Risk-Targets Identification and Source Apportionment Associated with Heavy Metals for Different Agricultural Soils in Sunan Economic Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
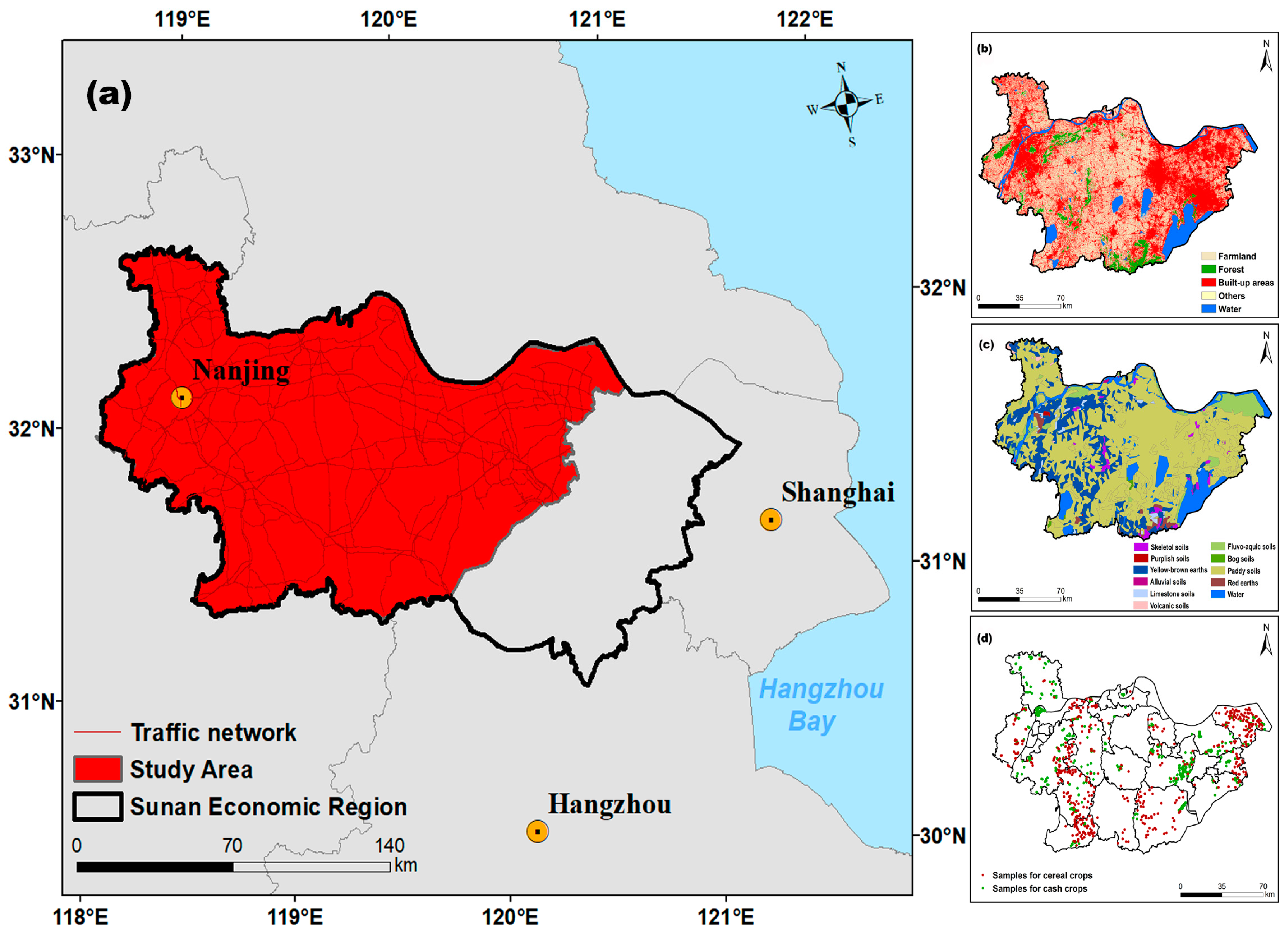
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collections
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Heavy Metal Contamination Indices
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Source Apportionment—PMF Model
2.6. Geostatistical Analysis and Targets Identification
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
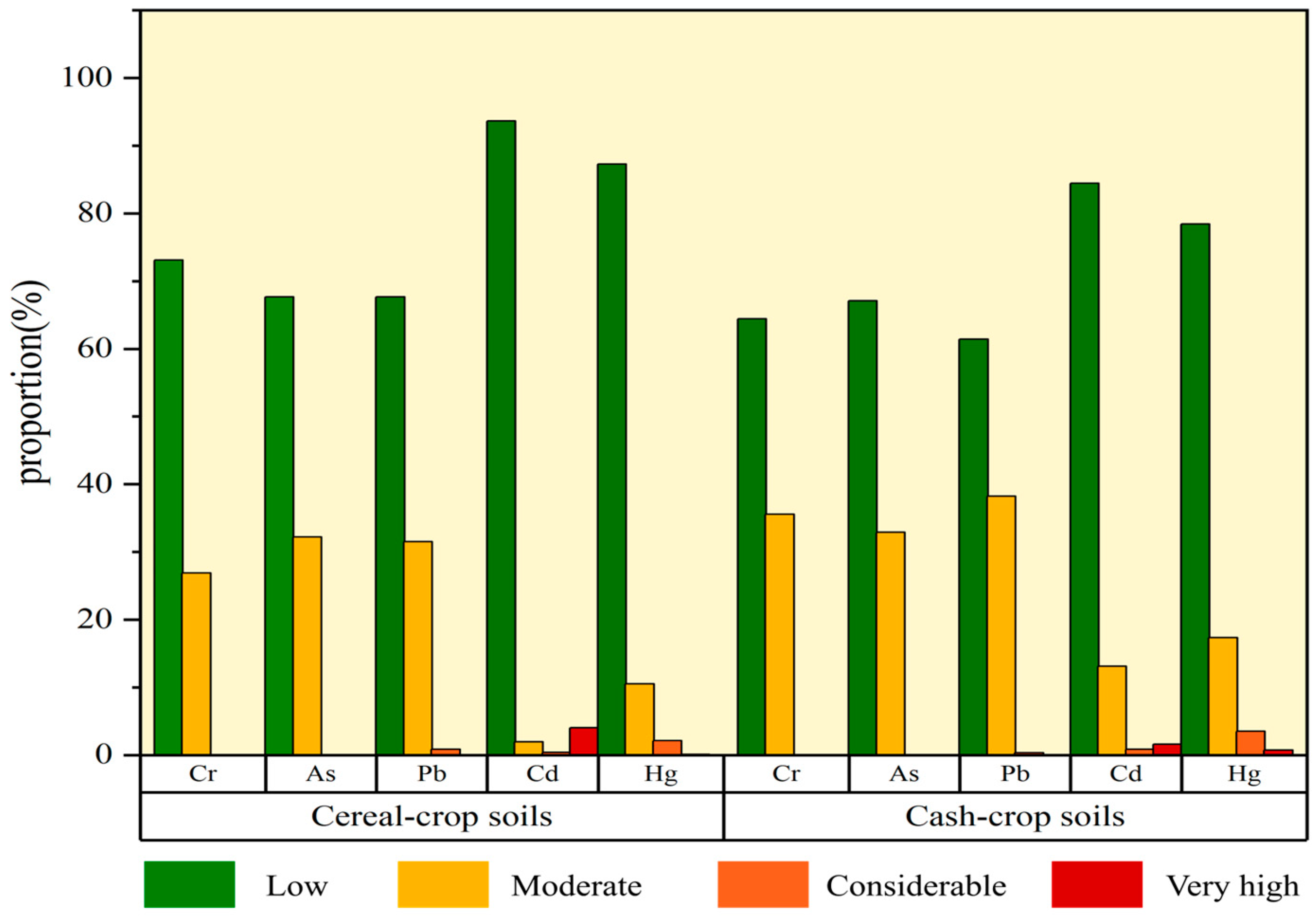
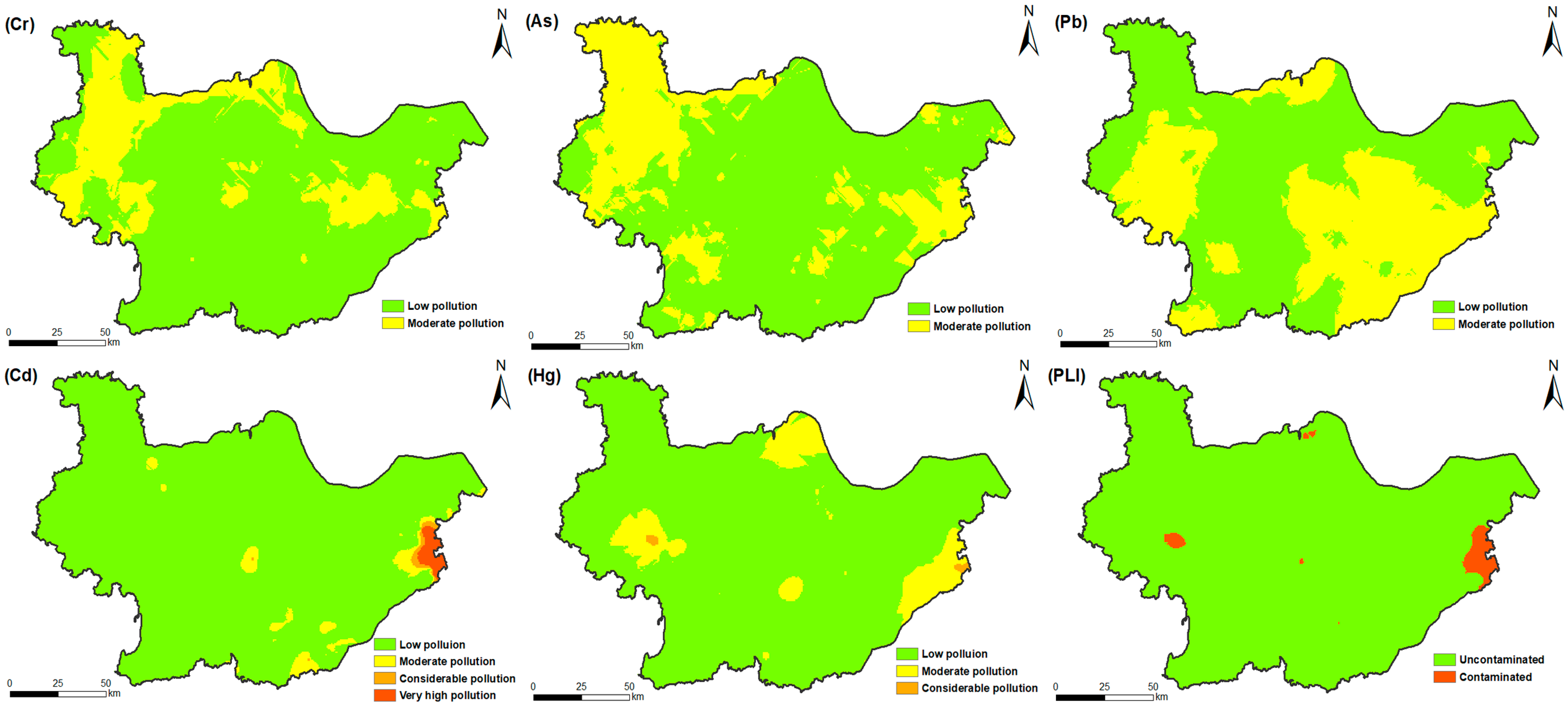
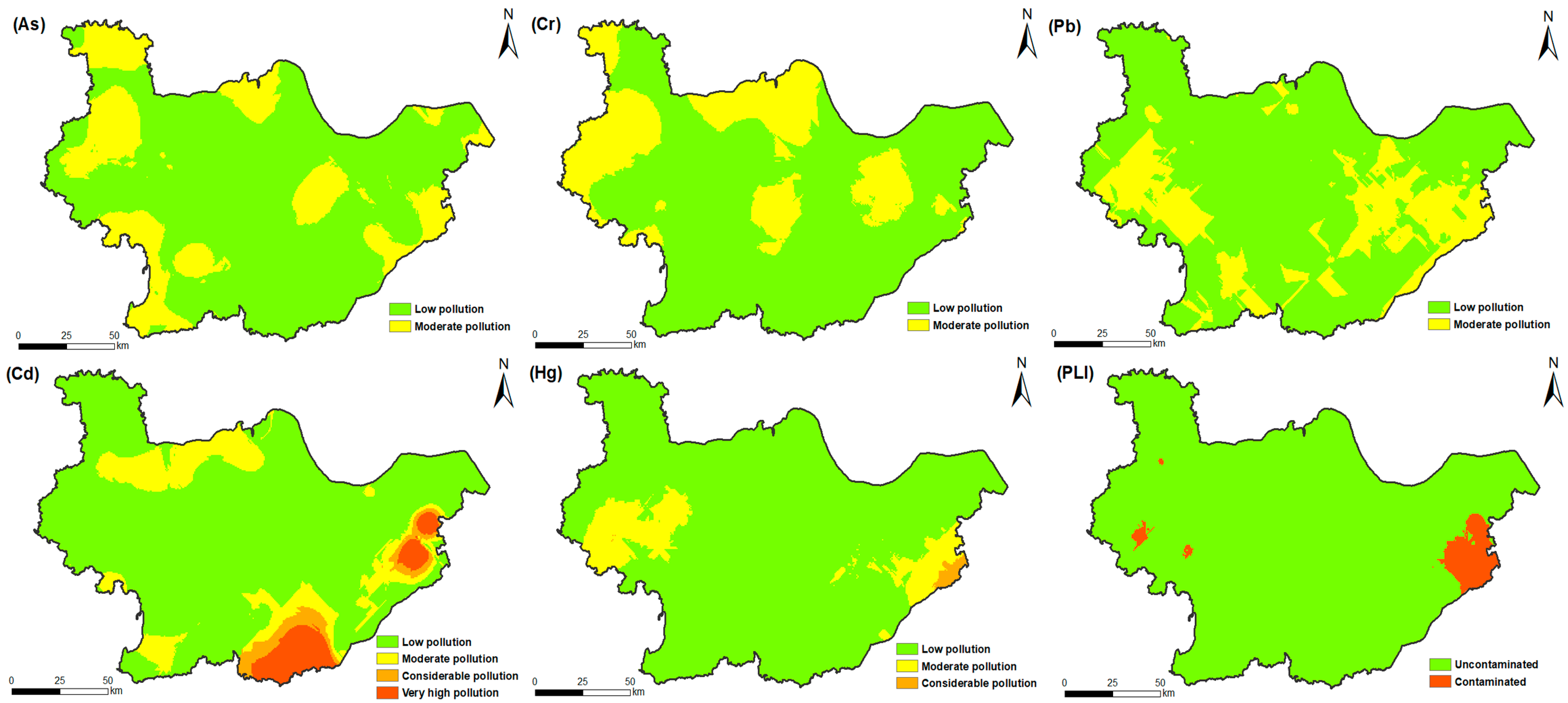
3.2. Soil Heavy Metals Pollution
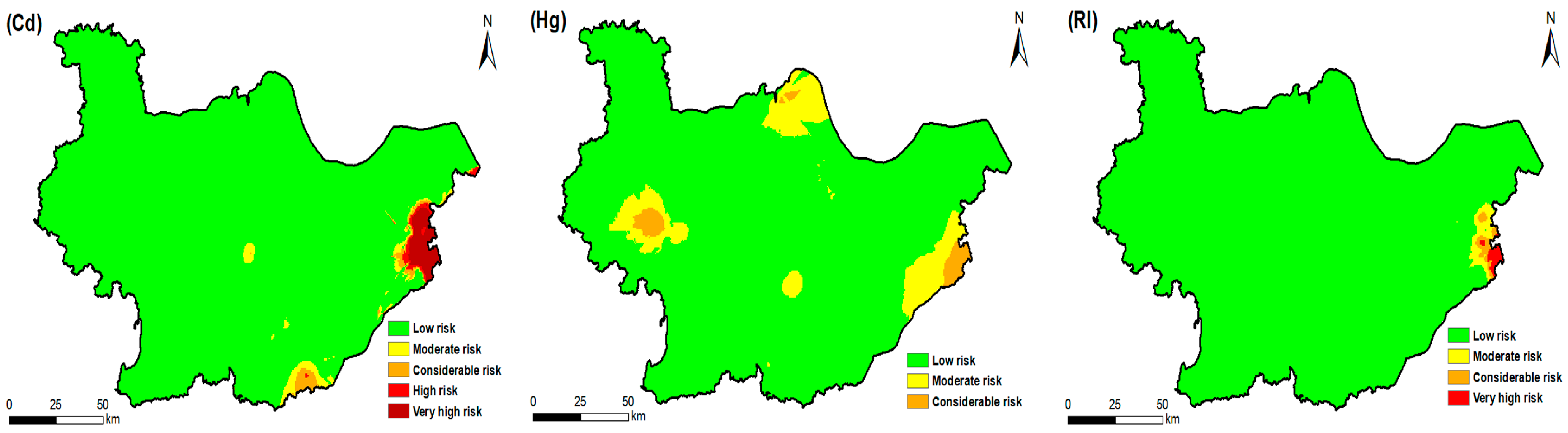
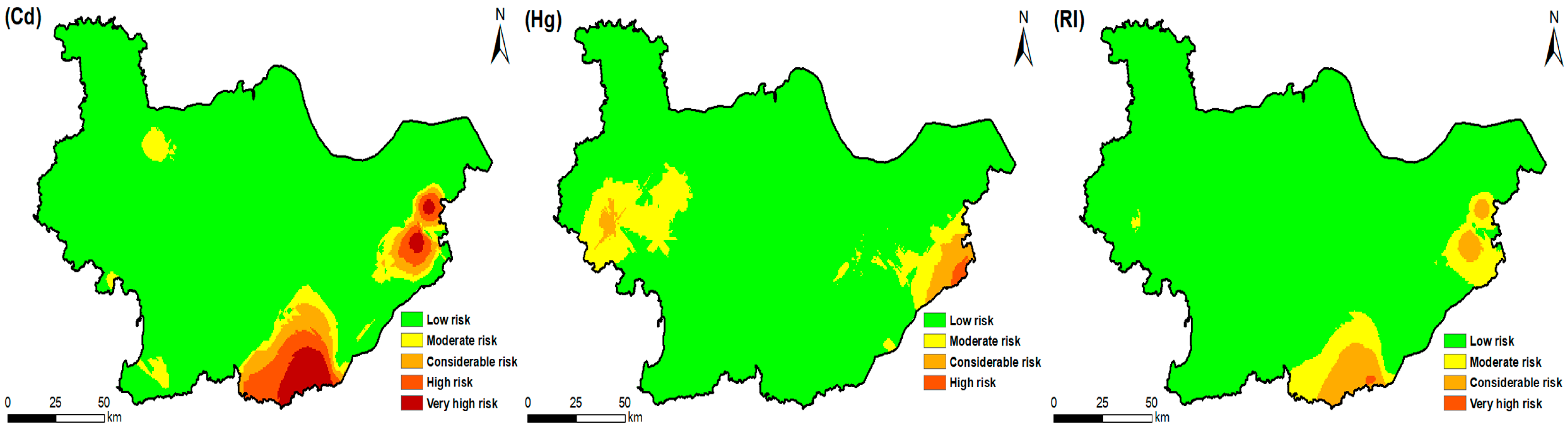
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk
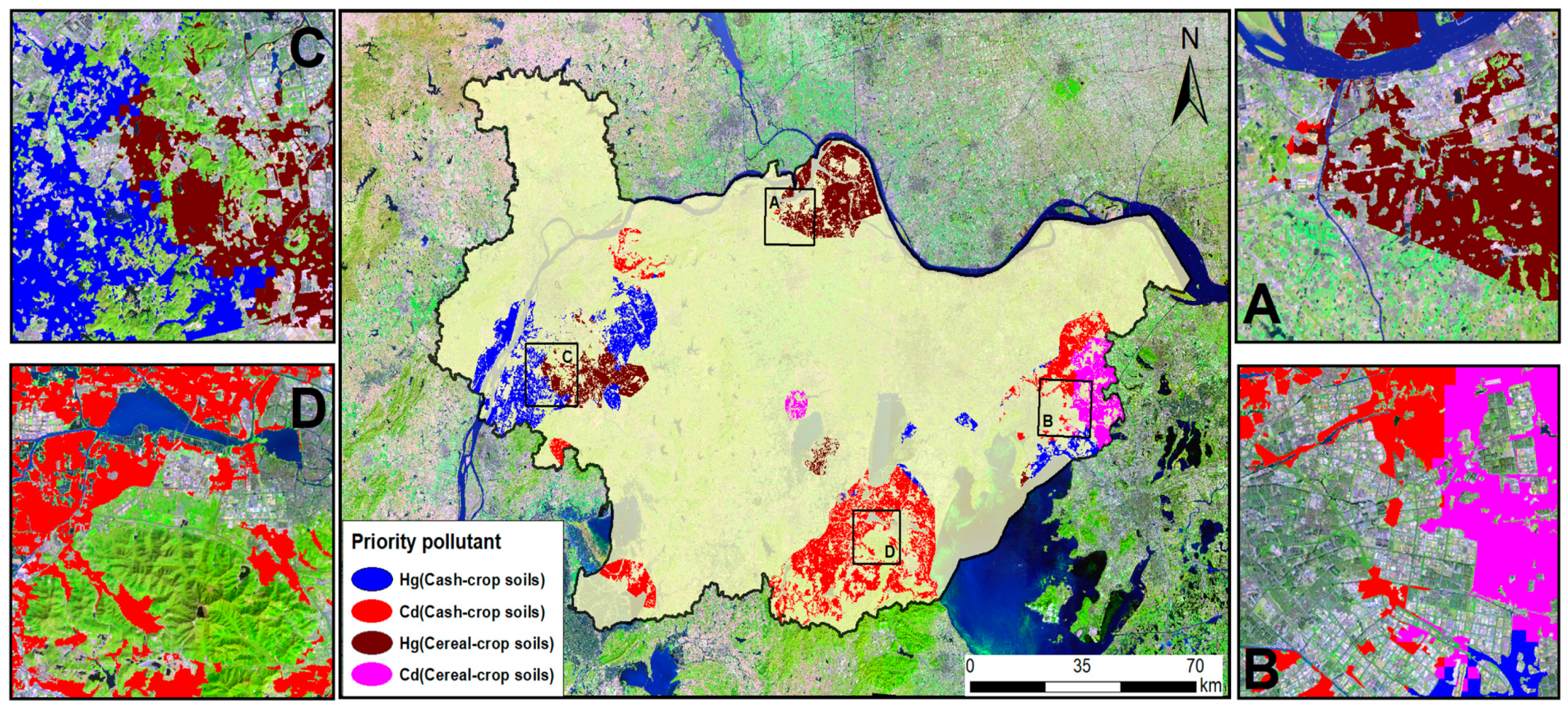
3.4. Targeted Zones and Priority Pollutants
3.5. Source Apportionment for Priority Pollutants
4. Discussion
4.1. Source Identification and Major Influencing Factors
4.2. Implications for Sustainable Soil Management and Policy Recommendations
4.3. Limitations and Outlooks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, K.C.; Ramankutty, N. Hidden linkages between urbanization and food systems. Science 2016, 352, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D.; McGranahan, G.; Tacoli, C. Urbanization and its implications for food and farming. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2809–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.C.; Huggins, D.R.; Jones, S.S. Characterizing nitrogen use efficiency in natural and agricultural ecosystems to improve the performance of cereal crops in low-input and organic agricultural systems. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.W.; Son, J. Contamination and spatial distribution of metal(loid)s in the stream sediment near the greenhouse. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A.; Ahmad, E. Soil Contamination, Nutritive Value, and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals: An Overview; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chileshe, M.N.; Syampungani, S.; Festin, E.S.; Tigabu, M.; Daneshvar, A.; Odén, P.C. Physico-chemical characteristics and heavy metal concentrations of copper mine wastes in Zambia: Implications for pollution risk and restoration. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; He, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Zhu, Y. Composition and function of soil fungal community during the establishment of Quercus acutissima (Carruth.) seedlings in a Cd-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hong, S.; Wen, M.; Zheng, C.; Liu, P. Speciation analysis and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of a typical mining area: A case study of Dachang tin polymetallic ore, Guangxi. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yun, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Shabala, S. Assessing impact of elevated CO2 on heavy metal accumulation in crops: Meta-analysis and implications for food security. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radfard, M.; Hashemi, H.; Baghapour, M.A.; Samaei, M.R.; Yunesian, M.; Soleimani, H.; Azhdarpoor, A. Prediction of human health risk and disability-adjusted life years induced by heavy metals exposure through drinking water in Fars Province, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, E.M.; Ramirez, K.S.; Fraser, T.D.; Wall, D.H. Soil biodiversity integrates solutions for a sustainable future. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma-Wardana, M.W.C. Fertilizer usage and cadmium in soils, crops and food. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2739–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnelo, L.G.L.; de Miguez, S.R.; Marbán, L. Heavy metals input with phosphate fertilizers used in Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 204, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Magdaleno, H.; Mancilla-Villa, O.R.; Mejía-Saenz, E.; Olmedo-Bolaños, M.D.C.; Bautista-Olivas, A.L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils and irrigation wastewater of Mixquiahuala, Hidalgo, Mexico. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 5505–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungai, T.M.; Owino, A.A.; Makokha, V.A.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, J. Occurrences and toxicological risk assessment of eight heavy metals in agricultural soils from Kenya, Eastern Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18533–18541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J. Soil physiochemical properties and landscape patterns control trace metal contamination at the urban–rural interface in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuswir, N.S.; Praveena, S.M.; Aris, A.Z.; Syed Ismail, S.N.; De Burbure, C.; Hashim, Z. Heavy metal contamination in urban surface soil of Klang district (Malaysia). Soil Sediment Contam. 2015, 24, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, G. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, H.; Sirin, M.; Gökbayrak, E.; Ozcelik, A.E. A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop Province, Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelepertzis, E. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: Insights from Argolida Basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 2014, 221, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Ning, Z.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Zhou, G. High cadmium concentration in soil in the Three Gorges region: Geogenic source and potential bioavailability. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gredilla, A.; de Vallejuelo, S.F.O.; Rodriguez-Iruretagoiena, A.; Gomez, L.; Oliveira, M.L.; Arana, G.; Silva, L.F. Evidence of mercury sequestration by carbon nanotubes and nanominerals present in agricultural soils from a coal-fired power plant exhaust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Driving factors on accumulation of cadmium, lead, copper, and zinc in agricultural soil and products of the North China Plain. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources, and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEPPRC); Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MLRPRC). Bulletin on National Survey of Soil Contamination; MEPPRC and MLRPRC: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Yang, B.; Jin, Z.; Guo, B. Source analysis and contribution estimation of heavy metal contamination in agricultural soils in an industrial town in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jia, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, D.; Xia, F.; Li, Y. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil–plant–human system in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Meng, F.; Prishchepov, A.V. How is urbanization shaping agricultural land-use? Unraveling the nexus between farmland abandonment and urbanization in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 214, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, G.; Meadows, M.E.; Zou, C. Spatio-temporal evolution of the early-warning status of cultivated land and its driving factors: A case study of Heilongjiang Province, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Meng, F.; Ji, C.; Xie, L.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, H. Linking food production and environmental outcomes: An application of a modified relative risk model to prioritize land-management practices. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Hu, W.; Xing, Z.; Huang, B.; Jia, M.; Wan, M. Determination and evaluation of heavy metals in soils under two different greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, G.; Zhang, D.; Lei, M. An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Liao, Q.L.; Hua, M.; Wu, X.M.; Bi, K.S.; Yan, C.