Abstract
Gully development is a significant geomorphological and environmental process that affects land degradation worldwide, with ephemeral gullies (EGs) and permanent gullies (PGs) being the two most common types. These two gully types are often spatially connected, and with such EG-PG connectivity can accelerate erosion. However, systematic research on this phenomenon remains limited, particularly at the regional scale. This study focuses on the spatial connectivity between EGs and PGs in the Songnen black soil region of northeast China. An unequal probability stratified sampling was used to establish 977 small watershed units, and a database of gullies and their connectivity was constructed based on sub-meter imagery. Among them, 55 representative units were randomly selected within geomorphic zones for field surveys and UAV validation to ensure data accuracy. Spatial patterns of gully connectivity were analyzed, and dominant controlling factors were identified using the Geodetector, which quantifies spatial stratified heterogeneity and evaluates the explanatory power of potential driving factors. The results are as follows: (1) Gully connectivity varies significantly across the region, with hotspot areas where more than 50% of permanent gullies are connected to ephemeral gullies, and cold spot clusters elsewhere. (2) Permanent gullies connected to ephemeral gullies differ significantly from unconnected ones in both length and width, with the former exhibiting a more elongated morphology. (3) Slope length and mean annual precipitation are the primary drivers of gully connectivity, both showing significant positive effects. Moreover, the interaction between mean annual precipitation and slope length shows the strongest explanatory power, indicating that precipitation, in combination with topographic features, plays a dominant role in shaping gully connectivity. By examining the spatial patterns of gully connectivity, this study contributes to a more refined understanding of gully morphological evolution and offers empirical insights for enhancing gully erosion models and optimizing regional soil and water conservation strategies.
1. Introduction
Soil erosion poses a persistent and globally significant threat to soil resources, contributing to land degradation and reduced agricultural productivity [1,2,3]. Gully erosion, as a severe and irreversible form of erosion, has attracted considerable attention. Among its types, ephemeral gullies (EGs) and permanent gullies (PGs) are the most common and have become key targets for current soil and water conservation efforts [4,5]. In recent years, increasing attention has been given to the connectivity between EGs and PGs as it has gained increasing research interest. Quantitative analysis of their spatial connectivity provides valuable insights into the morphological evolution of PGs and can guide the formulation of more effective gully control strategies.
EGs are small channels formed by concentrated runoff on farmland. They can be easily erased by normal tillage but tend to reform in the same locations after subsequent runoff events [6,7]. According to Liu et al. [8], EGs typically have a depth of approximately 20 cm and a width of 30–50 cm, which allows them to be crossed by conventional farming implements, although they cannot be completely eliminated. EGs represent a critical stage in the transition from rill to sheet erosion and are important sources of sediment, rapidly transporting soil from upper slopes to foot slopes or drainage outlets [1,9,10]. Under alternating periods of heavy rainfall and tillage, EGs undergo a cyclical process of formation, infilling, and reformation. This process not only damages surface soil structure but also creates washboard-like microtopography, alters runoff flow paths, and, if left uncontrolled, may accelerate the development of permanent gullies [11,12,13]. PGs are larger and deeper erosion channels, usually greater than 0.5 m in both width and depth and cannot be eliminated by regular tillage [7,8]. Their bottom lines run roughly parallel to the slope surface. Some PGs are initiated rapidly during high-intensity rainfall events, while others develop gradually through connection with EGs.
The development of gullies is influenced by a combination of factors. Recent studies have primarily focused on five categories of influencing factors: topography, climate, land use, soil properties, and human activities [14,15]. Among these, topographic factors are widely regarded as the primary drivers of gully development. The slope gradient determines the energy of surface runoff, while slope length affects the degree of flow accumulation. Together, they play a key role in the initiation of gully erosion [16]. Climatic factors are mainly reflected in rainfall amount and intensity, which provide both the volume and energy for runoff. Prolonged rainfall or concentrated infiltration can lead to soil saturation, causing the slumping of gully headcuts and sidewalls, as well as incision at the gully floor [17]. In addition, extreme rainfall events can significantly accelerate gully erosion processes [18]. Soil properties govern surface erodibility. Variations in particle size distribution, structural stability, soil morphology, and permeability influence both the depth of gully incision and the stability of gully sidewalls [19,20,21]. Under increasing human activity, changes in land use and tillage disturbance alter surface roughness, vegetation cover, and drainage pathways, which in turn affect landscape stability and promote gully development [22,23].
In recent years, connectivity has become a central concept in hydrological, geomorphological, and ecological studies for evaluating the transfer of materials and energy between spatial units [24]. Comparable efforts in tropical and agricultural landscapes have quantified or modeled gully-related connectivity, notably in Brazil’s semiarid regions using UAV-constrained process models and multi-temporal remote sensing [25,26]. Broader regional syntheses in Sub-Saharan Africa further underscore the role of gully networks in sediment transfer and landscape degradation [27,28]. Methodologically, recent reviews on sediment connectivity indices highlight opportunities to incorporate continuous connectivity metrics into agricultural settings [29]. In hillslope-scale erosion systems, connectivity governs the organization and convergence of runoff pathways, thereby influencing the sediment detachment, transport, and deposition processes [30,31]. In the context of EG-PG gully systems, connectivity typically refers to the hydraulic linkage between EGs and downstream PGs. This linkage can reduce surface resistance and enhance flow concentration, thereby linearizing scattered runoff paths and increasing the flow’s energy and erosive power. Empirical studies have demonstrated that gullies with established connectivity often exhibit more severe erosion [32,33]. In this study, we focus on spatial connectivity, identified through the spatial adjacency and continuity of gully features interpreted from remote sensing data. While spatial connectivity may influence hydrological connectivity by facilitating potential runoff pathways, the two are conceptually distinct.
