Abstract
Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry provides a basis for understanding soil ecosystem functions, with implications for land management and ecological protection. Long-term climatic factors and human interferences have caused significant land-use transformations in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region, affecting various ecological functions, such as soil nutrient cycling and chemical element balance. It is currently unclear how large-scale land-use conversion affects soil ecological stoichiometry. In this study, 763 soil samples were collected across three land-use types: farmland, grassland, and forest land. In addition, changes in soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activity and stoichiometry were determined. The soil available phosphorus (SAP) and total phosphorus (TP) concentrations were the highest in farmland soil. Bulk density, pH, SAP, TP, and NO3−-N were lower in forest soil, whereas NH4+-N, available nitrogen, soil organic carbon (SOC), available potassium, and the soil nutrient ratio increased. Land-use conversion promoted soil β-1,4-glucosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, and alkaline phosphatase activities, mostly in forest soil. The eco-enzymatic C:N ratio was higher in farmland soils but grassland soils had a higher enzymatic C:P and N:P. Soil microorganisms were limited by P nutrients in all land-use patterns. C limitation was the highest in farmland soil. The redundancy analysis indicated that the ecological stoichiometry in farmland was influenced by TN, whereas grass and forest soils were influenced by SOC. Overall, the conversion of cropland or grassland to complex land-use types can effectively enhance soil nutrients, enzyme activities, and ecosystem functions, providing valuable insights for ecological restoration and sustainable land management in alpine regions.
1. Introduction
Natural factors and human activities cause profound changes in land-use types and degrees, and consequently, have a great impact on soil health and ecosystem functions. Microorganisms, an indispensable part of the soil ecosystem, promote element cycling and organic matter transformation by secreting extracellular enzymes to obtain nutrients for absorption and utilization by living organisms and play a pivotal role in sustaining the functional stability of ecosystems [1,2,3]. However, microorganisms are often constrained by energy and nutrients, which can affect their growth and ability to synthesize ecological enzymes [4]. The activity of soil carbon (C)-, nitrogen (N)-, and phosphorus (P)-metabolizing enzymes indicates the nutrient cycling function of the soil, directly reflecting the functional status of soil ecosystems [5,6]. Therefore, soil enzyme stoichiometry characteristics are commonly used to assess microbial nutrient demands and limitations, serving as key indicators of soil nutrient status [7].
Soil eco-enzymatic characteristics are highly sensitive to land-use conversion [8]. The conversion of farmland to grassland can increase soil organic C and restore soil nutrients, resulting in higher soil enzyme activity [9,10]. In contrast, forest soil enzyme activity generally exhibits higher levels owing to high biodiversity and stable organic matter sources that promote microbial activity [8,11,12]. In high-altitude areas, changes in land types alter the habitat characteristic, significantly affecting soil hydrolase activities [13]. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry reflects the nutrient requirements of microorganisms, thereby maintaining geochemical balance [7,14,15]. Microbes in temperate grassland soils require more N and P [16]; in tropical and subtropical forests, soil microbes have a higher demand for N than for C [17], reflecting the differences in nutrient demands and limitations of soil microorganisms in different ecosystems. Therefore, clarifying the soil eco-enzymatic activity and stoichiometric characteristics is crucial for understanding the functional stability of soil ecosystems. However, the soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry under different land-use types in alpine ecosystems remains unclear.
Ground cover and litter input exhibited a variation across distinct land-use types, affecting soil structure, nutrient content, and microbial communities [18,19,20,21]. Therefore, land-use can alter soil enzymatic activity both directly through plant–microbial interactions, and indirectly by affecting soil properties [22]. Soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry are strongly correlated with soil properties such as pH, soil organic matter, and available nutrients [17,23]. Land-use conversion substantially changes soil nutrient content and stoichiometric ratios, thus affecting soil enzyme characteristics [9,20]. Differences in plant root residues and exudates caused by different land-uses can alter microbial community composition and activity [24]. These dynamics may cause substantial changes in soil enzyme activity, thereby affecting nutrient transformation and cycling [25,26]. Clarifying the relationship between soil variables, enzymatic activity, and enzymatic stoichiometry is crucial for understanding how land-use affects soil ecosystem functions. However, the complex relationship and impact between ecological enzyme stoichiometry and soil properties under large-scale land-use conversion remain unclear, especially in ecologically sensitive regions.
