Abstract
As urbanization accelerates, a host of negative ecological impacts have become increasingly prominent. Green roofs, as a sustainable solution, can effectively mitigate the urban heat island effect and reduce carbon footprints. However, the lack of datasets on plant species suitable for green roofs in China has hindered the advancement of relevant research and practical applications. Therefore, this study constructed a diversified dataset of plant species for green roofs in China, using data sources from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Web of Science (WoS). Generated by integrating the Kimi large language model (Kimi LLM) API with knowledge graph technology, the dataset contains 2248 plant records. It specifically includes a statistical CSV file with detailed plant information, a CSV file of species combinations, a CSV file linking plant combinations to cities, and original plant data extracted from research papers. Technical experiments have validated the accuracy and efficiency of this dataset in acquiring plant species. Suitable for plant selection in green roof projects, this dataset will provide strong support for in-depth research and wider applications in the field of urban sustainability.
1. Introduction
With the intensification of global climate change and the rapid pace of urbanization, urban ecosystems are facing increasing pressure. Issues such as the urban heat island effect, loss of biodiversity, and insufficient ecological resilience have emerged as common challenges constraining the sustainable development of cities worldwide [1]. Against this backdrop, green roofs—an ecological restoration strategy with significant potential—have garnered extensive global attention and practical implementation due to their comprehensive benefits in mitigating the heat island effect, purifying air, increasing urban green coverage, and conserving biodiversity [2]. However, the ecological performance and sustainability of green roofs largely depend on the scientific selection of plant species. The adaptability of plants to specific climatic conditions, substrate environments, and maintenance levels directly determines the stability and functional efficacy of green roof systems [3]. Therefore, the identification and selection of suitable plant species tailored to regional characteristics, as well as the development of a systematic plant selection and configuration framework, have become crucial topics in global urban ecological research.
Globally, research on the selection and application of green roof plant species has yielded substantial progress [4]. Scholars have conducted numerous empirical studies focusing on core indicators such as plant stress resistance (e.g., drought tolerance, cold resistance, and nutrient-poor soil adaptability) [5], ecological functions (e.g., carbon sequestration and water retention), and landscape value [6]. For instance, in response to the unique environmental conditions of shallow-substrate roofs, researchers have systematically evaluated the growth characteristics of Sedum species, confirming their survival and coverage performance under extreme conditions [7,8]. Several countries and regions have established regional plant databases to support the design and implementation of green roof projects [9,10]. While these efforts lay a solid foundation for the scientific application of green roof vegetation, they also reveal common global challenges: First, plant adaptability data are often dispersed across various independent research projects, lacking cross-regional and cross-scale integration, which hampers the optimization of plant selection at larger scales [11]. Second, in-depth investigations into the long-term ecological benefits of plant community configurations and the general adaptability patterns of plants across different climate zones remain limited [12], thereby constraining the large-scale promotion of green roof technologies [13].
From an information-processing perspective, advancing green roof plant research is hindered by a “data barrier”. Key information, such as plant adaptability, ecological performance metrics, and regional environmental parameters, often exists in the form of unstructured text (e.g., scientific papers and technical reports), making it difficult to efficiently extract value using conventional information extraction methods [14]. Rule-based approaches rely heavily on manually crafted logic, which is insufficient to handle the linguistic diversity of textual expressions [15]. Traditional machine learning methods are constrained by the high cost of annotated data and exhibit limited generalization across domains [16]. These inefficiencies in data processing exacerbate the difficulties of data integration and sharing, thereby impeding the global translation of localized green roof experiences into universally applicable scientific guidance.
In recent years, the emergence of large-scale pre-trained language models (LLMs) has provided a promising solution to this dilemma [17]. Trained on massive corpora, LLMs possess strong semantic understanding capabilities and can extract key cross-domain information under few-shot or even zero-shot conditions, without requiring extensive labeled data [18,19,20,21]. Moreover, the integration of LLMs with knowledge graph technologies not only enhances semantic parsing but also enables the structured organization and efficient retrieval of information [22]. This combined approach offers robust support for the integration and in-depth mining of fragmented plant-related data. Applied to the domain of green roofs, this methodology holds the potential to overcome traditional data-processing limitations [23]: by extracting scattered information on plant adaptability traits and environmental correlations using LLMs, and constructing a structured plant information system via knowledge graphs, it becomes possible to conduct rapid comparative analyses of plant suitability across different regions, thereby enabling intelligent support for plant selection in green roof applications [24,25].
In summary, constructing a comprehensive green roof plant information dataset is of great significance for promoting the sustainable development of urban ecosystems. This study systematically collects and integrates plant adaptability data across multiple cities and climate zones in China. It not only addresses the critical gap in plant species selection and ecological benefit assessment in China’s green roof research but also provides an important basis for the scientific screening and optimization of vegetation. Furthermore, by leveraging key information extraction techniques based on large language model APIs and knowledge graph construction, this research enables the efficient organization and intelligent retrieval of plant information. This lays a technological foundation for sharing and promoting green roof practices across cities, ultimately facilitating the precise implementation of green roof strategies on a broader scale.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
The China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) [26] is one of the world’s largest Chinese academic resource databases. These resources cover multiple fields such as natural science, social science, technology, and medicine, and include various types of documents like academic journals, doctoral and master’s theses, conference papers, etc., ensuring comprehensive coverage of academic content. Secondly, the literature has been strictly screened and audited to ensure the high quality and authority of the resources. Its powerful search engine and literature management tools enable researchers to find, organize, and cite literature efficiently. In addition, it provides a convenient full-text access function, which allows users to directly download the complete PDF file, saving a lot of time. It also supports interdisciplinary collaborative research, helping scholars to conduct cross-field research. Therefore, the CNKI is not only a core platform for Chinese academic research but also an important channel for scholars around the world to understand Chinese academic achievements.
