Enzymatic Stoichiometry and Driving Factors Under Different Land-Use Types in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Property Analysis
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity and Enzyme Stoichiometry Analysis
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrient and Stoichiometric Ratio Between Different Land-Use Types
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activity and Enzyme Stoichiometry Between Different Land-Use Types
3.3. Factors Affecting Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Land-Use Types on Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
4.2. Driving Factors of Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waring, B.G.; Weintraub, S.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Dlugosz, A.; Dlugosz, J.; Gryta, A.; Frac, M. Responses of N-cycling enzyme activities and functional diversity of soil microorganisms to soil depth, pedogenic processes and cultivated plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Bol, R.; Herre, M.; Marschner, B.; Heinze, S. Catchment scale spatial distribution of soil enzyme activities in a mountainous German coniferous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.S.; Guo, J.F.; Li, Y.Q. Enzyme stoichiometry indicates the variation of microbial nutrient requirements at different soil depths in subtropical forests. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0220599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y. Effects of conservation tillage on soil enzyme activities of global cultivated land: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.B.; Wei, X.R.; Wu, Y.H.; Shao, M.G.; Zhang, Q.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Reich, P.B.; Wei, G.H.; Jiao, S.; et al. Afforestation can lower microbial diversity and functionality in deep soil layers in a semiarid region. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6086–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.Q.; Lin, Z.W.; Penttinen, P.; Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.C.