Evaluating Urban Underground Space Supply–Demand Imbalances Based on Remote Sensing and POI Data: Evidence from Nanjing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Construct an indicator system for UUS supply and demand based on remote sensing and POI data;
- (2)
- Identify the supply–demand patterns of underground space in Nanjing;
- (3)
- Propose development strategies tailored to different types of underground space regions.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Evaluation of UUS Supply and Demand
2.2. Applications of Remote Sensing and Geospatial Big Data in Urban Spatial Studies
3. Study Area and Data Sources
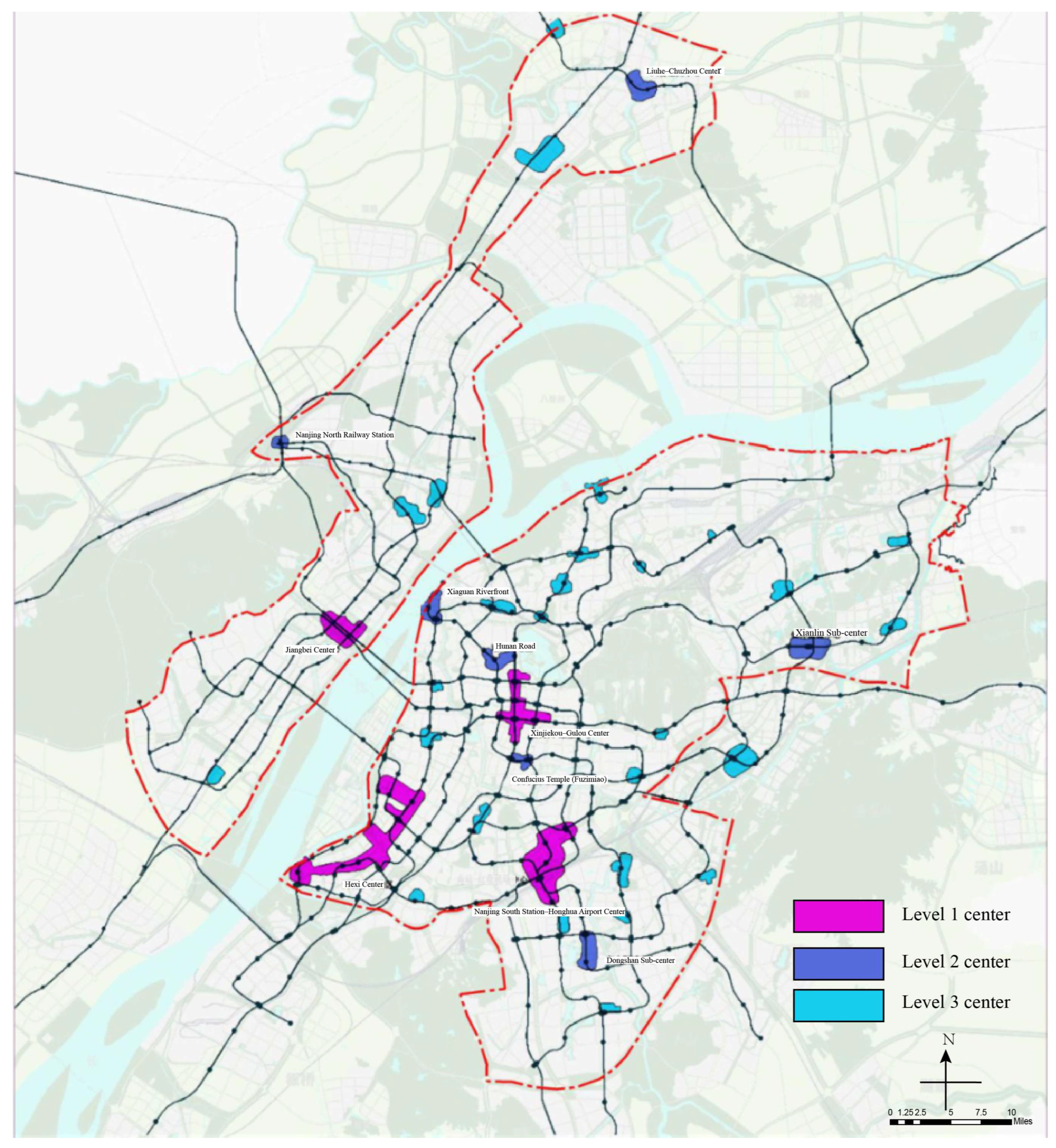
3.1. Study Area
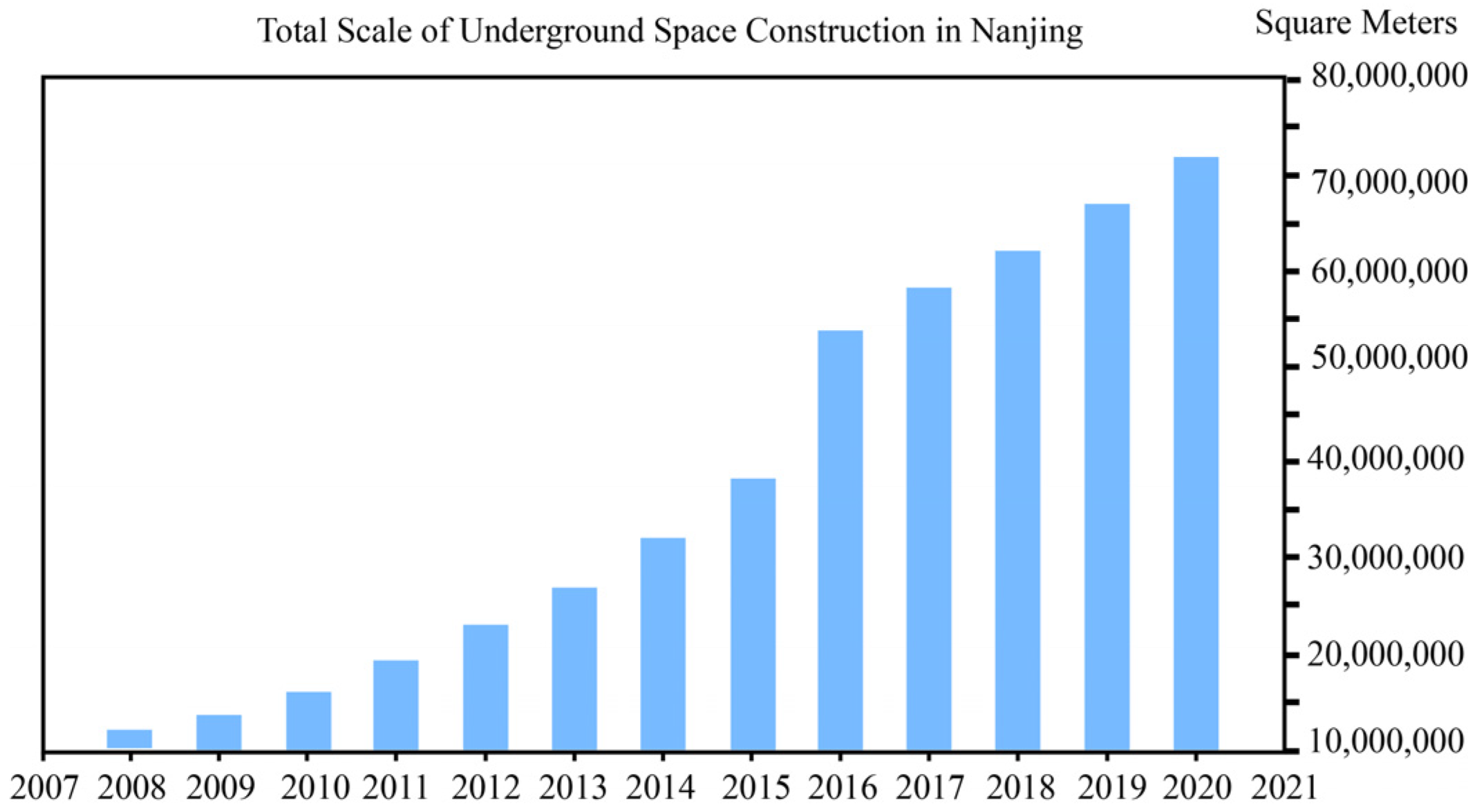
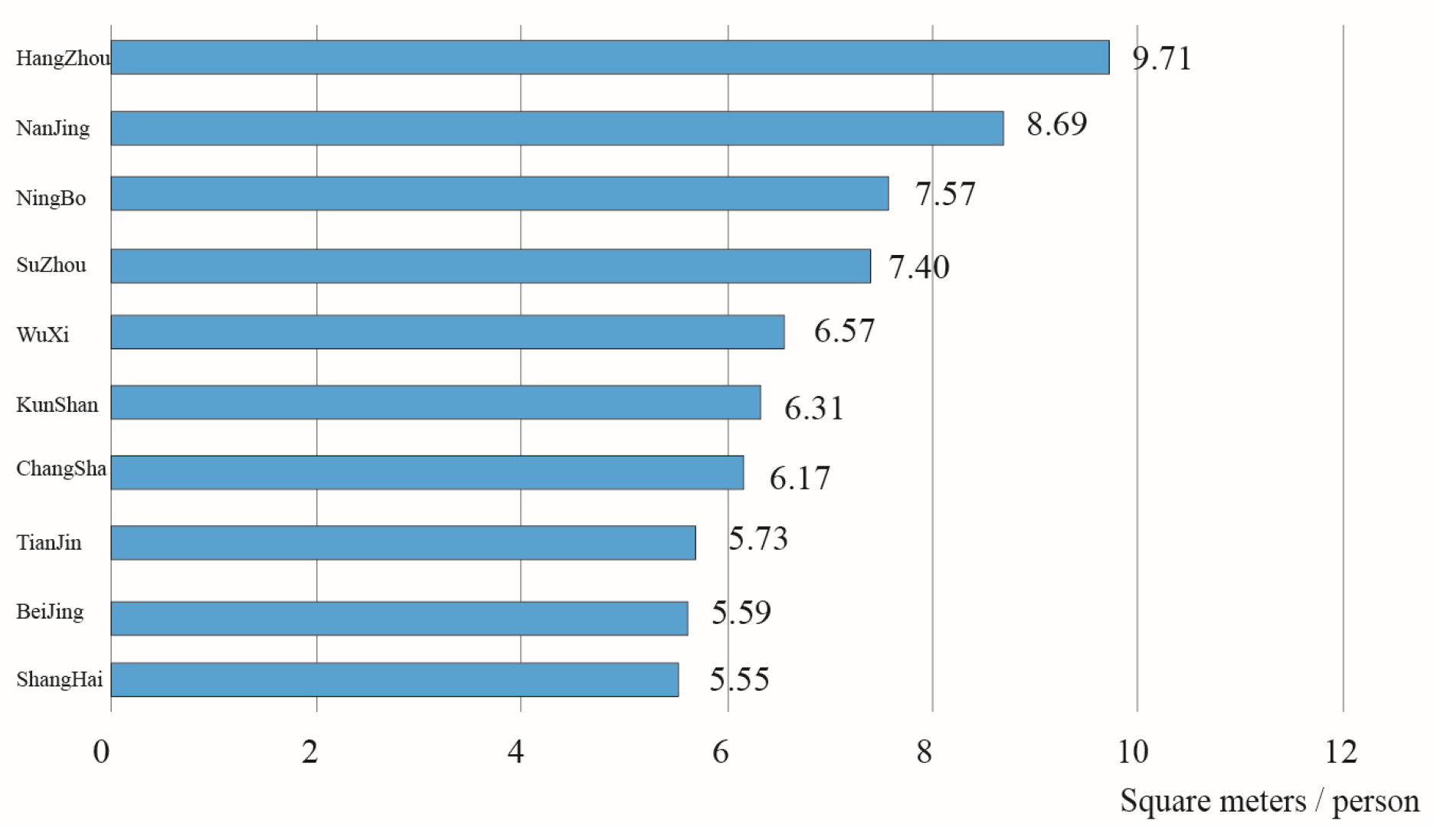
The Development Status of Underground Space in Nanjing
3.2. Data Sources
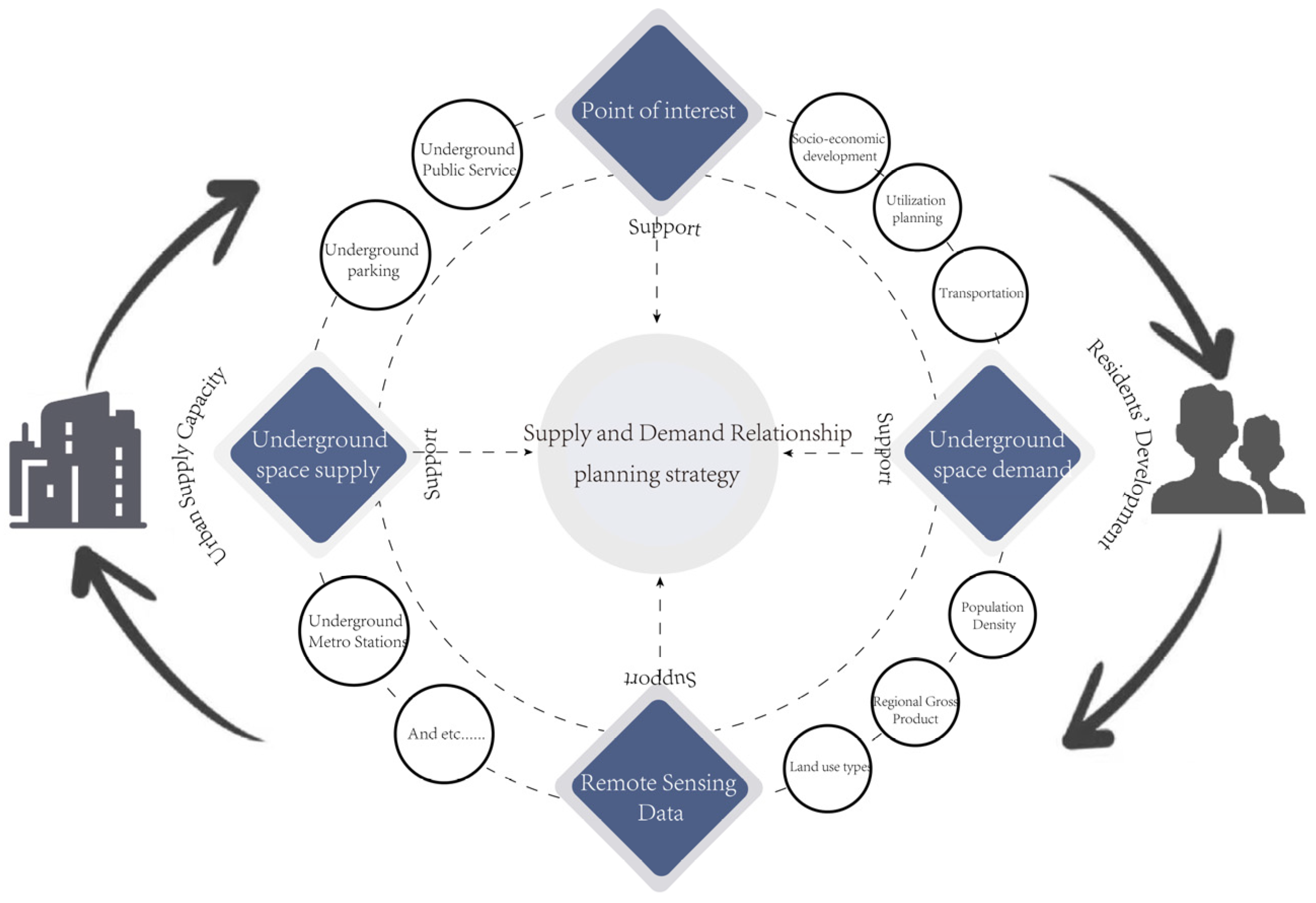
4. Methods
4.1. Evaluation of UUS Supply Intensity
4.1.1. Underground Parking Facilities
4.1.2. Underground Public Service Facilities
4.1.3. Underground Metro Stations
4.1.4. Comprehensive Evaluation
4.2. Evaluation of UIUS Development Demand
4.2.1. Urban Spatial Location
4.2.2. Socioeconomic Development
4.2.3. Urban Planning
4.2.4. Comprehensive Evaluation
4.3. Supply–Demand Ratio Evaluation
5. Results
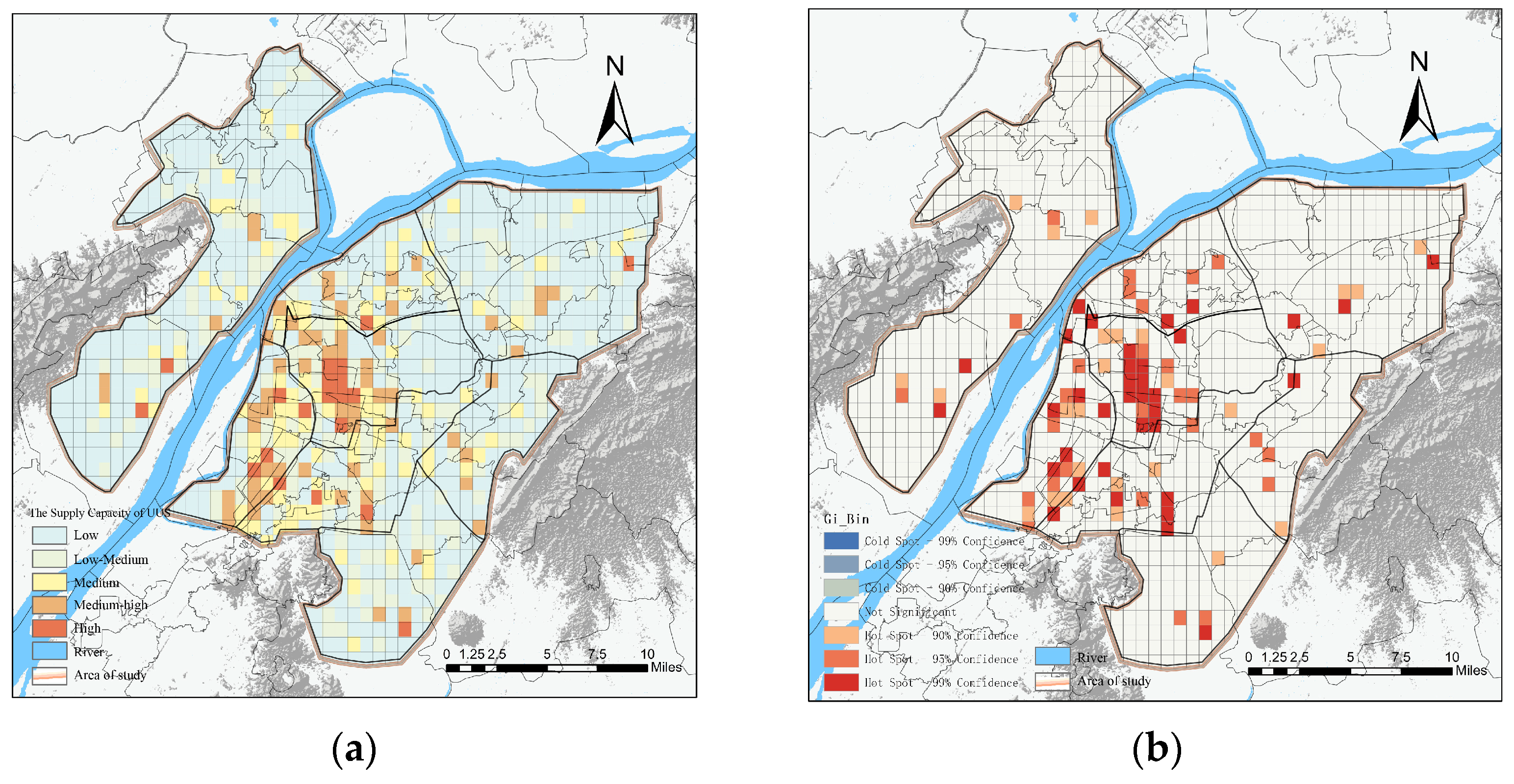
5.1. Evaluation of UUS Supply Capacity
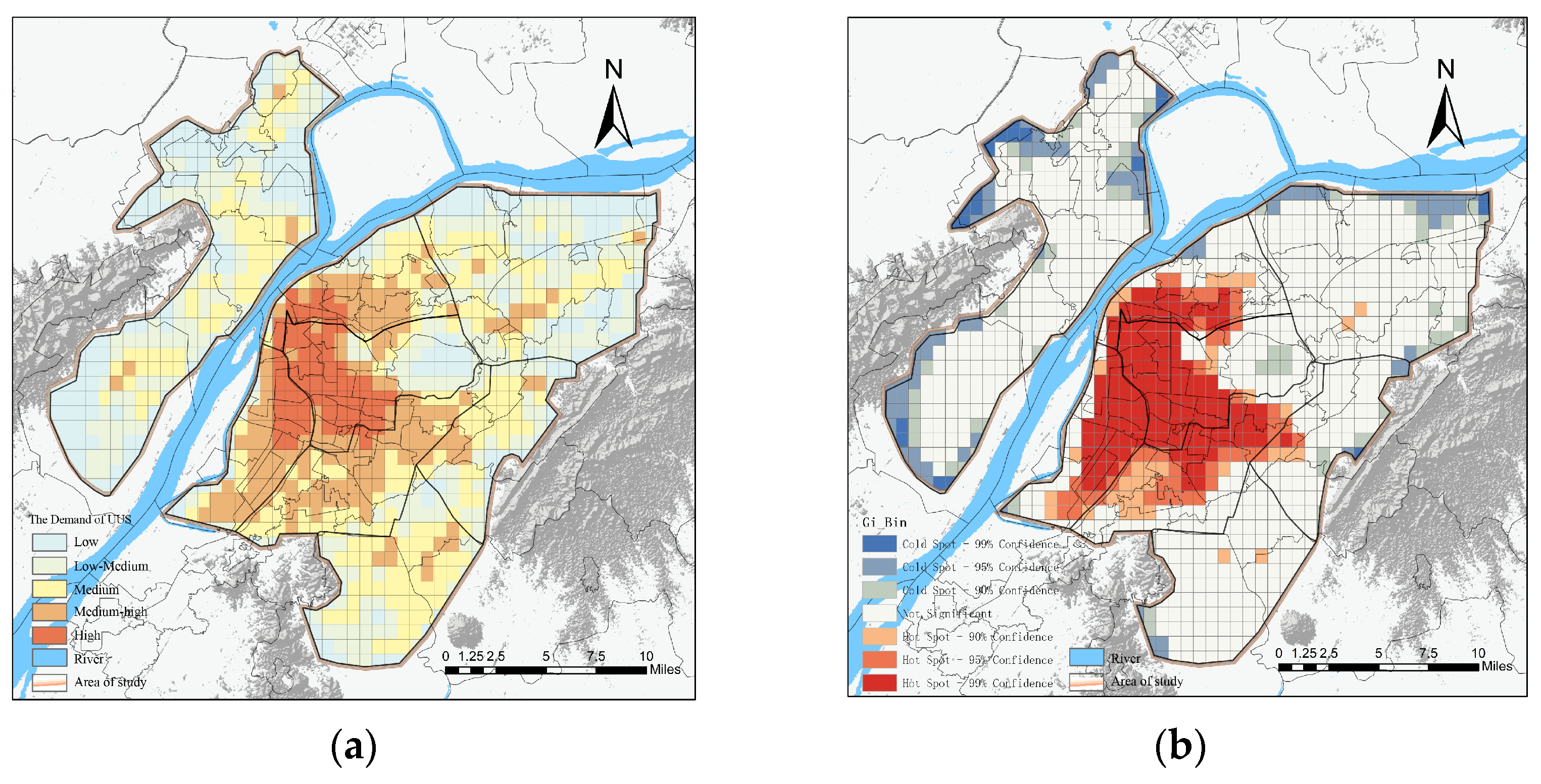
5.2. Evaluation of UUS Demand
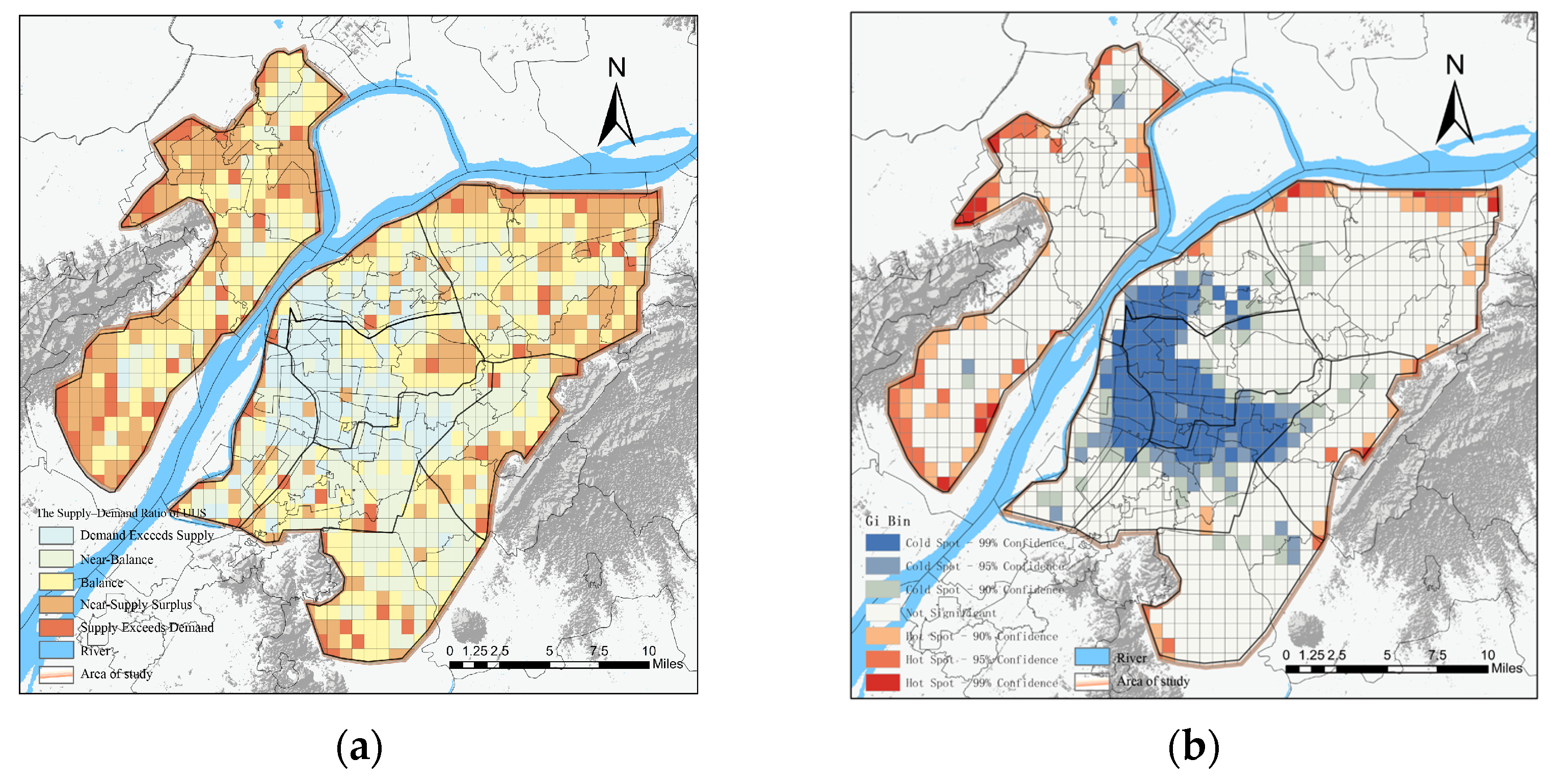
5.3. Evaluation of the Supply–Demand Ratio of UUS
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Discussion
6.1.1. A Supply–Demand Evaluation Framework for UUS Supported by Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data
6.1.2. Identification and Optimization of the Supply–Demand Relationship of UUS in the Central Urban Area of Nanjing
6.1.3. Limitations
6.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunt, D.V.L.; Makana, L.O.; Jefferson, I.; Rogers, C.D.F. Liveable Cities and Urban Underground Space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-L.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.-F. Present Status and Development Trends of Underground Space in Chinese Cities: Evaluation and Analysis. