Deformation Monitoring Along Beijing Metro Line 22 Using PS-InSAR Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
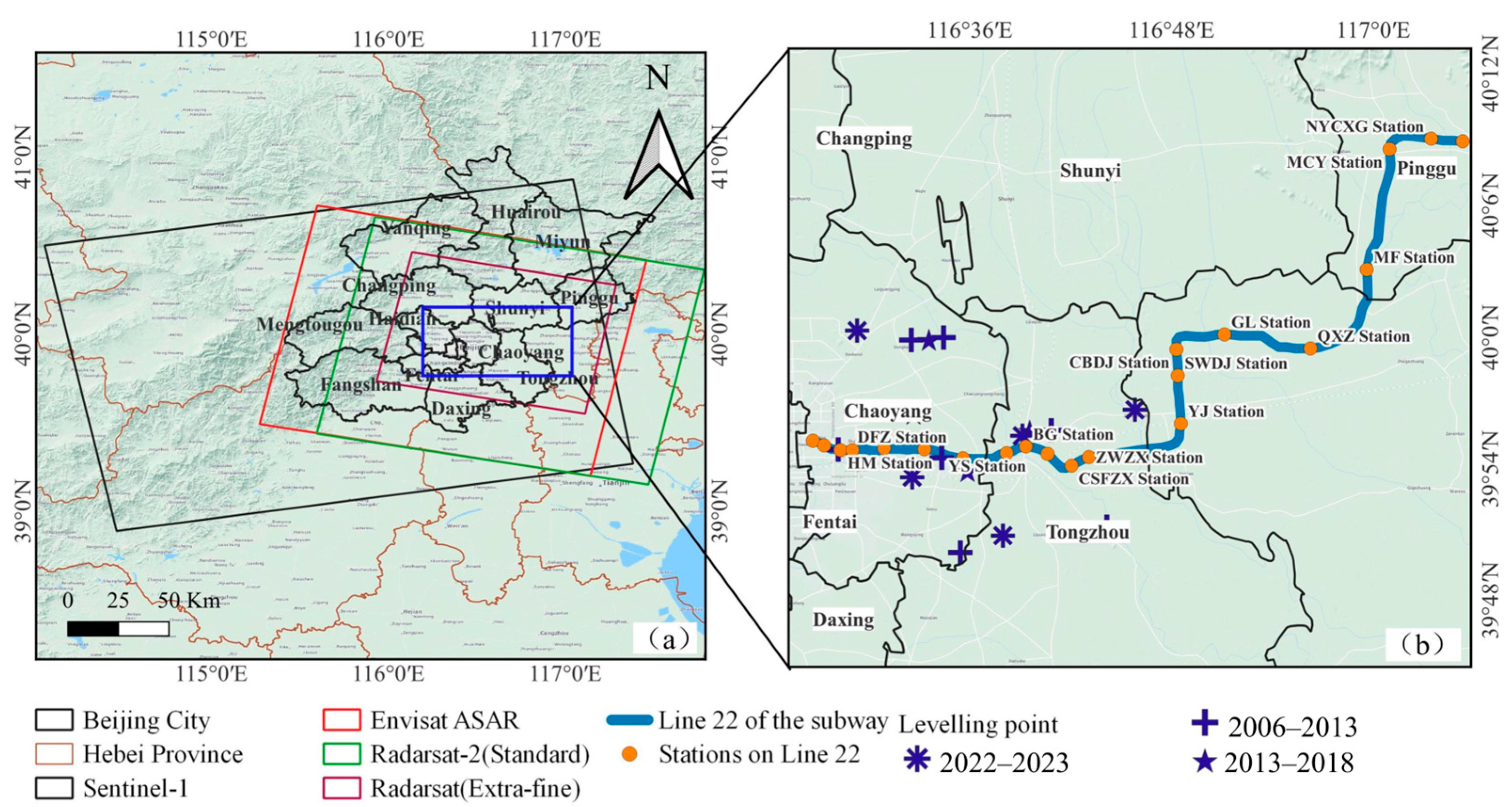
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
3. Methodology
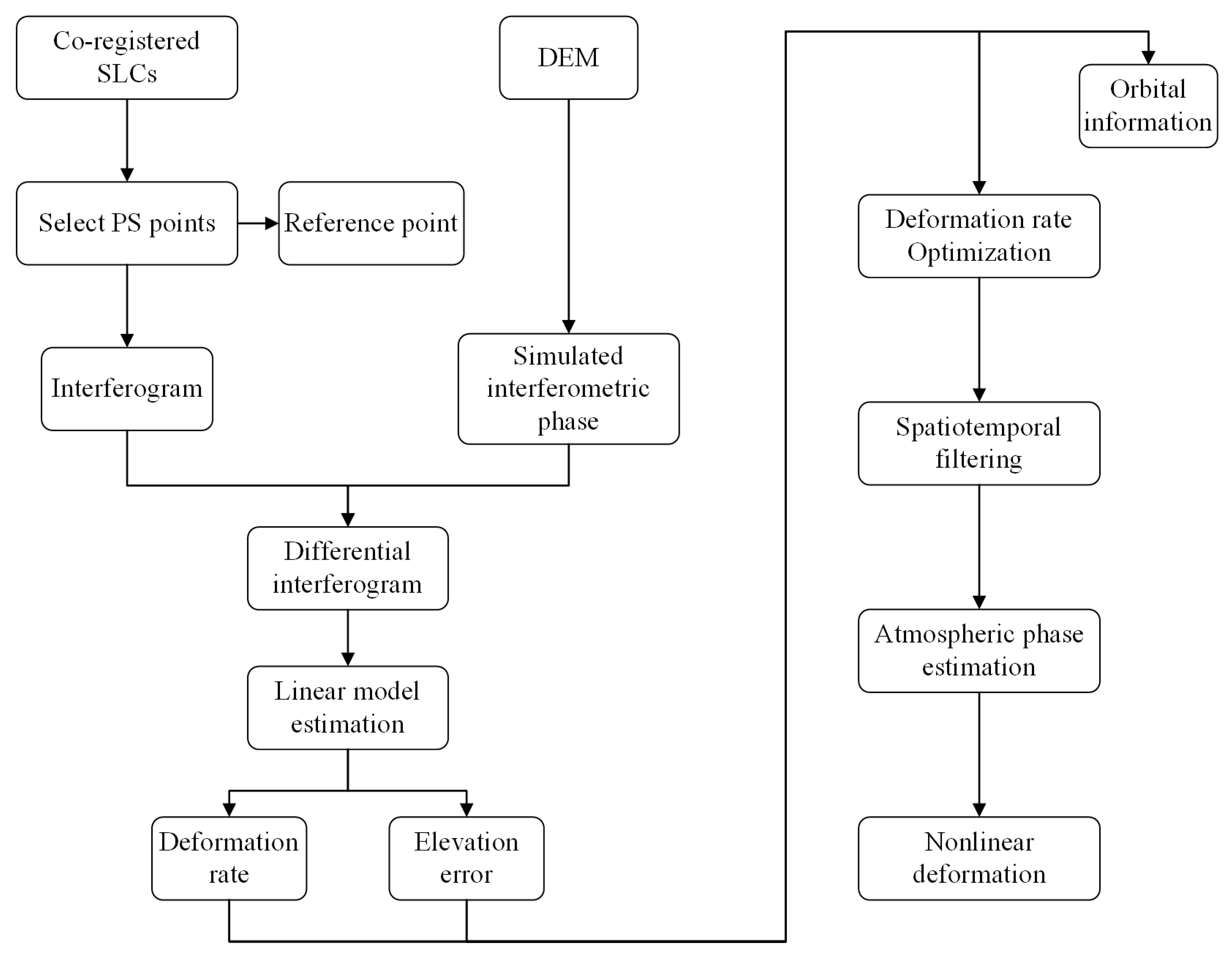
3.1. PS-InSAR Method
3.2. Timing Result Stitching Method
3.3. PDL Method
4. Results
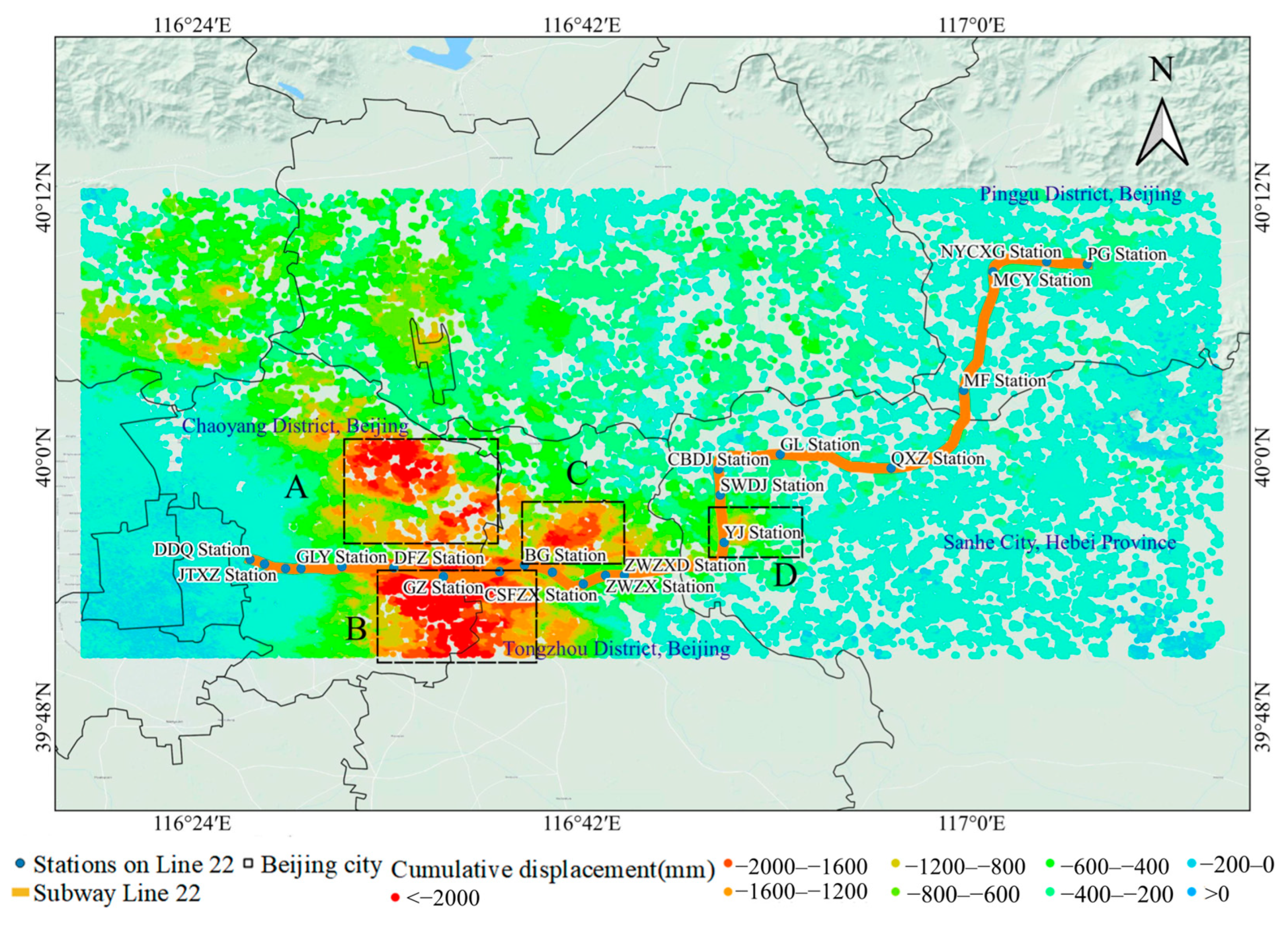
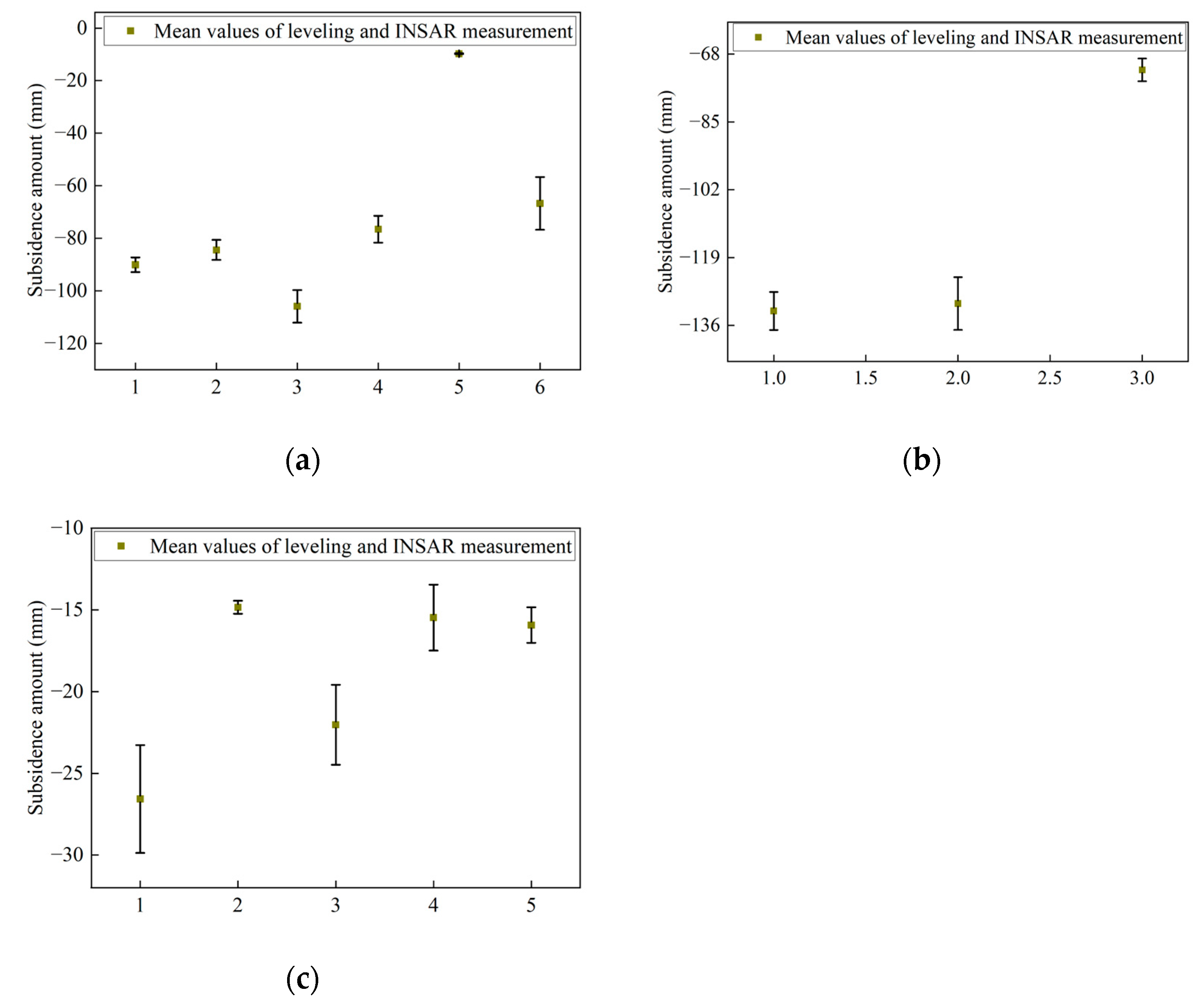
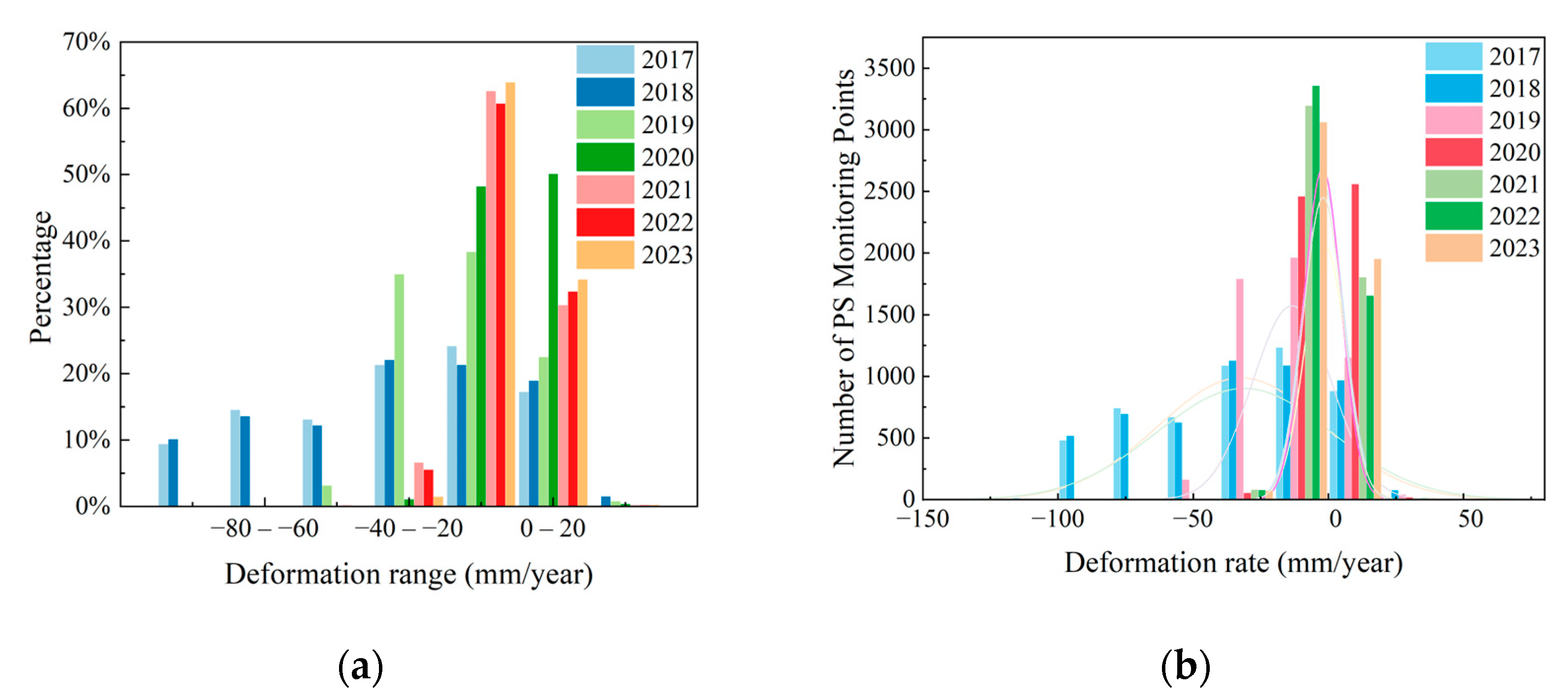
4.1. PS-InSAR and Verification Results
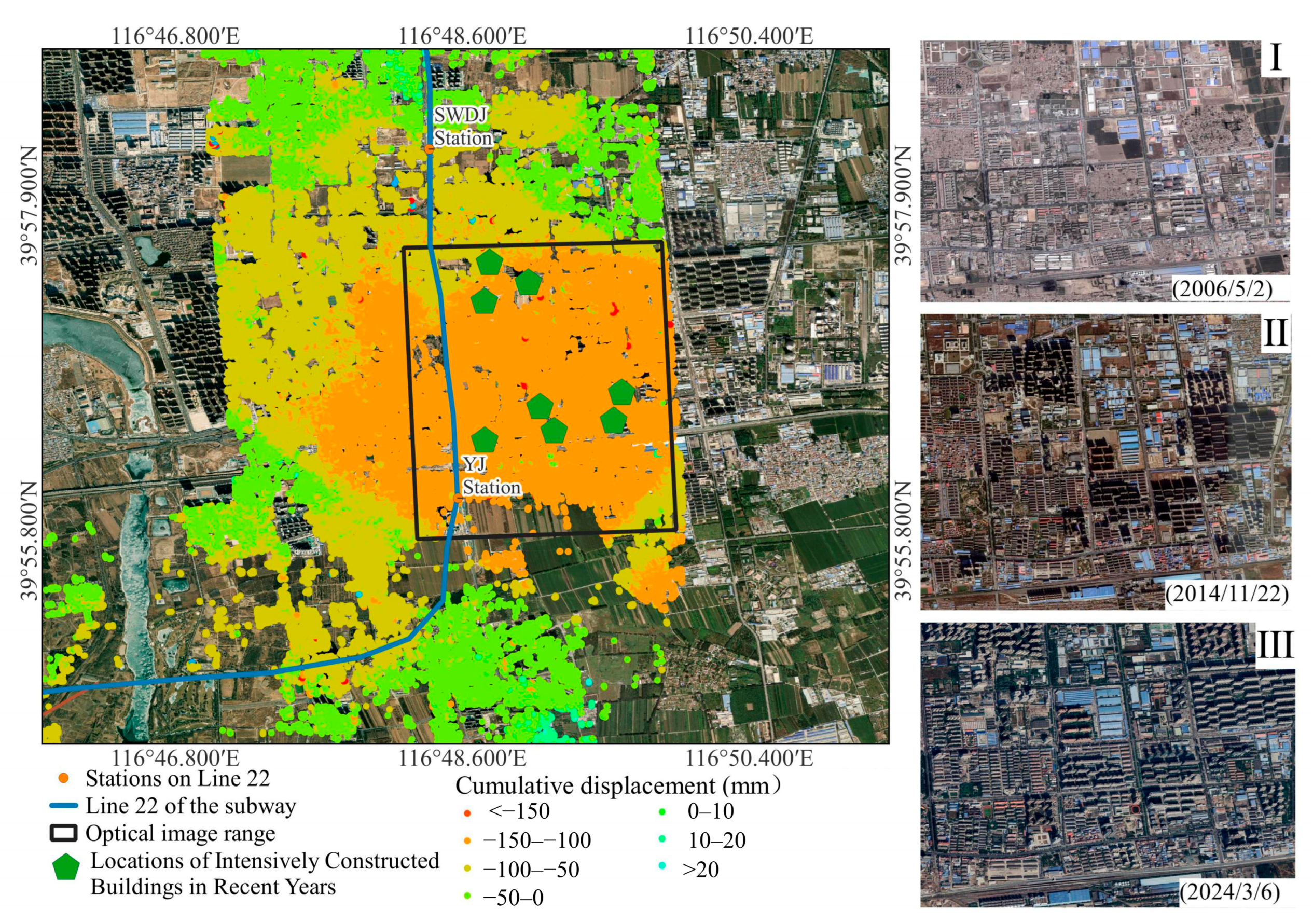
4.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Land Subsidence in Areas Along the Subway Line
5. Analysis
5.1. Changes in Groundwater Level
5.2. Distribution of Fault Zones
5.3. Subway Construction
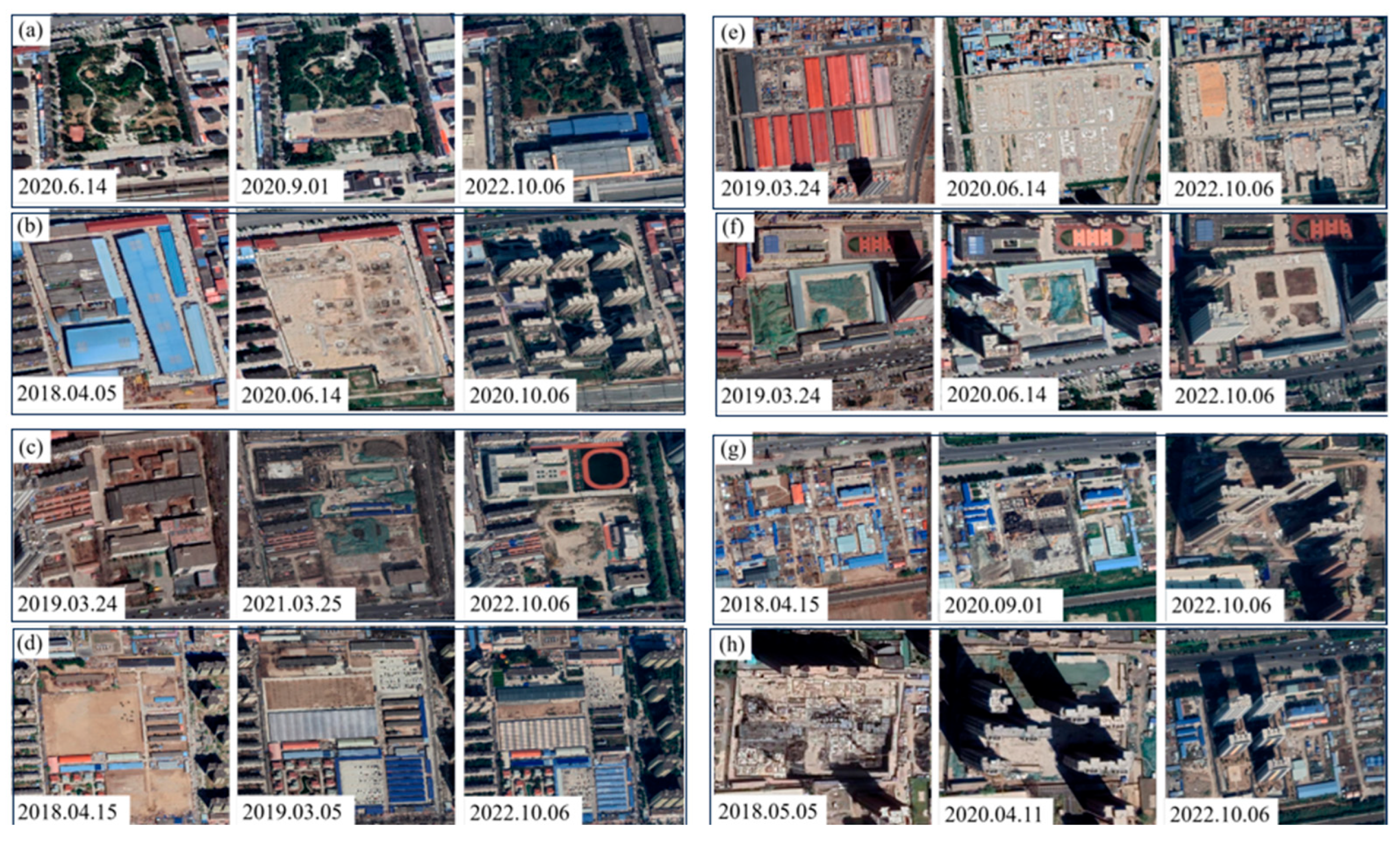
5.4. Changes in Urban Construction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, L. Monitoring and Analysis of Land Subsidence in Cangzhou Based on Small Baseline Subsets Interferometric Point Target Analysis Technology. Land 2023, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Li, X.; Ke, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, L.; Xu, Z.; Tang, P.; Gong, H.; et al. Nonlinear Evolutionary Pattern Recognition of Land Subsidence in the Beijing Plain. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Balz, T. Beijing Land Subsidence Revealed Using PS-InSAR with Long Time Series TerraSAR-X SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Hou, C. Unveiling the driving factors of urban land subsidence in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of land subsidence in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Lin, J.