Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
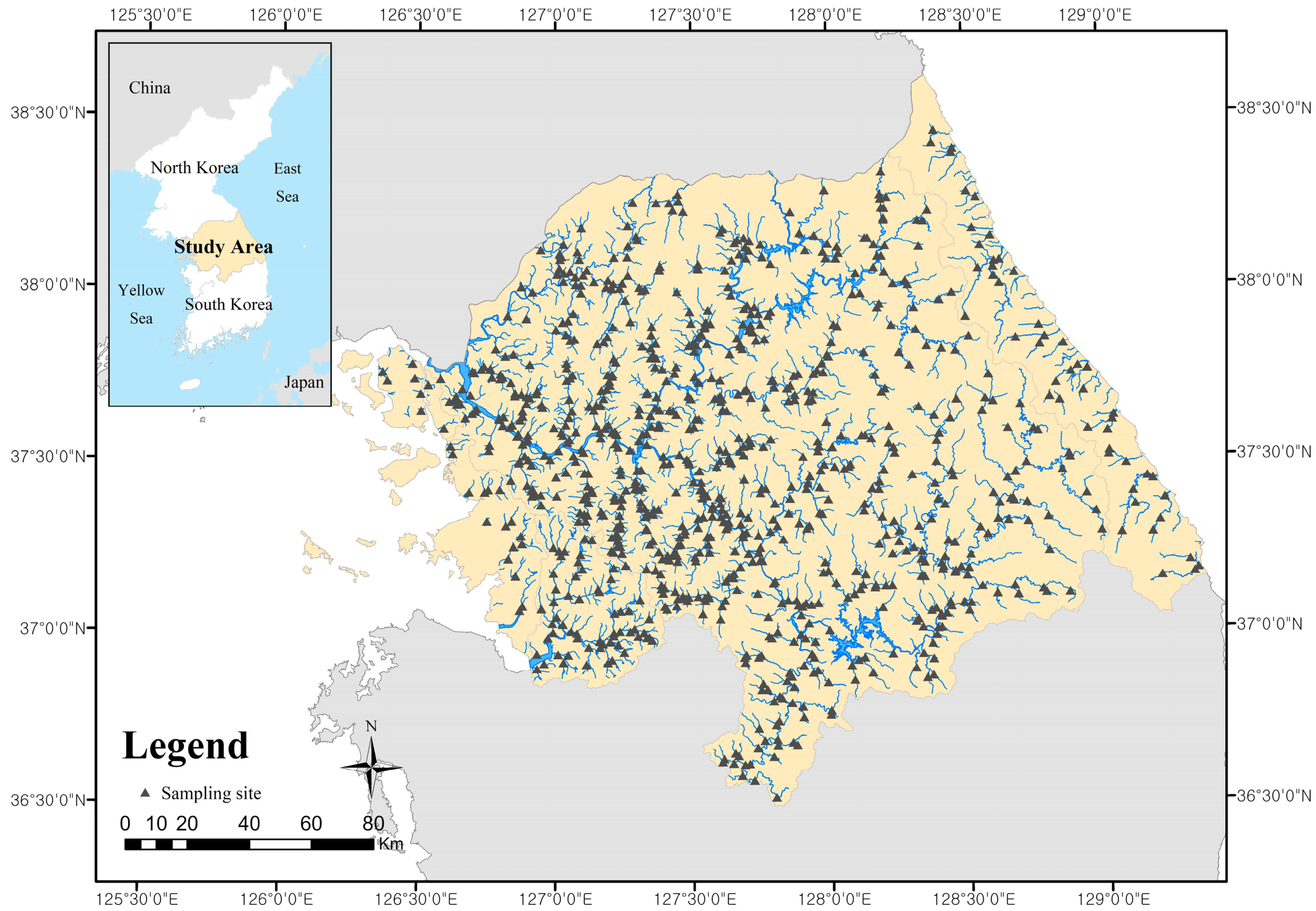
2.1. Study Area
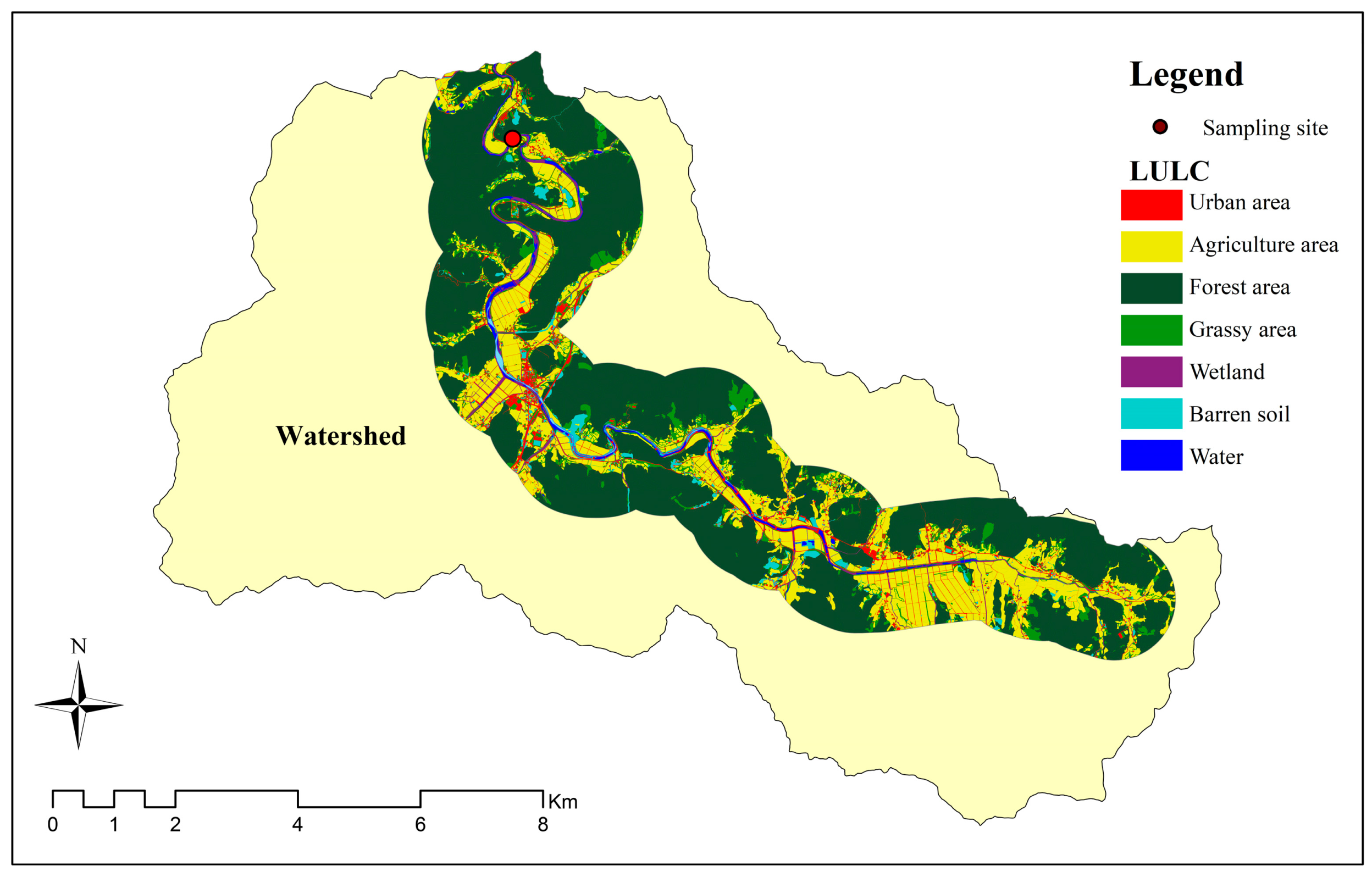
2.2. Stream Monitoring Data and Riparian Zones
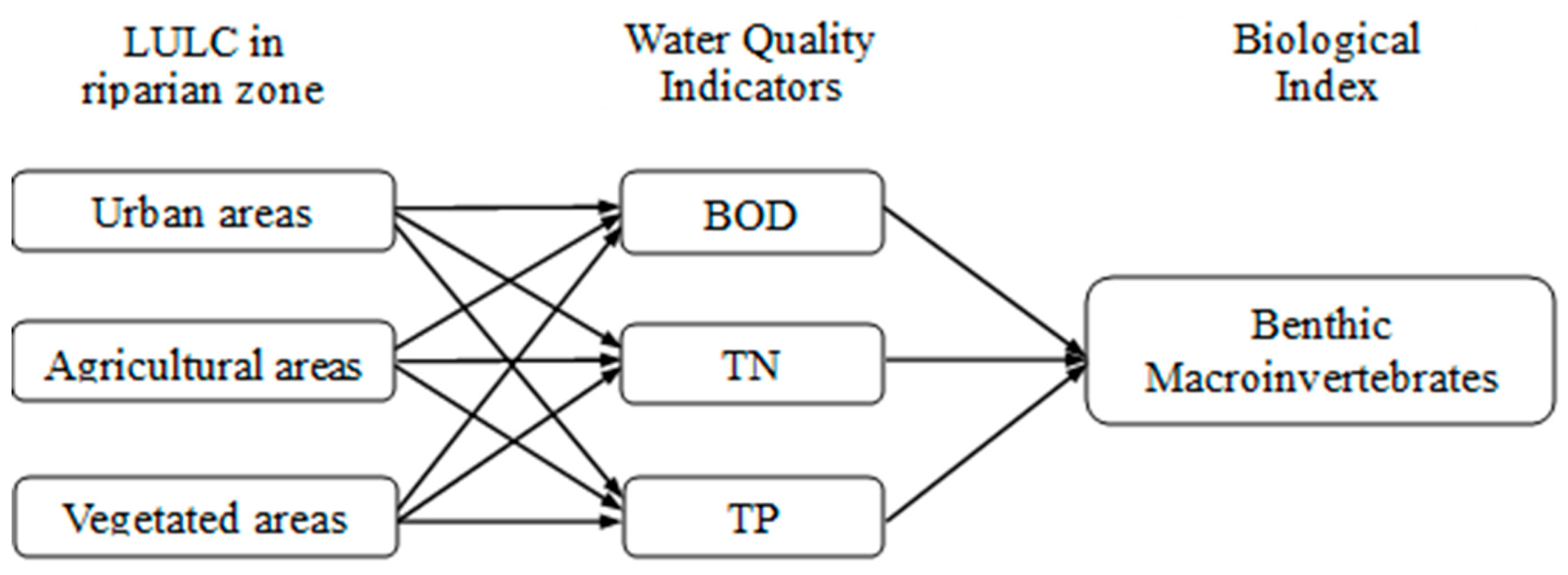
2.3. Estimation of Bayesian Network (BN) Models
2.4. Scenario-Based Analysis of Riparian Zone Management
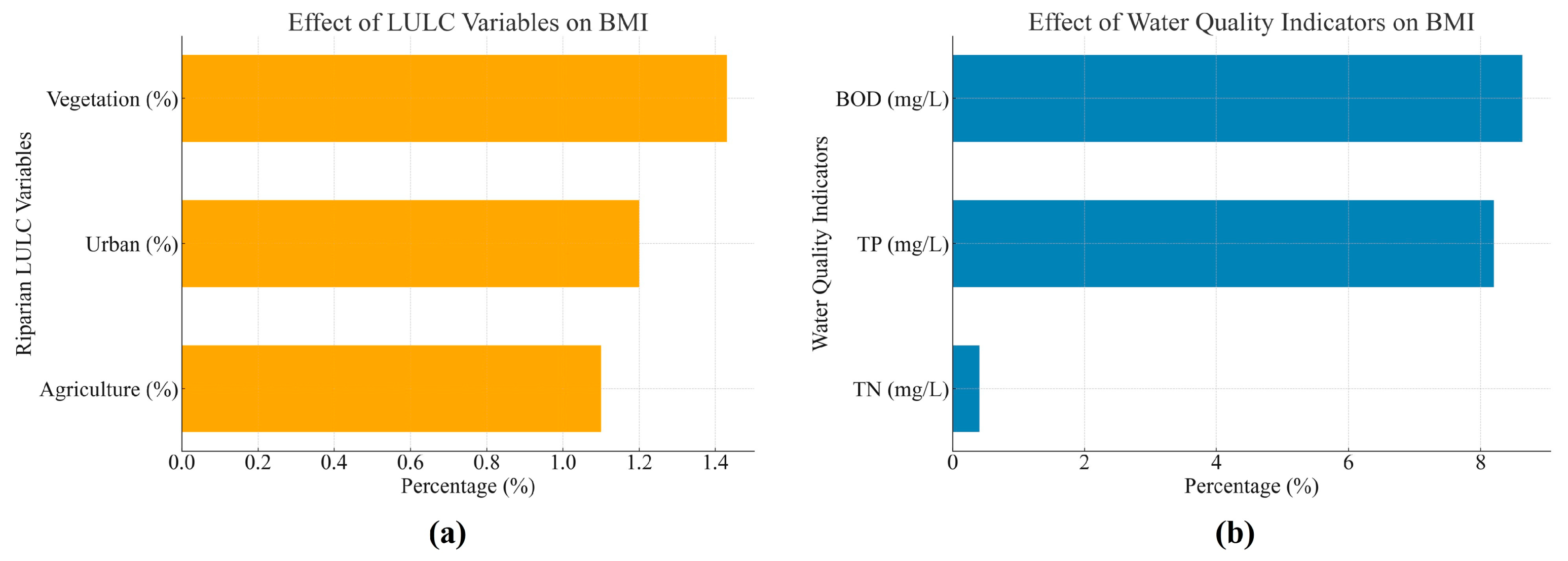
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis and Model Evaluation in BNs
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Estimated Bayesian Network Model and Model Performance
3.3. Scenario Analysis Results: High and Low Riparian Vegetation
3.4. Comparison of Scenario Analysis Results with Current State
3.5. Comparison of Effects of Improving Riparian Vegetation in Urban and Agricultural Areas
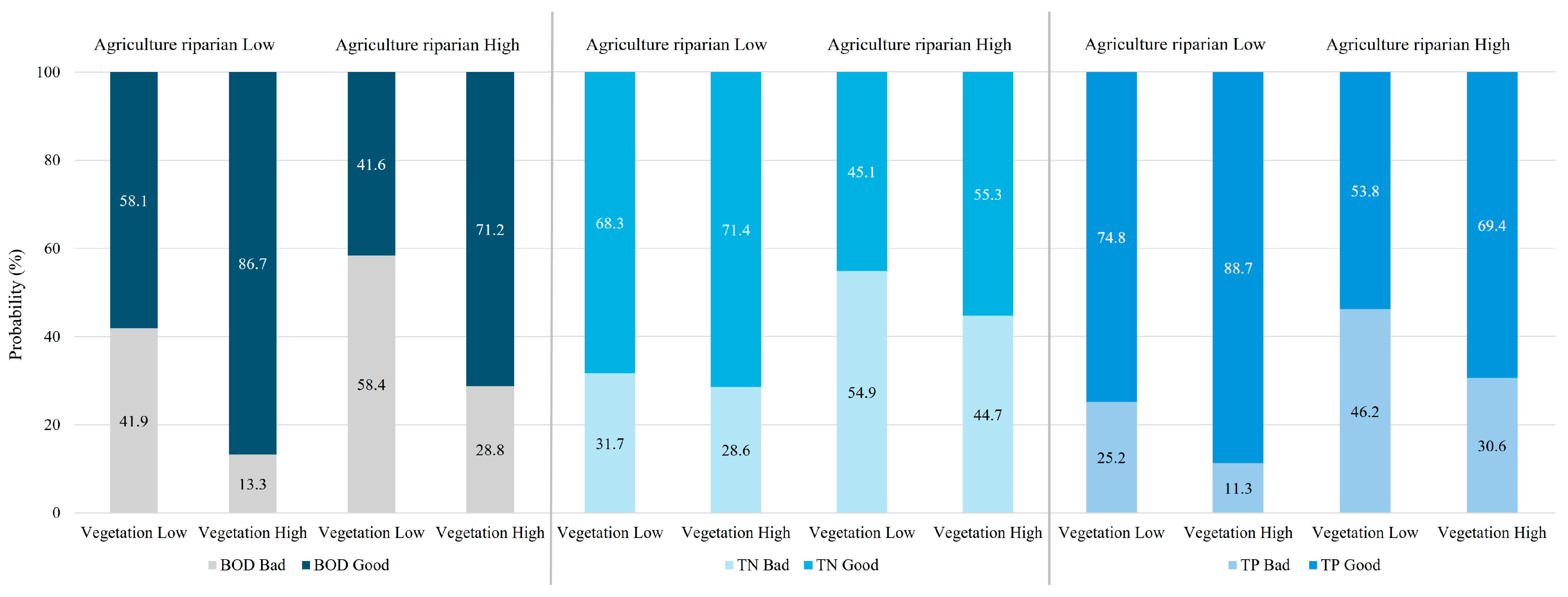
3.6. Effects of Riparian Vegetation on Water Quality Indicators in Urban and Agricultural Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, B.L.; Richardson, W.B.; Naimo, T.J. Past, Present, and Future Concepts in Large River Ecology. Bioscience 1995, 45, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems; Gulf Professional Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; ISBN 0127447601. [Google Scholar]
- Elosegi, A.; Sabater, S. Effects of Hydromorphological Impacts on River Ecosystem Functioning: A Review and Suggestions for Assessing Ecological Impacts. Hydrobiologia 2013, 712, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonansea, M.; Ledesma, C.; Rodriguez, M.C. Assessing the Impact of Land Use and Land Cover on Water Quality in the Watershed of a Reservoir. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2016, 14, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Engel, B.A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Lim, K.J. Forecasting Land Use Change and Its Environmental Impact at a Watershed Scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 76, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological Resilience in Urban Ecosystems: Linking Urban Patterns to Human and Ecological Functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, B.M.; Reis, R.; Vale, M.J.; Saraiva, R. Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Zêzere Watershed (Portugal)—Water Quality Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L. Land Use/Cover Change Impacts on Hydrology in Large River Basins. In Terrestrial Water Cycle and Climate Change; Geophysical Monograph Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 103–134. ISBN 9781118971772. [Google Scholar]