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 71, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-W.; Peng, F.-L.; Wang, T.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Jiang, B.-N. Advances in Master Planning of Urban Underground Space (UUS) in China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-C.; Peng, F.-L.; Qiao, Y.-K.; Dong, Y.-H. Quantitative Evaluation of the Contribution of Underground Space to Urban Resilience: A Case Study in China. Undergr. Space 2024, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Ji, X. Spatial Pattern of Underground Space Development in Major Cities in China: Evaluation and Analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2125776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Rabczuk, T. Quantitative Assessment of Engineering Geological Suitability for Multilayer Urban Underground Space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 59, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobylev, N. Mainstreaming Sustainable Development into a City’s Master Plan: A Case of Urban Underground Space Use. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.; Admiraal, H.; Bobylev, N.; Parker, H.; Godard, J.-P.; Vähäaho, I.; Rogers, C.D.F.; Shi, X.; Hanamura, T. Sustainability Issues for Underground Space in Urban Areas. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.—Urban Des. Plan. 2012, 165, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Weng, Q.; Wang, K. Characterizing Urban Land Changes of 30 Global Megacities Using Nighttime Light Time Series Stacks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Lei, Y.; Tan, G.; Du, S. Mapping the First Dataset of Global Urban Land Uses with Sentinel-2 Imagery and POI Prompt. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 327, 114824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. (Cecilia) Contribution of Urban Functional Zones to the Spatial Distribution of Urban Thermal Environment. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Baklanov, A.; He, B.; Ge, Q. Mainstreaming the Local Climate Zone Framework for Climate-Resilient Cities. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.-X.; Peng, F.-L. Evaluation of Spatial Performance and Supply-Demand Ratios of Urban Underground Space Based on POI Data: A Case Study of Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 131, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-C.; Peng, F.