Abstract
Controlling the conversion of cultivated land to non-grain uses is of great significance for ensuring global food security. Currently, the research on the conversion of Main Grain Land (MGL) to non-grain uses lacks a theoretical framework that can support differentiated and targeted governance. In this study, a “Resource Cost-Negative Effect-Remediation Potential” (RC-NE-RP) evaluation framework for the conversion of cultivated MGL to non-grain uses was established based on the definition of “non-grain conversion of MGL” and the theory of the production function in economics, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL and the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the Bohai Rim (BR) region, China, during the period from 1990 to 2020 were quantitatively evaluated using an improved SBM model, and the non-grain land to be remediated in the BR region was zoned through cluster analysis. The results show that: (1) The process of non-grain conversion of MGL in the Bohai Rim region shows a trend of fast conversion followed by slow conversion, with increasingly significant characteristics of spatial differentiation. (2) For the period from 1990 to 2020, the negative effects of non-grain conversion generally exhibit an upward trend, and the negative effects of non-grain conversion in coastal economic zones are generally stronger than those in hinterlands; the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL shows a downward trend followed by an upward trend, and the remediation potential of non-grain land in coastal economic zones is lower compared to hinterland areas. (3) The areas represented by Beijing and the Bohai Economic Rim (BER) are classified as priority remediation zones, and the other areas are classified as low-priority remediation zones. The BR region is divided into three types of zones for remediation, namely, Quantity–Quality Priority Zones, Quantity–Landscape Priority Zones, and Quality–Landscape Priority Zones. This study provides a scientific basis for the management and control of non-grain conversion of cultivated land and the protection of cultivated land.
1. Introduction
As the material basis for grain production, arable land is one of the most important strategic resources in the world. With the intensification of climate change, continuous population growth and rapid economic development, global food security is facing multiple challenges, such as land and water shortages [1]. The Sustainable Development Goal 2 among the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 2030 aims to, by 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular the poor and people in vulnerable situations, to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round. However, The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World Report 2024 notes that the process of ending hunger globally has seriously regressed, and food insecurity has fallen back to the level between 2008 and 2009. Given that there are only five years left to achieve the goal of ending hunger globally by 2030, ensuring food security has become an imperative for global governance.
The conversion of cultivated land to non-grain uses (non-grain conversion of cultivated land) is one of the major factors threatening food security and is a typical and universal agricultural phenomenon across the world. China is a country with a large population exceeding 1.4 billion, accounting for nearly 18% of the global population. Under the complex current situation of global food security, China’s food security is closely linked to global food security. However, due to factors such as the low comparative benefits of grain farming, the phenomenon of non-grain conversion of cultivated land in China is becoming increasingly prominent. According to China’s National Land Survey reports and data, the total area of cultivated land measured during the Third National Land Survey is 113 million mu less than the total cultivated land area of 2.03 billion mu at the time of the Second National Land Survey. The decrease in the total area of cultivated land has directly resulted in a reduction in the total planting area of grain crops, threatening national food security [2].
Main Grain Land (MGL) is a major part of cultivated land for grain production and plays a pivotal role in ensuring food security. MGL is defined as the land used for growing rice, wheat and maize. Rice, wheat and maize, which serve as the primary food sources for humans, account for a large proportion of the global food supply. Compared to cultivated land, MGL contributes more directly to food security. The non-grain conversion of MGL not only represents changes in the use of cultivated land, but it also indicates the weakening of food supply capacity. In 2008, the Chinese government proposed the concept of “permanent basic farmland”—basic farmland whose intended purposes cannot be changed under any circumstances and which cannot be used in any way for non-agricultural purposes. The Opinions on Preventing Non-grain Conversion on Cultivated Land and Stabilizing Grain Production issued by the General Office of the State Council of China in 2020 clearly defines the priority levels of cultivated land uses and points out the necessity of using permanent basic farmland primarily for grain production and ensuring the planting area of three major grain crops: rice, wheat, and maize [3]. Since MGL is mostly designated for use as permanent basic farmland, the non-grain conversion of MGL has already touched the bottom line of food security.
The problem of non-grain conversion has posed many practical challenges. The current policy and governance systems are confronted with two major challenges. The first challenge is to accurately identify key areas with outstanding problems of non-grain conversion, and the second challenge is to develop targeted remediation strategies based on the characteristics of non-grain conversion in different regions. Due to the significant differences in the agricultural resource endowments, industrial structures and land revenues of different areas, non-grain conversion exhibits unique characteristics such as regional non-uniformity and diversity in type across different areas [4]. If the key areas could not be effectively and accurately identified, it would be difficult to carry out coordinated and targeted governance of cultivated land resources in such areas, which can easily lead to the dispersion of resources subject to governance and limited effects of governance. In addition, even if key areas with serious problems of non-grain conversion could be identified, it would still be impossible to achieve effective governance without scientific and reasonable governance pathways and classified governance strategies. Therefore, exploring differentiated and targeted governance pathways at the regional level for cultivated land used for non-grain purposes is a core issue that urgently needs to be solved.
In recent years, numerous theoretical and empirical studies have been conducted on the non-grain conversion of cultivated land from multiple perspectives including the definition of non-grain conversion of cultivated land [5], measurement methods [6], driving mechanisms [7], and multivariate effects [8]. In terms of definition, most scholars have defined the concept and characteristics of non-grain conversion of cultivated land in both the narrow and broad senses [9]. For measurement methods, in most of the existing studies, the ratio of the planting area of grain crops to the planting area of agricultural crops is used as an index for reverse estimation of the degree of non-grain conversion of cultivated land [10], and based on national land survey data or high-resolution remote sensing image interpretation results, techniques such as deep learning and GIS spatial analysis are used to extract and classify the types of land use, carry out dynamic monitoring of cultivated land changes, and reveal the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of non-grain conversion of cultivated land [11]. In terms of driving mechanisms, many studies have shown that non-grain conversion of cultivated land is the result of interactions among multiple factors, including economic benefits, resource endowment constraints, and farmers’ behavioral decisions [12]. In terms of adverse impacts, non-grain conversion of cultivated land has multi-dimensional impacts at different levels. In terms of ecological and environmental effects, non-grain conversion of cultivated land can cause problems such as over-fertilization, soil acidification, and plow layer compaction and weaken the ecological function and production capacity of cultivated land [13]. In terms of farmers’ livelihood, due to its high comparative benefits, non-grain production on cultivated land is an important means for farmers to increase their operating income, but in the meantime, it is accompanied by uncertainties in related production operations and can therefore pose certain risks.
In general, previous studies on non-grain conversion of cultivated land have achieved many results, but there are still some deficiencies in these studies. (1) The research objects are generalized. Most studies focus on cultivated land as a whole and pay little attention to MGL, making it difficult to accurately understand the current status of non-grain conversion of cultivated land. (2) There is no systematic and comprehensive evaluation framework for the non-grain conversion of cultivated land. Most of the existing evaluations are limited to the quantity of changes in the use of cultivated land, do not use the perspective of land resource allocation, and lack a comprehensive understanding of related aspects such as resource input, impacts and effects, and resource redundancy. (3) There is a lack of differentiated and targeted governance strategies for cultivated land remediation. Existing studies mostly focus on monitoring the phenomenon of non-grain conversion and investigating the factors driving non-grain conversion, and there is a lack of research on the quantitative identification of the remediation potential of cultivated land used for non-grain purposes and guidance for classification of non-grain cultivated land [14].
To address the aforementioned limitations, this study proposes the following improvements and research framework: (1) Refinement of research focus: The study centers on MGL rather than the entirety of arable land, thereby mitigating analytical bias arising from overly generalized targets. (2) Enhancement of the evaluation system: Indicators related to land quality and connectivity are incorporated into the assessment of resource costs, moving beyond traditional methods that rely solely on sown area proportions or land-use changes. By including evaluations of negative effects and remediation potential, the study provides a more nuanced and realistic understanding of non-grain conversion in terms of both its severity and the complexity of remediation. (3) Optimization of analytical methodology: An improved SBM model is employed to quantify the negative effects and compressible inefficiencies associated with non-grain conversion, facilitating the formulation of targeted strategies and enhancing the practical applicability of policy recommendations.