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T.; Jiang, P.K.; Fu, W.J. Effects of conversion from a natural evergreen broadleaf forest to a Moso bamboo plantation on the soil nutrient pools, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a subtropical area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Xu, Q.; Fan, G.H.; Huang, Y.X.; Zhou, D.W. Response of soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios to short-term land use conversions in a salt-affected region, northeastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Han, K.X.; Guan, S.C.; Zhou, D.W. Conversion of cropland to forage land and grassland increases soil labile carbon and enzyme activities in northeastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 245, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of Long-Term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Amelung, W.; Lehmann, J.; Kästner, M. Quantitative assessment of microbial necromass contribution to soil organic matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Yang, Y.; Geng, Y.Q.; Huang, G.L.; Cui, X.Q.; Hou, M. Effects of different land types on soil enzyme activity in the Qinghai Lake region. Wetlands 2018, 38, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, P.H.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.L.; Lin, X.W.; Xie, Z.B. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals stronger microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in biochar amendment soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Li, Q.; Guo, Z.Q.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Zhai, J.Y.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient limitation under a natural secondary succession of vegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Q.; Wang, W. Stoichiometry of soil extracellular enzyme activity along a climatic transect in temperate grasslands of northern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Yu, G.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Wang, S.Z.; Wang, R.L.; Zhao, N.; Jia, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the north-south transect in eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.P.