Gully erosion has been extensively investigated worldwide, with numerous international studies examining its spatial distribution, controlling factors, susceptibility assessment, and so on [34,35,36]. However, the majority of current studies still treat EGs and PGs as independent entities, thereby overlooking the potential influence of their connectivity on gully development. Existing research on connectivity indices primarily focuses on topography-based calculations, with comparatively limited attention given to the functional linkage between EGs and PGs. This gap may have constrained our understanding of the initiation and morphological evolution of permanent gullies, while also reducing the accuracy of gully erosion models.
Based on the gap, we hypothesize that spatial connectivity between EGs and PGs has a significant impact on the morphological characteristics of PGs. By introducing connectivity as a variable and conducting quantitative analysis, this study aims to provide new insights into the mechanisms of gully evolution and to improve gully modeling and management approaches.
The black soil region of northeast China, one of the four major black soil regions in the world, is predominantly classified as Chernozems in the World Reference Base (WRB) for Soil Resources [37], corresponding to Mollisols in the Soil Taxonomy (ST) [38]. This region is renowned for its high soil fertility and strategic importance to national food security, having sustained stable and high agricultural productivity for decades [39]. However, in recent years, gully erosion has become increasingly severe. Soil loss attributed to gully erosion has been estimated to account for approximately 65% of total soil loss [40,41], posing a serious threat to the sustainability of cultivated land. Therefore, this study focuses on the Songnen black soil region, examining the role of connectivity between EGs and PGs in shaping the morphological characteristics of PGs. The specific objectives are as follows: (1) To identify the spatial distribution of EGs-PGs connectivity. (2) To assess the influence of spatial connectivity on the morphological parameters of PGs. (3) To investigate the dominant factors influencing the connectivity between EGs and PGs. This study aims to advance the theoretical understanding of gully evolution and to improve erosion control strategies in the black soil region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in the Songnen black soil region of northeast China (122°7′29″–128°9′53″ E, 43°3′25″–50°15′43″ N; Figure 1), with geographical boundaries defined following Liu et al. [42], covering approximately 212,000 km2. The region mainly consists of tablelands and plains, with scattered low hills in the northwest and southeast. It has a temperate continental monsoon climate, with a mean annual precipitation ranging from 330 to 740 mm, most of which falls during the summer months. The dominant soil types include Black soils (Chernozems, WRB; Mollisols, ST), Chernozems, and Meadow soils (Phaeozems, WRB) [37,43]. These soils are characterized by a thick, dark surface horizon rich in organic matter, with a stable structure and high natural fertility, making them highly suitable for crop production [44]. As one of China’s most important grain-producing regions, the area is predominantly cultivated with maize and soybeans [45,46]. EGs and PGs are the main types of gully erosion in the region. In some sloping farmland areas, EGs are commonly found in the upper slope positions, while PGs occur downslope, forming a connected distribution pattern. In total, 977 sampling units were established across the study area, and 55 units were randomly selected for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based measurements and field surveys to validate the interpretation results.
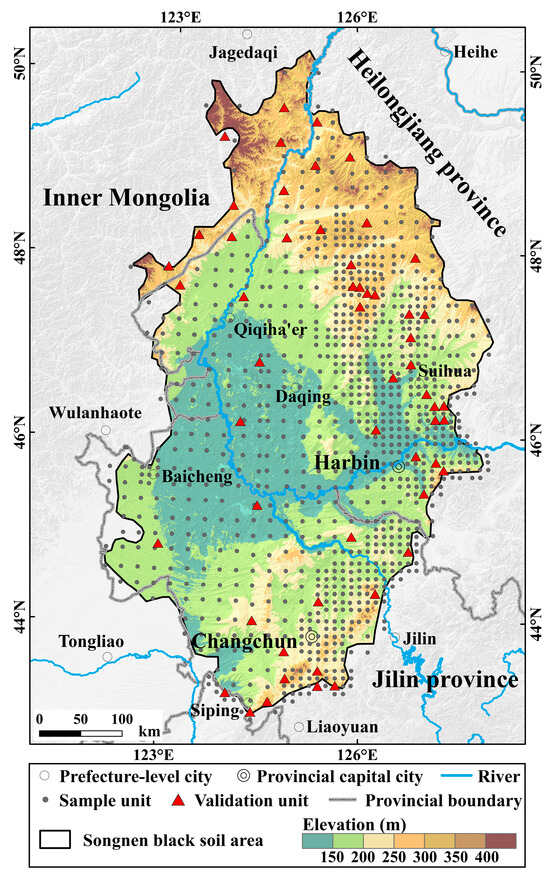
Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Sampling Unit Design
This study adopted the unequal probability stratified sampling method and sampling units used in the First National Water Resources Census of China [47], selecting a total of 977 sampling units across the Songnen black soil region. To account for regional geomorphic features and the spatial distribution of gullies, differentiated sampling ratios were applied based on erosion intensity. In the relatively flat, sparsely eroded central and western areas, a sampling ratio of 0.25% of the total area was used. Conversely, the sampling ratio was increased to 1% in the northeastern and hilly areas where gully erosion is more prevalent [48]. Sampling units were delineated based on local terrain characteristics. In hilly regions, small watersheds of approximately 1.5 km2 were used, whereas in flatter plains, a regular 1 km × 1 km grid was employed. In addition, to check the interpretation accuracy of the 977 sampling units, 55 representative units were selected for field surveys and UAV verification. These 55 units were randomly selected from the full set of 977 sampling units based on geomorphic zoning.
