The Impact of Climate and Land Use Change on Greek Centipede Biodiversity and Conservation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
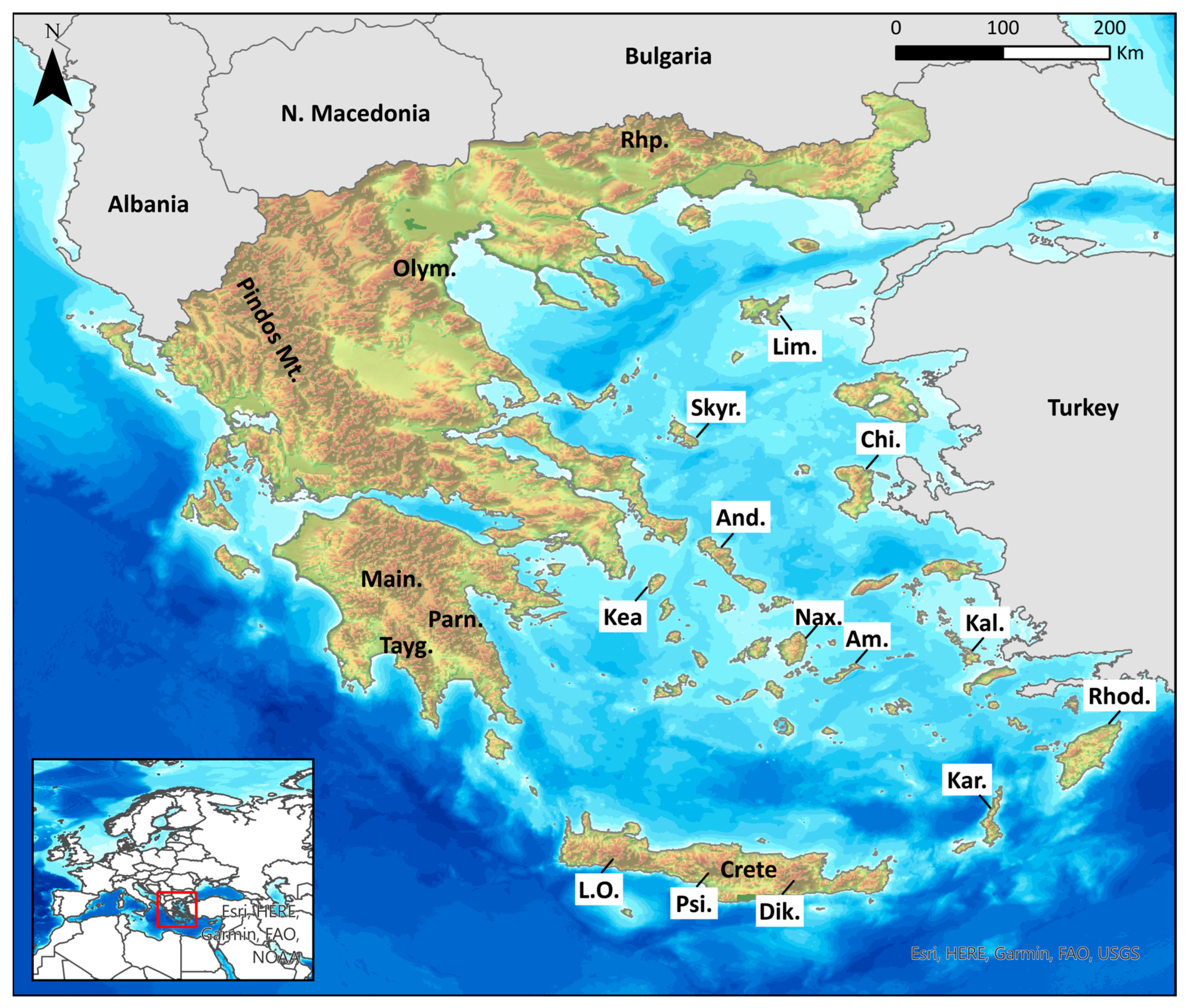
2.1. Species Occurrence Data
2.2. Sampling Bias and Data Completeness
2.3. Environmental Data
2.4. Species Distribution Models
2.5. Biodiversity Hotspots Detection
2.6. Assessment of Protected Area Effectiveness and Conservation Gaps in Greece
3. Results
3.1. Species Occurrence Data
3.2. Sampling Bias and Data Completeness
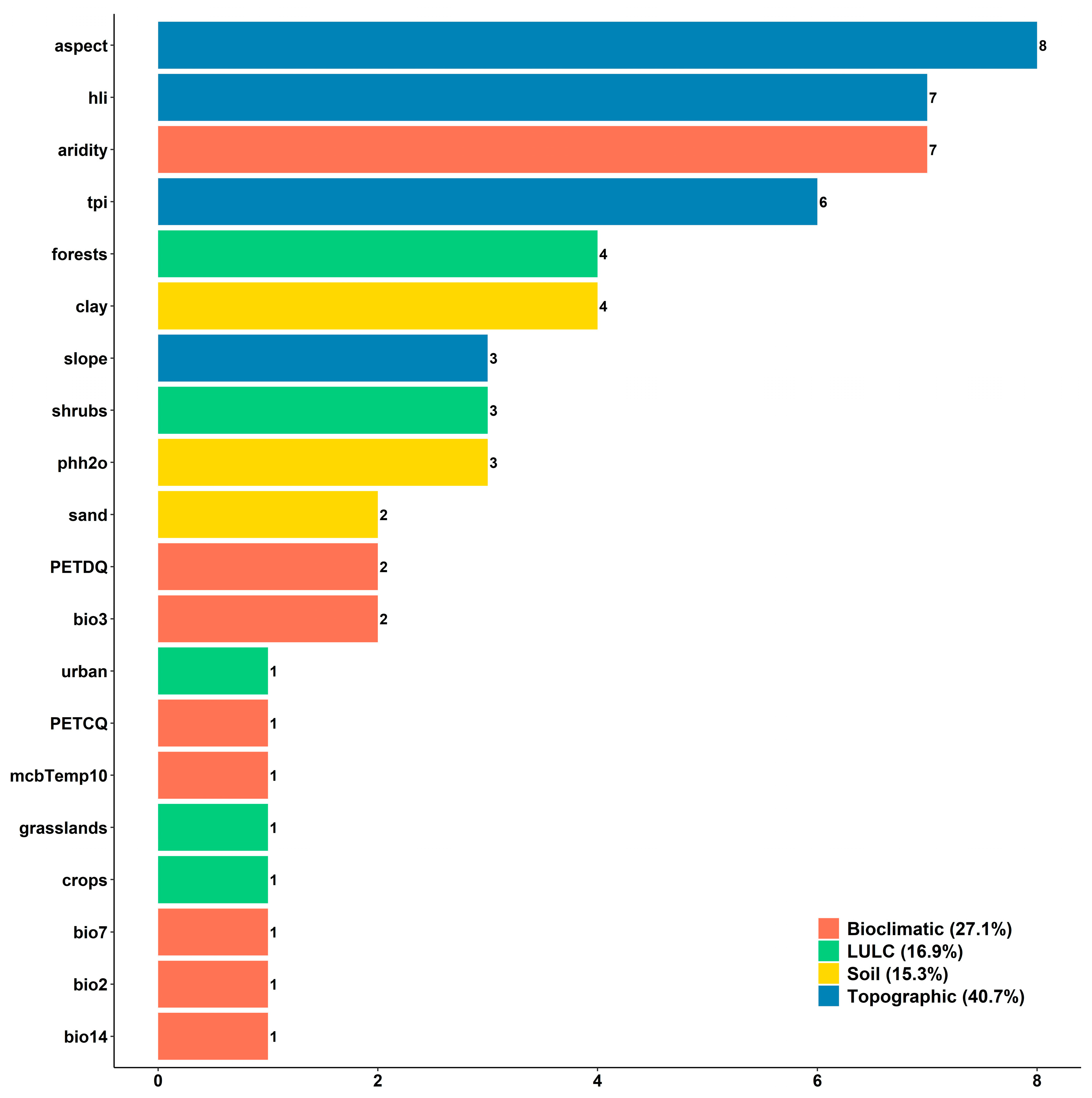
3.3. Species Distribution Models
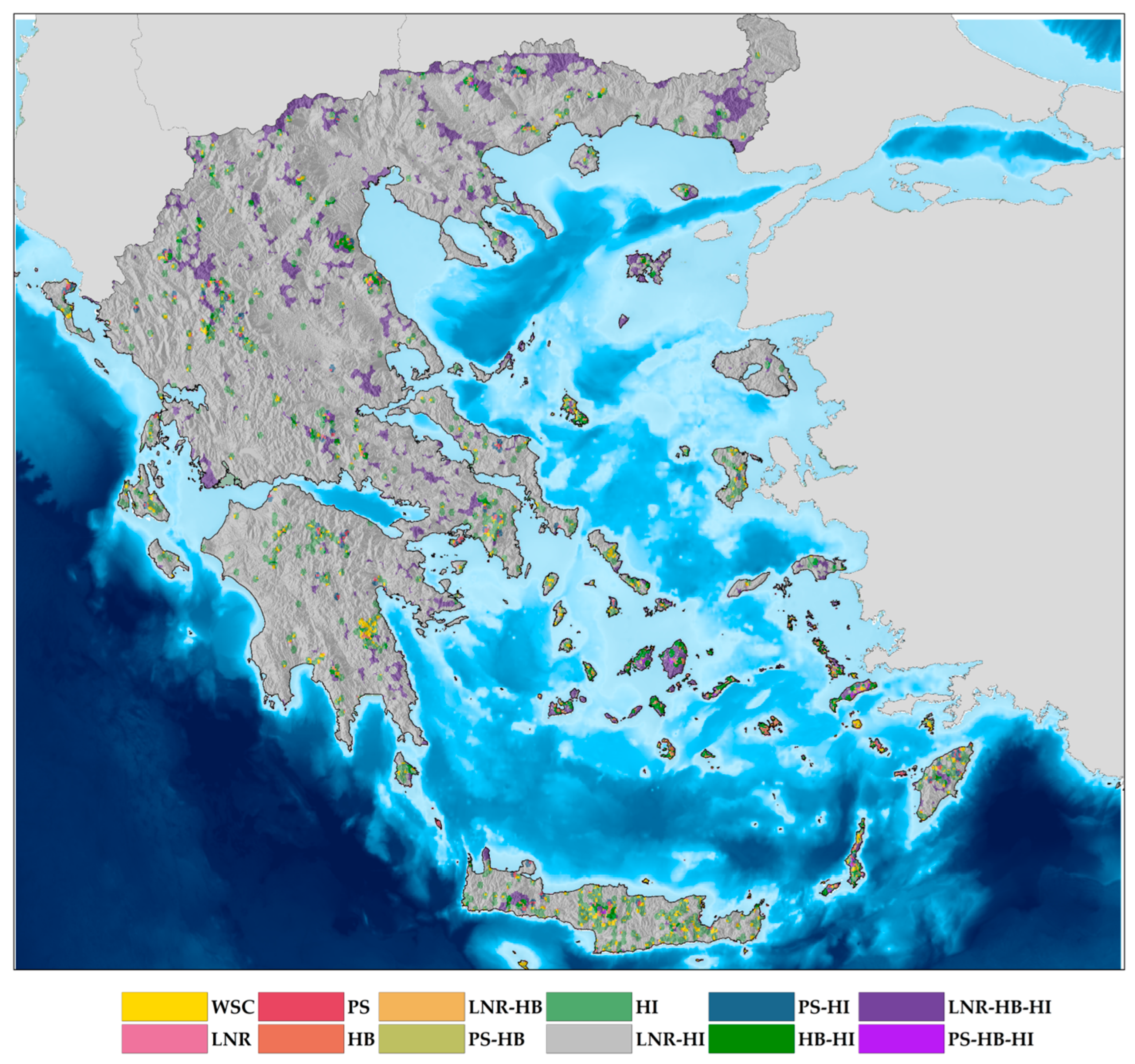
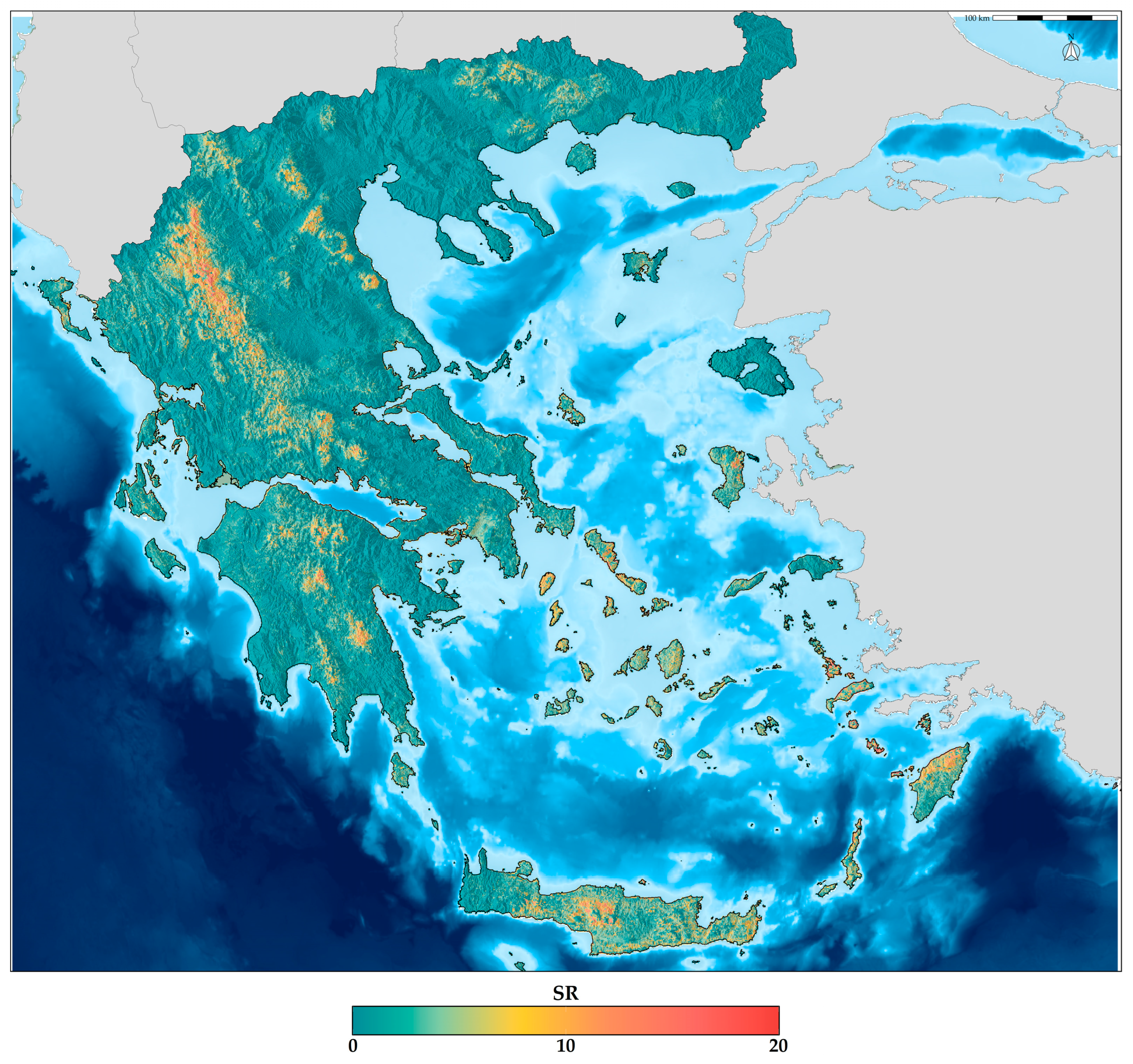
3.4. Biodiversity Hotspots and Assessment of Protected Area Effectiveness in Greece
4. Discussion
4.1. Greek Centipede Diversity
4.2. Centipede Diversity Hotspots
4.3. Climate and Land Use Change Impact on Species Distribution
4.4. Mapping Species Range Shifts and Richness Hotspots over Time
4.5. Conservation Implications—Greek Natura 2000 Network Coverage
4.6. Research Limitations and Future Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SR | Species Richness |
| CWE | Corrected-Weighted Endemism |
| SDM | Species Distribution Modeling |
| GCM | Global Circulation Model |
| RCP | Representative Concentration Pathway |
| SSP | Shared Socioeconomic Pathway |
| LULC | dynamic land use/land cover |
| RPC | Representative Concentration Pathways |
References
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Barnosky, A.D.; García, A.; Pringle, R.M.; Palmer, T.M. Accelerated Modern Human–Induced Species Losses: Entering the Sixth Mass Extinction. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.H.; Bouchet, P.; Fontaine, B. The Sixth Mass Extinction: Fact, Fiction or Speculation? Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.; Barton, P.S.; Birkhofer, K.; Chichorro, F.; Deacon, C.; Fartmann, T.; Fukushima, C.S.; Gaigher, R.; Habel, J.C.; Hallmann, C.A.; et al. Scientists’ Warning to Humanity on Insect Extinctions. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 242, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A.; Tougeron, K.; Gols, R.; Heinen, R.; Abarca, M.; Abram, P.K.; Basset, Y.; Berg, M.; Boggs, C.; Brodeur, J.; et al. Scientists’ Warning on Climate Change and Insects. Ecol. Monogr. 2023, 93, e1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rull, V. Biodiversity Crisis or Sixth Mass Extinction? EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity Hotspots for Conservation Priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S., III; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global Biodiversity Scenarios for the Year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsarrat, S.; Jarvie, S.; Svenning, J.-C. Anthropocene Refugia: Integrating History and Predictive Modelling to Assess the Space Available for Biodiversity in a Human-Dominated World. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20190219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgecombe, G.D.; Giribet, G. The Molecularization of Centipede Systematics. In Perspectives on Evolutionary and Developmental Biology Essays for Alessandro Minelli; Padova University Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, L.; Zapparoli, M. Chilopoda—Geographical Distribution. In The Myriapoda; Treatise on Zoology-Anatomy, Taxonomy, Biology; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, L.; Chagas Junior, A.; Edgecombe, G.D.; Lewis, J.G.E.; Minelli, A.; Pereira, L.A.; Shelley, R.M.; Stoev, P.; Zapparoli, M. ChiloBase 2.0—A World Catalogue of Centipedes (Chilopoda). ChiloBase 2.0. 2016. Available online: https://chilobase.biologia.unipd.it/ (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Edgecombe, G. Chilopoda—Phylogeny. In The Myriapoda; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 339–354. [Google Scholar]
