Effects of Management Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure on Eucalyptus Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
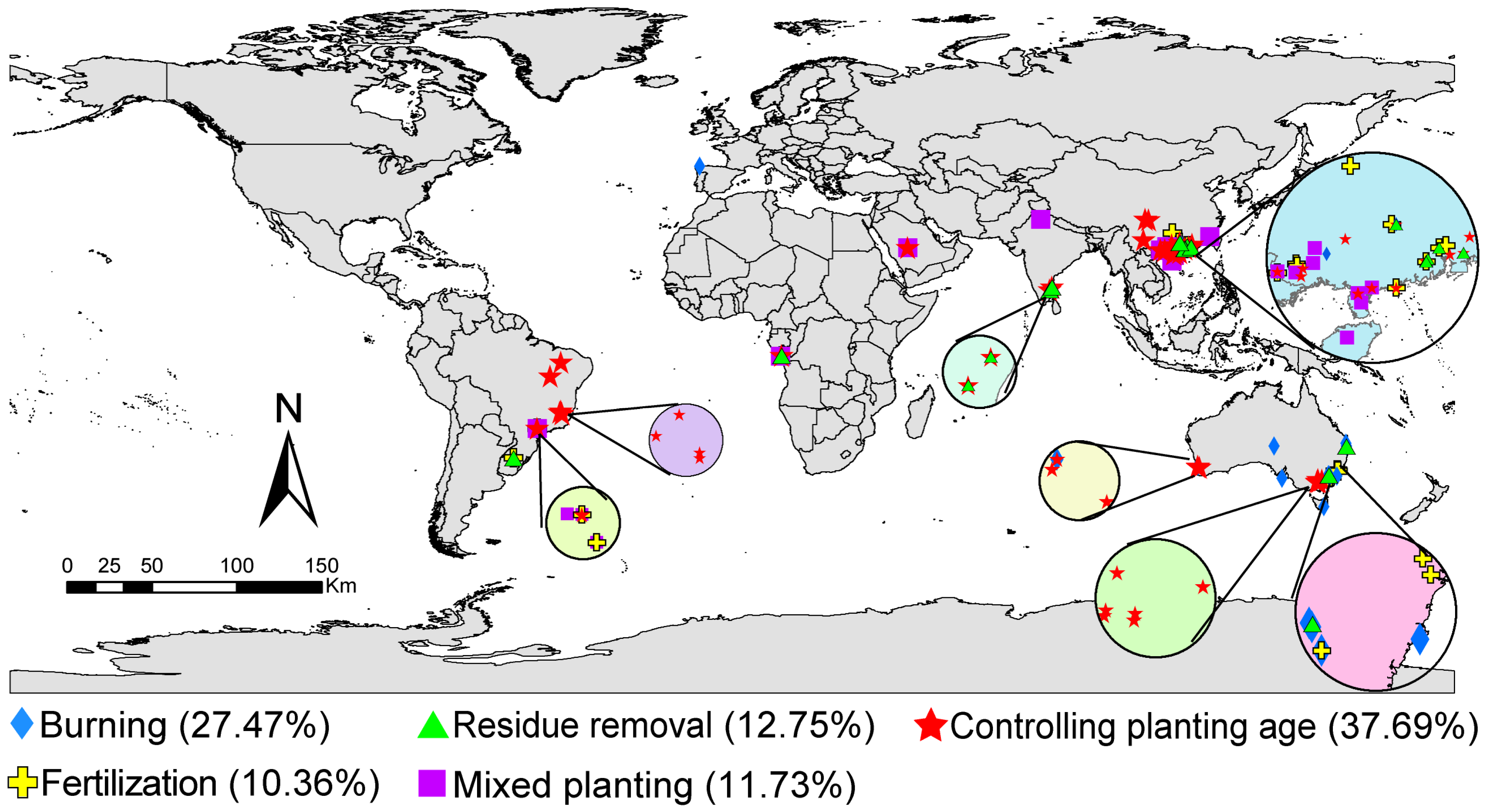
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Calculations
2.3. Statistical Analyses
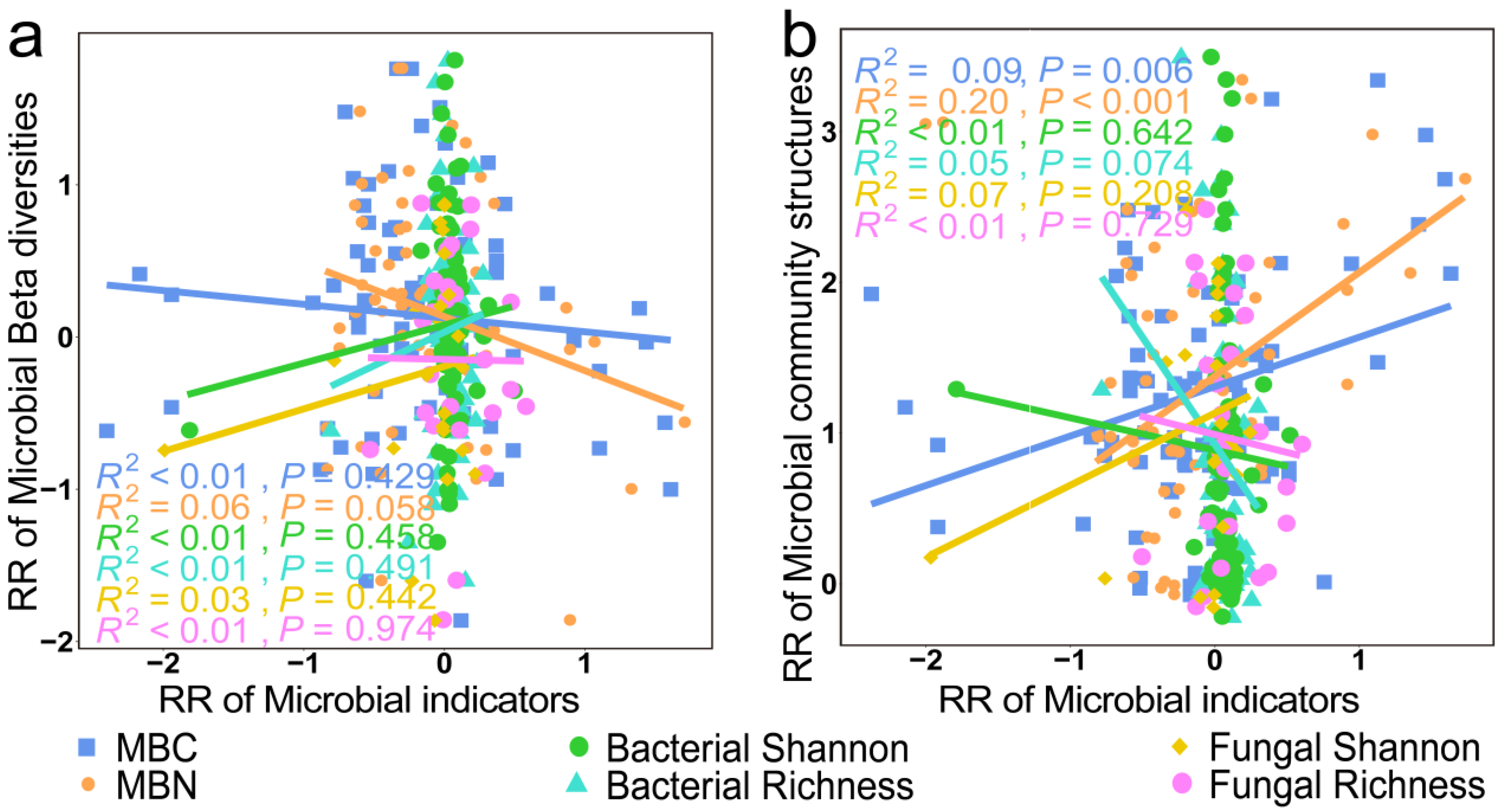
3. Results
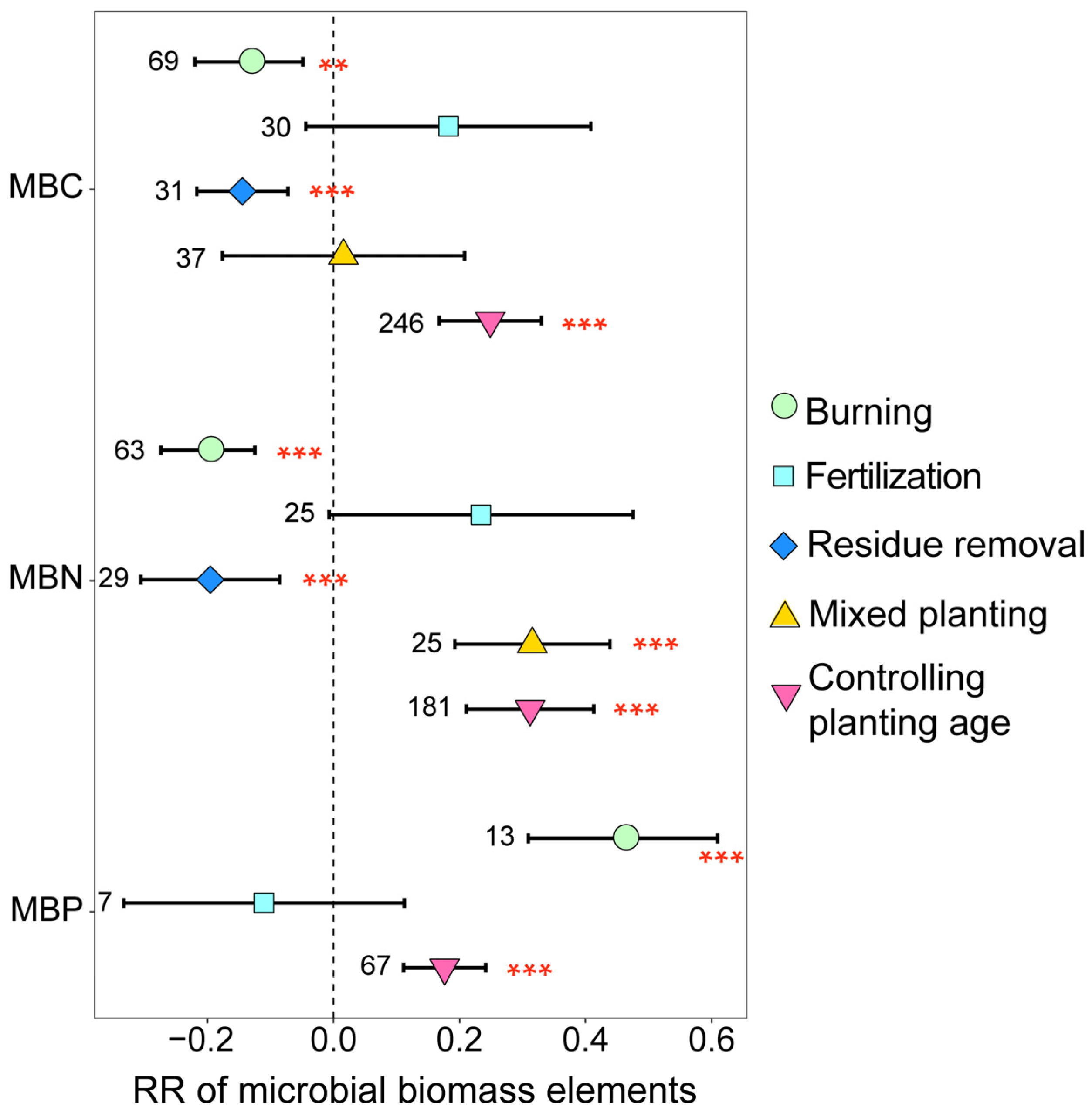
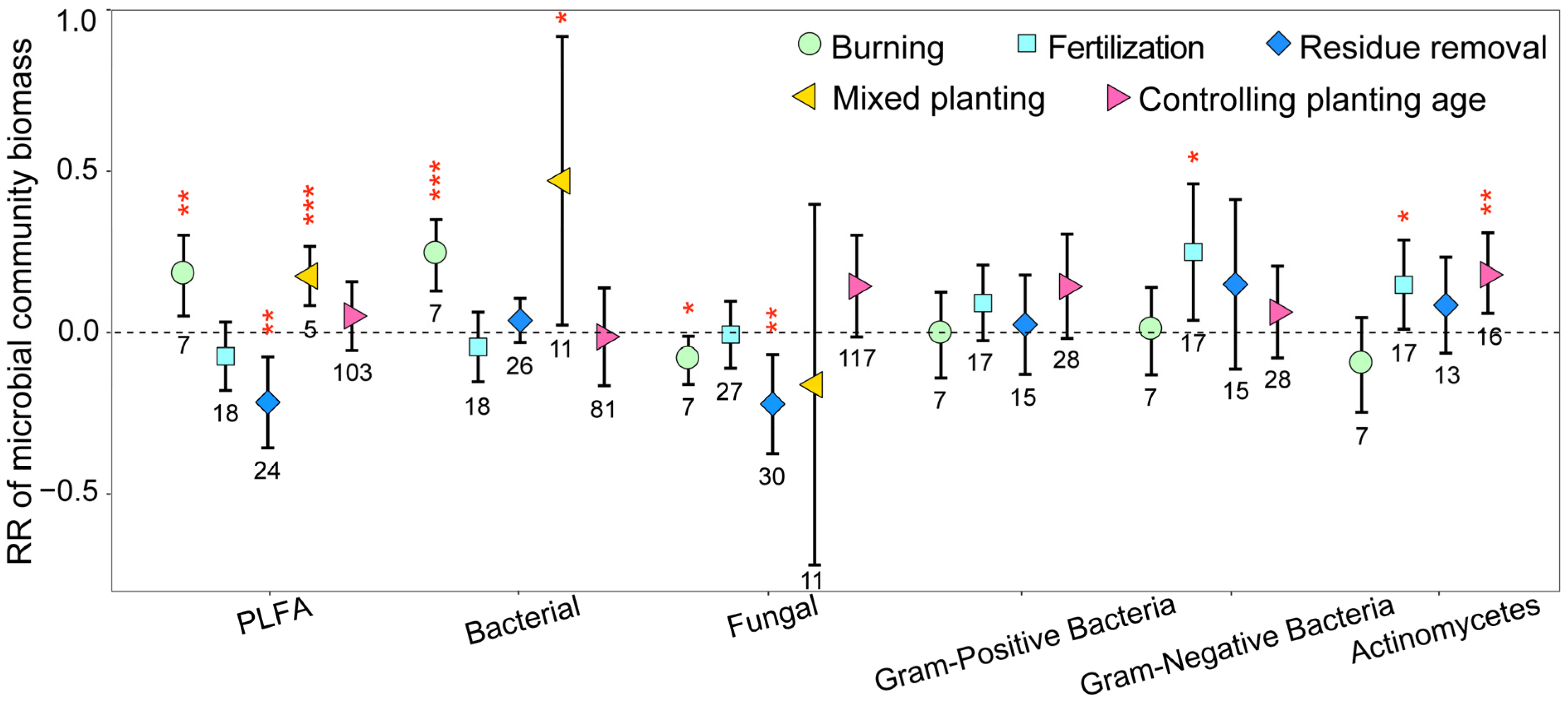
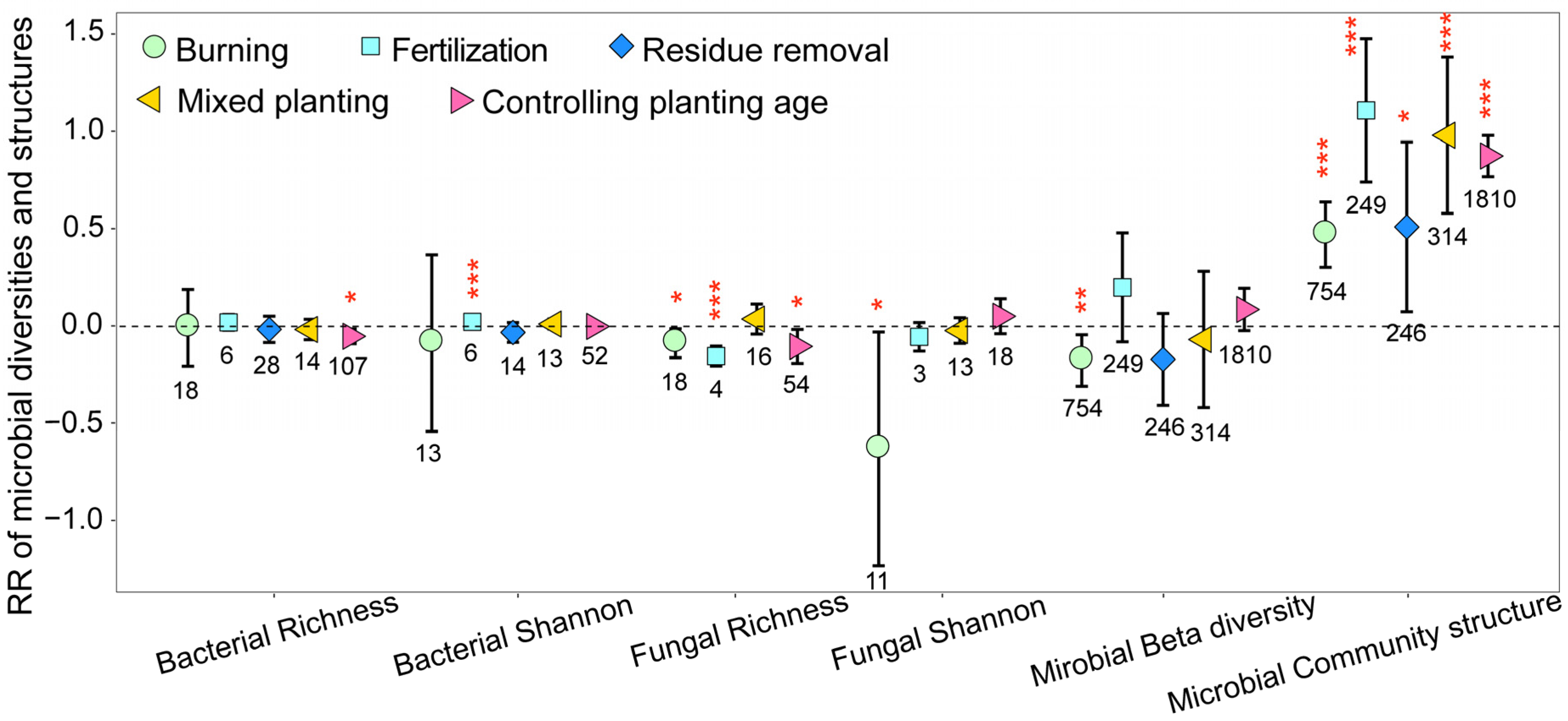
3.1. Variation in Soil Microbial Community Biomass, Diversity, and Structure
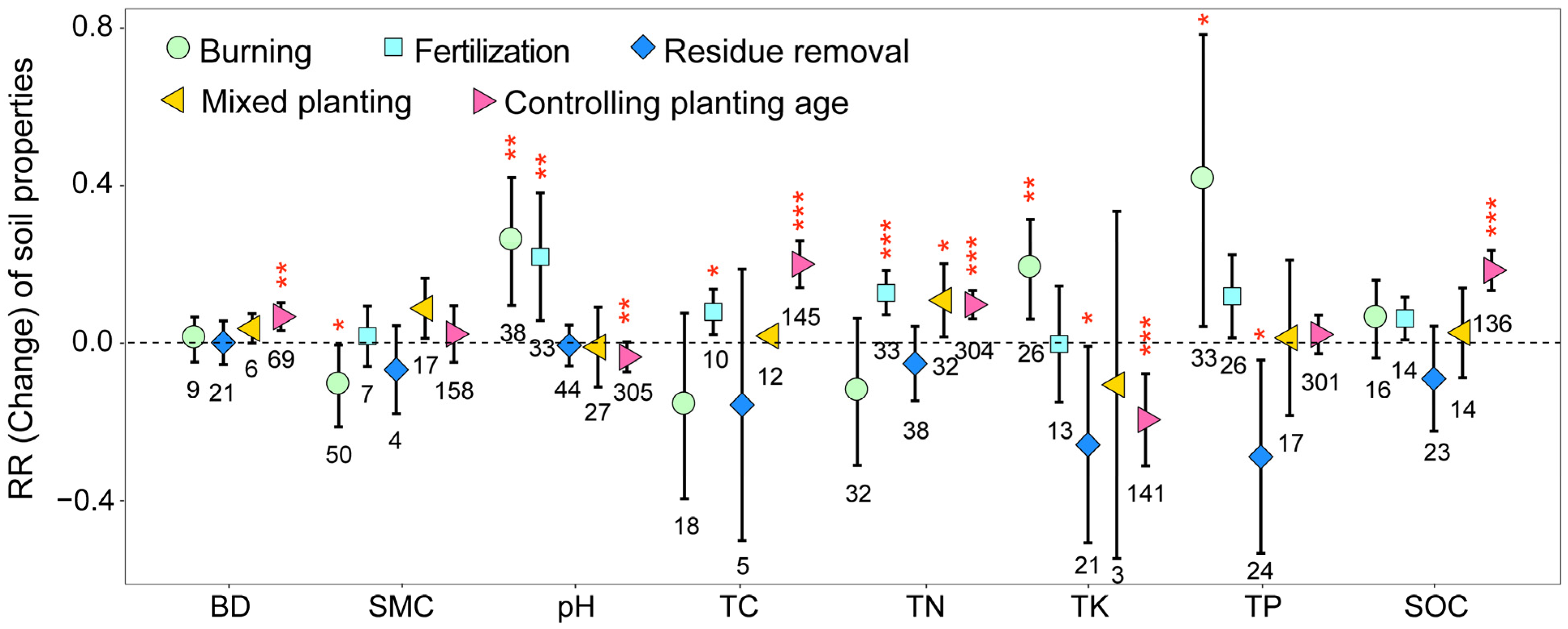
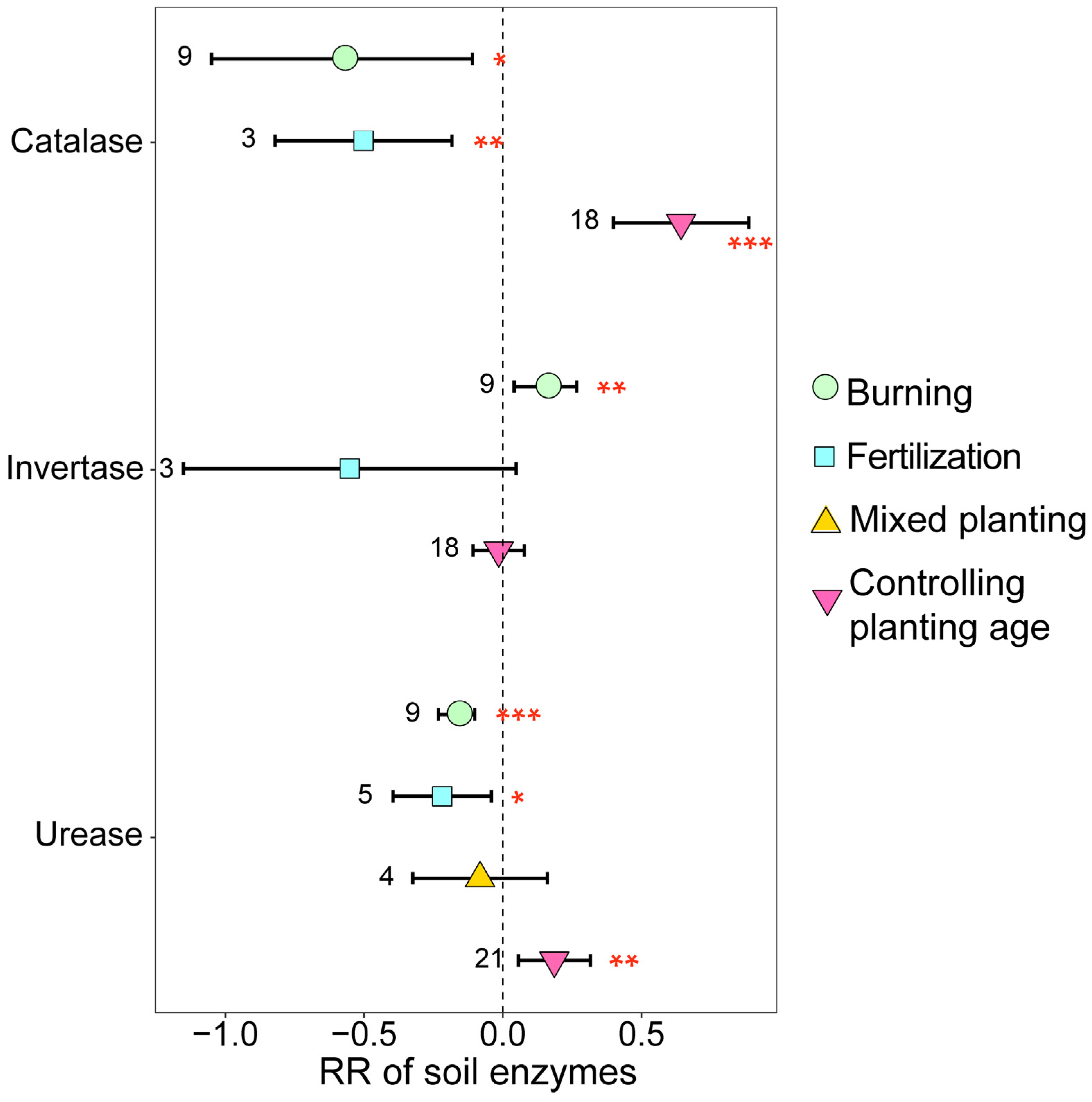
3.2. Variation in Soil Properties and Enzymes
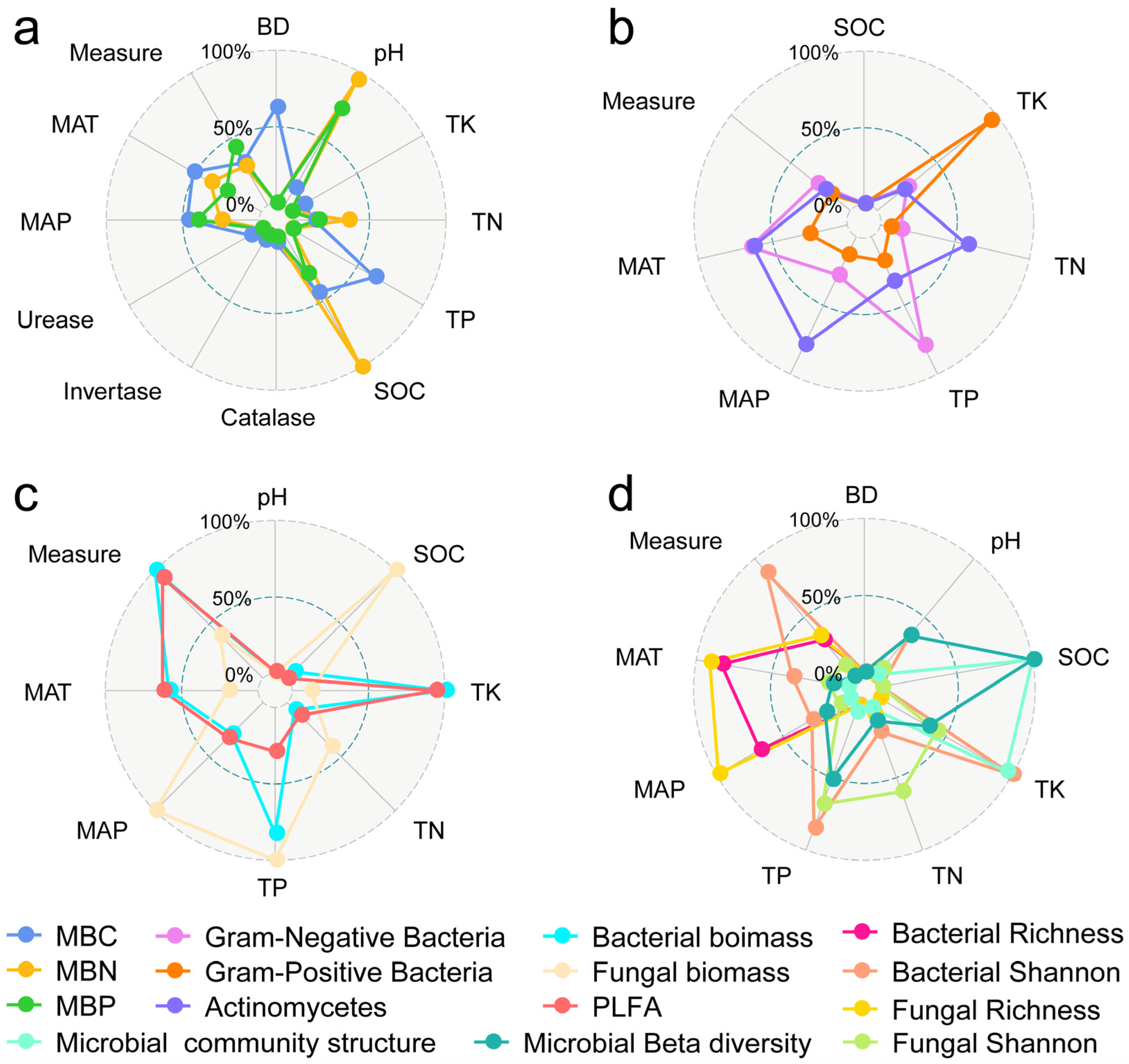
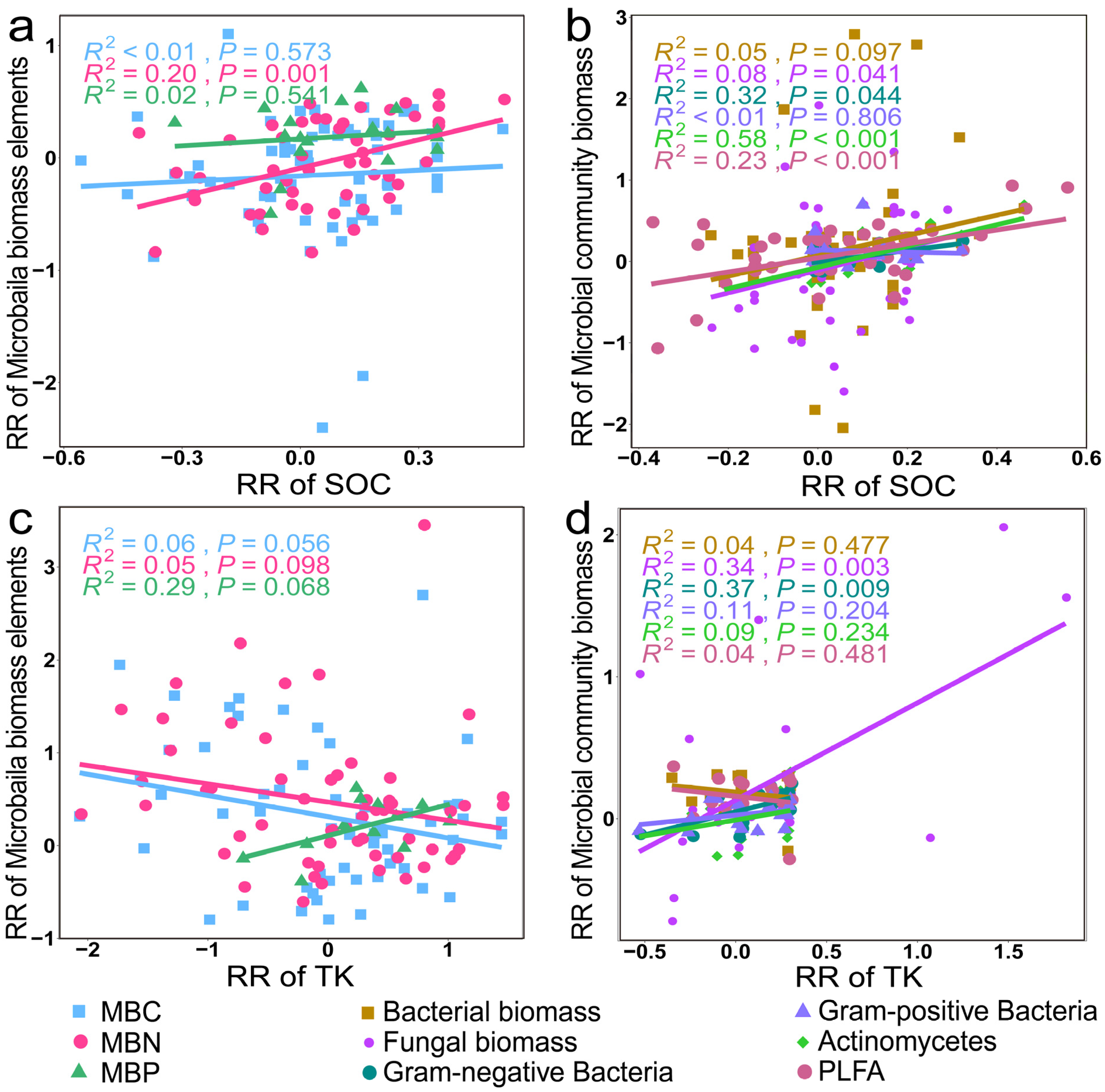
3.3. Mechanisms of Soil Microbial Biomass, Diversity, and Structural Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Affecting Microbial Community Biomass, Diversity, and Structure
4.2. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laclau, J.P.; Ranger, J.; Boullet, J.P.; Nzila, J.D.; Deleporte, P. Nutrient cycling in a clonal stand of Eucalyptus and an adjacent savanna ecosystem in Congo. 1. Chemical composition of rainfall and stem flow solutions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 176, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Laclau, J.P.; Ranger, J.; Boullet, J.P.; Nzila, J.D.; Deleporte, P. Nutrient cycling in a clonal stand of Eucalyptus and an adjacent savanna ecosystem in Congo. 2. Chemical composition of soil solutions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, J.S.; Verboom, W.H. Contemporary biogenic formation of clay pavement by eucalypts: Further support for the phytotarium concept. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 673–685. [Google Scholar]
- Phalan, B.; Bertzky, M.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Donald, P.F.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Stattersfield, A.J.; Balmfordet, A. Crop expansion and conservation priorities in tropical countries. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51759. [Google Scholar]
- Eufrade Junior, H.J.; Melo, R.X.; Sartori, M.M.P.; Guerra, S.P.S.; Ballarin, A.W. Sustainable use of eucalypt biomass grown on short rotation coppice for bioenergy. Biomass Bioenerg. 2016, 90, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jagger, P.; Pender, J. The role of trees for sustainable management of less-favoured lands: The case of eucalyptus in Ethiopia. For. Policy Econ. 2003, 5, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Nouvellon, Y.; Epron, D.; Marsden, C.; Kinana, A.; Maire, G.L.; Deleporte, P.; SaintAndre, L.; Bouillet, J.P.; Laclau, J.P. Age-related changes in litter inputs explain annual trends in soil CO2 effluxes over a full Eucalyptus rotation after afforestation of a tropical savannah. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 515–533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, X.J. Geographical spatial distribution and productivity dynamic change of Eucalyptus plantations in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19764. [Google Scholar]
