Abstract
The Loess Plateau (LP), the cradle of Chinese civilization, has a long history of agricultural activities closely linked to ecological changes. This study addresses a fundamental question: what was the maximum sustainable cropland area threshold for the LP prior to modern soil and water conservation measures? To answer this, we analyzed the historical data to investigate changes in the cropland area and their ecological impacts over the past 4000 years, with the specific aim of examining the long-term interactions between land exploitation and the ecosystem that defined sustainable thresholds. Three key stages of cropland area development were identified: slow growth (2000–500 BC), a fluctuating phase (500 BC–1000 AD), and rapid expansion (1000–2000 AD). During the slow-growth and rapid-expansion stages, the cropland areas were estimated at 34.9 ± 23.4 and 117.9 ± 34.1 thousand km2, with growth rates of 2.9 and 8.7 thousand km2/100 years, respectively, while the fluctuating period stabilized at 62.1 ± 18.1 thousand km2. Population growth was the primary driver of cropland expansion (56.9%), followed by agricultural technology and policy adjustments (27%) and climate change (16.1%). Particularly over the past 1000 years, climate deterioration and a population surge due to the abolition of the poll tax accelerated cropland expansion, resulting in deforestation, intensified soil erosion specific to the LP, and frequent flooding of the lower Yellow River (YR). In contrast, during the fluctuating period, rapid social development did not lead to major ecological issues, suggesting that moderate cropland expansion can balance social development and ecological sustainability. Based on the historical conditions, without modern soil and water conservation measures, this study determined that the upper limit of the cropland area during the fluctuating period (80.2 thousand km2) is the maximum sustainable cropland area for the LP, establishing a scientific basis to guide future land-use strategies. Especially in the face of population pressure and climate deterioration, developing agriculture and adjusting policies to increase grain production will be essential to balance the ecological risks and maintenance of food security while remaining within this threshold. These findings offer insights into the agricultural history and ecological management of the LP and can serve as a reference for similar studies of other regions.
Keywords:
cropland area; Loess Plateau; Yellow River; ecological impacts; population; climate change 1. Introduction
Human activities have significantly altered the natural environment, with the intensity and scale of these changes increasing substantially over the past few centuries [1]. Land use/cover change (LUCC) is a key manifestation of human influence on terrestrial environments [2]. Research estimates indicate that the proportion of cropland with respect to the total global land area was less than 1% from the emergence of agriculture (approximately 12,000 years ago) until 1000 AD, but increased to 4.4% by 1850 and 12.2% by 2015 [3]. Cropland expansion has not only reshaped the terrestrial landscape but has also profoundly affected regional and global environmental changes by altering the physical conditions of land surfaces and biogeochemical cycles [4]. A comprehensive understanding of historical land development processes, their influencing factors, and ecological effects is crucial for formulating sustainable land-use strategies to maintain ecological balance and promote social development.
The Loess Plateau (LP) is located in northcentral China along the middle reaches of the Yellow River (YR) (Figure 1). The LP’s loose loess and its arid-to-semi-arid climate impede vegetation growth, making it a major source of sediment for the YR, contributing approximately 90% of its sediment load [5,6]. Despite these challenges, the fertile soil and agricultural suitability of the LP made it the cradle of Chinese civilization [7]. However, the expansion of agriculture and increased human activity led to large-scale deforestation, exacerbating natural erosion processes [8]. By 1990, soil erosion affected approximately 500,000 km2 of the LP, with 145,000 km2 experiencing severe erosion rates exceeding 5000 t/km2/year [9]. This erosion has exacerbated local drought conditions, reduced soil fertility, and prompted farmers to adopt extensive, low-yield cultivation practices, further aggravating land desertification and creating a vicious cycle [10]. For the YR Basin, intensified soil erosion led to sediment loads exceeding 1.6 Gt/year from 1967 to 1973 [11], far surpassing the pre-250 AD natural sediment load of 0.1 Gt/year [12]. Upon reaching the downstream North China Plain, these excessive sediment volumes raised the riverbed’s levels, reduced the river’s flood discharge capacity, and transformed the YR into a “suspended river”, thus increasing the flood risk [13]. When floods exceed the river’s discharge capacity, they often breach levees, submerging farmland and villages, and causing significant economic and social losses [14]. These historical lessons reveal that the LP has a critical cropland intensity threshold—when the development intensity remained below this threshold, the system maintained a balance between social development and ecological functions (i.e., an ecologically sustainable state), whereas exceeding it triggered systemic collapse. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the LP’s land development history is crucial for advancing ecological conservation, ensuring the sustainable development of the YR Basin, and maintaining flood safety in downstream areas.
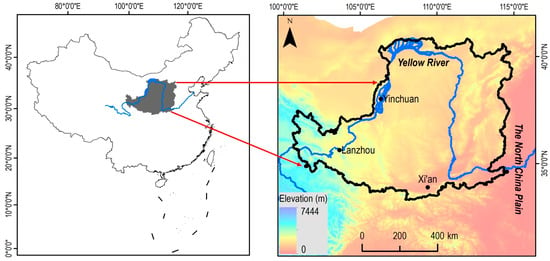
Figure 1.
Location of the Loess Plateau (LP).
