Assessing Spatiotemporal Changes and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Youjiang River Valley Using RSEI and Random Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
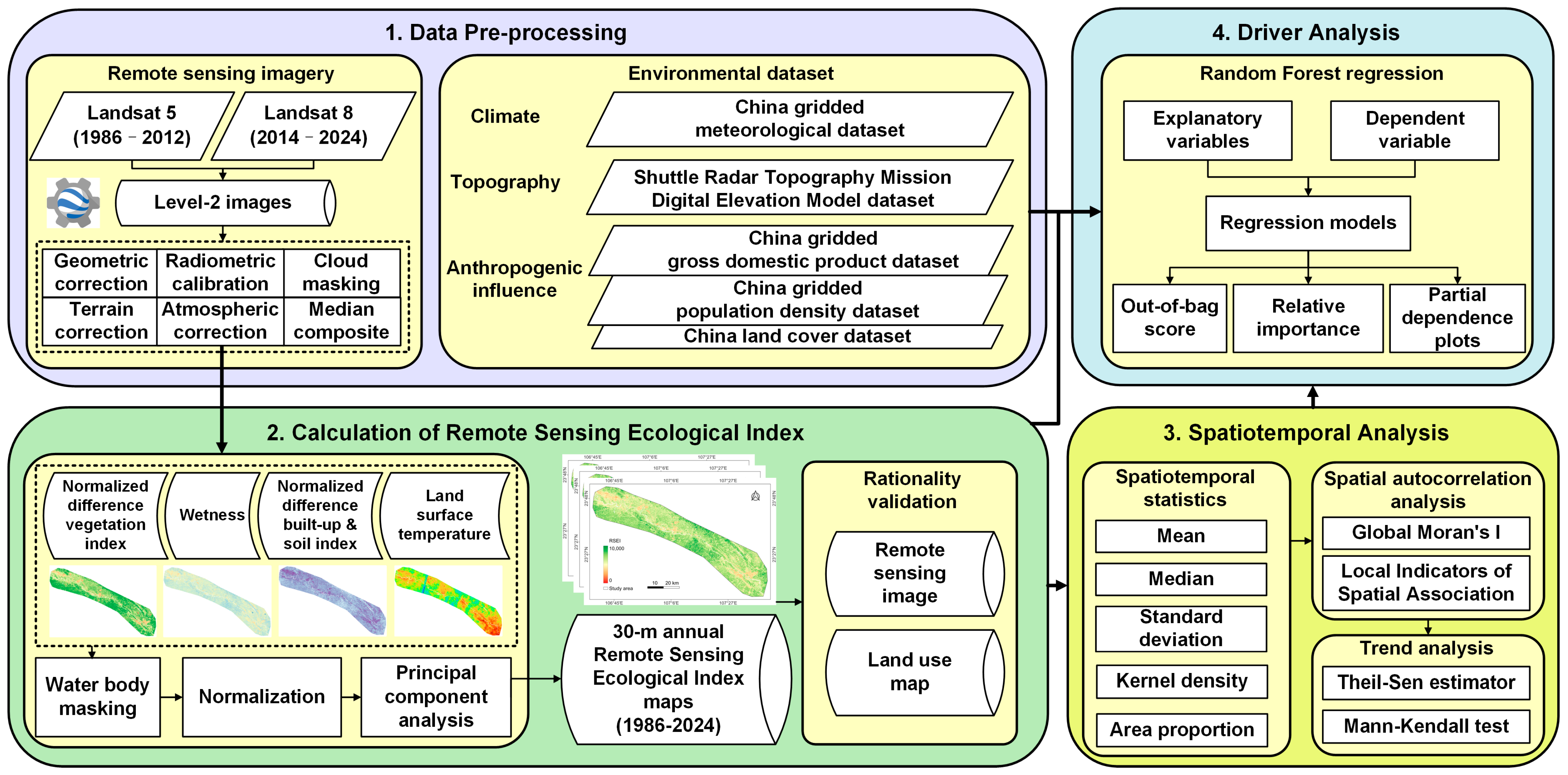
2. Materials and Methods
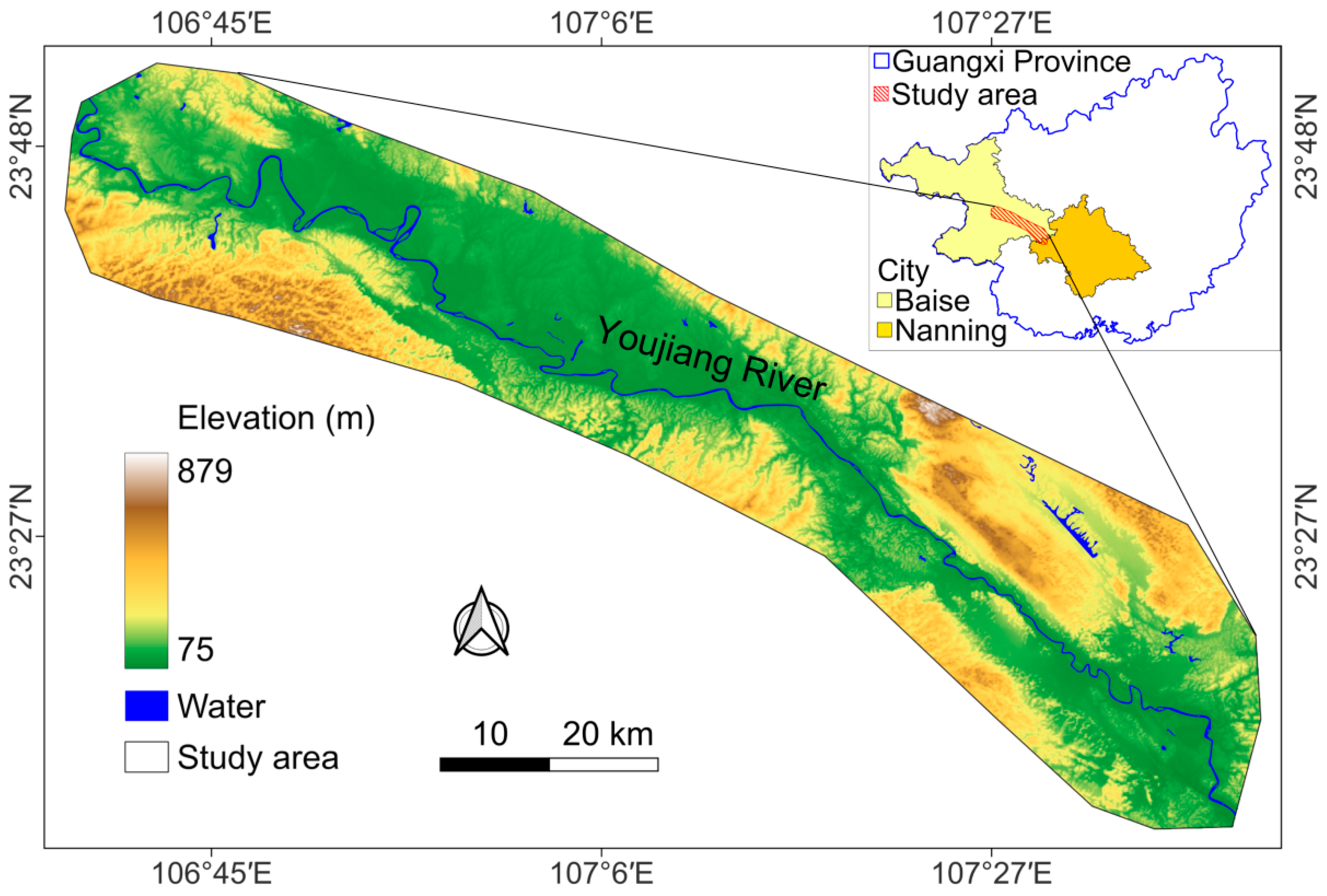
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Pre-Processing
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Calculation of RSEI
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.3. Trend Analysis
2.3.4. Random Forest Regression
3. Results
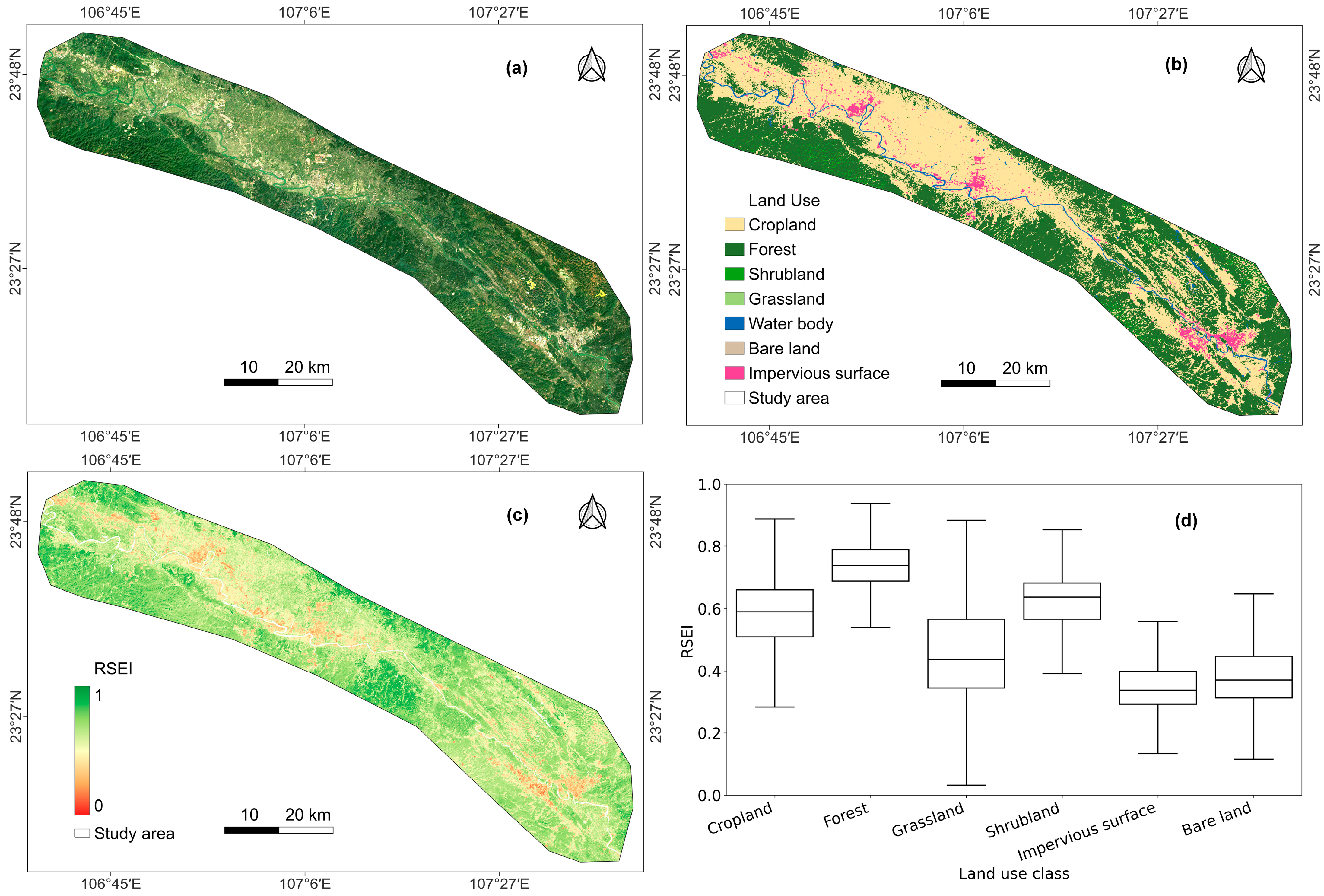
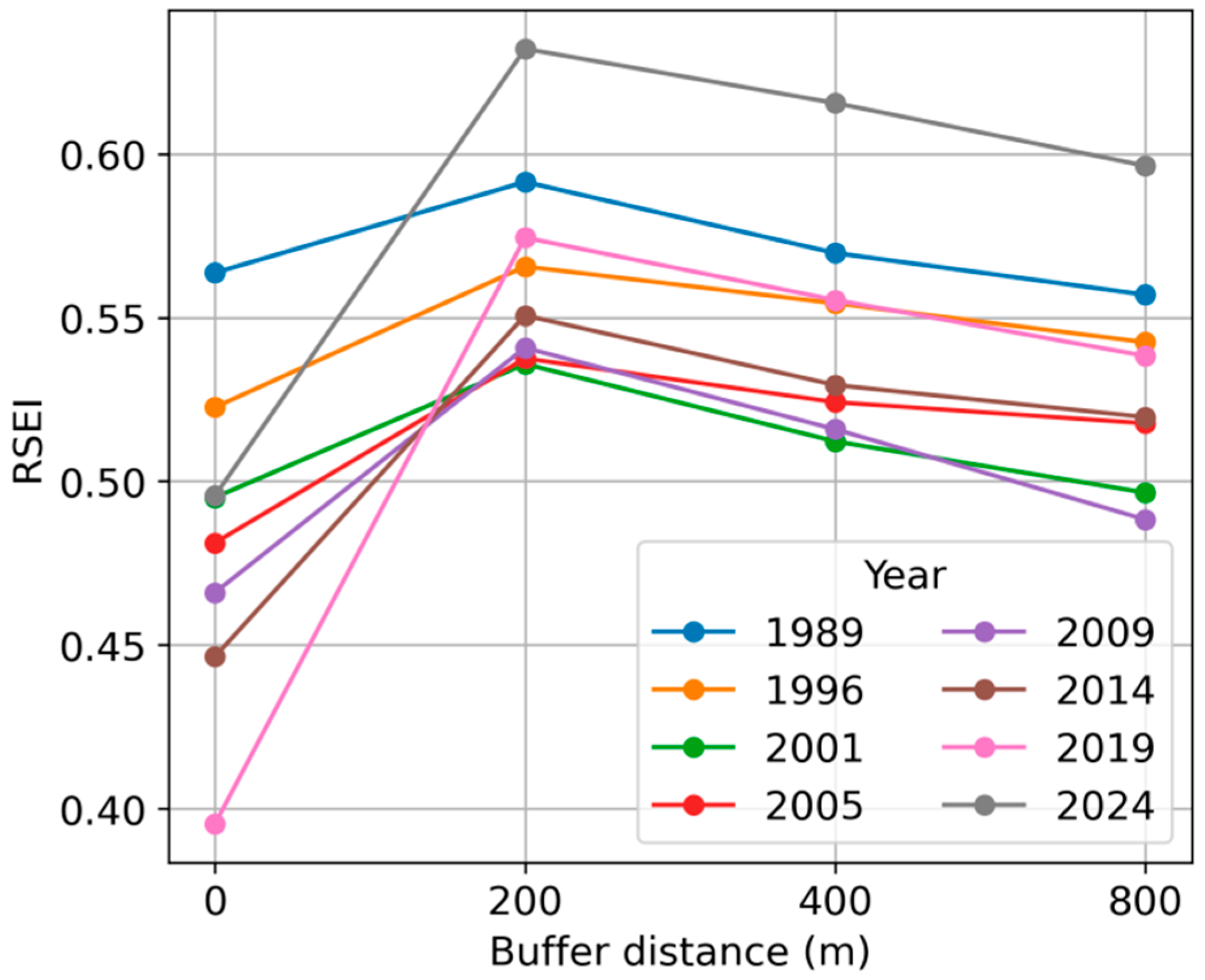
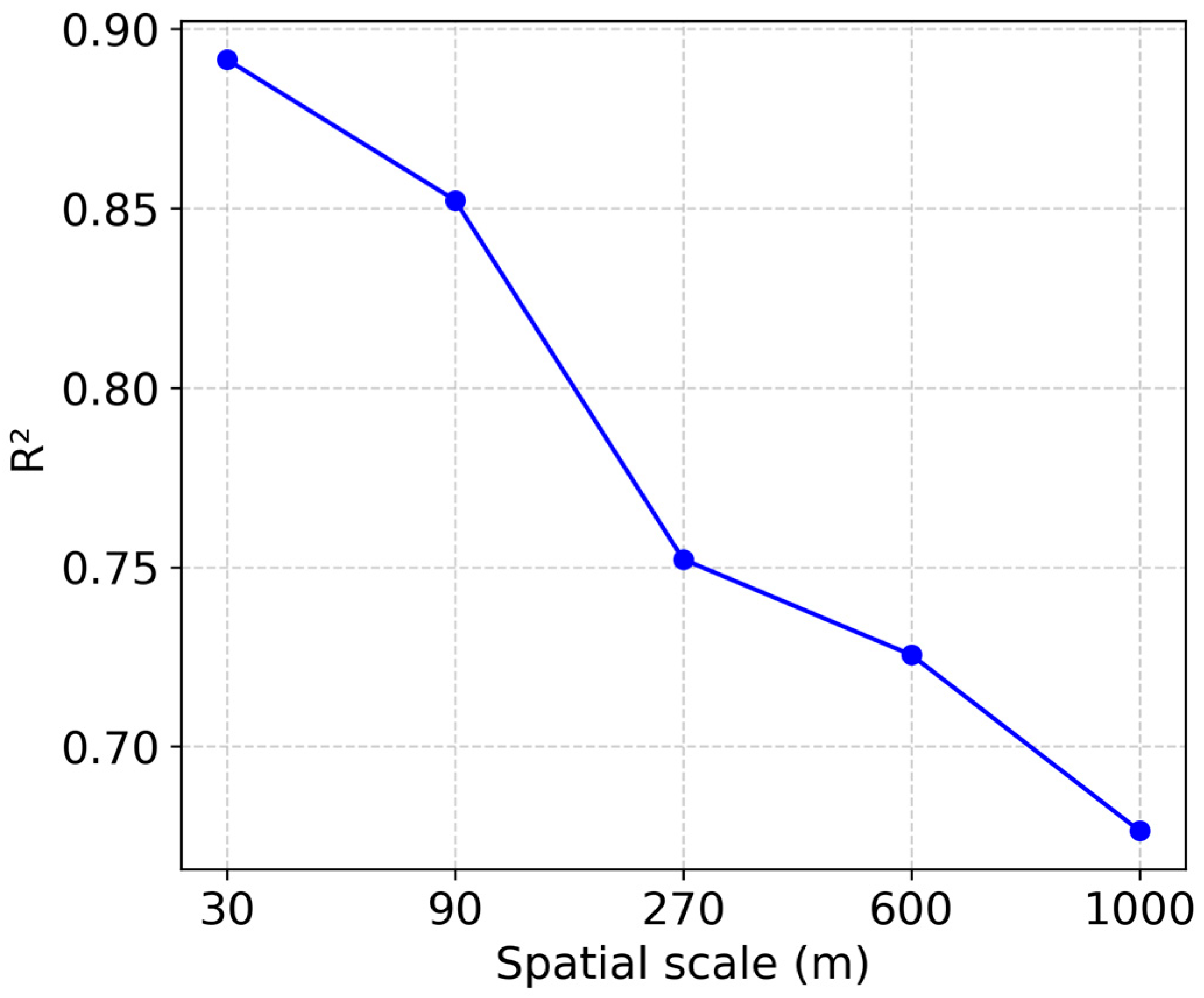
3.1. Rationality of RSEI
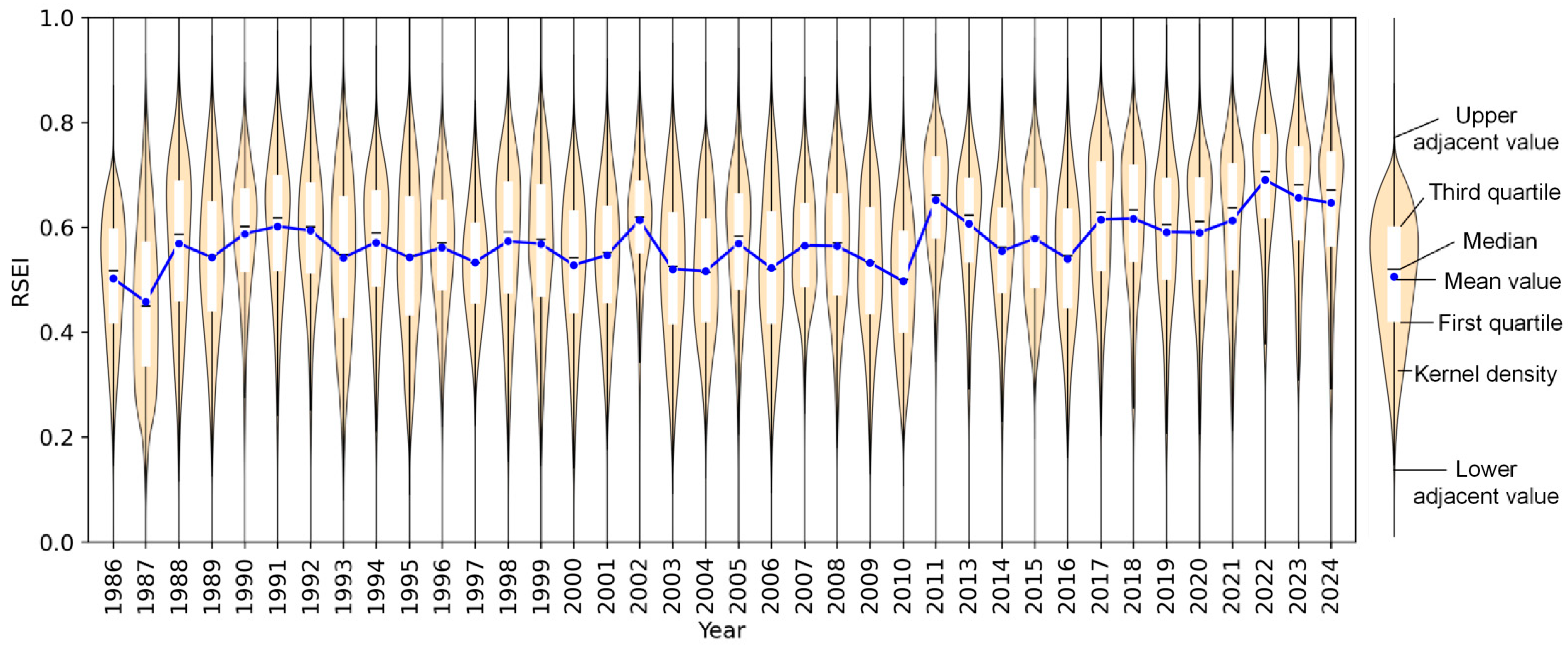
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Ecological Quality
3.3. Change Trends of Ecological Quality
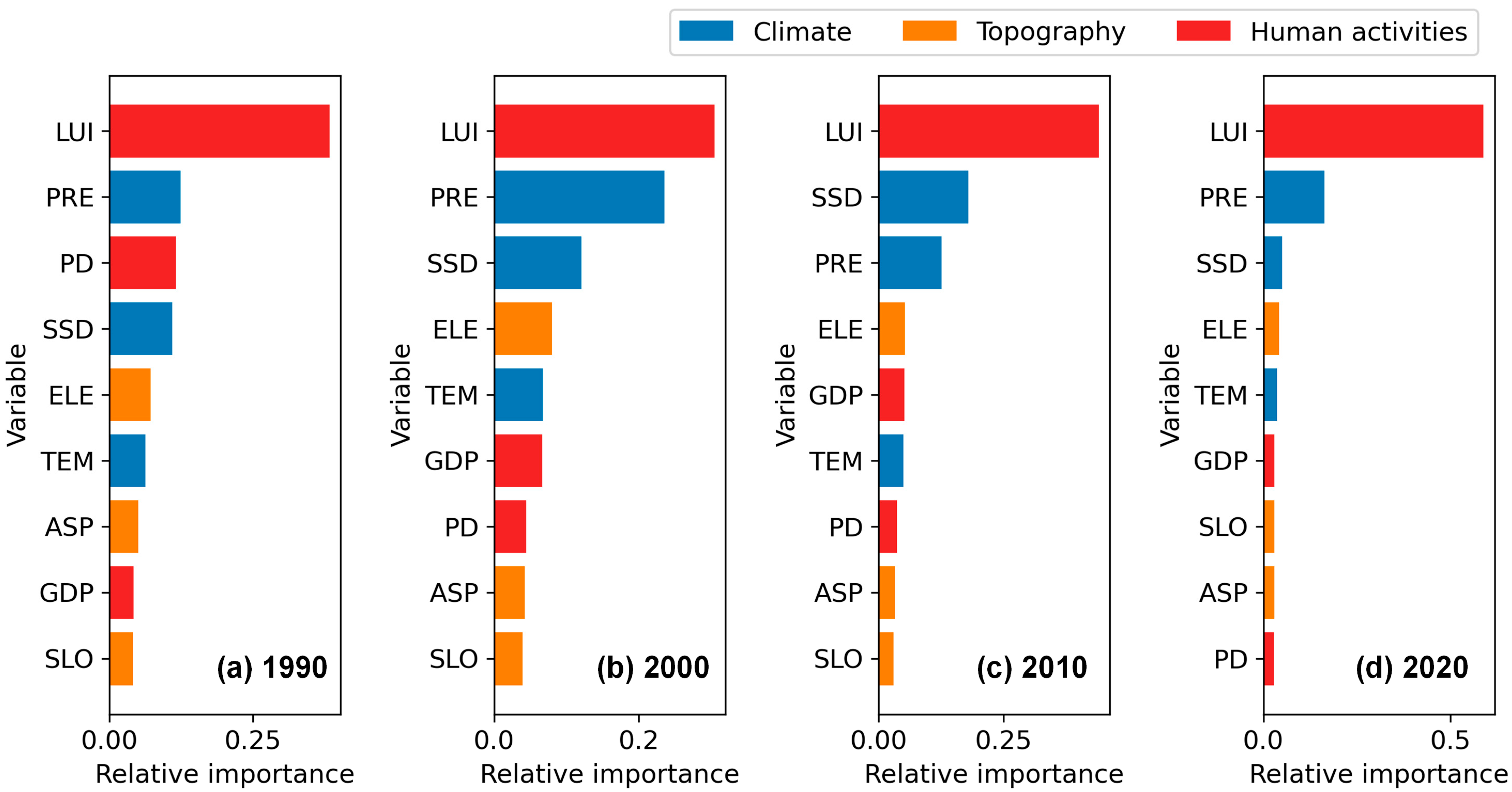
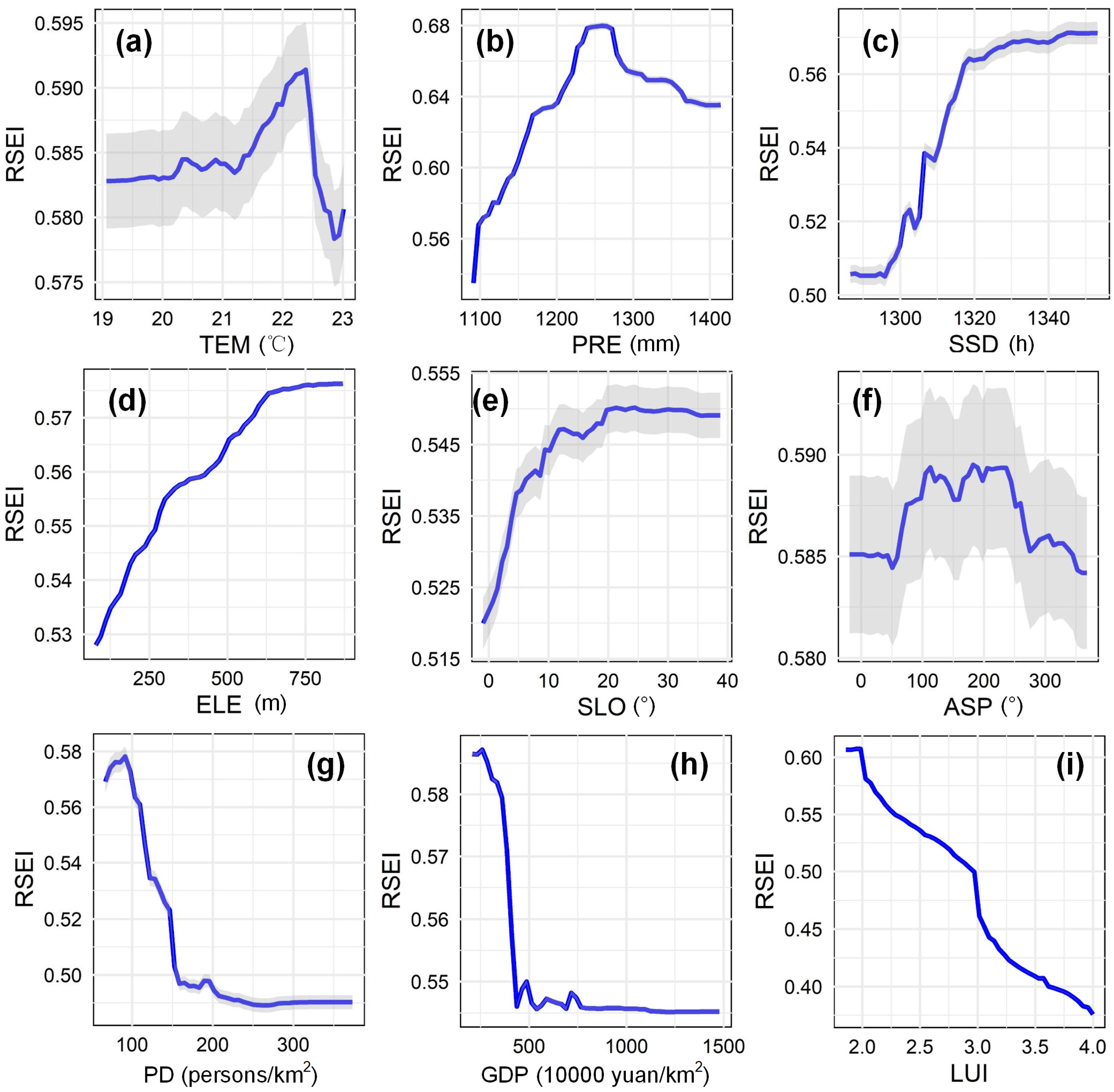
3.4. Driving Factors of Ecological Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term and Fine-Scale Ecological Quality Assessment
4.2. Driving Mechanisms of Ecological Quality Changes
4.3. Limitations and Future Perspective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinclair, J.S.; Welti, E.A.R.; Altermatt, F.; Álvarez-Cabria, M.; Aroviita, J.; Baker, N.J.; Barešová, L.; Barquín, J.; Bonacina, L.; Bonada, N.; et al. Multi-decadal improvements in the ecological quality of European rivers are not consistently reflected in biodiversity metrics. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 8, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.; Ripple, W.J.; Newsome, T.; Barnard, P.; Beamer, K.; Behl, A.; Bowen, J.; Cooney, M.; Crist, E.; Field, C.; et al. Earth at risk: An urgent call to end the age of destruction and forge a just and sustainable future. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prăvălie, R.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Chappell, A.; Miguez-Macho, G.; Maggi, F.; Peng, J.; Niculiță, M.; et al. A unifying modelling of multiple land degradation pathways in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.; Farooq, H.; Harfoot, M.; Pires, M.M.; Villar, N.; Sales, L.; Carvalho, C.; Bello, C.; Emer, C.; Bovendorp, R.S.; et al. A global map of species at risk of extinction due to natural hazards. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2321068121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, H.M.; Martins, I.S.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Kim, H.; Leadley, P.; Popp, A.