Web of Science (WoS) [27] is a world-renowned academic citation indexing database. The platform integrates high-quality academic journals, conference papers, patent documents, and other resources in multiple subject areas, and through its unique citation indexing system, researchers can track the citations of academic achievements, analyze the research trends, and assess the academic impact. Its core functions include literature search, citation analysis, journal impact factor query, etc., which provide a powerful research assistance tool for the academic community. The databases it covers mainly include the Science Citation Index (SCI), Social Science Citation Index (SSCI), and Arts and Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI), etc., which are widely used in the fields of academic research, institutional assessment, and research management.
Green roofs, also known as “vegetated roofs” or “ecological roofs,” refer to greening systems established on the surfaces of building rooftops through deliberate design, construction, and maintenance, with vegetation as the central element. This definition applies exclusively to exposed rooftop structures, such as flat or gently sloped roofs, and excludes other building components such as façades, balconies, and underground roof slabs. Based on this definition, a literature search is conducted using the combined keyword “Chinese rooftop greening plants” in the CNKI database [28] and the Web of Science database. To ensure the timeliness of this study, the period is set from 1994 to 2024. A total of 986 relevant papers on rooftop greening plants in China are initially identified through this screening process. The distribution of the number of publications between 1994 and 2024 and the distribution of paper types are shown in Figure 1. These papers cover the information on the names and species of the corresponding plants in several cities in China, and the types of papers include journal articles, conference papers, and other types of papers. By analyzing the data from this collection of papers, it is possible to extract information on plant species for green roofs in multiple cities in China.
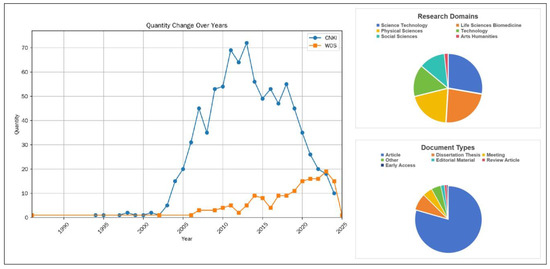
Figure 1.
Data source analysis.
In the data-preprocessing stage, CiteSpace 6.2.4 [29] is used to statistically analyze the title, year, keywords, abstract, and source of all the papers, and 908 papers containing valid data are further screened to form the original paper dataset. In the key data extraction stage, the initial dataset of plant names and species in each paper is extracted by programmatically utilizing the Kimi large language model K1.5 (Kimi LLM K1.5) API interface and utilizing its powerful text comprehension capability. Subsequently, all unique plant name data are obtained by summarizing the plant names involved in all the papers and deduplicating the data using Python’s pandas library 1.1.0 [30]. A more complete dataset is formed by further matching the plant names and supplementing the detailed information of the plants through the online proofreading tool for plant taxonomic names. Finally, the dataset in China is obtained through diversified processing.
This dataset not only provides a more comprehensive reference for plant selection for green roofs in China but also provides solid data support for research needs, such as plant relationship visualization and intelligent Q&A based on the knowledge graph approach.
2.2. Dataset Creation
The dataset in China presents the names and categories of green roof plants in different regions of China, along with their corresponding cities. The creation process is shown in Figure 2.
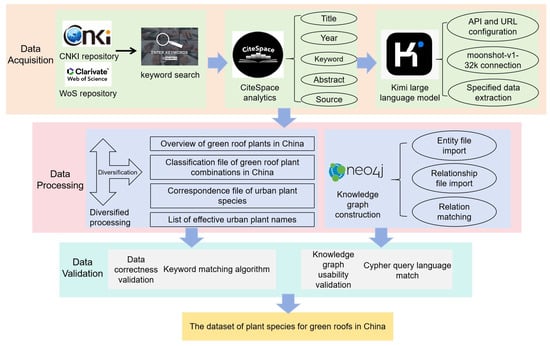
Figure 2.
Dataset construction flowchart.
The dataset is specifically created through the following four steps:
Obtaining the original dataset for the thesis: Articles with the keyword “plant species for green roofs” are searched in the CNKI and WoS. These articles are saved in PDF format. Then, CiteSpace is used to analyze the information of each article, including the title, year, keywords, abstract, and source. Specifically, articles are filtered based on whether the extracted titles, keywords, or abstracts contain relevant terms such as “Chinese green roof plants” while excluding those related to topics such as green roof implementation technologies. Furthermore, the publication years are restricted to the range from 1994 to 2024 to ensure the timeliness of the research. Based on source information, only academic journal articles, theses, and conference papers are included to ensure the rigor and reliability of the dataset. Through the analysis of the extracted information, 908 valid papers are screened out. All the papers are saved in PDF format in the specified directory to facilitate the LLM in extracting key information.
Plant species extraction: The current development of LLM technology is rapid and powerful, demonstrating high accuracy and efficiency in processing textual content [3].
