Current Status and Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse Research Based on Bibliometric Analysis: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods and Data Sources
2.1. Research Methods
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Data Processing
3. Comprehensive Analysis of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse
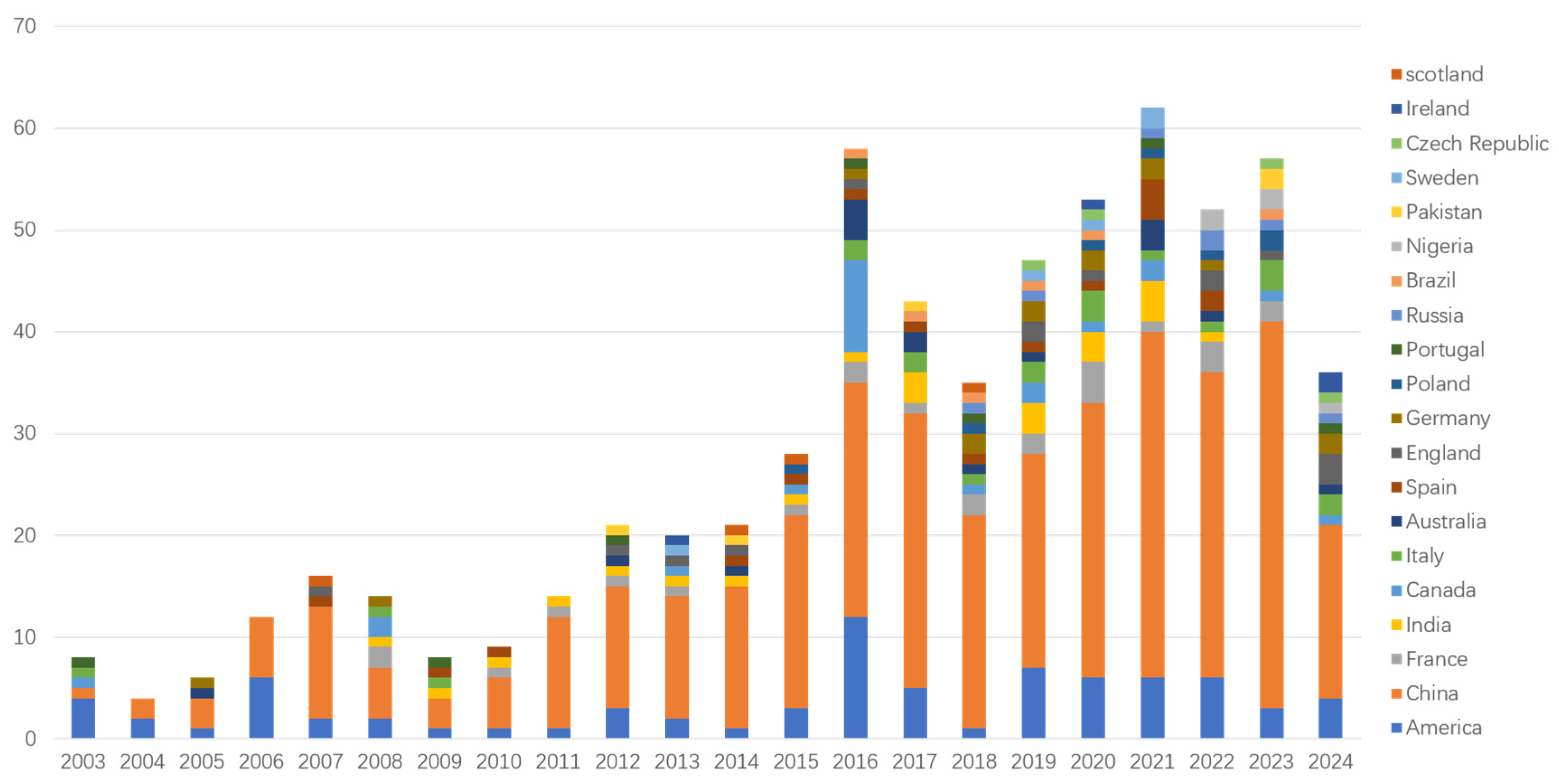
3.1. The Publishing Trends of Publications from Different Countries
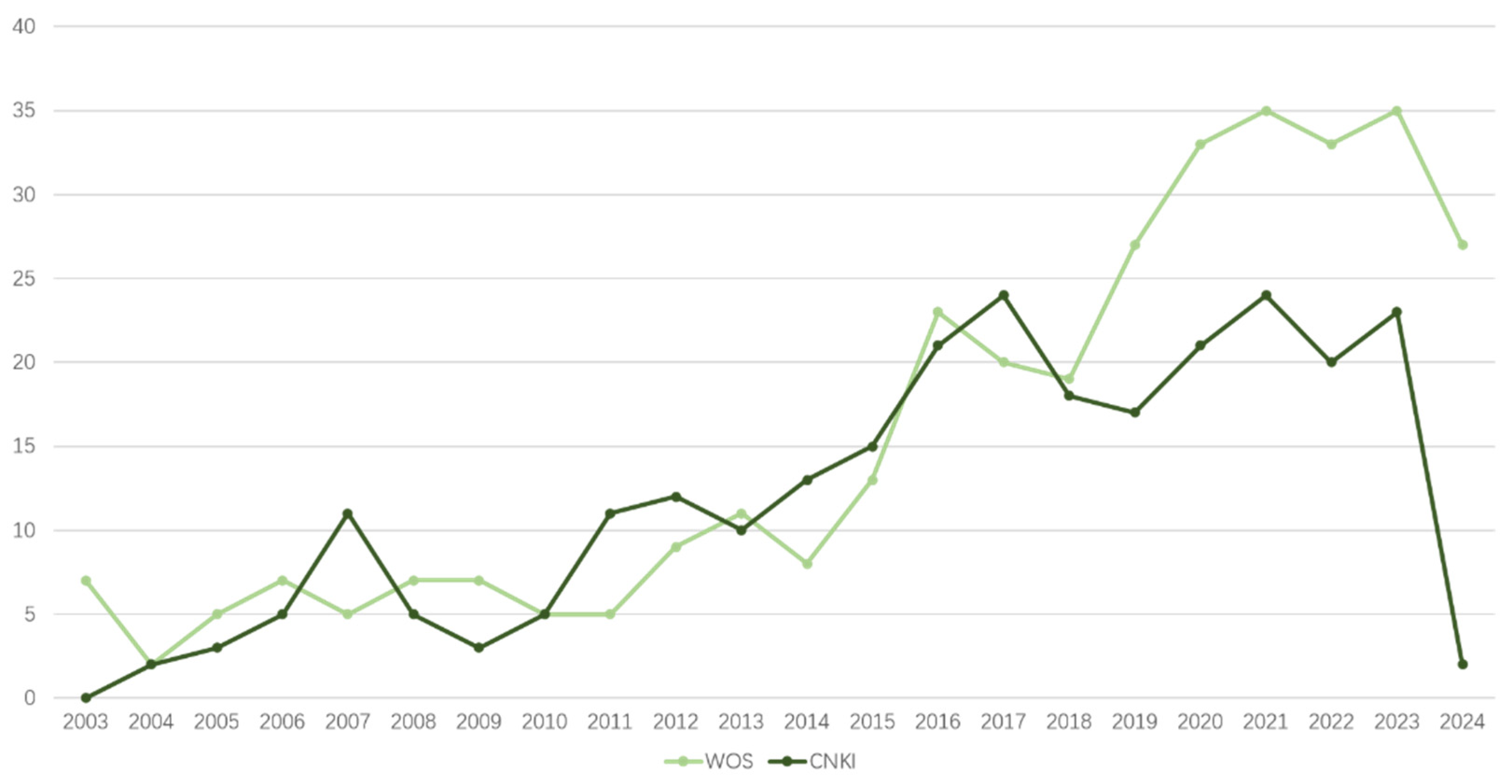
3.2. Research Dynamic Trends Between WOS and CNKI
3.3. Network Characteristics of Cooperative Institutions Between WOS and CNKI
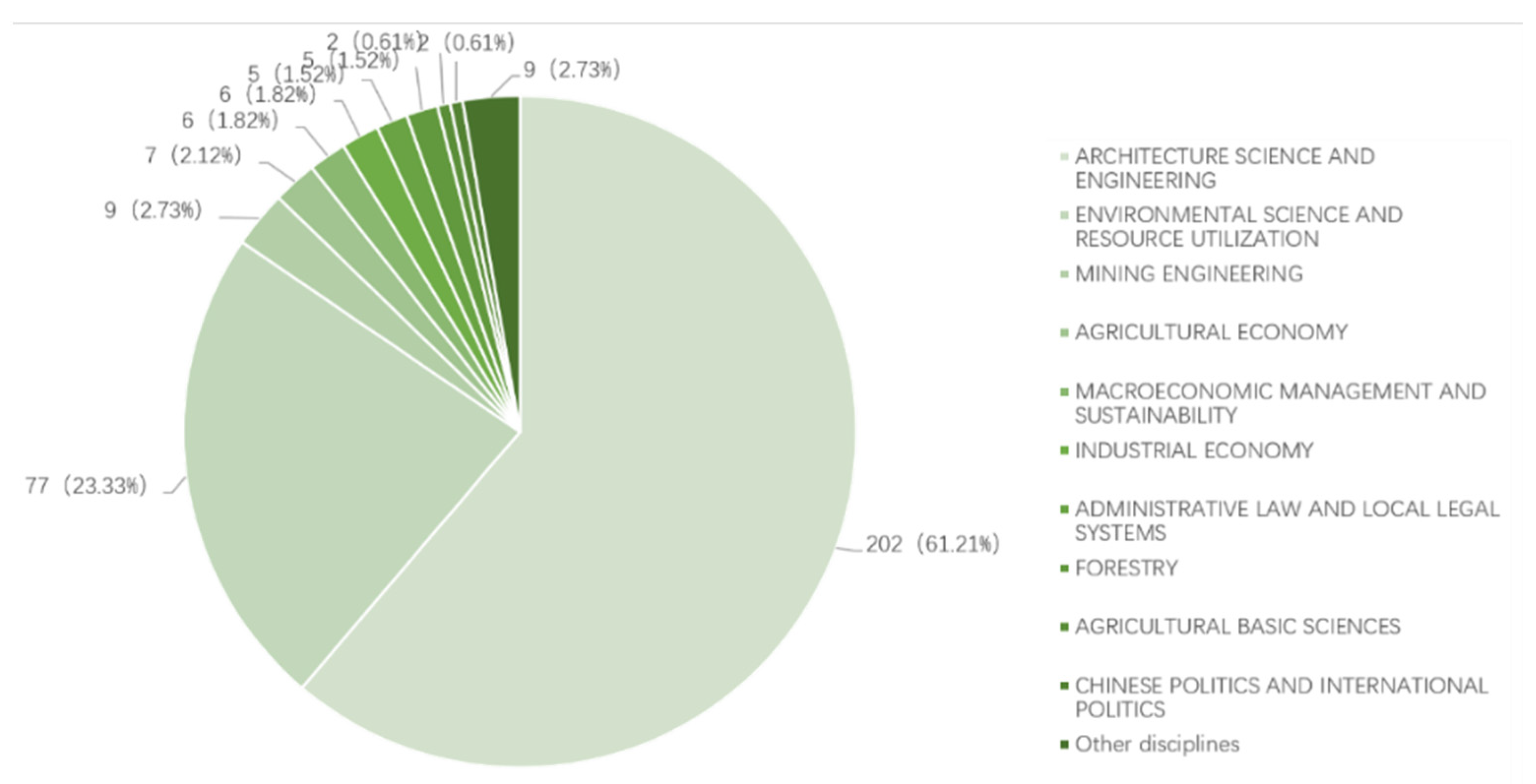
3.4. The Contribution of Different Disciplines in Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse
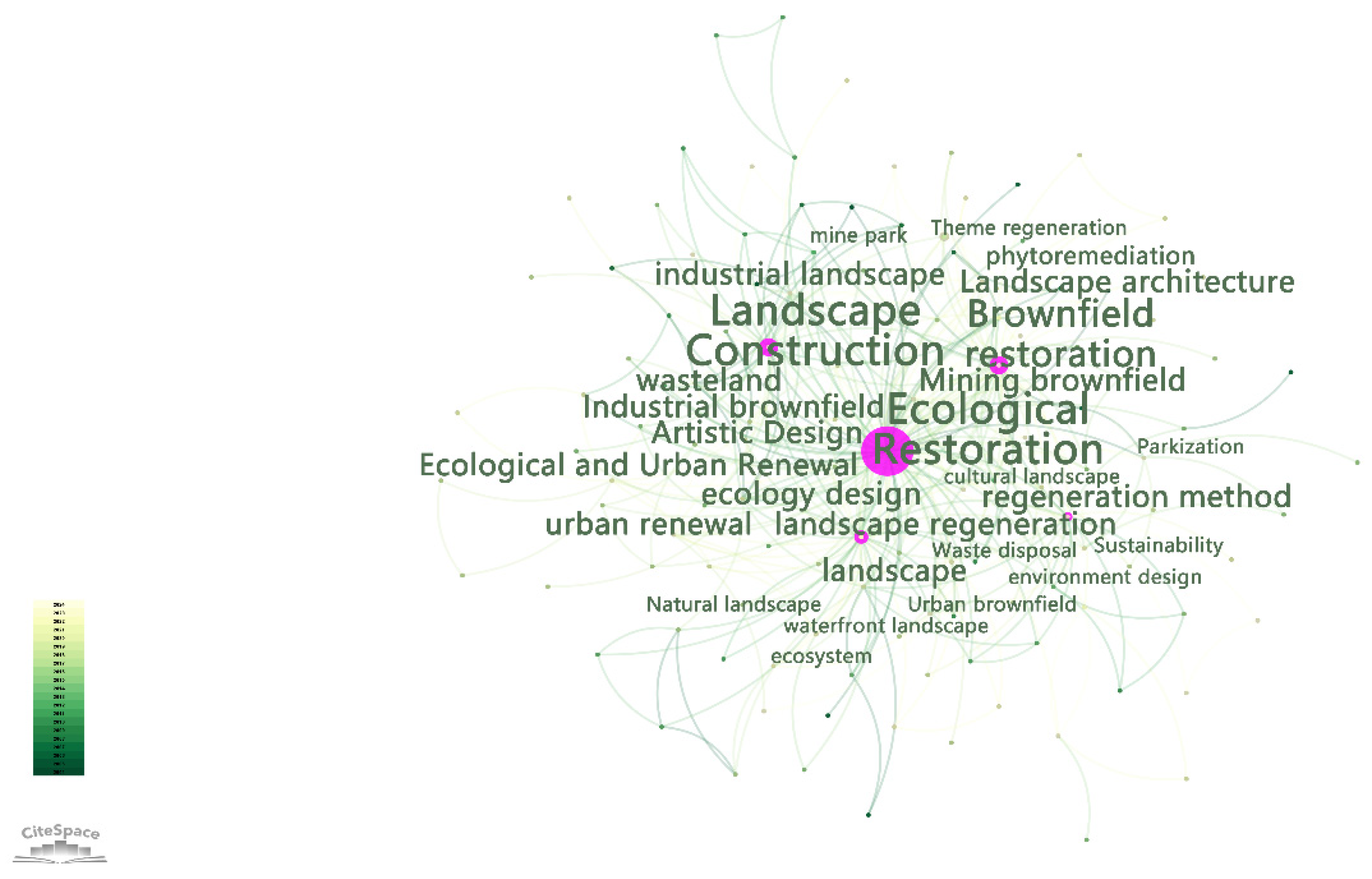
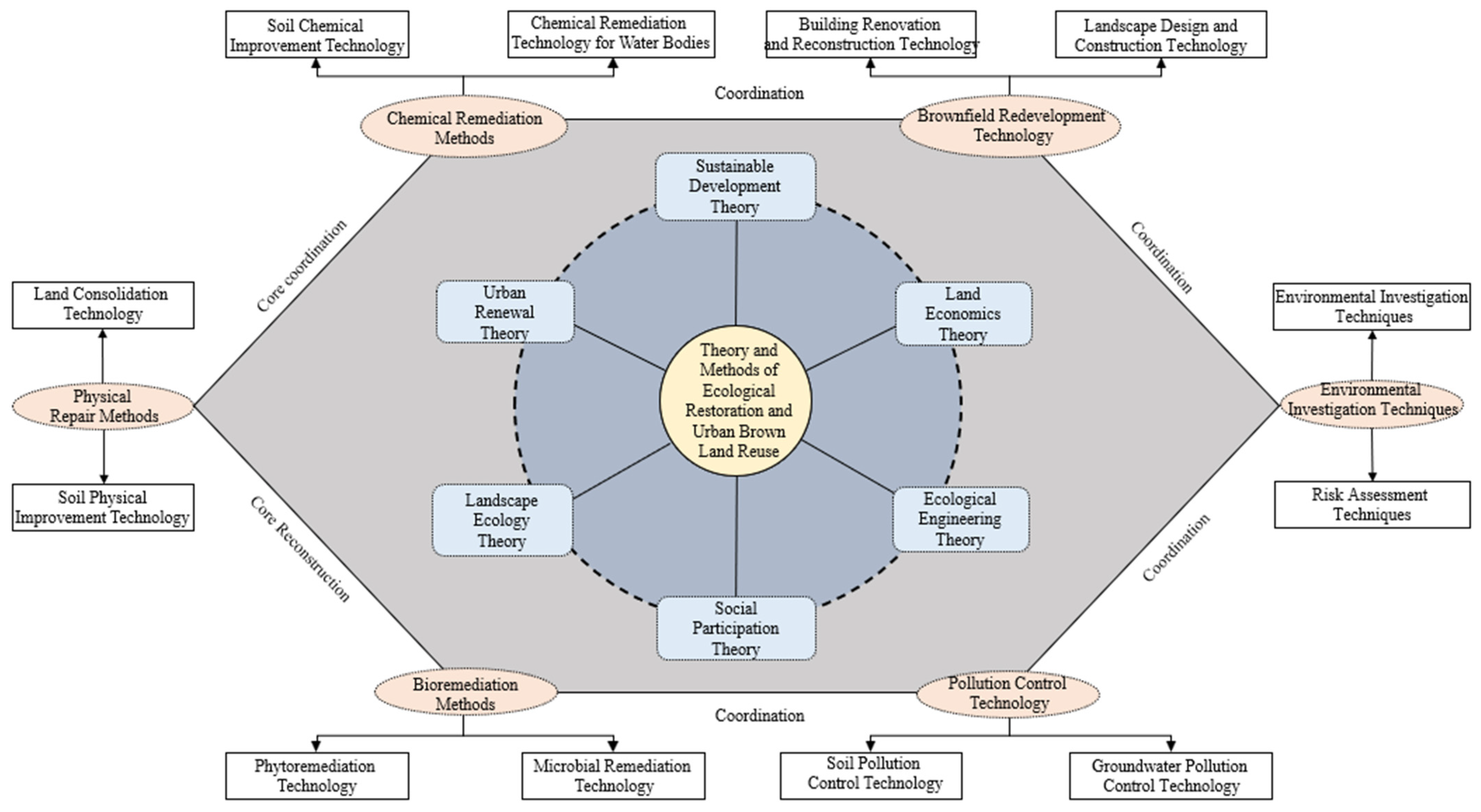
3.5. Analysis of the Main Research Theories and Methods of Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse
3.5.1. Related Theories of Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse
- (1)
- Sustainable Development Theory: Promoting Coordinated Development of Society, Economy, and Ecology
- (2)
- Landscape Ecology Theory: Constructing Organic Landscape Systems
- (3)
- Social Participation Theory: Promoting Diversified Development
- (4)
- Ecological Engineering Theory: Enhancing System Self-Regulation Capability
- (5)
- Land Economics Theory: Optimizing Land Resource Allocation
- (6)
- Urban Renewal Theory: Guiding the Reshaping of Urban Functions
3.5.2. The Main Methods of Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse
- (1)
- Physical Repair Technology: With the Help of Engineering Methods and Technical Equipment, the Short-Term Effect Is Significant
- (2)
- Chemical Remediation Technology: Dispensing Specific Chemical Reagents, Fast, Efficient, and Highly Targeted
- (3)
- Bioremediation Technology: Utilizing Biological Metabolism with Strong Specificity and Environmental Friendliness
- (4)
- Site Investigation and Evaluation Techniques: Collecting Diverse Data and Conducting Risk Assessments
- (5)
- Pollution Control Technology: Cross-Cutting Composite Technology for Soil and Water Treatment
- (6)
- Architectural Renovation and Design Technology: Integration of Planning and Design to Create Distinctive Landscapes
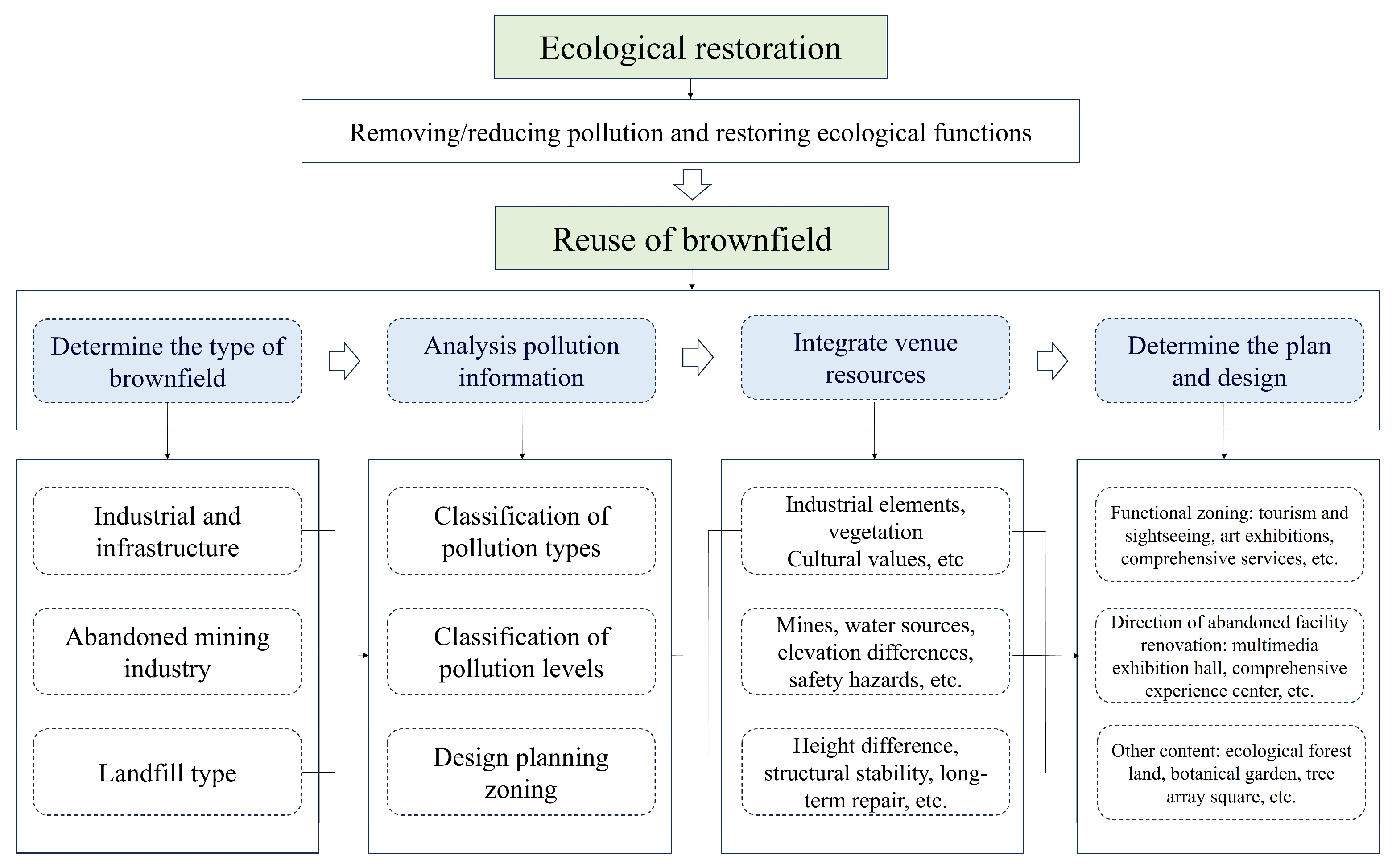
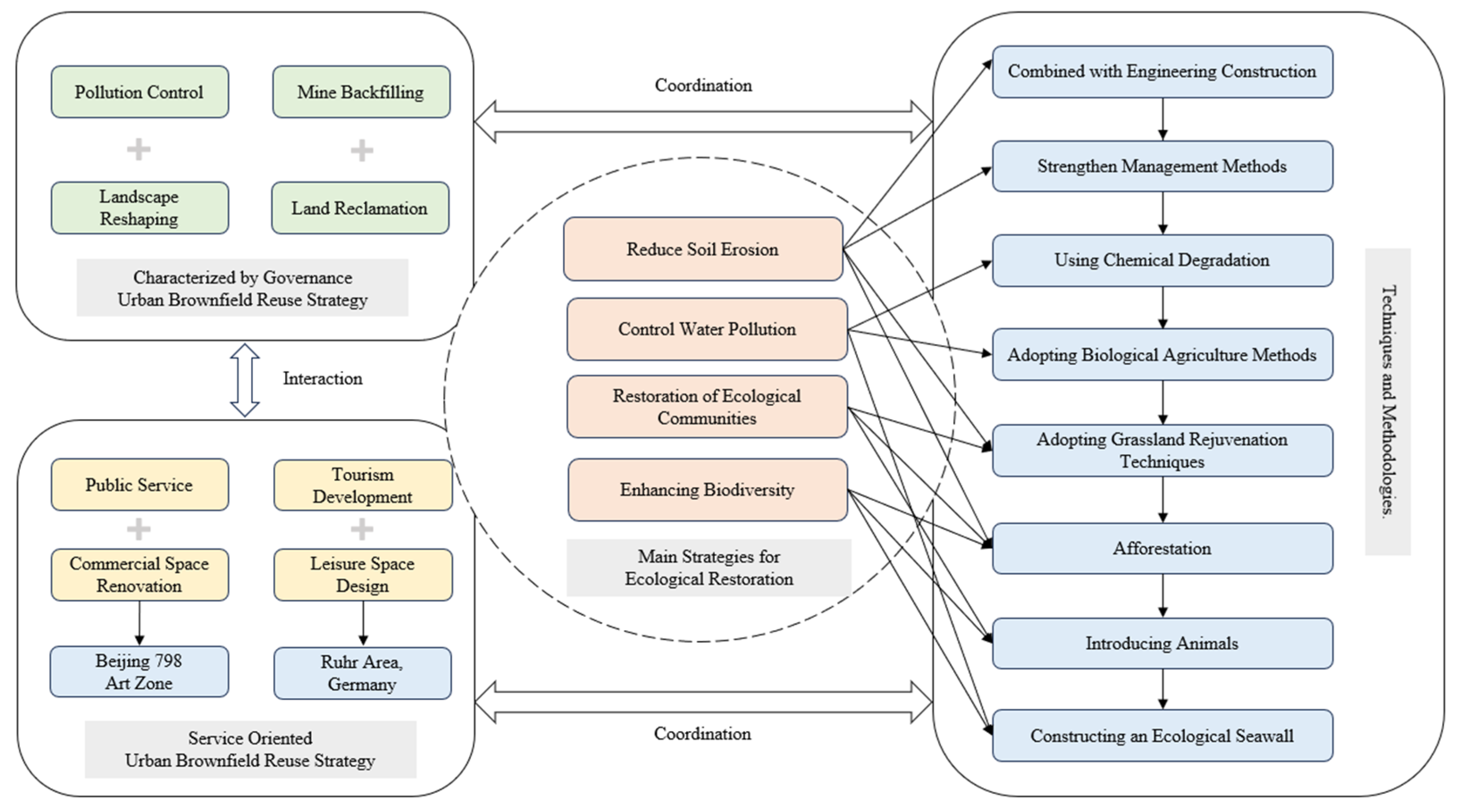
3.6. Main Strategies for Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse in Different Regions
3.6.1. Main Strategies for Ecological Restoration
- (1)
- Combining Engineering Construction and Strengthening Management Methods to Reduce Soil Erosion
- (2)
- Using Chemical Degradation and Biological Agriculture Methods to Treat Water Pollution
- (3)
- Adopting Grassland Rejuvenation Techniques and Afforestation to Restore Ecological Communities
- (4)
- Enhancing Biodiversity Through Animal Introduction and Construction of Ecological Seawalls
3.6.2. The Main Strategies for Urban Brownfield Reuse
- (1)
- Pollution Control and Landscape Reshaping
- (2)
- Mine Backfilling and Land Reclamation
- (3)
- Public Service and Commercial Space Renovation
- (4)
- Tourism Development and Leisure Space Design
4. The Main Challenges and Future Research Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse
4.1. The Main Challenges Currently Facing Ecological Restoration and Urban Brownfield Reuse
4.1.1. Technical Dilemma: Lack of Targeted Ecosystem Reconstruction Technology
4.1.2. Legal Dilemma: Insufficient Policy Support and Imperfect Laws and Regulations
4.1.3. Financial Difficulties: Difficulty in Raising Funds and Lack of Sustained Financial Support
4.1.4. Management Dilemma: Complex Land Ownership and Uneven Distribution of Benefits
4.1.5. Social Dilemma: Insufficient Public Awareness and Poor Channels for Participation
4.2. The Main Strategy of Urban Brownfield Reuse
4.2.1. Multi-Domain Integration: Research on System Coupling and Resilience Enhancement
4.2.2. Digitalization-Driven: Research on Technological Innovation and Combined Applications
4.2.3. Multidisciplinary Intersection: Theoretical Mutual Learning and Technology Integration Research