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Hurtt, G.; Quoss, L.; Arneth, A.; et al. Global trends and scenarios for terrestrial biodiversity and ecosystem services from 1900 to 2050. Science 2024, 384, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Tang, H.; Jiang, H.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y. Ten key issues for ecological restoration of territorial space. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, R.M.; Orme, C.D.L.; Pearse, W.D.; Zulkifli, N.; Yvon-Durocher, G.; Yusah, K.M.; Yoh, N.; Yeo, D.C.J.; Wong, A.; Williamson, J.; et al. Thresholds for adding degraded tropical forest to the conservation estate. Nature 2024, 631, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Guan, Q.; Shao, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Luo, H. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving mechanism of arable ecosystem stability in arid and semi-arid areas based on Pressure-Buffer-Response process. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Zong, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, W. Remote sensing application in ecological restoration monitoring: A systematic review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ding, A.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S. Geodetector model-based quantitative analysis of vegetation change characteristics and driving forces: A case study in the Yongding River basin in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE. Technical Specification for Investigation and Assessment of National Ecological Status—Ecosystem Quality Assessment. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/stzl/202106/W020210910456717871866.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Xu, H. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhu, D.; Jia, K.; Plaza, A. RSEIFE: A new remote sensing ecological index for simulating the land surface eco-environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Hua, L.; Tang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, C. Advancing ecological quality assessment in China: Introducing the ARSEI and identifying key regional drivers. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nian, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Hu, T.; Li, Z. Monitoring of ecological environment changes in open-pit mines on the Loess Plateau from 1990 to 2023 based on RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; An, S.