Although significant progress has been made in reconstructing historical cropland areas across China in recent years [15,16,17,18,19], quantitative studies on cropland expansion in the LP remain limited. In particular, the research on land development and its impacts on the ecological balance of the YR Basin for the historical periods prior to the implementation of soil and water conservation measures is insufficient. While the Global Land Use/Cover Change (LUCC) project, promoted by the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP), has made notable progress [20], including the development of databases, such as the Historical Database of the Global Environment (HYDE) [21] and the Global Land Use Database (SAGE) [22], these global-scale datasets often exhibit notable discrepancies when applied to regional studies. These discrepancies primarily arise from the limitations of the original data and the spatial allocation models [23,24,25,26]. These limitations are particularly acute for determining the precise carrying capacity of the LP’s ecosystems. However, integrating these datasets with the historical land-use data and performing appropriate calibrations could substantially improve their accuracy for and applicability to regional studies [27]. To quantify this critical threshold, this study establishes a quantitative relationship between the HYDE dataset and the historically estimated cropland area in China to calibrate the cropland area for the LP derived from the HYDE, and uses this calibration to analyze the drivers and ecological impacts of cropland area changes in the LP over the past 4000 years, with an explicit consideration of the ecological thresholds, revealing for the first time the upper limit of cropland area necessary to maintain ecological balance without soil conservation measures. This research will not only deepen our understanding of the relationship between land use and ecosystems in the YR Basin during previous historical periods, but also provide a historical framework for evaluating the effectiveness of modern soil and water conservation policies, informing strategies to enhance the social and ecological benefits of current conservation efforts.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Loess Plateau (Figure 1) is located in the middle–upper reaches of the Yellow River, spanning 33°43′–41°16′ N and 100°54′–114°33′ E, with a total area of 640,000 km2 and a population of 98 million (2005 data). This region exhibits a typical continental monsoon climate. Over the past century, mean annual temperatures have displayed a spatial gradient, decreasing from 14.3 °C in the southeast to 4.3 °C in the northwest, paralleled by annual precipitation, declining from 700 mm in the southeast to 200 mm in the northwest. As the world’s largest loess deposit, formed during the Quaternary period, it has preserved the most complete loess–paleosol sequences globally, averaging 100 m in thickness [28]. The natural ecosystem is dominated by grassland vegetation, while agricultural development has created a distinct agro-pastoral transitional system. This constitutes a classic ecologically fragile zone, where degraded environments show limited short-term recovery capacity. Its complex topography, loose soil texture, concentrated heavy rainfall events, and intensive human activities have collectively made the Loess Plateau one of the world’s most severe soil erosion hotspots and the primary sediment source for the Yellow River. Approximately 70% of the river’s sediment is ultimately deposited in downstream channels and the delta, directly driving the historical frequency of levee breaches and channel avulsions of the lower Yellow River.
2.2. Cropland Area
The cropland grid data are from the HYDE version 3.1 dataset, developed by the Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency. The dataset covers the time range from 10,000 BC to 2000 AD, with a spatial resolution of 5′ × 5′ and temporal resolutions of 1000 years before 0 AD, 100 years between 0 and 1700 AD, and 10 years from 1700 to 2000 AD. The dataset can be downloaded from http://themasites.pbl.nl/en/themasites/hyde/download/index.html (accessed on 1 October 2024). The procedure for acquiring the cropland area in this study consisted of three steps [29]: (1) Extracting the cropland area from the HYDE dataset. Geographic registration was performed using the LP and China’s geographical boundaries, counting the number of cropland grid cells within these boundaries and multiplying by the area of a single grid cell to calculate the cropland area for different periods in the LP and China. (2) Establishing a functional relationship (using linear regression) between the cropland area derived from the HYDE dataset and historical literature estimates for China. (3) Using this functional relationship to adjust the cropland area in the LP as provided by the HYDE dataset. The cropland area for different periods in China was derived from previous research (Table 1).

Table 1.
Historical cropland area in China.
2.3. Farming–Grazing Boundary
The LP is a region where both agriculture and pastoralism can thrive. Historically, the southern and northern parts of the plateau were inhabited by agricultural and nomadic societies, respectively. The boundary between these areas has largely been transformed over time. Initially, this boundary was a natural demarcation. However, as the dominance of farming and pastoral societies fluctuated, it evolved into a man-made division [30]. The location of the farming–grazing boundary (FGB) used in this study was based on historical records, including local customs, production relations, and economic factors [31]. Specifically, this was accomplished through systematic compilation and quantitative analysis of key economic–geographic parameters documented in historical records of the Loess Plateau region, including the following: (1) production modes (particularly the cultivation-to-grazing ratio), and (2) livestock composition (notably species distribution and quantitative proportions of cattle, sheep, and other domesticated animals), which collectively enabled precise demarcation of the FGB boundary.
Historically, the FGB was not a straight line but a complex, interwoven zone, making it difficult to track its shifts over different periods. To quantify these changes, we calculated the relative movement of the FGB for each period by measuring the distance from the boundary between 105° E and 114° E longitude to the 34° N latitude, which marks the southern edge of the LP [29]. The calculation followed the following formula:
In this formula, Distance represents the distance from the FGB between the 105° E and 114° E longitudes to the 34° N latitude; Area is the area enclosed by the FGB, between the 105° E and 114° E longitudes to the 34° N latitude; and Length refers to the length of the 34° N latitude between the 105° E and 114° E longitudes. Both Area and Length were calculated using ArcMap 10.8 (ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA).
2.4. Population
There were three methods used for obtaining population data: (1) direct acquisition, which was used for the following years: 2000–771 BC, 2 AD, 140, 280, 609, 742, 1291, 1820, 1840, 1873, 1911, 1928, 1949, and 2000 AD [9,32,33,34]; (2) aggregating population data from published works on counties in Ningxia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu, and Inner Mongolia, located in the LP, for the years 340, 202 BC, 639 AD, 983, 1102, 1207, 1330, 1381, 1578, and 1661 AD [35]; and (3) since the LP largely encompasses the middle reaches of the YR (estimated to cover ~70% of its drainage area based on our geospatial analysis), it was assumed that the population ratio between two adjacent periods in both regions remained constant. Based on this assumption, the population for the LP in 25 AD, 105, 581, and 934 AD was estimated by multiplying the population ratio of the middle YR for each of these years and the preceding year (when both the LP and the middle YR have population data for the same years) with the population of the LP for preceding year [29]. The population data for the middle YR were sourced from the study ‘Research on Environmental Evolution and Sediment Transport Patterns in the Yellow River Basin’ [36].