- Laclau, J.P.; Deleporte, P.; Ranger, J.; Bouilleti, J.P.; Kazotti, G. Nutrient dynamics throughout the rotation of Eucalyptus clonal stands in Congo. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 879–892. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.F.; Fu, S.L.; Zhao, H.T.; Xia, H.P. Effects of understory removal and N-fixing species seeding on soil N2O fluxes in four forest plantations in southern China. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2010, 56, 541–551. [Google Scholar]
- Florentine, S.K.; Fox, J.E.D. Allelopathic effects of Eucalyptus victrix L. on Eucalyptus species and grasses. Allelopath 2003, 11, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.L.; Fu, S.L. Allelopathic effects of eucalyptus and the establishment of mixed stands of eucalyptus and native species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, O.; Bolat, I.; Çakıroğlu, K.; Öztürk, M. Plant canopy effects on litter accumulation and soil microbial biomass in two temperate forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 45, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.Y. Research on the Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest and Cultivated Land; Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resource, Chinese Academy of Science: Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zheng, J.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Abdullah, K.M.; Zhou, Q.X. Effects of changed litter inputs on soil labile carbon and nitrogen pools in a eucalyptus-dominated forest of southeast Queensland, Australia. J. Soil Sediment. 2019, 19, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Mercedes, M.O.; Michael, B.; Richard, J.P.D.; Mark, K.J.O.; Miriam, M.R. Fire and land use impact soil properties in a Mediterranean dry sclerophyll woodland. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 324, 116245. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.S.; Luo, C.L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Ostle, N.J.; Cheng, Z.N.; Ding, P.; Shen, C.D.; Zhang, G. Radiocarbon evidence of the impact of forest-to-plantation conversion on soil organic carbon dynamics on a tropical island. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114484. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.L.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H. Differences in bacterial community structure and potential functions among Eucalyptus plantations with different ages and species of trees. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 149, 103515. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.P.A.; Santana, M.C.; Zagatto, M.R.G.; Brandani, C.B.; Wang, J.T.; Verma, J.P.; Singh, B.K.