2.3. Base Data
A summary of the datasets and their sources is provided in Table 1. High-resolution Google Earth (GE) imagery from the 2020s (with a spatial resolution of 0.11–0.43 m) were selected for gully interpretation across 977 sampling units. To improve interpretation accuracy and validate the results, UAV images were collected from May to June 2023 using a DJI Mavic 3 Multispectral drone (DJI, Shenzhen, China) at flight altitudes of 100–200 m, covering 55 randomly selected validation units. GNSS RTK (Global Navigation Satellite System Real Time Kinematic) ground surveys were conducted to assess the interpretation accuracy of gully and morphological parameters derived from the GE imagery. Topographic factors, including elevation, slope gradient, and slope length, were extracted from the SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) digital elevation model (DEM) with a spatial resolution of 30 m. Climatic and soil-related variables, such as mean annual precipitation and soil erodibility (K-factor), were obtained from the National Tibetan Plateau Data Center [49,50]. Vegetation cover was represented using the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from the Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform, while land-use data were used to calculate indicators such as the proportion of cultivated land [51,52]. In addition, regional geomorphological type data were sourced from the Geographic Remote Sensing Ecological Network Platform to support the subsequent statistical analysis of gully characteristics by geomorphic zones. These factors were selected based on their established relevance to gully formation and development in previous studies, particularly in the northeast China black soil region. The rationale behind the selection of these factors is further discussed in Section 4.2. To minimize temporal inconsistencies among datasets, multi-year averages and the most recent data available were used to ensure overall temporal representativeness.

Table 1.
Overview of data sources used in this study.
2.4. Gully Interpretation, Parameter Extraction, and Validation
Figure 2 illustrates an example of gully interpretation based on GE imagery. Manual visual interpretation was conducted using ArcGIS 10.8, referencing field survey data and the classification criteria for EG and PG proposed by Liu et al. [8]. The identification of PG focused on those occurring within farmland. Additionally, each PG was classified into one of two categories based on whether it was spatially connected to an EG.
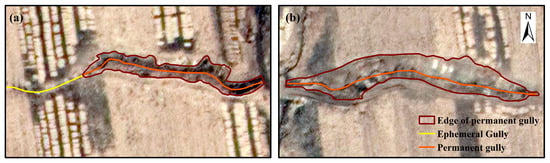
Figure 2.
Interpretation examples of gully based on sub-meter imagery. (a) EGs and PGs are connected; (b) EGs and PGs are disconnected.
Following visual interpretation, the morphological characteristics of PGs were quantitatively analyzed using ArcGIS 10.8. The primary parameters extracted included gully length and width. Gully length was defined as the horizontal projected distance from the gully head to the gully outlet along the gully bed. Gully width was measured perpendicular to the gully bed at one-quarter, one-half, and three-quarters of the total length, and the average of these three measurements was used. To ensure the accuracy and consistency of the interpretation data, a two-level quality control procedure was implemented. In the first stage, all interpretation results were reviewed individually by a project supervisor. If any issues were identified, the original interpreter was required to revise and update the results. In the second stage, gully erosion experts conducted a random re-examination of 20% of the initially approved data. If the interpretation accuracy of the sample exceeded 95%, the dataset was considered qualified and archived. If it fell below this threshold, the data were returned to the first stage for re-evaluation until the standard was met.
To further verify the reliability of gully interpretation, high-precision field measurements of EGs and PGs were conducted in 55 validation units using GNSS RTK (Figure 3). In addition, high-resolution UAV imagery was used to obtain more detailed morphological parameters of PGs, including width and depth. By comparing the results from field surveys and UAV-based interpretation with those derived from GE imagery, the accuracy and validity of the interpretation results were further assessed [53].

Figure 3.
Field photographs of EG-PG connectivity and field measurements. (a,b) Field photographs of EG-PG connectivity; (c) field photograph of field measurements.
2.5. Hotspot Analysis
Hotspot analysis is a widely used tool for identifying spatial-clustering patterns in geographic data. A “hotspot” refers to an area where high values are significantly clustered, while a “cold spot” denotes a cluster of low values [54]. In this study, hotspot analysis was used to explore the spatial distribution of connectivity between EGs and PGs. For each sampling unit, the number of PGs connected to EGs was counted. This count was then expressed as a proportion of the total number of PGs to derive a connectivity ratio index. The Getis-Ord Gi* statistic, implemented in ArcGIS 10.8, was applied to the connectivity ratio data to perform spatial-clustering analysis. This allowed the identification of areas with significantly high (hotspots) or low (cold spots) connectivity ratios, revealing the spatial-clustering patterns of gully spatial connectivity at the regional scale.
2.6. Geodetector Analysis
Geodetector is a statistical tool designed to assess the spatial differentiation of natural or socio-economic factors and to identify their dominant driving forces [55,56]. Its core principle is that if an explanatory variable significantly influences a response variable, the spatial distributions of the two tend to exhibit consistency. The method consists of four modules: factor detector, interaction detector, risk detector, and ecological detector. In this study, the factor detector and interaction detector modules were employed to analyze the spatial variation and interaction mechanisms. Specifically, the factor detector evaluates the explanatory power of each independent factor on the spatial distribution of the dependent variable, quantified by the q-value, which is calculated using the following formula:
In the equation, the q-value represents the explanatory power of a given factor for the spatial distribution of the dependent variable. It ranges from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating stronger explanatory power. The denotes the -th sub-region (or category) defined by the stratification of the independent factor, with a total of sub-regions. and represent the number of samples and the variance of the dependent variable in sub-region , respectively. and represent the total number of samples and the overall variance of the dependent variable.