- Edgecombe, G.D.; Bonato, L. Order Scolopendromorpha. In The Myriapoda; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 392–407. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtländer, K. Chilopoda—Ecology. In The Myriapoda; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- Simaiakis, S.M.; Tjørve, E.; Gentile, G.; Minelli, A.; Mylonas, M. The Species–Area Relationship in Centipedes (Myriapoda: Chilopoda): A Comparison between Mediterranean Island Groups. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 105, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, S.; Mesibov, R.; Giribet, G. Biogeography in a Continental Island: Population Structure of the Relict Endemic Centipede Craterostigmus tasmanianus (Chilopoda, Craterostigmomorpha) in Tasmania Using 16S rRNA and COI. J. Hered. 2012, 103, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeyen, J.P.; Funke, S.; Böhme, W.; Wesener, T. The Evolutionary History of the Rediscovered Austrian Population of the Giant Centipede Scolopendra cingulata Latreille 1829 (Chilopoda, Scolopendromorpha). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, E.; Djursvoll, P.; Simaiakis, S.M. Predicting Species Richness and Distribution Ranges of Centipedes at the Northern Edge of Europe. Acta Oecologica 2016, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Karanth, K.P. Coalescent Method in Conjunction with Niche Modeling Reveals Cryptic Diversity among Centipedes in the Western Ghats of South India. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, J.; Karanth, P.K.; Edgecombe, G.D. The Out-of-India Hypothesis: Evidence from an Ancient Centipede Genus, Rhysida (Chilopoda: Scolopendromorpha) from the Oriental Region, and Systematics of Indian Species. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 189, 828–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.M.; Rijsdijk, K.F.; Koene, E.F.M.; Norder, S.J.; Van Boxel, J.H.; Stocchi, P.; Hammoud, C.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Georgopoulou, E.; Van Loon, E.; et al. Geographic Changes in the Aegean Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum: Postulating Biogeographic Effects of Sea-Level Rise on Islands. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 471, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, C.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Rijsdijk, K.F.; Simaiakis, S.M.; Norder, S.J.; Foufopoulos, J.; Georgopoulou, E.; Van Loon, E.E. Past Connections with the Mainland Structure Patterns of Insular Species Richness in a Continental-Shelf Archipelago (Aegean Sea, Greece). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 5441–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fründ, H.-C. Zur Biologie eines Buchenwaldbodens. 14. Die Hundertfüßer (Chilopoda). Carolinea 1991, 49, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtländer, K.; Dunger, W. Centipedes of the Nature Reserve “Leutratal” near Jena (Thuringia, East Germany). In Soil Zoological Problems in Central Europe; Institute of Soil Biology, Academy of Science of the Czech Republik: České Budéjovice, Czech Republic, 1998; pp. 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Spelda, J. Verbreitungsmuster Und Taxonomie Der Chilopoda Und Diplopoda Südwestdeutschlands. Diskriminanzanalytische Verfahren Zur Trennung von Arten Und Unterarten Am Beispiel Der Gattung Rhymogona Cook, 1896 (Diplopoda: Chordeumatida: Craspedosomatidae). Teil 2 Abhandlung Der Einzelnen Arten. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Ulm, Ulm, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Voigtländer, K. Species Distribution and Assemblages of Centipedes (Chilopoda) in Open Xeric Sites of Saxony-Anhalt (Germany). Afr. Invertebr. 2003, 44, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Cuttelod, A.; García, D.A.; Malak, H.J.T.; Katariya, V. The Mediterranean: A Biodiversity Hotspot under Threat. Wildlife in a Changing World—An Analysis of the 2008 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. In The 2008 Review of The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lazoglou, G.; Papadopoulos-Zachos, A.; Georgiades, P.; Zittis, G.; Velikou, K.; Manios, E.M.; Anagnostopoulou, C. Identification of Climate Change Hotspots in the Mediterranean. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapparoli, M. Catalogue of the Centipedes from Greece (Chilopoda). Fragm. Entomol. 2002, 34, 1–146. [Google Scholar]
