Abstract
Corn is a globally important crop, requiring extensive soils and intensive practices to meet the growing human and animal consumption demand. However, intensive agriculture has caused soil deterioration and fertility loss. In response, the Mexican government established the National Soil Strategy for Sustainable Agriculture (ENASAS, acronym in Spanish) to ensure food security and maintain soil fertility. This study develops “Soil Quality Indexes” () to monitor soil quality under corn cultivation using four methodologies (additive (), weighted (), unified weighted (), and Nemoro ()) in the Bajio region of Guanajuato, Mexico. Twenty-four physicochemical indicators were analyzed, with four (CLY, WHC, Na, and C/N) identified as key indicators of soil quality and fertility through principal component analysis. Among these, was the most sensitive and efficient (SI = 2.32, ER = 50) in assessing soil quality, showing values from very low to low ( and respectively). Aligned with the ENASAS program, can help monitor and improve soil quality under corn cultivation, supporting food security through soil conservation. Moreover, performed similarly to the globally recognized Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF), making it a valuable tool for managing and improving agricultural soil quality under similar conditions in both Mexico and worldwide.
1. Introduction
Corn is one of the most produced and demanded crops globally [1,2]. It is used both for human consumption and to feed various animal species. The growing world demand for corn has led to an expansion in cultivation and the intensive use of agricultural practices to meet global needs. In Mexico—where corn is endemic—a similar trend is observed. As population demand increases, agricultural production tends to decrease due to the intensive or inadequate use of cultivated land, which in many cases leads to soil degradation and loss of fertility. This has forced the country to depend even more on corn imports from the United States, which has increased the cost of corn-derived products [2,3].
In response to this problem, the Mexican government has established the national program ENASAS (National Soil Strategy for Sustainable Agriculture) [4]. This program aims to prevent and remediate soil degradation and promote sustainable agricultural practices that ensure long-term food security.
Within the goals or objectives to be achieved by the abovementioned program, tools, and methods are required to evaluate its performance. These tools must be easy to use, inexpensive and simple to understand. One tool that meets these requirements is the soil quality index , which involves the analysis of physicochemical or biological parameters or indicators related to the problem of soil fertility loss. Moreover, there are several methodologies to develop , such as those based on expert opinion , the additive approach , the weighted approach , the unified weighted approach , and Nemoro methodology [5]. The choice of methodology for the development of the depends on the study area and the use of the analyzed soils. Currently, there is no consensus in the scientific community as to which model is the most appropriate for the development of . This is due to the diversity of factors that influence its formation, added to the heterogeneity of its properties. Therefore, multiple mathematical and methodological approaches are used to evaluate which one is best suited to the specific context and challenges of each study (tillage).
In the same context, several studies have focused on developing for soils under corn cultivation. A recent study by Adak et al. [6] looked at how corn cultivation with oat rotation and various conservation agriculture practices—tillage, organic amendments, and fertilization levels—affected agricultural soil quality. The were developed using two approaches: and . The outcomes showed that the most important indicators for soil quality were potassium (K), phosphorus (P), total organic carbon (TOC), electrical conductivity (EC), bulk density (BD), dehydrogenase activity (DHA), and microbial biomass carbon (MBC). Moreover, protection farming practices were found to decidedly affect the quality and soundness of the tried soil.
In a 15-year study, Amorim et al. [7] monitored soil quality in a no-till crop rotation experiment with cover crops, cotton, and corn. They evaluated indicators like hydrogen potential (pH), TOC, BD, extractable P and K, EC, and sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) using the Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF). While the SMAF distinguished soil quality in relation to crop rotation and cover crops, it did not differentiate soil quality in relation to depth.
On the other hand, an was created by Assunção et al. [8] using a total data set of 24 physicochemical and biological indicators. In the coastal plateaus of the State of Sergipe, in northeast Brazil, they conducted a 17-year study on plots with Ultisol soils and various corn management methods. The effects of cover crops and tillage on soil quality were investigated. According to the findings, conventional tillage significantly negatively impacted the soil quality, whereas no-tillage had the best results.
Due to the spatial variability of their properties, implementing techniques to maintain and restore agricultural soil quality requires using specific tools for each region [9]. As a result, this study utilized four distinct approaches to create an . The goal was to establish a tool to measure, maintain, or improve soil quality in corn crops in the Bajio region of the State of Guanajuato, Mexico. The hypothesis of the study was that the developed here would differentiate between the quality of the analyzed soils.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Agricultural Soils
For the selection of the agricultural soil sampling sites, the following tools were used: the database of the Federal ProAgro Program corresponding to the 2017 spring-summer cycle, the National Geostatistical Framework 2018, and the Land Use and Vegetation Chart Series V Guanajuato. The software ArcGIS version 10.1 was used for the cartographic projections of vector data from the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Informatics (INEGI, acronym in Spanish) and the National Agrarian Registry (RAN). These projections were matched according to the following uniformity criteria: type of soil, an area between 5 and 6 hectares, and different irrigation regime zones (furrow irrigation). A population of 969 agricultural soils from different municipalities of the Bajio region of Guanajuato that met the aforementioned criteria was formed. The selection of the sampling sites was carried out based on the population of agricultural soils per municipality, by means of cluster and random sampling, selecting 15 agricultural soils representative of the region based on the operational capacity of the laboratory personnel (Table 1 and Figure 1).

Table 1.
Agricultural soils sampled.
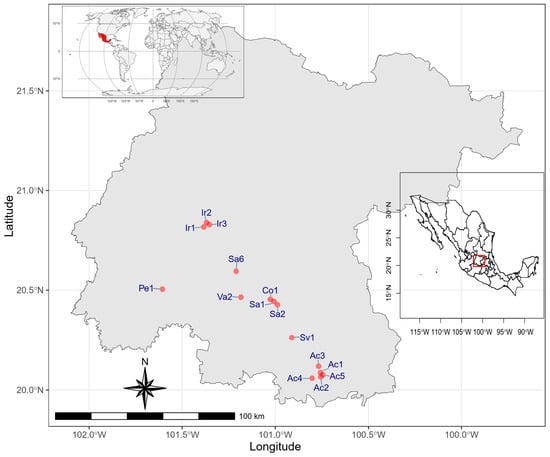
Figure 1.
Sampled sites (red dots); red box, state of Guanajuato, and red shading, country Mexico.