For the purposes of this study, non-grain conversion of MGL is broadly defined as all non-grain uses of cultivated land initially intended for growing main grain crops, including occupation for construction activities, abandonment, and cash crop cultivation [15,16].
Essentially, non-grain conversion is a process of land resource reallocation [17]. The rationality of land resource allocation can be evaluated from two key perspectives, namely the degree of resource misallocation and the space for resource redundancy. The evaluation of the degree of resource misallocation relates to the quantification of the negative effects of land use changes, while the evaluation of the space for resource redundancy involves quantifying the compressible resource costs in the non-grain conversion process and their reallocation potential. Based on the theory of the production function in economics, the degree of resource misallocation and the space for resource redundancy should be measured and evaluated considering the following three main dimensions: (1) the level of element input, including the quantity, landscape pattern, and quality of MGL; (2) the level of element output, i.e., the level of negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL; and (3) the level of element redundancy, i.e., the compressible space for MGL resources during the non-grain conversion process. Therefore, building a “Resource Cost-Negative Effect-Remediation Potential” (RC-NE-RP) evaluation framework for the non-grain conversion of cultivated land based on the theory of the production function is an effective way to evaluate the rationality of land input and utilization and provide a scientific theoretical basis for controlling cultivated land use and land resource allocation.
The Bohai Rim (BR) is a complex region in China that is densely populated, economically active, and rich in agricultural resources [18]. However, with the acceleration of urbanization, the MGL in this region has experienced significant losses, causing increasingly serious food security issues. According to existing studies, between 2000 and 2021, in China’s economically developed eastern coastal regions, the contribution to non-grain conversion was approximately 20.8% in the Bohai Rim region, 10% in the Yangtze River Delta, and 1.9% in Guangdong Province. By comparison, the Bohai Rim region’s contribution to China’s overall non-grain conversion was significantly higher than that of the other eastern coastal regions. Therefore, this study selects the Bohai Rim region as a case study area, given its strong representativeness. The main research procedure is as follows (Figure 1): (1) First, the MGL areas converted to non-grain uses were identified by detecting changes in land use types. (2) Then, the RC-NE-RP evaluation framework was established based on the theory of the production function in economics, and the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region and the remediation potential of the MGL converted to non-grain uses in the region were quantitatively evaluated using an improved SBM model. (3) Finally, the MGL converted to non-grain uses was divided into remediation zones through cluster analysis [19]. The purpose is to provide a scientific basis for the remediation and protection of cultivated land in the BR region and the optimization of regional land resource allocation and to provide theoretical support for developing and implementing land use controls and land protection policies.
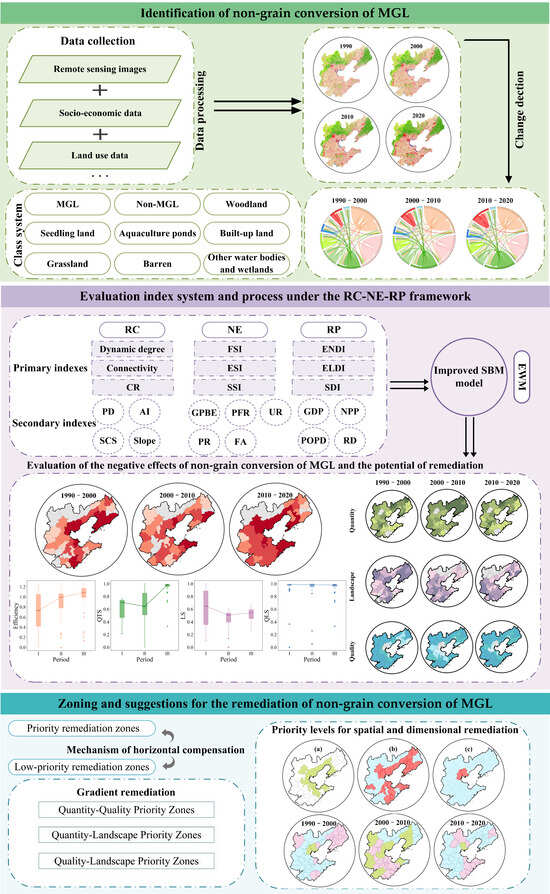
Figure 1.
Research process.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
The BR is a region with Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei as its core and the Liaodong Peninsula and Shandong Peninsula as its two wings (113°04′ E–125°46′ E, 34°25′ N–43°36′ N) (Figure 2) [20]. The BR region covers an area of about 520,000 km2 with a terrain that is dominated by mountains, hills, plains, valleys, and coastal mudflats, high-lying in the northwest and low-lying in the southeast. Located in the temperate monsoon climate zone, the BR region has a climate characterized by four distinct seasons and simultaneous rain and heat, with average annual temperatures mostly ranging between 8 °C and 13 °C and annual precipitation of about 500–800 mm. The administrative areas in the BR region include Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, and Shandong, among which Hebei, Shandong, and Liaoning are classified as main grain production areas, and Beijing and Tianjin are classified as main grain sales areas.

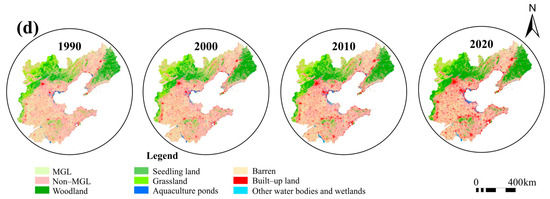
Figure 2.
Study area: (a) Geographical location of the BR; (b) distribution of major grain production and sales areas; (c) spatial distribution of elevation; (d) land use types in the BR region (1990–2020).
The BR region is one of China’s important agricultural bases with diverse cropping systems, and the winter wheat–summer maize double-cropping system is the primary cropping system. According to statistical data [21], the total grain production of the BR region in 2024 was about 124 million tons, accounting for more than 17% of China’s grain output in the same year. This region has a developed economy and is an important industrial base and sociocultural center in China. Its total population is about 250 million, accounting for 17.87% of China’s population, and its GDP is RMB 24 trillion, accounting for 19.04% of China’s GDP. With continued urbanization in the BR region, the intensity of land development is increasing continuously, the use of cultivated land has shown a trend of conversion to non-grain uses, and large amounts of cultivated land originally used for the production of main grains have been occupied for other uses, significantly compressing the space for grain production and posing severe challenges to food security.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.2.1. Data Collection
The data used in this study mainly include remote sensing data, land use data, and socioeconomic data. (1) Remote sensing data include satellite images and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Net Primary Production of Vegetation (NPP), Population Density (POPD), and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data. The satellite images used for this study are Landsat 5 and Landsat 8 remote sensing images provided by the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform covering the years 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 with a spatial resolution of 30 m. (2) Land use data mainly include the China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD) and the MGL dataset, which cover 16 types of land covers including cultivated land, woodland, shrubs, grassland, water bodies, single-season rice, and single-season wheat, cover the time ranges of 1985 and 1990–2020, and are suitable for conducting research on land use and land cover changes [22,23,24]. (3) Socioeconomic data include road vector data, gross domestic product (GDP) data, and other data from statistical yearbooks [25,26]. The detailed data sources are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data sources.
2.2.2. Data Processing
Non-grain conversion of cultivated land in the BR region is characterized by significant regional features, regional complexity, and complex driving mechanisms. On the one hand, with the acceleration of urbanization and industrialization, large amounts of high-quality cultivated land have been converted to built-up land; on the other hand, under the combined effect of multiple factors such as the constraints of natural resource endowments, the benefits of facility agriculture, the need for ecological restoration, and the abandonment of marginal lands, a pattern involving multiple types of converted land, such as cash crop land, seawater aquaculture ponds, and seedling land has gradually formed.