- Stoev, P. Centipedes (Chilopoda) from Greece in the Collection of the National Museum of Natural History, Sofia. Hist. Nat. Bulg. 2004, 16, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Simaiakis, S.M.; Strona, G. Patterns and Processes in the Distribution of European Centipedes (Chilopoda). J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.M. Chilopoda of Greece. In H Πανίδα της Ελλάδας-Βιολογία και Διαχείριση της Άγριας Πανίδας; Broken Hill Publishers Ltd.: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2020; p. 1109. [Google Scholar]
- Sfenthourakis, S.; Pafilis, P.; Parmakelis, A.; Poulakakis, N.; Triantis, K. Biogeography and Biodiversity of the Aegean. In Honour of Prof. Moysis Mylonas; Sfenthourakis, S., Pafilis, P., Parmakelis, A., Poulakakis, N., Triantis, K., Eds.; Broken Hill Publishers: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Panitsa, M.; Kallimanis, A.; Strid, A.; Dimopoulos, P. Plant Endemism Centres and Biodiversity Hotspots in Greece. Biology 2021, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantis, K.A.; Mylonas, M. Greek Islands, Biology. In Encyclopedia of Islands; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Valli, A.T.; Georgopoulou, E.; Simaiakis, S.M.; Triantis, K.A.; Trigas, P. Network Biogeography of a Complex Island System: The Aegean Archipelago Revisited. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfenthourakis, S.; Triantis, K.A. The Aegean Archipelago: A Natural Laboratory of Evolution, Ecology and Civilisations. J. Biol. Res. Thessalon. 2017, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.; Minelli, A.; Mylonas, M. The Centipede Fauna (Chilopoda) of Crete and Its Satelite Islands (Greece, Eastern Mediterranean). Isr. J. Zool. 2004, 50, 367–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.; Minelli, A.; Mylonas, M. The Centipede Fauna (Chilopoda) of the South Aegean Archilpelgo (Greece, Eastern Mediterranean). Isr. J. Zool. 2005, 51, 241–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Kaloveloni, A.; Petanidou, T. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Island Bees: The Aegean Archipelago. Biology 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniesta, L.F.M.; Bouzan, R.S.; Means, J.C.; Ivanov, K.; Brescovit, A.D. Where Are They from and Where Are They Going? Detecting Areas of Endemism, Distribution Patterns and Conservation Status of the Order Spirostreptida in Brazil (Diplopoda, Juliformia). Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 1591–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanakis, G.; Paragkamian, S.; Chatzaki, M.; Kotitsa, N.; Kardaki, L.; Trichas, A. The Conservation Status of the Cretan Endemic Arthropods under Natura 2000 Network. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 2635–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliopoulou, K.; Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Brooks, T.M.; Kelaidi, G.; Paragamian, K.; Kati, V.; Oikonomou, A.; Vavylis, D.; Trigas, P.; Lymberakis, P.; et al. The Natura 2000 Network and the Ranges of Threatened Species in Greece. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliopoulou, K.; Brooks, T.M.; Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Oikonomou, A.; Karavatsou, F.; Stoumboudi, M.T.; Triantis, K.A. Protected Areas and the Ranges of Threatened Species: Towards the EU Biodiversity Strategy 2030. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 284, 110166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B. enmSdm: Tools for Modeling Species Niches and Distributions. 