The interaction detector evaluates whether two independent factors jointly enhance their explanatory power for the dependent variable, thereby indicating the presence of an interaction effect. If the combined q-value of two factors is greater than the q-values of each factor individually, it indicates a synergistic enhancement effect. If the combined q-value is less than that of either factor alone, it may suggest a suppressive effect. If the combined q-value is equal to one of the individual q-values, it implies that the two factors influence the dependent variable independently and there is no interaction. Table 2 summarizes the types of interaction effects between two factors.

Table 2.
Interaction types between two factors based on q-statistic.
Sampling units were used as the basic analysis scale, and the proportion of PGs connected to EGs in each unit was used as the dependent variable. The seven independent variables included elevation, slope gradient, slope length, soil erodibility (K factor), NDVI, mean annual precipitation, and the proportion of cultivated land. The mean value of each factor was calculated for each unit. All factors were stratified using the Geodetector classification method. The factor detector and interaction detector modules were applied to identify the dominant factors influencing the spatial heterogeneity of gully spatial connectivity and to analyze the pairwise interaction effects between them.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution of EG-PG Gully Connectivity
Figure 4 illustrates the spatial distribution of gully connectivity and its hotspot patterns in the Songnen black soil region and highlights areas of significant clustering. Among the 977 sampling units, 330 contain permanent gullies. Connectivity ratios are notably higher in the northeastern low mountains and hills compared with other geomorphic zones. Hotspot analysis confirms that this region forms a statistically significant cluster of high connectivity, indicating concentrated areas where PGs are more likely to be linked to EGs. Specifically, in many units within the Suihua area, the proportion of PGs connected to EGs exceeds 50%, forming significant hotspot zones. In contrast, most units around Changchun exhibit connectivity ratios below 50% and are identified as cold spots. In the central and western plains, including Daqing and Qiqihar, PGs are sparse or absent, resulting in very low connectivity ratios and no significant hotspot features. In summary, the eastern hilly region is markedly higher in connectivity ratios than the central and western plains, forming distinct hotspot clusters at the regional scale.
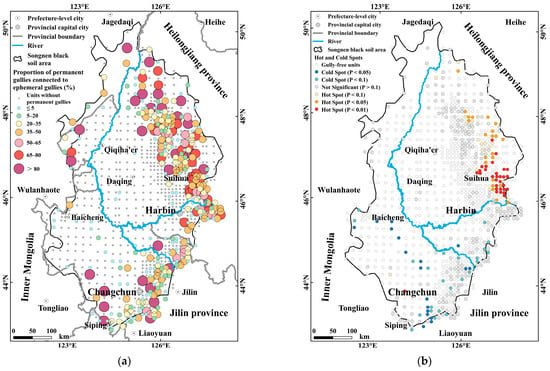
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution and hotspot analysis of the EG-PG connectivity between. (a) Proportion of PGs connected to EGs; (b) hotspot of the proportion of PGs connected to EGs.
Figure 5 presents the distribution and cumulative frequency of the proportion of PGs connected to EGs across different geomorphic types. Connectivity patterns vary significantly among geomorphic types, with tablelands exhibiting relatively high connectivity ratios. Overall, the number of sampling units declines as the connectivity ratio increases. In the plains, where PGs are sparse or absent, the cumulative frequency increases most slowly. In both tablelands and low mountains and hills, gully connectivity is generally higher. Once the connectivity ratio exceeds 5%, the cumulative frequency rises sharply in these regions. A large number of units are concentrated in the 20% to 50% range. Beyond the 50%, tablelands exhibit significantly higher connectivity ratios than low mountains and hills. These results indicate that geomorphic type influences the degree of EG-PG connectivity, with tablelands showing the highest connectivity and the plains the lowest.
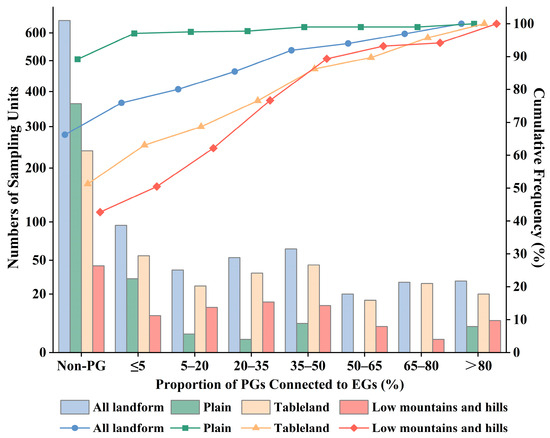
Figure 5.
Distribution and cumulative frequency of the proportion of PGs connected to EGs across different landform types.
3.2. Influence of Connectivity on PG Morphology
Table 3 summarizes the morphological characteristics of PGs across all sampling units. Among the 3883 identified PGs, 35% were connected to EGs. On average, connected PGs had a length of 196.54 m, which was greater than the 167.96 m of unconnected PGs. In contrast, the average width of connected PGs was 6.81 m, narrower than the 8.73 m of unconnected ones. These results indicate that PGs connected to EGs tend to be longer but narrower than those that are not connected.

Table 3.
Statistical table of permanent gully morphological parameters.
To further examine whether connectivity affects the morphology of permanent gullies, a Mann–Whitney U test was applied to compare gully length and width between connected and unconnected PGs (Figure 6). The results showed that connected PGs were significantly longer (p < 0.001) and narrower (p < 0.01) than unconnected ones. These differences suggest that connected gullies tend to exhibit a more elongated morphology.