2.5. Other Datasets
The forest cover [37], precipitation [38], and temperature [39] for the LP; sediment load of the YR [40]; and flooding and river management events in the lower reaches of YR [41] were obtained from published sources. Forest cover was estimated through reconstructed distribution maps based on historical species records, precipitation was reconstructed using palynological methods, and temperature was derived from phenological data. Sediment load was inferred from modern instrumental measurements combined with historical records, while flooding events and river management activities in the lower Yellow River were extracted from official historical archives. The population density atlas of the LP was constructed through the following steps: First, the population data for each historical period were extracted from monograph [35], and divided by the area of the respective administrative region to calculate the population density for each period. Next, these densities were weighted according to the proportion of each historical municipal administrative region within the modern administrative boundaries. This process resulted in population density maps for each historical period, standardized to modern municipal administrative divisions, enabling comparisons across different time periods.
2.6. Calculation of Contribution Rates
To understand the influence and contribution of multiple factors (independent variables) on cropland area (the dependent variable), a multiple regression equation was first established to obtain its coefficient of determination (R2). R2 represents the proportion of variance in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables, and can also be interpreted as the sum of the contribution rates of each independent variable. The unexplained variance, denoted as (1 − R2), was attributed to factors not included in the model. Next, the regression coefficients of each independent variable were standardized (Equation (2)). Finally, the contribution rate (Pi) of the nth independent variable to the dependent variable was calculated using the standardized regression coefficients and the Földi formula (Equation (3)) [42].
where βi is the standardized regression coefficient of the ith independent variable, bi is the regression coefficient of the ith independent variable, σi is the standard deviation of the ith independent variable, σy is the standard deviation of the dependent variable, and Pi is the contribution rate of the ith independent variable.
3. Results
3.1. 4000-Year Cropland Area Dynamics of the LP
The HYDE, with its extensive temporal coverage (10,000 BC–2000 AD), offers distinct advantages for long-term studies. In this study, a regression model was established between the cropland areas in China derived from the historical data and those extracted from the HYDE, in order to calibrate the cropland area for the LP.
The results show a linear relationship between the cropland area in China estimated based on the historical data and that derived from the HYDE (Figure 2), indicating that the cropland area from the HYDE is approximately twice the actual cropland area in China. A calibration using the regression equation reveals that the cropland area of the LP has grown exponentially over the past 4000 years (y = 4.6325 exp(0.0006t); R2 = 0.7648; where t represents the time and y represents the cropland area) (Figure 3). By 2000 AD, the cropland area had reached 187.3 thousand km2, 14.4 times that in 2000 BC (13,000 km2). The cropland area of the LP underwent three phases: slow growth (2000–500 BC), a fluctuating phase (500 BC-1000 AD), and rapid growth (1000–2000 AD). During the slow-growth phase, the cropland area averaged 34.9 ± 23.4 thousand km2, increasing at a rate of 2.9 thousand km2/100 years. In the rapid-growth phase, the cropland area reached 117.9 ± 34.1 thousand km2, growing at a faster rate of 8.7 thousand km2/100 years. During the fluctuating phase, the cropland area averaged 62.1 ± 18.1 thousand km2, peaking during the Han (206 BC–220 AD) and Sui–Tang (581–907 AD) dynasties at 87 and 85 thousand km2, respectively, and reaching troughs during the Wei–Jin Southern–Northern Dynasties (220–581 AD) and Five Dynasties Ten Kingdoms (907–960 AD) periods, at 26 and 53 thousand km2.
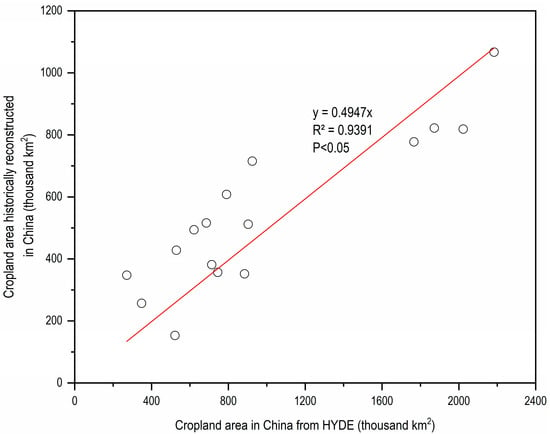
Figure 2.
Relationship between cropland area in China derived from historical reconstruction and HYDE dataset.
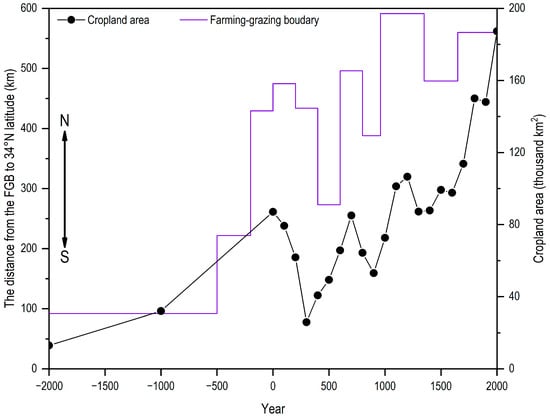
Figure 3.
Historical shifts in the relationship between the cropland area and the FGB in the LP.