2.2. Soil Sampling
Soil sampling was carried out in three 600 m2 subplots. In each subplot, pits with a depth of 30 cm and a width of 40 cm were dug at regular 18 m intervals in a zigzag pattern. A total of 45 samples of 2 kg were obtained from each agricultural soil making 675 excavations. Then, the samples were mixed to obtain a composite sample for each agricultural soil. At room temperature, these composite samples were taken to the laboratory in plastic bags. Afterwards, the samples were air-dried and sieved with a 2 mm mesh. Until analysis, the processed samples were kept in Ziploc® plastic bags (Ziploc bag, Thai Griptech Co., Ltd., Bangkok, Thailand) at 4 °C in the refrigerator.
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
Physicochemical indicators associated with soil fertility were chosen and determined in triplicate. The hydrometer method was used to determine the texture, which was expressed as a percentage of sand (SND), clay (CLY), and silt (SLT) [10]. The USDA texture diagram served as the basis for the establishment of the textural class [11]. The pH was determined utilizing a soil–water proportion of 1:2.5 (w v−1) [12]. The EC was determined using the method of Hendrickx et al. [13], reporting the results in dS m−1. The water holding capacity (WHC) was determined following Nannipieri’s method [14]; the weight difference was used to calculate WHC, which was expressed as a percentage of moisture. The TOC was determined by oxidation reactions with potassium dichromate, quantified colorimetrically at a wavelength of 660 nm [15], and reported as a percentage. The organic matter (OM) was calculated by multiplying the TOC value by the Van Bemmelen factor (1.724) [16], expressed as a percentage. The micro Kjeldahl method [17] was used to measure the total nitrogen (TN), which was measured colorimetrically at 660 nm and expressed as mg N kg−1 of dry soil. P, K, sulfur (S), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sodium (Na) were the macronutrients analyzed. Iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), and boron (B) were the micronutrients analyzed. The two categories of nutrients were decomposed by corrosive processing utilizing the microwave ICP method [18], all reported in meq 100 g−1 of dry soil. The cation exchange capacity (CEC) was reported in meq 100 g−1 of dry soil using the Cottenie method [19]. The exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) and the SAR were determined according to Webster [20,21], reported as a percentage.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical packages agricolae, corrplot, factoextra, FactoMineR, ggplot2, Hmisc, and psych [22,23,24,25,26,27,28] were used in the analyses performed with the statistical software R 4.0.5 [29]. The statistical analysis process started with a Shapiro–Wilk normality test with a significance level of . After that, a Spearman correlation matrix and a Mantel test were performed, with both analyses having a significance level of and considering correlations with values of as significant. Next, a Kruskal–Wallis variance analysis with subsequent Dunnett’s test of medians and Bonferroni adjustment with a significance level of was carried out. A Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) adequacy test served as the foundation for a principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the data’s dimensionality [30]. Those indicators that reduced the suitability of the data for applying the PCA were discarded, using a value of as a criterion [31]. Then, the data were normalized, verifying their normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk normality test with a significance level of . In order to select the principal components (PCs), the eigenvalue criterion was utilized [32,33]. Once the PCs that met the aforementioned criteria were selected, a Spearman correlation matrix was performed with the analyzed indicators and the established PCs, considering as significant correlations those that presented values of [34]. Lastly, a redundancy elimination process was performed using the following criteria in order of importance: number of significant interactions > PC membership (PC1 > PC2 > … > PCn) > correlation with its PC [35].
2.5. Establishment of SQIs
The SQIs were established using four different methodologies: the additive index , the weighted index , the unified weighted index , and the Nemoro index . Equation (1) was utilized in the process of establishing the [36].
where Si is the value of the indicator that resulted from the redundancy elimination process and is the number of indicators that were included in the .
Equation (2) was used to establish the and indexes. For the former, the weighting was established according to the role that the indicator plays in the soil [37]. The weights used for the were established from the proportion of variance explained by the established PCs [32].
where Wi is the weighting of the indicator established by experts , or the proportion of variance of the PCs with which the indicator is correlated . is the value of the indicator obtained from the redundancy elimination process.
For the establishment of the , Equation (3) was used [36].
where and are the average and minimum values of the indicators that resulted from the redundancy elimination process, and n is the number of indicators included in the .
Equation (4) was used to score indicators whose function in the soil was considered to be “more is better” or “less is better” for the , , and indexes. Equation (5) was used for the scoring of indicators whose function in the soil was considered “optimal”.
where a is the maximum standardized value of the indicator, is the mean value of the indicator, is the value of the analyzed indicator, and is the slope of the indicator’s score function ( and for indicators whose function in the soil is considered as “more is better” and “less is better”, respectively).
where B is the value of the indicator whose slope is equal to 0.5, is the lower limit value of the indicator, and is the value of the indicator. The aim of the is to obtain quality values between 0 and 1, with which the quality of the soils can be determined based on the classification presented in Table S1 [38].
To evaluate the performance of the developed here, we followed the methodology proposed by Zhou et al. [39], which uses a sensitivity index (SI) that represents the potential variability of the index (Equation (6)) and the efficiency ratio (ER) (Equation (7)), which measures the efficiency of each index in evaluating the quality of all the analyzed soils. The selection of the index with the best performance in evaluating the quality results depends on both criteria; low values for the SI and high values for the ER are considered the best.
where represents the maximum value of quality obtained by the index and represents the minimum value obtained by the index.
where K represents the significant correlations between the quality results of the index and the various indicators analyzed. would be the total number of possible correlations between the quality results of the index and the indicators analyzed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Textural Classification and Physicochemical Characterization of Sampled Soils
The textural class of the soils analyzed with respect to the USDA classification is shown in Figure S2. Regarding the physicochemical characterization of the sampled soils, Table 2 shows the descriptive statistics of the indicators that were analyzed.

Table 2.
General descriptive statistics.
High outliers were detected in the indicators EC, K, Na, Cu, and SAR. These could be associated with the use of chemical fertilizers and well water with high salinity (Table 1), common practices in the area studied [40,41]. On the other hand, the extreme values in the C/N ratio could be due to the presence of complex organic molecules in the soil. These substances, rich in carbon, would generate reduced microbial activity, which would delay their decomposition and mineralization.
The soils analyzed in the region are clayey (Figure S2c–e) classified as vertisols according to the World Reference Base for Soil Resources [42], which is typical in the Bajio region of the State of Guanajuato. Although soil is considered to have high fertility when the OM exceeds 3% [43,44], the soils analyzed here showed very low levels, less than 2%. These values indicate that the soil’s structure and fertility are degraded, probably due to intense agricultural activity and erosion caused by wind and water [40,45].