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Nitrogen-fixing trees in mixed forest systems regulate the ecology of fungal community and phosphorus cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143711. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.M.; Liu, S.R.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.D.; Li, Z.G.; You, Y.M. Changes of soil microbial biomass carbon and community composition through mixing nitrogen-fixing species with Eucalyptus urophylla in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 73, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.X.; Du, A.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhu, W.K.; Li, C.; Wu, L.C. Effects of different rotation periods of Eucalyptus plantations on soil physiochemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure and diversity. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 456, 117683. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, C.R.; Wang, W.J.; Hughes, J.M.; Lewis, T.; Hou, E.Q.; Shen, J.P. Soil environmental factors rather than denitrification gene abundance control N2O fluxes in a wet sclerophyll forest with different burning frequency. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Smith, A.R.; Godbold, D.L.; Jones, D.L.; Kuzyakov, Y. Response of soil microbial community to afforestation with pure and mixed species. Plant Soil 2017, 412, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.; Abdullaha, K.M.; Xu, Z.H.; Wang, W.J. Water extractable organic C and total N: The most sensitive indicator of soil labile C and N pools in response to the prescribed burning in a suburban natural forest of subtropical Australia. Geoderma 2020, 377, 114586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Weng, Y.L.; Chen, X.L.; Wu, L.C. Soil characteristics of Eucalyptus urophylla×Eucalyptus grandis plantations under different management practices for harvest residues with soil depth gradient across time. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.W.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, H.D.; Denham, A.J.; Ooi, M.K.J. Fire severity drives variation in post-fire recruitment and residual seed bank size of Acacia species. Plant Ecol. 2018, 219, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Rafique, R.; Ma, L.; Hu, L.; Luo, Y. Fire alters vegetation and soil microbial community in alpine meadow. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 27, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcenas-Moreno, G.; García-Orenes, F.