The Kimi large language model demonstrates significant advantages in long-text processing. As shown in Table 1, Yiming Tao et al. reported that when screening a large number of literature titles and abstracts, the Kimi model exhibited sufficiently high precision and recall. Similarly, Yunqiao Fei et al., in their work on fruit tree disease knowledge extraction, found that the model achieved precision levels fully adequate for research needs, even in complex multi-turn question-answering scenarios. Accordingly, conclusions drawn from extensive industry testing confirm that the Kimi model can readily handle long-text content, whether it involves mixed Chinese–English technical documents or lengthy materials for international communication, with robust comprehension and processing capabilities. In this study, we also calculated the model’s precision and recall during a manual random review stage. Although occasional omissions and misjudgments occurred due to the presence of multiple variants for a single plant species, plant variants are not a strict requirement for the dataset. Therefore, the model’s performance is considered fully adequate for the extraction tasks in this research.

Table 1.
Information extraction metrics of the Kimi LLM across different tasks.
Therefore, the information on plant species of each article can be obtained by utilizing the Kimi API interface to extract plant species by utilizing its characteristics for understanding long texts.
As shown in Figure 3, the corresponding API key and base URL are configured to establish the connection with the specified LLM “moonshot-v1-32k” [33]. Moonshot-v1-32k is one of the built-in models of Kimi, featuring a maximum context length of 32,768 tokens. It demonstrates strong multilingual capabilities, particularly in Chinese and English, and excels at generating safe, informative, and accurate responses. During the invocation process, requests are sent to the LLM by constructing input prompts that define the role of the model, include the text to be processed (extracted from PDF documents), and specify parameters such as temperature and maximum token length to control the characteristics of the generated output. To handle potential rate-limiting errors, a retry mechanism is implemented. This mechanism includes configurable settings such as initial wait time, maximum number of retries, and exponential backoff, thereby enhancing the stability and fault tolerance of the system. The extracted plant names and corresponding research cities are stored in a CSV file, forming the foundational dataset for plant species analysis.
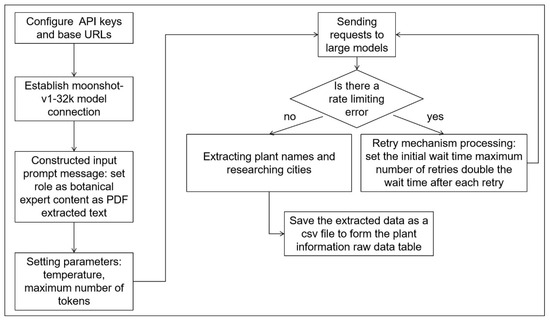
Figure 3.
Key information extraction flowchart.
Diversified integration of plant data: All plant names are compiled, and duplicate entries are automatically removed. The resulting list of unique plant names is then submitted to an online plant taxonomy verification tool to supplement detailed information, including Latin names, families, genera, authors of nomenclature, and species IDs from the PPBC. This process results in the construction of a comprehensive overview table of green roof plant species in China. Then, according to the most widely used combination of green roofs [34], all plants are categorized according to trees, shrubs, and groundcovers, and the names of each type of plant are deduplicated to construct a classification list of plant combinations for green roofs in China. Finally, the raw data are categorized according to the three categories and corresponding cities, and the plants categorized in each city are de-emphasized to construct the three types of plants for green roofs corresponding to each city. The number of current research papers on green roofs and the distribution of corresponding cities are shown in Figure 4.
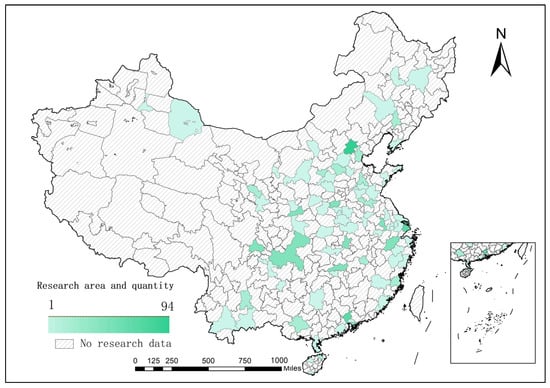
Figure 4.
Research area and number of research papers.
Construction of the knowledge graph (KG): In this study, the Neo4j 5.25.1 graph database is selected. Figure 5 shows the flowchart for constructing the knowledge graph. The specific operation is to organize the plant names, family names, and genus names into three entity files. Then, the relationships between the plant names and the genera, as well as the relationships between the genus names and the family names, are sorted into two relationship files. Subsequently, these entity files and relationship files are imported into the Neo4j graph database through the function of “LOAD CSV WITH HEADERS”. The “MATCH” function of Neo4j is utilized to match the entities and relationships to realize the construction of the plant KG, providing a basic dataset that can be directly used for the research on intelligent question answering of the LLM.
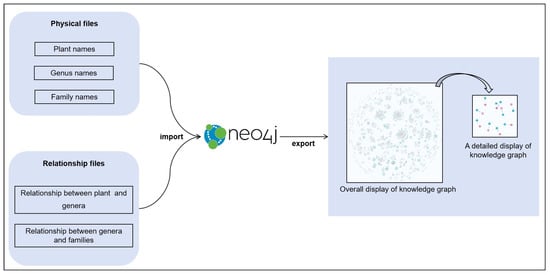
Figure 5.
Flowchart of knowledge graph construction.
2.3. Data Quality Control and Utilization Processes
To ensure data quality, a more comprehensive quality control process is implemented in key stages, including paper collection and screening, data extraction, data integration and deduplication, and KG construction. The quality control flow chart is shown in Figure 6.
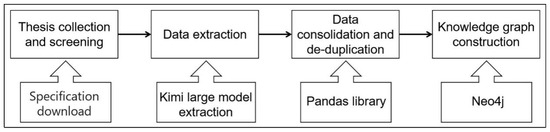
Figure 6.