4.2.4. Multi Subject Co-Construction: Research on Economic Development and Social Governance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, D.C. Forest restoration by direct seeding: A global bibliometric analysis. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.L.; Falk, D.A.; Banin, L.F.; Wagner, M.; Wilson, S.J.; Grabowski, R.C.; Suding, K.N. The intervention continuum in restoration ecology: Rethinking the active–passive dichotomy. Restor. Ecol. 2024, 32, e13535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, A.; Olsson, L.; Cowie, A.; Erb, K.-H.; Hurlbert, M.; Kurz, W.A.; Mirzabaev, A.; Rounsevell, M.D. Restoring degraded lands. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2021, 46, 569–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillson, L.; Dirk, C.; Gell, P. Using long-term data to inform a decision pathway for restoration of ecosystem resilience. Anthropocene 2021, 36, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosini, L.; Folzer, H.; Heckenroth, A.; Prudent, P.; Santonja, M.; Farnet, A.-M.; Salducci, M.-D.; Vassalo, L.; Labrousse, Y.; Oursel, B.; et al. Gain in biodiversity but not in phytostabilization after 3 years of ecological restoration of contaminated Mediterranean soils. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 157, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Fauk, T.; Mihai, F.C. Reclaiming Urban Brownfields and Industrial Areas–Potentials for Agroecology. In Agroecological Approaches for Sustainable Soil Management; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 409–436. [Google Scholar]
- Klaus, V.H.; Kiehl, K. A conceptual framework for urban ecological restoration and rehabilitation. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 52, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, C.; Carroll, A.M.M.; Whitehead, S.; Berman, L.; Coffin, S.; Heberle, L.; Hettiarachchi, G.; Martin, S.; Sullivan, K.; Van Der Kloot, J. A review of brownfields revitalisation and reuse research in the US over three decades. Local Environ. 2023, 28, 1629–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, C.; Rafael, C.H. What factors guide the recent Spanish model for the disposal of military land in the neoliberal era? Land Use Policy 2023, 134, 106911. [Google Scholar]
- Jevremović, L.; Stanojević, A.; Đorđević, I.; Turnšek, B. The redevelopment of military barracks between discourses of urban development and heritage protection: The case study of Niš, Serbia. Spatium 2021, 46, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, W.A. Executive framework of sustainable brownfield redevelopment, Applying to the cities of Al-Mahalla al-Kubra and Kafr al-Zayat. MSA Eng. J. 2024, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Kosson, D.S.; Brown, K.G.; Salisbury, J.; Jeitner, C. A paradigm for protecting ecological resources following remediation as a function of future land use designations: A case study for the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, A.B.; Reinfelder, J.R.; Gallagher, F.J.; Grabosky, J.C. Long-term Stability of Trace Element Concentrations in a Spontaneously Vegetated Urban Brownfield with Anthropogenic Soils. Soil Sci. 2017, 182, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Dong, J. Research on ecological restoration and its impact on society in coal resource-based areas: Lessons from the Ruhr area in Germany and the Liulin area in China. Geoforum 2024, 154, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiero, M.; Biasin, A.; Amato, G.; Malaggi, F.; Pettenella, D.; Nastasio, P.; Anelli, S. Urban forests and green areas as nature-based solutions for brownfield redevelopment: A case study from Brescia Municipal Area (Italy). Forests 2022, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacek, G.; Rozan, A.; Combroux, I. Are Mechanical and Biological Techniques Efficient in Restoring Soil and Associated Biodiversity in a Brownfield Site? Land 2022, 11, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, W.; Ghufran, B.; Abbas, M. Ecological footprint: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.B.; Agbozo, E.; Aboagye, E.M.; Effah, N.A.A. Investigating the research trends on the determinants of Environmental degradation: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 7775–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Qian, S. Exploring research trends and building a multidisciplinary framework related to brownfield: A visual analysis using citespace. Complexity 2021, 2021, 8882415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Bai, C.Q.; Liang, L.W.; Zhao, Z.C.; Song, W.X.; Zhang, Y. The evolution and frontier development of land ecological restoration research. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, W.; Liu, T.; Dai, L.; Wu, L.; Miao, H.; Yang, C. A bibliometric analysis of the impact of ecological restoration on carbon sequestration in ecosystems. Forests 2023, 14, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cooperative Movement as a Model of Ecological Equilibrium. Available online: https://www.fao.org/newsroom/story/Now-is-the-time-to-restore-our-ecosystems!/en (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- EPA Brownfields Report. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/remedytech/directory-technology-support-services-brownfields-localities (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Eagles, P.F.J. The Institutional Arrangements for Environmentally Sensitive Area Planning and Management in Ontario. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/norwood/comprehensive-environmental-response-compensation-and-liability-act-cercla (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- He, W. Study of Post-Industrial Landscape. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.H. Ecological restoration of mine degraded soils, with emphasis on metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.C.; Singh, K.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, B. Naturally growing Saccharum munja L. on the fly ash lagoons: A potential ecological engineer for the revegetation and stabilization. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus, P.; Clements, W.H.; Williamson, J.L.; Ranville, J.F.; Meyer, J.S.; Ginés, M.J.G. The Use of Field and Mesocosm Experiments to Quantify Effects of Physical and Chemical Stressors in Mining-Contaminated Streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7825–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit-Berghem, Y.; Rémy, É.; Canavese, M. Renaturation and ecosystem services of contaminated urban wastelands in France. In Urban Wastelands: A Form of Urban Nature? Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 243–264. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, E.; Laprise, M.; Lufkin, S. Neighbourhoods in Transition: Brownfield Regeneration in European Metropolitan Areas; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Laffont-Schwob, I.; Rabier, J.; Masotti, V.; Folzer, H.; Tosini, L.; Vassalo, L.; Salducci, M.-D.; Prudent, P. Functional Trait-Based Screening of Zn-Pb Tolerant Wild Plant Species at an Abandoned Mine Site in Gard (France) for Rehabilitation of Mediterranean Metal-Contaminated Soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, I.B.; Romero-Martínez, M.L.; Cavaliere, M.; Varrella, S.; Francescangeli, F.; Piredda, R.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Schirone, A.; Delbono, I.; et al. Encapsulated in sediments: eDNA deciphers the ecosystem history of one of the most polluted European marine sites. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Duan, W.; Zheng, X. Post-occupancy evaluation of brownfield reuse based on sustainable development: The case of Beijing Shougang Park. Buildings 2023, 13, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Das, A.P. Lead pollution: Impact on environment and human health and approach for a sustainable solution. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, J.; Chen, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Long, Y.; Zhu, M. Disturbance and restoration of soil microbial communities after in-situ thermal desorption in a chlorinated hydrocarbon contaminated site. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, A.; Kellett, J.; Palazzo, E.; Larbi, M. Policy integration for brownfield regeneration: An analytical tool. Sustain. Horiz. 2024, 10, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, M.R.; Russo, A.; Sica, F. Opinion paper on green deal for the urban regeneration of industrial brownfield land in Europe. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y. 2016 International Conference on Brownfields Regeneration and Ecological Restoration Held in Tsinghua University. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2016, 32, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko, L.; Muratova, A.; Dubrovskaya, E.; Golubev, S.; Turkovskaya, O. Dynamics of natural revegetation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soil and remediation potential of indigenous plant species in the steppe zone of the southern Volga Uplands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3260–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; Yan, Q.; Bian, Z.; Lu, Q. Landscape ecological network construction controlling surface coal mining effect on landscape ecology: A case study of a mining city in semi-arid steppe. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupar, S. Brownfields as waste/race governance: US contaminated property redevelopment and racial capitalism. In The Routledge Handbook of Waste Studies; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; pp. 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Morar, C. Achieving Sustainability in Ukraine through Military Brownfields Redevelopment; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.H. Research on the Planning and Design of Country Parks with the Regeneration of Industrial Brownfield—A Case Study of West Lake Country Park. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y. A Study on Planning and Design of Landscape Reconstruction in Industrial Waste Land—A Case Study of Wugang City. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Brown, K.G.; Ng, K.; Cortes, M.; Kosson, D. The importance of recognizing Buffer Zones to lands being developed, restored, or remediated: On planning for protection of ecological resources. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2024, 87, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M.; Bunn, A.; Looney, B.; Jeitner, C. Role of uncertainties in protecting ecological resources during remediation and restoration. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2021, 84, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, A.; Fievet, V.; Oustriere, N.; Epelde, L.; Garbisu, C.; Becerril, J.M.; Mench, M. Long-term phyto management with compost and a sunflower—Tobacco rotation influences the structural microbial diversity of a Cu-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, S.Q. Study on classic examples of Textile industry heritage conservation and regeneration--Boot Factory, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA. City Plan. J. 2021, 45, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.X.; Shi, F.; Cao, Y. Construction and evaluation of ecological security pattern of mining brownfield park. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2017, 49, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.D.; Fu, Q.C.; Wu, X. Spatial Pattern of “City-Brown-Green” in Resource-Exhausted Cities: A Case Study of Huangshi City, Hubei Province. Landsc. Archit. 2021, 28, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y. Approaches to Ecological Restoration and Landscape Renewal of Industrial Wasteland. City 2005, 4, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Meng, C.L. Taking Xiangfan Cement Factory as an Example to Discuss the Transformation and Reuse of Industrial Abandoned Land. J. Xiangfan Univ. 2012, 33, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Tian, H.Y. Regeneration Planning and Design of Industrial Abandoned Land in Changchun City under the Revival of Silk Road Cities. Low Temp. Build. Technol. 2019, 41, 28–31+40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.S. Research on the Theory and Planning of Ecological Restoration of Mining Sites Guided by Urban GI: A Case Study of Xuzhou City. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, X.K. Experience and Implications of Brownfield Ecological Restoration in Woolston Urban Ecological Park. Agric. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2013, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, F.Q.; Liu, K.Y.; Li, Q. The Regeneration of Urban Landscape after Desolation: A Case Study of the 798 Art District in Beijing. Art Educ. Res. 2021, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Di, J. Research on Landscape Transformation of Industrial Wasteland in Northeast China Based on Urban Dual Renovation. Master’s Thesis, Changchun University of Technology, Changchun, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raklami, A.; Meddich, A.; Pajuelo, E.; Marschner, B.; Heinze, S.; Oufdou, K. Combined application of marble waste and beneficial microorganisms: Toward a cost-effective approach for restoration of heavy metals contaminated sites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45683–45697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Karwadiya, J.; Srivastava, S.; Patra, P.K.; Venugopalan, V.P. Potential of indigenous plant species for phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated water and soil. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Landry, M.P.; Moore, A.; Coreas, R. The protein corona from nanomedicine to environmental science. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.S. Study on Landscape Regeneration of Chemical Brownfield in Small and Medium Sized Cities Based on the Concept of “Micro Renewal”—A Case Study of Baoding No.2 Chemical Plant. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.-L.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Chan, T.-S.; Zhang, L.-L.; Tsang, D.C.; Li, X.-D. Spatial distribution and molecular speciation of copper in indigenous plants from contaminated mine sites: Implication for phytostabilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frewert, A.; Trippe, K.; Cheeke, T.E. Can locally sourced inoculum and biochar synergistically improve the establishment of mycorrhizal fungi in mine tailings? Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Środek, D.; Rahmonov, O. The properties of black locust Robinia pseudoacacia L. to selectively accumulate chemical elements from soils of ecologically transformed areas. Forests 2021, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, M.; Latif, S.; Hameed, A.; Kanwal, Q.; Iqbal, D.N. Assessment of potentially toxic metal(loid)s contamination in soil near the industrial landfill and impact on human health: An evaluation of risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4353–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, T.; Pandey, V.C.; Praveen, A.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, N.; Singh, D.P. Phytoremediation ability of naturally growing plant species on the electroplating wastewater-contaminated site. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4101–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Huang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Shrestha, A.; Yuan, C.; Anand, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, G. Conservation and management of protected areas in China and India: A literature review (1990–2021). Climate 2023, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, J. Application for ecological restoration of contaminated soil: Phytoremediation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Chu, Z.; Xia, T.; Zheng, B. Application of ecological restoration technologies for the improvement of biodiversity and ecosystem in the river. Water 2022, 14, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, H. Effects of landscape restoration on migration of lead and cadmium at an abandoned mine site. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1057961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Shirakura, F.; Mallory, F.F. Woody plant communities after 40 years of pollution control and restoration in smelter-denuded landscapes. Northeast. Nat. 2022, 29, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, D.; Disante, K.B.; Valdecantos, A.; Cortina, J.; Vallejo, V.R. Sensitivity of Mediterranean woody seedlings to copper, nickel and zinc. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.Y. Research on Landscape Redesign of Industrial Wasteland Based on Land Art. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.W. Research on Landscape Reconstruction Design of Urban Industrial Wasteland Under the Background of “Regional Culture”. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tajani, F.; Morano, P.; Di Liddo, F. Redevelopment initiatives on brownfield sites: An evaluation model for the definition of sustainable investments. Buildings 2023, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washbourne, C.-L.; Goddard, M.A.; Le Provost, G.; Manning, D.A.; Manning, P. Trade-offs and synergies in the ecosystem service demand of urban brownfield stakeholders. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 42, 101074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabaev, A.; Wuepper, D. Economics of ecosystem restoration. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2023, 15, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortley, L.; Hero, J.M.; Howes, M. Evaluating ecological restoration success: A review of the literature. Restor. Ecol. 2013, 21, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.E.; Gann, G.D.; Walder, B.; Liu, J.; Cui, W.; Newton, V.; Nelson, C.R.; Tashe, N.; Jasper, D.; Silveira, F.A.; et al. International principles and standards for the ecological restoration and recovery of mine sites. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Y. Integrating soil pH, clay, and neutralizing value of lime into a new lime requirement model for acidic soils in China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Iqbal, H.M.; Tong, Y.W. Omics approaches in bioremediation of environmental contaminants: An integrated approach for environmental safety and sustainability. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahammedi, C.; Mahdjoubi, L.; Booth, C.; Butt, T. Framework for preliminary risk assessment of brownfield sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Goel, H.; Sharma, S.; Rathore, H.S.; Jamir, I.; Kumar, A.; Thimmappa, S.C.; Kesari, K.K.; Kashyap, B.K. Cutting edge technology for wastewater treatment using smart nanomaterials: Recent trends and futuristic advancements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 58263–58293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M. Seeking justice, eating toxics: Overlooked contaminants in urban community gardens. Agric. Hum. Values 2022, 39, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, R.; Minnick, D.J.; Krings, A.; Mitchell, F.M.; Teixeira, S.; Billiot, S. Strengthening the social responses to the human impacts of environmental change. In Social Work and the Grand Challenge of Ending Racism: Concepts, Theory, and Evidence-Based Approaches; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 335–364. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.X.; Li, H.T. Investigating Heavy Metal Pollution in Mining Brownfield and Its Policy Implications: A Case Study of the Bayan Obo Rare Earth Mine, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.K.; Hao, H.C.; Zhao, J.; Cao, K.Z.; Wang, H.S.; He, Z.C. Evaluation of Remote Sensing Ecological Index Based on Soil and Water Conservation on the Effectiveness of Management of Abandoned Mine Landscaping Transformation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.S.; Fuchsman, P.C.; Sacks, V.P.; Brown, L.E.; Epperson, C.; Magar, V.S. Monitored Natural Recovery of Contaminated Sediment in Cottonwood Bay, Texas. Soil Sediment Contam. 2022, 31, 905–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A.; Kittur, B.H.; Bargali, S.S.; Bargali, K.; Nema, S. Forest biodiversity conservation and restoration: Policies, plan, and approaches. In Ecorestoration for Sustainability; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 317–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ludovici, L.; Pastore, M.C. Informal Urban Biodiversity in the Milan Metropolitan Area: The Role of Spontaneous Nature in the Leftover Regeneration Process. Land 2024, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, B.; Zeng, X.; Du, C.; Ding, J.; Lei, J.; Du, W.; Zhang, C. Vitality behind desolation: Characteristics and succession process of plant communities in the Chongqing special steel plant brownfield. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.I.H.; Nepf, H. Marsh restoration in front of seawalls is an economically justified nature-based solution for coastal protection. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowska, M. Reclamation of polluted land in urban renewal projects. Literature review of suitable plants for phytoremediation. Environ. Chall. 2023, 13, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiwak, A.D. Ruderality and refugia in the ruins: Heritage, alienation, and post-industrial nature cultures in Northwest Wales. Landsc. Res. 2024, 50, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, C. What’s in a landscape? Nature, memory, and tourism in Bitterfeld-Wolfen’s post-mining landscape, East Germany. Landsc. Res. 2024, 49, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, L.; Morar, C.; Unkart, S.; Erdal, S. An overview of brownfields redevelopment in the United States through regulatory, public health, and sustainability lenses. J. Environ. Health 2022, 84, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Morar, C.; Berman, L.; Unkart, S.; Erdal, S. Sustainable brownfields redevelopment in the European Union: An overview of policy and funding frameworks. J. Environ. Health 2021, 84, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Lei, S.; Semple, K.T.; Coulon, F.; Hu, Q.; Gao, J.; Guo, G.; Gu, Q.; Jones, K.C. Redevelopment of urban brownfield sites in China: Motivation, history, policies and improved management. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, W.D.; Miller, E.; Jones, A.; García-Rangel, S.; Thornton, H.; McOwen, C. Enhancing climate change resilience of ecological restoration—A framework for action. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 19, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Q.; Duan, Q.S.; Bao, R.Q. Review on Concepts and Methods of Systematic Management of Mountains Rivers Forest Farmlands Lakes and Grasslands. Agric. Eng. 2024, 14, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Knoble, C.; Yu, D. Bridging the gap: Analyzing the relationship between environmental justice awareness on twitter and socio-environmental factors using remote sensing and big data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librán-Embid, F.; Klaus, F.; Tscharntke, T.; Grass, I. Unmanned aerial vehicles for biodiversity-friendly agricultural landscapes-A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himeur, Y.; Rimal, B.; Tiwary, A.; Amira, A. Using artificial intelligence and data fusion for environmental monitoring: A review and future perspectives. Inf. Fusion 2022, 86, 44–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouceur, E.; Shackelford, N.; Bouazza, K.; Brudvig, L.; Bucharova, A.; Conradi, T.; Erickson, T.E.; Garbowski, M.; Garvy, K.; Harpole, W.S.; et al. Knowledge sharing for shared success in the decade on ecosystem restoration. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2022, 3, e12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainaina, P.; Minang, P.A.; Muthee, K. Relational values within landscape restoration: A review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 64, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurui, L.; Xuanchang, Z.; Zhi, C.; Zhengjia, L.; Zhi, L.; Yansui, L. Towards the progress of ecological restoration and economic development in China’s Loess Plateau and strategy for more sustainable development. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Mu, B.; Liu, C. Understanding stakeholder relationships in sustainable brownfield regeneration: A combined FAHP and SNA approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 15823–15859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Author | Number of Publications (Articles) | Average Citation Frequency (Per Article) | Country | Research Keywords | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gochfeld, Michael | 11 | 13.64 | USA | Remediation, Department of Energy, Ecological resources, Risk evaluation. | [12,47,48] |
