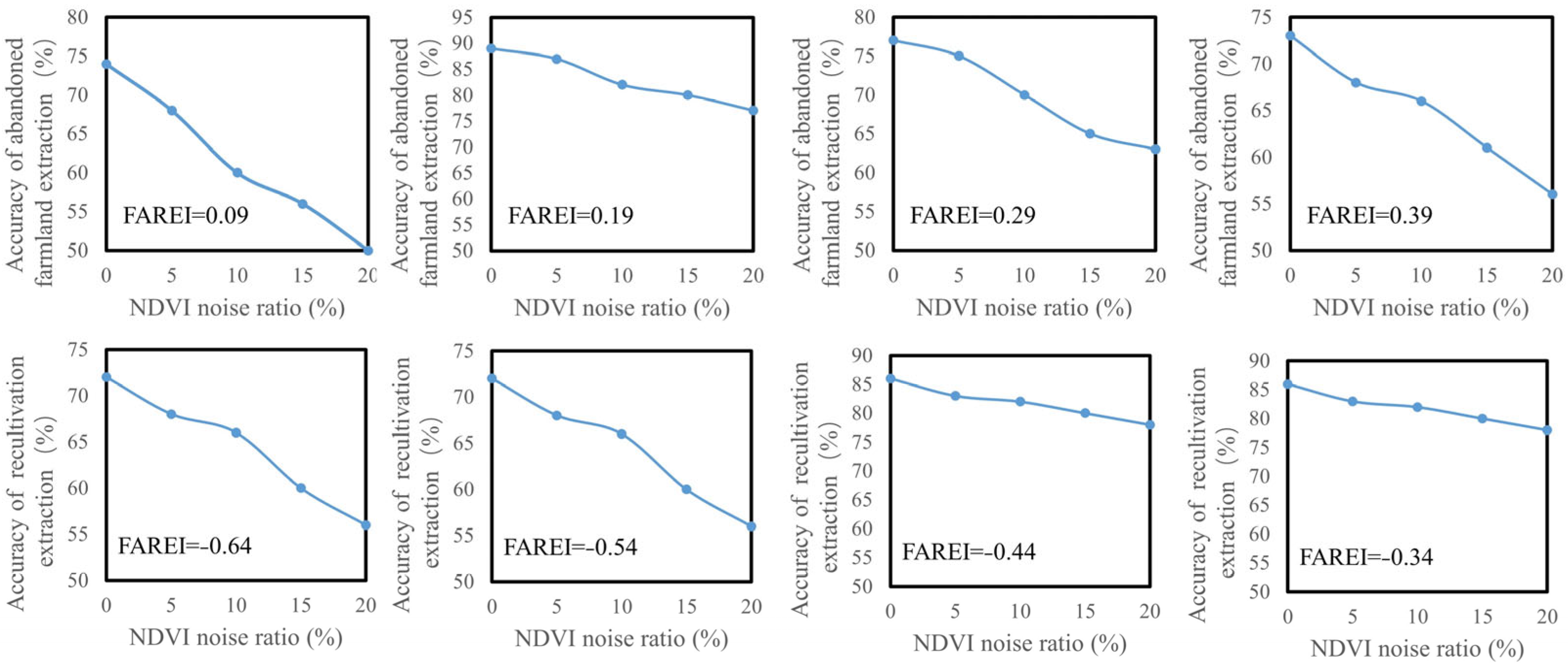
2.4. Model Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
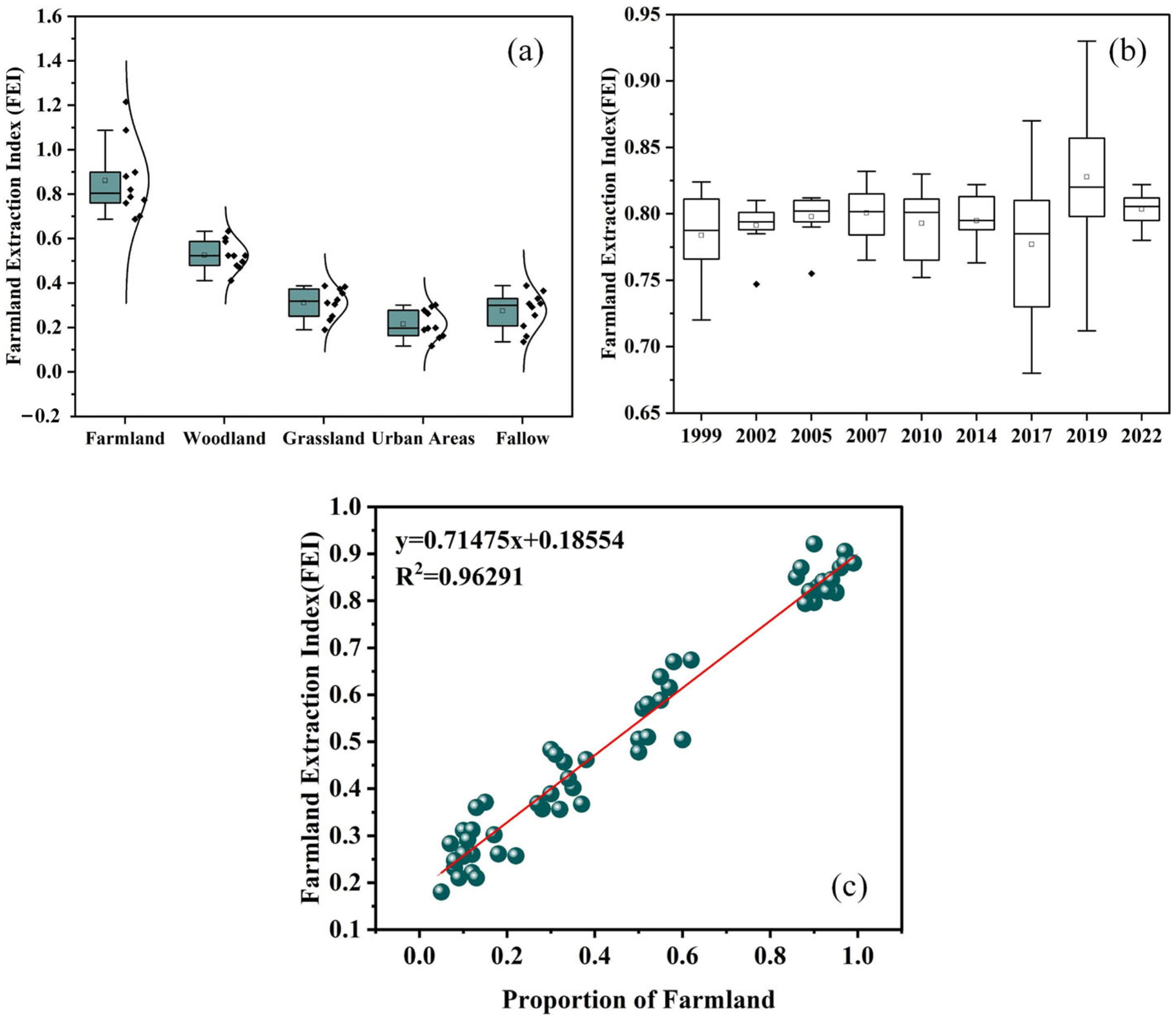
3.1. Phenological Information Acquisition
3.2. Accuracy Validation of Active Farmland, Abandonment, and Recultivation Extraction
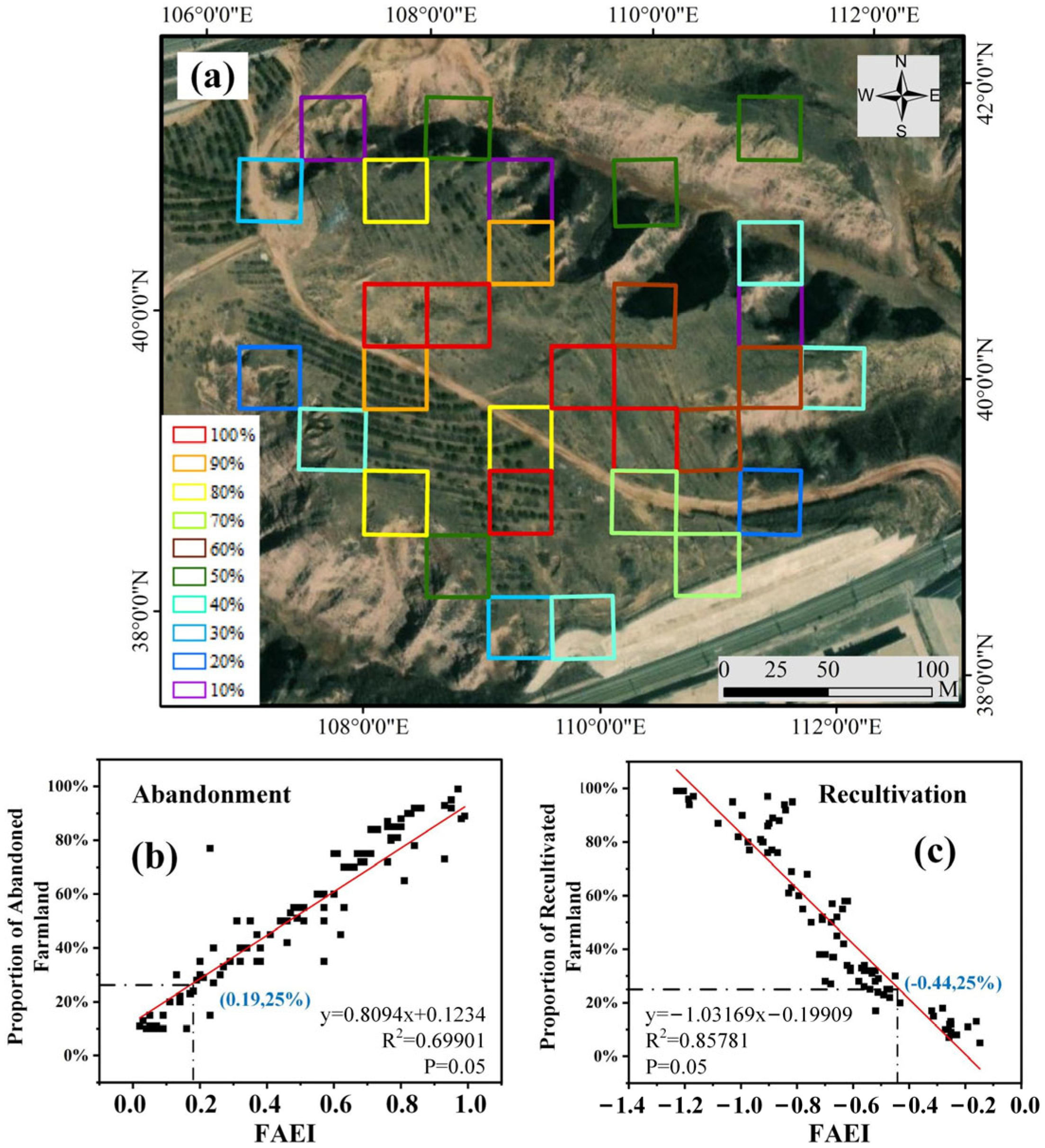
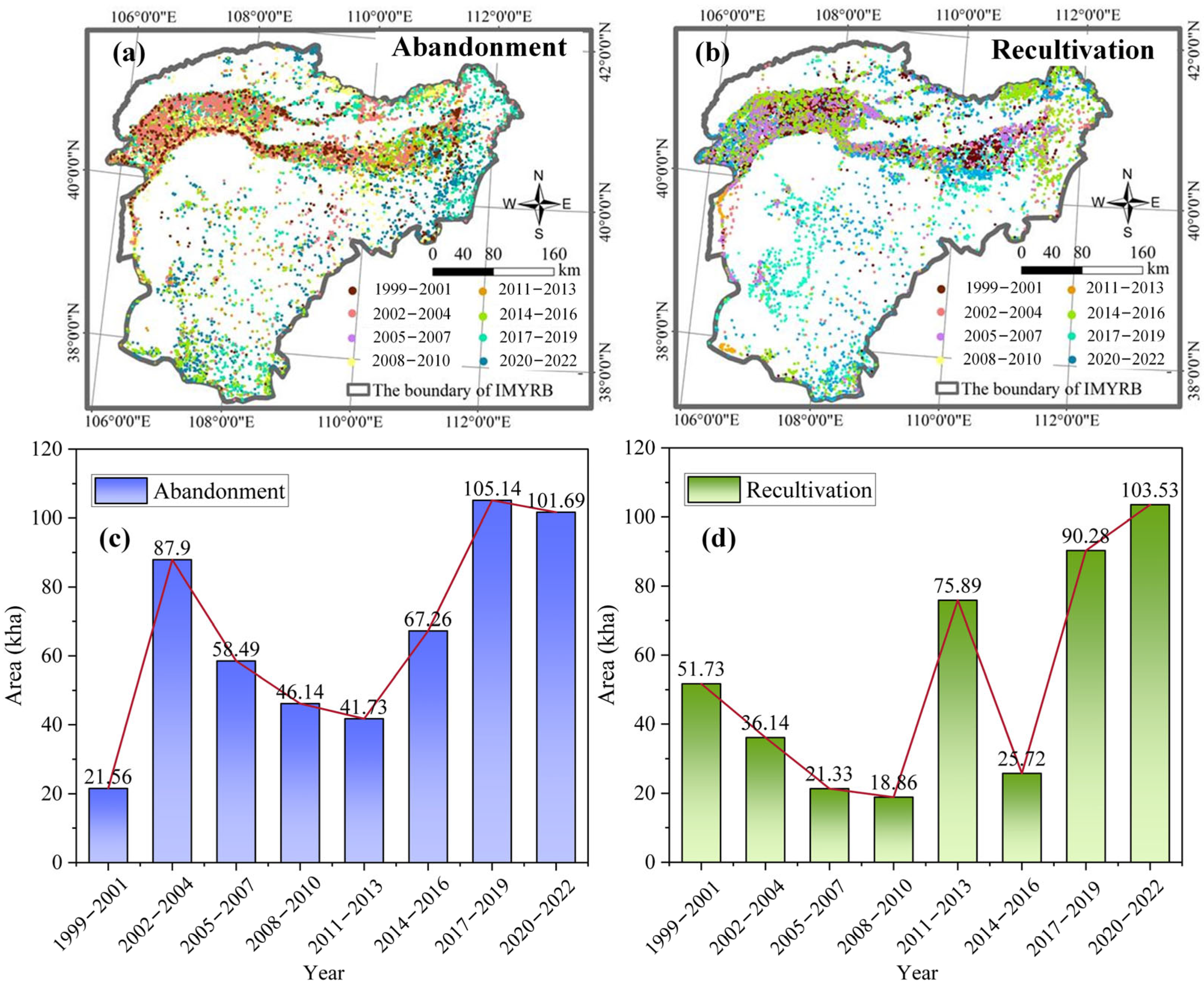
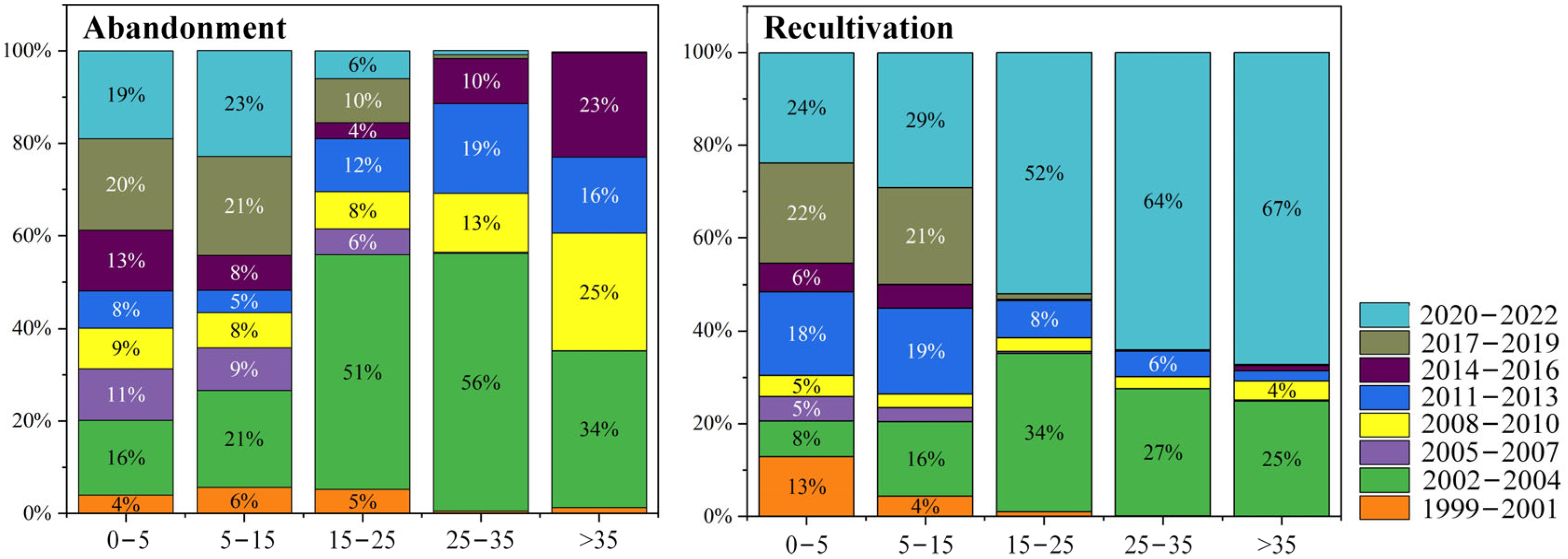
3.3. Mapping Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation
3.4. Monitoring Vegetation Restoration in Abandoned and Recultivated Areas
4. Discussion
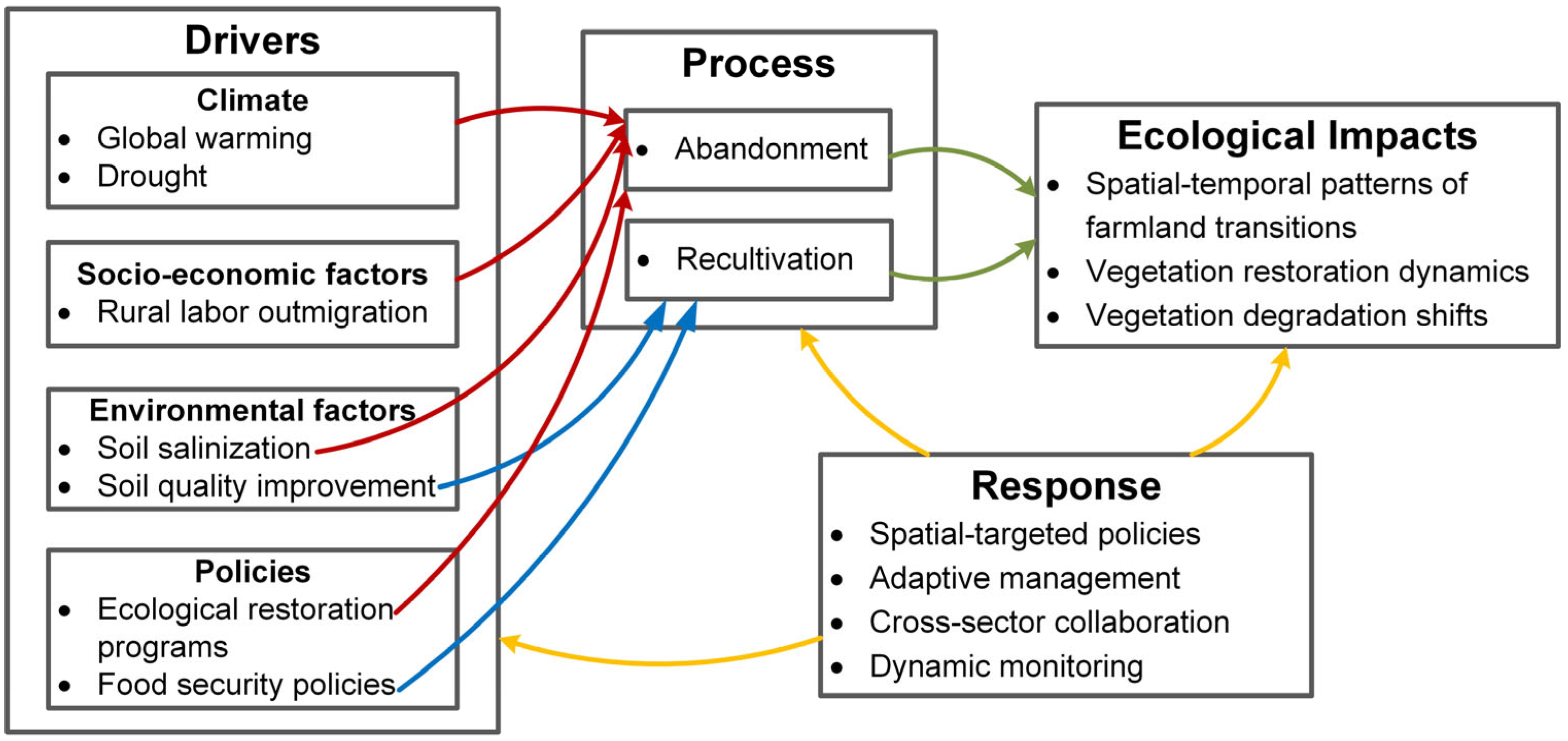
4.1. Drivers of Farmland Abandonment, Recultivation, and Vegetation Dynamics
4.2. Policy Implications for Trade-Offs Between Ecological Protection and Food Security
4.3. Robustness in Monitoring Abandonment and Recultivation Dynamics
4.4. Uncertainty and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.S. Understanding the impacts of ‘Grain for Green’ land management practice on land greening dynamics over the Loess Plateau of China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.; Crabtree, J.R.; Wiesinger, G.; Dax, T.; Stamou, N.; Fleury, P.; Gutierrez Lazpita, J.; Gibon, A. Agricultural abandonment in mountain areas of Europe: Environmental consequences and policy response. Environ. Manag. 2000, 59, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.D.; Yue, W.Z.; Yang, J.; Xue, B.; Xiao, W.; Li, M.M.; He, T.T.; Zhang, M.X.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Q.S. Cropland abandonment in China: Patterns, drivers, and implications for food security. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ha, T.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Zeng, Y.; Yin, H.; Koh, L.P. The neglected role of abandoned cropland in supporting both food security and climate change mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delang, C.O.; Yuan, Z. China’s Grain for Green Program; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Gong, Z.W.; Du, Y.X. Evolution characteristics and simulation prediction of forest and grass landscape fragmentation based on the “Grain for Green” projects on the Loess Plateau, P.R. China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Lana-Renault, N. Hydrological and erosive consequences of farmland abandonment in Europe, with special reference to the Mediterranean region—A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey Benayas, J.M.; Martins, A.; Nicolau, J.M.; Schulz, J.J. Abandonment of agricultural land: An overview of drivers and consequences. CABI Rev. 2007, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.S.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Q.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.; Lu, Y.H. Characteristics and influencing factors of farmland abandonment in the karst rocky desertification area of Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Xiao, J.; Lei, X.Y.; Wang, Y.H. Farmland abandonment in the mountainous areas from an ecological restoration perspective: A case study of Chongqing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Li, X.B.; Xin, L.J.; Tan, M.H.