2020. Available online: https://metadatacatalogue.lifewatch.eu/srv/api/records/4065ee67-2c4e-4a1c-8254-812bb1fcb98f (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. spThin: An R Package for Spatial Thinning of Species Occurrence Records for Use in Ecological Niche Models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.P.; Visser, V.; Hui, C. Biogeo: An R Package for Assessing and Improving Data Quality of Occurrence Record Datasets. Ecography 2016, 39, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudrý, V.; Bazzichetto, M.; Remelgado, R.; Devillers, R.; Lenoir, J.; Mateo, R.G.; Lembrechts, J.J.; Sillero, N.; Lecours, V.; Cord, A.F.; et al. Optimising Occurrence Data in Species Distribution Models: Sample Size, Positional Uncertainty, and Sampling Bias Matter. Ecography 2024, 2024, e07294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.D.; Smith, A.B. Modeling the Rarest of the Rare: A Comparison between Multi-Species Distribution Models, Ensembles of Small Models, and Single-Species Models at Extremely Low Sample Sizes. Ecography 2023, 2023, e06500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizka, A.; Antonelli, A.; Silvestro, D. Sampbias, a Method for Quantifying Geographic Sampling Biases in Species Distribution Data. Ecography 2021, 44, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.M.; Hortal, J.; Yela, J.L.; Millán, A.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; García-Roselló, E.; González-Dacosta, J.; Heine, J.; González-Vilas, L.; Guisande, C. KnowBR: An Application to Map the Geographical Variation of Survey Effort and Identify Well-Surveyed Areas from Biodiversity Databases. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez-Gómez, J.P.; Guedes, T.B.; Lohmann, L.G. Recovering the Drivers of Sampling Bias in Bignonieae (Bignoniaceae) and Identifying Priority Areas for New Survey Efforts. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 2319–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-Km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title, P.O.; Bemmels, J.B. ENVIREM: An Expanded Set of Bioclimatic and Topographic Variables Increases Flexibility and Improves Performance of Ecological Niche Modeling. Ecography 2018, 41, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4. CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Hijmans, R.; Philipps, S.; Leathwick, J.; Elith, J. Dismo: Species Distribution Modeling. R Package Version 1.1–4. 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dismo (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Wang, T.; Hamann, A.; Spittlehouse, D.L.; Murdock, T.Q. ClimateWNA—High-Resolution Spatial Climate Data for Western North America. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, A.; Wang, T.; Spittlehouse, D.L.; Murdock, T.Q. A Comprehensive, High-Resolution Database of Historical and Projected Climate Surfaces for Western North America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1307–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, M.; Castellanos-Acuña, D.; Hamann, A.; Wang, T.; Ray, D.; Menzel, A. ClimateEU, Scale-Free Climate Normals, Historical Time Series, and Future Projections for Europe. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengl, T.; de Jesus, J.M.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. SoilGrids250m: Global Gridded Soil Information Based on Machine Learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Global Land Projection Based on Plant Functional Types with a 1-Km Resolution under Socio-Climatic Scenarios. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Barbosa, M.; Bivand, R.; Brown, A.; Chirico, M.; Cordano, E.; Dyba, K.; Pebesma, E.; Rowlingson, B.; Sumner, M.D. Terra: Spatial Data Analysis. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/terra/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Evans, J.S.; Murphy, M.A.; Ram, K. spatialEco: Spatial Analysis and Modelling Utilities. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/spatialEco/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Cao, Y.; Wang, F.; Tseng, T.-H.; Carver, S.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, R. Identifying Ecosystem Service Value and Potential Loss of Wilderness Areas in China to Support Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Conservation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, B. Collinear: R Package for Seamless Multicollinearity Management. R Package Version 1.1.1. 2023. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/collinear/versions/1.1.1 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A Review of Methods to Deal with It and a Simulation Study Evaluating Their Performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broennimann, O.; Cola, V.D.; Petitpierre, B.; Breiner, F.; Scherrer, D.; D’Amen, M.; Randin, C.; Engler, R.; Hordijk, W.; Mod, H.; et al. Ecospat: Spatial Ecology Miscellaneous Methods. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ecospat/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Breiner, F.T.; Guisan, A.; Bergamini, A.; Nobis, M.P. Overcoming Limitations of Modelling Rare Species by Using Ensembles of Small Models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiner, F.T.; Guisan, A.; Nobis, M.P.; Bergamini, A. Including Environmental Niche Information to Improve IUCN Red List Assessments. Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiner, F.T.; Nobis, M.P.; Bergamini, A.; Guisan, A. Optimizing Ensembles of Small Models for Predicting the Distribution of Species with Few Occurrences. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavi, R.; Elith, J.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Guillera-Arroita, G. Modelling Species Presence-Only Data with Random Forests. Ecography 2021, 44, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavi, R.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Elith, J. Predictive Performance of Presence-Only Species Distribution Models: A Benchmark Study with Reproducible Code. Ecol. Monogr. 2022, 92, e01486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauby, G.; Stévart, T.; Droissart, V.; Cosiaux, A.; Deblauwe, V.; Simo-Droissart, M.; Sosef, M.S.M.; Lowry II, P.P.; Schatz, G.E.; Gereau, R.E.; et al. ConR: An R Package to Assist Large-Scale Multispecies Preliminary Conservation Assessments Using Distribution Data. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 11292–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Valverde, A. Prevalence Affects the Evaluation of Discrimination Capacity in Presence-Absence Species Distribution Models. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazco, S.J.E.; Rose, M.B.; de Andrade, A.F.A.; Minoli, I.; Franklin, J. Flexsdm: An r Package for Supporting a Comprehensive and Flexible Species Distribution Modelling Workflow. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, R.; Franklin, J.; Esque, T.; Nussear, K. Comparing Sample Bias Correction Methods for Species Distribution Modeling Using Virtual Species. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, N.; Préau, C.; Lenormand, M.; Papuga, G.; Monsarrat, S.; Denelle, P.; Louarn, M.L.; Heremans, S.; May, R.; Roche, P.; et al. Assessing the Effect of Sample Bias Correction in Species Distribution Models. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, N.; ter Steege, H. A Null-Model for Significance Testing of Presence-Only Species Distribution Models. Ecography 2007, 30, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, A.H.; Bell, J.F. A Review of Methods for the Assessment of Prediction Errors in Conservation Presence/Absence Models. Environ. Conserv. 1997, 24, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the Accuracy of Species Distribution Models: Prevalence, Kappa and the True Skill Statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirzel, A.H.; Le Lay, G.; Helfer, V.; Randin, C.; Guisan, A. Evaluating the Ability of Habitat Suitability Models to Predict Species Presences. Ecol. Model. 