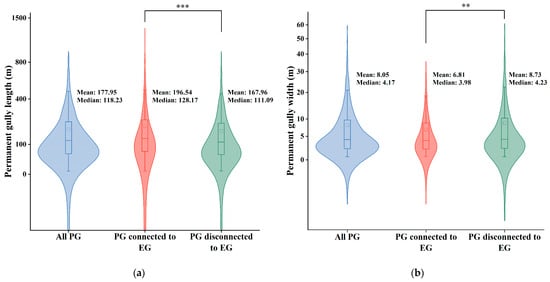
Figure 6.
Morphological differences in PGs connected and disconnected to EGs. The square symbol in the boxplot represents the mean. Statistical differences were tested using the Mann–Whitney U test. Significance levels: p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***). (a) Length differences in PGs connected and disconnected to EGs; (b) width differences in PGs connected and disconnected to EGs.
3.3. Influencing Factors of EG-PG Connectivity
Figure 7 displays the Pearson correlation matrix between gully connectivity and the selected factors. Each cell represents the strength of the linear relationship between two variables, with color intensity indicating the magnitude of the correlation coefficient. Asterisks denote statistically significant correlations (p < 0.05). EG-PG connectivity is significantly correlated with topographic and precipitation-related factors. Notably, strong positive correlations were observed with slope length and mean annual precipitation. These findings suggest that increases in slope length and precipitation may enhance the likelihood of EG-PG connectivity.
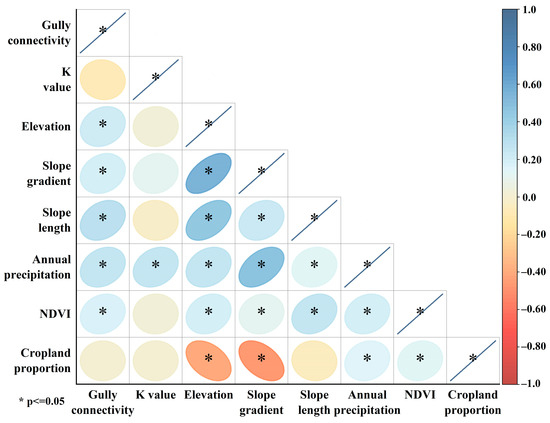
Figure 7.
Pearson correlation matrix among gully connectivity and environmental factors.
Further analysis using the Geodetector identified the dominant factors influencing the spatial distribution of EG-PG connectivity. As shown in Table 4, the results of the factor detector indicate that the most influential variables, ranked by descending q-values, were as follows: mean annual precipitation, slope length, slope gradient, elevation, NDVI, cropland proportion, and soil erodibility. Among these, mean annual precipitation and slope length exhibited the highest explanatory power, suggesting that they are the primary drivers of spatial heterogeneity in gully connectivity.

Table 4.
Results of the factor detector for EG-PG connectivity in the Songnen black soil region.
Figure 8 presents the interaction detector results for EG-PG connectivity. In general, the combined explanatory power of two-factor interactions is generally higher than that of individual factors, indicating the important role of synergistic effects in shaping gully connectivity in the Songnen black soil region. Among all combinations, the three strongest interactions (based on q-values) are as follows: mean annual precipitation ∩ slope length (q = 0.709), NDVI ∩ mean annual precipitation (q = 0.588), and mean annual precipitation ∩ cropland proportion (q = 0.570). The interaction of q-values involving mean annual precipitation range from 0.535 to 0.709, reflecting strong synergistic effects. These results highlight that mean annual precipitation is not only the most influential individual factor but also plays a dominant role in pairwise interactions affecting gully connectivity.
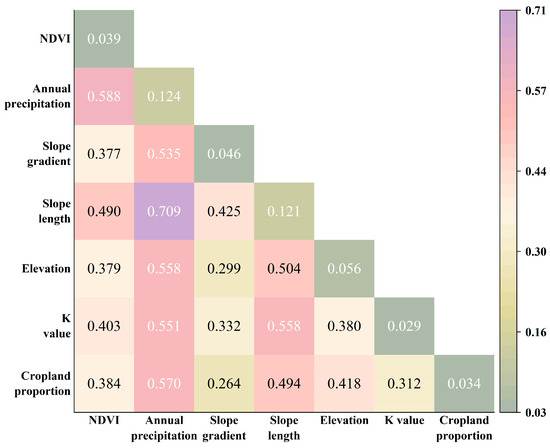
Figure 8.
The q-value and pairwise correlation matrix of factors influencing the EG-PG connectivity.
4. Discussion
Our findings confirmed the initial hypothesis that gully spatial connectivity exerts a direct influence on the morphological characteristics of PGs. This offers novel insights into gully evolution and broadens the scope for more effective erosion modeling and land management strategies. The following section further explores the mechanisms behind these patterns and their implications for understanding erosion processes in cultivated landscapes.