As a result of the Shapiro normality test, it was concluded that the soil indicator data did not have a normal distribution. Therefore, nonparametric statistical tests were performed. The Kruskal–Wallis test applied to the indicators revealed that there were no significant differences among soils regarding their pH, EC, C/N, and Mg indicators (Figure 2a,b,j,u, respectively). However, for the other indicators, the analysis divided the soils into at least two distinct groups (Figure 2).
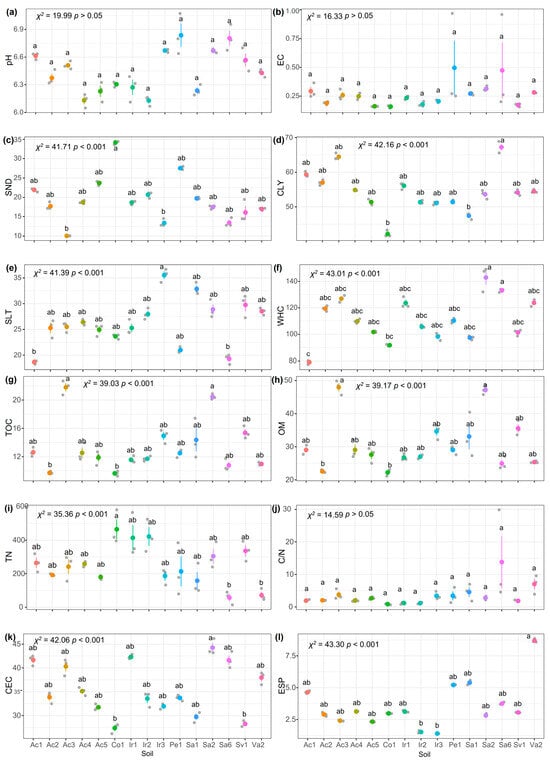
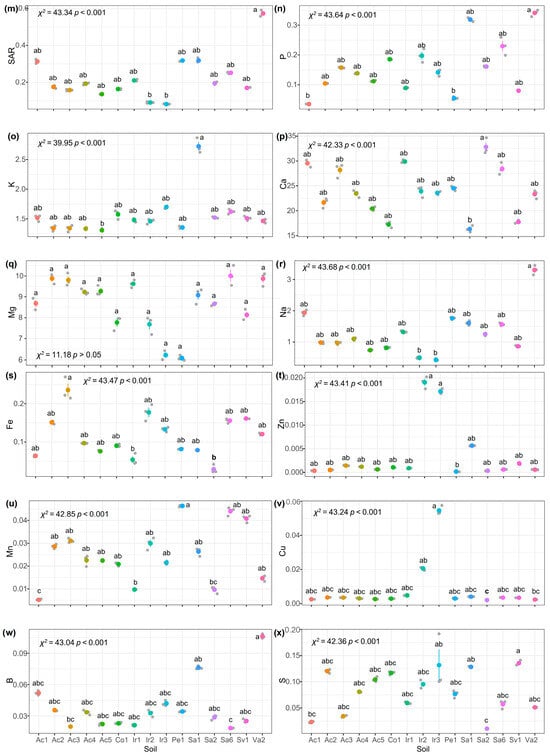
Figure 2.
Kruskal–Wallis analysis for sampled soil indicators with subsequent Dunnett’s median test with Bonferroni adjustment at a significance level . Bars indicate SD (n = 3). (a) pH, potential of hydrogen; (b) EC, electrical conductivity (dS m−1); (c) SND, sand (%); (d) CLY, clay (%); (e) SLT, silt (%); (f) WHC, water holding capacity (%); (g) TOC, total organic C (mg C kg−1); (h) OM, organic matter (mg C kg−1), (i) TN, total N (mg N kg−1); (j) C/N, C and N ratio; (k) CEC, cation exchange capacity (meq/100 g); (l) ESP, exchangeable sodium percentage (%); (m) SAR, sodium adsorption ratio (%); (n) P, phosphorous (meq 100 g−1); (o) K, potassium (meq 100 g−1); (p) Ca, calcium (meq 100 g−1); (q) Mg, magnesium (meq 100 g−1); (r) Na, sodium (meq 100 g−1); (s) Fe, iron (meq 100 −1 g); (t) Zn, zinc (meq 100 g−1); (u) Mn, manganese (meq 100 g−1); (v) Cu, copper (meq 100 g−1); (w) B, boron (meq 100 g−1); (x) S, sulfur (meq 100 g−1). Same letters indicate that there is no significant difference between treatments using a Kruskal–Wallis analysis with subsequent Dunnett’s median test with Bonferroni adjustment at a significance level .
The analysis of the soil’s pH (Figure 2a) revealed two main groups under the Mexican standard NOM-021-RECMAT-2002 [20]. The first group showed neutral pH values (6.6–7.3), while the second group exhibited slightly acidic pH (6.1–6.5). No significant differences were found between them . Chen et al. [46] suggested that soil microorganisms can decompose urea-based fertilizers, releasing organic acids that may influence pH. Additionally, the use of low-salt irrigation water—unlike saline well water—prevented significant salt accumulation in soils [47].
Regarding soil EC (Figure 2b), it was observed that all the soils were in the non-saline category [20], with no significant differences between them . These results align with the use of irrigation water—rather than saline well water—as discussed earlier. However, soils Pe1 and Sa6 showed higher variability in EC values.
The WHC indicator (Figure 2f), classified soils Ac1, Co1, Ir3, and Sa1 as low WHC, while others showed moderate WHC, under the Mexican standard NOM-021-RECMAT-2002 [20,21]. Despite high CLY content—typically linked to high WHC—the soils exhibited physical degradation from intensive farming and low OM levels, aligning with the observed WHC values [48]. This degradation could reduce water retention, raising erosion risks from water and wind. Consequently, crops may face water scarcity, impairing growth, and metabolic functions.
Analysis of soil OM revealed very low concentrations of TOC and TN across all soils (TOC < 10,000 mg kg−1, TN < 1000 mg kg−1) (Figure 2g–j). The lowest values occurred in Ac2 and Co1, while Ac3 and Sa2 showed the highest concentrations (Figure 2g,h). However, only soil Co1 had low WHC. This suggests that factors beyond OM—such as tillage practices or agricultural land use history—may drive WHC variability. Low OM levels could also hinder soil microorganism activity, disrupting nutrient cycling and crop growth [49].