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.H. Extent and distribution of cropland abandonment in Chinese mountainous areas. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Moiwo, J.P. Rapid monitoring of abandoned farmland and information on regulation achievements of government based on remote sensing technology. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 132, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Brandão, A., Jr.; Buchner, J.; Helmers, D.; Iuliano, B.G.; Kimambo, N.E.; Lewińska, K.E.; Razenkova, E.; Rizayeva, A.; Rogova, N.; et al. Monitoring cropland abandonment with Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Collier, M.J. Farmland abandonment in Europe: An overview of drivers, consequences, and assessment of the sustainability implications. Environ. Rev. 2018, 26, 396–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemmerle, T.; Hostert, P.; Radeloff, V.C.; Linden, S.V.D.; Perzanowski, K.; Kruhlov, I. Cross-border comparison of post-socialist farmland abandonment in the Carpathians. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D.; Shackleton, C.M.; Mograbi, P.J. Cropland abandonment in South African smallholder communal lands: Land cover change (1950–2010) and farmer perceptions of contributing factors. Land 2018, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, F.; Fliemann, E.; Abdullaev, I.; Conrad, C.; Lamers, J.P.A. Mapping abandoned agricultural land in Kyzyl-Orda, Kazakhstan using satellite remote sensing. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Ponkina, E.V.; Sun, Z.L.; Bavorova, M.; Yekimovskaja, O.A. Revealing the intentions of farmers to recultivate abandoned farmland: A case study of the Buryat Republic in Russia. Land Use Policy 2021, 107, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.X.; Li, J.B.; Wu, S.F.; Yu, L.M.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Monitoring abandoned cropland in the hilly and gully regions of the Loess Plateau using Landsat time series images. J. Integr. Agric. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.W.; Song, W. Mapping Abandoned Cropland Changes in the Hilly and Gully Region of the Loess Plateau in China. Land 2021, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, G.B.; Shangguan, Z.P. Effects of age and land-use changes on soil carbon and nitrogen sequestrations following cropland abandonment on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shao, H.; Xian, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, J.; Qi, J. Extraction of Abandoned Land in Hilly Areas Based on the Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, G.S.; Yang, L.Y. Remote sensing extraction and feature analysis of abandoned farmland in hilly and mountainous areas: A case study of Xingning, Guangdong. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Jin, S.F.; Zhu, G.L.; Guo, J. Monitoring of cropland abandonment based on long time series remote sensing data: A case study of Fujian Province, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.Q.; Sun, J.; Wellens, J.; Colinet, G.; Wu, W.B.; Meersmans, J. Mapping the spatiotemporal dynamics of cropland abandonment and recultivation across the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, A.; Baumann, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Pflugmacher, D.; Rabe, A.; Griffiths, P.; Hölzel, N.; Kamp, J.; Freitag, M.; Hostert, P. Mapping the timing of cropland abandonment and recultivation in northern Kazakhstan using annual Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 213, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, C.; Kuemmerle, T.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Radeloff, V.C. Mapping abandoned agriculture with multi-temporal MODIS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L. Mapping abandoned farmland in China using time series MODIS NDVI. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, L.R.; Yuan, J.; Xie, L.L.; Guo, Y.L.; Yin, P. Semantic Web Techniques for Extracting and Analyzing of Cropland Abandonment in Hilly Areas. Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst. 2024, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Y.; Xia, N.; Wu, W.; Zhou, C. Extraction of Abandoned Cropland Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images in Suburban Regions: A Case Study of Zengcheng, Guangdong Province. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 18055–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Mapping Cropland Abandonment in Mountainous Areas Using an Annual Land-Use Trajectory Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, L.M.; Rao, X.; Ran, W.J.; Xu, C.X. Monitoring and analysis of abandoned cropland in the Karst Plateau of eastern Yunnan, China based on Landsat time series images. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, H.; Millington, A.; Takeuchi, W.; Yamagata, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of deforestation in the Chapare region of Bolivia using LANDSAT images. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3024–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, Y.Z.; Zheng, R.B.; Liu, X.P. Understanding the spatiotemporal patterns of seasonal, annual, and consecutive farmland abandonment in China with time-series MODIS images during the period 2005–2019. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1608–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vintrou, E.; Desbrosse, A.; Bégué, A.; Traoré, S.; Baron, C.; Seen, D.L. Crop area mapping in West Africa using landscape stratification of MODIS time series and comparison with existing global land products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 14, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estel, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Alcántara, C.; Levers, C.; Prishchepov, A.; Hostert, P. Mapping farmland abandonment and recultivation across Europe using MODIS NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen, M. Land reform and land fragmentation in Central and Eastern Europe. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.D.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.Y. Phenology-based cropland retirement remote sensing model: A case study in Yan’an, Loess Plateau, China. Gisci Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyun, D.J.; Duan, M.Q.; Sun, L.; Crusiol, L.G.T.; Wu, N.T.; Chen, Z.X. Pixel-wise parameter assignment in LandTrendr algorithm: Enhancing cropland abandonment monitoring using satellite-based NDVI time-series. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakun, S.; Franch, B.; Vermote, E.; Roger, J.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Justice, C.; Kussul, N. Early season large-area winter crop mapping using MODIS NDVI data, growing degree days information and a Gaussian mixture model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, S. Detecting abandoned farmland using harmonic analysis and machine learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Guzman, J.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Remote sensing of mangrove forest phenology and its environmental drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Xiang, D.X.; Hu, S.; Li, D. A review of vegetation phenological metrics extraction using time-series, multispectral satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszak, I.; Iturrate-Garcia, M.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Schaepman, M.E.; Maximov, T.C.; Schaepman-Strub, G. Drivers of shortwave radiation fluxes in Arctic tundra across scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.W.; Alfieri, J.G.; Kustas, W.P.; Mueller, R.; Johnson, D.M.; Prueger, J.H. Toward mapping crop progress at field scales through fusion of Landsat and MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Guan, Q.F.; Gao, H.; Xia, W. Enhanced spatial-temporal Savitzky-Golay method for reconstructing high-quality NDVI time series: Reduced sensitivity to quality flags and improved computational efficiency. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3190475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terres, J.M.; Scacchiafichi, L.N.; Wania, A.; Ambar, M.; Anguiano, M.; Buckwell, A.; Coppola, A.; Gocht, A.; Källström, H.N.; Pointereau, P.; et al. Farmland abandonment in Europe: Identification of drivers and indicators, and development of a composite indicator of risk. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Müller, D.; Dubinin, M.; Baumann, M.; Radeloff, V.C. Determinants of agricultural land abandonment in post-Soviet European Russia. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Sun, L. Drivers of cropland abandonment in mountainous areas: A household decision model on farming scale in Southwest China. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Pascual, N.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Errea, M.P.; Lana-Renault, N. Space-time process and drivers of land abandonment in Europe. Catena 2017, 149, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.A.; Gao, Y.L.; Pu, C.X. Do agricultural productive services alleviate farmland abandonment? Evidence from China rural household panel survey data. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1072005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.X.; Yuan, X.F.; Zhao, Y.H. Effects of Off-Farm Employment on the Eco-Efficiency of Cultivated Land Use: Evidence from the North China Plain. Land 2024, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Wang, Y.K.; Dixit, A.M.; Khanal, N.R.; Xu, P.; Fu, B.; Yan, K.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.F.; Li, M. A Synopsis of Farmland Abandonment and Its Driving Factors in Nepal. Land 2020, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaliychuk, A.; Müller, D.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Levers, C.; Kruhlov, I.; Kuemmerle, T. Recultivation of abandoned agricultural lands in Ukraine: Patterns and drivers. Global. Environ. Chang. 2016, 38, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Chen, Y.J.; Huan, H.T.; Duan, N. Analyzing cultivated land protection behavior from the perspective of land fragmentation and farmland transfer: Evidence from farmers in rural China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 901097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, S.D.; Liu, K.; Huang, X.K.; Shi, J.L.; Li, X.K. Projecting Response of Ecological Vulnerability to Future Climate Change and Human Policies in the Yellow River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. ESSD 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, M.J.; Denham, R.J.; Devadas, R. Identification of cropping activity in central and southern Queensland, Australia, with the aid of MODIS MOD13Q1 imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2012, 19, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.; Schmidt, G. The MODIS reprojection tool. Earth Sci. Satell. Remote Sens. 2006, 2, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.G.; Tian, J.Y.; Li, X.J.; Yin, D.M.; Li, J.W.; Gong, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, D.L. An enhanced pixel-based phenological feature for accurate paddy rice mapping with Sentinel-2 imagery in Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.H.; Ding, M.D.; Xie, K.; Li, J.R. Driving Mechanisms of Cropland Abandonment from the Perspectives of Household and Topography in the Poyang Lake Region, China. Land 2022, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gong, P. Google Earth as a virtual globe tool for Earth science applications at the global scale: Progress and perspectives. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3966–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.M.; Gong, J.H.; Li, W.H. Applications and impacts of Google Earth: A decadal review (2006–2016). ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2018, 146, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Dong, R.M.; Fu, H.H.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Gong, P. Integrating Google Earth Imagery with Landsat Data to Improve 30-m Resolution Land Cover Mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, X.Y. Mapping Crop Phenology in Near Real-Time Using Satellite Remote Sensing: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 8379391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Huang, Q.Z.; Xiong, Y.W.; Yang, Q.R.; Li, H.Z.; Hou, Z.L.; Huang, G.H. Tracking the spatio-temporal change of the main food crop planting structure in the Yellow River Basin over 2001–2020. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, T.X.; Wang, S.D.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.Y. Cropland abandonment mapping at sub-pixel scales using crop phenological information and MODIS time-series images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, T.X.; Wang, S.D.; Li, H. Fractional evergreen forest cover mapping by MODIS time-series FEVC–CV methods at sub-pixel scales. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.D.; Long, X.; Li, X.K. A rapid model (COV_PSDI) for winter wheat mapping in fallow rotation area using MODIS NDVI time-series satellite observations: The case of the Heilonggang region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Qamer, F.M.; Ali, H.; Usman, M.; Ahmad, A.; Salman, A.; Akhter, A.M. Monitoring of large-scale forest restoration: Evidence of vegetation recovery and reversing chronic ecosystem degradation in the mountain region of Pakistan. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Somee, B.S.; Zadeh, M.R. Testing for long-term trends in climatic variables in Iran. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarozzo, M.; Noto, L.V.; Viola, F. Spatial distribution of rainfall trends in Sicily (1921–2000). Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.F.; Rosa, R.D.; Shi, H.B.; Paredes, P.; Zhu, L.; Dai, J.X.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Pereira, L.S. Modeling water use, transpiration and soil evaporation of spring wheat-maize and spring wheat-sunflower relay intercropping using the dual crop coefficient approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Li, S.X.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Chen, X.D. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delang, C.O. The second phase of the grain for green program: Adapting the largest reforestation program in the world to the new conditions in rural China. Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Farooq, S.; Hasan, W.; Ul-Allah, S.; Tanveer, M.; Farooq, M.; Nawaz, A. Drought stress in sunflower: Physiological effects and its management through breeding and agronomic alternatives. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolın, G.; Tinaut, F.V.; Briceno, Y.; Castaño, V.; Pérez, C.; Ramĺrez, A.I. Optimisation of biodiesel production by sunflower oil transesterification. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ma, J.Q.; Luo, Y.; He, C.S.; Liu, T.G. Hydrologic Simulation of a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping System in an Irrigation District of the Lower Yellow River Basin, China. Water 2017, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.; Zhuguo, M.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Saleem, F. Natural and anthropogenic influences on the recent droughts in Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Wang, K.B.; Lin, Y.S.; Shi, W.Y.; Song, Y.; He, X.H. Balancing green and grain trade. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.; Gao, Y.B.; Guo, H.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, J.B.; Xu, J.S. Physiological adaptations of four dominant Caragana species in the desert region of the Inner Mongolia Plateau. J. Arid. Environ. 2008, 72, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Z.; Miao, Q.F.; Shi, H.B.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Li, R.P. Water Saving and Environmental Issues in the Hetao Irrigation District, the Yellow River Basin: Development Perspective Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H.; Sharma, R.C.; Tomita, M.; Hara, K. Evaluating multiple classifier system for the reduction of salt-and-pepper noise in the classification of very-high-resolution satellite images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2542–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Collection | Temporal Range | Spatial Resolution | Spectral Features | Product Level | Access Date | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODIS | 2000 to 2022 | 250 m | NDVI | MOD13Q1 | accessed on 23 March 2023 | https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ |
| Landsat 5 | 1999 to 2012 | 30 m | Red 1 and NIR 2 channel | TM Reflectance | accessed on 5 August 2023 | https://earthengine.google.com/ |
| Landsat 8 | 2013 to 2022 | 30 m | Red 3 and NIR 4 channel | OLI Reflectance | accessed on 22 August 2023 | https://earthengine.google.com/ |
| SRTM | – | 30 m | DEM | SRTMGL1_003 | accessed on 13 May 2023 | https://earthengine.google.com/ |
| CLCD | 1999 to 2021 | 30 m | Land Cover | Version 1.0 | accessed on 6 July 2023 | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4417809 |
| GLC30 | 2020 | 30 m | Land Cover | – | accessed on 9 July 2023 | http://www.webmap.cn/commres.do?method=globeIndex |
| Google Earth Image | 1999 to 2022 | Better than 15 m | True color | – | accessed on 10 September 2023 | https://earth.google.com/web/ |
| Coefficients | Value | Coefficients | Value | Coefficients | Value | Coefficients | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1672 | 0.5479 | 218 | −0.6059 | ||||
| 0.5067 | 128 | 0.6400 | – | – |