- Näschen, K.; Diekkrüger, B.; Evers, M.; Höllermann, B.; Steinbach, S.; Thonfeld, F. The Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change (LULCC) on Water Resources in a Tropical Catchment in Tanzania under Different Climate Change Scenarios. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, W.D.; Bonta, J.; Thurston, H.; Warnemuende, E.; Smith, D.R. Impacts of Impervious Surface on Watershed Hydrology: A Review. Urban Water J. 2005, 2, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek Uygun, B.; Albek, M. Determination Effects of Impervious Areas on Urban Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2272–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, N.; Claggett, P.; Sample, D.J.; Easton, Z.M.; Yazdi, M.N. Evaluating the Joint Effects of Climate and Land Use Change on Runoff and Pollutant Loading in a Rapidly Developing Watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Sinshaw, T.; Forshay, K.J. Review of Watershed-Scale Water Quality and Nonpoint Source Pollution Models. Geosciences 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Lai, Z.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, J. Critical Source Areas’ Identification for Non-Point Source Pollution Related to Nitrogen and Phosphorus in an Agricultural Watershed Based on SWAT Model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47162–47181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Assessing the Impacts of Land Use on Downstream Water Quality Using a Hydrologically Sensitive Area Concept. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papotto, J.; Rodrigues, L.J.; Siebert, E.M.; Wagner, E.J.; Goldsmith, S.T. Spatial Controls on Riverbed Sediment Chemistry in Three Anthropogenically Modified Tropical Mountainous Watersheds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, B.; Rundle, S. Threats to the Running Water Ecosystems of the World. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, R.A.; Procopio, N.A.; Lathrop, R.G.; Dow, C.L. Relationship of Land-Use/Land-Cover Patterns and Surface-Water Quality in the Mullica River Basin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Liu, W.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q. Water Quality in Relation to Land Use and Land Cover in the Upper Han River Basin, China. Catena 2008, 75, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilawar, A.P.; Waikar, M.L. Use of SWAT to Determine the Effects of Climate and Land Use Changes on Streamflow and Sediment Concentration in the Purna River Basin, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Fan, X.; Gan, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Hydrological Impacts of Land Use/Cover Changes in the Lake Victoria Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Singh, R. From Changing Environment to Changing Extremes: Exploring the Future Streamflow and Associated Uncertainties Through Integrated Modelling System. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1889–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Sale, M.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Poff, N.L. Impacts of Climate Change on Aquatic Ecosystem Functioning and Health. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.A.; Lowe, W.H.; Allendorf, F.W.; Erős, T.; Finn, D.S.; Gillanders, B.M.; Hadwen, W.L.; Harrod, C.; Hermoso, V.; Jennings, S.; et al. Human Effects on Ecological Connectivity in Aquatic Ecosystems: Integrating Scientific Approaches to Support Management and Mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, P.; Esmaeilzadeh, H.; Barghjelveh, S.; Sadeghi, S.M.M.; Marcu, M.V. Habitat Integrity in Protected Areas Threatened by Lulc Changes and Fragmentation: A Case Study in Tehran Province, Iran. Land 2022, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.; Erickson, D.; Fay, J. The Influence of Catchment Land Use on Stream Integrity across Multiple Spatial Scales. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.; Mooney, H.A. The Nature and Value of Ecosystem Services: An Overview Highlighting Hydrologic Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Bourgeois, B.; Boz, B.; Nilsson, C.; Palmer, G.; Sher, A.A. Integrative Conservation of Riparian Zones. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 211, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacchi, E.; Lambs, L.; Guilloy, H.; Planty-Tabacchi, A.-M.; Muller, E.; Décamps, H. Impacts of Riparian Vegetation on Hydrological Processes. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 2959–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palt, M.; Hering, D.; Kail, J. Context-specific Positive Effects of Woody Riparian Vegetation on Aquatic Invertebrates in Rural and Urban Landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkkinen, M.; Vaarala, S.; Aroviita, J. The Importance of Riparian Forest Cover to the Ecological Status of Agricultural Streams in a Nationwide Assessment. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4009–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupilas, B.; Burdon, F.J.; Thaulow, J.; Håll, J.; Mutinova, P.T.; Forio, M.A.E.; Witing, F.; Rîșnoveanu, G.; Goethals, P.; McKie, B.G. Forested Riparian Zones Provide Important Habitat for Fish in Urban Streams. Water 2021, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, N.M.; Pearson, R.G.; Loong, D.; Maughan, M.; Brodie, J. Water Quality Variation along Streams with Similar Agricultural Development but Contrasting Riparian Vegetation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, G.S. Managing Riparian Zones for River Health Improvement: An Integrated Approach. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 17, 195–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, C.; Du, H.; Guo, Y. Responses of Water Quality to Land Use in Riparian Buffers: A Case Study of Huangpu River, China. GeoJournal 2021, 86, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirigui, Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Herman, M.R.; Lee, J.-W. Relationships between Riparian Forest Fragmentation and Biological Indicators of Streams. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. EC Dir. 2000, 23, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Overview of the Clean Water Act; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, C.; Neils, A.; Hooper, D. Impacts of Land Use at the Catchment Scale Constrain the Habitat Benefits of Stream Riparian Buffers. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, P.; Bertrán, C.; Tapia, J.; Hauenstein, E.; Peña-Cortés, F.; Vergara, C.; Cerna, C.; Vargas-Chacoff, L. Effects of Local Land-Use on Riparian Vegetation, Water Quality, and the Functional Organization of Macroinvertebrate Assemblages. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromboni, F.; Dodds, W.K. Relationships Between Land Use and Stream Nutrient Concentrations in a Highly Urbanized Tropical Region of Brazil: Thresholds and Riparian Zones. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserendino, M.L.; Casaux, R.; Archangelsky, M.; Di Prinzio, C.Y.; Brand, C.; Kutschker, A.M. Assessing Land-Use Effects on Water Quality, in-Stream Habitat, Riparian Ecosystems and Biodiversity in Patagonian Northwest Streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, J.S. Developing Flow–Ecology Relationships: Implications of Nonlinear Biological Responses for Water Management. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1305–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Jim, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, M.L.; Liu, C.; Chan, N.W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Impact of Land-Use/Land-Cover and Landscape Pattern on Seasonal in-Stream Water Quality in Small Watersheds. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatially Varying Relationships between Land Use and Water Quality across an Urbanization Gradient Explored by Geographically Weighted Regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, A.R.; Salajegheh, A.; Sadoddin, A.; Allan, M.G. Application of Bayesian Networks for Sustainability Assessment in Catchment Modeling and Management (Case Study: The Hablehrood River Catchment). Ecol. Model. 