The Qinghai–Tibet Plateau has a unique high-altitude ecosystem with a fragile ecological environment and a susceptibility to climate change and human activities; this is of research value and ecological significance. Over the past few decades, land-use conversion occurs in the region, resulting in significant changes in vegetation cover, soil properties, and ecological functions. Investigating how varying land-use patterns affect soil nutrient status, enzyme activity, and ecological stoichiometry is essential for developing rational land management strategies. Therefore, we selected three typical land-uses (farmland, grassland, and forest land) in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region to (1) evaluate the impacts of land-use conversion on soil nutrients, enzyme activity, and ecological stoichiometry; (2) identify microbial nutrient demands and limitations under different land-use types; and (3) uncover the driving factors of soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry. The results elucidate soil nutrient status and ecological effects under different land-use patterns in high-altitude regions and provide a basis for sustainable land management and ecological protection in ecologically fragile regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
The experiment was conducted in Milin County, Linzhi City, Xizang Autonomous Region, on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (Figure S1). The area is characterized by a temperate semi-humid plateau climate, with an average altitude of 3000 m, a mean annual precipitation of 670 mm, a mean annual air temperature of 8.6 °C, and an annual evaporation of 1239.6 mm. The study area has experienced strong soil erosion and large terrain undulations, forming a “U”-shaped wide valley section, which belongs to a typical high mountain canyon landform. The study area is characterized by a dominant vegetation cover of alpine grasslands, alpine meadows, and alpine shrub vegetation, with a coverage of approximately 60%. The natural vegetation community is dominated by Carex parvula, C. alatauensis, Potentilla chinensis, and Sophora viciifolia, with accompanying species such as C. giraldiana, Leontopodium nanum, and Gentiana scabra; simultaneously distributed are artificial forests of Populus szechuanica Var. Tibetica Schneid, Pinus, and Hippophae rhamnoides.
2.2. Sample Collection
Soil sampling was conducted in July 2023. Considering the geomorphology, vegetation type, and level of human disturbance, 763 sampling points were established according to a grid layout, including 229 farmland points, 99 grassland points, and 436 forest land points. Taking the preset sampling point as the center, nearby plots with similar soil types, landscapes, and land-use status were selected as the sample collection range. A total of 5–8 bulk soils (depth = 0–20 cm) were collected in the shape of a plum blossom and mixed into a composite sample. The samples were then passed through a 2 mm sieve, and approximately 1 kg was retained using the quartering method to remove excess soil. All soil samples were air-dried to analyze the soil properties.
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Property Analysis
The soil bulk density (SBD), pH, soil electrical conductivity (SEC), soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), soil ammonium (NH4+-N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), available phosphorus (SAP), and available potassium (SAK) were analyzed. SBD was determined using the ring knife method, pH was determined using a pH meter (Metrohm 702, Herisau, Switzerland) with a 1:2.5 mixture of soil and water [27], SEC was determined with a soil-to-water ratio of 1:5 using electrical conductivity meter (LEICI DDS-307A, Shanghai, China) [28], SOC was analyzed using H2SO4–K2Cr2O7 oxidation [27], TN was measured using the Kjeldahl method [29], and TP levels were analyzed using the colorimetric method after digestion with H2SO4 and HClO4 [30]. NH4+-N and NO3−-N were measured using a flow-injection autoanalyzer (AutAnalyel, Bran+Luebbe GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany) and available nitrogen (AN) = NH4+-N + NO3−-N [31]. SAP was determined colorimetrically after extracting with 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 (pH = 8.5) [30]. The SAK was measured using flame photometry. The physicochemical characteristics are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Soil physicochemical properties of different land-use types.