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong District, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, L.; Dubs, F.; Gignoux, J.; Lata, J.C.; Lerch, T.Z.; Mathieu, J.; Barot, S. Trace element concentrations along a gradient of urban pressure in forest and lawn soils of the Paris region (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Kwon, E.; Song, H.; Wang, S.L.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Rinklebe, J. Soil contamination by potentially toxic elements and the associated human health risk in geo- and anthropogenic contaminated soils: A case study from the temperate region (Germany) and the arid region (Egypt). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: A case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Tu, L.; Sun, L. Historical records and contamination assessment of potential toxic elements (PTEs) over the past 100 years in Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, E.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X.; Lei, P.; Qiao, X.; Gao, Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks associated with heavy metals in the Fuyang River system in North China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J. Multivariate receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, S.; Sobiecka, E.; Contini, S.; Locoro, G.; Free, G.; Gawlik, B.M. The application of positive matrix factorization in the analysis, characterisation and detection of contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Chan, C.K.; Paatero, P. Application of positive matrix factorization in source apportionment of particulate pollutants in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3201–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, C.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.; Qin, M.; Yang, D.; Dick, R.P. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.T.; Sousa, A.J.; Abreu, M.M. Ordinary kriging and indicator kriging in the cartography of trace elements contamination in São Domingos mining site (Alentejo, Portugal). J. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 98, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, W.; Fu, W. Risk assessment, spatial patterns and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical Chinese hickory plantation region of southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, M.; Baur, P.; Koch, B.; Zimmermann, N.E. Agricultural land abandonment and natural forest re-growth in the Swiss mountains: A spatially explicit economic analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, T.; Karakaş, D.; Yenisoy-Karakaş, S. Source identification of exhaust and non-exhaust traffic emissions through the elemental carbon fractions and positive matrix factorization method. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juda-Rezler, K.; Reizer, M.; Maciejewska, K.; Błaszczak, B.; Klejnowski, K. Characterization of atmospheric PM2.5 sources at a Central European urban background site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrot, N.; Wojciechowska, E.; Rezania, S.; Walkusz-Miotk, J.; Pazdro, K. The effects of urban vehicle traffic on heavy metal contamination in road sweeping waste and bottom sediments of retention tanks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, C.; Zeng, G.; Zhong, M.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Mo, D. Atmospheric deposition of mercury and cadmium impacts on topsoil in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Guo, D.; Ali, A.; Mi, S.; Liu, T.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Z. Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: A case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Hao, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chan, M.; Tian, H.; Feng, X. Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7789–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Yu, Y.J.; Ye, T.T.; Fei, J.C.; Song, X.Y.; Peng, J.W.; Wu, H.H. Distribution characteristics and environmental risk assessment following metal(loid)s pollution incidents at Southwest China mining site. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 4062–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Jabbari, M.; Khademi, H. Multiple linear modeling between soil properties, magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals in various land uses. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Al-Mamun, M.H.; Islam, S.M.A. Sources and ecological risks of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in Bangladesh. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, E.; Oshvandi, Z. Spatial patterns, hotspot, and risk assessment of heavy metals in different land uses of urban soils (case study: Malayer city). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Shen, Z.; Dou, C.; Dou, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q. Effects of soil properties on heavy metal bioavailability and accumulation in crop grains under different farmland use patterns. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cereal-Crop Soils | Cash-Crop Soils | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | As | Hg | Cd | Pb | Cr | As | Hg | Cd | Pb | |
| Maximum (mg/kg) | 128.04 | 38.6 | 0.16 | 11.5 | 89.27 | 144.00 | 21.10 | 0.20 | 2.38 | 70.67 |
| Minimum (mg/kg) | 10.00 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 7.24 | 3.25 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 2.40 |
| Mean (mg/kg) | 64.64 | 8.67 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 20.89 | 70.50 | 8.90 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 21.55 |
| Median (mg/kg) | 67.40 | 8.64 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 20.00 | 71.64 | 8.61 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 20.33 |