Therefore, the non-grain lands converted from MGL in the study area are classified into the following seven types based on the characteristics of non-grain conversion: built-up land, cash crop land, artificial wetland, aquaculture pond, seedling land, and wasteland. The data collected from the study area were processed according to the procedure detailed below. First, the required land types were extracted by performing cloud removal, median synthesis, and random forest classification on the remote sensing images. Subsequently, reclassification and raster calculation were performed based on the land use data. Finally, the land use classification system for the BR region was reconstructed (Table 2). The nine classes of land under the new classification system are MGL, non-MGL, woodland, seedling land, grassland, aquaculture ponds, barren, built-up land, and other water bodies and wetlands (Figure 3).

Table 2.
BR land use classification system.
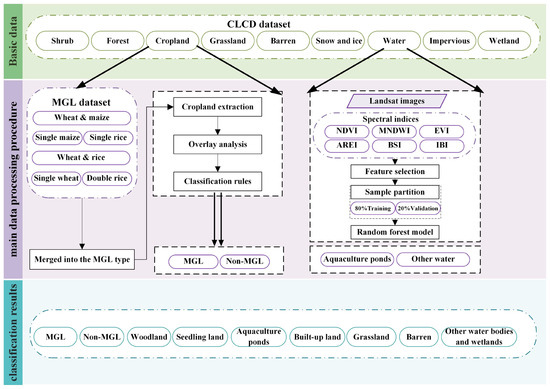
Figure 3.
Data processing flowchart.
In this study, the Random Forest (RF) algorithm was implemented on the GEE platform to extract the aquaculture pond land use class. After multiple experimental trials, the number of decision trees was set to 50 to achieve an optimal balance between classification accuracy and computational efficiency. Six surface reflectance bands and six derived spectral indices were selected as input features: bands blue, green, red, Near-Infrared (NIR), Shortwave Infrared 1 (SWIR1), and Shortwave Infrared 2 (SWIR2); NDVI, Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), Aquatic Reflectance Enhancement Index (AREI), Bare Soil Index (BSI), and Index of Building Intensity (IBI). Training samples were selected through visual interpretation, with 80% of the samples used for training and 20% for validation. The water body class from CLCD was used as a spatial mask to ensure that aquaculture ponds were extracted only within known water areas. Using this approach, the water body data were reclassified into aquaculture ponds and other water bodies, achieving an average overall accuracy of 91% and an average Kappa coefficient of 0.82.
For the classification of MGL and non-MGL types, cropland pixels were first extracted from CLCD, which was developed by the Remote Sensing Information Processing Center of Wuhan University, to serve as the baseline layer. To further distinguish major grain-producing areas, the MGL dataset, representing the spatial distribution of major grain crop cultivation, was incorporated. All spatial datasets were projected into a unified coordinate system and resampled to ensure raster alignment. Data processing in ArcGIS Pro 3.4 followed these steps: First, cropland rosters were extracted from the CLCD based on land use type codes; second, the MGL dataset was overlaid on the extracted cropland layer to identify cropland pixels within major grain-producing areas; finally, cropland pixels intersecting with the MGL dataset were classified as MGL, while the remaining cropland pixels were classified as Non-MGL.
3. Methodology
3.1. Evaluation Index System
In this study, the RC-NE-RP evaluation framework for the non-grain conversion of MGL was built based on the theory of the production function in economics.
In economics, “resource cost” refers to the economic value of the resources that society must give up for other optimal purposes in order to produce goods and services [27]. The resource cost in the process of non-grain conversion of cultivated land refers to the value of cultivated land in ensuring food security, maintaining spatial pattern stability, and providing ecological services that society gives up when converting cultivated land to particular non-grain purposes (e.g., development and construction, improvement of economic benefits).
In this study, resource costs in the process of non-grain conversion of cultivated land were evaluated from three perspectives, namely quantity, landscape pattern, and quality. (1) The quantity cost refers to the reduction in the total quantity of cultivated land caused by the conversion of MGL to other uses. A land dynamics index was introduced to measure the intensity of land use change using the ratio of the net change in MGL to the initial area of MGL, thereby quantifying the loss of cultivated land resources [28]. (2) The landscape pattern cost is reflected in the spatial fragmentation and reduced connectivity of cultivated land resulting from the conversion of cultivated land to non-grain uses. In intensive agricultural systems, crops that rely on animal pollination exhibit a hump-shaped relationship between yield and the proportion of remaining natural land [29,30]. If originally contiguous farmland is fragmented into smaller plots, the stability of pollination services declines, causing greater fluctuations in crop yields and thereby threatening food security [31]. A connectivity index was used to evaluate the resource loss implied by changes in cultivated land pattern from the perspective of landscape ecology [32]. (3) The quality cost is manifested in the degradation of the ecological functions of cultivated land after it is converted to non-grain uses, such as reduced soil fertility and carbon storage. This type of degradation not only reduces the grain yield per unit area of farmland but also weakens crops’ resistance to drought, high temperatures, and pests, thereby exacerbating yield fluctuations and food supply instability. Soil security assessment, as an important component of land suitability analysis, is receiving increasing attention. For example, China and Papua New Guinea have gradually applied soil security assessments in agricultural production [33,34]. Soil security management is playing an increasingly important role in ensuring food production and protecting the ecological environment [35]. In this study, carbon retention (CR) was used as an indicator of the degradation of ecosystem services to quantify the carbon loss caused by the non-grain conversion of cultivated land [36].
Output represents negative effects. In economics, “output” refers to the quantity of goods or services produced from a certain resource input and is a core indicator of the benefits of production activities [37]. Output not only includes quantifiable material results (such as product quantity and economic benefits), but it also covers added value in institutional, ecological, and social aspects. It reflects the comprehensive impacts or effects of resource inputs, including both positive economic growth and social benefits and negative environmental impacts and resource costs. In the process of non-grain conversion of cultivated land, resource inputs such as land occupation, spatial reconstruction, and ecological conversion do not always lead to desirable outputs and returns. On the contrary, these inputs often produce negative effects such as financial loss, ecological damage and social security issues.
“Resource redundancy” refers to the situation where the resource input exceeds the necessary amount for given output. It reflects the ineffective or inefficient use of resources and is used to reveal the resource potential that can be released through structural optimization or technological improvements [38]. In the context of land use, resource redundancy can be construed as the situation where the amount of land occupied to achieve the current output or social goal exceeds the amount of land required under optimal conditions. By analyzing the efficiency variance between the land input structure and output benefits, it is possible to identify the areas and types of resource redundancy in the non-grain conversion process and thereby determine the remediation potential of land resources.
In this study, an index system consisting of 9 primary indexes and 13 secondary indexes for evaluating non-grain conversion of MGL under the RC-NE-RP framework was established (Table 3). The primary indexes include the dynamic degree, connectivity, carbon retention, Fiscal Stress Index (FSI), Ecological Stress Index (ESI), Social Stress Index (SSI), Economic Development Index (ENDI), Ecological Development Index (ELDI), and Social Development Index (SDI). The secondary indexes include the Patch Density (PD), Aggregation Index (AI), Soil Carbon Storage (SCS), and other relevant indexes.

Table 3.
Evaluation index system under the RC-NE-RP framework.
First, three primary indexes for resource costs were set as input variables, the primary indexes for negative effects were set as output variables, and the efficiency level of converting resource costs to negative effects measured through the model was used to evaluate the negative regional environmental impacts of non-grain conversion of MGL. Subsequently, the three primary indexes for resource costs were set as input variables, the primary indexes for remediation potential were set as output variables, and the compressible space of resource costs measured through the model was used to quantify the remediation potential of MGL converted to non-grain uses. Finally, the evaluation results for negative effects and remediation potential with respect to non-grain conversion of MGL were obtained.
3.2. Evaluation Model
Traditional SBM models evaluate the efficiency of decision-making units by optimizing slack variables [39,40,41], but such models do not consider the differences in importance among indexes, which may cause the key business logic to be neglected. To solve this problem, an SBM model improved using the entropy weight method was proposed. The improved SBM model performs objective weighting and optimizes the penalty direction for slack variables based on the theory of information entropy. The core advantage of this model is that it automatically calculates the weights of indexes based on the degree of data dispersion to avoid subjective bias, focuses on improving the operability of recommendations by optimizing the redundancy or deficiency of high-weight indexes, and reduces the sensitivity to outliers relying on standardization and weight constraints (Figure 4).