Quality control flowchart.
The thesis data are searched and downloaded for storage by skilled technicians using standardized operating procedures. When utilizing the Kimi LLM API interface for information extraction of plant species, the accuracy of the LLM’s extraction results is validated through manual random sampling and review of the corresponding papers. This process ensures that all extracted data are derived directly from the original document content rather than being hallucinated by the LLM, and that no duplicate entries are present within the same article.
During the data aggregation process, plant data from multiple papers are combined, which inevitably results in the inclusion of duplicate entries. Python programming is utilized to remove these duplicates while retaining the removed data for subsequent comparative verification, thereby ensuring the accuracy of the deduplication process.
The pandas library is employed to perform deduplication on the plant name data within the CSV file. First, the CSV file is read from the specified path, and the column containing plant names is identified. A new column is then added to store the removed duplicate entries. The program iterates through each row, splitting the plant name strings in the specified column according to a predefined delimiter. By checking for duplicate elements within the list, unique plant names and duplicates are separately identified. Subsequently, the unique and duplicate plant names are reassembled into strings, updating the corresponding columns with the processed data. Finally, the deduplicated data, along with the recorded duplicates, are saved into a new Excel file, ensuring both the removal of duplicates and the documentation of removed entries.
In the KG construction phase, the widely recognized Neo4j tool is used for construction, which guarantees the correctness, scalability, and usability of the KG.
3. Results
3.1. Detailed Description of the Dataset
The dataset comprises a total of four CSV files. The categorization map of the dataset is shown in Figure 7.
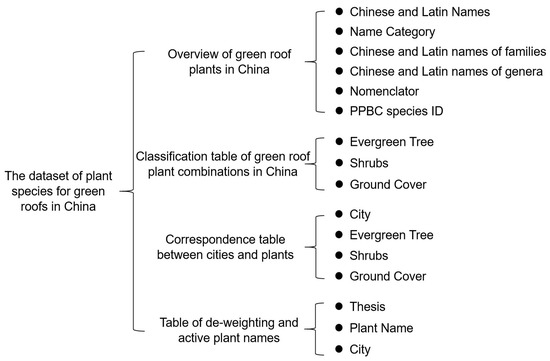
Figure 7.
Dataset classification chart.
The dataset can be found in the Zenodo repository. The repository consists of four CSV files: an overview CSV file of plants for green roofs in China, a classification CSV file of plants for green roof combinations in China, a CSV file of urban plant correspondences, and a CSV file of valid urban plant names.
The CSV file of plant species for green roofs in China: A total of 2248 plant species for green roofs have been extracted and summarized from the existing literature in this CSV file. It includes the plant species for green roofs in the main climatic regions of China. The detailed information includes the common name of plants, category, the Chinese name of the family, the Latin name of the family, the Chinese name of the genus, the Latin name of the genus, the Chinese scientific name, the Latin scientific name, the author of the name, and the species ID on the PPBC, etc. The specific title name and the corresponding explanation are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Notes on the overview of plants for green roofs in China.
The families and genera with the highest number of cultivated plant species are illustrated in Figure 8. Analysis of the growth habits of these taxa reveals several shared characteristics: they exhibit strong ecological adaptability, enabling them to occupy diverse habitats; they possess both ornamental and practical value, leading to widespread use in both landscape architecture and agriculture; and they display a wide range of growth forms and reproductive strategies, including entomophily, zoochory, and vegetative propagation. These traits collectively underpin their ecological benefits and utility for human applications.
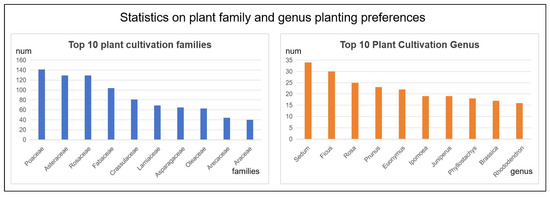
Figure 8.
Statistics on plant family and genus planting preferences.
The CSV file of plant combinations for green roofs in China: This file is based on the most widely adopted plant combination models for green roofs, categorizing plants into three types: trees, shrubs, and ground covers. It contains a total of 4344 data entries, including multiple varieties of the same plant. The specific titles and corresponding explanations are provided in Table 3, as well as the three plant type classifications corresponding to the statistical table.

Table 3.
Notes on the classification of plants for green roof combinations in China.
As shown in Figure 9, the planted species are categorized into three major growth forms, with shrubs and groundcover plants totaling 2087 and 1623 species, respectively, significantly exceeding the 634 species of trees. This indicates a general preference across cities for plant types with lower maintenance requirements and reduced structural load on rooftops. The use of mixed plantings of shrubs and groundcovers, or solely groundcover species, is characteristic of minimalist green roof designs and is more suitable for retrofitting the rooftops of most buildings.
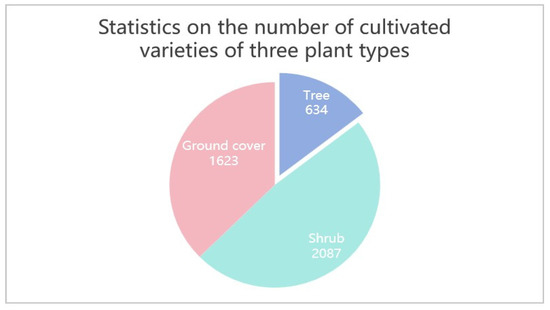
Figure 9.
Statistics on the number of cultivated varieties of the three plant types.