2013, 268, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.S.; Kennen, J.G.; May, J.; Freeman, M.C.; Cuffney, T.F. Evaluating the Impact of Watershed Development and Climate Change on Stream Ecosystems: A Bayesian Network Modeling Approach. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, K.K.; Cronan, C.S.; Meyer, S.R.; Lilieholm, R.J.; Danielson, T.J.; Tsomides, L.; Owen, D. Predicting Stream Vulnerability to Urbanization Stress with Bayesian Network Models. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 170, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gericke, A.; Nguyen, H.H.; Fischer, P.; Kail, J.; Venohr, M. Deriving a Bayesian Network to Assess the Retention Efficacy of Riparian Buffer Zones. Water 2020, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperotto, A.; Molina, J.L.; Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Marcomini, A. Water Quality Sustainability Evaluation under Uncertainty: A Multi-Scenario Analysis Based on Bayesian Networks. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Han River Basin Water Environment Management Plan (‘16~‘25); Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.; Mishra, R.K.; Sahu, K.C.; Lotliker, A.A.; Panda, U.S.; Mishra, P. Monsoonal Influence and Variability of Water Quality, Phytoplankton Biomass in the Tropical Coastal Waters—A Multivariate Statistical Approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, B.K.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Bhowmik, A.R. Pollution Status and Water Quality Assessment in Pre-Monsoon Season: A Case Study of Rural Villages in Allahabad District, Uttar Pradesh, India. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 32, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.; Marvan, P. Zur Präzisierung der biologischen Klassifikation der Reinheit fließender Gewässer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1961, 57, 389–407. [Google Scholar]
- Won, D.H.; Jun, Y.C.; Kwon, S.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Ahn, K.G.; Lee, J.K. Development of Konan Saprobic Index Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Its Application to Biological Stream Environment Assessment. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2006, 22, 768–783. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Son, S.-H.; Hwang, S.-J.; Won, D.H.; Kim, M.C.; Park, J.H.; Jeon, T.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Development of Benthic Macroinvertebrates Index (BMI) for Biological Assessment on Stream Environment. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Puga, J.L.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Points of Significance: Bayes’ Theorem. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, I. Bayesian Networks. In Encyclopedia of Statistics in Quality and Reliability; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780470061572. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, C.J.; Bradford, J.R.; Bulpitt, A.J.; Westhead, D.R. Inference in Bayesian Networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, J. Bayesian Networks; UCLA Cognitive Systems Laboratory: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, F.V.; Nielsen, T.D. Bayesian Networks and Decision Graphs, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pourhaji, S.; Moattar, M.H. Developing a Pieces of Data Allocation Method in Distributed Databases Using Bayesian Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Congress on Technology, Communication and Knowledge (ICTCK), Mashhad, Iran, 11–12 November 2015; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kersting, K.; Landwehr, N. Scaled Conjugate Gradients for Maximum Likelihood: An Empirical Comparison with the EM Algorithm. In Advances in Bayesian Networks; Gámez, J.A., Moral, S., Salmerón, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 235–254. ISBN 978-3-540-39879-0. [Google Scholar]
- Almond, R.G. An IRT-Based Parameterization for Conditional Probability Tables. In Proceedings of the Twelfth UAI Conference on Bayesian Modeling Applications Workshop, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 6–10 July 2015; CEUR-WS.org: Aachen, Germany, 2015; Volume 1565, pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Biek, R.; Funk, W.C.; Maxell, B.A.; Mills, L.S. What Is Missing in Amphibian Decline Research: Insights from Ecological Sensitivity Analysis. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Liska, R.; Saltelli, A. The Role of Sensitivity Analysis in Ecological Modelling. Ecol. Model. 2007, 203, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenett, R.S. Bayesian Networks: Theory, Applications and Sensitivity Issues. Encycl. Semant. Comput. Robot. Intell. 2017, 1, 1630014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mahadevan, S. Sensitivity Analysis of a Bayesian Network. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part B Mech. Eng. 2018, 4, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskey, K.B. Sensitivity Analysis for Probability Assessments in Bayesian Networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. 1995, 25, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A. Construction and Assessment of Classification Rules; University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Marcot, B.G. Metrics for Evaluating Performance and Uncertainty of Bayesian Network Models. Ecol. Model. 