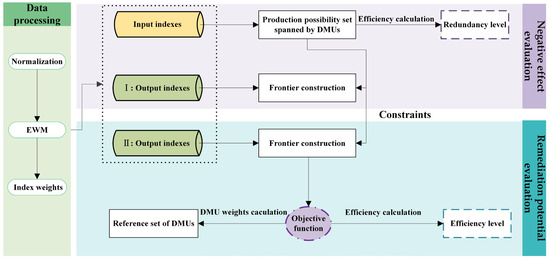
Figure 4.
Model flowchart.
(1) The data were standardized to eliminate dimension differences. The input and output data were normalized using the min–max normalization method and the following equations [42]:
(2) The weights of indexes were calculated using the Entropy Weight Method (EWM) and the following equations [43,44]:
(3) The weights calculated by EWM were embedded into the SBM objective function to establish an optimized slacks-based model, i.e., the improved SBM model, using the following equation:
The constraints are as follows:
Here, m is the number of input indexes, s is the number of output indexes, and are the values of the input and output indexes of the current decision-making unit, is the weighting factor of the decision-making unit j, and are the redundant variables for insufficient input and excess output, and and are the weights of input and output indexes determined by EWM.
3.3. Cluster Analysis
As an unsupervised learning method, cluster analysis mainly aims to divide unlabeled data into clusters with internal homogeneity and external heterogeneity by calculating the similarity or distance between samples, thereby revealing the underlying distribution or behavior patterns of the data [45].
Its basic principle can be expressed as follows: Assuming that there are n geographical units in the study area, and each unit xi consists of m standardized attribute variables, i.e., , the algorithm aims to divide the n units into k clusters so as to minimize the following objective function:
Here, is a cluster set, is the mean vector (centroid) of the cluster, and is the squared Euclidean distance between a sample and the centroid of its cluster. During each iteration, the cluster centroid is updated by the following equation:
In this study, the spatial and dimensional priorities for the remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL were determined through cluster analysis based on the evaluation results for negative effects and remediation potential with respect to non-grain conversion of MGL and used as the basis for subsequent remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL.
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Non-Grain Conversion of MGL in the BR Region
During the period from 1990 to 2020, the BR region experienced a rapid process of conversion of MGL to non-grain land. The land use transition matrixes (Figure 5) show that, during the period from 1990 to 2020, the total area of MGL in the BR region decreased significantly, while the total area of built-up land, aquaculture ponds, and seedling land increased significantly.
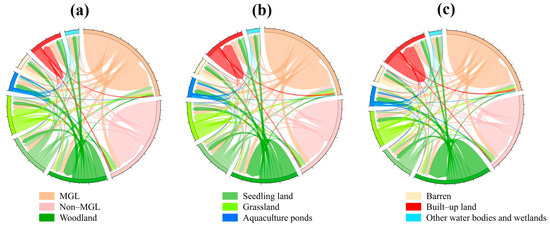
Figure 5.
Land use transition matrixes of the BR region for three periods (1990–2020): (a) 1990–2000; (b) 2000–2010; (c) 2010–2020.
From the perspective of quantity, the median of the dynamic degree was 0.0704 during the period from 1990 to 2000, increased significantly by 418.4% to 0.365 during the period from 2000 to 2010, and declined slightly but remained at a relatively high level during the period from 2010 to 2020. Over the 30 years from 1990 to 2020, the dynamic degree had generally increased by 401.4%, indicating that the conversion of MGL to non-grain uses in the BR region had accelerated dramatically. The dynamic degree reached its peak during the period from 2000 to 2010, which is consistent with the fact that the land urbanization rate of the BR region increased continuously during these ten years. The dynamic rate of the BR region shows significant spatial differences and is characterized by expansion from the coastal areas around the Bohai Bay to the hinterlands, forming a broad spatial pattern with the Bohai Bay as the core and extending to the north, west, and south. In terms of landscape pattern, the median of connectivity was 65.23 during the period from 1990 to 2000, decreased to 53.2 during the period from 2000 to 2010, and increased to 55.19 during the period from 2010 to 2020. During the period from 1990 to 2020, the overall connectivity decreased by 15.4%. A possible reason for this trend could be that dense and contiguous MGL was mostly concentrated in the early stage, and with the progress of urbanization, MGL became increasingly fragmented over time, leading to subsequent changes in land use based on fragmented MGL. The connectivity index of the BR region exhibits significant spatial differences and is characterized by an overall shift of focus to the south. In terms of quality, from 1990 to 2020, the median of CR increased steadily during the period from 1990 to 2020. The high CR values of the BR region have been distributed near Beijing and the Bohai Economic Rim (BER) at all times (Figure 6 and Figure 7).
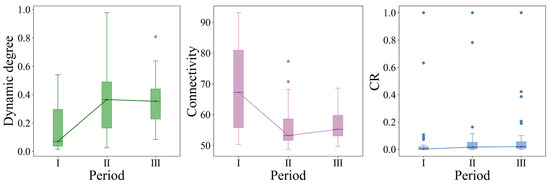
Figure 6.
Temporal evolution characteristics of the quantity, landscape pattern, and quality of non-grain land converted from MGL: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020.
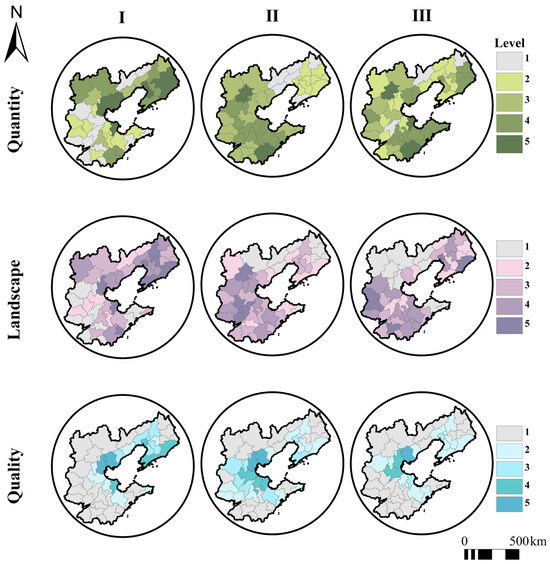
Figure 7.
Spatial evolution characteristics of the quantity, landscape pattern, and quality of non-grain land converted from MGL: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020 (Numbers 1–5 represent the degrees of severity of non-grain conversion in ascending order).
4.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of the Negative Effects of Non-Grain Conversion of MGL in the BR Region
During the period from 1990 to 2020, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region on regional comprehensive development showed an upward trend. The median of such negative effects was 0.729 during the period from 1990 to 2000, increased to 0.993 during the period from 2000 to 2010, and further increased to 1.085 during the period from 2010 to 2020, representing an overall increase of 48.83% over the 30 years from 1990 to 2020 (Figure 8), and the difference in negative effects between areas decreased. These trends indicate that, with the progress of urbanization, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in various areas of the BR region are becoming increasingly serious.
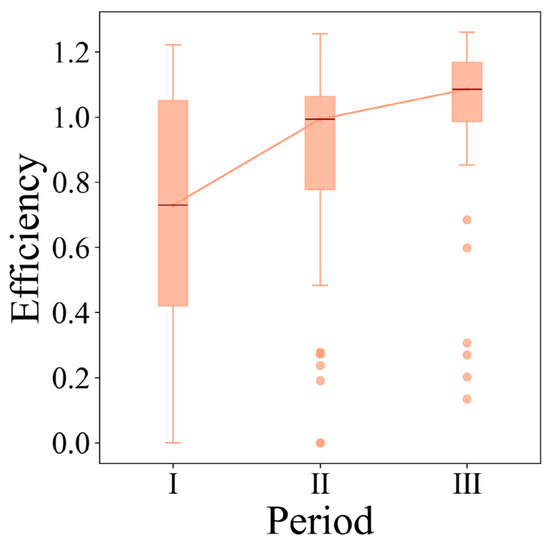
Figure 8.
Temporal evolution characteristics of the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020.
