Urban Spatial Blessing: Effect of Land Use Intensity on Human Development Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review, Theoretical Analysis, and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Spatial Spillover Effect of Land Use Intensity on Urban Welfare
2.2.1. Local Facilitation Effects of Land Use Intensity
2.2.2. Spatial Spillover Effects of Land Use Intensity
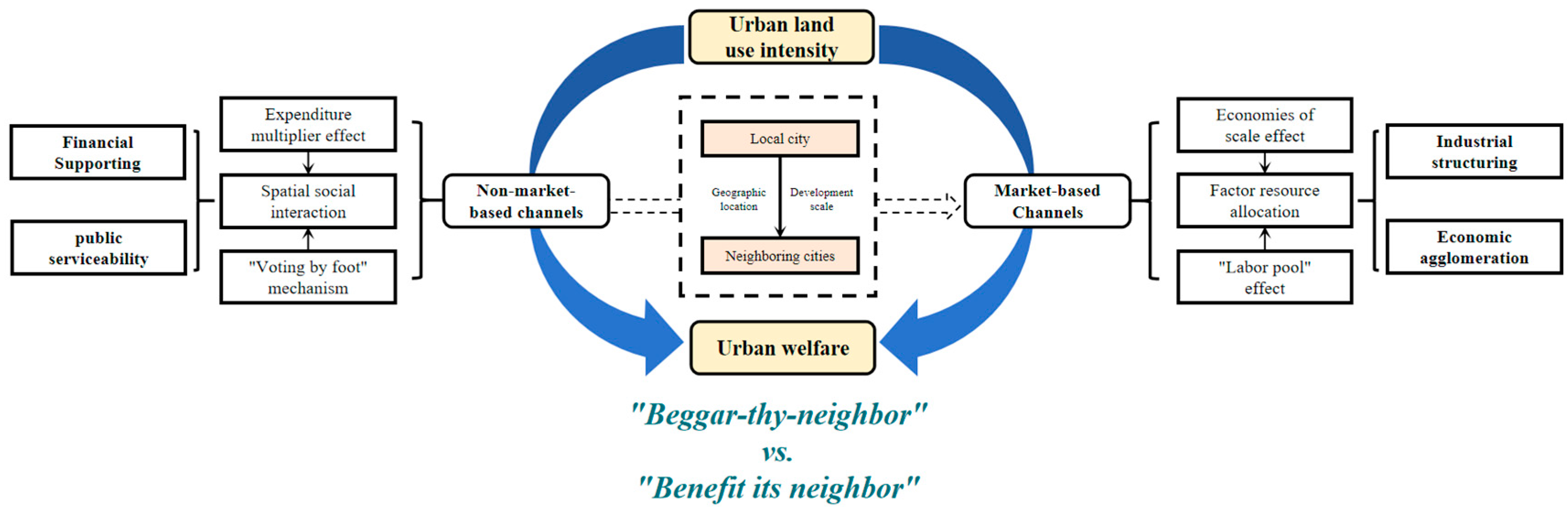
2.3. Spatial Impact Mechanisms of Land Use Intensity on Urban Welfare
2.3.1. Market-Based Channels: Industrial Structuring and Economic Agglomeration
2.3.2. Non-Market-Based Channels: Financial Supporting and Public Serviceability
3. Methods and Data
3.1. Setting of Econometric Model
3.1.1. Spatial Durbin Model
3.1.2. Spatial Heterogeneity Model
3.1.3. Spatial Mechanism Model
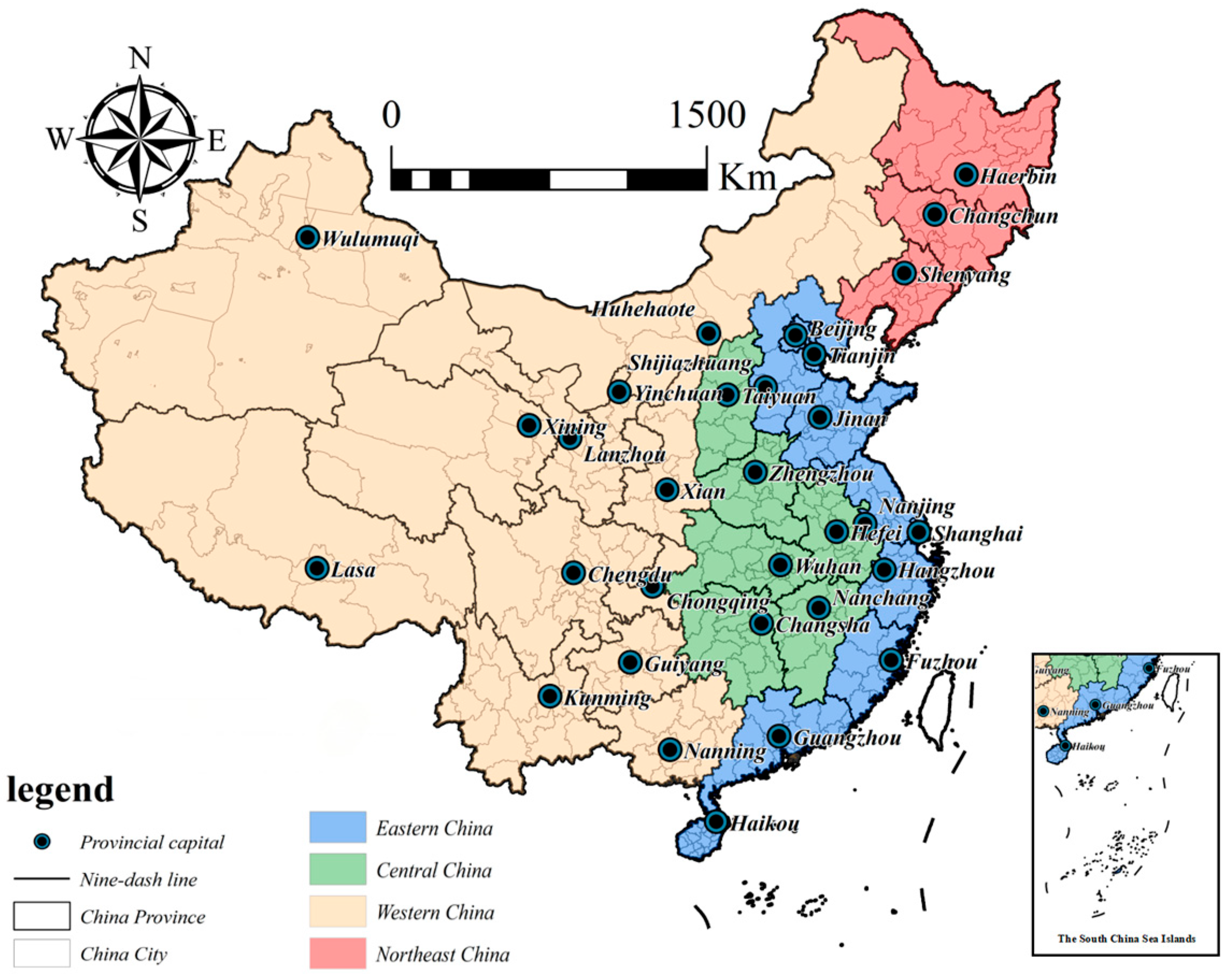
3.2. Variables and Data Sources
3.2.1. Explained Variable
3.2.2. Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Mediating Variables
3.2.4. Control Variables
4. Empirical Results and Interpretation
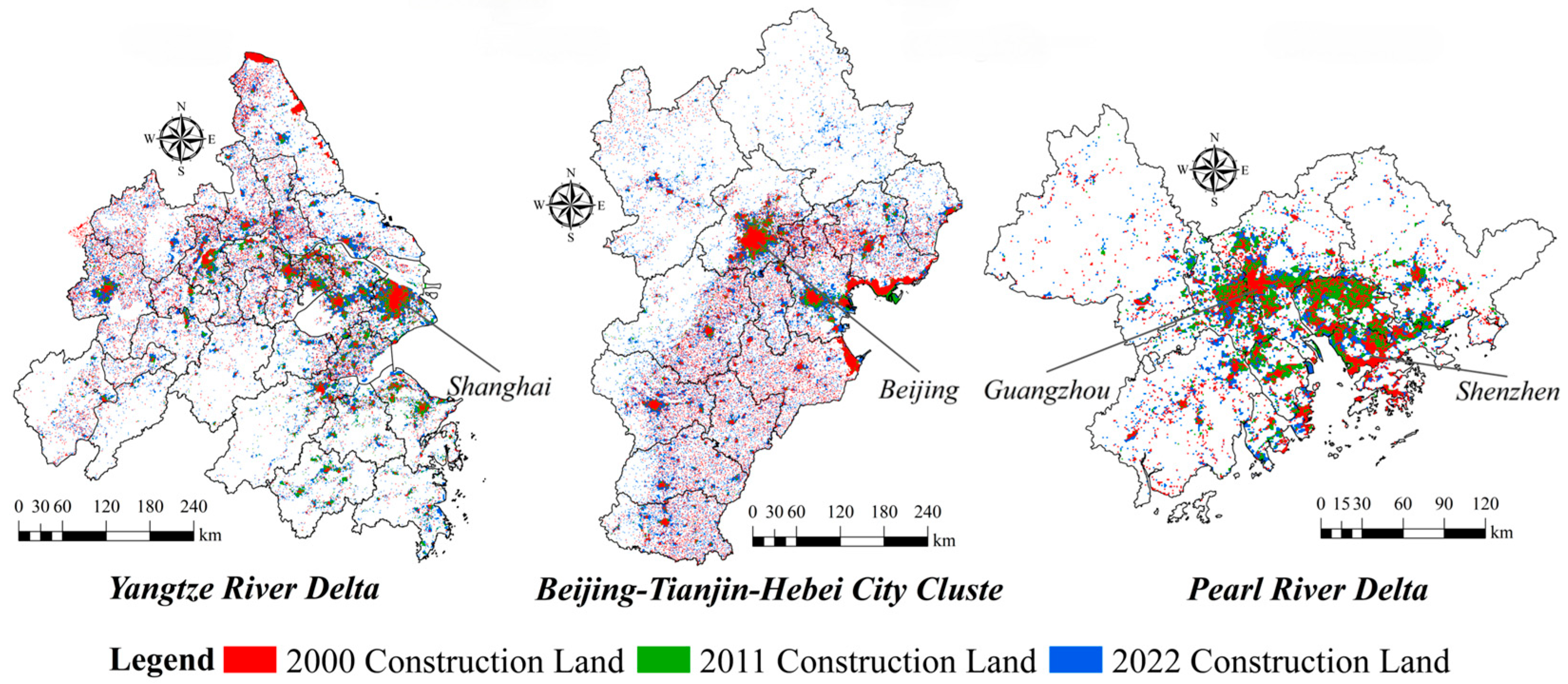
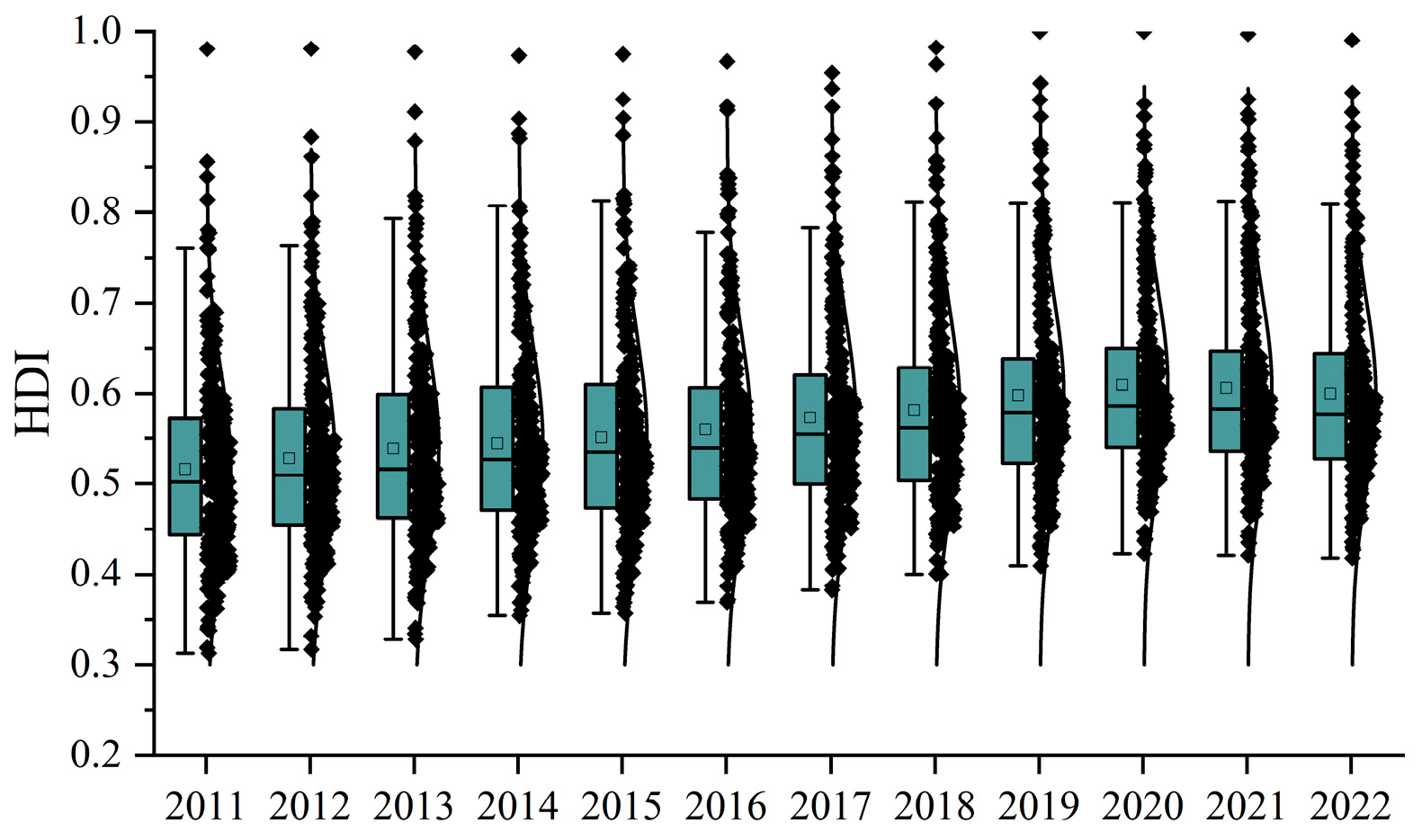
4.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern Analysis
4.2. Model Selection and Testing
4.3. Spatial Spillover Effects
4.3.1. Spatial Baseline Regression
4.3.2. Spatial Effect Decomposition
4.3.3. The Analysis of the Regional Boundary of the Spatial Spillover Effect
4.3.4. Robustness Test
4.4. Analysis of Spatial Heterogeneity
4.4.1. Geographic Location Heterogeneity
4.4.2. Development Scale Heterogeneity
4.5. Further Analysis: Spatial Impact Mechanisms
4.5.1. Market-Based Channels
4.5.2. Non-Market-Based Channels
5. Discussion
5.1. Further Interpretation of Results
5.2. Policy Recommendations
5.3. Limitations and Constraints
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Mean Years of Schooling = (6 × Pelementary school + 9 × Pmiddle school + 12 × Phigh school + 16 × Ppost-secondary or above)/(Total population over 6 years of age); Pi is the number of students enrolled in that type of school. |
| 2 | This is the standardized coefficient, 0.377 = 0.354 × 0.116 (standard deviation of the explanatory variables) ÷ 0.109 (standard deviation of the explained variables), below. |
References
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.R.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The Dimensions of Global Urban Expansion: Estimates and Projections for All Countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.L.; He, T.T.; Xiao, W.; Chen, W.Q.; Lu, D.B.; Liu, S.C. Measuring the Coupling of Built-up Land Intensity and Use Efficiency: An Example of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppe, S.; Haase, D.; Kötter, T. Towards sustainable settlement growth: A new multi-criteria assessment for implementing environmental targets into strategic urban planning. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2012, 32, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisu, K.; Holford, T.; Belanger, K.; Leaderer, B.; Bell, M.L. Urban Land-Use and Respiratory Symptoms in Infants. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertus, M.; Espinoza, M.; Fort, R. Land reform and human capital development: Evidence from Peru. J. Dev. Econ. 2020, 147, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolking, S.; Mahtta, R.; Milliman, T.; Esch, T.; Seto, K.C. Global urban structural growth shows a profound shift from spreading out to building up. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yin, Y.Z.; Guo, L.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. Integrating the administrative spillover effect into the spatial governance system to revisit land development: A study in urban-rural fringe areas of Wuhan and neighboring cities, China. Land Use Policy 2024, 139, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tu, J.; He, Y. Measurement of China’s Human Development Index and Analysis of Its Influencing Factors from the Perspective of New Development Concept. Soc. Indic. Res. 2023, 167, 213–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, R. Land use change and economic growth in urban China: A structural equation analysis. Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 2880–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Qi, J.G. Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use change and landscape pattern in response to rapid urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basel, S.; Gopakumar, K.U.; Rao, R.P. Broad-based index for measurement of development. J. Soc. Econ. Dev. 2020, 22, 182–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Hart, M.; Posner, S.; Talberth, J. Beyond GDP: The Need for New Measures of Progress; Pardee Working Paper, 4; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2144/22665 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Sen, A.; Anand, S. Human Development and Economic Sustainability. World Dev. 2000, 28, 2029–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, P.A. A Theoretical Foundation to Support the Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare (ISEW), Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI), and Other Related Indexes. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 44, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavandas, M. Development of multifactor index for assessing quality of life of a tribal population of India: Multilevel analysis approach. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Pervaiz, Z.; Chaudhary, A.R. Do Poverty and Income Inequality Mediate the Association Between Agricultural Land Inequality and Human Development? Soc. Indic. Res. 2020, 151, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, A.D.; Najam, A. The human development index: A critical review. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Sung, J.; Davis, W.; Tchernis, R. Using spatial factor analysis to measure human development. J. Dev. Econ. 2018, 132, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, R.; Feeny, S.; Li, J.; Zuhair, S. Aggregating the Human Development Index: A Non-compensatory Approach. Soc. Indic. Res. 2024, 172, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cao, S.S.; Du, M.Y.; Lu, L. Distinctive roles of land-use efficiency in sustainable development goals: An investigation of trade-offs and synergies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 382, 134889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.L.; Jin, Y.X.; Yang, R.R. An approach to exploring the spatial distribution and influencing factors of urban problems based on Land use types. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 104, 105321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Responses of Ecosystem Services to Land Use/Cover Changes in Rapidly Urbanizing Areas: A Case Study of the Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Ecosystem Service Value Based on the Markov–FLUS Model in Ezhou City, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.A.; Kafy, A.; Saha, M.; Fattah, M.A.; Almulhim, A.I.; Faisal, A.-A.; Al Rakib, A.; Jahir, D.M.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Bakshi, A.; et al. Modelling the impacts of land use/land cover changing pattern on urban thermal characteristics in Kuwait. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelens, B.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Black, J.B.; Chen, D. Neighborhood-based differences in physical activity: An environment scale evaluation. Am. J. Public Health 2003, 93, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, M.; Squire, L. The simultaneous evolution of growth and inequality. Econ. J. 2003, 113, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.N.; Cheng, Z.M.; Smyth, R. Parental early-life exposure to land reform and household investment in children’s education. World Dev. 2024, 173, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdsall, N.; Londono, J.L. Asset Inequality Matters: An Assessment of the World Bank’s Approach to Poverty Reduction. Am. Econ. Rev. 1997, 87, 32–37. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2950879?seq=1 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Pan, S.Q.; Zhang, P.; Tian, L.; Chen, Z. Unfolding the spatial spillover effect of urbanization on composite ecosystem services: A case study in cities of Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fu, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.H. Time-varying and land use-induced spillover effects of urban redevelopment: Evidence from Hong Kong. Cities 2024, 146, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.Y.; Guo, D.; Xu, Y.P.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Xie, Y. How does circulation industry agglomeration help close the income gap between urban and rural areas?—Evidence from China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2024, 94, 101952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y. The long-term health and economic consequences of improved property rights. J. Public Econ. 2021, 201, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Zhao, S.Q.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, H.; Soromessa, T.; Argaw, M.; Dewan, A. Spatio-temporal changes in habitat quality and linkage with landscape characteristics in the Beressa watershed, Blue Nile basin of Ethiopian highlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Ke, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, W. Spatial effects and influence mechanisms of urban land use green transition on urban carbon emissions. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, C.F. Environmental regulation, land use efficiency and industrial structure upgrading: Test analysis based on spatial durbin model and threshold effect. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Yu, W.Q.; Zhao, X.J.; Xu, W. Reassessing the linkage between natural resources and economic growth in China: Delving into the impacts of national resource taxes, renewable energy, financial advancements, and provincial fiscal expenditures. Resour. Policy 2023, 86, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, J.C. Government and Happiness in 130 Nations: Good Governance Fosters Higher Level and More Equality of Happiness. Soc. Indic. Res. 2011, 102, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediating Effects and Moderating Effects in Causal Inference. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 05, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.G.; Zhang, D.; Yu, K.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, J. Spatial distribution characteristics and variability of urban ecological welfare performance in the Yangtze River economic Belt: Evidence from 70 cities. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.Y.; Dong, Z.Y.Z.; Wu, P.; Dong, F.; Fang, K.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Shao, Z.; Yu, Z. How urban land-use intensity affected CO2 emissions at the county level: Influence and prediction. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Yu, B.L.; Yang, C.S.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhou, L. Three-dimensional intergovernmental competition and urban sprawl: Evidence from Chinese prefectural-level cities. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.T.; Zhang, N.H.; Ye, H.P.; Li, Y. Urbanization in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in China based on long-term nighttime light data. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Yue, W.; Wei, F.; Yang, G.; He, T.; Pan, K. Density pattern of functional facilities and its responses to urban development, especially in polycentric cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 76, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Industrial structure, technological innovation, and total-factor energy efficiency in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8371–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Hong, T. How can local government capacity lift the ‘resource curse’? A study from the perspective of industrial structure transformation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Z.; Jin, H. Labor Agglomeration, Industrial Structure Upgrading and Low-carbon Economic Development. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 74, 106703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ding, T.; Wang, H.S. Incentives for local government expenditures on people’s livelihood: The role of high-speed rail. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 89, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, Y.W.; Dai, L.T. How Does the Supply of Urban Public Services Promote Regional Innovation: A Test Based on the Agglomeration Effects of Talents and Industries. Econ. Surv. 2024, 41, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.H.; Ju, Y.; Hassan, S.T. Investigating the determinants of human development index in Pakistan: An empirical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19294–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Rizov, M.; Kernohan, D. Growth, human development, and trade: The Asian experience. Econ. Model. 2017, 61, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.X.; Peng, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zou, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, T.; Ma, P.X.; He, Y.; et al. Equity of health resource distribution in China during 2009–15: An analysis of cross-sectional nationwide data. Lancet 2017, 390, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Najam, H.; Oskenbayev, Y.; Alisher, S.; Hairis, K. Impact of rapid urban construction land expansion on spatial inequalities of ecosystem health in China: Evidence from national, economic regional, and urban agglomeration perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Zeng, J.; Li, N. Change in land-use structure due to urbanisation in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Advanced Econometrics and Stata Applications, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; He, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. How does rapid urban construction land expansion affect the spatial inequalities of ecosystem health in China? Evidence from the country, economic regions and urban agglomerations. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamsiraroj, S. The foreign direct investment-economic growth nexus. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2016, 42, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y. How heterogeneous industrial agglomeration impacts energy efficiency subject to technological innovation: Evidence from the spatial threshold model. Energy Econ. 2024, 136, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Meng, F.; Li, B. Spatial effects of innovation ecosystem development on low-carbon transition. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.J.; Yu, B.X. Empirical study on family planning and insufficient demand for resident consumption-Theory of life cycle under the dual economic structure. Economist 2016, 08, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.S.; Xiong, S.P.; Li, J.M.; Zhu, X.Y. Research on the Impact and Mechanism of Digital Inclusive Finance on Urban Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction. J. Manag. 