| Standard deviation | 19.84 | 2.71 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 8.75 | 17.62 | 2.32 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 7.96 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 30.70 | 31.30 | 94.70 | 85.60 | 41.90 | 24.99 | 26.07 | 100.09 | 87.84 | 36.95 |
| Skewness | −0.42 | 2.20 | 3.65 | 6.96 | 2.92 | −0.28 | 0.88 | 3.74 | 7.98 | 1.46 |
| Kurtosis | 0.23 | 19.73 | 17.44 | 47.53 | 14.93 | 2.21 | 1.80 | 16.79 | 64.25 | 5.16 |
| Heavy Metals | Cereal-Crop Soils | Cash-Crop Soils | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| Cr | 12.36 | 25.89 | 58.32 | 3.43 | 67.70 | 2.28 | 0.02 | 30.00 |
| Pb | 48.99 | 30.69 | 18.59 | 1.72 | 0.00 | 4.31 | 21.92 | 73.77 |
| Cd | 1.44 | 5.41 | 4.48 | 88.67 | 0.00 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| As | 1.10 | 64.05 | 34.86 | 0.00 | 36.48 | 4.14 | 59.25 | 0.12 |
| Hg | 26.71 | 12.71 | 37.61 | 22.98 | 12.30 | 3.00 | 0.00 | 84.69 |
| Total | 18.12 | 27.75 | 30.77 | 23.36 | 23.30 | 22.75 | 16.24 | 37.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, D.; Xie, H.; Yang, L. Risk-Targets Identification and Source Apportionment Associated with Heavy Metals for Different Agricultural Soils in Sunan Economic Region, China. Land 2025, 14, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051058
Hou D, Xie H, Yang L. Risk-Targets Identification and Source Apportionment Associated with Heavy Metals for Different Agricultural Soils in Sunan Economic Region, China. Land. 2025; 14(5):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Dawei, Hu Xie, and Lixiao Yang. 2025. "Risk-Targets Identification and Source Apportionment Associated with Heavy Metals for Different Agricultural Soils in Sunan Economic Region, China" Land 14, no. 5: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051058
APA StyleHou, D., Xie, H., & Yang, L. (2025). Risk-Targets Identification and Source Apportionment Associated with Heavy Metals for Different Agricultural Soils in Sunan Economic Region, China. Land, 14(5), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051058