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Mataix-Beneyto, J. Plant community influence on soil microbial response after a wildfire in Sierra Nevada National Park (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendham, D.S.; Sankaran, K.V.; OConnell, A.M.; Grove, T.S. Eucalyptus globulus harvest residue management effects on soil carbon and microbial biomass at 1 and 5 years after plantation establishment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachid, C.T.C.C.; Balieiro, F.C.; Peixoto, R.S.; Pinheiro, Y.A.S.; Piccolo, M.C.; Chaer, G.M.; Rosado, A.S. Mixed plantations can promote microbial integration and soil nitrate increases with changes in the N cycling genes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.P.A.; Durrer, A.; Gumierec, T.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Robina, A.; Bouillet, J.P.; Wang, J.T.; Vermab, J.P.; Singh, B.K.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Mixed Eucalyptus plantations induce changes in microbial communities and increase biological functions in the soil and litter layers. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 332–342. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.X.; Ren, S.Q.; Liang, Y.F.; Du, A.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhu, W.K.; Wu, L.C. Soil nutrient supply and tree species drive changes in soil microbial communities during the transformation of a multi-generation Eucalyptus plantation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103991. [Google Scholar]
- Bini, D.; dos Santos, C.A.; Bouillet, J.P.; Goncalves, J.L.D.M.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Eucalyptus grandis and Acacia mangium in monoculture and intercropped plantations: Evolution of soil and litter microbial and chemical attributes during early stages of plant development. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 63, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.Z.; Zhu, K.X.; Zhuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.Z. Soil nutrient cycling and bacterial community structure in response to various green manures in a successive Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus urophylla × Eucalyptus grandis) plantation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2809–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.K.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, Y.X. Responses to N and P fertilization in a young Eucalyptus dunnii plantation: Microbial properties, enzyme activities and dissolved organic matter. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kjoller, R.; Nilsson, L.O.; Hansen, K.; Schmidt, I.K.; Vesterdal, L.; Gundersen, P. Dramatic changes in ectomycorrhizal community composition, root tip abundance and mycelial production along a stand-scale nitrogen deposition gradient. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselquist, N.J.; Hgberg, P. Dosage and duration effects of nitrogen additions on ectomycorrhizal sporocarp production and functioning: An example from two N-limited boreal forests. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, P.; Armstrong, G.W.; Adamowicz, W.L. Carbon sequestration and the optimal forest harvest decision: A dynamic programming approach considering biomass and dead organic matter. J. For. Econ. 2011, 17, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cavagnaroa, T.R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Fitzpatrick, S. Pastures to woodlands: Changes in soil microbial communities and carbon following reforestation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyde, M.V.D.; Bunce, M.; Dixon, K.; Wardell-Johnson, G.; White, N.E.; Nevill, P. Changes in soil microbial communities in post mine ecological restoration: Implications for monitoring using high throughput DNA sequencing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142262. [Google Scholar]
- Trogisch, S.; He, J.S.; Hector, A.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M. Impact of species diversity, stand age and environmental factors on leaf litter decomposition in subtropical forests in China. Plant Soil 2015, 400, 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effects of different leaf litters on the physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in Panax ginseng-growing soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 111, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Ma, T.F.; Raza, W.; Jing, L.; Howland, J.G.; Huang, Q.W.; Shen, Q.R. Impacts of inorganic and organic fertilization treatments on bacterial and fungal communities in a paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 112, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z. Distribution of microbial biomass and activity within soil aggregates as affected by tea plantation age. CATENA 2017, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; An, S. The restoration age of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation impacts soil microbial biomass and microbial community structure in the Loess Plateau. CATENA 2018, 165, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Li, C.; Wu, L. Effects of the successive planting of Eucalyptus urophylla on the soil bacterial and fungal community structure, diversity, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 636–646. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.H.; Feng, H.L.; McNie, P.; Liu, Q.Y.; Xu, X.; Pan, C.; Yan, K.; Feng, L.; Goitom, E.A.; Yu, Y.C. Species mixing improves soil properties and enzymatic activities in Chinese fir plantations: A meta-analysis. CATENA 2023, 220, 106723. [Google Scholar]
- Curtright, A.J.; Tiemann, L.K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, C.K.; Zheng, M.H.; Jiang, L.F.; Luo, Y.Q. Patterns and mechanisms of responses by soil microbial communities to nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Waring, B.; Gee, A.; Liang, G.P.; Adkins, S. A quantitative analysis of microbial community structure-function relationships in plant litter decay. iScience 2022, 25, 104523. [Google Scholar]