2024, 37, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yang, R.D.; Xu, X.X. The Economics of Great Powers: Toward a Long-Term, Global, and Multidimensional Development of China, 1st ed.; Shanghai People’s Publishing House Co., Ltd.: Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Duranton, G.; Puga, D. Urban Growth and Its Aggregate Implications. Econometrica 2023, 91, 2219–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.; Henderson, J.V. Are Chinese Cities Too Small? Rev. Econ. Stud. 2006, 73, 549–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Qiao, X. Internal Migration, City Size and Productivity in China. Q. J. Econ. 2020, 19, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Jiao, L.; Su, J. Urban land system change: Spatial heterogeneity and driving factors of land use intensity in Wuhan, China. Habitat Int. 2025, 159, 103380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
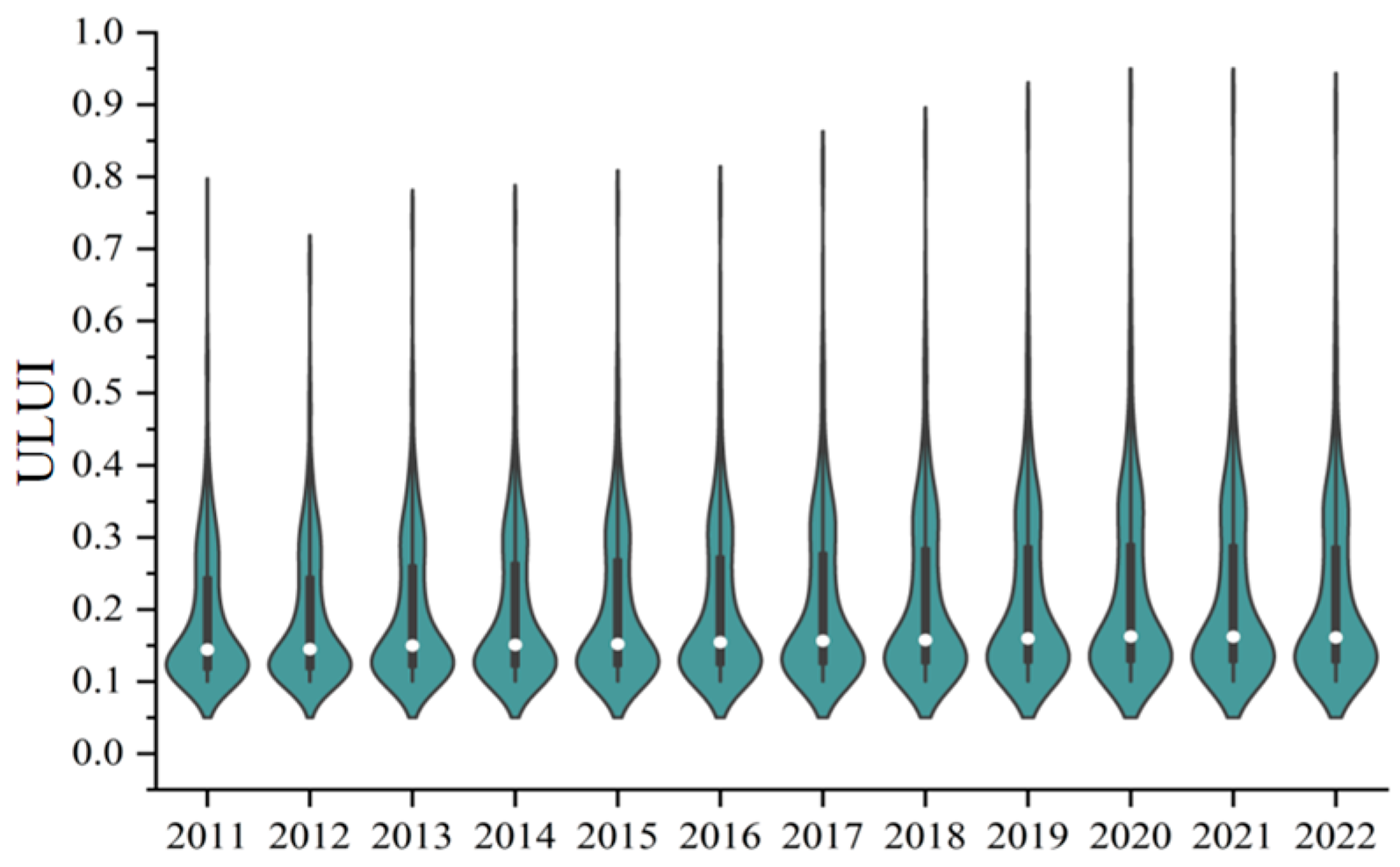
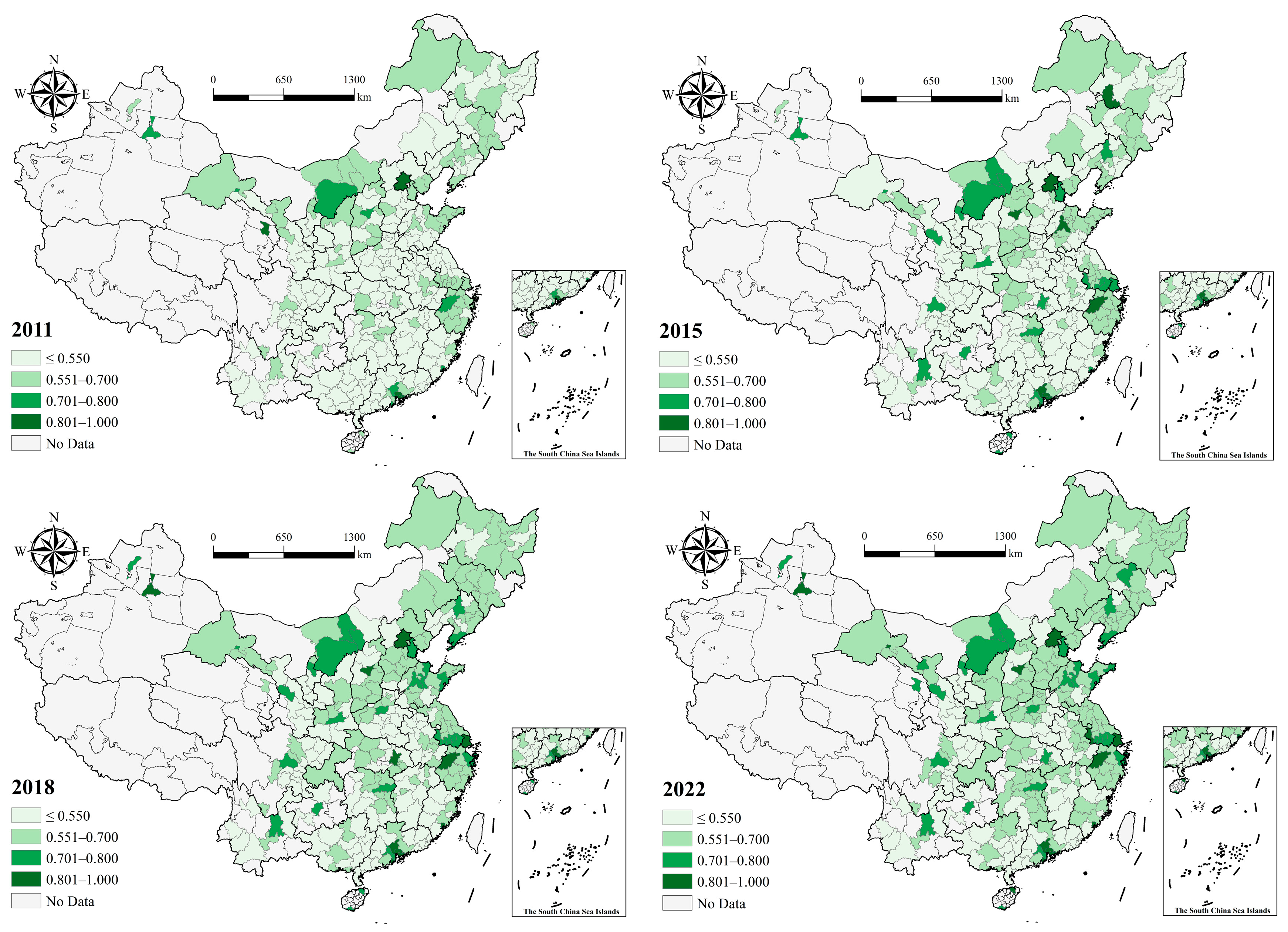

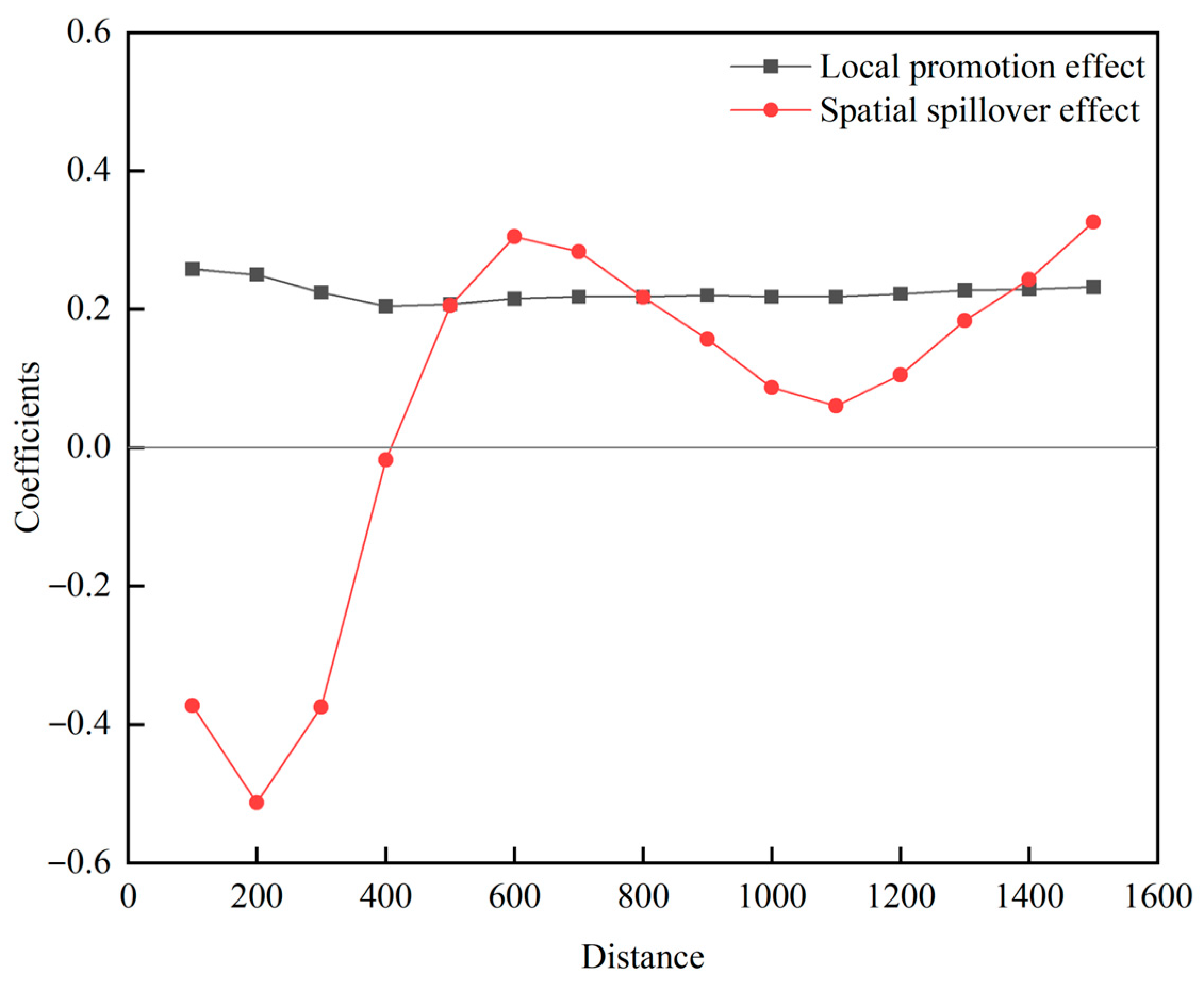
| Variable Categories | Variables | Obs | Mean | Sd | Min | Max | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | HDI | 3408 | 0.567 | 0.109 | 0.313 | 1.000 | -- |
| Explanatory variable | ULUI | 3408 | 0.205 | 0.116 | 0.100 | 0.929 | 1.90 |
| Mediating variables | lnRat | 3408 | 1.673 | 1.057 | −0.213 | 7.589 | 2.10 |
| lnAdv | 3408 | 1.090 | 0.613 | 0.114 | 5.348 | 1.61 | |
| lnAgg | 3408 | 0.079 | 0.263 | 0.004 | 5.147 | 2.40 | |
| lnSca | 3408 | 13.977 | 1.057 | 10.101 | 18.241 | 4.72 | |
| lnStr | 3408 | 0.417 | 0.056 | 0.159 | 0.610 | 1.42 | |
| lnPub | 3408 | 0.018 | 0.032 | 0.001 | 0.485 | 2.47 | |
| Control variables | urb | 3408 | 57.315 | 14.836 | 20.788 | 100.000 | 4.59 |
| lnGDP | 3408 | 10.755 | 0.561 | 8.773 | 12.456 | 4.83 | |
| lnFD | 3408 | 9.888 | 2.092 | −0.622 | 14.941 | 2.32 | |
| lnIC | 3408 | 7.626 | 0.571 | 5.583 | 9.142 | 2.87 | |
| lnMed | 3408 | 9.683 | 0.723 | 7.209 | 12.086 | 2.69 |
| Year | HDI | ULUI | Year | HDI | ULUI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.326 *** | 0.606 *** | 2017 | 0.310 *** | 0.610 *** |
| (8.30) | (15.47) | (7.88) | (15.54) | ||
| 2012 | 0.311 *** | 0.624 *** | 2018 | 0.323 *** | 0.609 *** |
| (7.90) | (15.88) | (8.21) | (15.52) | ||
| 2013 | 0.325 *** | 0.611 *** | 2019 | 0.307 *** | 0.609 *** |
| (8.25) | (15.57) | (7.81) | (15.51) | ||
| 2014 | 0.303 *** | 0.616 *** | 2020 | 0.304 *** | 0.613 *** |
| (7.70) | (15.67) | (7.72) | (15.62) | ||
| 2015 | 0.305 *** | 0.616 *** | 2021 | 0.306 *** | 0.612 *** |
| (7.75) | (15.67) | (7.77) | (15.61) | ||
| 2016 | 0.301 *** | 0.615 *** | 2022 | 0.309 *** | 0.612 *** |
| (7.66) | (15.66) | (7.87) | (15.60) |
| Test Type | SEM | SAR | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM test | 532.065 *** | 8.904 *** | SDM |
| Robust LM test | 648.798 *** | 125.636 *** | |
| LR test | 28.29 *** | 30.90 *** | SDM |
| Wald test | 85.65 *** | 102.59 *** | SDM |
| Hausman test | chi2(6) = −715.66 < 0 | ||
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | SDM-RE | SDM-FE | |
| ULUI | 0.086 *** | 0.357 *** | 0.203 *** |
| (7.44) | (10.30) | (11.14) | |
| urb | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.003 *** |
| (36.69) | (19.54) | (11.00) | |
| lnGDP | 0.055 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.021 *** |
| (16.69) | (9.36) | (6.48) | |
| lnFD | −0.006 *** | −0.002 *** | −0.002 *** |