-L.; Qiao, Y.-K.; Zhang, J.-B. Evaluating Disaster Prevention Benefits of Underground Space from the Perspective of Urban Resilience. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 58, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-X.; Peng, F.-L. Monetary Evaluation Method of Comprehensive Benefits of Complex Underground Roads for Motor Vehicles Orienting Urban Sustainable Development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikos, A.; Kaliampakos, D. An Integrated Methodology for Estimating the Value of Underground Space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 109, 103770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Peng, F.-L. A GIS-Based Evaluation Method of Underground Space Resources for Urban Spatial Planning: Part 2 Application. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 77, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobylev, N. Underground Space in the Alexanderplatz Area, Berlin: Research into the Quantification of Urban Underground Space Use. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2010, 25, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zou, B.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.; Shen, C. Research on the Driving Factors and Prediction Model of Urban Underground Space Demand in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, R. Study on the Demand and Driving Factors of Urban Underground Space Use. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Song, Y.; Dai, S.; Durbak, K. Quantitative Research on the Capacity of Urban Underground Space—The Case of Shanghai, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 32, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X. Grey Relation Analysis and Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis Method Model for Suitability Evaluation of Underground Space Development. Eng. Geol. 2024, 338, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-X.; Peng, F.-L.; Qiao, Y.-K.; Li, H. Evaluation of Spatial Performance of Metro-Led Urban Underground Public Space: A Case Study in Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z. Factors Influencing the Development Potential of Urban Underground Space: Structural Equation Model Approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, D.