The CSV file of urban plant species correspondence: This file primarily associates the extracted city names with corresponding plant names. A total of 94 research cities mentioned in the papers and their associated plants are systematically analyzed. Furthermore, the plants are classified into three categories: trees, shrubs, and ground covers. The specific titles and corresponding explanations are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Explanatory notes for the urban plant species correspondence table.
As shown in Figure 10, an analysis of the ten cities with the highest total number of planted species further confirms the strong preference for shrubs and groundcover plants over trees in urban green roof practices.
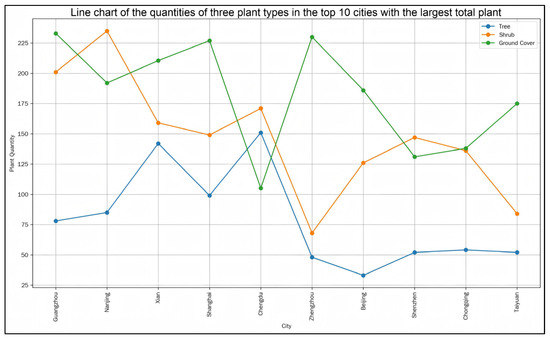
Figure 10.
Chart of the quantities of three plant types in the top 10 cities with the largest total plant.
The CSV file of initial deduplication and valid plant names: This file is a statistical record of effective plants in various cities, compiled by extracting plant names and their corresponding research cities from numerous relevant papers with the assistance of the Kimi LLM. Through a detailed analysis of this statistical file, the research findings from previous studies on green roof plants in each city can be thoroughly examined, enabling the accurate identification and categorization of the most commonly planted plant types in each city, as presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Study cities and plants.
Further analysis of the statistical data enables a clear identification of the plant species with the highest number of occurrences. As shown in Figure 11, the top ten most frequently used species include Sedum lineare, Lagerstroemia indica, Rosa chinensis, Wisteria sinensis, Hedera helix, Sedum sarmentosum, Vitis vinifera, Osmanthus fragrans, Parthenocissus tricuspidata, and Campsis grandiflora. These species have consistently appeared with high frequency in previous studies, underscoring their prominent role in the practice of urban green roof development.
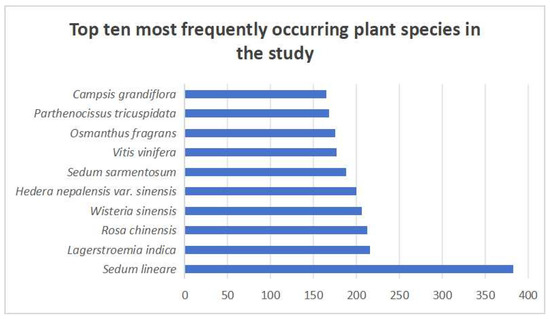
Figure 11.
Top 10 most frequently occurring plant species in this study.
The statistical file of effective plants for this city provides researchers with a convenient and efficient method for data retrieval. It allows for the rapid and accurate extraction of relevant information regarding the city and its associated plants from previous research, offering valuable data support and a solid reference for further in-depth studies on plants for urban green roofs.
KG of plant species: The “apoc.export.json.all” method is employed to export the complete graph data, including nodes and relationships, into a specified JSON file. Upon completion of the export, the JSON file can be re-imported into Neo4j for purposes such as data reuse, graph migration, or further experimentation. To ensure data consistency, it is optional to clear the existing database before the operation. This can be achieved by executing the “MATCH (n) DETACH DELETE n” command, which removes all nodes and relationships, thus creating a clean environment for the subsequent import. Subsequently, the “apoc.import.json” method, provided by the APOC plugin, is used to parse the JSON file and progressively reconstruct the KG structure and data within Neo4j. It is important to note that, to ensure proper installation and configuration of the APOC plugin, its usage is restricted by default in some Neo4j versions. Therefore, it is necessary to manually modify the “neo4j.conf” file, uncomment the relevant apoc. Configuration settings, and restart the Neo4j service before proceeding with the import operation.
3.2. Verification of the Accuracy of Green Roof Plant Data and Type Classification
To validate the accuracy of the plant information and classification obtained in this study, the “Catalogue of Life China: 2024 Annual Checklist “dataset is downloaded from the Plant Science Data Center for plant name verification [35]. In addition, the “Data set of community characteristics in tree layer of forest community in 2020” [36], “Data set of community characteristics in shrub layer of forest community in 2020” [37], and “Data set of community characteristics in herb layer of forest community in 2020” [38] are obtained from the Vegetation Big Data Platform to verify plant type classifications. A fuzzy matching algorithm is employed to cross-check the extracted data, ensuring the correctness of plant names and their corresponding classifications.
As shown in Figure 12 and Algorithm S1 in the Supplementary Materials, a Python-based data-processing workflow is implemented to perform fuzzy keyword matching between two Excel datasets. Specifically, the script loads two spreadsheets, file1.xlsx and file2.xlsx, using the pandas library. The first file contains the primary dataset to be annotated, while the second file holds a list of Chinese keyword entries. After extracting and cleaning the keyword list to remove missing or blank values, a custom function is defined to perform fuzzy matching by determining whether any of the keywords appear as substrings within the target text field of the primary dataset. This function is then applied across all entries in the specified matching column, and the results are annotated with a “match” label where applicable. Finally, the processed dataset is exported to a new Excel file, enabling straightforward identification of records containing relevant keywords.