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity and Enzyme Stoichiometry Analysis
The activities of soil β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase (NAG), and alkaline phosphatase (AP) were measured using fluorimetric microplate assays [32]. Microplate samples were maintained at 25 °C for 2 h in a temperature-controlled incubator, and fluorescence values were measured using a multifunctional microplate reader (excitation: 365 nm; emission: 450 nm) [15]. The extracellular enzyme activity ratio was determined as previously described [33]:
EC/N = BG/NAG
EC/P = BG/AP
EN/P = NAG/AP
Vector length (VL) and vector angle (VA) were used to indicate the limitations of the microbial nutrient requirements for C, N, and P [33]. The calculation is as follows:
in which x corresponds to the ratio of C- to P-acquiring enzyme activities and y indicates the ratio of C- to N-acquiring activities [34].
VL = SQRT (x2 + y2)
VA = Degrees (Atan2 (x, y))
2.5. Data Analyses
The Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s test (p < 0.05) were conducted to analyze the differences in soil nutrients, enzyme activity, and stoichiometric ratio between different treatments, with p values corrected using the Bonferroni method. The boxplot was visualized using the “ggplot2” packages [35] in R software (v4.2.0). Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to assess the relationships among soil nutrients, enzymatic activity, and enzymatic stoichiometry. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was performed using Canoco 5.0 to evaluate the effects of soil properties on soil enzyme activity and enzyme stoichiometry.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrient and Stoichiometric Ratio Between Different Land-Use Types
SBD, pH, and NO3−-N concentrations decreased considerably in forest soils. NH4+-N, AN, and AK were substantially higher in the forest soil samples than in the farmland and grassland samples (Table 1). Farmland soil exhibited the peak SAP concentration, significantly higher than those of grassland and forestland soils (Table 1). SOC was significantly higher in forest soils than in farmland and grassland soils, whereas TP was significantly higher in farmland soils than in grassland and forestland soils (Figure 1a,c). The TN concentration was similar among vegetation types (Figure 1b). Land-use type significantly affected soil nutrient stoichiometry (Figure 1d,e). The nutrient ratios (SOC:TN, SOC:TP, and TN:TP) were significantly higher in forest soils than in farmland and grassland soils; however, no statistical differences were observed in these ratios between farmland and grassland soils (Figure 1d,e).
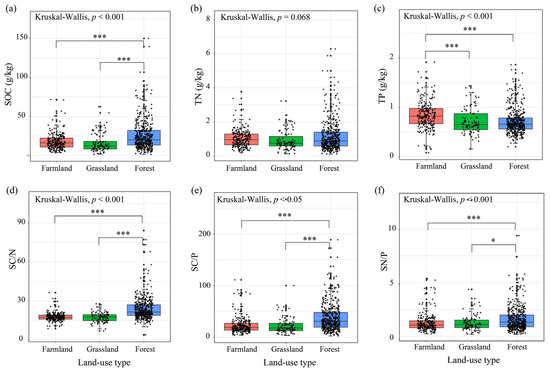
Figure 1.
Soil nutrient and stoichiometric ratio of different land-use types. (a–c) Soil nutrient concentration of different land-use types; (d–f) Soil nutrient stoichiometric ratio of different land-use types. Note: SOC: soil organic carbon; TN: soil total nitrogen; TP: soil total phosphorus; SC/N: SOC/TN; SC/P: SOC/TP; SN/P: TN/TP. * indicates significant differences among three land-use types by Dunn’s test (*** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05).