Further confirming the numerical accuracy of the calibration, the calibrated cropland area of the LP in 2000 AD (187.3 thousand km2) closely matches the remote sensing data at a 30 m × 30 m resolution [43], which is 192.9 thousand km2. Additionally, based on the spatial map of the FGB (Figure 4), we calculated the distance from the boundary to the 34° N latitude and found that it fluctuated synchronously with the cropland area (Figure 3). The LP, being suitable for both farming and grazing, reflects the shifting balance of agricultural and pastoral forces through the movement of the FGB [30]. Therefore, the north–south movement of the FGB indicates changes in the extent of the agricultural land or cropland area.
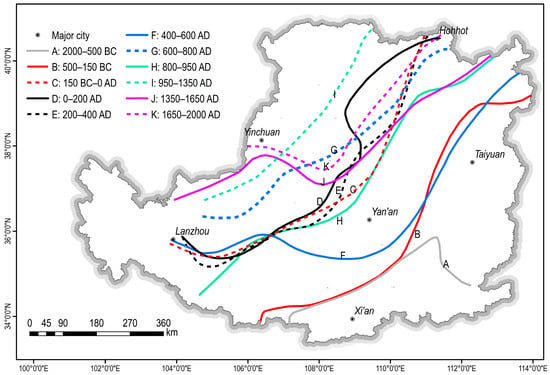
Figure 4.
The changes to the farming–grazing boundary (FGB) in the LP over the past 4000 years (adapted from [13,31]).
3.2. Drivers of Changes in Cropland Area
The population of the LP fluctuated cyclically with dynastic changes, but shows an overall exponential growth over time (y = 3.05 exp(0.0011t); R2 = 0.75; p < 0.05; where t represents the time and y represents the population). This growth can be divided into three main stages: stagnation (2000–500 BC), fluctuating changes (500 BC–1400 AD), and linear growth (1400–2000 AD), with average population levels of 0.377, 6.86, and 33.43 million, respectively (Figure 5B). The head tax system was introduced during the Western Han Dynasty (202 BC–8 AD) and abolished during the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911 AD) (Figure 5A). The straight-shaft plow and oxen-drawn plowing were introduced during the Western Han Dynasty, and later replaced by the curved-shaft plow during the Northern Song Dynasty (960 AD–1127 AD) (Figure 5A). The annual rainfall and temperature declined linearly over time, at rates of 2.8 mm/100 years and 0.05 °C/100 years, respectively (Figure 5A). The rainfall for 2000 BC to 290 BC was significantly higher than that for 290 BC to the present (526.8 mm vs. 438.9 mm, p < 0.05), and while the rainfall fluctuated after 290 BC, there was no significant declining trend (p > 0.05). The temperature fluctuated until 1000 AD, then dropped rapidly at a rate of 0.11 °C/100 years from 1000 AD (p < 0.05), with warming beginning in the 1850s.
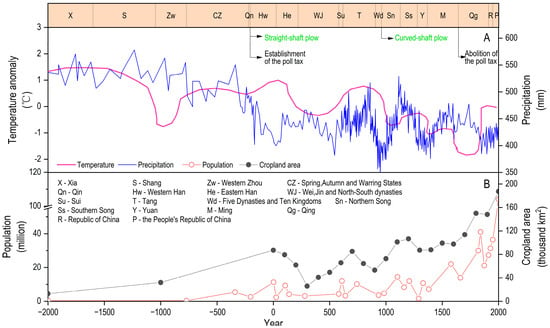
Figure 5.
The cropland area of the LP and its influencing factors: (A) temperature, rainfall, agricultural technology, and policy adjustments in the LP; (B) population and cropland area of the LP.
The relationship between these influencing factors and cropland area shows a significant positive correlation with the population (p < 0.05), and significant negative correlations with the temperature and rainfall (p < 0.05) (Figure 6). Despite the negative impact of climate factors, the positive feedback effects from population growth, policy reforms (e.g., taxation reforms), and technological innovations were more pronounced. For example, during the rapid-growth phase, despite the adverse temperature decline for agricultural production, the cropland area showed a linear growth trend, indicating that the positive feedback from the other factors outweighed the negative climatic feedback. The multiple linear regression model (cropland area = 16.264 − 0.019 × rainfall − 1.603 × temperature + 0.134 × population; R2 = 0.73; p < 0.05) and the Holocene formula (see Methods) indicates that the population and climate together accounted for 73% of the variation in the cropland area, with the population contributing 56.9% and the climate contributing 16.1% (temperature: 10.6%; rainfall: 5.5%). This indicates that, although the climate factors had some impact, population growth played the dominant role. Additionally, policy and technological innovations likely contributed to the remaining 27% of cropland area changes.
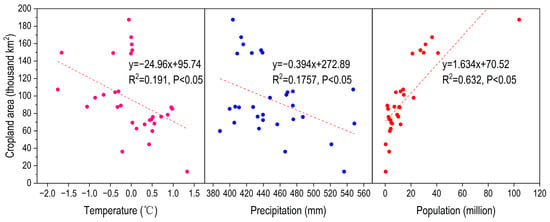
Figure 6.
The relationship between the cropland area and temperature, rainfall, and population of the LP.
3.3. Local and Spillover Effects of Cropland Area Changes
The effects of the changes in the cropland area of the LP have evolved over time (Figure 7). These effects can be divided into two categories: local effects and spillover effects. The local effects refer to changes in forest cover and soil erosion (represented by the sediment load in the YR, as approximately 90% of it originates from the LP) caused by vegetation degradation and restoration. The spillover effects refer to the changes in the downstream flooding frequency during the process of vegetation degradation and restoration of the LP.