All soils presented low levels of N content (TN < 1000 mg kg−1) [20,21] (Figure 2i), despite the intensive use of fertilizers in the Bajio of Guanajuato (Table 1). This could be explained by the high mobility of N in fertilizers, high doses increase volatilization and denitrification, reducing its availability [50]. In addition, low TN, and C generated C/N ratios < 15 (Figure 2j), with no significant differences between soils (p > 0.05). This imbalance suggests that N and C are limiting, restricting microbial activity and nutrient cycling, which would affect crop development [51,52].
In reference to the ion exchange capacity, which is related to the CEC, ESP, and SAR indicators (Figure 2k–m), all soils exhibited moderate to high CEC (CEC > 12), consistent with their CLY content (Table 2). CLY’s negative charges enhance its ability to retain positively charged ions, explaining the higher CEC in CLY-rich soils [53]. However, only soil Va2—located in a volcanic area—showed moderately sodic conditions in ESP and SAR analyses [21]. Other soils showed no sodicity issues, aligning with the low-salt irrigation water used.
Moreover, the macronutrients (K, Ca, Mg, Na, P, and S) were analyzed (Figure 2n,o–r,x). For the indicators K, Ca, and Mg, all the soils showed high concentrations under the Mexican standard NOM-021-RECMAT-2002 (Ca > 10 meq 100 g−1, K > 0.6 meq 100 g−1, Mg > 3 meq 100 g−1) [20,21]. Soil Sa1 had the highest K and Ca levels, likely linked to NPK-rich fertilizers for corn cultivation (Table 1). Plants use K to activate enzymes and synthesize photosynthetic proteins; its deficiency impairs growth [54]. Similarly, Ca acts as a structural component and photosynthetic cofactor—low levels hinder development [55]. For Na, only Ir2 and Ir3 had optimal concentrations (Na, 0.3–0.7 meq 100 g−1), while volcanic soil Va2 showed excess Na (Na > 3 meq 100 g−1). High K, Ca, and Na levels may result from intensive fertilizers, liming, and saline irrigation. Excess Na can reduce CEC efficiency and limit microbial access to OM [56]. Soils Sa1 and Va2 presented the highest concentrations of the P indicator; however, all presented soil concentrations were considered high (p > 0.3 meq 100 g−1) (Figure 2n), which is probably due to recent phosphate fertilization (Table 1) [20,21]. Other soils showed deficiencies, suggesting aging fertilizer applications. P is vital for energy production and cell membrane formation. The S levels were adequate (S, 0.004–0.021 meq 100 g−1) in all soils except Ac1 and Sa2, likely due to sulfate accumulation from S-based fertilizers.
When analyzing the micronutrients (Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, and B) (Figure 2s–w), Fe was the only micronutrient with adequate levels in soil Ac3 (Fe > 0.02 meq 100 g−1), while the other soils showed deficiencies (Fe < 0.02 meq 100 g−1) (Figure 2s). Fe is essential for chlorophyll synthesis and electron transport in plants; its shortage can reduce photosynthesis and cause chlorosis [57]. The Zn (Figure 2t), crucial for enzyme activation and auxin production, showed variability among soils. Low Zn levels (Zn < 0.003 meq 100 g−1) could limit root growth and pathogen resistance, low concentrations were found for all soils except for soils Ir2 and Ir3. Mn (Figure 2u), involved in N assimilation and water photolysis, showed heterogeneous concentrations and was considered to be adequate (Mn > 0.004 meq 100 g−1) [58]. Cu (Figure 2v), vital for lignin formation and cellular respiration, showed similar trends to Mn, with concentrations considered to be adequate (Cu > 0.001 meq 100 g−1) with possible implications for crop structural integrity. Finally, B (Figure 2x), important for cell wall development and carbohydrate metabolism, showed concentrations, considered to be adequate (Zn, 0.02–0.04 meq 100 g−1). These variations reflect the influence of local agricultural practices and the need for specific monitoring to optimize micronutrient management [58].
3.2. PCA
PCA began by evaluating correlations (Spearman matrix and Mantel test) among soil indicators (Figure 3). Indicators, such as pH, SND, P, K, and B, showed no significant correlations (r2 < ±0.6, p > 0.05), while others had at least one strong correlation . Notably, CLY correlated positively with Ca and CEC—key factors for soil nutrient availability [58,59,60]. This occurs because higher CLY content increases the surface area with negative charges, enhancing cation retention (e.g., Ca2+) [61].
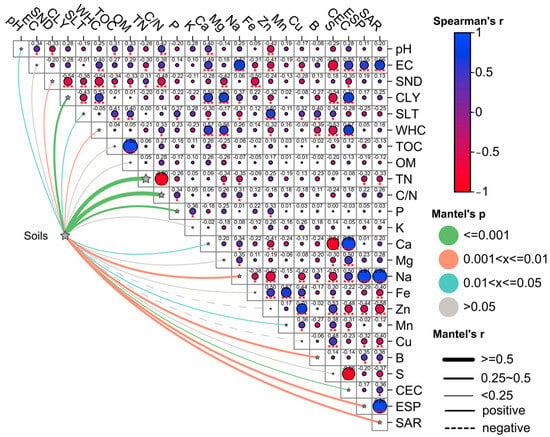
Figure 3.
Spearman correlation matrix with the Mantel test for analyzed indicators of sampled soils. Blue circle, positive correlation, red circle, and negative correlation. Large circle correlation close to 1, small circle no correlation. Significance of the Mantel test, gray color no significance, blue, orange and green color, significance under , and respectively, wide line, continuous and discontinuous positive and negative correlation, respectively, thin line no correlation. *, significant value at ; **, significant value at ; ***, significant value at . The meaning of acronyms are described in Table 2.
In terms of macronutrients, the CEC indicator showed significant correlations with the WHC, Ca, and S indicators (Figure 3). Ca is involved in the improvement of soil structure possibly due to its bivalency, contributing to the generation of essential macro and micropores in the soil for good aeration, water retention (WHC), and filtration [6]. Regarding the S indicator, this is a crucial element for enzyme formation and the response against abiotic stress in crops and has been shown to be a key element in the formation of enzymes [62]. The S indicator presented a negative correlation, possibly due to its non-metallic nature, which could limit its attraction to the negative charges of the soil matrix, composed mainly of a higher fraction of CLY. Moreover, low retention of this element (S) by the soil matrix causes its leaching into nearby bodies of water [62].