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, T.; Zhang, C. Underground Space Use of Urban Built-up Areas in the Central City of Nanjing: Insight Based on a Dynamic Population Distribution. Undergr. Space 2022, 7, 748–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Evaluation of urban underground space resources using digitalization technologies. Undergr. Space 2016, 1, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y.-Y.; Ma, B.; He, L. Suitability Evaluation of Underground Space Based on Finite Interval Cloud Model and Genetic Algorithm Combination Weighting. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Peng, F.-L.; Bao, Z.-H.; Qiao, Y.-K. Identification of the Spatial Distribution Pattern and Driving Forces of Underground Parking Space Based on Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Fuzhou City in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liao, Z.; Guo, J.; Xie, H.; Peng, Q. An Intelligent Planning Model for the Development and Utilization of Urban Underground Space with an Application to the Luohu District in Shenzhen. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 112, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kikon, N.; Verma, P. Impact of Land Use Change and Urbanization on Urban Heat Island in Lucknow City, Central India. A Remote Sensing Based Estimate. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Han, Z.; Sun, G.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, H. An Impervious Surfaces Extraction Method Based on Optical, Ascending and Descending SAR Remote Sensing Imagery in High-Density Urban Core Areas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 140, 104595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Su, X.; Yuan, Q.; Jiao, H.; He, J.; Zheng, L. Urban Region Function Classification via Fusing Optical Imagery and Social Media Data: A Spatio-Temporal Transformer Interaction Approach. Inf. Fusion 2025, 121, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Ren, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C. Relationship between Urban Spatial Form and Seasonal Land Surface Temperature under Different Grid Scales. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Creutzig, F.; Zhao, B.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Ge, Q. Continuous Assessment of the Factors Driving the Urban Surface Thermal Environment in 1469 Cities Worldwide. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2025, 1, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Feng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, F. Assessing Regional Public Service Facility Accessibility Using Multisource Geospatial Data: A Case Study of Underdeveloped Areas in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, X. Quantitative Analysis of Spatial Vitality and Spatial Characteristics of Urban Underground Space (UUS) in Metro Area. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 111, 103875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Dong, Y.H.; Peng, F.L. Identification of Driving Factors for Underground Parking Space in Xi’an Based on POI Data. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2022, 18, 554–572. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Li, T.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D. Morphological and Functional Polycentric Structure Assessment of Megacity: An Integrated Approach with Spatial Distribution and Interaction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.W. Research on transportation planning for spatial development in large cities. Planners 2005, 8, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Qiao, Z.M.; Hu, R.J.; Cai, Y. Research on the layout patterns of underground space in metro station areas. Urban Mass. Transit. 2021, 24, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakoulaki, D.; Mavrotas, G.; Papayannakis, L. Determining Objective Weights in Multiple Criteria Problems: The Critic Method. Comput. Oper. Res. 1995, 22, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Q.F. Research on demand forecasting of urban underground space. Planners 2007, 10, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.L. China’s monthly nighttime light dataset. Resour. Environ. Sci. Data Platf. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Peng, F.-L. A GIS-Based Evaluation Method of Underground Space Resources for Urban Spatial Planning: Part 1 Methodology. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 74, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, S. Social Justice Performance Evaluation of the Distribution of the Rail Transit Network in Central Shanghai. Shanghai Urban Plan. 2016, 2, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L. Methods for the Performance Evaluation and Design Optimization of Metro Transit-Oriented Development Sites Based on Urban Big Data. Land 2024, 13, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Xu, S.L.; Cui, J. Demand forecasting for urban underground space resource development and utilization: An economic analysis. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 36, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Jin, G. Scale Effects on the Supply–Demand Mismatches of Ecosystem Services in Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.; Xu, J. Indicators for Spatial–Temporal Comparisons of Ecosystem Service Status between Regions: A Case Study of the Taihu River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dislocation of Urbanization and Ecological Construction Increased the Ecosystem Service Supply and Demand Imbalance. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Sun, J.Y.; Gu, G.B.; Zhong, C.J.; Wang, T. Taxi driver passenger-seeking route optimization method based on trajectory data. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. 2024, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Guo, M.; Tran, D.; Alwah, A.A.Q.; Xu, D. Evaluating the Disparity between Supply and Demand of Park Green Space Using a Multi-Dimensional Spatial Equity Evaluation Framework. Cities 2022, 121, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; He, B. Suitability of Human Settlements in Mountainous Areas from the Perspective of Ventilation: A Case Study of the Main Urban Area of Chongqing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.-K.; Peng, F.-L. Lessons Learnt from Urban Underground Space Use in Shanghai—From Lujiazui Business District to Hongqiao Central Business District. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M. Research on the development history, current situation, and regional differences of urban underground space utilization in Nanjing. Mod. Urban Res. 2018, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar]