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Meng, M.J.; Biswas, S.R.; Ye, L.X.; Zhang, J.C. Effects of land use change on the composition of soil microbial communities in a managed subtropical forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 373, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Xu, Y.M.; Hao, F.H.; Wang, X.; Siyang, C.; Lin, C.Y. Effect of long-term agricultural cultivation and land use conversion on soil nutrient contents in the Sanjiang Plain. Catena 2013, 104, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.S.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K.L. Soil aggregate mediates the impacts of land uses on organic carbon, total nitrogen, and microbial activity in a Karst ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Meng, X.X.Y.; Li, M.S.; Mu, L.Q.; Lei, J.P.; Sui, X. Conversion from natural wetlands to forestland and farmland alters the composition of soil fungal communities in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenius, K.; Rita, H.; Mikkonen, A.; Lappi, K.; Lindstr, M.K.; Hartikainen, H.; Raateland, A.; Niemi, R.M. Effects of land use on the level, variation and spatial structure of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.D.; Gao, D.X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.C.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Y.; Hou, W.P.; Liu, J.; Malik, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.L.; Tang, M.; Zhu, R.Q.; Cheng, C.; et al. Effects of different land use types and soil depths on soil mineral elements, soil enzyme activity, and fungal community in karst area of southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Shi, W. Short-term effects of plant litter on the dynamics, amount, and stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity in agroecosystems. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 65, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Liang, C.F.; Shao, S.; Chen, J.H.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q.F. Linkages of litter and soil C: N: P stoichiometry with soil microbial resource limitation and community structure in a subtropical broadleaf forest invaded by Moso bamboo. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Feng, W.; Lai, Z.R.; Fa, K.Y.; Qin, S.G. Metagenomic and 13C tracing evidence for autotrophic atmospheric carbon absorption in a semiarid desert. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; He, Y.Y.; Li, J.H.; Lv, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, M.X.