As for micronutrients, only the indicators Cu, Zn, and B showed significant correlations (Figure 3). Cu was positively correlated with Zn, both essential for the proper functioning of enzymes related to growth and photosynthesis in crops [57]. The absence of Cu can lead to poor growth and discoloration of leaves [58]. With respect to B, it correlated positively but not significantly with Na, ESP, and SAR (). The latter two are related to high Na concentrations and possible toxicity. A high concentration of B can be toxic to crops and microorganisms in general, while its deficiency can cause incorrect synthesis of proteins related to photosynthesis, thus reducing crop yields.
The different soils sampled in this study presented significant positive correlations with the TN and C/N indicators, both related to the quality of OM present in the soils (Figure 3) [49]. The PCA resulted in the establishment of three PCs, which met the criterion of , representing 71.3% of the variability of the sampled soil indicator data. The variability of the data were distributed in the first three PCs as shown in Figure S2.
Figure 4a,b displays that the soil indicators are significantly correlated with their PCs) CLY, WHC, Ca, Na, and CEC were positively correlated with PC1, whereas S showed a negative correlation . In contrast, PC2 was negatively correlated with ESP and SAR, while PC3 only correlated negatively with the C/N ratio.
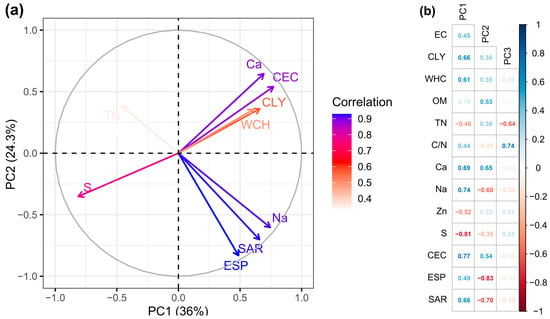
Figure 4.
(a) Bi-graph of indicators and PCs. (b) Spearman correlation matrix between indicators and PCs. Strong blue value equals positive correlation, strong red value equals negative correlation, weak value or no value equals no correlation. The meaning of acronyms is described in Table 2.
3.3. Establishment of SQIs
At the end of the redundancy elimination process, from the indicators significantly correlated with the PCs, the WHC, Na, CLY, and C/N indicators were selected. The WHC and Na indicators were scored using Equation (4), while the CLY and C/N indicators were scored using Equation (5).
The PC1 can be considered as the one related to soil structure. The indicators correlated with PC2 were not selected to be integrated into the different indexes; therefore, this PC was discarded. PC3, composed of the C/N indicator, was found to be related to OM quality and crop nutrition, being C/N an indicator previously considered to be related to soil quality [49].
Finally, the developed were as follows:
Once the were developed, they were evaluated on the sampled soils (Figure 5). The presented quality values for the different soils in the range of low quality (Ir2, = 0.22) to moderate quality (Ac1, = 0.50) (Figure 5a). For , quality values were in the range of very low quality (Ir2, = 0.16) to low quality (Ac1, = 0.36) (Figure 5b). Regarding , it presented quality values for the sampled soils in the range of moderate (Ir2, = 0.55) to very high quality (Ac1, , > 1.00) (Figure 5c). Lastly, the presented quality values in the range from very low quality (Sa2, = 0.19) to low quality (Ac1, = 0.34) (Figure 5d). It was possible to observe variability in the quality results obtained by the various developed, being the the one that showed the greatest range of values, while the was the one with the least variation.
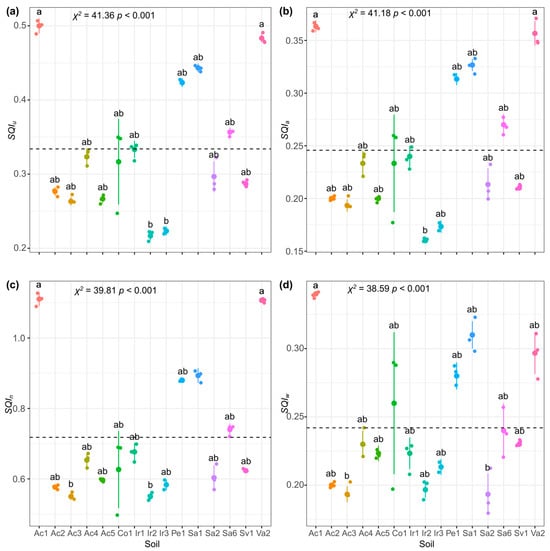
Figure 5.
Kruskal–Wallis analysis for sampled soil quality results with subsequent Dunnett’s test of medians with Bonferroni adjustment at significance level . (a) SQIu, the unified weighted index; (b) SQIa, the additive index; (c) SQIn, the Nemoro index; (d) SQIw, the weighted index. Large colored dot means mean value of the measurement; bars indicate SD (n = 3). Black dotted line means mean value of soil quality for all soils. Same letters indicate that there is no significant difference between treatments using a Kruskal–Wallis analysis with subsequent Dunnett’s median test with Bonferroni adjustment at a significance level .
It was observed that the indexes , , and were able to divide the soils into two groups, while the was able to group the various soils into three groups. In general, all the indexes exhibited similar patterns in the quality results of the analyzed soils (Figure 5), presenting soil Ac1 as the one with the best quality.
To quantify the similarity of these patterns, a correlation analysis was conducted between the different indexes, the results of which are presented in Figure 6. It is important to note that all the developed indexes presented high correlations with significance levels of . The indexes that presented the highest correlation were the and (Figure 6a), while the and were those that presented the lowest correlation (Figure 6c). The similarity between the indices developed can be explained by the mathematical approach used and the assumed behavior of their indicators in the soil. On the one hand, the and indices assume that the indicators vary linearly. The assigns equal weights to all indicators, while the uses expert-defined weights. On the other hand, the and indices assign weights to indicators according to specific criteria. The bases its weights on the relationship with the principal components obtained from the PCA. The , on the other hand, determines the weights according to the distance of each indicator to the mean value of the data analyzed. It should be noted that the presented values above the quality limit of 1. This could be due to the mathematical treatment that was applied, which could be far from the reality of the soil conditions. All the indexes developed in this study exhibited a significant positive correlation, suggesting that they have similar behaviors (Figure 6). This makes it difficult to select the index that would be the most suitable to analyze the sampled soils.