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activity and Enzyme Stoichiometry Between Different Land-Use Types
Land-use significantly affected the soil enzyme activity (Figure 2). BG and AP activities were lowest in grassland soils and were significantly lower than those in farmland and forestland soils (Figure 2a,c). NAG activity gradually increased with changes in land-use type and was significantly higher in forest soil than in farmland and grassland soils (Figure 2b). The eco-enzymatic C:N ratio was significantly higher in the farmland soils than in the grassland and forest soils. Eco-enzymatic C:P was significantly higher in grassland soils than in forestland soils. Eco-enzymatic N:P was the lowest in farmland soils and was significantly lower than that in grassland and forestland soils (Figure 3a–c). The VL gradually decreased with land-use conversion and was significantly higher in farmland soil than in grassland and forestland soils (Figure 3d). The VA was highest in farmland soils and was significantly higher than that in grassland and forest land soils (Figure 3e).
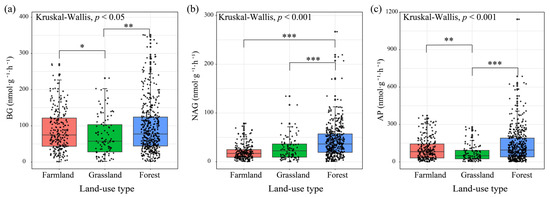
Figure 2.
Soil enzyme activity of different land-use types. (a) Soil BG activity of different land-use types; (b) Soil NAG activity of different land-use types; (c) Soil AP activity of different land-use types. Note: BG: β-1,4-glucosidase; NAG: N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase; AP: alkaline phosphatase. * indicates significant differences among three land-use types by Dunn’s test (*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05).
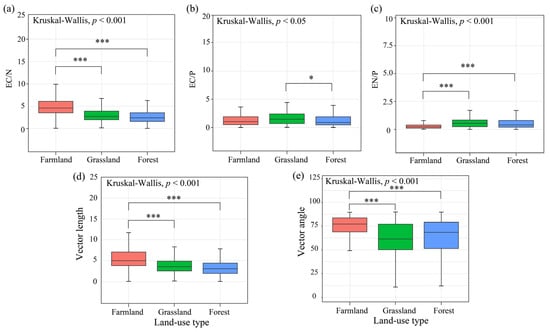
Figure 3.
Soil enzyme stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitations of different land-use types. (a–c) Soil enzyme stoichiometry of different land-use types; (d) Vector length characteristics of different land-use types; (e) Vector angle characteristics of different land-use types. Note: EC/N: eco-enzymatic C:N (BG/NAG); EC/P: eco-enzymatic C:P (BG/AP); EN/P: eco-enzymatic N:P (NAG/AP). * indicates significant differences among three land-use types by Dunn’s test (*** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05).
3.3. Factors Affecting Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
Soil enzyme activities showed significant positive associations with soil attributes such as SEC, NH4+-N, available N and K, SOC, TN, and nutrient ratios, but negative relationships with SBD and pH (Figure 4). Conversely, soil enzyme stoichiometry was strongly negatively correlated with NH4+-N, available N and K, SOC, TN, and nutrient ratios, and positively correlated with soil bulk density and pH (Figure 4). The soil eco-enzymatic C:N ratio was also positively correlated with SEC, NO3−-N, and TP. Vector length was strongly positively correlated with soil bulk density, pH, and NO3−-N and negatively correlated with NH4+-N, available N and K, SOC, TN, and nutrient ratios. The vector angle was strongly positively correlated with soil properties, such as SEC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and available N and K (Figure 4).
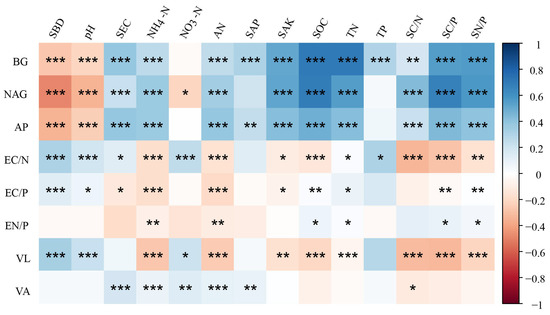
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis between soil enzymatic activity, stoichiometry, and soil properties. Note: * indicates significant correlation (*** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05).
