A Large-Language-Model-Based Dataset of Plant Species for Green Roofs in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
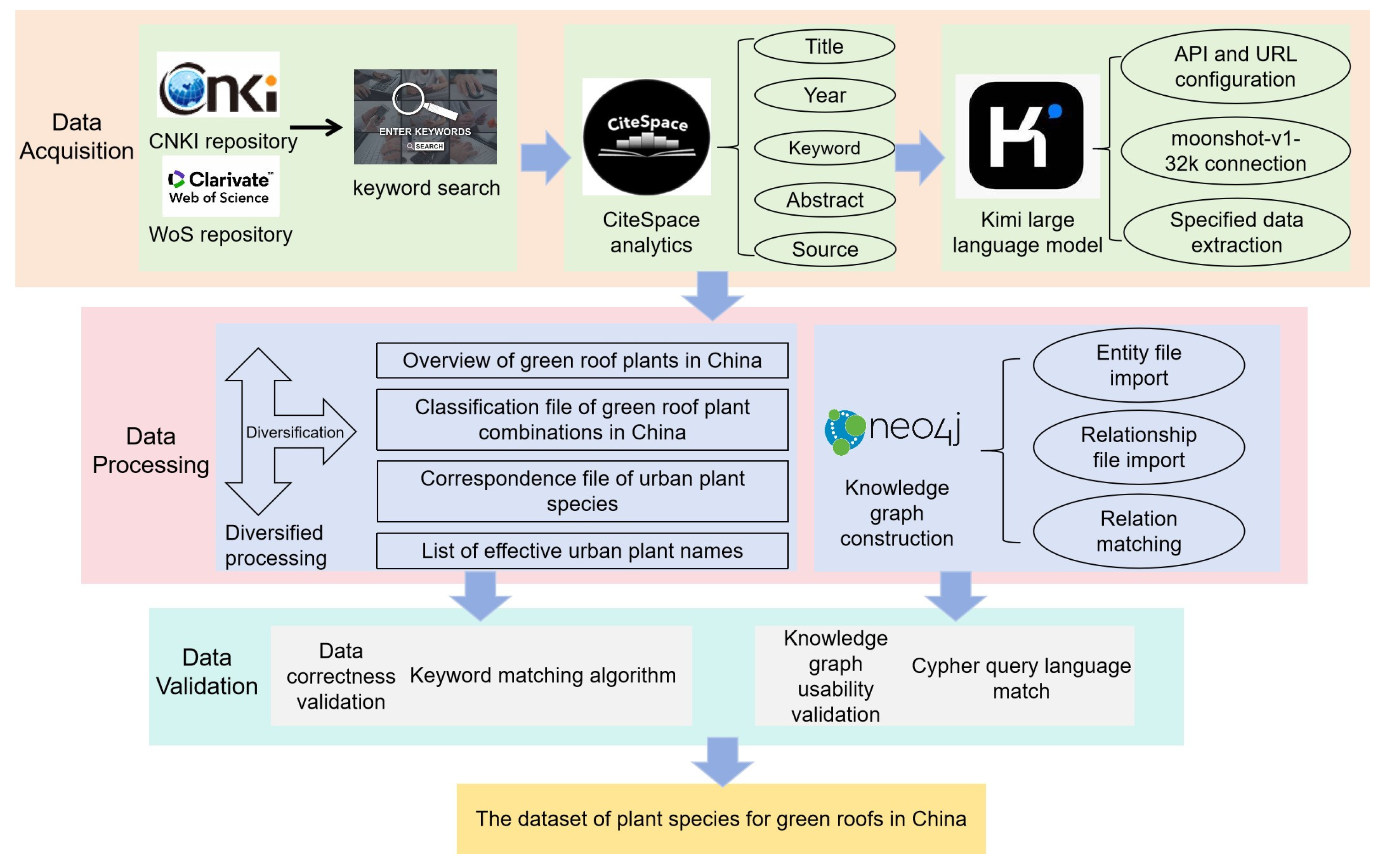
2.1. Data Sources
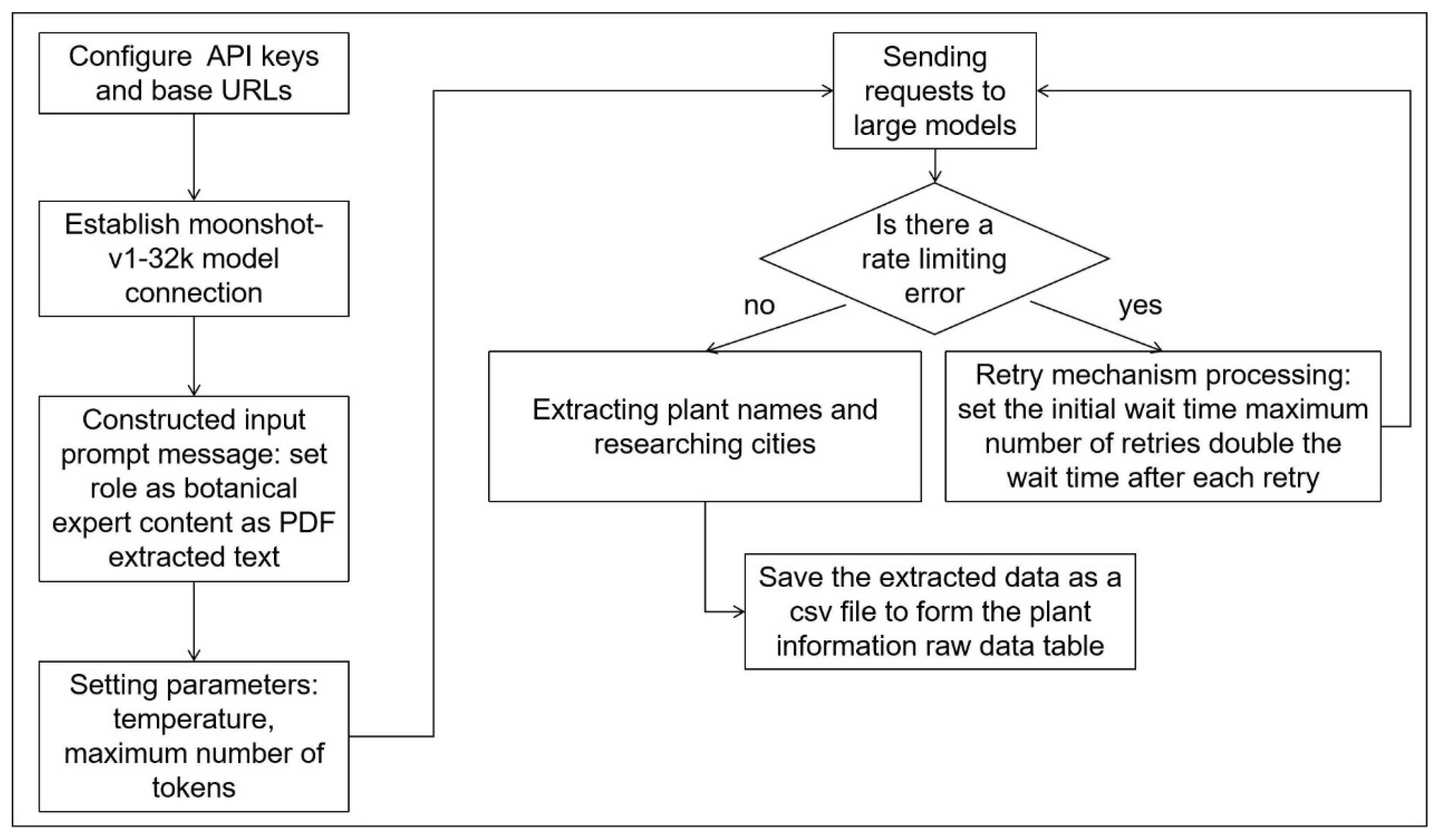
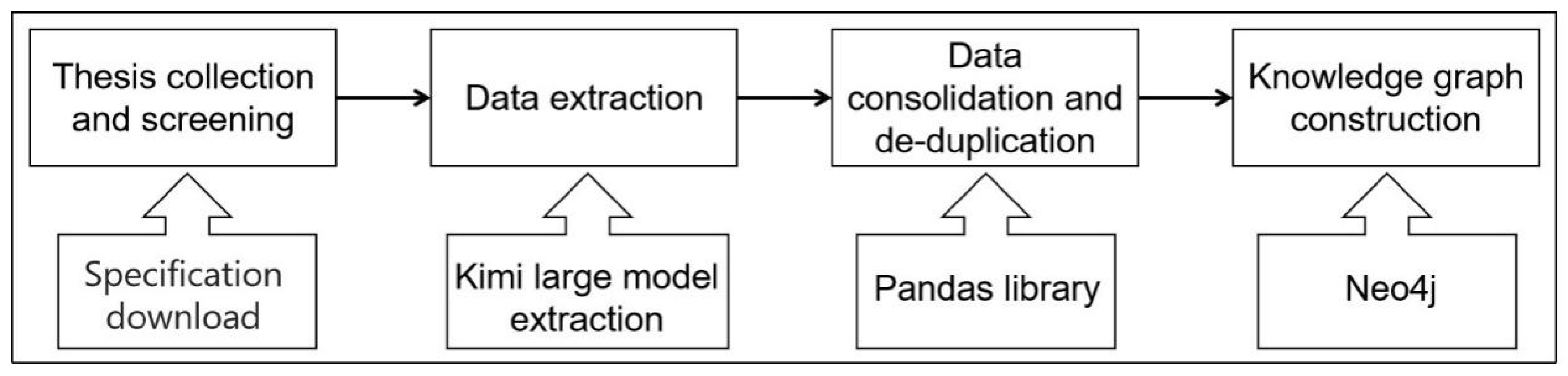
2.2. Dataset Creation
2.3. Data Quality Control and Utilization Processes
3. Results
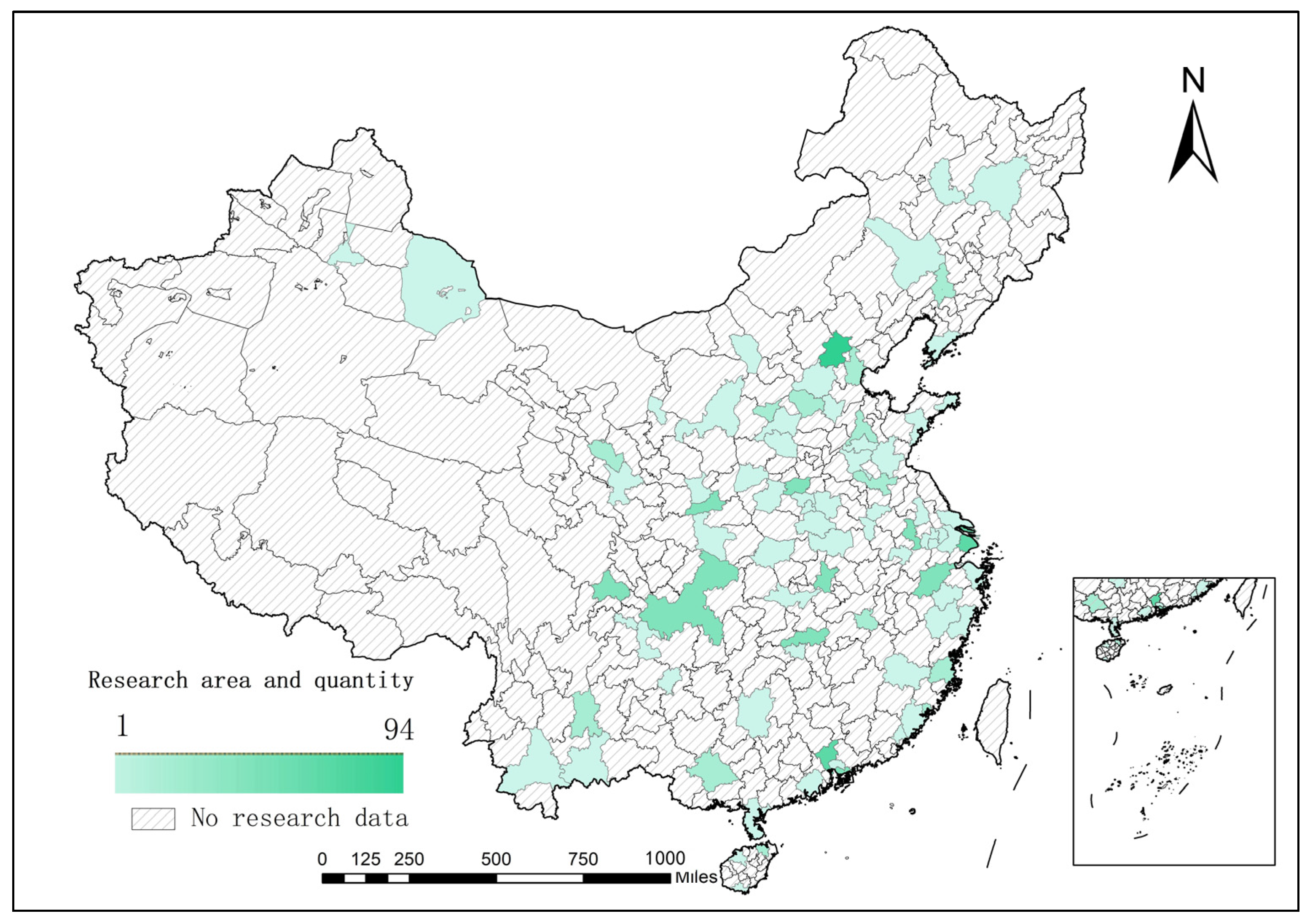
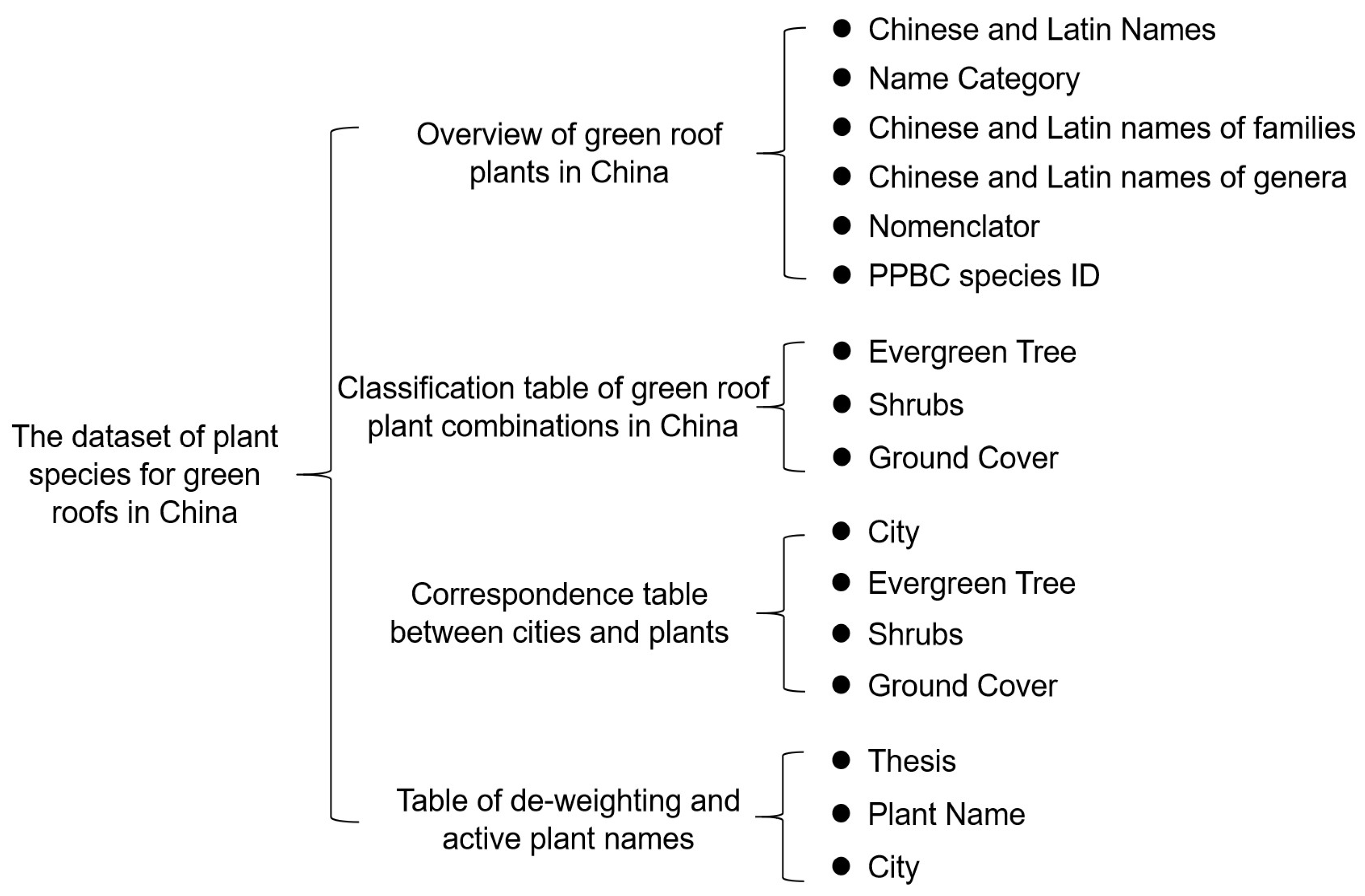
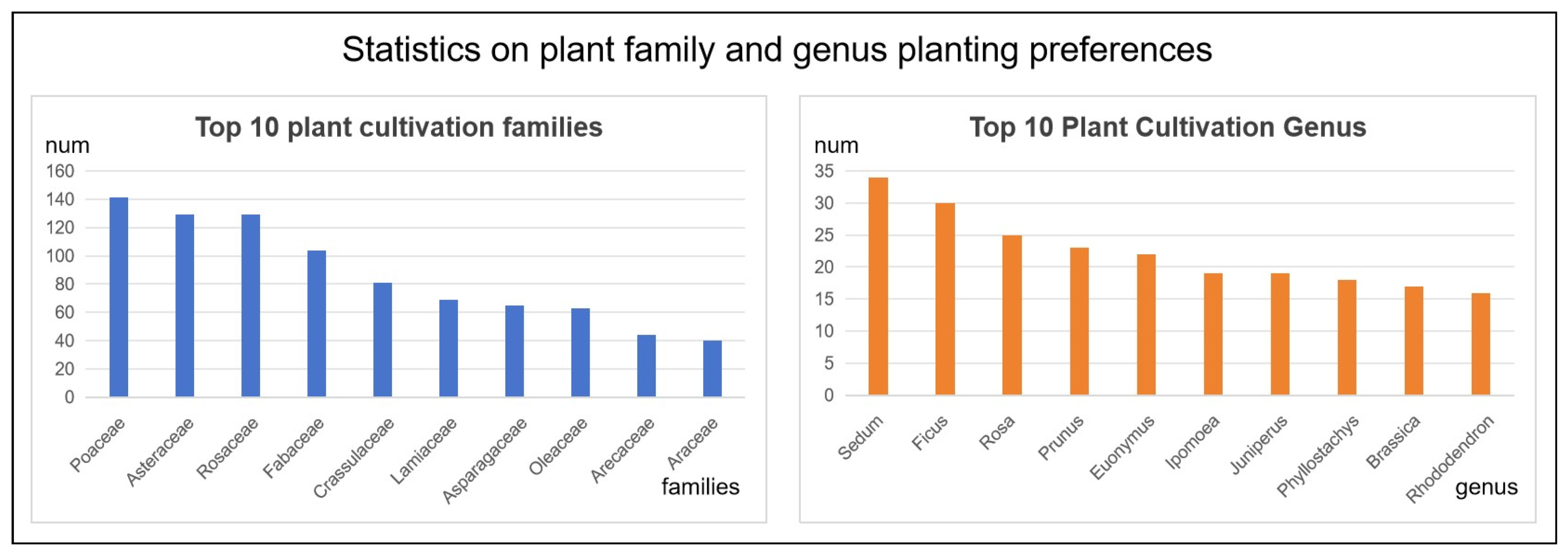
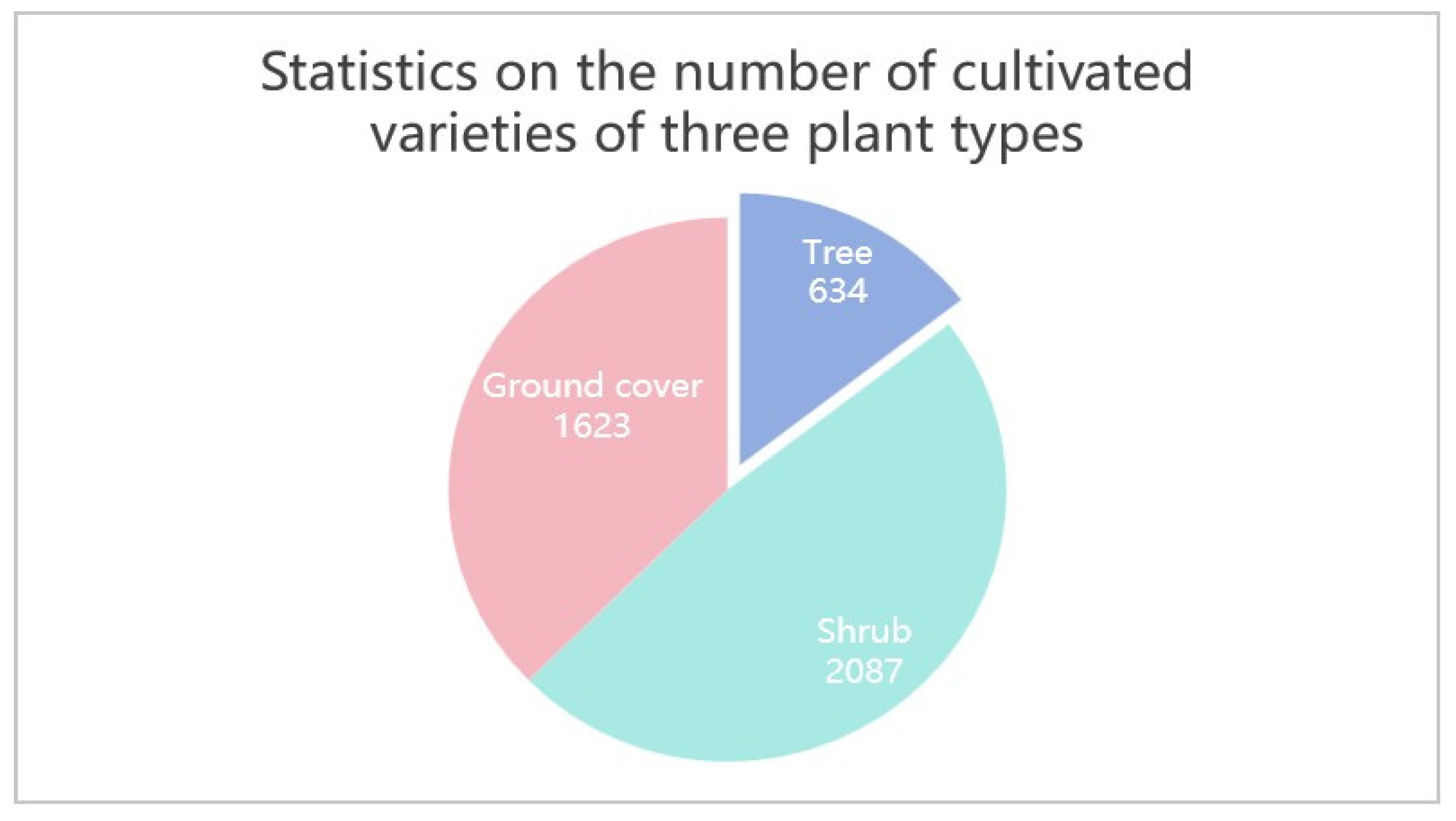
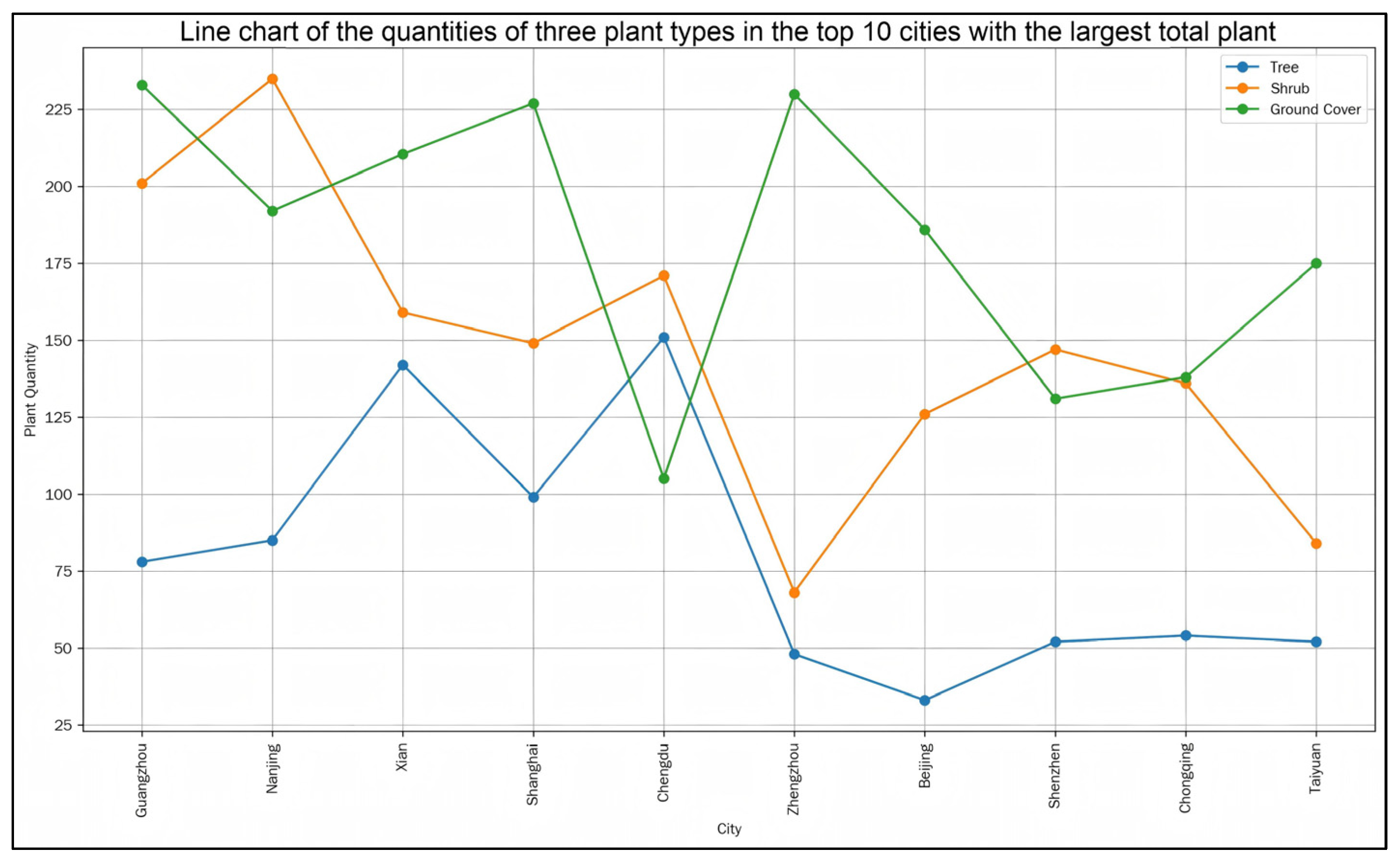
3.1. Detailed Description of the Dataset
3.2. Verification of the Accuracy of Green Roof Plant Data and Type Classification
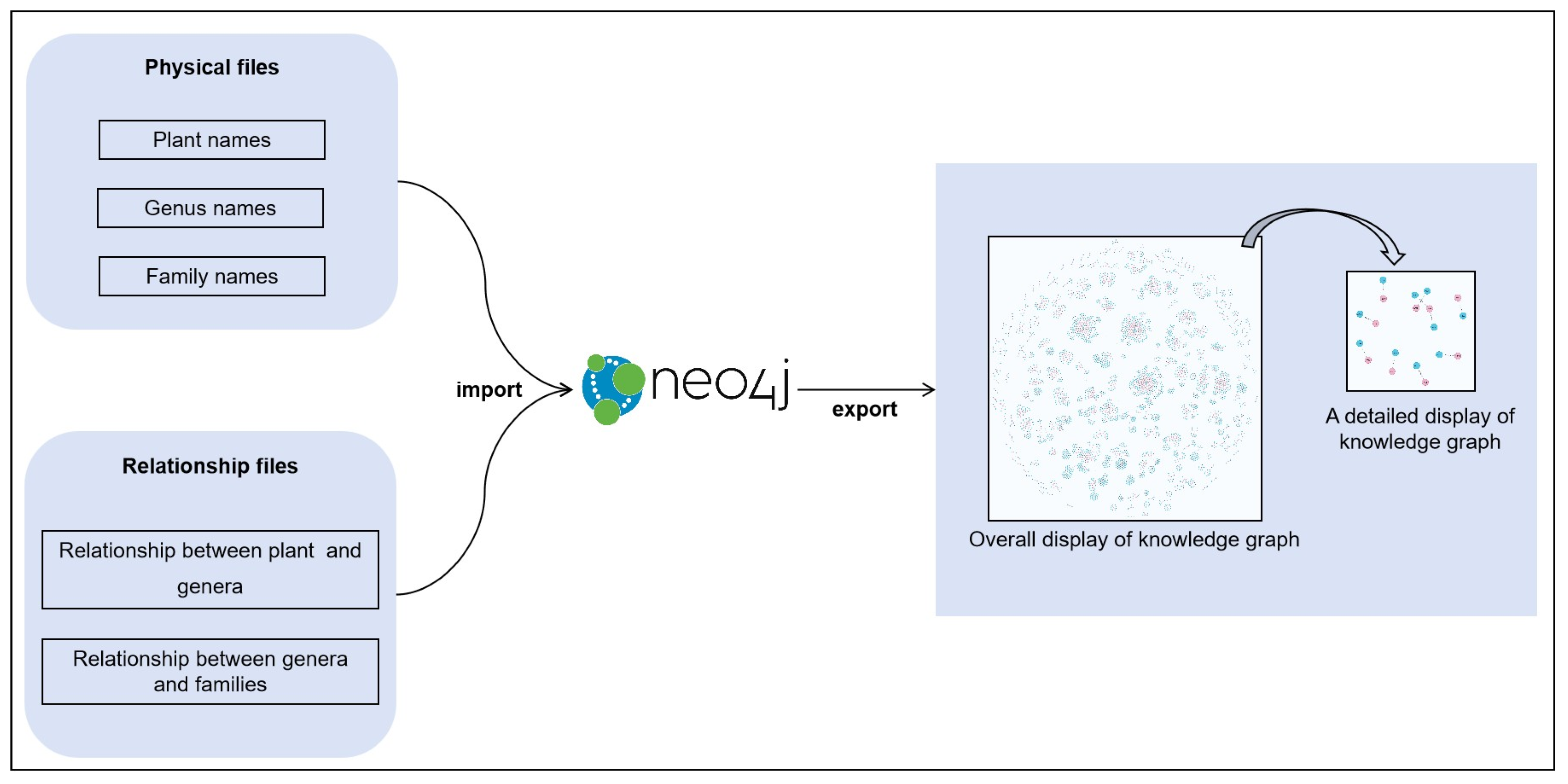
3.3. Validation of KG Usability and Usage Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Utilization of the Dataset
4.2. Tools for Building the Dataset
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Middel, A.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Wen, Z. Impacts of Green Roofs on Water, Temperature, and Air Quality: A Bibliometric Review. Build. Environ. 2021, 196, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, P. The Effectiveness of Green Roofs in Reducing Building Energy Consumptions across Different Climates. A Summary of Literature Results. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Mai, G.; Lin, J.; Wei, C.; Yu, W. BB-GeoGPT: A Framework for Learning a Large Language Model for Geographic Information Science. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K. Green Roofs: A Critical Review on the Role of Components, Benefits, Limitations and Trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuring, C.E.; Dunnett, N. Vegetation Composition of Old Extensive Green Roofs (from 1980s Germany). Ecol. Process. 