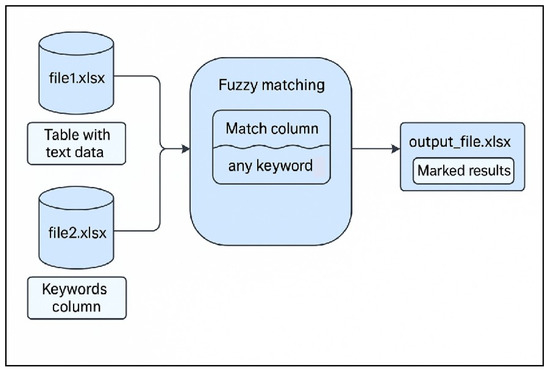
Figure 12.
Fuzzy matching.
3.3. Validation of KG Usability and Usage Process
In this study, a KG representing the relationships among plant names, family names, and genus names is constructed using the Neo4j database. To thoroughly validate the functionality of this KG, we utilize the built-in command-line interface of Neo4j and the Cypher query language to query relevant data, ensuring that all data with direct relationships can be successfully matched.
To enable testing by non-expert Neo4j users, several functions are defined in PyCharm 2024.2.3 for verification. With proper credentials, users can establish a connection to the Neo4j database. Subsequently, they can simply click to execute the program. In response to the program prompts, users are able to input the data they intend to query. All data with direct relationships will be output.
To achieve structured retrieval and intelligent querying of green roof plant knowledge, this study constructs a knowledge graph interaction framework based on Neo4j, which consists of two core functional modules. The first is the knowledge graph connection and query module, which is responsible for establishing and managing connections with the database. It creates connection instances by initializing connection parameters (such as database address, username, and password), provides a connection closing function to release resources, and supports submitting query requests through a session mechanism, returning query results in a structured form. The second is the natural language question parsing module, which undertakes the function of converting users’ natural language into graph query instructions. This module predefines four types of core query templates (e.g., association queries between plants and families/genera, list queries of plants included in families/genera, etc.) and associates specific sentence patterns with corresponding processing logics through regular expressions.
As shown in Figure 13 and Algorithm S2 in the Supplementary Materials, in the parsing process, it first extracts key entities (such as plant names, family or genus names) from users’ natural language questions, and then invokes the matched processing logic to generate corresponding query statements. For example, for the question “Which family does a certain plant belong to?”, it generates a corresponding path-matching query to realize the associated retrieval from the plant node through the genus node to the family node. Through modular design, this framework realizes efficient access to the knowledge graph and natural language interaction, providing technical support for the rapid retrieval of green roof plant information.
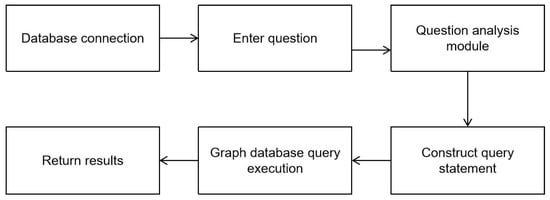
Figure 13.
Knowledge graph utilization process.
The usability and accuracy of this KG of plant species for green roofs in China are fully confirmed by the above methodological validation.
4. Discussion
4.1. Utilization of the Dataset
Currently, research on rooftop greening plant information datasets remains limited, particularly in the context of China. The existing datasets are primarily concentrated in European countries. For example, Carmen Van Mechelen et al. [39] constructed a plant species list for green roofs in parts of Europe based on five key literature sources authored by internationally recognized green roof experts or scientists, as well as species lists from two international green roof companies. This dataset includes a total of 483 plant species. However, the study mainly focuses on plant attributes and planting frequency, with limited statistical coverage of plant species information, restricted to certain regions of Europe. Moreover, it lacks intelligent methods for data extraction and information retrieval. So, the dataset provided in this study is in CSV format, which provides a more intuitive approach for directly selecting plant species for the implementation of green roofs in China, especially for widely used green roof combinations, and offers the corresponding plant species classification. In addition, this study systematically summarizes and categorizes the plants used in urban green roofs in the existing literature to provide detailed information on plant species for the design of green roof retrofit programs in various cities. This effort serves to provide a scientific foundation and reference for plant selection and configuration in practical applications. The method of invoking the LLM used to construct the dataset also provides a reference basis for the extraction of long text information. At the same time, the construction of the KG for the future intelligent Q&A scenarios of the LLM will also greatly facilitate the researchers’ use of the dataset, and the KG constructed by utilizing the Neo4j graph database can be saved in the JSON format, which is convenient for other people to quickly import and use.
4.2. Tools for Building the Dataset
The Kimi LLM has demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text comprehension, particularly when handling complex texts across multiple languages and domains. It can be effectively employed to analyze semantic relationships, extract fine-grained information, and provide contextually informed insights. This makes it highly efficient and accurate in tasks such as text classification, information extraction, and content generation. The model is especially well suited for high-demand applications, such as the analysis of academic papers and the parsing of technical documents. Furthermore, when processing texts that contain ambiguous language or implicit information, it can offer interpretations that are both logically rigorous and contextually consistent, underscoring its significant potential in natural language processing. It should be acknowledged that many large language models are susceptible to hallucination, generating content that appears fluent and reasonable but is inaccurate, non-existent, or unverified. These models also depend heavily on the consistency and quality of the source texts. In this study, all source data are derived from PDF documents, ensuring standardized and consistent inputs. To further minimize the risk of hallucinations and ensure, as much as possible, the quality of the dataset, we employ well-designed prompts, control the volume of input data per session, and incorporate manual verification throughout the process.