- Achat, D.L.; Deleuze, C.; Landmann, G.; Pousse, N.; Ranger, J.; Augusto, L. Quantifying consequences of removing harvesting residues on forest soils and tree growth—A meta-analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 348, 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; Tian, D.S.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.L.; Yi, C.X.; Niu, S.L. Global soil acidification impacts on belowground processes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074003. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paliy, O.; Shankar, V. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in microbial ecology. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1032–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, C.K.; Luo, Y.Q. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; OHara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community ecology package. R. Package Version 2019, 2, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.P.; Gao, B.L.; Peng, Y.T.; Gao, X.; Fan, B.B.; Chen, Q. A meta-analysis of heavy metal bioavailability response to biochar aging: Importance of soil and biochar properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144058. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ding, C.; Heino, J.; Jiang, X.; Tao, J.; Ding, L.; Su, W.; Huang, M.; He, D. What explains the variation in dam impacts on riverine macroinvertebrates? A global quantitative synthesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 124028. [Google Scholar]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stati. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Calcagno, V.; de Mazancourt, C. glmulti: An R package for easy automated model selection with (generalized) linear models. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.J. Study on Soil Microorganism and Soil Enzyme Activity Along a Chronosequence of Eucalyptus plantation. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Certini, G. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: A review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, C.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Han, C.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, B. Competitive interaction with keystone taxa induced negative priming under biochar amendments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.G.; Chen, Z.X.; Zhang, J.T. Variations and controls of soil microbial necromass carbon in grasslands along aridity gradients. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111188. [Google Scholar]
- González-pérez, J.A.; González-Vila, F.J.; Almendros, G.; Knicker, H. The effect of fire on soil organic matter: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.C.; DeLuca, T.H.; Newman, G.S.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Boyle, S.I. Post-fire vegetative dynamics as drives of microbial community structure and function in forest soil. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 220, 166–184. [Google Scholar]