2014, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberalesso, T.; Oliveira Cruz, C.; Matos Silva, C.; Manso, M. Green Infrastructure and Public Policies: An International Review of Green Roofs and Green Walls Incentives. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, M.; Peng, H. Aesthetic Evaluation of Commercial Rooftop Plants Based on Beauty Degree Evaluation Method: A Case Study of Chengdu City, China. World J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 11, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, H.; Ozaki, A.; Dong, N. Thermal and Energy Performance of Green Roof and Cool Roof: A Comparison Study in Shanghai Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Che, Y.; Ge, Z.; Mao, L. The Relationship between Green Roofs and Urban Biodiversity: A Systematic Review. Biodivers. Conserv. 2022, 31, 1771–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Prado, P.; Pons-Gumí, D.; Toboso-Chavero, S.; Parada, F.; Josa, A.; Gabarrell, X.; Rieradevall, J. Perceptions on Barriers and Opportunities for Integrating Urban Agri-Green Roofs: A European Mediterranean Compact City Case. Cities 2021, 114, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yixuan, W.; Jiayu, W.; Tian, C. Multi-Scenario Analysis of Rooftop Greening Regulation on Runoff Effects Based on Adaptive Evaluation: A Case Study of Macau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Ren, C. China’s Adaptation to Climate & Urban Climatic Changes: A Critical Review. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Assessing Climate-Adaptation Effect of Extensive Tropical Green Roofs in Cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, Z.; Jaffry, S.W.; Malik, M.K. Information Extraction from Scientific Articles: A Survey. Scientometrics 2018, 117, 1931–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluegl, P.; Toepfer, M.; Beck, P.-D.; Fette, G.; Puppe, F. UIMA Ruta: Rapid development of rule-based information extraction applications. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2016, 22, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, T.D. Automated Analysis of Reflection in Writing: Validating Machine Learning Approaches. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2019, 29, 217–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, M. Recent Named Entity Recognition and Classification Techniques: A Systematic Review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 29, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, J.; Yangarber, R. Information Extraction: Past, Present and Future. In Multi-Source, Multilingual Information Extraction and Summarization; Poibeau, T., Saggion, H., Piskorski, J., Yangarber, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 23–49. ISBN 978-3-642-28569-1. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.; Ross, H.; Sulem, E.; Veyseh, A.P.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sainz, O.; Agirre, E.; Heintz, I.; Roth, D. Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing via Large Pre-Trained Language Models: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xing, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, H.; Lu, J. Let’s Discover More API Relations: A Large Language Model-Based AI Chain for Unsupervised API Relation Inference. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2024, 33, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Pu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; et al. When Large Language Models Meet Personalization: Perspectives of Challenges and Opportunities. World Wide Web 2024, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjæveland, M.G.; Balog, K.; Bernard, N.; Łajewska, W.; Linjordet, T. An Ecosystem for Personal Knowledge Graphs: A Survey and Research Roadmap. AI Open 2024, 5, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Aboulela, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Kashef, R. A Survey on Augmenting Knowledge Graphs (KGs) with Large Language Models (LLMs): Models, Evaluation Metrics, Benchmarks, and Challenges. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Pan, S.; Cambria, E.; Marttinen, P.; Yu, P.S. A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A Review: Knowledge Reasoning over Knowledge Graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Cheng, J.; Guo, H.; Li, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Research on Strategic Mineral Resource Security: A Visual Analysis Using CiteSpace. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, W.; Huang, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Homestead Management in China from the “Separation of Two Rights” to the “Separation of Three Rights”: Visualization and Analysis of Hot Topics and Trends by Mapping Knowledge Domains of Academic Papers in China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Maimaituerxun, M. Bibliometric Review of Carbon