| Indicator Category | Specific Indicators |
|---|---|
| Urban Spatial Location | Urban Spatial Position [17,22] |
| Metro Service Accessibility [17,23] | |
| Bus Service Accessibility [24] | |
| Socioeconomic Development | Population Density [20,21,25] |
| Gross Regional Product [26,27,28] | |
| Land Use Planning | Land Use Type [17,29] |
| Floor Area Ratio (FAR) [15,19] |
| Secondary Factor | WS | j | Wj,s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underground Parking Facilities | 40.18% | x1 | 24.86% |
| x2 | 75.14% | ||
| Underground Public Service Facilities | 14.77% | x3 | 48.02% |
| x4 | 51.98% | ||
| Underground Metro Stations | 40.05% | x5 | -- |
| Location | Sl |
|---|---|
| Core areas | 1.0 |
| Key areas | 0.8 |
| General area | 0.6 |
| Other areas | 0.4 |
| Land Use Type | Sl | |
|---|---|---|
| Urban Construction Land | Commercial land | 1.0 |
| Administrative land, cultural land, and transportation hub land (road land) | 0.8 | |
| Residential land | 0.6 | |
| Public service facility land | 0.4 | |
| Other urban construction land | 0.2 | |
| Non-urban Construction Land | Data | 0.0 |
| Secondary Factor | WS | j | Wj,s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban spatial location | 43.61% | y1 | 29.62% |
| y2 | 41.49% | ||
| y3 | 28.89% | ||
| Socioeconomic development | 33.01% | y4 | 36.16% |
| y5 | 63.84% | ||
| Urban planning | 23.38% | y6 | 23.10% |
| y7 | 76.90% |
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Data Types | Indicator Calculation | Data Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of UUS Supply Intensity | Underground Parking Facilities | Supply Intensity of Underground Parking Facilities | POI | The underground parking POI data in each grid divided by the grid area. | Web scraping |
| Underground Parking Rate | POI | The number of underground parking POIs in each grid divided by the total number of parking POIs in the grid. | Web scraping | ||
| Underground Public Service Facilities | Supply Intensity of Underground Public Service Facilities | POI | The total number of underground public service facility POIs in each grid divided by the grid area. | Web scraping | |