2006, 199, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konowalik, K.; Nosol, A. Evaluation Metrics and Validation of Presence-Only Species Distribution Models Based on Distributional Maps with Varying Coverage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas-Castro, S.; Regos, A.; Martins, I.; Honrado, J.; Alonso, J. Effects of Input Data Sources on Species Distribution Model Predictions across Species with Different Distributional Ranges. J. Biogeogr. 2022, 49, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Georges, D.; Gueguen, M.; Engler, R.; Breiner, F.; Lafourcade, B.; Patin, R.; Blancheteau, H. Biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/biomod2/index.html (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Velazco, S.J.E.; Rose, M.B.; De Marco, P., Jr.; Regan, H.M.; Franklin, J. How Far Can I Extrapolate My Species Distribution Model? Exploring Shape, a Novel Method. Ecography 2024, 2024, e06992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Kearney, M.; Phillips, S. The Art of Modelling Range-Shifting Species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbarth, M.H.K.; Sciaini, M.; With, K.A.; Wiegand, K.; Nowosad, J. Landscapemetrics: An Open-Source R Tool to Calculate Landscape Metrics. Ecography 2019, 42, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, H.P. Plant Diversity and Endemism in Sub-Saharan Tropical Africa. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, H.P. On Areas of Endemism, with an Example from the African Restionaceae. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 892–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Orozco, C.E.; Pollock, L.J.; Thornhill, A.H.; Mishler, B.D.; Knerr, N.; Laffan, S.W.; Miller, J.T.; Rosauer, D.F.; Faith, D.P.; Nipperess, D.A.; et al. Phylogenetic Approaches Reveal Biodiversity Threats under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daru, B.H.; Karunarathne, P.; Schliep, K. Phyloregion: R Package for Biogeographical Regionalization and Macroecology. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, E.M.; Fenu, G.; Peñas, J.; Lorite, J.; Mattana, E.; Bacchetta, G. Hotspots within Hotspots: Endemic Plant Richness, Environmental Drivers, and Implications for Conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.O. Wdpar: Interface to the World Database on Protected Areas. J. Open Source Softw. 2022, 7, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, J.; Naqinezhad, A.; Talebi, A.; Doostmohammadi, M.; Plutzar, C.; Rumpf, S.B.; Asgarpour, Z.; Schneeweiss, G.M. Hotspots of Vascular Plant Endemism in a Global Biodiversity Hotspot in Southwest Asia Suffer from Significant Conservation Gaps. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ying, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zang, R.; Jiang, Y. Hotspot Analyses Indicate Significant Conservation Gaps for Evergreen Broadleaved Woody Plants in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfenthourakis, S.; Legakis, A. Hotspots of Endemic Terrestrial Invertebrates in Southern Greece. Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 1387–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardinoyannis, K.; Parmakelis, A.; Triantis, K.A.; Giokas, S. Land Molluscs in Greece: The Rich, Unique, Diverse and Unprotected Animal Models. In Biogeography and Biodiversity of the Aegean. In Honour of Prof. Moysis Mylonas; Broken Hill Publishers Ltd.: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2018; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dunger, W.; Voigtländer, K. Soil Fauna (Lumbricidae, Collembola, Diplopoda and Chilopoda) as Indicators of Soil Eco-Subsystem Development in Post-Mining Sites of Eastern Germany—A Review. Soil Org. 2009, 81, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Papastefanou, G.; Panayiotou, E.; Mylonas, M.; Simaiakis, S.M. Centipede Assemblages along an Urbanization Gradient in the City of Heraklion, Crete (Greece). Zookeys 2015, 510, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.M.; Martínez-Morales, M.A. Nestedness in Centipede (Chilopoda) Assemblages on Continental Islands (Aegean, Greece). Acta Oecologica 2010, 36, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardaki, L.; Nikolakakis, M.; Trichas, A.; Georgopoulou, E.; Simaiakis, S. A Review of Geophilid Centipedes (Chilopoda: Geophilomorpha: Geophilidae) Collected in the Aegean Archipelago: A Hidden Treasure at the Natural History Museum of Crete. In Biogeography and Biodiversity of the Aegean. In Honour of Prof. Moysis Mylonas; Broken Hill Publishers Ltd.: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2018; pp. 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Willemse, L.; Kleukers, R.; Odé, B. The Grasshoppers of Greece; EIS Kenniscentrum Insecten: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pamperis, L.N. The Butterflies of Greece; An Update of Distribution Maps, Plates and Diagrams 3.3, in Map 3.4, in Chart 4.15, and in Chart 4.16, Pamperis; Hellenic Society for the Protection of Nature: Athens, Greece, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lymberakis, P.; Pafilis, P.; Poulakakis, N.; Sotiropoulos, K.; Valakos, E.D. The Amphibians and Reptiles of the Aegean Sea. In Biogeography and Biodiversity of the Aegean. In Honour of Prof. Moysis Mylonas; Broken Hill Publishers Ltd.: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2018; pp. 169–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stoev, P. A Catalogue and Key to the Centipedes (Chilopoda) of Bulgaria; Pensoft: Sofia, Bulgaria; Moscow, Russia, 2002; Volume 103. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltsas, D.; Simaiakis, S. Seasonal Patterns of Activity of Scolopendra cretica and S. cingulata (Chilopoda, Scolopendromorpha) inEast Mediterranean Maquis Ecosystem. Int. J. Myriapodology 2012, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaiakis, S.M.; Akkari, N.; Zapparoli, M. The Centipedes of Peloponnisos and First Records of Genus Eurygeophilus in the East Mediterranean (Myriapoda: Chilopoda). Zootaxa 2016, 4061, 301–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, R.L.H.; Shreeve, T.G.; Olivier, A.; Coutsis, J.G. Contemporary Geography Dominates Butterfly Diversity Gradients within the Aegean Archipelago (Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea, Hesperioidea). J. Biogeogr. 2000, 27, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenkamp, J.E. Aspects of the Late Cenozoic Evolution of the Aegean Region. In Geological Evolution of the Mediterranean Basin: Raimondo Selli Commemorative Volume; Stanley, D.J., Wezel, F.-C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasakis, G.C.; Dermitzakis, M. Post-Middle-Miocene Paleogeographic Evolution of the Central Aegean Sea and Detailed Quaternary Reconstruction of the Region. Its Possible Influences on the Distribution of the Quaternary Mammals of the Cyclades Islands. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Paläontol. Monatshefte 1990, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantis, K.A.; Vardinoyannis, K.; Mylonas, M. Biogeography, Land Snails and Incomplete Data Sets: The Case of Three Island Groups in the Aegean Sea. J. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantis, K.A.; Mylonas, M.; Weiser, M.D.; Lika, K.; Vardinoyannis, K. Species Richness, Environmental Heterogeneity and Area: A Case Study Based on Land Snails in Skyros Archipelago (Aegean Sea, Greece). J. Biogeogr. 2005, 32, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Panitsa, M.; Trigas, P.; Strid, A.; Dimopoulos, P. Plant Diversity Patterns and Conservation Implications under Climate-Change Scenarios in the Mediterranean: The Case of Crete (Aegean, Greece). Diversity 2020, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagalinski, B.; Stoev, P. An Annotated Checklist of the Myriapods of the Western Rhodopes Mts (Bulgaria and Greece). In Biodiversity of Bulgaria. 