Neutrality with CiteSpace: Evolution, Trends, and Framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76668–76686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, J. Python Data Analysis with Pandas. In Python Recipes Handbook: A Problem-Solution Approach; Bernard, J., Ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 37–48. ISBN 978-1-4842-0241-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Yisha, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhan, S.; Sun, F. LitAutoScreener: Development and Validation of an Automated Literature Screening Tool in Evidence-Based Medicine Driven by Large Language Models. Health Data Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, G. Extracting Fruit Disease Knowledge from Research Papers Based on Large Language Models and Prompt Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Xue, D.; Bi, Y.; Huang, Z. Cluster-Based Effective Generation of AI-Driven Literature Surveys. In Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing; Wong, D.F., Wei, Z., Yang, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.; Gheibi, M.; Wacławek, S.; Behzadian, K. A Novel Smart Framework for Optimal Design of Green Roofs in Buildings Conforming with Energy Conservation and Thermal Comfort. Energy Build. 2023, 291, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, T.; Huang, R.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y. Native Useful Vascular Plants of China: A Checklist and Use Patterns. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Tree Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/08310D3C51DBCE13 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Shrub Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/9FFAF77E0BDD5B8A (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Normative References: Data Set of Community Characteristics in Herb Layer of Forest Community in 2020, 2023, Big Data of Vegetation. Available online: https://www.iplant.cn/vgbd/dataset/3F054839AAD862BD (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Van Mechelen, C.; Dutoit, T.; Kattge, J.; Hermy, M. Plant Trait Analysis Delivers an Extensive List of Potential Green Roof Species for Mediterranean France. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capris, T.; Melo, P.; Garcia, N.M.; Pires, I.M.; Zdravevski, E. Comparison of SQL and NoSQL Databases with Different Workloads: MongoDB vs MySQL Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI), Virtual Conference, 25–26 October 2022; pp. 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Mehta, A.; Ganguli, R.; Sen, S. Recommendation of Influenced Products Using Association Rule Mining: Neo4j as a Case Study. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, S.; Lavanya, K. Chapter Ten—An Application of Cypher Query-Based Dynamic Rule-Based Decision Tree over Suicide Statistics Dataset with Neo4j. In Intelligent IoT Systems in Personalized Health Care; Sangaiah, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Eds.; Cognitive Data Science in Sustainable Computing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 293–313. ISBN 978-0-12-821187-8. [Google Scholar]




| Yiming Tao [31] | Yunqiao Fei [32] | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|
| precision | 96.88% | 85.27% | 96.77% |
| recall | 99.13% | - | 97.05% |