The FSI has shown an upward trend, and the difference in FSI between various areas within the BR region has increased significantly. The ESI has shown an upward trend followed by a downward trend, and the difference in ESI between various areas within the BR region first increased and then decreased. The SSI has shown a slight downward trend without significant overall changes, and the difference in SSI between various areas within the BR region has decreased (Figure 9).
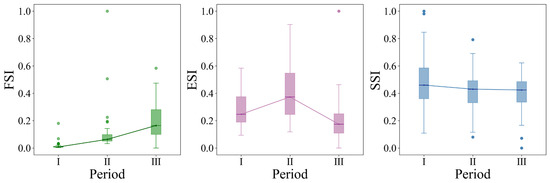
Figure 9.
Temporal evolution characteristics of FSI, ESI, and SSI: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020.
The negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region show significant spatial differences, generally exhibiting a trend of increase from Beijing–BER to the southeast hinterland (Figure 10). During the period from 1990 to 2000, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL varied greatly from one area to another in the BR region. Specifically, Tianjin and its surrounding areas experienced significant negative effects of non-grain conversion, while most areas in Hebei Province experienced moderate or low negative effects of non-grain conversion. The negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in Liaoning Province varied significantly from one area to another, with the Liaodong Peninsula subjected to relatively strong negative effects and the northern areas experiencing negative effects to varying extents. The negative effects of the non-grain conversion of MGL in Shandong Province show a spatial pattern featuring stronger negative effects in the middle and weaker negative effects on both flanks. During the period from 2000 to 2010, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL spread significantly in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and intensified in many areas of central and southern Hebei, showing a trend of intensification within the region; the original severe negative effects on many areas in Liaoning Province weakened, the range of negative effects caused by non-grain conversion of MGL in Shandong Province further expanded, and the areas subjected to strong negative effects (high-value areas) gradually shifting to coastal cities represented by Yantai City. During the period from 2010 to 2020, the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region generally showed an upward trend, and large high-value areas appeared in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, and the negative effects were highly concentrated in space; the overall level of such negative effects in Liaoning Province rebounded. Almost all areas of Shandong Province turned into high-value areas, indicating that Shandong Province experienced the most severe negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL.
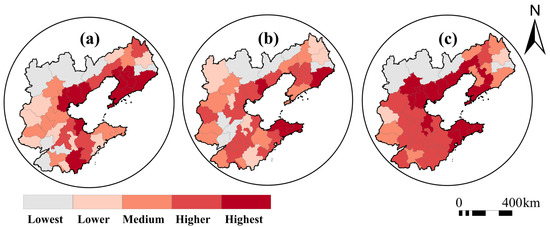
Figure 10.
Spatial evolution characteristics of the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL: (a) 1990–2000; (b) 2000–2010; (c) 2010–2020.
4.3. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of the Remediation Potential of Non-Grain Land Converted from MGL in the BR Region
During the period from 1990 to 2020, the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region changed significantly over time (Figure 11 and Figure 12). In terms of quantity, the median of the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL was 0.706 during the period from 1990 to 2000, slightly decreased to 0.643 during the period from 2000 to 2010, and rose sharply to 0.98 during the period from 2010 to 2020. In terms of landscape pattern, the median of remediation potential was 0.645 during the period from 1990 to 2000, slightly decreased to 0.507 during the period from 2000 to 2010, and slightly rebounded to 0.546 during the period from 2010 to 2020. In terms of quality, the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL remained stable at high levels above 0.98.
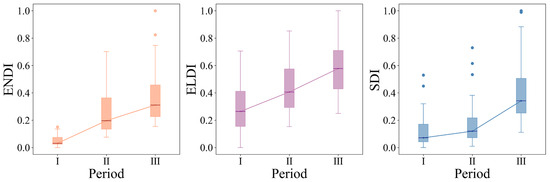
Figure 11.
Temporal evolution characteristics of ENDI, ELDI, and SDI: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020.
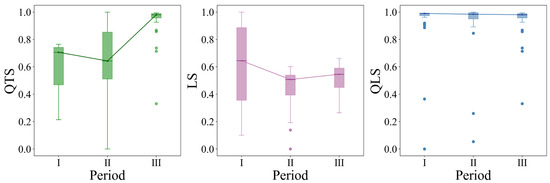
Figure 12.
Temporal evolution characteristics of the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020.
The remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL shows significant spatial differences (Figure 13). In terms of quantity, during the period from 1990 to 2000, the distribution of the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region was relatively uniform; during the period from 2000 to 2010, the areas with high remediation potential (high-value areas) were concentrated in some parts of the Liaodong Peninsula; and during the period from 2010 to 2020, the differences in remediation potential between various areas became more obvious. It is to be noted that the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in Beijing remained at relatively high levels during the period from 1990 to 2000 and declined to low levels during the period from 2000 to 2020. The main reason for this trend could be that Beijing is a megacity with rapid urbanization and highly tight land supply, making it very difficult to convert land for other uses to MGL while protecting the existing MGL. In terms of landscape pattern, the high-value areas were mainly concentrated in some municipal cities in the Liaodong Peninsula and BR region during the period from 1990 to 2000, shifted to inland areas during the period from 2000 to 2010, and became concentrated primarily in the municipal cities in southern Hebei Province and central Shandong Province. In general, during the three decades from 1990 to 2020, the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region was relatively high and evenly distributed. However, it is worth noting that, in terms of quality, the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in several cities represented by Tianjin and Tangshan was relatively low during the period from 2000 to 2010.
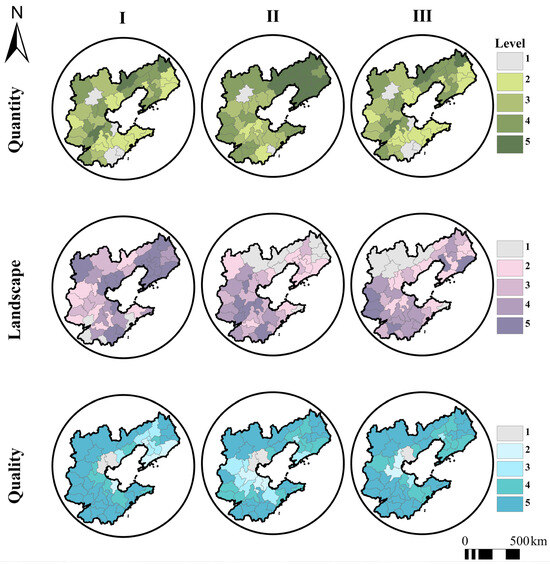
Figure 13.
Spatial evolution characteristics of the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL: I—1990–2000; II—2000–2010; III—2010–2020 (Numbers 1–5 represent the levels of remediation potential in ascending order).
4.4. Zoning of Non-Grain Land Converted from MGL in the BR Region for Remediation
4.4.1. Priority Levels for Spatial Remediation
For the identification of non-grain land to be remediated, based on the evaluation results in respect of the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region, the priority levels for spatial remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL in this region were determined, and such non-grain land was divided into two types of zones, namely priority remediation zones and low-priority remediation zones. Low-priority remediation zones are areas where the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL are relatively weak and grain production function still remains stable, while priority remediation zones are areas where the negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL are relative strong and policy intervention and functional restoration are urgently needed. Based on the analysis from the traditional perspective of resource security, the priority remediation zones only include Tianjin and Tangshan. However, when the measure of negative effects is considered, the priority remediation zones expand significantly, covering almost the entirety of Beijing–BER and showing a pattern of outward radiation, which is consistent with the general law of regional development (Figure 14).
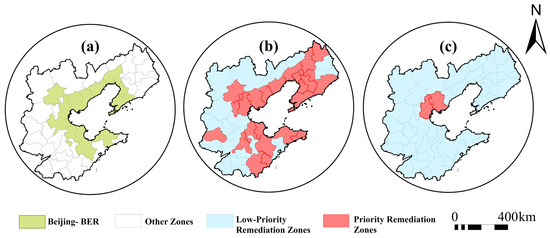
Figure 14.
Zoning results with priority levels for spatial remediation: (a) Scope of Beijing–BER; (b) zoning results from the perspective of negative effects; (c) zoning results from the traditional perspective of resource security.