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Dynamic monitoring and drivers of ecological environmental quality in the Three-North region, China: Insights based on remote sensing ecological index. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Peng, Y. Spatial differentiation of ecological environment quality and the influencing factors in cities within the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region based on LCZ and RSEI. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 15477–15494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Optimization strategies for ecological security pattern based on the Remote Sensing Ecological Index in Yunnan Province, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 1326–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ren, C.; Yu, W.; Ren, H.; Xia, C. Exploring the ecological quality and its drivers based on annual remote sensing ecological index and multisource data in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Mengjie, R.; and Lin, M. Cross-comparison of Landsat-8 and Landsat-9 data: A three-level approach based on underfly images. GISci. Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2318071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, S.; He, B.-J. Assessing the spatiotemporal evolution and drivers of ecological environment quality using an enhanced remote sensing ecological index in Lanzhou City, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, D. Drivers of eco-environmental quality in China from 2000 to 2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 396, 136408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal change and driving factors of the Eco-Environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S.; Xie, Z.; Shen, W.; Zheng, Z.; Li, M.; Rong, P.; Qin, Y. Detection of spatiotemporal changes in ecological quality in the Chinese mainland: Trends and attributes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H. Analyses of driving factors on the spatial variations in regional eco-environmental quality using two types of species distribution models: A case study of Minjiang River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xiu, L.; Yao, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, X. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors analysis of the eco-quality in the Lanxi urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lyu, F.