2012, 230, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Newbold, J.D. Streamside Forest Buffer Width Needed to Protect Stream Water Quality, Habitat, and Organisms: A Literature Review. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 560–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds Jr, S.K.; McCutchen, M.D.; Canfield, T.J. Meta-analysis of Nitrogen Removal in Riparian Buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargac, J.; Johnson, R.K.; Burdon, F.J.; Truchy, A.; Rîşnoveanu, G.; Goethals, P.; McKie, B.G. Forested Riparian Buffers Change the Taxonomic and Functional Composition of Stream Invertebrate Communities in Agricultural Catchments. Water 2021, 13, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosskey, M.G.; Vidon, P.; Gurwick, N.P.; Allan, C.J.; Duval, T.P.; Lowrance, R. The Role of Riparian Vegetation in Protecting and Improving Chemical Water Quality in Streams 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Helmers, M.J.; Asbjornsen, H.; Kolka, R.; Tomer, M.D. Perennial Filter Strips Reduce Nitrate Levels in Soil and Shallow Groundwater after Grassland-to-cropland Conversion. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 2006–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrina, M.Z.; Yap, C.K.; Rahim Ismail, A.; Ismail, A.; Tan, S.G. Anthropogenic Impacts on the Distribution and Biodiversity of Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Water Quality of the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Kiesel, J.; Peters, K.; Hering, D.; Sinclair, J.S.; Haase, P. Stream Macroinvertebrate Community Metrics Consistently Respond to a Spatiotemporal Disturbance Gradient but Composition Is More Context-Dependent. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 3133–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Li, X.; Dzakpasu, M.; Ifon, B.E.; Manirakiza, B.; Muyembe, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guadie, A. Nutrient and Sediment Retention by Riparian Vegetated Buffer Strips: Impacts of Buffer Length, Vegetation Type, and Season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 369, 109050. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon, M.S.; An, K.-G. An Influence of Mesohabitat Structures (Pool, Riffle, and Run) and Land-Use Pattern on the Index of Biological Integrity in the Geum River Watershed. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jargal, N.; Kim, J.-E.; Ariunbold, B.; An, K.-G. Ecological River Health Assessments, Based on Fish Ordination Analysis of Ecological Indicator Entities and the Biological Integrity Metrics, Responding to the Chemical Water Pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 28306–28320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, L. Linking Land Use with Riverine Water Quality: A Multi-Spatial Scale Analysis Relating to Various Riparian Strips. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1013318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, A.K.; Schorr, M.S. Correlations of Catchment Landscape Features with Instream Environmental Conditions and Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages in the Lookout Creek System (Tennessee River Drainage). Southeast. Nat. 2023, 22, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

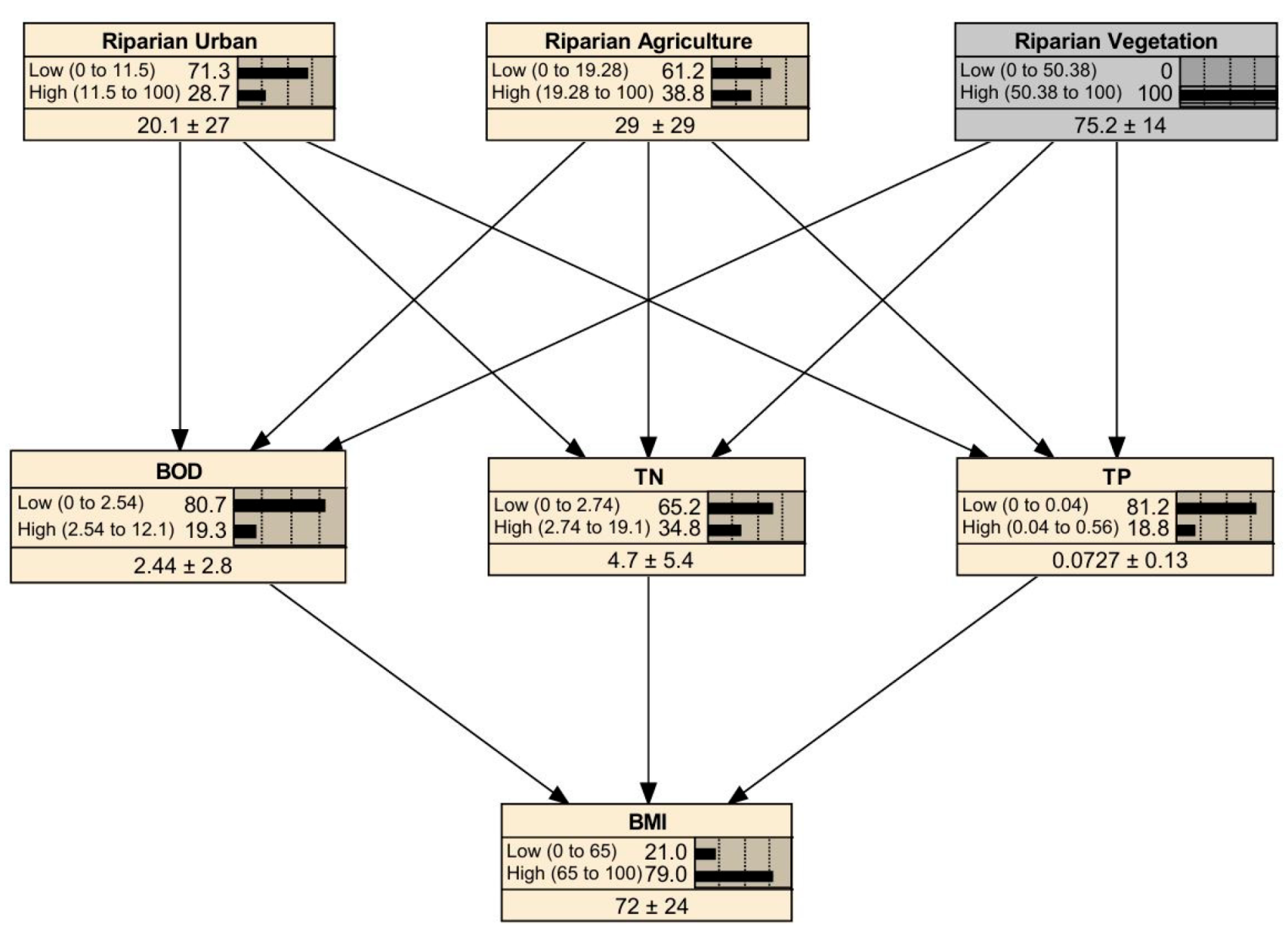
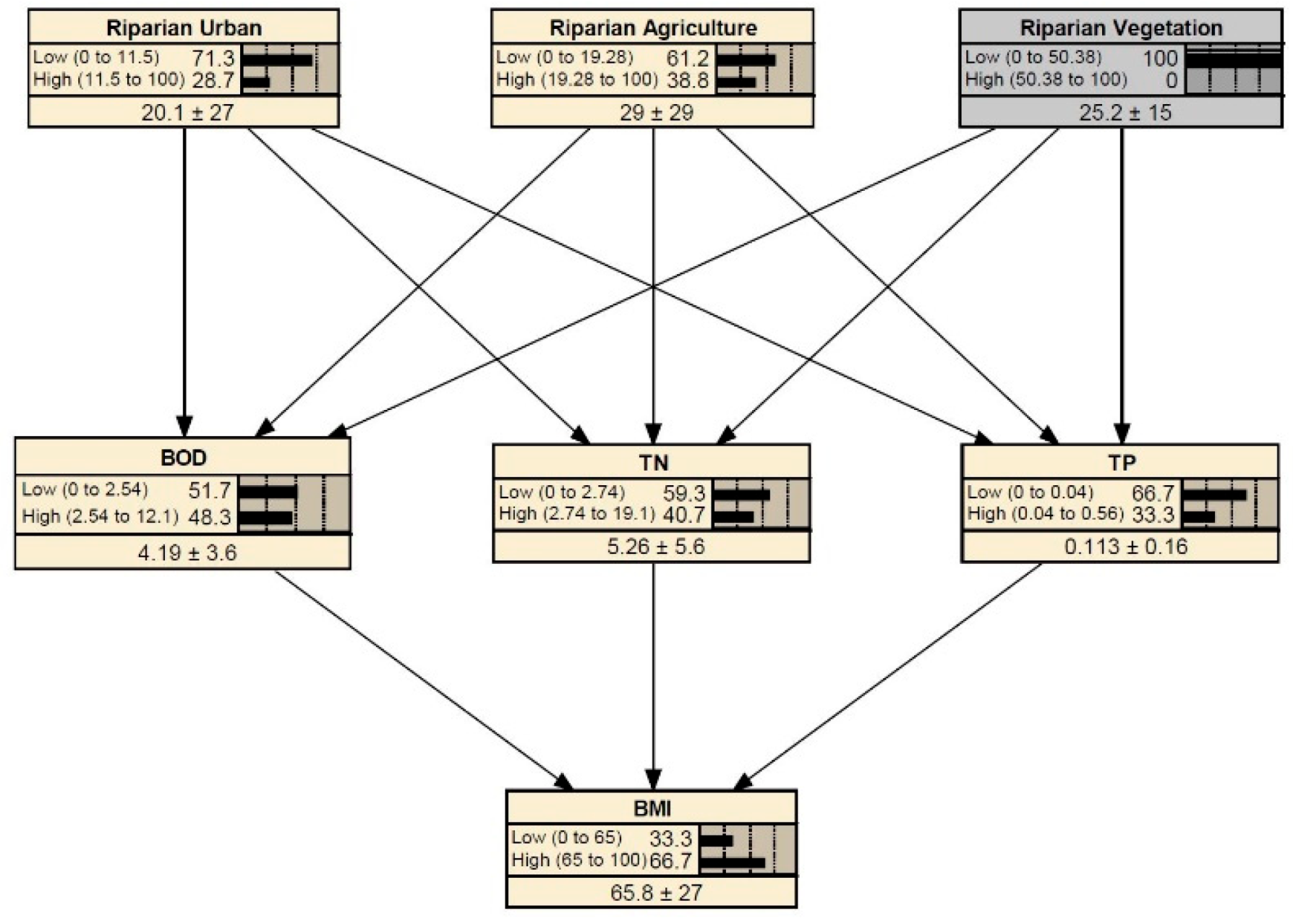
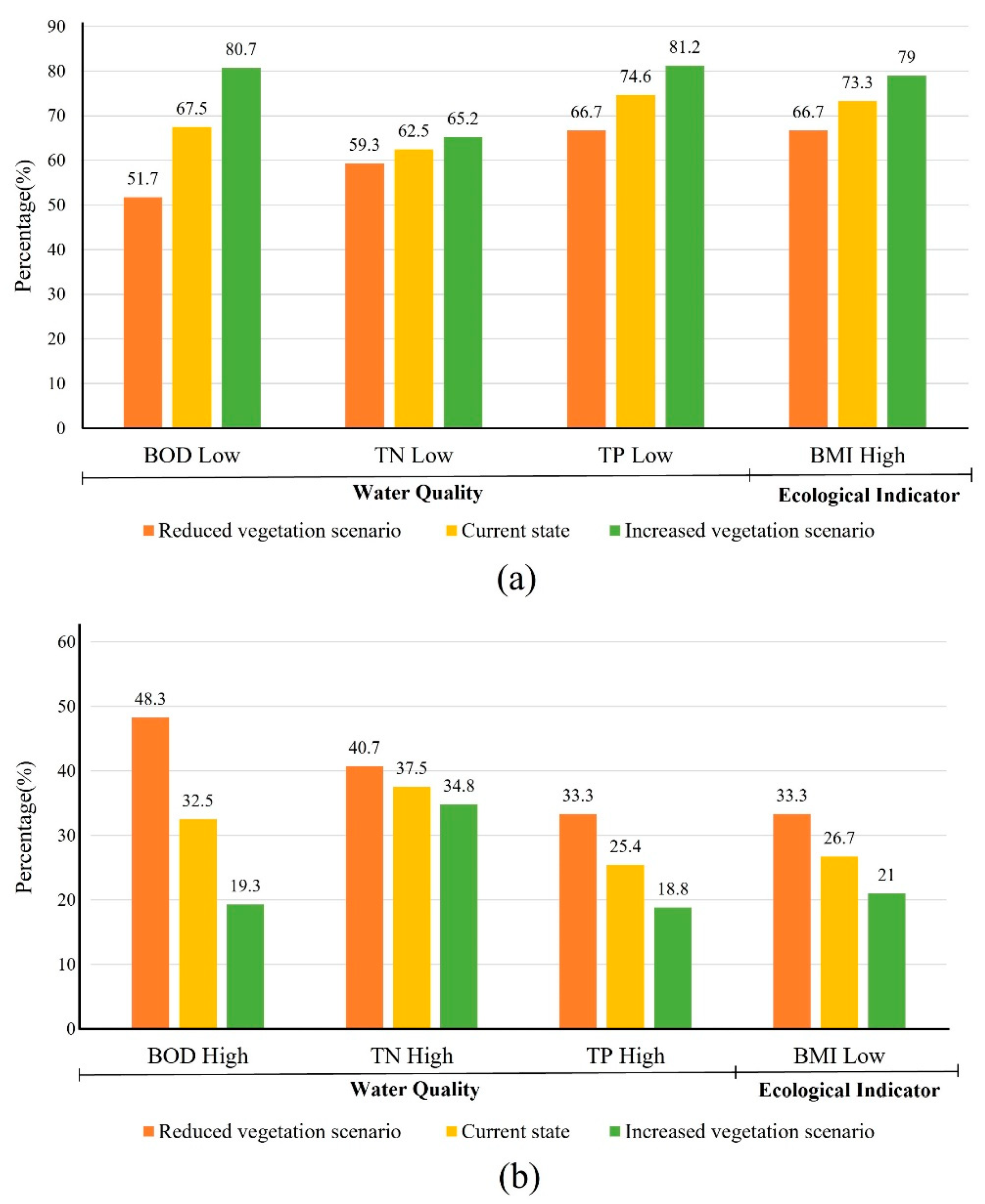
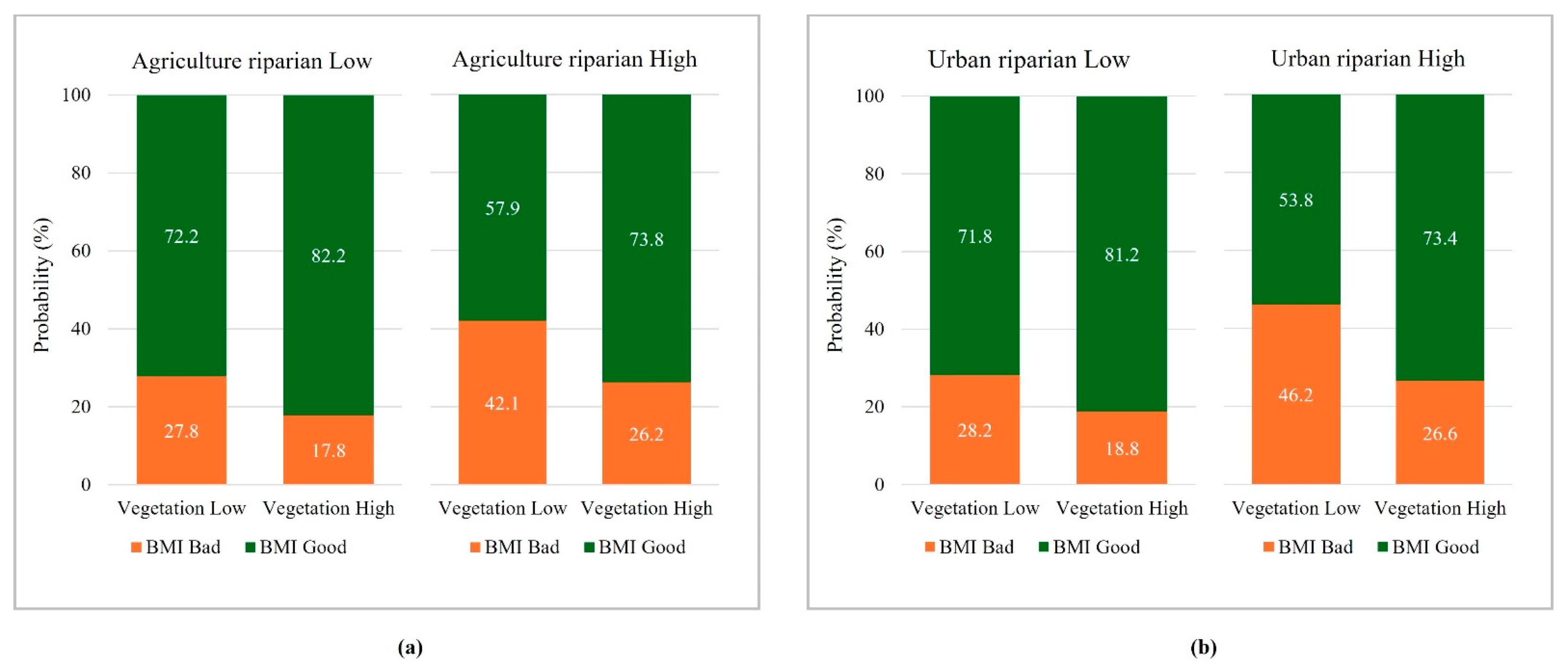

| Classification | Variable | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of Riparian LULC | Urban (%) | 11.50 | 14.57 | 0.19 | 89.43 |
| Agriculture (%) | 19.28 | 15.99 | 0.00 | 83.71 | |
| Vegetation (%) | 50.38 | 25.82 | 0.00 | 96.48 | |
| Water Quality Indicators | BOD (mg/L) | 2.54 | 1.71 | 0.60 | 12.05 |
| TN (mg/L) | 2.74 | 1.89 | 0.16 | 19.09 | |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.56 | |
| Biological Indicators | BMI (0–100) | 70.46 | 21.25 | 15.10 | 97.60 |
| Category | Variable | Discretization Value | Value Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of Riparian LULC | Urban (%) | Low | 0 to 11.5 |
| High | 11.5 to 100 | ||
| Agriculture (%) | Low | 0 to 19.28 | |
| High | 19.28 to 100 | ||
| Vegetation (%) | Low | 0 to 50.38 | |
| High | 50.38 to 100 | ||
| Water Quality Indicators | BOD (mg/L) | Low | 0 to 2.54 |
| High | 2.54 to 12.1 | ||
| TN (mg/L) | Low | 0 to 2.74 | |
| High | 2.74 to 19.1 | ||
| TP (mg/L) | Low | 0 to 0.04 | |
| High | 0.04 to 0.56 | ||
| Biological Indicators | BMI (0–100) | Low | 0 to 65 |
| High | 65 to 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, S.-W.; Park, Y.; Park, S.-R. Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management. Land 2025, 14, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061248
Gu J-Y, Lee J-W, Lee S-W, Park Y, Park S-R. Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management. Land. 2025; 14(6):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061248
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Jeong-Yun, Jong-Won Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Yujin Park, and Se-Rin Park. 2025. "Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management" Land 14, no. 6: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061248
APA StyleGu, J.-Y., Lee, J.-W., Lee, S.-W., Park, Y., & Park, S.-R. (2025). Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management. Land, 14(6), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061248