4.4.2. Priority Levels for Dimensional Remediation
In terms of non-grain land remediation methods, based on the evaluation results in respect to the remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region, the priority levels for dimensional remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL in the region were determined from the perspective of resource costs and inputs, and such non-grain land was divided into three types of zones, including Quantity–Quality Priority Zones, Quantity–Landscape Priority Zones, and Quality–Landscape Priority Zones. During the period from 1990 to 2000, the Quantity–Quality Priority Zones included most areas of Hebei Province and Shandong Province, the Quantity–Landscape Priority Zones only included Tianjin and Tangshan, and the Quality–Landscape Priority Zones were mainly concentrated in the Liaodong Peninsula and its surrounding areas. During the period from 2000 to 2010, the scope of the Quantity–Quality Priority Zones shrank, the scope of the Quantity–Landscape Priority Zones expanded, some areas of the Liaodong Peninsula and some cities in southern Hebei Province, including Handan City and Xingtai City, were transformed from Quantity–Quality Priority Zones to Quantity–Landscape Priority Zones, and the Quality–Landscape Priority Zones were mainly concentrated in Shandong Province and cities in central Hebei Province. During the period from 2010 to 2020, the scope of the Quantity–Quality Priority Zones gradually expanded, and northern Hebei Province, the Jiaodong Peninsula, and its surrounding areas gradually became Quality–Landscape Priority Zones (Figure 15).
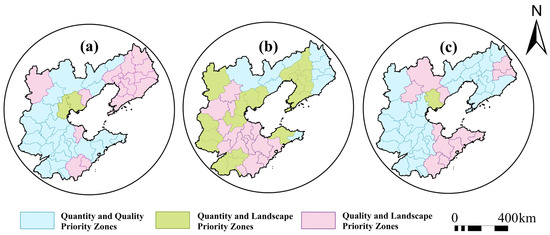
Figure 15.
Zoning Results with priority levels for dimensional remediation: (a) 1990–2000; (b) 2000–2010; (c) 2010–2020.
5. Discussion
5.1. Causes of Non-Grain Conversion of MGL in the BR Region
Non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region—a densely populated, economically active, and highly urbanized region in China—is a comprehensive and typical process with distinctive characteristics. Under the combined effects of multiple factors such as urban expansion, economic benefits, and the structural transformation of the agricultural sector, the conversion of MGL to diversified non-grain uses has shown a significant trend characterized by spatial reconstruction and industrial redistribution [46,47,48].
First, the expansion of urban built-up land has led to the conversion of large amounts of cultivated land to other purposes [49]. With the coordinated development of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region and the strategic development of the Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt (LCEB), large amounts of high-quality cultivated land have been used for urban infrastructure and industrial construction. For example, the urbanization rate of the Tianjin Binhai New Area has increased significantly since 2009, and a large amount of original MGL has been converted to land uses such as industrial parks, residential communities, and transportation facilities, which is a typical case of MGL conversion to non-agricultural uses. Such non-grain conversion of MGL caused by urban expansion has not only changed the land use structure, but it has also gradually compressed the space for growing main grain crops.
Second, the expansion of aquaculture is also one of the important causes of non-grain conversion of cultivated land [50]. The coastal areas along the BR have natural advantages for the development of aquaculture. To meet the demand for aquatic products and increase agricultural income, large amounts of traditional MGL in these areas have been converted into aquaculture ponds. For example, Pikou Town in Liaoning Province covers an area of 93 km2, almost all of which is used for sea cucumber farming, resulting in a situation where the original cultivated land has basically been replaced by aquaculture ponds. Such conversion of cultivated land has not only compressed the space for main grain production, but it has also caused ecosystem disturbances such as the eutrophication of water bodies and shoreline degradation.
Third, the expansion of the nursery industry and land occupation by facility agriculture have also contributed to the non-grain conversion of cultivated land [51]. With the increase in demand for greening and urban gardening, nursery farming has become an important alternative industry in some areas around the Bohai Sea. For instance, in some counties in Langfang and Baoding, Hebei Province, nursery farming has become a new channel for farmers to increase their income, and large amounts of cultivated land originally used for main grain production have been converted to nurseries. Nursery land still falls under the category of agricultural land, but such land use, which is characterized by long crop growth period, monoculture, and long income cycle, has substantially weakened the grain production function of cultivated land. More importantly, this type of land use is often accompanied by the construction of facilities such as greenhouses, sunshades, and irrigation systems, which intensifies the “structural non-grain conversion” of land and makes it difficult to restore nursery land to the purpose of grain production.
5.2. Implications of Comprehensive Remediation of Non-Grain Land Areas Converted from MGL in the BR Region
For the remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region, several recommendations are made herein from the perspectives of the supervision over land use transitions, the establishment of regional complementary links, and the identification of key remediation aspects.
(1) The first recommendation is to strictly supervise MGL occupation by built-up land, aquaculture ponds, and nursery land in the BR region, strengthen the control of cultivated land use, strictly control the tendency for non-agricultural and non-grain conversion of MGL; improve the cultivated land protection system, enhance the implementation mechanisms of systems such as the Cultivated Land Acquisition–Compensation Balance (CLACB) System and Land Manager System to protect the cultivated land and production capacity of main grain production areas; coordinate the needs of regional development and the resource carrying capacity, provide guidance on the orderly shift of non-grain industries to non-basic farmland areas or ecologically suitable areas, promote spatial separation between industrial land and the red line for the protection of MGL, and prevent disorderly expansion of non-grain production activities. In addition, in light of the vulnerability and land resource pressures of the coastal areas in the BR region, particularly the further reduction of arable land availability caused by salinization and flooding, a zoning-based management strategy should be adopted [52,53]. Based on remote sensing and soil monitoring data, coastal lowlands and severely salinized areas can be classified into high-vulnerability, medium-vulnerability, and low-vulnerability zones, with differentiated governance measures implemented accordingly. In high-vulnerability zones, salt-tolerant or flood-resistant crops (e.g., salt-tolerant rice and tuber crops) should be promoted alongside soil improvement measures such as gypsum amendment and drainage infrastructure construction [54]. In medium-vulnerability zones, crop rotation, intercropping, and flood-control facilities should be implemented to enhance soil resilience and reduce disaster risks [55]. From a land-use planning perspective, non-grain expansion should be strictly limited in high-vulnerability zones, while non-grain industries should be concentrated in low-vulnerability zones or non-prime farmland areas, in order to mitigate further land degradation and achieve the dual goals of securing food production and safeguarding the ecological environment.
(2) The second recommendation is to establish complementary links between Beijing–BER and other areas of the BR region, classify Beijing–BER as a priority remediation zone and other areas as low-priority remediation zones, and coordinate the establishment of a horizontal inter-city benefit compensation mechanism for priority remediation zones and low-priority remediation zones. Considering that the gap between food supply and demand in priority remediation zones is constantly widening due to factors such as changes in crop planting structure, expansion of built-up land, and intensified population movements and that priority remediation zones bear primary responsibility for ensuring food security, priority remediation zones should scientifically optimize their agricultural production structure, improve grain production systems and the conditions of grain production facilities, and enhance local food self-sufficiency. In view of the fact that the level of economic development of low-priority remediation zones is relatively low due to factors such as the low comparative benefits and limited financial contribution of grain farming, it is recommended to implement diversified compensation measures in low-priority remediation zones, establish a mechanism of horizontal compensation between priority remediation zones and low-priority remediation zones, leverage the industrial resources and economic strengths of priority remediation zones to compensate for the concessions made by low-priority remediation zones to ensure food security, and thereby effectively motivate low-priority remediation zones to promote grain production [56,57,58]. Considering the practical feasibility of relevant policies, several concrete measures can be proposed. At the financial level, priority remediation zones should support low-priority remediation zones through fiscal transfers and dedicated funds for high-standard farmland construction, grain reserve system improvement, and the dissemination of agricultural technologies, thereby directly enhancing their production capacity [59]. At the industrial level, priority remediation zones should be guided to allocate parts of the agricultural value chain, such as food processing, cold-chain logistics, and grain storage, to low-priority remediation zones, thereby promoting local economic development through industrial extension and regional division of labor. At the technological and human resource level, priority remediation zones can rely on their advantages in research and education to promote the application of smart and green agriculture in low-priority remediation zones while establishing permanent mechanisms for expert placement and farmer training to raise productivity and quality. At the policy and market level, the creation of a long-term and stable grain purchase–sale coordination mechanism is recommended, including the establishment of green channels and price support for grain products from low-priority remediation zones, complemented by tax incentives and financial assistance to enhance farmers’ comparative returns and motivation. Through these diversified compensation measures, a stable framework of benefit-sharing and responsibility-sharing can be formed between priority and low-priority remediation zones [60]. In this process, priority remediation zones will reinforce their capacity for food security, while low-priority remediation zones will gain development resources and institutional incentives, thereby achieving the dual objectives of regional food security and coordinated economic development.