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal change and drivers of ecosystem quality in the Loess Plateau based on RSEI: A case study of Shanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Spatio-temporal evolutionary analysis of surface ecological quality in Pingshuo open-cast mine area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 7312–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, W. Using the geodetector method to characterize the spatiotemporal dynamics of vegetation and its interaction with environmental factors in the Qinba Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Sang, L.; Wang, J. Characterizing forest cover and landscape pattern using multi-source remote sensing data with ensemble learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, C. Turning points of the relationship between human activity and environmental quality in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive assessment of the ecosystem in Yellow River Basin based on Pattern-Quality-Service Model. Environ. Model. Assess. 2025, 30, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dai, E.; Xing, S.; Zhou, L. Two decades of ecological quality evolution along the Sichuan-Tibet Highway: Improvement, localized degradation and grazing intensity dominating changes post-2010. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 0, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, D.; Barr, B.; Bertini, E. PDPilot: Exploring partial dependence plots through ranking, filtering, and clustering. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Waheed, A.; Kuerban, A.; Muhammad, M.; Aili, A. Dynamic approaches to ecological restoration in China’s mining regions: A scientific review. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 214, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Yu, H.; Liang, W.; Sun, J. Dynamic monitoring of ecological restoration of abandoned mines based on GF-2 remote sensing images- Take Dawukou Ditch of Helan Mountain as an example. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 207, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Wang, K.; Xu, S.; Xiao, W.; Tong, T.; Sun, H.; Li, C. Identification of surface mining and assessment of ecological restoration effects using GEE and Sentinel-2 image data—A case study on Yangtze River watershed, China. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 212, 107525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, F.; Lin, T.; Xu, Q.; Yu, P.; Wang, C.; Aili, A.