Because KG data contain entities, attributes, relationships, and other features that common relational databases such as MySQL [40] cannot adequately reflect, these are typically stored in graph databases, with Neo4j being one of the most commonly used.
Neo4j [41], as a leading graph database, offers distinct advantages in managing and analyzing complex relational data through efficient graph data modeling and query capabilities. Its storage and query mechanisms, based on a graph structure, enable users to intuitively model and analyze intricate relationships between entities, facilitating efficient traversal, aggregation, and pattern recognition. Neo4j supports the flexible Cypher query language [42], which is well suited for handling large volumes of nodes and relational data. It proves particularly effective in applications involving deep relationships, social networks, and recommendation systems. Optimized graph traversal algorithms ensure high performance even with large-scale datasets, demonstrating the significant capabilities of graph databases in processing highly connected data.
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Although this study provides a reference dataset of green roof plant species in China, the construction of the dataset is primarily based on information compiled from previous publications. The timeliness of data in some of these sources may lead to misleading plant selections for current urban green roof applications, thereby affecting the overall data quality. Moreover, the lack of systematic field investigations may limit the accuracy of suitability assessments for certain species. In addition, the dataset lacks detailed plant attribute information, which may hinder its direct application in studies requiring comprehensive quantitative evaluations.
To address these issues, future work will incorporate the latest research findings and collaborate with local landscape and greening agencies to collect diverse data and expand the dataset. Furthermore, we aim to enrich the dataset by including additional data types, such as indicators of carbon sequestration potential and cooling effects, to enhance its ecological relevance and applicability. Finally, we plan to construct a more comprehensive knowledge graph for green roof plant species, integrating ecological indicators to enable intelligent and diversified information retrieval and question answering.
5. Conclusions
This study constructs a plant species dataset tailored for green roof applications in China, integrating large-scale literature mining, advanced information extraction using the Kimi large language model, and knowledge graph construction. The dataset encompasses ecological and taxonomic information derived from over 900 academic publications across 94 cities, providing a structured foundation for scientific plant selection, regional adaptability assessment, and ecological benefit evaluation. By leveraging the semantic understanding capabilities of large language models and the structured reasoning framework of Neo4j-based knowledge graphs, this study significantly enhances both the accessibility and analytical utility of plant-related data.
The dataset demonstrates value not only for academic research but also for practical applications. In urban planning and landscape design, the categorized plant information can support plant suitability analysis, species selection, and ecological performance evaluation in different regions. It also provides a reference for differentiated greening strategies in the context of environmental management and policy-making. Moreover, the constructed knowledge graph offers technical support for semantic-based plant information retrieval, enabling future extensions such as intelligent Q&A systems, urban green space databases, and integration with GIS platforms. The use of open formats (CSV and JSON) facilitates interoperability and secondary development.
Regarding the current limitations of this study, which involve the relatively small number of cities covered and the absence of vegetation indices, future work will aim to expand the dataset’s geographical scope through further investigations, even though certain cities may not be suitable for green roof implementation. Additionally, efforts will be made to incorporate ecological function indicators, as well as to integrate multimodal data such as plant images and environmental parameters. Furthermore, in response to the potential risk of hallucinations in large models during targeted information extraction, we will consider enriching the model’s corpus and optimizing its architecture to further ensure data accuracy.
Overall, this dataset provides a structured information foundation for research and applications in urban green infrastructure, supporting more scientifically informed and regionally adapted plant selection for green roof development.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land14081684/s1, Algorithm S1: Fuzzy Matching; Algorithm S2: Query for the family to which the plant belongs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and S.L.; Funding Acquisition, S.L.; Investigation, H.H.; Methodology, X.L., S.L., Y.C., S.D. and J.Z.; Software, H.H. and Y.C.; Supervision, X.L., S.L., S.D. and J.Z.; Validation, H.H.; Visualization, J.Z.; Writing—Original Draft, H.H.; Writing—Review and Editing, X.L. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program, grant number 2020YFB2104400.
Data Availability Statement
The data extraction method, data-processing method, etc., proposed in this study are publicly available: Data extraction method. In this study, the API interface of the Kimi LLM is utilized to leverage its advanced semantic understanding capabilities for extracting key data from the thesis based on custom requirements. The “requirements.txt” file outlines the necessary libraries for executing this method, while the “README.md” file provides implementation instructions, including key considerations and a detailed explanation of the code principles and functionality. Additionally, the corresponding code for executing this method is available on the GitHub platform, accessible via the following URL: https://github.com/hhyaaassss/kimitest.git, accessed on 30 April 2025.