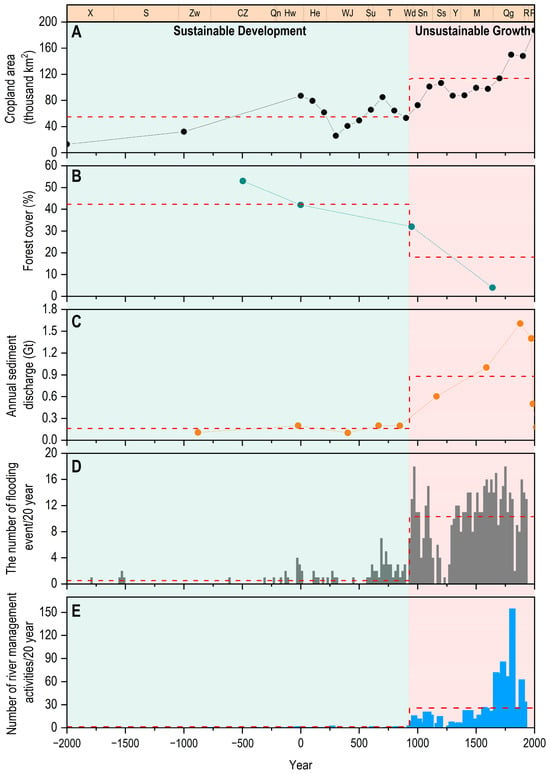
Figure 7.
Social–ecological effects induced by cropland area changes. (A) Cropland area of the LP. (B) Forest cover of the LP. (C) Annual sediment load of the YR. (D) Flooding frequency of the lower YR. (E) The frequency of river management activities for the lower YR. The light green area (left) in the figure indicates the sustainable development phase of the social-ecological system, while the pink area (right) represents the unsustainable development phase.
Over the past 4000 years, the cropland area of the LP has fluctuated in parallel with the sediment load in the YR, showing a significant positive correlation (Figure 7A,C). It is negatively correlated with the forest cover of the LP and positively correlated with the downstream flooding frequency of the YR (Figure 7A,B,D). This indicates that land reclamation of the LP led to vegetation destruction, increased soil erosion, and ultimately raised the flooding frequency downstream. An analysis of these indicators over different periods reveals the evolution of ecological effects. In the slow-growth phase, the forest cover reached 53%, with the sediment load in the YR and downstream flooding frequency at 0.11 Gt/a and 0.4 times/100 years, respectively. In the fluctuating phase, the forest cover declined to 42% during the Western Han Dynasty (202 BC–8 AD) and 32% during the Northern Song Dynasty (960–1127 AD), while the sediment load and downstream flooding frequency increased to 0.18 Gt/a and 5.1 times/100 years, respectively. In the rapid-growth phase, the forest cover plummeted to 4% during the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911 AD), while the sediment load and flooding frequency rose to 1.02 Gt/a and 51.9 times/100 years (approximately every 2 years), respectively.
Over the past 4000 years, the periods from 2000 BC to 930 AD and from 930 to 2000 AD can be considered phases of sustainable and unsustainable development, respectively. This indicates that the ecological effects were much more significant during the rapid-growth phase than during the slow-growth and fluctuating phases. From 930 to 2000 AD, the frequency of river management of the downstream regions was 115 times per 100 years, compared to just 2 times per 100 years from 2000 BC to 930 AD, highlighting the significant ecological impact and increased societal costs of managing the YR floods. In contrast, the period from 2000 BC to 930 AD was marked by a more gradual and less disruptive expansion of cropland, contributing to social development without significant ecological harm. Especially during the fluctuating phase, the Western Han and Tang dynasties reached political stability and economic prosperity, providing the historical context for the expansion of cropland. Therefore, the upper limit of the cropland area during the fluctuating phase (80.2 thousand km2, with a range of 62.1 ± 18.1 thousand km2) can be considered the historical maximum threshold for sustainable land exploitation of the LP, while exceeding this threshold would disrupt the balance between social development and ecological sustainability.
4. Discussions
4.1. Multi-Factor Driving Mechanisms of Cropland Expansion
The changes in the cropland area of the LP are the result of the interaction of multiple factors. Population growth and food demands have historically been central social issues in this arid region [44]. During the slow-growth phase, although the warm and humid climate was conducive to crop growth, the cropland area was only 34,900 km2 (Figure 5A,B), primarily due to the sparse population and limited demand for agricultural land. At this time, the population was mainly concentrated in the flat southern river valleys, and the bronze artifacts unearthed in Shaanxi and Shanxi exhibit strong nomadic characteristics, indicating that pastoralism predominated during this period [32] with the limited cultivation of millet and barley. A warm and humid climate generally boosts food production and the expansion of agricultural land, while a dry and cold climate acts as a limiting factor [45]. As the population grew, the demand for agricultural land increased, leading to more deforestation and soil erosion, which marked the transition from primitive agriculture [4]. During the fluctuating phase, the cropland area increased significantly compared to the slow-growth phase, with the fluctuations mainly driven by technological advances and social conditions. The straight-shaft plow significantly enhanced human capacity to modify nature [13]. During the Western Han period (202 BC–8 AD), innovations in agricultural technologies, such as the invention of the straight-shaft plow, significantly increased food production per unit area (from 68 t/km2 to 104–115 t/km2) [15,44], stimulating the expansion of cultivated land primarily for wheat and millet systems. Concurrently, in periods of social stability (e.g., the Han, Sui, and Tang dynasties), the population expanded to the northwest, while during the period of the Wei–Jin Southern–Northern Dynasties (420–581 AD), marked by frequent wars, the population contracted to the southeast (Figure 8A–E). In the rapid-growth phase, despite the adverse effects of cooling temperatures on agricultural production, the cropland area showed linear growth (Figure 5A,B), indicating that the population growth, policy reforms, and technological advancements outweighed the suppressive effects of climate change. The curved-shaft plow enabled the large-scale reclamation of sloped farmland [46]. During the Northern Song period (960–1127 AD), although the population size and precipitation were similar to those of the Tang dynasty, the cropland area expanded significantly, likely due to further developments in agricultural technology, particularly the invention and dissemination of the curved-shaft plow, which facilitated the reclamation of the LP’s hilly terrain [13] for diversified cropping (wheat, millet, and early rice). Despite the temperature decline during this period (Figure 5A), food production per unit area reached historical highs (139–172 t/km2) [44], highlighting the significant impact of technological progress. After the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368 AD), the cropland area showed a linear growth trend, primarily because, following the agricultural technological reforms of the Northern Song Dynasty, the Qing Dynasty (1644–1911 AD) abolished the head tax system that had been in place since the Western Han Dynasty and implemented a land-based tax system, thereby lowering the cost of childbearing and promoting rapid population growth [47]. This was further supported by the northwestward population distribution (Figure 8G–I). However, despite the introduction of drought-resistant crops, such as potatoes and maize, as staple supplements, the cooling climate during the Little Ice Age caused a decrease in food production per unit area during the Ming and Qing periods, to 45–52 t/km2 and 50–100 t/km2, respectively [44]. This suggests that the rapid increase in cropland area was primarily a response to the dual pressures of population growth and declining food production, leading to a model of extensive cultivation with low yields. In other words, the population growth and declining grain yield per unit area forced farmers to expand their cropland into the northern Loess Plateau regions (with a drier climate and steeper terrain). As soil erosion worsened on steep slopes, farmers continued migrating to even harsher northern areas, ultimately creating a vicious cycle of “increased reclamation leading to greater poverty, with extensive cultivation yielding meager returns”.