RDA was used to analyze the relationship between soil eco-enzymatic activity, stoichiometry, and environmental variables among different land-use types. The first two RDA axes explained 36.95%, 52.52%, and 42.32% of the variance, respectively (Figure 5). TN was the most important factor affecting the enzymatic activity and stoichiometry of farmland soil, and SEC, NH4+-N, SOC, and SAP were also important factors affecting the changes in soil ecological stoichiometry (Figure 5a; Table 2). SOC was the driving factor affecting the enzymatic activity and stoichiometry of grassland and forest land soils (Figure 5b,c; Table 2). These variables were also influenced by SEC, pH, and SAK (Table 2).
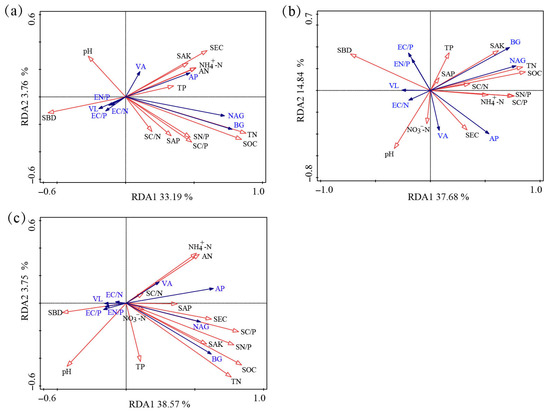
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis of soil enzymatic activity, enzymatic stoichiometry, and soil properties at different land-use types. (a) farmland soils; (b) grassland soils; (c) forest land soils.

Table 2.
The effects of soil variables on soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Land-Use Types on Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
Soil enzyme activity is a sensitive indicator of soil nutrient dynamics and fertility and is markedly affected by changes in land-use types [36]. In this study, land-use conversion significantly affected soil BG, NAG, and AP activities, with higher levels observed in forest soil (Figure 2). A more complex composition of forest vegetation communities, richer litter, and higher underground carbon inputs are conducive to microbial growth and activity, which could enhance soil enzymatic activity [8,12]. Compared with forest soil, enzymatic activity in grassland soil was significantly lower, indicating a low ability of microorganisms to secrete ecological enzymes (Figure 2). This likely results from the low content of organic C, available N, and P nutrients in grassland soils, which limit the enzyme synthesis ability of microorganisms [37]. In the farmland soil, although the input of fertilizers supplemented the available N and P nutrients, lower soil enzyme activity was observed (Figure 2b,c). This may be related to the competition between plant roots and soil microbes for resources, as crops rely on large amounts of nutrients to maintain their own growth and development [38].
Compared to farmland, eco-enzymatic C:N in grassland and forest soils was significantly reduced (Figure 3a), indicating that soil microbial N limitation was greater. Plant species and litter quality typically affect the nutritional limitations of microorganisms [15,39]. In complex vegetation communities, more resources are allocated to the structure of plant leaves, and limited resources are available to maintain photosynthesis and respiration, which may result in a certain degree of nitrogen limitation in microorganisms [15]. Notably, microorganisms may alleviate this situation by increasing the synthesis of NAG enzymes (Figure 2b). The eco-enzymatic C:P and N:P in grassland and forest soils were obviously higher than those in farmland soils (Figure 2c), indicating that farmland soil microorganisms are more strongly limited by P. Therefore, complex vegetation types may be beneficial for the soil microbial P demand and nutrient turnover.