| Development Ratio of Underground Public Service Facilities within Metro Catchment Areas | POI | The total number of underground public service facility POIs in each grid divided by the grid area. | Web scraping | ||
| Underground Metro Stations | Supply Intensity of Underground Metro Stations | POI | The number of public service facility POIs within a 500 m radius of the subway station in each grid divided by the grid area. | Web scraping | |
| Evaluation of UIUS Development Demand | Urban Spatial Location | Urban Spatial Location | Nighttime lighting data | Directly use the dataset | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform |
| Metro Accessibility | POI | Assign values based on distance decay | Web scraping | ||
| Bus Accessibility | POI | The number of bus stop POIs in each grid divided by the grid area. | Web scraping | ||
| Socioeconomic Development | Population Density | Population data | Directly use the dataset | WorldPop | |
| Regional Economic Value | Economic data | Directly use the dataset | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform | ||
| Urban Planning | Land Use Type | Planning data | Assign values based on land use type codes. | ||
| Floor Area Ratio | Building footprint data | The total building area in each grid divided by the grid data. | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, Y.; Sun, L. Evaluating Urban Underground Space Supply–Demand Imbalances Based on Remote Sensing and POI Data: Evidence from Nanjing, China. Land 2025, 14, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081671
Wang Z, Liu G, Hu Y, Sun L. Evaluating Urban Underground Space Supply–Demand Imbalances Based on Remote Sensing and POI Data: Evidence from Nanjing, China. Land. 2025; 14(8):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081671
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ziyi, Guojie Liu, Yi Hu, and Liang Sun. 2025. "Evaluating Urban Underground Space Supply–Demand Imbalances Based on Remote Sensing and POI Data: Evidence from Nanjing, China" Land 14, no. 8: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081671
APA StyleWang, Z., Liu, G., Hu, Y., & Sun, L. (2025). Evaluating Urban Underground Space Supply–Demand Imbalances Based on Remote Sensing and POI Data: Evidence from Nanjing, China. Land, 14(8), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081671