- Raison, R.J. Modification of the soil environment by vegetation fires, with particular reference to nitrogen transformations: A review. Plant Soil 1979, 51, 73–108. [Google Scholar]
- Neary, D.G.; Klopatek, C.C.; DeBano, L.F.; Ffolliott, P.F. Fire effects on belowground sustainability: A review and synthesis. For. Ecol. Manag. 1999, 122, 51–71. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; He, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, T.; et al. Contrasting pathways of carbon sequestration in paddy and upland soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Paula, R.R.; Bouillet, J.P.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Trivelin, P.C.O.; Balieiro, F.C.; Nouvellon, Y.; Oliveira, J.C.; Júnior, J.C.D.; Bordron, B.; Laclau, J.P. Nitrogen fixation rate of Acacia mangium wild at mid rotation in Brazil is higher in mixed plantations with Eucalyptus grandis hill ex maiden than in monocultures. Ann. Forest Sci. 2018, 75, 14. [Google Scholar]
- So, H.B.; Grabski, A.; Desborough, P. The impact of 14 years of conventional and no-till cultivation on the physical properties and crop yields of a loam soil at Grafton NSW, Australia. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Blagodatskaya, E.V.; Blagodatsky, S.A.; Anderson, T.H.; Kuzyakov, Y. Priming effects in Chernozem induced by glucose and N in relation to microbial growth strategies. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 37, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Demoling, F.; Figueroa, D.; Bååth, E. Comparison of factors limiting bacterial growth in different soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2485–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Cizungu, L.; Staelens, J.; Huygens, D.; Walangululu, J.; Muhindo, D.; Van Cleemput, O.; Boeckx, P. Litterfall and leaf litter decomposition in a central African tropical mountain forest and Eucalyptus plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 326, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Rottstock, T.; Joshi, J.; Kummer, V.; Fischer, M. Higher plant diversity promotes higher diversity of fungal pathogens, while it decreases pathogen infection per plant. Ecology 2014, 95, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Wardle, D.A.; Jonsson, M.; Bansal, S.; Bardgett, R.D.; Gundale, M.J.; Metcalfe, D.B. Linking vegetation change, carbon sequestration and biodiversity: Insights from island ecosystems in a long term natural experiment. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.D.; Pan, P.; Xiao, S.H.; Ouyang, X.Z. Influence of Eucalyptus plantation on soil organic carbon and its fractions in severely degraded soil in Leizhou Peninsula, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombao, A.; Barreiro, A.; Carballas, T.; Fontúrbel, M.T.; Martín, A.; Vega, J.A.; Fernández, C.; Díaz-Raviña, M. Changes in soil properties after a wildfire in Fragas do Eume Natural Park (Galicia, NW Spain). CATENA 2015, 135, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, F.C.C.; Ferreira, G.W.D.