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhang, J.L. Planting halophytes increases the rhizosphere ecosystem multifunctionality via reducing soil salinity. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Mulvaney, C. Nitrogen total. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.; Sommers, L.; Page, A. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties of Phosphorus; ASA Monograph: London, UK, 1982; Volume 9, pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Kong, W.D.; Wang, F.; Long, X.E.; Guo, C.Y.; Yue, L.Y.; Yao, H.Y.; Dong, X.B. Desert and steppe soils exhibit lower autotrophic microbial abundance but higher atmospheric CO2 fixation capacity than meadow soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForest, J.L. The influence of time, storage temperature, and substrate age on potential soil enzyme activity in acidic forest soils using MUB-linked substrates and L-DOPA. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C., N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Weintraub, M.N. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: Informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front. Terr. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moghimian, N.; Hosseini, S.M.; Kooch, Y.; Darki, B.Z. Impacts of changes in land use/cover on soil microbial and enzyme activities. Catena 2017, 157, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, A.; Chen, R.; Cheng, X.L. Afforestation inhibited soil microbial activities along the riparian zone of the upper Yangtze River of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 538, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.M.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Wang, P.; Zhu, B.A.; Cheng, W.X. Rhizosphere priming effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics among tree species with and without intraspecific competition. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weand, M.P.; Arthur, M.A.; Lovett, G.M.; Mcculley, R.L.; Weathers, K.C. Effects of tree species and N additions on forest floor microbial communities and extracellular enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Weintraub, M.N. The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: A theoretical model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranguit, D.; Guillaume, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Land-use change affects phosphorus fractions in highly weathered tropical soils. Catena 2017, 149, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananbeh, H.; Stojanovic, M.; Pompeiano, A.; Voberková, S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Use of soil enzyme activities to assess the recovery of soil functions in abandoned coppice forest systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.L.; Wei, Y.A.; Wang, F.W.; Guo, J.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Hu, S.J. Sensitivity of plant species to warming and altered precipitation dominates the community productivity in a semiarid grassland on the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 7628–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; Starke, R.; Martinovic, T.; Parente, F.M.L.; Orgiazzi, A.; Bastida, F. Distribution of phosphorus cycling genes across land uses and microbial taxonomic groups based on metagenome and genome mining. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 174, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
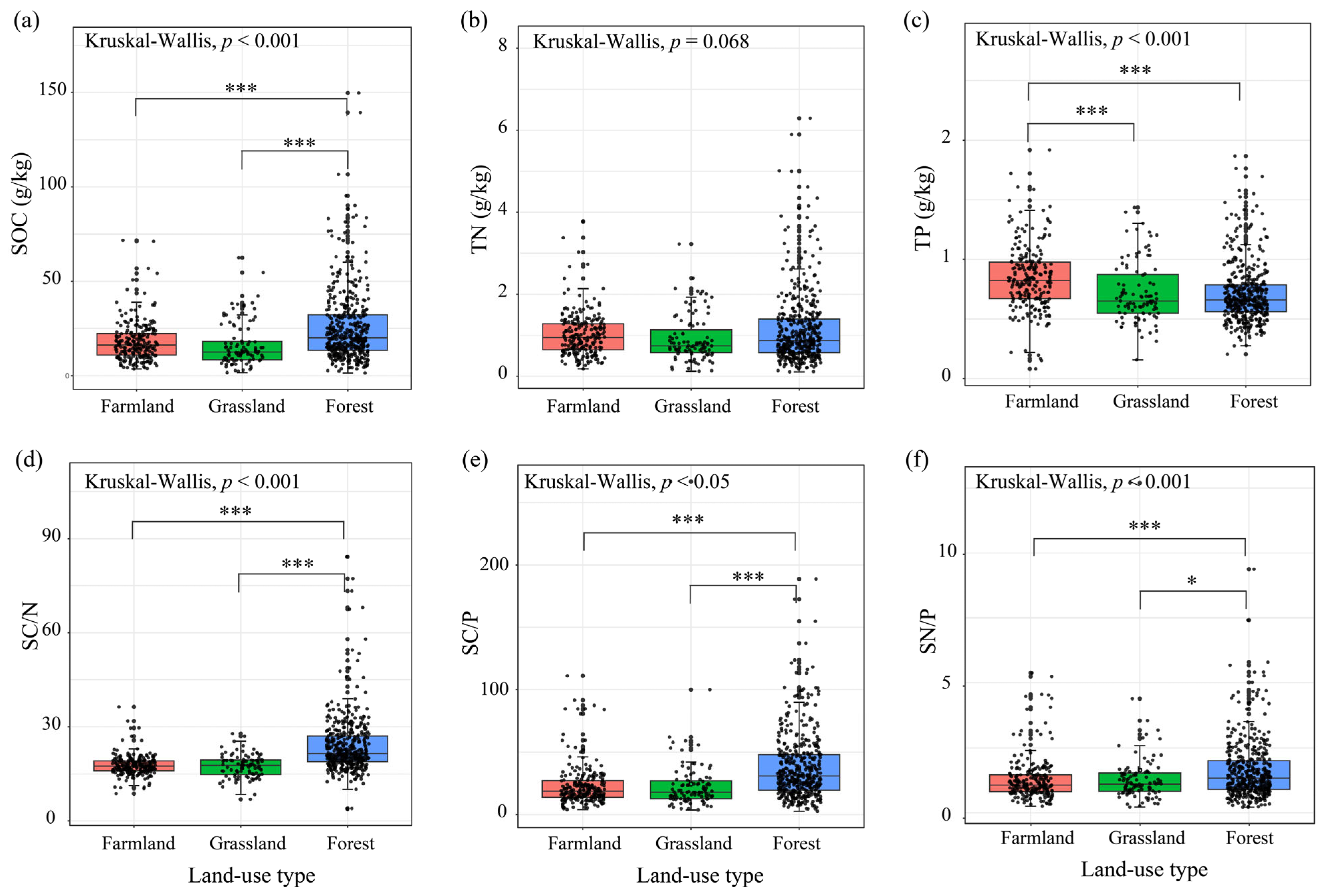

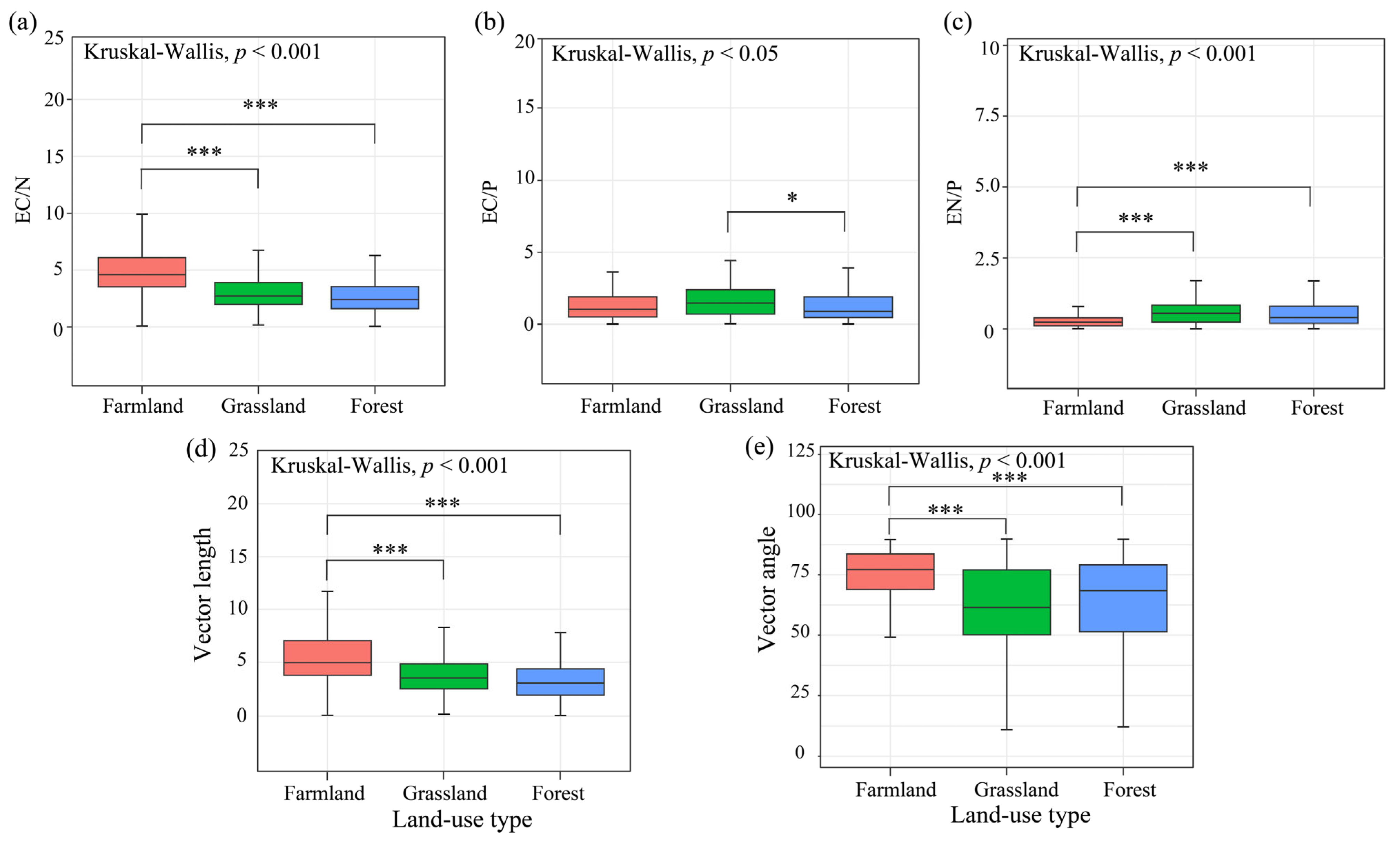
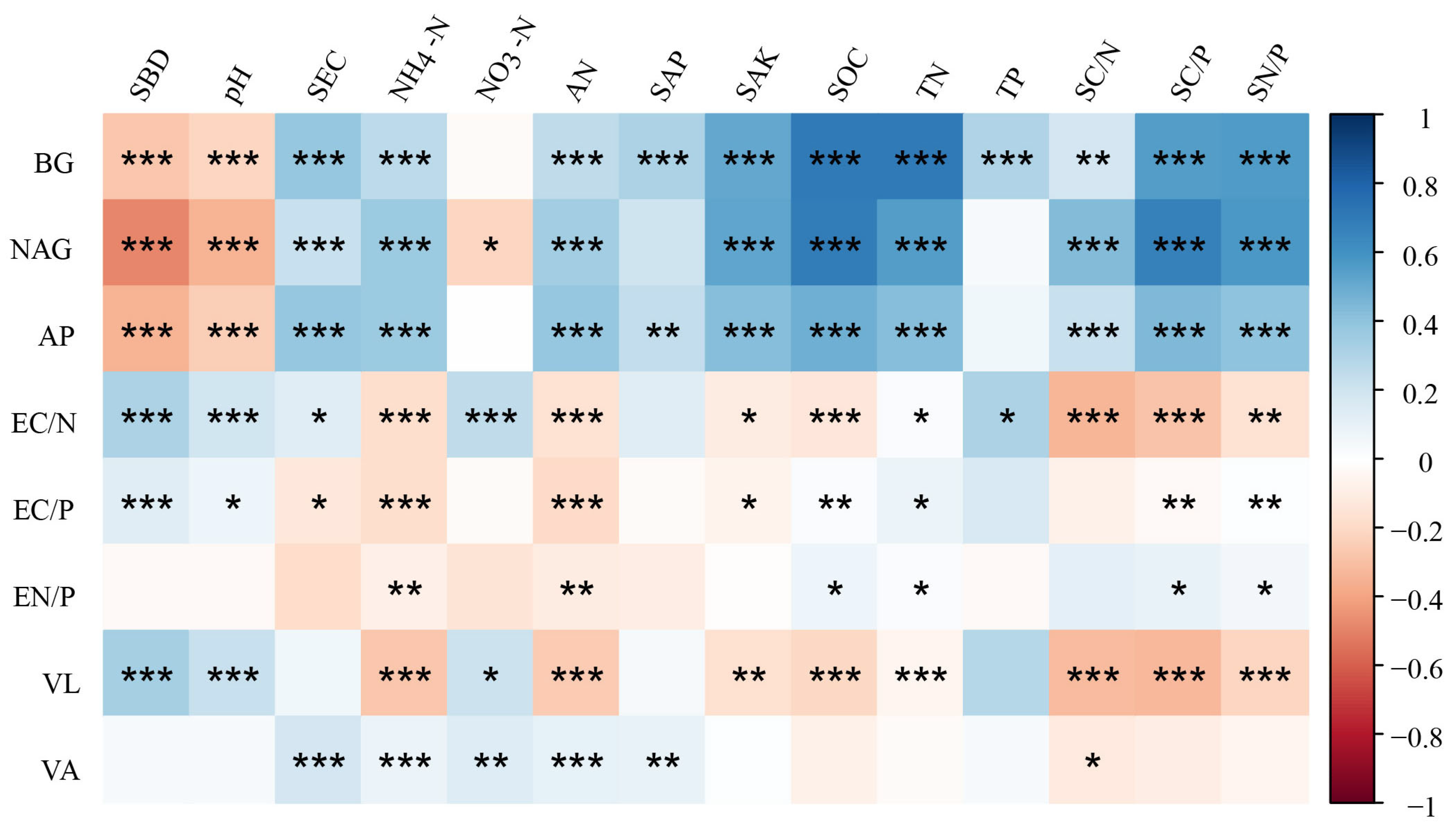
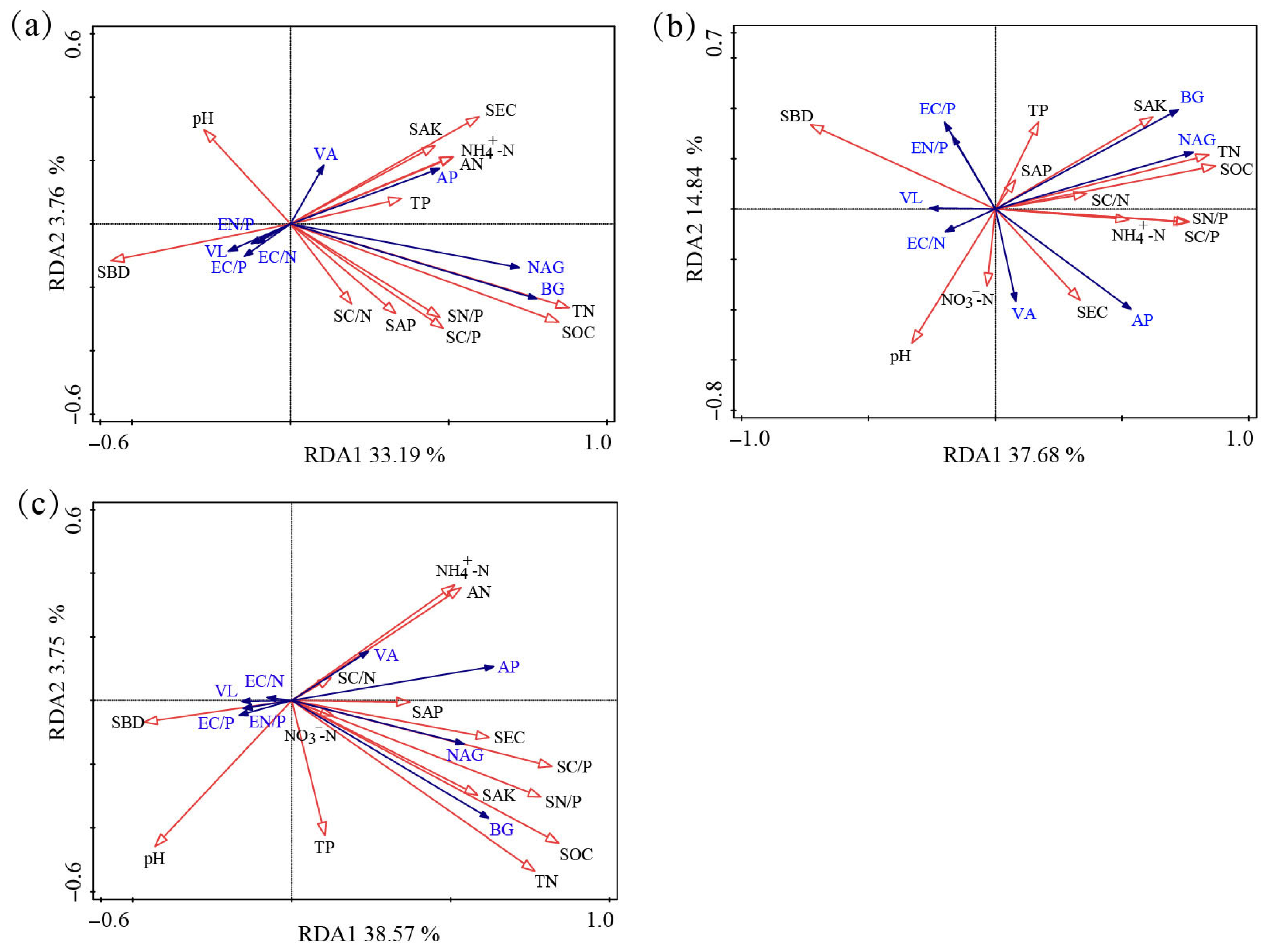
| Land-Use Type | Kruskal Test | A vs. B | A vs. C | B vs. C | Kruskal Test | A vs. B | A vs. C | B vs. C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | SBD (g/cm3) | <0.001 | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | pH | <0.001 | — | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Grassland | ||||||||||
| Forest | ||||||||||
| Farmland | SEC (us/cm) | 0.158 | — | — | — | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.01 | <0.001 |
| Grassland | ||||||||||
| Forest | ||||||||||
| Farmland | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | <0.001 | — | <0.001 | — | AN (mg/kg) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.05 | <0.001 |
| Grassland | ||||||||||
| Forest | ||||||||||
| Farmland | SAP (mg/kg) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | — | SAK (mg/kg) | <0.001 | — | <0.001 | <0.01 |