Acknowledgments
The authors express deep gratitude to the anonymous reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, H.; Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Middel, A.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Wen, Z. Impacts of Green Roofs on Water, Temperature, and Air Quality: A Bibliometric Review. Build. Environ. 2021, 196, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, P. The Effectiveness of Green Roofs in Reducing Building Energy Consumptions across Different Climates. A Summary of Literature Results. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Mai, G.; Lin, J.; Wei, C.; Yu, W. BB-GeoGPT: A Framework for Learning a Large Language Model for Geographic Information Science. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K. Green Roofs: A Critical Review on the Role of Components, Benefits, Limitations and Trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuring, C.E.; Dunnett, N. Vegetation Composition of Old Extensive Green Roofs (from 1980s Germany). Ecol. Process. 2014, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberalesso, T.; Oliveira Cruz, C.; Matos Silva, C.; Manso, M. Green Infrastructure and Public Policies: An International Review of Green Roofs and Green Walls Incentives. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, M.; Peng, H. Aesthetic Evaluation of Commercial Rooftop Plants Based on Beauty Degree Evaluation Method: A Case Study of Chengdu City, China. World J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 11, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, H.; Ozaki, A.; Dong, N. Thermal and Energy Performance of Green Roof and Cool Roof: A Comparison Study in Shanghai Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Che, Y.; Ge, Z.; Mao, L. The Relationship between Green Roofs and Urban Biodiversity: A Systematic Review. Biodivers. Conserv. 2022, 31, 1771–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Prado, P.; Pons-Gumí, D.; Toboso-Chavero, S.; Parada, F.; Josa, A.; Gabarrell, X.; Rieradevall, J. Perceptions on Barriers and Opportunities for Integrating Urban Agri-Green Roofs: A European Mediterranean Compact City Case. Cities 2021, 114, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yixuan, W.; Jiayu, W.; Tian, C. Multi-Scenario Analysis of Rooftop Greening Regulation on Runoff Effects Based on Adaptive Evaluation: A Case Study of Macau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Ren, C. China’s Adaptation to Climate & Urban Climatic Changes: A Critical Review. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Assessing Climate-Adaptation Effect of Extensive Tropical Green Roofs in Cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, Z.; Jaffry, S.W.; Malik, M.K. Information Extraction from Scientific Articles: A Survey. Scientometrics 2018, 117, 1931–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluegl, P.; Toepfer, M.; Beck, P.-D.; Fette, G.; Puppe, F. UIMA Ruta: Rapid development of rule-based information extraction applications. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2016, 22, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, T.D. Automated Analysis of Reflection in Writing: Validating Machine Learning Approaches. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2019, 29, 217–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, M. Recent Named Entity Recognition and Classification Techniques: A Systematic Review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 29, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, J.; Yangarber, R. Information Extraction: Past, Present and Future. In Multi-Source, Multilingual Information Extraction and Summarization; Poibeau, T., Saggion, H., Piskorski, J., Yangarber, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 23–49. ISBN 978-3-642-28569-1. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing via Large Pre-Trained Language Models: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xing, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, H.; Lu, J. Let’s Discover More API Relations: A Large Language Model-Based AI Chain for Unsupervised API Relation Inference. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2024, 33, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Pu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; et al. When Large Language Models Meet Personalization: Perspectives of Challenges and Opportunities. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjæveland, M.G.; Balog, K.; Bernard, N.; Łajewska, W.; Linjordet, T. An Ecosystem for Personal Knowledge Graphs: A Survey and Research Roadmap. AI Open 2024, 5, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Aboulela, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Kashef, R. A Survey on Augmenting Knowledge Graphs (KGs) with Large Language Models (LLMs): Models, Evaluation Metrics, Benchmarks, and Challenges. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Pan, S.; Cambria, E.; Marttinen, P.; Yu, P.S. A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A Review: Knowledge Reasoning over Knowledge Graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Cheng, J.; Guo, H.; Li, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Research on Strategic Mineral Resource Security: A Visual Analysis Using CiteSpace. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, W.; Huang, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Homestead Management in China from the “Separation of Two Rights” to the “Separation of Three Rights”: Visualization and Analysis of Hot Topics and Trends by Mapping Knowledge Domains of Academic Papers in China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Maimaituerxun, M. Bibliometric Review of Carbon Neutrality with CiteSpace: Evolution, Trends, and Framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76668–76686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, J. Python Data Analysis with Pandas. In Python Recipes Handbook: A Problem-Solution Approach; Bernard, J., Ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 37–48. ISBN 978-1-4842-0241-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Yisha, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhan, S.; Sun, F. LitAutoScreener: Development and Validation of an Automated Literature Screening Tool in Evidence-Based Medicine Driven by Large Language Models. Health Data Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, G. Extracting Fruit Disease Knowledge from Research Papers Based on Large Language Models and Prompt Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Xue, D.; Bi, Y.; Huang, Z. Cluster-Based Effective Generation of AI-Driven Literature Surveys. In Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing; Wong, D.F., Wei, Z., Yang, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.; Gheibi, M.; Wacławek, S.; Behzadian, K. A Novel Smart Framework for Optimal Design of Green Roofs in Buildings Conforming with Energy Conservation and Thermal Comfort. Energy Build. 2023, 291, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, T.; Huang, R.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y. Native Useful Vascular Plants of China: A Checklist and Use Patterns. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Tree Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/08310D3C51DBCE13 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Shrub Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/9FFAF77E0BDD5B8A (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Herb Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/3F054839AAD862BD (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Van Mechelen, C.; Dutoit, T.; Kattge, J.; Hermy, M. Plant Trait Analysis Delivers an Extensive List of Potential Green Roof Species for Mediterranean France. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capris, T.; Melo, P.; Garcia, N.M.; Pires, I.M.; Zdravevski, E. Comparison of SQL and NoSQL Databases with Different Workloads: MongoDB vs MySQL Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI), Virtual Conference, 25–26 October 2022; pp. 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Mehta, A.; Ganguli, R.; Sen, S. Recommendation of Influenced Products Using Association Rule Mining: Neo4j as a Case Study. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, S.; Lavanya, K. Chapter Ten—An Application of Cypher Query-Based Dynamic Rule-Based Decision Tree over Suicide Statistics Dataset with Neo4j. In Intelligent IoT Systems in Personalized Health Care; Sangaiah, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Eds.; Cognitive Data Science in Sustainable Computing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 293–313. ISBN 978-0-12-821187-8. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).