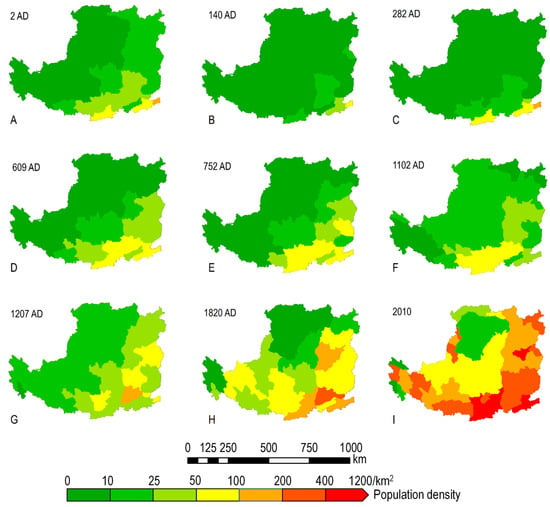
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of population density of the LP across nine historical years. Subfigures (A–I) show the population density distribution of the LP at prefecture-level administrative units across nine time sections (2000-year span). Specific years are labeled in the top-left corner of each subfigure.
4.2. Historical Evolution of Ecological Effects and Thresholds
Ecologically, during the slow-growth phase, the ecosystem was stable, with high forest cover in the LP, low sediment levels in the YR, and a low flooding frequency in the lower reaches of the river. However, during the fluctuating phase, even during periods of prosperity, the forest cover declined, and the sediment levels in and flooding frequency of the YR increased, indicating that land reclamation began to negatively impact the environment. In the rapid-growth phase, ecological problems were further exacerbated, with a sharp decline in the forest cover and a significant increase in both the sediment load in and flooding frequency of the YR, primarily due to severe soil erosion triggered by over-cultivation. The LR’s loess soil is fertile and easy to cultivate, which has contributed to its long history of reclamation [48]. However, due to its hilly and ravine-dominated topography, the cultivated land is predominantly located on slopes, accounting for 70–90% of the total cultivated area [49]. Studies have shown that the forests and grasslands of the LP are largely unaffected by erosion in their natural state, but cultivation increases runoff and sediment production, leading to higher peak flows of and sediment in the YR [10,50]. As sediment accumulation and peak flows increased, flooding of the lower YR became more severe, breaching levees and causing significant socio-economic losses [13]. Therefore, the frequent flooding and the rising frequency of river management over the past millennium (Figure 7D,E) indicate that the continued land development has far exceeded the ecological carrying capacity.
While land reclamation during the fluctuating phase was less intense than during the rapid-growth phase, it still supported social development without causing major ecological degradation. Thus, 80.2 thousand km2 is a reasonable historical upper limit for the area of cultivated land in the LP, beyond which ecological degradation becomes critical. This upper limit reflects the historical ecological impacts of land reclamation and provides important insights for the sustainable development of the YR basin ecosystem. Based on this analysis, we can better understand the potential for land reclamation in the LP in the absence of soil and water conservation measures, as well as assess the effectiveness of modern soil and water conservation efforts.
4.3. Implications for Modern Ecological Governance
Since the 1950s, large-scale soil and water conservation measures, such as terracing, check dams, and the “Grain for Green” Program, have significantly improved the ecological environment. Quantitatively, terracing has reduced sediment yield by 0.21 Gt/yr−1 and the check dams have trapped 0.20–0.33 Gt yr−1 of sediment, while the ‘Grain for Green’ program has increased vegetation cover to 59.6% and reduced the sediment load by 57% [51]. These changes have (1) lowered the soil loss per unit of cropland area and (2) improved water retention capacity, thereby permitting more intensive cultivation within the same ecological constraints. Between 1999 and 2013, the vegetation cover increased from 31.6% to 59.6%, and the sediment levels in the YR significantly decreased, even reaching historic lows [40,52]. During this period, despite the population reaching historic peaks, no flooding events occurred in the lower reaches (Figure 5B and Figure 7D), demonstrating the effectiveness of soil and water conservation measures. However, the “Grain for Green” program also led to a decline in the per capita arable land, posing a threat to food security [53]. Therefore, under the current context of soil and water conservation measures in the LP, it is crucial to set a scientifically reasonable upper limit for the cropland area based on historical experience, in order to achieve a balance between economic development and environmental protection. Specifically, to ensure food security, it is necessary to establish high-standard farmland (leveled terrain, fertile soil, irrigation access, and transportation convenience) to increase the grain yield per unit area, thereby balancing the relationship between ecological restoration and food security. The scale of land retirement can be determined by setting the actual required total grain output and sediment reduction targets, then comparing the yields between ordinary sloping farmland and high-standard farmland.