| Grassland | ||||||||||
| Forest | ||||||||||
| Factors | Farmland | Grassland | Forest Land | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explains % | p | Explains % | p | Explains % | p | |
| SBD | 1.1 | 0.038 | 7 | 0.002 | 0.1 | 0.364 |
| pH | 0.2 | 0.518 | 2.7 | 0.014 | 2 | 0.002 |
| SEC | 2.8 | 0.002 | 4.4 | 0.012 | 3.4 | 0.002 |
| SOC | 0.9 | 0.042 | 28.8 | 0.002 | 28 | 0.002 |
| TN | 26 | 0.002 | 0.4 | 0.46 | 0.3 | 0.14 |
| TP | 0.6 | 0.16 | 0.6 | 0.32 | 0.2 | 0.246 |
| NH4+-N | 3 | 0.004 | 1.6 | 0.052 | 2.3 | 0.004 |
| NO3−-N | — | — | 0.7 | 0.318 | 0.1 | 0.334 |
| AN | <0.1 | 0.864 | — | — | 4.8 | 0.002 |
| SAP | 1 | 0.04 | 0.7 | 0.246 | <0.1 | 0.564 |
| SAK | 0.3 | 0.354 | 2.6 | 0.024 | 0.4 | 0.048 |
| SNP | <0.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.712 | 0.7 | 0.024 |
| SCN | 0.4 | 0.236 | 0.7 | 0.272 | 0.3 | 0.094 |
| SCP | 0.9 | 0.072 | 2.8 | 0.02 | <0.1 | 0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Xiong, F.; Wu, D.; Zhao, B.; Wang, W.; Bi, B.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; Xue, S. Enzymatic Stoichiometry and Driving Factors Under Different Land-Use Types in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region. Land 2025, 14, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081550
Zhu Y, Xiong F, Wu D, Zhao B, Wang W, Bi B, Liu Y, Liang M, Xue S. Enzymatic Stoichiometry and Driving Factors Under Different Land-Use Types in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region. Land. 2025; 14(8):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081550
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yonggang, Feng Xiong, Derong Wu, Baoguo Zhao, Wenwu Wang, Biao Bi, Yihang Liu, Meng Liang, and Sha Xue. 2025. "Enzymatic Stoichiometry and Driving Factors Under Different Land-Use Types in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region" Land 14, no. 8: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081550
APA StyleZhu, Y., Xiong, F., Wu, D., Zhao, B., Wang, W., Bi, B., Liu, Y., Liang, M., & Xue, S. (2025). Enzymatic Stoichiometry and Driving Factors Under Different Land-Use Types in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region. Land, 14(8), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081550