Enzyme vector length and angle can reveal changes in microbial nutrient requirements [40]. We found that the VL tended to decrease with land-use conversion (Figure 3d). In forest soils, the input of large amounts of available carbon sources can stimulate microbial activity and enzyme secretion, thereby accelerating organic matter decomposition [12]. Therefore, more litter increases the organic C content in the soil (Figure 1a), thereby alleviating microbial C demand. Moreover, the soil enzyme VA of all three land types was greater than 45° (Figure 3e), suggesting that soil microbial growth was limited by P. As vegetation types became more complex, microbial P limitation decreased (Figure 3e). The soil TP content gradually decreased (Figure 1c), whereas the BG, NAG, and AP activities increased overall (Figure 2), indicating that in soils with total P deficiency, microorganisms may satisfy their P needs by secreting more hydrolytic enzymes to decompose the litter. The decomposition of litter returns P to the soil, thereby alleviating microbial P limitation [41]. We also found that the VL and VA were both greater in farmland soil (Figure 3d,e), suggesting that farmland soil microbes were most strongly limited by C and P nutrients, consistent with the significant decrease in farmland eco-enzymatic C:P and N:P. Competition between the crop roots and microorganisms may also be an important factor [38].
4.2. Driving Factors of Soil Enzymatic Activity and Stoichiometry
Soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometric characteristics are closely related to soil attributes [17,23]. Microorganisms promote nutrient flow in the soil by synthesizing hydrolytic enzymes that decompose organic matter [1]. An increase in soil nutrients is beneficial for microbial growth and metabolism, and promotes soil enzyme activity [8,16]. We observed a strong positive correlation among soil nutrient content (i.e., NH4+-N, available N and K, SOC, and TN), nutrient ratios (i.e., soil C:N, C:P, and N:P), and soil enzyme activity (Figure 4), consistent with previous results [15]. Resource allocation theory suggests that soil microbes regulate enzyme secretion in soil to increase the availability of limiting nutrients, leading to the positive interactions between soil enzymatic activity and available nutrients [15,42]. SOC and TN can serve as the main sources of enzymatic substrates in soil, accelerating microbial metabolism and maintaining soil enzyme activity and stability [8,42,43]. Soil BD and pH were also strongly correlated with soil enzyme activity; however, these attributes may have inhibited soil enzyme activity (Figure 4).
Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and vector length were strongly negatively correlated with soil NH4+-N, available N and K, SOC, and TN concentrations and strongly positively correlated with soil BD and pH (Figure 4). Reasonable porosity and moisture can promote microbial growth, resulting in an enhanced secretion of extracellular enzymes to decompose nutrients [44]. Therefore, poor soil structure may lead to ecological enzyme imbalance and increased microbial C limitation. The soil ecological enzyme ratio was also strongly negatively correlated with the soil C/P and N/P (Figure 4), consistent with Wu et al. [15]. P is a major limiting nutrient, and soil microorganisms increase P availability by participating in substance transformation [45]. The VA was strongly positively correlated with available soil N and P (Figure 4). Therefore, soil microorganisms may obtain available nutrients by enhancing related enzyme activities, thereby alleviating P limitation [46]. We also found that TN was the driving factor affecting soil eco-enzymatic activity and stoichiometry in farmlands, whereas ecological stoichiometry in grassland and forest land soils was driven by SOC (Figure 5; Table 2). Therefore, in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region, nutrient cycling and the balance of soil ecosystems must focus on the changing characteristics of these indicators.