| (−9.25) | (−5.31) | (−4.40) | |
| lnIC | 0.006 ** | 0.008 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (2.51) | (3.83) | (3.00) | |
| lnMed | 0.022 *** | 0.022 *** | 0.027 *** |
| (12.40) | (7.38) | (7.14) | |
| W* ULUI | −0.244 *** | −0.081 *** | |
| (−5.35) | (−3.37) | ||
| ρ | 0.086 *** | 0.105 *** | |
| (4.47) | (4.49) | ||
| R2 | 0.787 | 0.761 | 0.505 |
| Observations | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 |
| Variables | SDM-RE | SDM-FE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | |
| ULUI | 0.354 *** | −0.227 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.202 *** | −0.065 *** | 0.137 *** |
| (10.16) | (−5.03) | (4.21) | (11.00) | (−2.74) | (8.16) | |
| urb | 0.004 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (20.30) | (4.21) | (19.54) | (11.62) | (4.15) | (11.82) | |
| lnGDP | 0.031 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.021 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.024 *** |
| (9.66) | (4.04) | (9.73) | (6.67) | (3.66) | (6.70) | |
| lnFD | −0.002 *** | −0.000 *** | −0.003 *** | −0.002 *** | −0.000 *** | −0.002 *** |
| (−5.51) | (−3.59) | (−5.58) | (−4.53) | (−3.08) | (−4.52) | |
| lnIC | 0.007 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (4.05) | (3.17) | (4.10) | (3.17) | (2.72) | (3.22) | |
| lnMed | 0.022 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.024 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.030 *** |
| (7.48) | (3.71) | (7.44) | (7.27) | (3.48) | (7.09) | |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replacing the Weight Matrix | Adjusting Control Variables | Revising Weighting Method | Recomputing Explained Variables | Incorporating Environmental Dimension | Excluding Exogenous Events | Lagging Core Variables | IV (GS2SLS) | |
| W.HDI | −0.009 *** | |||||||
| (−3.73) | ||||||||
| ULUI | 0.227 *** | 0.180 *** | 0.336 *** | 2.268 *** | 1.423 *** | 0.359 *** | 0.335 *** | 0.226 *** |
| (8.08) | (4.06) | (12.75) | (12.36) | (2.74) | (8.86) | (9.72) | (10.58) | |
| W* ULUI | −0.316 *** | −0.171 *** | −0.348 *** | −2.282 *** | −1.258 * | −0.268 *** | −0.249 *** | |
| (−3.16) | (−3.22) | (−9.61) | (−8.97) | (−1.89) | (−5.15) | (−5.52) | ||
| Direct effect | 0.227 *** | 0.180 *** | 0.313 *** | 2.168 *** | 1.432 *** | 0.357 *** | 0.332 *** | |
| (7.95) | (4.01) | (12.38) | (12.08) | (2.71) | (8.73) | (9.57) | ||
| Indirect effect | −0.436 ** | −0.166 *** | −0.327 *** | −2.130 *** | −1.218 * | −0.256 *** | −0.237 *** | |
| (−1.97) | (−3.03) | (−7.00) | (−8.04) | (−1.91) | (−4.95) | (−5.27) | ||
| Total effect | −0.209 | 0.014 | −0.014 | 0.039 | 0.214 | 0.101 *** | 0.095 *** | |
| (−0.99) | (0.41) | (−0.33) | (0.19) | (0.52) | (2.94) | (3.24) | ||
| ρ | 0.505 *** | 0.045 ** | 0.474 *** | 0.276 *** | 0.040 *** | 0.068 *** | 0.075 *** | |
| (8.90) | (1.99) | (30.50) | (14.44) | (2.57) | (3.13) | (3.82) | ||
| R2 | 0.756 | 0.798 | 0.514 | 0.360 | 0.435 | 0.759 | 0.770 | |
| F-statistic | 898.166 | |||||||