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, P.; et al. A systematic review and comprehensive analysis on ecological restoration of mining areas in the arid region of China: Challenge, capability and reconsideration. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, Y. Assessment of ecological quality and analysis of influencing factors in coal-bearing hilly areas of northern China: An exploration of human mining and natural topography. Land 2024, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Xu, D.; Keenan, R.J. Effect of income, industry structure and environmental regulation on the ecological impacts of mining: An analysis for Guangxi Province in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Deng, S.; Yang, N. Spatial and temporal variations of spring drought in Southwest China and its possible teleconnection with the global climate events. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNR. Ecological Restoration Plan for Territorial Space of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (2021–2035). Available online: https://dnr.gxzf.gov.cn/zfxxgk/fdzdgknr/ghjh/ghjh/W020230317555916270160.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Santosh, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Multi-stage tectonics and metallogeny associated with Phanerozoic evolution of the South China Block: A holistic perspective from the Youjiang Basin. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 211, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guan, T. Genesis of the Permian karstic Pingguo bauxite deposit, western Guangxi, China. Miner. Depos. 2017, 52, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, S.; Storey, J.; Rengarajan, R. The new Landsat Collection-2 Digital Elevation Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Roger, J.-C.; Franch, B.; Skakun, S. LaSRC (Land Surface Reflectance Code): Overview, application and validation using MODIS, VIIRS, LANDSAT and Sentinel 2 data’s. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 8173–8176. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, G.; Jenkerson, C.B.; Masek, J.; Vermote, E.; Gao, F. Landsat Ecosystem Disturbance Adaptive Processing System (LEDAPS) Algorithm Description; 2331-1258; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; Open-File Report 2013–1057; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RESDC. Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Zhang, S.; Du, G.; Yan, C.; Wu, S.; Li, R.; Lu, D.; Pan, T.; Ning, J.; Guo, C.; et al. Monitoring periodically national land use changes and analyzing their spatiotemporal patterns in China during 2015–2020. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1705–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse Jr, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.; Deering, D. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite-1 Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 1973; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Crist, E.P. A TM Tasseled Cap equivalent transformation for reflectance factor data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.; Shuai, T.; Tong, Q. Derivation of a tasselled cap transformation based on Landsat 8 at-satellite reflectance. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Clinton, N.; Bai, Y.; Liang, S. Annual dynamics of global land cover and its long-term changes from 1982 to 2015. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1217–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liao, T.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Guan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. Fine-grained wetland classification for national wetland reserves using multi-source remote sensing data and Pixel Information Expert Engine (PIE-Engine). GISci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2286746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Sang, L.; Zhao, C.; Hu, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Miao, S.; Ju, Z. Evaluation of spatiotemporal changes in cropland quantity and quality with multi-source remote sensing. Land 2023, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhou, X.; Mo, W.; Chen, Y. Analysis of vegetation ecological quality change and its driving forces in Guangxi from 2000 to 2020. Guihaia 2024, 44, 907–924. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, X.; Tang, R.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Bai, T. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of eological environment quality in China from 2002 to 2019 and influencing factors. Land 2024, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Qin, K.; Dai, S.; Lu, H.; Lu, M.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Jia, P. Long-term dynamic monitoring and driving force analysis of eco-environmental quality in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, T.; Wang, R.; Hu, S.; Yuan, S. Beyond the Remote Sensing Ecological Index: A comprehensive ecological quality evaluation using a deep-learning-based Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, M.