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Liao, M. Investigating overlapping deformation patterns of the Beijing Plain by independent component analysis of InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 135, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.H.T.; Hanssen, R.; Rocca, F. Radar Interferometry: 20 Years of Development in Time Series Techniques and Future Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camós, C.; Molins, C. 3D analytical prediction of building damage due to ground subsidence produced by tunneling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 50, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, M.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Jin, L. Analysis of factors influencing surface settlement during shield construction of a double-line tunnel in a mudstone area. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Cui, T.; He, K.; Guo, C. Surface subsidence pattern of construction of pipe jacking in water-rich sand layer cross passage measured and numerical simulation analysis. Structures 2024, 60, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Shao, K. Estimation of inelastic skeletal storativity based on SAR-derived land subsidence and groundwater variation in Beijing Plain, China. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Dai, K.; Xing, C.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Clark, B.; Shi, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Qiu, Q.; et al. Land subsidence in Beijing and its relationship with geological faults revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 82, 101886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of surface deformation based on MT-InSAR and mechanism analysis along Zhengzhou Metro, China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 156, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Lei, K.; Zhu, L.; Gao, M.; Zhou, C. Characterization and causes of land subsidence in Beijing, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 38, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Overview and Analysis of Ground Subsidence along China’s Urban Subway Network Based on Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, F. Monitoring Ground Subsidence Along the Shanghai Maglev Zone Using TerraSAR-X Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, C.; Huang, P.; Yin, B.; Tan, W.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Du, S. Research on Time Series Monitoring of Surface Deformation in Tongliao Urban Area Based on SBAS-PS-DS-InSAR. Sensors 2024, 24, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Managhebi, T.; Azadnejad, S. Collapse Hotspot Detection in Urban Area Using Sentinel-1 and TerraSAR-X Dataset with SBAS and PSI Techniques. Land 2024, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavrezou, I.E.; Melgar, I.C.; Nika, D.; Gatsios, T.; Lalechos, S.; Parcharidis, I. Application of Time Series INSAR (SBAS) Method Using Sentinel-1 for Monitoring Ground Deformation of the Aegina Island (Western Edge of Hellenic Volcanic Arc). Land 2024, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of Hohhot Subway Subsidence Using StaMPS-PS Based on Two DEMS. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Peng, X.; Wen, D. Understanding Land Subsidence Along the Coastal Areas of Guangdong, China, by Analyzing Multi-Track MTInSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-Pass SAR Interferometry With Partially Coherent Targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.I.N.; Oliveira, L.G.S.; Henriques, M.J.; Falcão, A.P.; Lima, J.N.P.; Cooksley, G.; Ferretti, A.