4.1. Mechanistic Analysis of Gully Connectivity Effects on PG Morphology
The combined effects of EG erosion and long-term tillage progressively reshape initially smooth hillslopes into a series of alternating ridges and shallow depressions, creating a corrugated microtopography. This localized landform evolution alters surface microstructures and changes the extent of areas exposed to rainfall-driven erosion, which in turn can influence runoff generation, soil infiltration, and sediment production [57]. Acting as preferential flow paths, EGs can accelerate runoff concentration, increase both flow velocity and discharge, and may amplify surface hydrodynamic forces [58]. The presence of EGs strengthens the potential hydraulic connectivity between the slope surface and downslope channels, forming stable pathways for sediment and water transport toward permanent gullies [31]. As EGs deepen and become spatially connected with PGs, erosional pathways are extended downslope, potentially accelerating channel development. Such spatial connections may create geomorphic and hydrodynamic conditions for the initiation and evolution of PGs. During peak flows, flow energy is concentrated at gully heads, which may drive intense vertical incision and undermining sidewall stability, often resulting in collapse. This concentrated force can enhance vertical incision at the gully head and destabilize gully sidewalls, likely triggering collapse. Consequently, gullies often extend longitudinally with limited lateral growth, forming a typical pattern of vertical elongation accompanied by minor side expansion [59,60]. Comparable morpho-dynamic processes have been documented. Comparable morpho-dynamic patterns have been observed in other geographies. For instance, Breunig et al. [26] used a combination of UAV and aerial imagery to monitor gully expansion in southern Brazil over a 25-year period, revealing substantial increases in gully area and volume linked to connectivity dynamics. In East Africa, Stenfert Kroese et al. [61] demonstrated via sediment fingerprinting in montane agricultural catchments that although gullies contribute a smaller fraction of sediment, their connectivity within the erosion network plays an essential role in sediment mobilization under changing land-use conditions. These cases suggest that while the hydraulic processes driving connectivity may be widely applicable, the morphological outcomes and sediment transfer impact can differ significantly across regional contexts. Our findings further show that PGs connected to EGs are generally longer and narrower than those without such spatial connectivity. This morphological difference may reflect a shift in erosion dynamics; surface runoff can rapidly concentrate at the gully head via EGs, and could enhance downslope incision and upslope extension. At the same time, lateral erosion may remain limited due to focused flow energy, ultimately forming deeper and narrower gully profiles.
4.2. Formation of Gully Connectivity
The formation of EG-PG connectivity is influenced by multiple interacting factors. In this study, slope length and mean annual precipitation are the dominant factors of gully connectivity in the Songnen black soil region. It should be noted that our analysis identifies spatial adjacency between EGs and PGs, which may influence hydrological connectivity. Both factors exhibited significant positive correlations with the proportion of PGs connected to EGs. Slope morphology plays a critical role in controlling the concentration and energy distribution of surface runoff [62]. The gentle slope gradients and relatively long slope lengths typical of the region may facilitate the downslope accumulation of runoff energy, thereby increasing the likelihood of EG formation and their eventual spatial connection to PGs. Our findings reveal that connectivity ratios are relatively higher in tableland areas. Given this high connectivity ratio, erosion control in tablelands should not only focus on stabilizing PG headcuts but also prioritize the early interception of EG development. For example, by constructing small drainage ditches or contour bunds to disrupt runoff concentration before it reaches downslope channels. Previous studies have also reported a positive relationship between slope length and the intensity of EG erosion [63]. Rainfall is the primary climatic driver influencing connectivity formation by generating surface runoff and facilitating sediment detachment and transport [1,64]. During high-intensity precipitation events, when runoff accumulation exceeds the storage capacity of EGs, flow may accelerate along the channel, deepening and extending it downslope. This process can plausibly lead to spatial connectivity with existing PGs. Soil properties in the region may further contribute to connectivity formation. The predominantly shallow, loose soils with low organic matter content and weak structural stability offer relatively low resistance to erosion, particularly in farmland subject to frequent tillage and low vegetation cover. Once EGs form, the absence of stabilizing vegetation and the repeated tillage disturbance can accelerate surface destabilization, increasing the probability of spatial linkage to PGs. Under such conditions, EG erosion intensifies due to increasing surface undulations and expanding contributing areas, eventually evolving into permanent gully erosion in the lower slopes [63]. While soil morphology-related factors may also play an important role, they are beyond the scope of this study. Moreover, the dominant factors governing EG-PG connectivity may vary considerably across different environmental settings due to differences in climate, soil properties, and land management practices.
4.3. Limitation and Future Works
This study offers a novel perspective on understanding the development of PGs by analyzing the spatial distribution and influencing factors of EG-PG connectivity. However, several limitations should be acknowledged, which may influence the interpretation of the results and, in turn, indicate clear directions for future research. First, the analysis relies on high-resolution but infrequently updated remote sensing imagery, which limits the ability to capture short-term variability, seasonal changes, or post-rainfall gully adjustments. This limitation could lead to underestimation of connectivity events occurring between image acquisition periods. Future work could address this by validating connectivity changes through repeated UAV surveys and high-frequency satellite imagery, enabling the classification of PGs based on their connectivity to EGs and revealing the temporal dynamics and rates of gully evolution across different geomorphic zones. Second, the definition and measurement of connectivity in this study are based on spatial adjacency observed in imagery, which does not directly measure hydrological connectivity. This may result in cases where mapped spatial proximity does not equate to actual sediment or water transfer. Although the existing Index of Connectivity (IC) primarily incorporates slope, flow direction, and surface roughness [65], and offers some physical interpretability, it remains limited in its ability to represent dynamic erosion pathways within complex agricultural environments [30]. Future research could embed field-validated EG-PG spatial linkages into the IC framework, thereby improving its accuracy in simulating sediment transport routes and energy transfer along dynamic gully networks. Third, the analysis was conducted at a regional scale, which may not fully capture micro-scale processes such as soil–water interactions or short-lived erosion events. This scale mismatch means that certain local mechanisms may be overlooked, particularly in heterogeneous agricultural landscapes. Future studies could bridge this gap by combining regional-scale analyses with targeted field monitoring, allowing multi-scale assessments of connectivity formation and persistence. Moreover, linking EG-PG connectivity to erosion modeling applications offers a promising avenue for improving predictive gully development models. When combined with other environmental factors, it could support the development of early warning systems for soil erosion and inform region-specific gully control measures, such as prioritizing interventions in high-connectivity tableland areas. In summary, EG-PG connectivity represents an important intermediary variable in hillslope erosion processes. It holds considerable research value and application potential, particularly in advancing erosion modeling and remote sensing-based monitoring efforts.