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Tang, F. Quantitatively exploring the influence of geographical conditions on ecological quality using a novel remote sensing model: A comparison between two geographical disparity regions in China. Geo Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 28, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeren, Z.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Raval, S.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Y. An index-based approach to evaluate ecological environment in various surface coal mines using Google Earth Engine. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ning, G.; Xu, B. Production of global daily seamless data cubes and quantification of global land cover change from 1985 to 2020—iMap World 1.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, T. Monitoring and evaluation of ecological restoration in open-pit coal mine using remote sensing data based on a OM-RSEI model. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sweet, L.-b.; Blougouras, G.; Brenning, A.; Li, W.; Reichstein, M.; Denzler, J.; Shangguan, W.; Yu, G.; Huang, F.; et al. How interpretable machine learning can benefit process understanding in the geosciences. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Hartig, F. Machine learning and deep learning—A review for ecologists. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2023, 14, 994–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Long, T.; He, G.; Jiao, W.; Jiang, W. Temporally enhanced RSEI and nighttime lights reveal long-term ecological changes and effective protection in China’s inaugural national parks. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 112981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ruibo, C.; Lijuan, H.; Rundong, L.; Shuhong, M.; Chanling, P.; Jiaxing, C.; and Zhou, G. Ecological quality assessment of large-scale regions using RSEI improved with YTT temperature rectification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 46, 4274–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, T.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y. Land ecology for achieving China’s ecological civilization: Key issues and frontier topics. Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

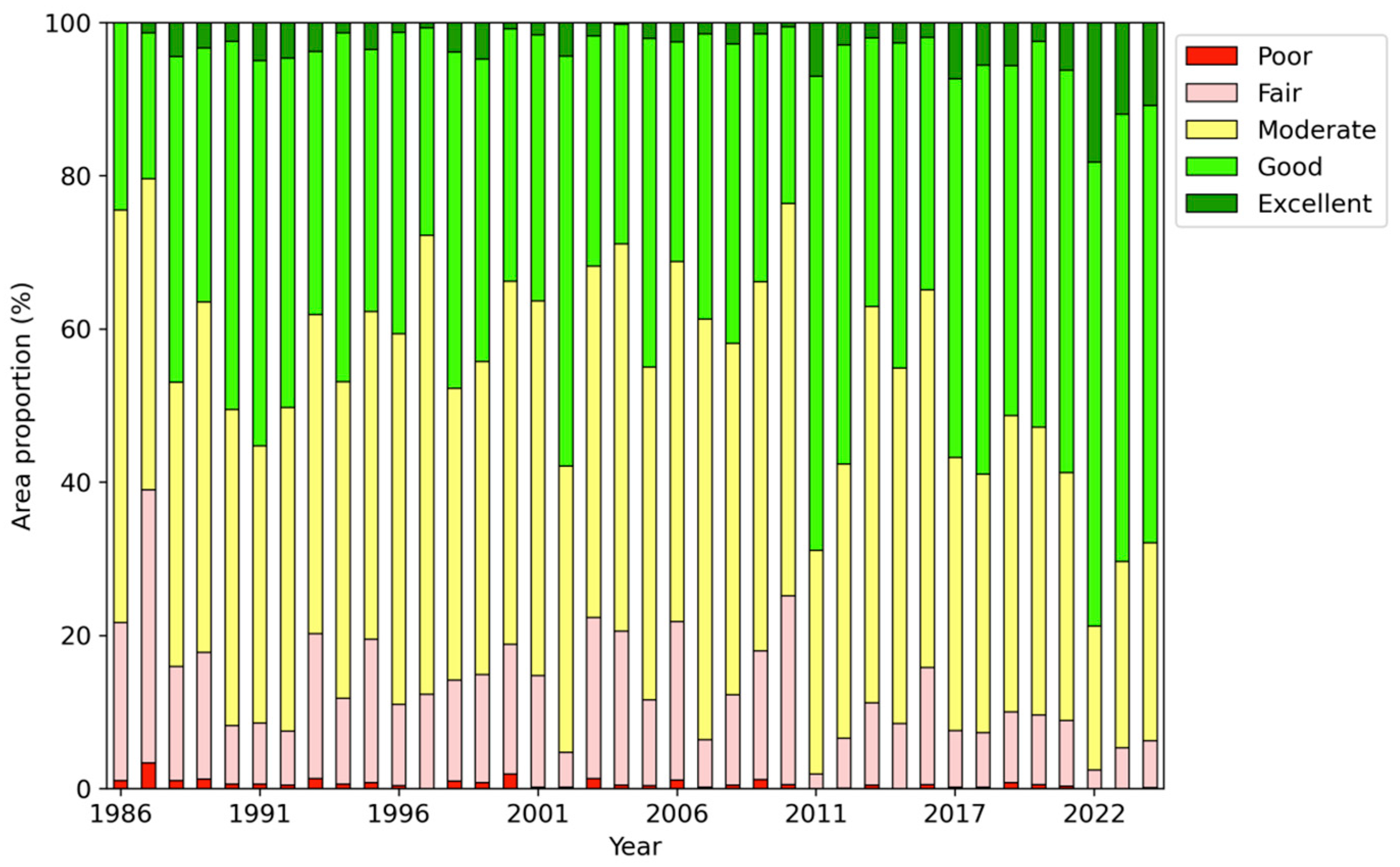

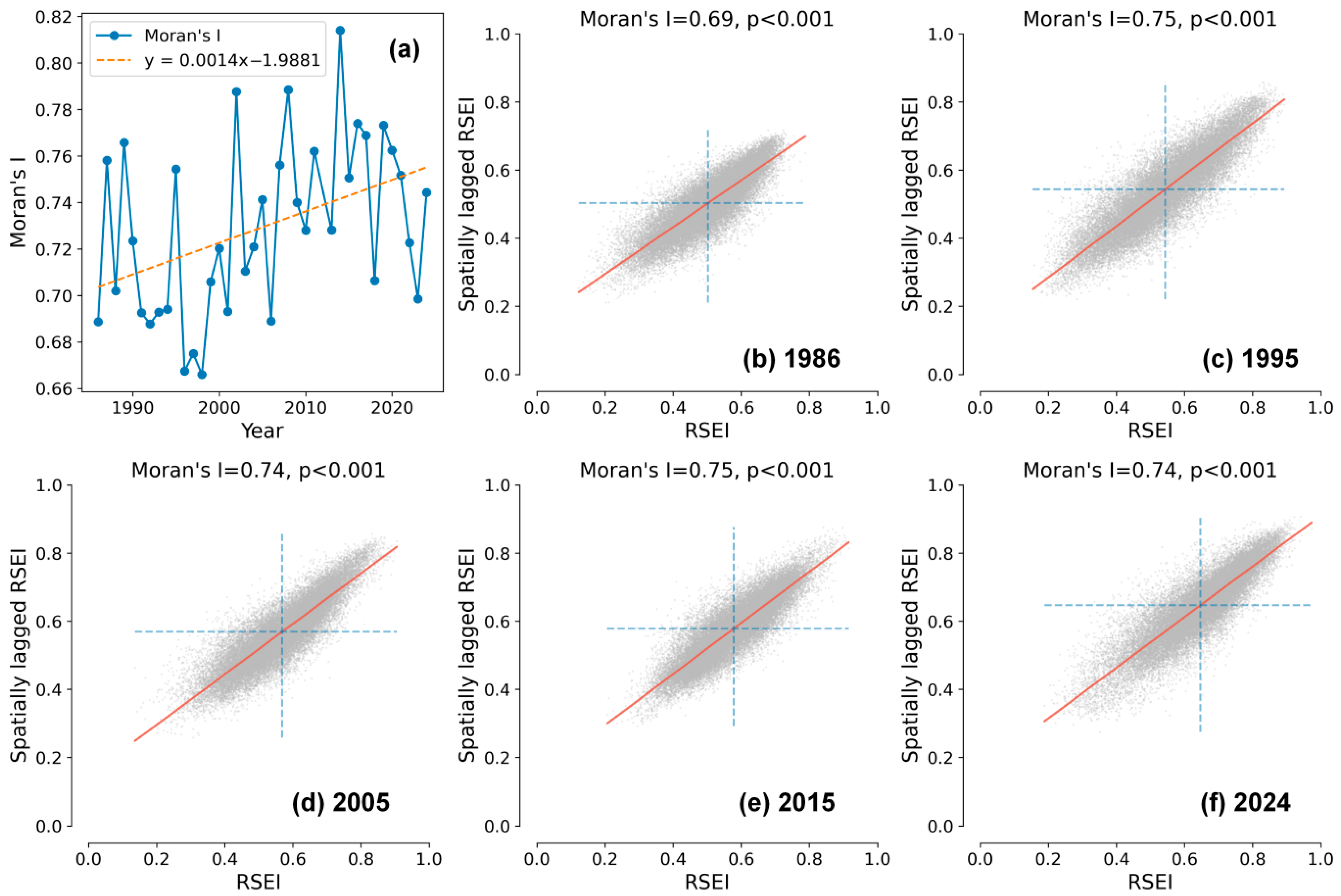
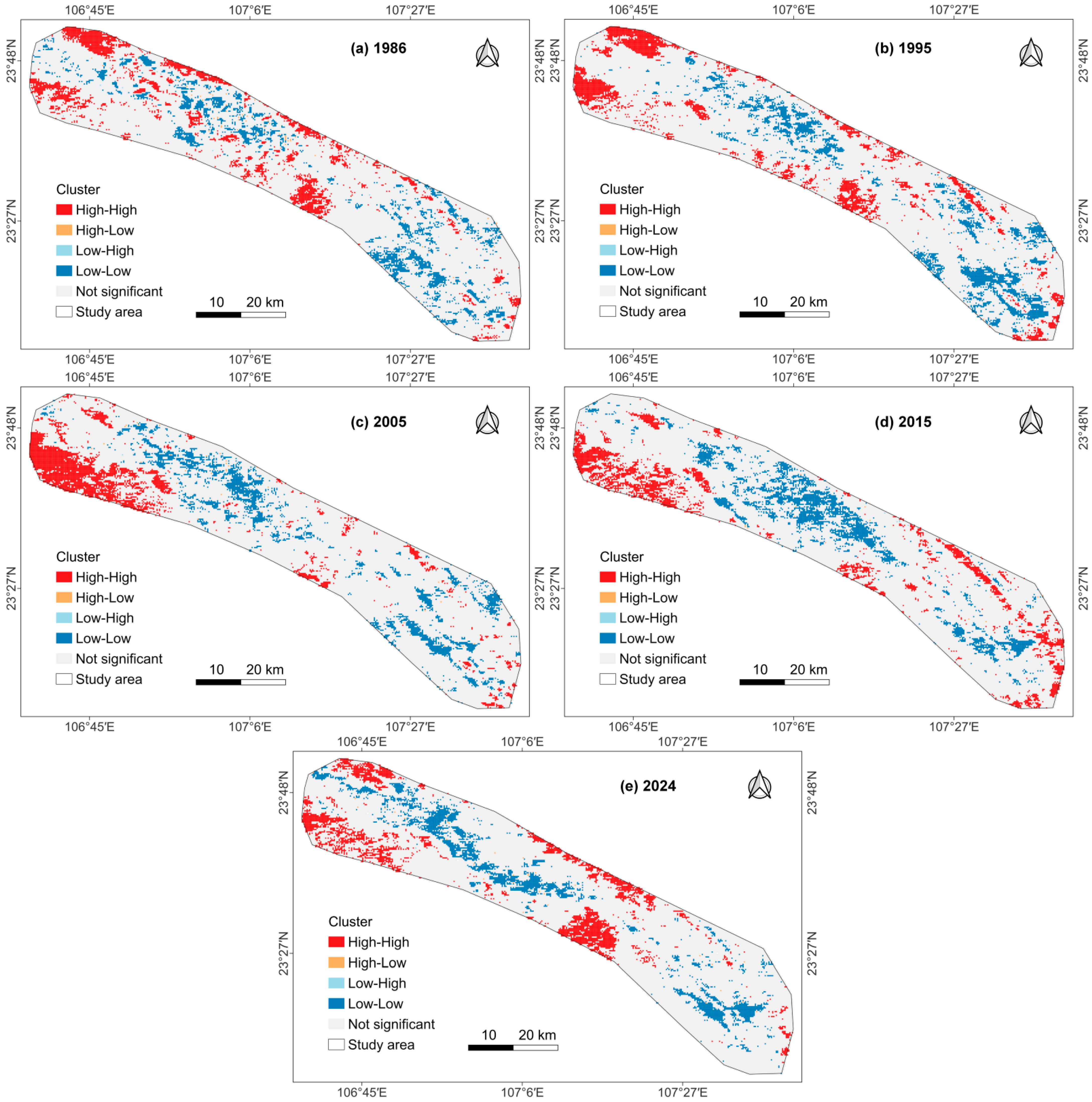
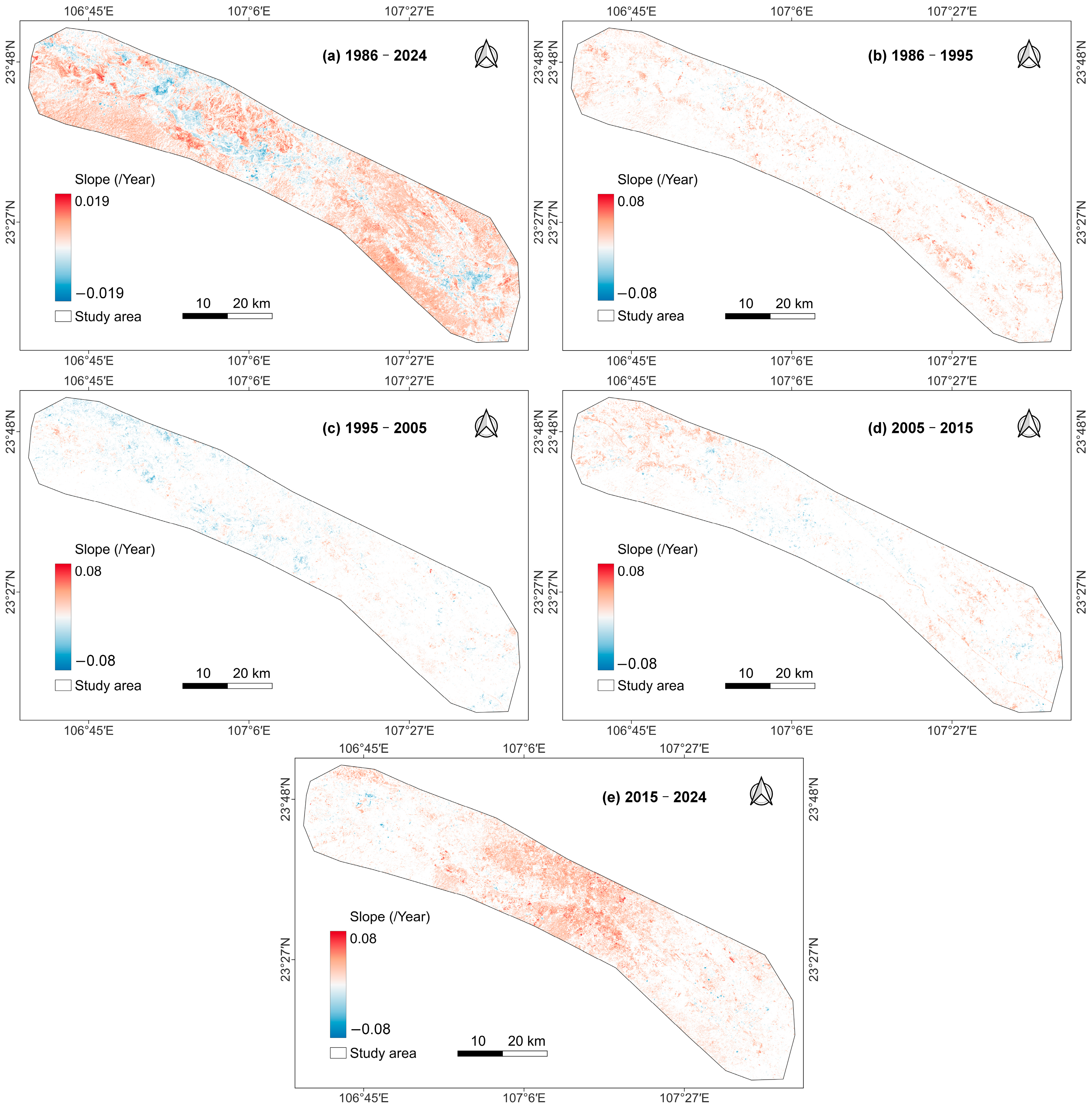