This study provides key insights for land management, balancing ecological sustainability and agricultural development in the YR basin. It also provides scientific evidence for land management policy formulation. Particularly under current global warming with increasing climate extremes, this research highlights that maintaining appropriate cropland thresholds can reduce soil erosion and sediment load, thereby preventing downstream areas from repeating historical flooding patterns. Under the “population-technology-climate” synergistic framework we constructed based on a 4000-year cropland evolution study of the Loess Plateau, we find that (1) population growth is the main driver of cropland expansion; (2) agricultural technology advancement can increase yields to alleviate ecological pressure; and (3) climate deterioration will intensify cropland expansion demands—, developing agricultural technologies to increase the grain yield per unit area while maintaining cropland area limitations is the optimal approach to mitigate risks. The methodology proposed in this study can also be extended to other regions with similar agricultural and ecological histories by implementing three steps: (1) identifying the core environmental issues (e.g., soil erosion, aridification) and selecting the key indicators (e.g., sediment load, vegetation coverage); (2) determining the ecological thresholds via a long-term time-series analysis; and (3) deriving the upper limits for human activities (e.g., cropland area, grazing intensity).
4.4. Research Limitations and Future Directions
However, this study is limited by the resolution of the data and the ecological assessment methods, particularly the lack of systematic historical records on biodiversity and soil nutrient quantification. Future research could enhance the accuracy and comprehensiveness of this analysis by utilizing more historical data and considering ecological indicators, such as biodiversity, through advanced techniques like ancient DNA analysis and sediment geochemistry.
5. Conclusions
Over the past 4000 years, the cropland area of the LP evolved through three phases: slow growth (2000–500 BC), a fluctuating phase (500 BC–1000 AD), and rapid growth (1000–2000 AD). During the slow-growth and rapid-growth phases, the cropland area was 34.9 ± 23.4 and 117.9 ± 34.1 thousand km2, with growth rates of 2.9 and 8.7 thousand km2/100 years, respectively. In contrast, the cropland area during the fluctuating phase averaged 62.1 ± 18.1 thousand km2, fluctuating significantly. The primary driving factors behind the changes in cropland area include population growth (contributing 56.9%), rainfall (10.6%), temperature (5.5%), and a combined contribution of agricultural technological advances and policy adjustments (27%). Particularly over the past 1000 years, agricultural technological advances enhanced land reclamation capacity, while climate deterioration reduced crop yields, and the abolition of the head tax led to a dramatic population increase, collectively escalating land demand and driving the adoption of the ‘extensive farming’ model, thereby accelerating cropland expansion. The rapid expansion of cropland caused significant environmental impacts, resulting in decreased forest cover, intensified soil erosion in the LP, a higher flooding frequency of the lower YR, and increased pressure on flood control and river management. By comparing cropland expansion and ecological imbalances across the phases, this study proposes that, under historical conditions without soil and water conservation measures, the maximum sustainable cropland area of the LP should be limited to 80.2 thousand km2, beyond which ecological sustainability would be compromised. To address population growth and climate change impacts, enhancing agricultural productivity through technological development and policy adaptation will be crucial for maintaining both ecological stability and food security within the established cropland area limits. In conclusion, the changes in the cropland area over the past 4000 years not only reveal the trend of the human overexploitation of land resources, but also warn of the risks of ecological imbalance, providing valuable theoretical and practical insights for the formulation of future land management and ecological protection policies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; Methodology, T.H.; Formal analysis, T.H.; Writing—original draft, T.H.; Writing—review & editing, W.H. and B.L.; Supervision, B.L.; Project administration, S.A.; Funding acquisition, S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077072).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request due to privacy/ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LP | Loess Plateau |
| YR | Yellow River |
| LUCC | Land Use/Cover Change |
| IGBP | International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme |
| HYDE | Historical Database of the Global Environment |
| SAGE | Global Land Use Database |
| FGB | Farming–Grazing Boundary |
References
- Goldewijk, K.K. Estimating global land use change over the past 300 years: The HYDE database. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Zhang, Y.; Basanta, P.; Narendra, R.K.; Bipin, K.A. Satellite Image-based Monitoring of Urban Land Use Change and Assessing the Driving Factors in Pokhara and Bharatpur Metropolitan Cities, Gandaki Basin, Nepal. J. Resour. Ecol. 2020, 11, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldewijk, K.K.; Beusen, A.; Doelman, J.; Stehfest, E. Anthropogenic land use estimates for the Holocene-HYDE 3.2. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 927–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, C. Cropland cover change and its environmental impacts in the history of China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2019, 21, 160–174. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.W. On the factors of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Sci. Bull. 1954, 6, 65–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jing, K.; Wang, B.K. Modern erosion environment and sediment yield effect of the Loess Plateau. People’s Yellow River 1992, 4, 35–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.M.; Wu, J.G.; Kou, X.J.; Oliver, C.; Mou, P.; Ge, J.P. Ecologically asynchronous agricultural practice erodes sustainability of the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.X.; Zhang, D.D. A sediment budget of the lower Yellow River, China, over the period from 1855 to 1968. Geogr. Ann. 2005, 87, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive scientific investigation team of Loess Plateau; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Population Problems in the Loess Plateau; China Economic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q. Why did the Yellow River keep a calm period for a long time after the Eastern Han Dynasty—To verify the view that the rational use of land in the middle reaches of the Yellow River is the decisive factor to eliminate water disasters in the lower reaches from the perspective of history. Acad. Mon. 1962, 2, 23–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Tang, K.L.; Jiao, J.Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Cao, Q.; Xiao, P.Q.; Wei, X.; Fu, S.H.; Miao, C.Y.; et al. The Spatial-Temporal Atlas of Water and Sediment in the Yellow River, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.E. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River, China: Past, present and future—A synthesis. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Gao, S.; Overeem, I.; Kettner, A.J. Socio-economic impacts on flooding: A 4000-year history of the Yellow River, China. AMBIO 2012, 41, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, F. Response of lower Yellow River bank breachings to La Niña events since 924 CE. CATENA 2019, 176, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.X. Assessment on the level of food security in traditional agriculture period of China. Agric. Hist. China 2007, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Q.S.; Dai, J.H.; He, F.N.; Pan, Y.; Wang, M.M. Land use/cover change and carbon cycle in China over the past 300 years. Chin. Sci. 2008, 38, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.N.; Li, S.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Ge, Q.S.; Dai, J.H. Comparisons of reconstructed cropland area from multiple datasets for the traditional cultivated region of China in the last 300 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.N.; Li, M.J.; Liu, H.L. Reconstruction of cropland area at Lu scale and its spatial temporal characteristics in the Northern Song Dynasty. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; He, F.N.; Yang, F.; Li, S.C. Reconstruction of cropland area at the provincial level in the early Yuan Dynasty. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 832–842. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L.; Meyer, W.B.; Skole, D.L. Global Land-Use/Land-Cover Change: Towards an Integrated Study. AMBIO 1994, 23, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Goldewijk, K.K.; Battjes, J.J. A Hundred Year (1890—1990) Database for Integrated Environmental Assessments (HYDE, version 1.1); Rijksinstituut Voor Volksgezondheid En Milieu Rivm: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Estimating historical changes in global land cover: Croplands from 1700 to 1992. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 997–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.O.; Krumhardt, K.M.; Zimmermann, N. The prehistoric and preindustrial deforestation of Europe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 3016–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.C.; Costa, M.H.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Hissa, L.B.V. Historical land use change and associated carbon emissions in Brazil from 1940 to 1995. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumkehr, A.; Campbell, J.E. Historical US cropland areas and the potential for bioenergy production on abandoned croplands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3840–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Ye, Y.; Tang, C.C.; Fang, X.Q. Accuracy Comparison of Gridded Historical Cultivated Land Data in Jiangsu and Anhui Provinces. China Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Fang, X.Q.; Ren, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Chen, L. Northeast China’s Past 300 Years of Cultivated Land Cover Change. Chin. Sci. D Ser. Earth Sci. 2009, 32, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.S. The Loess Deposits of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1964. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T. The Impact of Human Activities on Sediment Deposition and Flooding in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River in the Past 4000 Years. Doctoral Dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, N. A Study of the Historical Geography of the Loess Plateau; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.Y. Climate Change in Chinese History; Shandong Science and Technology Press: Jinan, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q. Soil and Water Conservation in Loess Plateau; Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y. Population Growth and Temporal-spatial Differentiation in Loess Plateau Region in the last 2000 Years. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 1, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, Conservation and Eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Teng, Z. A Study of Historical Population by Province and Region in China (Hardcover Edition); Shandong Peoples’ Publishing House: Jinan, China, 2006; Volumes I and II. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Vegetation Changes, Human Factors Change and Runoff and Sediment of the Yellow River in the Loess Plateau in Historical Period. In Collection of Researches on Environment Changes of the Yellow River and Laws of Water and Sediment Transportation; Wang, S., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume 5, pp. 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sang, G. Vegetation Variation of Loess Plateau during human history. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2005, 19, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Birks, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; An, C.; Telford, R.; Cao, X. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K. A preliminary study on climate change in China in recent 5000 years. Sci. Sin. 1973, 2, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Balancing green and grain trade. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 10, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, D. Chronology of the Yellow River. Military Committee and Resources Committee of the Republic: Nanjing, China, 1935. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Фoлoд, Н.И.; Tan, J.W.; Liu, T.F. Prediction of Agricultural Production Effect; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1983. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.J.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.J.; Jin, Z.; Yan, N.N. Spatial and temporal changes of cultivated land and quantitative analysis of ration safe cultivated land on the Loess Plateau in recent years. Arid. LAND Geogr. 2020, 43, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Bi, N.; Saito, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Cong, S.; Yang, Z. Climate and human battle for dominance over the Yellow River’s sediment discharge: From the Mid-Holocene to the Anthropocene. Mar. Geol. 2020, 425, 106188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, A.A.; Pereira, L.S. Drought concepts and characterization. Water Int. 2006, 31, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvin, M. The Retreat of the Elephants: An Environmental History of China; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhao, Y.G. The demographic changes and their driving forces on the Loess Plateau since 4000 years BP. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Zhang, K.L.; Lei, A.L. Research and Argumentation on the Maximum Slope for Returning Farmland to Forests and Grasslands in the Loess Hilly Region. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.L.; Zhang, K.L.; Zheng, F.L.; Zha, X.; Wang, W.L.; Cai, Q.; Bai, H.Y. Analyzing on natural erosion and man-made accelerated erosion in the Ziwuling forest area. Mem. NISWC Acad. Sin. Minist. Water Resour. 1993, 17, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Lü, Y.H.; Ciais, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the yellow river due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, F. Variability of annual sediment load and runoff in the Yellow River for the last 100 years (1919-2018). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. The creation of farmland by gully filling on the Loess Plateau: A double-edged sword. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).