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P.; Fonseca, J.F.B.D. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry detects and measures ground subsidence in Lisbon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2152–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Xu, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhu, J. Deriving Spatio-Temporal Development of Ground Subsidence Due to Subway Construction and Operation in Delta Regions with PS-InSAR Data: A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Gao, M.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal evolution of land subsidence around a subway using InSAR time-series and the entropy method. GIScience Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Gao, M.; Yu, H.; Cao, Q.; Cao, J. An Improved Multi-Sensor MTI Time-Series Fusion Method to Monitor the Subsidence of Beijing Subway Network during the Past 15 Years. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xu, X.; Tian, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, K.; Niu, W.; Ni, J.; et al. Regional tectono-sedimentary evolution in the northeastern Beijing Sub-plain: Evidence from the Yx02 core chronostratigraphy in the buried Daxing Uplift. Geosci. J. 2024, 28, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Shi, X.; Gou, J.; Hu, L.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Dong, X.; Li, Z. Diagnosing Subsidence Geohazard at Beijing Capital International Airport, from High-Resolution SAR Interferometry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Ke, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Guo, L.; Gong, H. Detection of Seasonal Deformation of Highway Overpasses Using the PS-InSAR Technique: A Case Study in Beijing Urban Area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, Z.; Ahmad, M.H.; Zaman, A. The Supply and Demand for Exports of Pakistan: The Polynomial Distributed Lag Model (PDL) Approach [with Comments]. Pak. Dev. Rev. 2003, 42, 961–972. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Z.; Beibei, C.; Huili, G.; Kunchao, L.; Chaofan, Z.; Zhaozhao, L.; Danni, Z. Inversion of Groundwater Storage Variations Considering Lag Effect in Beijing Plain, from RadarSat-2 with SBAS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 991. [Google Scholar]
- Khorrami, M.; Alizadeh, B.; Tousi, E.G.; Shakerian, M.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Rahgozar, P. How Groundwater Level Fluctuations and Geotechnical Properties Lead to Asymmetric Subsidence: A PSInSAR Analysis of Land Deformation over a Transit Corridor in the Los Angeles Metropolitan Area. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, R.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Xu, L.; Wang, X. Land subsidence and rebound response to groundwater recovery in the Beijing Plain: A new hydrological perspective. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulki, F.M.; Rizqiyanto, A.A.; ChangWook, L. Integration of InSAR Time-Series Data and GIS to Assess Land Subsidence along Subway Lines in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, South Korea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3505. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.P. Two Approaches to Polynomial Distributed Lags Estimation: An Expository Note and Comment. Am. Stat. 2012, 26, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Bai, Y. The Subsidence–Distance Relationship for Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Abstraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudehus, G. Implications of the principle of effective stress. Acta Geotech. 2020, 16, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Y.; Jia, W.; Hu, F. Soil pore characteristics, morphology, and soil hydraulic conductivity following land subsidence caused by extraction of deep confined groundwater in Xi’an, China: Quantitative analysis based on X-ray micro-computed tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 211, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, T. Experimental study on ground subsidence caused by pumping and recharging. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 1163–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Mechanism of Abnormal Surface Subsidence Induced by Fault Instability. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar]
- Doglioni, C.; Dagostino, N.; Mariotti, G. Normal Faulting vs. Regional Subsidence and Sedimentation Rate. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1998, 15, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, J.; Deng, Y.; An, H.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Characteristics, causes and significance of subsurface stress field of Beijing earth fissures group. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2287974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Deng, T.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Y. THM modeling of ground subsidence induced by excavation of subway tunnel. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, X.; Zou, B.; Mu, J.; Hu, R.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, S. Monitoring Study of Long-Term Land Subsidence during Subway Operation in High-Density Urban Areas Based on DInSAR-GPS-GIS Technology and Numerical Simulation. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, 134, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, D.; Ma, C.; Lian, D. Monitoring Subsidence Deformation of Suzhou Subway Using InSAR Timeseries Analysis. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 3400–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Lv, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X. Multi-Scale Analysis of the Relationship between Land Subsidence and Buildings: A Case Study in an Eastern Beijing Urban Area Using the PS-InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca, C.; Deodato, T. Urban Growth and Land Subsidence: Multi-Decadal Investigation Using Human Settlement Data and Satellite InSAR in Morelia. Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 811, 152211. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.D.; Yang, J.Q.; Yuan, L. Land Subsidence Caused by the Interaction of High-Rise Buildings in Soft Soil Areas. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| SAR Sensor | Envisat ASAR | Radarsat-2 (Standard) | Radarsat~2 (Extra-Fine) | Sentinel-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band | C | C | C | C |
| Wavelength (cm) | 5.6 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| Polarization | VV | VV | VV | VV |
| ascending/descending orbit | descending | descending | descending | ascending |
| Incidence Angle | 22.8 | 33.9 | 22.5 | 39.5 |
| No. images | 51 | 37 | 43 | 60 |