| Farmland Extraction Accuracy (%) | Year | PA (%) | Margin of Error (PA, %) | UA (%) | Margin of Error (UA, %) | OA (%) | Margin of Error (OA, %) |
| 1999 | 93.05 | 3.5 | 90.16 | 4.1 | 89.33 | 4.3 | |
| 2002 | 95.19 | 2.9 | 93.19 | 3.5 | 92.67 | 3.6 | |
| 2005 | 93.09 | 3.5 | 91.62 | 4.1 | 90.33 | 4.1 | |
| 2008 | 92.39 | 3.5 | 90.05 | 4.1 | 89.84 | 3.7 | |
| 2011 | 92.82 | 3.5 | 90.16 | 4.1 | 89.67 | 4.2 | |
| 2014 | 93.22 | 3.5 | 89.67 | 4.2 | 89.27 | 4.2 | |
| 2017 | 95.18 | 2.9 | 90.16 | 4.1 | 90.67 | 4.1 | |
| 2019 | 93.33 | 3.5 | 90.06 | 4.1 | 89.33 | 4.3 | |
| 2021 | 88.55 | 4.4 | 93.63 | 3.4 | 90.33 | 4.1 |
| This paper | Class | Farmland | Non-farmland | User Accuracy | Margin of Error (PA, %) | Margin of Error (UA, %) | Margin of Error (PA, %) |
| Farmland | 137 | 8 | 94.48% | 3.9 | 3.2 | 4.3 | |
| Non-farmland | 13 | 42 | 76.36% | ||||
| Producer Accuracy | 91.33% | 84% | Overall Accuracy 89.5% | ||||
| GLC30 | Class | Farmland | Non-farmland | User Accuracy | 4.8 | 4.5 | 5.1 |
| Farmland | 128 | 17 | 88.28% | ||||
| Non-farmland | 22 | 33 | 60% | ||||
| Producer Accuracy | 85.33% | 66% | Overall Accuracy 80.5% | ||||
| CLCD | Class | Farmland | Non-farmland | User Accuracy | 5.2 | 4.9 | 5.5 |
| Farmland | 118 | 27 | 81.38% | ||||
| Non-farmland | 32 | 23 | 41.82% | ||||
| Producer Accuracy | 78.67% | 46% | Overall Accuracy 70.5% |
| Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Accuracy (%) | Year | PA (%) | Margin of Error (PA, %) | UA (%) | Margin of Error (UA, %) | OA (%) | Margin of Error (OA, %) |
| 1999–2002 | 94 | 4.6 | 81.03 | 7.7 | 86 | 6.8 | |
| 2002–2005 | 90 | 5.9 | 91.84 | 5.4 | 91 | 5.6 | |
| 2005–2008 | 76 | 8.4 | 80.85 | 7.7 | 79 | 8.1 | |
| 2008–2011 | 90 | 5.9 | 86.54 | 6.7 | 88 | 6.4 | |
| 2011–2014 | 78 | 8.1 | 79.59 | 7.9 | 79 | 8.1 | |
| 2014–2017 | 82 | 7.5 | 85.42 | 6.9 | 84 | 7.2 | |
| 2017–2019 | 78 | 8.1 | 82.98 | 7.4 | 81 | 7.7 | |
| 2019–2022 | 88 | 6.4 | 89.80 | 5.8 | 89 | 6.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, L.; Ma, C.; Naing, S.Y.; Liu, K.; Li, H. Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Using Phenological Metrics. Land 2025, 14, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091745
Liu X, Wang S, Zhang X, Zhen L, Ma C, Naing SY, Liu K, Li H. Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Using Phenological Metrics. Land. 2025; 14(9):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xingtao, Shudong Wang, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Lin Zhen, Chenyang Ma, Saw Yan Naing, Kai Liu, and Hang Li. 2025. "Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Using Phenological Metrics" Land 14, no. 9: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091745
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, S., Zhang, X., Zhen, L., Ma, C., Naing, S. Y., Liu, K., & Li, H. (2025). Monitoring Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Farmland Abandonment and Recultivation Using Phenological Metrics. Land, 14(9), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091745