| Data Type | Variable | Dataset | Provider | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multispectral imagery | RSEI | Landsat Level-2 SR and LST image collection | USGS | 30 m | 1986–2011, 2013–2024 |
| Climate | TEM | China gridded meteorological dataset | RESDC | 1 km | 1990/2000/ 2010/2020 |
| PRE | |||||
| SSD | |||||
| Topography | ELE | SRTM DEM | NASA | 30 m | 2000 |
| SLO | |||||
| ASP | |||||
| Anthropogenic influence | GDP | China gridded GDP dataset | RESDC | 1 km | 1990/2000/ 2010/2020 |
| PD | China gridded PD dataset | ||||
| LUI | CLCD | Wuhan University | 30 m | 1990–2023 |
| Period | Area Proportion (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significant Decreasing Trend (p < 0.05) | Non-Significant Decreasing Trend (p ≥ 0.05) | No Trend | Non-Significant Increasing Trend (p ≥ 0.05) | Significant Increasing Trend (p < 0.05) | |
| 1986–2024 | 9.11 | 17.24 | 0.06 | 24.88 | 48.71 |
| 1986–1995 | 0.54 | 21.63 | 0.09 | 65.63 | 12.11 |
| 1995–2005 | 4.81 | 46.50 | 0.13 | 44.70 | 3.86 |
| 2005–2015 | 1.56 | 31.54 | 0.09 | 58.40 | 8.40 |
| 2015–2024 | 0.76 | 14.29 | 0.06 | 58.12 | 26.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Sang, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, T.; Jiang, F.; Cai, J.; Lai, K. Assessing Spatiotemporal Changes and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Youjiang River Valley Using RSEI and Random Forest. Land 2025, 14, 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091708
Wang Y, Liu H, Wang L, Sang L, Wang L, Hu T, Jiang F, Cai J, Lai K. Assessing Spatiotemporal Changes and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Youjiang River Valley Using RSEI and Random Forest. Land. 2025; 14(9):1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091708
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Han Liu, Li Wang, Lingling Sang, Lili Wang, Tengyun Hu, Fan Jiang, Jinlin Cai, and Ke Lai. 2025. "Assessing Spatiotemporal Changes and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Youjiang River Valley Using RSEI and Random Forest" Land 14, no. 9: 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091708
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, H., Wang, L., Sang, L., Wang, L., Hu, T., Jiang, F., Cai, J., & Lai, K. (2025). Assessing Spatiotemporal Changes and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Youjiang River Valley Using RSEI and Random Forest. Land, 14(9), 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091708