| Date range | 14 January 2004~ 19 September 2010 | 22 November 2010~ 21 October 2016 | 25 January 2017~ 10 January 2020 | 5 January 2020~ 3 November 2024 |
| Unified Number | Geographical Location | Monitoring Depth (m) | Aquiferous Medium and Burial Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 131082210331 | Gaolou Village, Gaolou Town, Sanhe City, Hebei Province | 31.31–34.41 | Pore phreatic water |
| 110112210004 | Dongxiaoying, Tongzhou District, Beijing | 72.00–116.00 | Pore confined water |
| 110105210003 | Qingnian Road Auto Parts City, Chaoyang District, Beijing | 52.00–108.50 | Pore confined water |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Lyu, M.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, K.; Luo, H.; Wang, F. Deformation Monitoring Along Beijing Metro Line 22 Using PS-InSAR Technology. Land 2025, 14, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051098
Guo F, Lyu M, Li X, Jiang J, Wang L, Guo L, Zhang K, Luo H, Wang F. Deformation Monitoring Along Beijing Metro Line 22 Using PS-InSAR Technology. Land. 2025; 14(5):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051098
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Fenze, Mingyuan Lyu, Xiaojuan Li, Jiyi Jiang, Lan Wang, Lin Guo, Ke Zhang, Huan Luo, and Fengzhou Wang. 2025. "Deformation Monitoring Along Beijing Metro Line 22 Using PS-InSAR Technology" Land 14, no. 5: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051098
APA StyleGuo, F., Lyu, M., Li, X., Jiang, J., Wang, L., Guo, L., Zhang, K., Luo, H., & Wang, F. (2025). Deformation Monitoring Along Beijing Metro Line 22 Using PS-InSAR Technology. Land, 14(5), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051098