| Burger, Joanna | 11 | 11.73 | USA | Assessment, Remediation, Polluted sites, Department of Energy. | [12,47,48] |
| Jeitner, Christian | 6 | 5.33 | USA | Ecological resources, Ecological risk, Restoration, Assessment. | [48] |
| Mench, Michel | 4 | 22.00 | France | Biodiversity, Phytoremediation, Metal pollution, Soil functions, Organic amendments. | [49] |
| Clements, William | 4 | 17.75 | USA | Future land use designations, Resource evaluations, Ecological risk, Contaminated sites. | [30] |
| Prudent, Pascale | 4 | 17.75 | France | Passive ecological restoration, Native plant selection, Phytoremediation strategy, Metal tolerance, Heavy metal pollution. | [33] |
| Musco, Luigi | 4 | 13.75 | Italy | Benthic biodiversity, Food web, Industrial contamination, Mediterranean Sea, Sediment pollution. | [34] |
| Brown, Kevin G. | 4 | 9.25 | USA | Biodiversity, Contaminated sites, Ecosystem functions and services, Heavy metals, Stream restoration. | [47] |
| Kosson, David | 4 | 9.25 | USA | Ecological resources, Ecological risk, Human consequences, Ecological and eco-cultural consequences. | [12] |
| Becerril, Jose | 3 | 34.67 | Spain | Phytostabilization, Heavy metals, Mine tailing, Revegetation, Metal pollution. | [49] |
| Author | Number of Publications (Articles) | Average Citation Frequency (Per Article) | Research Keywords | References | |
| Liu, F.Y. | 4 | 49.50 | Collaborative regeneration, Optimization of industrial structure, Maintaining social interests, Industrial abandoned land, Activation regeneration. | [50] | |
| Feng, Y.X. | 4 | 17.25 | Mining brownfield, Ecological design, Ecological restoration, Landscape urbanism, Mining Park. | [51] | |
| Zheng, X.D. | 4 | 7.00 | Soil pollution management, Sponge city construction, Ecological restoration, Brownfield regeneration, Urban renewal. | [52] | |
| Li, H.Y. | 3 | 31.67 | Ecological restoration, Urban green space system, Natural reserves, Industrial abandoned land, Landscape renewal. | [53] | |
| Cheng, W. | 3 | 15.67 | Industrial abandoned land, Ecological restoration, Landscape renewal, Old cement factory, Reform. | [54] | |
| Zheng, X. | 3 | 5.00 | Landfill sites, Industrial abandoned land, Ecological restoration, Regeneration planning and design, Urban renewal. | [55] | |
| Feng, S.S. | 2 | 15.50 | Industrial abandoned land, Ecological restoration, Landscape renewal, Mining site, Green infrastructure, Landscape connectivity. | [56] | |
| Chen, X. K. | 2 | 10.00 | Ecological restoration, Urban green space system, Ecopark, Natural reserves. | [57] | |
| Li, Q. | 2 | 7.00 | Industrial abandoned land, Ecological restoration, Urban double repair, Landscape design, Landscape regeneration. | [58] | |
| Di, J. | 2 | 5.00 | Ecological restoration, Urban restoration, Urban renewal, Industrial abandoned land, Landscape renovation. | [59] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Shi, Y. Current Status and Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse Research Based on Bibliometric Analysis: A Literature Review. Land 2025, 14, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061185
Zhang L, Wang Y, Ding Q, Shi Y. Current Status and Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse Research Based on Bibliometric Analysis: A Literature Review. Land. 2025; 14(6):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061185
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lin, Yuzhou Wang, Qi Ding, and Yang Shi. 2025. "Current Status and Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse Research Based on Bibliometric Analysis: A Literature Review" Land 14, no. 6: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061185
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, Y., Ding, Q., & Shi, Y. (2025). Current Status and Prospects of Ecological Restoration and Brownfield Reuse Research Based on Bibliometric Analysis: A Literature Review. Land, 14(6), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061185