5. Conclusions
We demonstrated that land-use type strongly affected soil nutrients, eco-enzymatic activity, and enzyme stoichiometry. Land-use conversion from farm-land to forest reduced soil BD, pH, AP, TP, and NO3−-N concentrations, while increasing NH4+-N, AN, AK, and SOC. BG, NAG, and AP activities were higher in the forest soil. The eco-enzymatic C:N ratio was significantly higher in farmland soils than in the other soil types, whereas grassland soils exhibited higher enzyme C:P and N:P ratios. Furthermore, microbial C and P nutrient limitations were the highest in farmland soil and changed with land-use patterns. These dynamics were closely related to soil properties. RDA indicated that eco-enzymatic activity and stoichiometry in farmland soils were mainly influenced by TN, whereas those of grassland and forest soils were dominated by SOC. These results elucidate soil nutrient cycling and ecological functions under land-use conversion in high-altitude regions, but ignore the impact of specific vegetation on soil properties and microbial processes. Future research should identify the connections between soil ecological functions, plant characteristics, and soil microbial communities under different land-use patterns to more accurately assess regional soil quality and health, as well as their driving mechanisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land14081550/s1, Figure S1: Geographical location of the study area.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, Y.Z., F.X. and D.W.; funding acquisition, S.X.; investigation, Y.Z., F.X. and D.W.; methodology, S.X.; visualization, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, B.Z., W.W., B.B., Y.L. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Shaanxi Creative Talents Promotion Plan-Technological Innovation Team (2023-CX-TD-37).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Yonggang Zhu, Feng Xiong, Derong Wu, Baoguo Zhao, Wenwu Wang, Biao Bi and Yihang Liu were employed by the company Chengdu Engineering Corporation Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Waring, B.G.; Weintraub, S.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Dlugosz, A.; Dlugosz, J.; Gryta, A.; Frac, M. Responses of N-cycling enzyme activities and functional diversity of soil microorganisms to soil depth, pedogenic processes and cultivated plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Bol, R.; Herre, M.; Marschner, B.; Heinze, S. Catchment scale spatial distribution of soil enzyme activities in a mountainous German coniferous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.S.; Guo, J.F.; Li, Y.Q. Enzyme stoichiometry indicates the variation of microbial nutrient requirements at different soil depths in subtropical forests. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0220599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y. Effects of conservation tillage on soil enzyme activities of global cultivated land: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.B.; Wei, X.R.; Wu, Y.H.; Shao, M.G.; Zhang, Q.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Reich, P.B.; Wei, G.H.; Jiao, S.; et al. Afforestation can lower microbial diversity and functionality in deep soil layers in a semiarid region. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6086–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.Q.; Lin, Z.W.; Penttinen, P.; Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.C.; Luo, Y.; Yue, T.; Jiang, P.K.; Fu, W.J. Effects of conversion from a natural evergreen broadleaf forest to a Moso bamboo plantation on the soil nutrient pools, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a subtropical area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 422, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Xu, Q.; Fan, G.H.; Huang, Y.X.; Zhou, D.W. Response of soil nutrients and stoichiometric ratios to short-term land use conversions in a salt-affected region, northeastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Han, K.X.; Guan, S.C.; Zhou, D.W. Conversion of cropland to forage land and grassland increases soil labile carbon and enzyme activities in northeastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 245, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of Long-Term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Amelung, W.; Lehmann, J.; Kästner, M. Quantitative assessment of microbial necromass contribution to soil organic matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Yang, Y.; Geng, Y.Q.; Huang, G.L.; Cui, X.Q.; Hou, M. Effects of different land types on soil enzyme activity in the Qinghai Lake region. Wetlands 2018, 38, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, P.H.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.L.; Lin, X.W.; Xie, Z.B. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals stronger microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in biochar amendment soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Li, Q.; Guo, Z.Q.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Zhai, J.Y.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient limitation under a natural secondary succession of vegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Q.; Wang, W. Stoichiometry of soil extracellular enzyme activity along a climatic transect in temperate grasslands of northern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Yu, G.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Wang, S.Z.; Wang, R.L.; Zhao, N.; Jia, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the north-south transect in eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.P.