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the EG-PG spatial connectivity, emphasizing its influence on the morphological characteristics of PGs. It further identified the dominant environmental factors associated with the formation of such connectivity. A comprehensive gully database was constructed by integrating field surveys, UAV-based aerial photography, and sub-meter visual interpretation of satellite imagery, following a multi-level accuracy control framework. This enabled a detailed analysis of gully spatial connectivity patterns. The results revealed that the connectivity ratio was significantly higher in the eastern low mountains and hills than the central and western plains, with clear spatial clustering of hotspots. Among the various geomorphic types, tableland areas displayed the highest degree of connectivity, significantly exceeding that of other landforms. Morphologically, PGs connected to EGs were generally longer and relatively narrower than unconnected ones, forming a distinctive elongated geometric profile. Slope length and mean annual precipitation were identified as the dominant factors with the highest explanatory power for EG-PG connectivity. Increases in both factors were associated with a higher likelihood of EG-PG connectivity. Furthermore, mean annual precipitation showed strong synergistic interaction with other factors, highlighting its critical role in shaping the spatial patterns of gully connectivity. This study underscores the role of spatial connectivity in gully evolution and provides a theoretical basis for improving erosion modeling strategies. The findings have practical implications for watershed management, suggesting that high-connectivity zones such as tableland areas should be prioritized for interventions. Recommended measures include contour bunds, small drainage ditches, and vegetation restoration to prevent EG-PG connectivity and enhance soil conservation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.W. and H.L.; methodology, C.W., H.L. and Q.W.; validation, G.P., Y.L., L.W. and L.M.; investigation, G.P., Y.L. and L.W.; resources, Q.W., S.L. and H.L.; data curation, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, C.W. and Q.Y.; project administration, Q.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Grant No. 2024YFD1501205 and 2021YFD1500603.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change, importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, S.; Dialynas, Y.G.; Bras, R.L.; Noto, L.V.; Istanbulluoglu, E. The role of vegetation on gully erosion stabilization at a severely degraded landscape: A case study from Calhoun Experimental Critical Zone Observatory. Geomorphology 2018, 308, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Alewell, C.; Ballabio, C.; de Oliveira Fagundes, H.; Haregeweyn, N.; Lugato, E.; Maerker, M.; Poesen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; et al. Policy implications of multiple concurrent soil erosion processes in European farmland. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Panagos, P.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Hayas, A.; Foerster, S.; Borrelli, P.; Rossi, M.; Torri, D.; Casali, J.; Borselli, L.; et al. Measuring, modelling and managing gully erosion at large scales: A state of the art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts, factors and control. Catena 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R. Modeling ephemeral gully erosion for conservation planning. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2005, 20, 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- SSSA. Glossary of Soil Science Terms; American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2020; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Lu, S. Discriminations on common soil erosion terms and their implications for soil and water conservation. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 16, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandaele, K.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; van Wesemael, B. Geomorphic threshold conditions for ephemeral gully incision. Geomorphology 1996, 16, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G. Understanding ephemeral gully erosion. Soil Conserv. 1986, 2, 90–125. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Annual variation of ephemeral gully erosion in a cultivated catchment. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.; Wells, R.; Dabney, S.; Zhang, T. Filling an ephemeral gully channel: Impacts on physical soil quality. Catena 2019, 174, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Ephemeral gullies caused by snowmelt: A ten-year study in northeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, F.; Wilson, G.V.; Xu, X.; Liu, C. Three decades of ephemeral gully erosion studies. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Dong, H.; Liu, G. Effects of rainfall characteristics and contour tillage on ephemeral gully development in a field in Northeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, G. Impact of farmland landscape characteristics on gully erosion in the black soil region of Northeast China. Catena 2025, 249, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Rowntree, K.M.; Le Roux, J.J. An interrogation of research on the influence of rainfall on gully erosion. Catena 2021, 206, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ma, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, W.; Ling, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Magnitude and hotspots of soil erosion types during heavy rainstorm events on the Loess Plateau: Implications for watershed management. Catena 2024, 246, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cao, W.; Nie, Y.; Xiong, D.; Cheng, S.; Duan, X. Influence of soil geography on the occurrence and intensity of gully erosion in the Hengduan Mountain region. Catena 2023, 222, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Cai, C. Influence of gully erosion on hydraulic properties of black soil-based farmland. Catena 2023, 232, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, M. Root Distribution and Soil Properties of Gully Heads and Their Effects on Headcut Migration in the Mollisols Region of Northeast China. Land 2022, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Nyssen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J. Gully prevention and control: Techniques, failures and effectiveness. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.; Chen, W.; Soleimanpour, S.M.; Kapović-Solomun, M.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kazemabady, N.K. Contribution of physical and anthropogenic factors to gully erosion initiation. Catena 2022, 210, 105925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baartman, J.E.; Nunes, J.P.; Masselink, R.; Darboux, F.; Bielders, C.; Degré, A.; Cantreul, V.; Cerdan, O.; Grangeon, T.; Fiener, P. What do models tell us about water and sediment connectivity? Geomorphology 2020, 367, 107300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Alencar, P.H.; de Araújo, J.C.; dos Santos Teixeira, A. Physically-based model for gully simulation: Application to the Brazilian Semiarid Region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Breunig, F.M.; Mancuso, M.A.; Coimbra, A.C.A.; Santos, L.J.C.; Hempe, T.C.; Frick, E.d.C.d.L.; Nascimento, E.R.d.; Sampaio, T.V.M.; Gaida, W.; Berra, E.F.; et al. Multiscale Remote Sensing Data Integration for Gully Erosion Monitoring in Southern Brazil: Case Study. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yibeltal, M.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Meshesha, D.T.; Aklog, D.; Masunaga, T.; Tsubo, M.; Billi, P.; Vanmaercke, M.; et al. Analysis of long-term gully dynamics in different agro-ecology settings. Catena 2019, 179, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, A.J.D.; Annys, S.; Dessie, M.; Nyssen, J.; Dondeyne, S. To What Extent Is Hydrologic Connectivity Taken into Account in Catchment Studies in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia? A Review. Land 2022, 11, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liang, Y.; Qin, W.; Ding, L.; Cao, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q. Review of sediment connectivity: Conceptual connotations, characterization indicators, and their relationships with soil erosion and sediment yield. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2025, 264, 105091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Du, M. Investigating sediment connectivity of a small catchment on the Loess Plateau using an appropriate index at an optimal spatial resolution. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Z.; Xing, S. Sediment connectivity of small watershed affected by gully development and vegetation restoration on the loess plateau. Geoderma 2022, 410, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Jiao, J.; Yan, Z.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Jian, J. Response of road erosion to hydrological connectivity under a heavy rainstorm in an agricultural watershed on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2024, 240, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Torreño, A.; Schnabel, S.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, Á.; Crema, S.; Cavalli, M. Effects of gully control measures on sediment yield and connectivity in wooded rangelands. Catena 2022, 214, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathololoumi, S.; Saurette, D.D.; Mann, H.S.; Kadota, N.; Vasava, H.B.; Naeimi, M.; Daggupati, P.; Biswas, A. An Upscaling-Based Strategy to Improve the Ephemeral Gully Mapping Accuracy. Land 2025, 14, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, J.d.P.M.; Guerra, A.J.T.; Cruz, C.B.M.; Jorge, M.d.C.O.; Booth, C.A. Machine Learning Models for the Spatial Prediction of Gully Erosion Susceptibility in the Piraí Drainage Basin, Paraíba Do Sul Middle Valley, Southeast Brazil. Land 2024, 13, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Zhong, Y.; Pang, G.; Wang, L.; Long, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tang, B. Factors Influencing Ephemeral Gullies at the Regional Scale: Formation and Density. Land 2024, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB; FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources; FAO: Rome, Italy; ISRIC: Valhongen, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Staff, S.S. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, United States Department of Agriculture, 13th ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Yue, H. Black soil conservation will boost China’s grain supply and reduce agricultural greenhouse gas emissions in the future. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Han, X. Historical evolution of gully erosion and its response to land use change during 1968–2018 in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Cruse, R.M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Yan, Y.; Guo, M. Morphological characteristics and influencing factors of permanent gully and its contribution to regional soil loss based on a field investigation of 393 km2 in Mollisols region of northeast China. Catena 2022, 217, 106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Y.; Shen, B.; Gu, Z.; Ding, Y. Delineating the black soil region and typical black soil region of northeastern China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Wan, Y. Variation in soil infiltration properties under different land use/cover in the black soil region of Northeast China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, B.; Niu, B.; Xu, F.; Yin, L.; Wang, S. Regional suitability assessment for different tillage practices in Northeast China: A machine learning aided meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 240, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J.; Huang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Yang, T.; Di, Y.; Xiao, X. The 10-m crop type maps in Northeast China during 2017–2019. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Yin, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; et al. The assessment of soil loss by water erosion in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Regional soil erosion assessment based on a sample survey and geostatistics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1695–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q. Soil Erodibility Factor (K) Dataset of Pan-Third Pole 65 Countries (2021); National Tibetan Plateau: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2023); National Tibetan Plateau: Beijing, China, 2024; Available online: https://www.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/faae7605-a0f2-4d18-b28f-5cee413766a2 (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Xu, X. Annual NDVI and EVI 1 km Dataset in China; Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. China’s Multi-Period Land Use Land Cover Remote Sensing Monitoring Dataset (CNLUCC); Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Long, Y.; Pang, G.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. Comparative Analysis of Gully Morphology Extraction Suitability Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Google Earth Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Fu, B. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K. Study on the effects of ephemeral gully development on soil erosion. Soil Conserv. China 1991, 4, 19–21+65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Guo, M.; Wang, W. Ephemeral gully erosion in concentrated flow channels induced by rainfall and upslope inflow on steep loessial slopes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5037–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J. Ephemeral Gully Development Process at Loess Steep Hillslope. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2006, 26, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, D.; Xiao, L.; Dong, Y.; Su, Z.; Lu, X. Impacts of headcut height on flow energy, sediment yield and surface landform during bank gully erosion processes in the Yuanmou Dry-hot Valley region, southwest China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenfert Kroese, J.; Batista, P.V.G.; Jacobs, S.R.; Breuer, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Rufino, M.C. Agricultural land is the main source of stream sediments after conversion of an African montane forest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Meng, L. Effect of topographic variations and tillage methods on gully erosion in the black soil region: A case-study from Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3786–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, B. Effect of topography on ephemeral gully erosion in Northeast China with black soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 35–38+49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Porto, P.; Scicolone, B. Relationships between rainfall characteristics and ephemeral gully erosion in a cultivated catchment in Sicily (Italy). Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, L.; Cassi, P.; Torri, D. Prolegomena to sediment and flow connectivity in the landscape: A GIS and field numerical assessment. Catena 2008, 75, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).