4. Biodiversity of Western Rhodopes (Bulgaria and Greece) II; Ensoft and National Museum of Natural History: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2011; pp. 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Auffret, A.G.; Nenzén, H.; Polaina, E. Underprediction of Extirpation and Colonisation Following Climate and Land-Use Change Using Species Distribution Models. Divers. Distrib. 2024, 30, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, L.; Zapparoli, M.; Minelli, A. Morphology, Taxonomy and Distribution of Diphyonyx Gen. n., a Lineage of Geophilid Centipedes with Unusually Shaped Claws (Chilopoda: Geophilidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapparoli, M. The Present Knowledge on the European Fauna of Lithobiomorpha (Chilopoda). Bull. Br. Myriap. Isopod Group 2003, 19, 20–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Tsakiri, M.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Trigas, P.; Iatrou, G.; Lamari, F.N.; Tzanoudakis, D.; Koumoutsou, E.; Dimopoulos, P.; Strid, A.; et al. Assessing the Vulnerability of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants to Climate and Land-Use Changes in a Mediterranean Biodiversity Hotspot. Land 2024, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, Z.; Vacek, S.; Cukor, J. European Forests under Global Climate Change: Review of Tree Growth Processes, Crises and Management Strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyderski, M.K.; Paź-Dyderska, S.; Jagodziński, A.M.; Puchałka, R. Shifts in Native Tree Species Distributions in Europe under Climate Change. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, P.; Decaëns, T.; Aubert, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Bureau, F.; Margerie, P.; Mora, P.; Rossi, J.-P. Soil Invertebrates and Ecosystem Services. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity Loss and Its Impact on Humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, D.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Harrower, C.A.; Collen, B.; van Strien, A.J.; Roy, D.B. The Use of Opportunistic Data for IUCN Red List Assessments. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 115, 690–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochet, A.; Schmeller, D. Effectiveness of the Natura 2000 Network to Cover Threatened Species. Nat. Conserv. 2013, 4, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Order | Unique Occurrences | Species Richness | Endemic Richness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scutigeromorpha | 147 | 1 | 0 |
| Lithobiomorpha | 1322 | 51 | 9 |
| Scolopendromorpha | 631 | 16 | 6 |
| Geophilomorpha | 1223 | 42 | 5 |
| Total | 3323 | 110 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgopoulou, E.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Simaiakis, S.M. The Impact of Climate and Land Use Change on Greek Centipede Biodiversity and Conservation. Land 2025, 14, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081685
Georgopoulou E, Kougioumoutzis K, Simaiakis SM. The Impact of Climate and Land Use Change on Greek Centipede Biodiversity and Conservation. Land. 2025; 14(8):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081685
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgopoulou, Elisavet, Konstantinos Kougioumoutzis, and Stylianos M. Simaiakis. 2025. "The Impact of Climate and Land Use Change on Greek Centipede Biodiversity and Conservation" Land 14, no. 8: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081685
APA StyleGeorgopoulou, E., Kougioumoutzis, K., & Simaiakis, S. M. (2025). The Impact of Climate and Land Use Change on Greek Centipede Biodiversity and Conservation. Land, 14(8), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081685