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Meng, M.J.; Biswas, S.R.; Ye, L.X.; Zhang, J.C. Effects of land use change on the composition of soil microbial communities in a managed subtropical forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 373, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Xu, Y.M.; Hao, F.H.; Wang, X.; Siyang, C.; Lin, C.Y. Effect of long-term agricultural cultivation and land use conversion on soil nutrient contents in the Sanjiang Plain. Catena 2013, 104, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.S.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K.L. Soil aggregate mediates the impacts of land uses on organic carbon, total nitrogen, and microbial activity in a Karst ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Meng, X.X.Y.; Li, M.S.; Mu, L.Q.; Lei, J.P.; Sui, X. Conversion from natural wetlands to forestland and farmland alters the composition of soil fungal communities in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenius, K.; Rita, H.; Mikkonen, A.; Lappi, K.; Lindstr, M.K.; Hartikainen, H.; Raateland, A.; Niemi, R.M. Effects of land use on the level, variation and spatial structure of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.D.; Gao, D.X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.C.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and nutrient dynamics along a revegetation chronosequence in the soils of abandoned land and Robinia pseudoacacia plantation on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Y.; Hou, W.P.; Liu, J.; Malik, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.L.; Tang, M.; Zhu, R.Q.; Cheng, C.; et al. Effects of different land use types and soil depths on soil mineral elements, soil enzyme activity, and fungal community in karst area of southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Shi, W. Short-term effects of plant litter on the dynamics, amount, and stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity in agroecosystems. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 65, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Liang, C.F.; Shao, S.; Chen, J.H.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q.F. Linkages of litter and soil C: N: P stoichiometry with soil microbial resource limitation and community structure in a subtropical broadleaf forest invaded by Moso bamboo. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Feng, W.; Lai, Z.R.; Fa, K.Y.; Qin, S.G. Metagenomic and 13C tracing evidence for autotrophic atmospheric carbon absorption in a semiarid desert. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; He, Y.Y.; Li, J.H.; Lv, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, M.X.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhang, J.L. Planting halophytes increases the rhizosphere ecosystem multifunctionality via reducing soil salinity. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Mulvaney, C. Nitrogen total. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.; Sommers, L.; Page, A. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties of Phosphorus; ASA Monograph: London, UK, 1982; Volume 9, pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Kong, W.D.; Wang, F.; Long, X.E.; Guo, C.Y.; Yue, L.Y.; Yao, H.Y.; Dong, X.B. Desert and steppe soils exhibit lower autotrophic microbial abundance but higher atmospheric CO2 fixation capacity than meadow soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForest, J.L. The influence of time, storage temperature, and substrate age on potential soil enzyme activity in acidic forest soils using MUB-linked substrates and L-DOPA. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C., N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Weintraub, M.N. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: Informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front. Terr. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moghimian, N.; Hosseini, S.M.; Kooch, Y.; Darki, B.Z. Impacts of changes in land use/cover on soil microbial and enzyme activities. Catena 2017, 157, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, A.; Chen, R.; Cheng, X.L. Afforestation inhibited soil microbial activities along the riparian zone of the upper Yangtze River of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 538, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.M.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Wang, P.; Zhu, B.A.; Cheng, W.X. Rhizosphere priming effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics among tree species with and without intraspecific competition. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weand, M.P.; Arthur, M.A.; Lovett, G.M.; Mcculley, R.L.; Weathers, K.C. Effects of tree species and N additions on forest floor microbial communities and extracellular enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Weintraub, M.N. The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: A theoretical model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranguit, D.; Guillaume, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Land-use change affects phosphorus fractions in highly weathered tropical soils. Catena 2017, 149, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananbeh, H.; Stojanovic, M.; Pompeiano, A.; Voberková, S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Use of soil enzyme activities to assess the recovery of soil functions in abandoned coppice forest systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.L.; Wei, Y.A.; Wang, F.W.; Guo, J.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Hu, S.J. Sensitivity of plant species to warming and altered precipitation dominates the community productivity in a semiarid grassland on the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 7628–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; Starke, R.; Martinovic, T.; Parente, F.M.L.; Orgiazzi, A.; Bastida, F. Distribution of phosphorus cycling genes across land uses and microbial taxonomic groups based on metagenome and genome mining. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 174, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).