(3) The third recommendation is to develop and implement plans for gradient remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL taking into account the differences in remediation potential in different regions and dimensions; in terms of quantity, prioritize the management and control of land use transitions with respect to MGL and strictly control the red-line quantity of MGL; in terms of landscape, give priority to solving land connectivity issues with respect to MGL and, through policy guidance and technology-enabled management, establish an agricultural production pattern characterized by “land concentration and contiguousness, suitability for both traditional and mechanized farming, high and stable yields”; in terms of quality, give priority to solving quality issues with respect to MGL, improve the land environment serving grain production, increase grain production per unit area, and tap the grain production potential. For regions with different levels of remediation potential, adaptive strategies can be proposed. In urbanized areas, vertical farming, rooftop farming, and indoor greenhouses can be encouraged to increase yield per unit area and reduce land occupation [61,62]. At the same time, cooperation between urban agricultural supply chains and priority remediation zones should be promoted to achieve coordinated grain production and marketing [63]. In high-potential remediation zones, measures such as soil nutrient improvement, smart irrigation, and precision fertilization can be adopted to enhance land recovery capacity and grain yield alongside the promotion of stress-resistant crops and climate-adapted cropping patterns to improve the stability of grain production. In low-potential remediation zones, ecological compensation and policy incentives should be prioritized, with large-scale production postponed in favor of land conservation and ecological restoration, so as to ensure the long-term sustainable use of land resources.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Within the scope of this study, several limitations should be noted which can be further investigated in future studies. (1) Due to the limitation of data acquisition capacity, this study remains at the municipal scale, and further studies need to be conducted on the evaluation of non-grain conversion of MGL at the prefectural scale. Analyses at the prefectural scale can better reveal the changes in non-grain conversion of MGL during urbanization and provide reference data for developing more accurate and adaptive remediation strategies. (2) This study only considers some indexes within the data acquisition capacity. For future studies, other indexes that can characterize non-grain conversion of MGL in a more detailed and comprehensive manner can be developed. (3) This study has been conducted from a perspective combining resource costs, negative effects and remediation potential, but it has not fully considered the potential impacts of policies and other factors. For future studies, scenario-based predictive modeling should be conducted to evaluate the impacts of climate change and accelerated urbanization. Furthermore, a more comprehensive investigation should be carried out to assess the rationality of MGL resource allocation and the effectiveness of restoration in priority remediation zones during the non-grain conversion process of MGL. These efforts will provide decision-makers with forward-looking, evidence-based recommendations.
6. Conclusions
In this study, the resource costs, negative effects, and remediation potential with respect to non-grain conversion of MGL in economically developed coastal areas represented by the BR region during the period of from 1990 to 2020 were evaluated. Specifically, a Resource Cost-Negative Effect-Remediation Potential (RC-NE-RP) evaluation framework was established, and the negative effects and remediation potential with respect to non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region during the period from 1990 to 2020 were systematically evaluated using the RC-NE-RP framework. Based on the evaluation results, the non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region was divided into separate remediation zones. It was found that, during the period from 1990 to 2020, the cultivated land in the BR region was gradually converted from MGL to non-grain uses such as construction and development, aquaculture, and nursery farming, and such conversion showed a trend of rapid conversion followed by slow conversion. The negative effects of non-grain conversion of MGL in the BR region gradually extended from Beijing–BER to the Liaoning Peninsula in the northwest and the Shandong Peninsula in the southeast, forming a spatial pattern with “extended effects on both flanks and concentrated effects in coastal areas” and showing the characteristics of “radiation from the center and attenuation at the margins”. The overall remediation potential of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region had remained at high levels until 2020. The quantity and quality of MGL have become the focus of remediation in most areas of this region. The Shandong Peninsula cities represented by Yantai and Qingdao should focus on solving problems related to the quality and landscape pattern of MGL. In addition, three recommendations were proposed with respect to the comprehensive remediation of non-grain land converted from MGL in the BR region. These recommendations can be used as scientific references for the protection and sustainable development of cultivated land in economically developed regions. In general, this study provides a theoretical framework for the remediation of non-grain land converted from cultivated land and the protection of cultivated land.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.G.; methodology, Q.G. and J.L.; software, J.L.; validation, Q.G.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, J.L.; resources, Q.G.; data curation, J.L. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, Q.G.; visualization, J.L., H.L., J.C. and T.M.; supervision, Q.G.; project administration, Q.G.; funding acquisition, Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 42476246), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (grant number ZR2021QD064), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant number 22CX06033A).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the developers for their tools and the respective agencies that provided the data. We further thank all editors and anonymous reviewers for spending their time working on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BR | Bohai Rim |
| BER | Bohai Economic Rim |
| MGL | Main Grain Land |
| CLCD | China Land Cover Dataset |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| NPP | Net Primary Production of Vegetation |
| POPD | Population Density |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| RC | Resource Cost |
| NE | Negative Effect |
| RP | Remediation Potential |
| CR | Carbon retention |
| PD | Patch density |
| AI | Aggregation index |
| SCS | Soil carbon storage |
| GPBE | General public budget expenditure |
| PFR | Pesticide and fertilizer dosages per unit area |
| PR | PM2.5 emissions per unit area |
| FA | Per capita food availability |
| UR | Unemployment rate |
| RD | Road density |
| FSI | Fiscal stress index |
| ESI | Ecological stress index |
| SSI | Social stress index |
| ENDI | economic development index |
| ELDI | Ecological development index |
| SDI | Social development index |
References
- Sun, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, G.J.; Chen, F. Spatial Differentiation of Non-Grain Production on Cultivated Land and Its Driving Factors in Coastal China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Huang, A.; Xiong, B.; Song, C. Characteristics and Driving Forces of Non-Grain Production of Cultivated Land from the Perspective of Food Security. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Hall, C.A.; Wang, H. Land Use Change in Rice, Wheat and Maize Production in China (1961–1998). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 95, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, X. Understanding the Structural Imbalance in Non-Grain Land Utilization: Insights from China’s Arable Land Policy. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 181, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Yin, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y. Formation Mechanism and Sustainable Productivity Impacts of Non-grain Croplands: Evidence from Sichuan Province, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, R.J.; Wheeler, P.N.; O’Dogherty, M.J.; Watt, C.D.; Richards, T. Cumulative Mass Determination for Yield Maps of Non-Grain Crops. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1999, 23, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Qian, K.; Lin, L.; Wang, K.; Guan, T.; Gan, M. Identifying the Driving Forces of Non-Grain Production Expansion in Rural China and Its Implications for Policies on Cultivated Land Protection. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, H. The Impact of the Fragmentation of the Cultivated Land on “non-Grain” Usage. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2025, 71, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, X. Evolutionary Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Non-Grain of Cultivated Land in Main Grain-Producing Areas—A Case Study of Lianyungang City, China. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0325259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xiao, D.; Yin, M. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Factors of Non-Grain Cultivated Land in China’s Three Main Functional Grain Areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, M.; Gong, J.; Yang, J. Spatial Correlation of Non-Agriculturalization and Non-Grain Utilization Transformation of Cultivated Land in China and Its Implications. Land 2025, 14, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Song, Y. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of “Non-Grain Production” in Hubei Province Based on a Non-Grain Index. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Deng, J.; Shahtahmassebi, A.R.; Zhang, L.; Ao, W.; Guan, T.; Pan, Y.; Gan, M. Quantifying the Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Multi-Aspect Performance of Non-Grain Production during 2000–2015 at a Fine Scale. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Yan, X.; Zheng, X.; Mao, Y.; Fu, X.; Yao, X.; Jiang, S. Exploring the Impacts of Land Use/Cover Change on Ecosystem Services in Multiple Scenarios—The Case of Sichuan-Chongqing Region, China 2023. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2401.01363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, P.; Sun, Z. Spatiotemporally Mapping Non-Grain Production of Winter Wheat Using a Developed Auto-Generating Sample Algorithm on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.; Zhu, Z. The Impact of Non-Grain Conversion of Cultivated Land on the Relationship between Agricultural Carbon Supply and Demand. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 162, 103166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Song, G.; Wang, Q.; Sui, H. Impact of “Non-Grain” in Cultivated Land on Agricultural Development Resilience: A Case Study from the Major Grain-Producing Area of Northeast China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Duan, L. The Bohai Sea. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 377–394. [Google Scholar]