| Observations | 3408 | 1988 | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 | 2556 | 3124 | 3408 |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Longitude | Eastern Cities | Non-Eastern Cities | City Scale | Megacities | Non-Megacities | |
| Direct effect, ULUI | 0.323 *** | 0.176 *** | 0.433 *** | 0.331 *** | 0.193 *** | 0.176 *** |
| (9.16) | (4.66) | (6.07) | (8.43) | (5.31) | (3.26) | |
| Indirect effect, ULUI | −0.193 *** | 0.083 | −0.378 *** | −0.212 *** | 0.043 | −0.053 |
| (−4.08) | (1.34) | (−4.17) | (−4.62) | (1.08) | (−0.79) | |
| Total effect, ULUI | 0.130 *** | 0.258 *** | 0.055 | 0.119 *** | 0.236 *** | 0.123 ** |
| (3.82) | (5.42) | (0.98) | (3.70) | (6.36) | (2.53) | |
| Direct effect, ULUI*P | 0.011 ** | 0.000 *** | ||||
| (2.48) | (2.68) | |||||
| Indirect effect, ULUI*P | 0.001 ** | 0.000 ** | ||||
| (2.17) | (2.29) | |||||
| Total effect, ULUI*P | 0.012 ** | 0.000 *** | ||||
| (2.48) | (2.70) | |||||
| ρ | 0.088 *** | 0.185 *** | 0.081 *** | 0.073 *** | 0.138 *** | 0.083 *** |
| (4.64) | (4.91) | (2.70) | (3.79) | (4.56) | (3.38) | |
| R2 | 0.769 | 0.817 | 0.756 | 0.773 | 0.858 | 0.686 |
| Observations | 3408 | 1368 | 2040 | 3408 | 1080 | 2328 |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnRat | lnAdv | lnAgg | lnSca | lnStr | lnPub | LnSyn | |
| ULUI | 4.299 *** | 1.329 *** | 0.145 * | 1.611 *** | 0.068 ** | 0.035 ** | 0.214 *** |
| (7.84) | (4.15) | (1.84) | (4.48) | (2.09) | (2.50) | (8.95) | |
| Direct effect | 4.166 *** | 1.233 *** | 0.155 ** | 1.678 *** | 0.078 ** | 0.033 ** | 0.209 *** |
| (7.83) | (3.99) | (1.98) | (4.73) | (2.45) | (2.43) | (8.97) | |
| Indirect effect | −2.680 *** | −1.959 *** | 0.211 * | 1.409 *** | 0.142 *** | −0.055 *** | −0.118 *** |
| (−3.18) | (−3.86) | (1.84) | (2.59) | (3.08) | (−2.76) | (−3.26) | |
| Total effect | 1.486 ** | −0.727 * | 0.366 *** | 3.087 *** | 0.219 *** | −0.022 | 0.091 *** |
| (2.24) | (−1.89) | (4.72) | (8.03) | (5.76) | (−1.62) | (3.25) | |
| ρ | 0.328 *** | 0.313 *** | 0.176 *** | 0.203 *** | 0.359 *** | 0.180 *** | 0.296 ** |
| (15.25) | (15.08) | (8.30) | (8.93) | (19.05) | (6.35) | (13.22) | |
| R2 | 0.368 | 0.358 | 0.001 | 0.743 | 0.202 | 0.043 | 0.346 |
| Observations | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 | 3408 |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Niu, S.; Li, X.; Jing, L.; Qin, J.; Tang, Y. Urban Spatial Blessing: Effect of Land Use Intensity on Human Development Index. Land 2025, 14, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051085
Luo X, Niu S, Li X, Jing L, Qin J, Tang Y. Urban Spatial Blessing: Effect of Land Use Intensity on Human Development Index. Land. 2025; 14(5):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051085
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xiang, Shuchen Niu, Xin Li, Liwei Jing, Jingjing Qin, and Yue Tang. 2025. "Urban Spatial Blessing: Effect of Land Use Intensity on Human Development Index" Land 14, no. 5: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051085
APA StyleLuo, X., Niu, S., Li, X., Jing, L., Qin, J., & Tang, Y. (2025). Urban Spatial Blessing: Effect of Land Use Intensity on Human Development Index. Land, 14(5), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051085