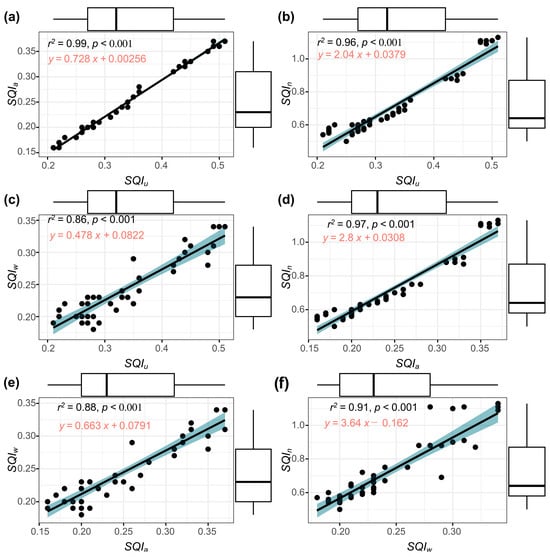
Figure 6.
(a–f) Correlation analysis between the various developed. , unified soil quality index; , additive soil quality index; , weighted soil quality index; , Nemoro soil quality index; p, probability value; , correlation coefficient. Blue area refers to standard deviation with 95% confidence interval.
The sensitivity and efficiency of the developed indexes are shown in Figure 7. The had the lowest variability and highest precision, while showed the highest variability (Figure 7a). However, precision differences were minimal among indices. In terms of soil quality representation efficiency, achieved 50%, contrasting with presented only a 13% efficiency.
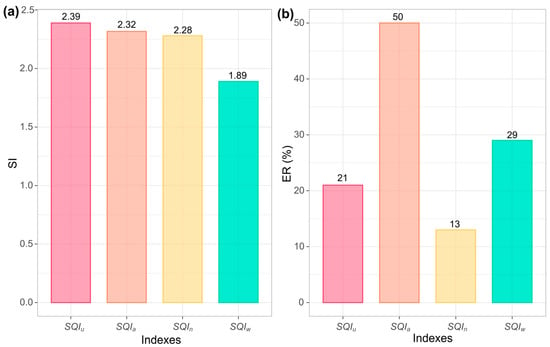
Figure 7.
(a) SI, sensitivity index and (b) ER, efficiency ratio of developed SQIs. , unified soil quality index; , additive soil quality index; , weighted soil quality index; , Nemoro soil quality index.
The low variability and higher efficiency of the makes it an accurate and reliable tool for assessing the quality of agricultural soils under corn cultivation. The reduced number of indicators in makes it easy to use and guarantees an accurate reading of soil fertility and soil quality conditions.
The for agricultural soils used for corn production in various regions of the world have been developed by a number of different researchers. In a 15-year study, Amorim et al. [7] monitored soil quality in a no-till crop rotation (cotton and corn) experiment with cover crops. They evaluated indicators such as pH, TOC, BD, extractable P and K, EC, and SAR through the Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF). The SMAF distinguished soil quality based on depth, presenting moderate quality conditions, but failed to distinguish quality relative to crop rotation and cover crops, indicating moderate quality values for both. Unlike the SMAF, the index selected in our study uses a different combination of indicators, but it addresses the same soil characteristics. These include structure-linked indicators (CLY, WHC, and Na in our study), salt concentration toxicity (Na in our study), and soil nutritional conditions (C/N in our study), considering local soil quality conditions. These similarities provide support for the developed in the present study.
An was created by Assunção et al. [8] using a total data set of 24 physicochemical and biological indicators, in the coastal plateaus of the State of Sergipe in northeastern Brazil. Their study was conducted over a long term (17 years) on plots with Ultisol soils under different corn management systems. The impact of farming practices and cover crops on soil quality was examined. It was determined that soils under no-tillage had the best soil quality while conventional tillage had a significant impact on soil quality. In terms of cover crops, peas, and millet presented good quality conditions in minimal tillage and no-tillage systems, respectively. An is more accurate when a high number of indicators are used, but its complexity and high cost may limit its use in other areas with comparable characteristics. In comparison, our study implements a PCA that makes it possible to reduce the number of indicators in the , lowering its cost and simplifying its interpretation, which facilitates the application of this tool in other regions whose agricultural conditions are similar. Moreover, analyzing 15 agricultural soils representative of the region with diverse characteristics takes into consideration environmental variability, unlike the research carried out by Assunção et al. [8]. One aspect to highlight about the developed by Assunção et al. [8] is the use of biological indicators, which could provide greater sensitivity to the to small disturbances in the analyzed soils.
Utilizing a minimal data set of marsh soils reclaimed from coal mining residues, Hu et al. [63] developed an through a PCA and assessed its effectiveness under corn cultivation conditions. Indicators of texture, pH, EC, and TOC formed the basis of this index. The tested soils had values ranging from 0.18 (very low quality) to 0.66 (high quality). Nonetheless, applying linear functions to score the selected indicators may lead to erroneous results as a consequence of including indicators whose behavior in the soil is nonlinear—e.g., pH and texture—which may reduce the sensitivity of the as well, due to only considering physicochemical indicators. On the contrary, our research included nonlinear scoring functions, integrating the nonlinear behavior of the indicators, and increasing efficiency while reducing the variability of the quality results obtained.
3.4. Limitations and Perspectives
A possible shortcoming of the developed could be the exclusion of biological indicators in its selection and creation process. Biological indicators are considered highly sensitive to small changes, as they are closely related to microbial communities. In terms of prospects, the relationship of the index with crop characteristics—such as productivity, efficiency, and quality of harvested feed, as well as its variability over time, different agricultural management systems—could be analyzed.