- Gavioli, A.; de Souza, E.G.; Bazzi, C.L.; Schenatto, K.; Betzek, N.M. Identification of Management Zones in Precision Agriculture: An Evaluation of Alternative Cluster Analysis Methods. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 181, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, E.L. A Historical Review on the Role of the Bohai Coastal Region in China’s History: Qingdao, Dalian, and Economic Rim. In From Colonial Seaports to Modern Coastal Cities; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 59–85. ISBN 978-981-99-9076-4. [Google Scholar]
- Announcement on China’s 2024 Grain Production Data—National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202412/t20241213_1957744.html (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Guan, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, T.; Zhou, X. Assessment of Coastal Carbon Storage and Analysis of Its Driving Factors: A Case Study of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Land 2024, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. The Dataset of Main Grain Land Changes in China over 1985–2020. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Divergent Shifts in Peak Photosynthesis Timing of Temperate and Alpine Grasslands in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Major Road Dataset 2000—Population and Transportation—Human Geography Data—Data Catalog-College of Urban and Environmental Sciences, Peking University [v1.0.0]. Available online: https://geodata.pku.edu.cn/index.php?c=content&a=show&id=1399 (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Mankiw, N.G. Principles of Economics; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Huang, B.; Huang, J.; Li, S. Measuring Land Change in Coastal Zone around a Rapidly Urbanized Bay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; et al. Habitat Fragmentation and Its Lasting Impact on Earth’s Ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybicki, J.; Abrego, N.; Ovaskainen, O. Habitat Fragmentation and Species Diversity in Competitive Communities-Rybicki-2020-Ecology Letters-Wiley Online Library. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, D.; Haegeman, B.; Gaba, S.; Mazancourt, C.D.; Loreau, M. Habitat fragmentation and food security in crop pollination systems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2401.01363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L. Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-M.; Minasny, B.; Ma, Y.-X.; Field, D.; McBratney, A.; Wu, C.-F. A Preliminary Soil Security Assessment of Agricultural Land in Middle-Eastern China. Soil Use Manag. 2018, 34, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Sanderson, T.; Field, D.; Fidelis, C.; Yinil, D. Soil Security for Developing and Sustaining Cocoa Production in Papua New Guinea. Geoderma Reg. 2019, 17, e00212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozza, L.E.; Field, D.J. The Science of Soil Security and Food Security. Soil Secur. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Zhang, L.; Waletzko, E.; Bernal, B. Validation of the Ecosystem Services of Created Wetlands: Two Decades of Plant Succession, Nutrient Retention, and Carbon Sequestration in Experimental Riverine Marshes. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 72, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varian, H.R. Intermediate Microeconomics: A Modern Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, M.J. The Measurement of Productive Efficiency. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 1957, 120, 253–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, T.; Shan, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, M.; Li, F.; de Vries, W.T. Applying SBM-GPA Model to Explore Urban Land Use Efficiency Considering Ecological Development in China. Land 2021, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Su, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. Assessment and Decomposition of Regional Land Use Efficiency of the Service Sector in China. Land 2022, 11, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yin, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y.; Xia, R. Industrial Carbon Emission Efficiency of Cities in the Pearl River Basin: Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces. Land 2022, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, M.; Huang, N.; Duan, W.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Song, W. Relationship between Urbanisation and Habitat Quality in the Grand Canal, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdan, A.; Bezdan, J.; Marković, M.; Mirčetić, D.; Baumgertel, A.; Salvai, A.; Blagojević, B. An Objective Methodology for Waterlogging Risk Assessment Based on the Entropy Weighting Method and Machine Learning. Catena 2025, 249, 108618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banadkouki, M.R.Z. Selection of Strategies to Improve Energy Efficiency in Industry: A Hybrid Approach Using Entropy Weight Method and Fuzzy TOPSIS. Energy 2023, 279, 128070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhulatha, T.S. An Overview on Clustering Methods 2012. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1205.1117. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Tao, Y.; Huang, C.; Yi, J.; Yi, D.; Wang, F.; Tao, Q.; Xi, H.; Ou, W. Unraveling the Causal Mechanisms for Non-Grain Production of Cultivated Land: An Analysis Framework Applied in Liyang, China. Land 2022, 11, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Shi, H.; Zhang, S. Assessing the Environmental Impact of Agricultural Production Structure Transformation—Evidence from the Non-Grain Production of Cropland in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. Driving Factors of Farmers’ Non-Grain Production of Cropland in the Hilly and Mountainous Areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 461, 142658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Yi, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; et al. The Changing Patterns of Cropland Conversion to Built-up Land in China from 1987 to 2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, J.; Cao, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Da, C.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lai, S. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Spatial Pattern Analysis of Non-Grain Production of Cultivated Land in Anhui Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Sun, A. Progress and Prospects of Non-Grain Production of Cultivated Land in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.; She, D.; Chen, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Qureshi, A.S.; Singh, A.; et al. Monitoring, Reclamation and Management of Salt-Affected Lands. Water 2025, 17, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Arkema, K.K.; Han, B.; Lu, F.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Ouyang, Z. Coastal Vulnerability to Climate Change in China’s Bohai Economic Rim. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ji, R.; Xu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Pu, L.; Jia, Z.; Wu, T.; Xu, F.; Hu, J.; Miu, Y.; et al. Effect of Salt-Tolerant Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivation on Soil Bacterial Community and Ecological Function Groups in Coastal Saline Land. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 201, 105511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Huai, Y.; Hassan, M.U.; Cui, Z.; Ning, P. Enhancing Crop Productivity and Resilience by Promoting Soil Organic Carbon and Moisture in Wheat and Maize Rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 368, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, X.; Jiang, C.; Dang, Y.; Kong, X.; Lin, C. Establishment of an Inter-Provincial Compensation System for Farmland Protection in China: A Framework from Zoning-Integrative Transferable Development Rights. Land Use Policy 2025, 150, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hong, J.; Shen, X.; Xie, F.; Li, X. Grain Self-Sufficiency versus Environmental Stress: An Integration of System Dynamics and Life Cycle Assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 159, 112153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Du, H.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y. Horizontal Ecological Compensation Zoning and Standard in China’s Major Grain-Producing Areas Based on Virtual Cultivated Land Flow. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1578780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAP at a Glance—European Commission. Available online: https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/common-agricultural-policy/cap-overview/cap-glance_en (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Peng, Z.; Pu, H.; Huang, X.; Zheng, R.; Xu, L. Study on Public Willingness and Incentive Mechanism of Ecological Compensation for Inter-Basin Water Transfer in China in the Carbon Neutral Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kodmany, K. The Vertical Farm: A Review of Developments and Implications for the Vertical City. Buildings 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintuyi, O.B. Vertical Farming in Urban Environments: A Review of Architectural Integration and Food Security. Open Access Res. J. Biol. Pharm. 2024, 10, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Spatial Characteristics of the Non-Grain Production Rate of Cropland and Its Driving Factors in Major Grain-Producing Area: Evidence from Shandong Province, China. Land 2023, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).