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Araújo, E.F.; Soares, E.M.B.; Silva, I.R. Eucalypt harvest residue management influences microbial community structure and soil organic matter fractions in an afforested grassland. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 205, 104787. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Rabbi, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Young, I.M.; Jones, A.R.; Dennis, P.G.; Menzies, N.W.; Kopittke, P.M.; Dalal, R.C. Soil organic carbon is significantly associated with the pore geometry, microbial diversity and enzyme activity of the macro-aggregates under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146286. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wuertz, S. Bacteria and archaea on earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, R.T.; Yang, L.B.; Xu, N.; Zhong, H.X.; Wang, J.F.; Ni, H.W. Bacterial community functional diversity of Calamagrostis angustifolia wetland in Sanjiang Plain. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1479–1486. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Courty, P.E.; Buee, M.; Diedhiou, A.G.; Frey Klett, P.; Le Tacon, F.; Rineau, F.; Turpault, M.P.; Uroz, S.; Garbaye, J. The role of ectomycorrhizal communities in forest ecosystem processes: New perspectives and emerging concepts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 679–698. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y. Distribution and Accumulation of Microbial-Derived Organic Carbon in Soils: The Regulatory Mechanism of Minerals and Substrates; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences in Chinese: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, M. Effects of Management Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure on Eucalyptus Plantations. Land 2025, 14, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040692
Xue Y, Liu W, Feng Q, Zhang J, Wang L, Chen Z, Li X, Zhu M. Effects of Management Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure on Eucalyptus Plantations. Land. 2025; 14(4):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040692
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yuanyuan, Wei Liu, Qi Feng, Jutao Zhang, Lingge Wang, Zexia Chen, Xuejiao Li, and Meng Zhu. 2025. "Effects of Management Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure on Eucalyptus Plantations" Land 14, no. 4: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040692
APA StyleXue, Y., Liu, W., Feng, Q., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Chen, Z., Li, X., & Zhu, M. (2025). Effects of Management Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structure on Eucalyptus Plantations. Land, 14(4), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040692