4. Conclusions
PCA reduced the number of soil quality indicators from 24 to four: CLY, WHC, Na, and C/N ratio. The first three indicators are directly linked to soil structure. A high CLY content is associated with soil structure degradation caused by intense farming. This degradation promotes nutrient loss and reduces the soil’s ability to retain water, worsening erosion. Na, linked to salt accumulation from saline irrigation water, disrupts soil structure by breaking down aggregates and reducing pore spaces. In semi-arid regions—like the study area—this salt buildup causes osmotic stress, hindering crop growth. Thus, monitoring Na is critical. The C/N ratio, which reflects OM quality, was included due to its role in corn growth and soil microbial activity. Among the developed indices, the performed best, showing low variability and strong correlation with key indicators. The methodology simplified soil data into a single quality value, easing result interpretation and application in similar agricultural contexts. Notably, the aligns with the SMAF—a globally used soil assessment tool. This consistency supports its use for managing corn-production soils under programs like ENASAS (national level) and in international settings conditions, both nationally—in accordance with the ENASAS program—and internationally.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land14040861/s1. Figure S1. Textural classification of sampled soils. Figure S2. Proportion of variability explained by PCs. Table S1. Agricultural soil quality scale. Reference [64] is cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
E.C.-B.: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing—original draft, resources, validation, writing—review and editing. M.d.l.L.X.N.-R.: Supervision, writing—review and editing. D.Á.-B.: Methodology, writing—review and editing. F.P.G.-V.: Investigation, validation. M.A.L.-H.: Methodology, data curation. H.P.-G.: Data curation, validation. G.A.S.-M. and F.E.T.-F.: Writing—review and editing. H.I.B.-R.: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing—original draft, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by SECIHTI postgraduate scholarship No. 491864 (2019 to 2023).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available by request from the corresponding author (H.I.B.-R.). The data are not yet publicly available because they are being utilized in other current studies.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the Environmental Biotechnology and Bioprocesses Laboratory of the National Technological Institute of Mexico/Technological Institute of Celaya for making their facilities and equipment available to us for the development of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ENASAS | National Soil Strategy for Sustainable Agriculture |
| Soil Quality Index | |
| Additive Soil Quality Index | |
| Weighted Soil Quality Index | |
| Unified Weighted Soil Quality Index | |
| Nemoro Soil Quality Index | |
| SMAF | Soil Management Assessment Framework |
| CLY | Clay |
| WHC | Water Holding Capacity |
| Na | Sodium |
| C/N | Carbon Nitrogen Ratio |
| K | Potassium |
| P | Phosphorus |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| BD | Bulk Density |
| DHA | Dehydrogenase Activity |
| MBC | Microbial Biomass Carbon |
| pH | Hydrogen Potential |
| SAR | Sodium Adsorption Ratio |
| INEGI | National Institute of Statistics Geography and Informatics |
| RAN | National Agrarian Registry |
| t | Tons |
| ha | Hectare |
| NPK | Nitrogen Phosphorus Potassium Units |
| SND | Sand |
| SLT | Silt |
| USDA | United States Department of Agriculture |
| OM | Organic Matter |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| S | Sulfur |
| Ca | Calcium |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| Fe | Iron |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Mn | Magnesium |
| Cu | Cupper |
| B | Boron |
| ICP | Inductively Coupled Plasma |
| CEC | Catio Exchange Capacity |
| ESP | Exchangeable Sodium Percentage |
| KMO | Kaiser Meyer Olkin Test |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PCs | Principal Components |
| SI | Sensitivity Index |
| ER | Efficiency Ratio |
| Mean | |
| Min | Minimum Value |
| Max | Maximum Value |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Han, N.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Z. Rapid Diagnosis of Nitrogen Nutrition Status in Summer Maize over Its Life Cycle by a Multi-Index Synergy Model Using Ground Hyperspectral and UAV Multispectral Sensor Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Agricultural Production Statistics 2010–2023; FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ureta, C.; González, E.J.; Espinosa, A.; Trueba, A.; Piñeyro-Nelson, A.; Álvarez-Buylla, E.R. Maize Yield in Mexico under Climate Change. Agric. Syst. 2020, 177, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural [Agricultura]. Estrategia Nacional de Suelo Para La Agricultura Sostenible (ENASAS); Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural: Mexico City, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, E.B.S.; Zabala, S.A.F.; Echeverri, L.F.G. Índices de calidad del suelo. Una revisión sistemática. Ecosistemas 2018, 27, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Adak, S.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Sen, S.; Sahoo, R.N.; Shrivastava, M.; Krishnan, P. Impact of Contrasting Tillage, Residue Mulch and Nitrogen Management on Soil Quality and System Productivity under Maize-Wheat Rotation in the North-Western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1230207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, H.C.S.; Ashworth, A.J.; Wienhold, B.J.; Savin, M.C.; Allen, F.L.; Saxton, A.M.; Owens, P.R.; Curi, N. Soil Quality Indices Based on Long-Term Conservation Cropping Systems Management. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, S.J.R.; Pedrotti, A.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; Nobrega, J.C.A.; Holanda, F.S.R. Soil Quality Index of an Ultisol under Long-Term Plots in the Coastal Tablelands in Northeastern Brazil. Rev. Caatinga 2023, 36, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Khosravi Aqdam, M.; Abbas Fadel, H.; Wang, L.; Waheeb, K.; Kadhim, A.; Hekmati, J. Evaluation of Soil Fertility Using Combination of Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 Data in Agricultural Lands. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils 1. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Soil Survey Manual; United Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1951.
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Summer, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Das, B.; Corwin, D.L.; Wraith, J.M.; Kachanoski, R.G. Relationship Between Soil Water Solute Concentration and Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 1275–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Elsevier: London, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-12-513840-6. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Methods for Determining Soil Organic Matter and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Sönmez, M. The Role of Organic/Bio–Fertilizer Amendment on Aggregate Stability and Organic Carbon Content in Different Aggregate Scales. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Summer, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Bettinelli, M.; Baroni, U. A Microwave Oven Digestion Method for the Determination of Metals in Sewage Sludges by ICP-AES and GFAAS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1991, 43, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottenie, A. Soil and Plant Testing as a Basis of Fertilizer Recommendations; FAO Soil’s Bulletin, 38/2; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1980; pp. 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-021-RECNAT-2000, Que Establece las Especificaciones de Fertilidad, Salinidad y Clasificaciónde Suelos. Estudios, Muestreo y Análisis. 2002, p. 73. Available online: https://www.ordenjuridico.gob.mx/Documentos/Federal/wo69255.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Webster, R. Interpreting Soil Test Results: What Do All the Numbers Mean? 2nd ed.; Hazelton, P., Murphy, B., Eds.; Csiro Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2007; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- de Mendiburu, F. Agricolae; Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.; Dupont, C. Hmisc; Harrell Miscellaneous; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. factoextra; Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W. psych; Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. corrplot: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R; Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Juhos, K.; Czigány, S.; Madarász, B.; Ladányi, M. Interpretation of Soil Quality Indicators for Land Suitability Assessment—A Multivariate Approach for Central European Arable Soils. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, G.; Das, B.; Morajkar, S.; Desai, A.; Murgaokar, D.; Kulkarni, R.; Sale, R.; Patel, K. Soil Quality Assessment of Coastal Salt-Affected Acid Soils of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26221–26238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the Minimum Data Set and Quantitative Soil Quality Indexing of Alkaline Soils Under Different Land Uses in Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Erickson, T.E.; Dixon, K.W.; Merritt, D.J. Soil Quality Indicators to Assess Functionality of Restored Soils in Degraded Semiarid Ecosystems. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, S43–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villazón Gómez, J.; Martín-Gutiérrez, G.; Cobo-Vidal, Y. Análisis Multivariado de Las Propiedades Químicas de Los Suelos Pardos Erosionados. Cent. Agric. 2017, 44, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of Agricultural Management Practices on Soil Quality: A Review of Long-Term Experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiollahi, K.; Golmohamadi, F.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R.; Davari, M. Assessing the Effects of Slope Gradient and Land Use Change on Soil Quality Degradation through Digital Mapping of Soil Quality Indices and Soil Loss Rate. Geoderma 2018, 318, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.C.R.; Brussaard, L.; Totola, M.R.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; de Goede, R.G.M. A Functional Evaluation of Three Indicator Sets for Assessing Soil Quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 64, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-González, D.E.; Muñoz-Iniestra, D.J.; López-Galindo, F.; Hernández-Moreno, M.M. Impact of Land Use on Soil Quality in a Semi-Arid Zone of the Mezquital Valley, Hidalgo, Mexico. BIOCyT 2018, 11, 792–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Ding, G.; Liu, X. Soil Quality Index Evaluation Model in Responses to Six-Year Fertilization Practices in Mollisols. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 68, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedolla-Rivera, H.I.; Xochilt Negrete-Rodríguez, M.d.l.L.; Medina-Herrera, M.d.R.; Gámez-Vázquez, F.P.; Álvarez-Bernal, D.; Samaniego-Hernández, M.; Gámez-Vázquez, A.J.; Conde-Barajas, E. Development of a Soil Quality Index for Soils under Different Agricultural Management Conditions in the Central Lowlands of Mexico: Physicochemical, Biological and Ecophysiological Indicators. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora Ravelo, S.G.; Gavi Reyes, F.; Peña Cabriales, J.J.; Pérez Moreno, J.; Tijerina Chávez, L. Evaluación de La Recuperación Del Nitrógeno y Fósforo de Diferentes Fuentes de Fertilizantes Por El Cultivo de Trigo Irrigado Con Aguas Residuales y de Pozo. Acta agron. 2014, 63, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2022: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2022; ISBN 979-8-9862451-1-9. [Google Scholar]
- Castelán Vega, R.D.C. Susceptibilidad Ambiental a La Desertificación En La Microcuenca Del Río Azumiatla, Puebla, México. Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2019, 6, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Vitti, C. Use of Organic Amendments to Reclaim Saline and Sodic Soils: A Review. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 2019, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.; Karlen, D.L.; Moorman, T.B. Tillage Intensity Effects on Soil Structure Indicators—A US Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Activities of Soil Nitrogen Acquisition enzymes: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.; Pastor, J.; Rivas, W.; Gonzalez, O.; González, L. Evaluación de La Calidad Del Suelo Bajo Diferentes Sistemas Agrícolas En La Península de Paraguaná Mediante El Uso de Indicadores de Sustentabilidad. Koinonia 2017, 2, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Libohova, Z.; Seybold, C.; Wysocki, D.; Wills, S.; Schoeneberger, P.; Williams, C.; Lindbo, D.; Stott, D.; Owens, P.R. Reevaluating the Effects of Soil Organic Matter and Other Properties on Available Water-Holding Capacity Using the National Cooperative Soil Survey Characterization Database. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, M.; Shahbazi, K.; Kharazi, N.; Rezaei, M. The Influence of Organic Amendment Source on Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization in Different Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Ferdous, J.; Mumu, N.J.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Eckhardt, C.; Zaman, M.; Müller, C.; Jahangir, M.M.R. Crop Residues Integration with Nitrogen Rates Reduces Yield-Scaled Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Improves Maize Yield and Soil Quality. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2024, 21, 2310856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Norton, J.M. Short-Term Nitrogen Fertilization Affects Microbial Community Composition and Nitrogen Mineralization Functions in an Agricultural Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 86, e02278-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, R.; Guo, S. Responses of Nitrification and Denitrification to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization: Does the Intrinsic Soil Fertility Matter? Plant Soil 2019, 440, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, L.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wanek, W. Wide-Spread Limitation of Soil Organic Nitrogen Transformations by Substrate Availability and Not by Extracellular Enzyme Content. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zungu, N.S.; Egbewale, S.O.; Olaniran, A.O.; Pérez-fernández, M.; Magadlela, A. Soil Nutrition, Microbial Composition and Associated Soil Enzyme Activities in KwaZulu-Natal Grasslands and Savannah Ecosystems Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Lee, S.H.; Ji, H.C.; Kabir, A.H.; Jones, C.S.; Lee, K.W. Importance of Mineral Nutrition for Mitigating Aluminum Toxicity in Plants on Acidic Soils: Current Status and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Greene, R.S.B.; Dalal, R.C.; Murphy, B.W. Soil Carbon Dynamics in Saline and Sodic Soils: A Review. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, T.; Hakeem, K.R. (Eds.) Plant Micronutrients: Deficiency and Toxicity Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-49855-9. [Google Scholar]
- Denton-Thompson, S.M.; Sayer, E.J. Micronutrients in Food Production: What Can We Learn from Natural Ecosystems? Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, D.S.; Silva, L.D.C.M.D.; Melo, L.B.B.D.; Azevedo, R.P.; Araújo, B.C.L.; Carvalho, T.S.D.; Moreira, S.G.; Curi, N.; Silva, B.M. Occasional Tillage in No-Tillage Systems: A Global Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Padilla-Gasca, E.; López-Corrales, R.; Medina, J.R.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.; Amabilis-Sosa, L.E.; Rodríguez-Mata, A.E.; Osuna-Enciso, T. Robust Soil Quality Index for Tropical Soils Influenced by Agricultural Activities. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2017, 6, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kacprzak, M.; Kupich, I.; Jasinska, A.; Fijalkowski, K. Bio-Based Waste’ Substrates for Degraded Soil Improvement—Advantages and Challenges in European Context. Energies 2022, 15, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Dong, A.; Duan, H. Revisiting Sulphur—The Once Neglected Nutrient: It’s Roles in Plant Growth, Metabolism, Stress Tolerance and Crop Production. Agriculture 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Gong, Y. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Maize Growth in Different Profiles of Reclaimed Land with Coal Gangue Filling. Land 2021, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Méndez, J.; Prieto-García, F.; Acevedo-Sandoval, O.A.; Méndez-Marzo, M.A. Indicadores e índices de calidad de los suelos (ICS) cebaderos del sur del estado de Hidalgo, México. Agron. Mesoam. 2013, 24, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).