| Row Name | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Serial number | Plant name number |
| Input name | Name of plant extracted |
| Form | Division of plant names into proper names and aliases |
| Family Chinese name | Chinese name of the family to which the plant belongs |
| Family Latin name | The Latin name of the family to which the plant belongs |
| The Chinese name of the genus | Chinese name of the genus to which the plant belongs |
| The Latin name of the genus | Latin name of the genus to which the plant belongs |
| Chinese name | Chinese names of plants correspond to their proper names |
| Latin name (of plant or animal) | Latin names of plants corresponding to proper names |
| Nomenclator | Nomenclature of plant names |
| PPBC species ID | An identifier for the Phytosanitary Species Code, which is used to record and uniquely identify plant species |
| Row Name | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Tree | Plants whose type is the tree type |
| Shrub | Plants of the shrub type |
| Ground cover | Plants whose type is ground cover |
| Row Name | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Municipalities | Name of the city covered by the literature |
| Evergreen | Study of the corresponding tree types in the city |
| Shrub | Study of shrub types corresponding to cities |
| Ground cover | Study of ground cover types corresponding to cities |
| Municipalities | Plant Name (Number of Occurrences) |
|---|---|
| Shanghai | Forsythia (38), Cinnamon (24), Pitcher plant (20), Azalea (20), Nandina (18) |
| Beijing | Forsythia (59), Lobelia (30), Chinese poplar (29), TaiWanJingTian (28), Chinaberry (27) |
| Nanjing | Forsythia (12), Cinnamon (7), Pendula (6), Heliconia (6), Creeper (6) |
| Nanchang | Forsythia (5), Chasteberry (4), Helianthus annuus (4), Heather (4), Flowering bush (4) |
| Xiamen | Eggplant (7), Delphinium (5), Laurel (5), Nandina (4), Anemone (4) |
| Xian | Bamboos (19), Forsythia (18), Laurel (17), Red maple (15), Chaste tree (14) |
| Zhengzhou | Campsis grandiflora (8), Wisteria (8), Grapevine (8), Spring (8), Forsythia (8) |
| Chongqing | Forsythia (8), Anise (6), Anemone (5), Geranium (5), Laurel (5) |
| Changsha | Violet (9), Ivy (8), Helianthus annuus (8), Forsythia (7), Campsis grandiflora (7) |
| Qingdao | Ivy (4), Campsis grandiflora (3), Creeper (3), Grossularia (3), Grape (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, S.; Chang, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhang, J. A Large-Language-Model-Based Dataset of Plant Species for Green Roofs in China. Land 2025, 14, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081684
Han H, Liu X, Lin S, Chang Y, Ding S, Zhang J. A Large-Language-Model-Based Dataset of Plant Species for Green Roofs in China. Land. 2025; 14(8):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081684
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Haoyu, Xiliang Liu, Shaofu Lin, Yumiao Chang, Shimin Ding, and Jing Zhang. 2025. "A Large-Language-Model-Based Dataset of Plant Species for Green Roofs in China" Land 14, no. 8: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081684
APA StyleHan, H., Liu, X., Lin, S., Chang, Y., Ding, S., & Zhang, J. (2025). A Large-Language-Model-Based Dataset of Plant Species for Green Roofs in China. Land, 14(8), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081684






