Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
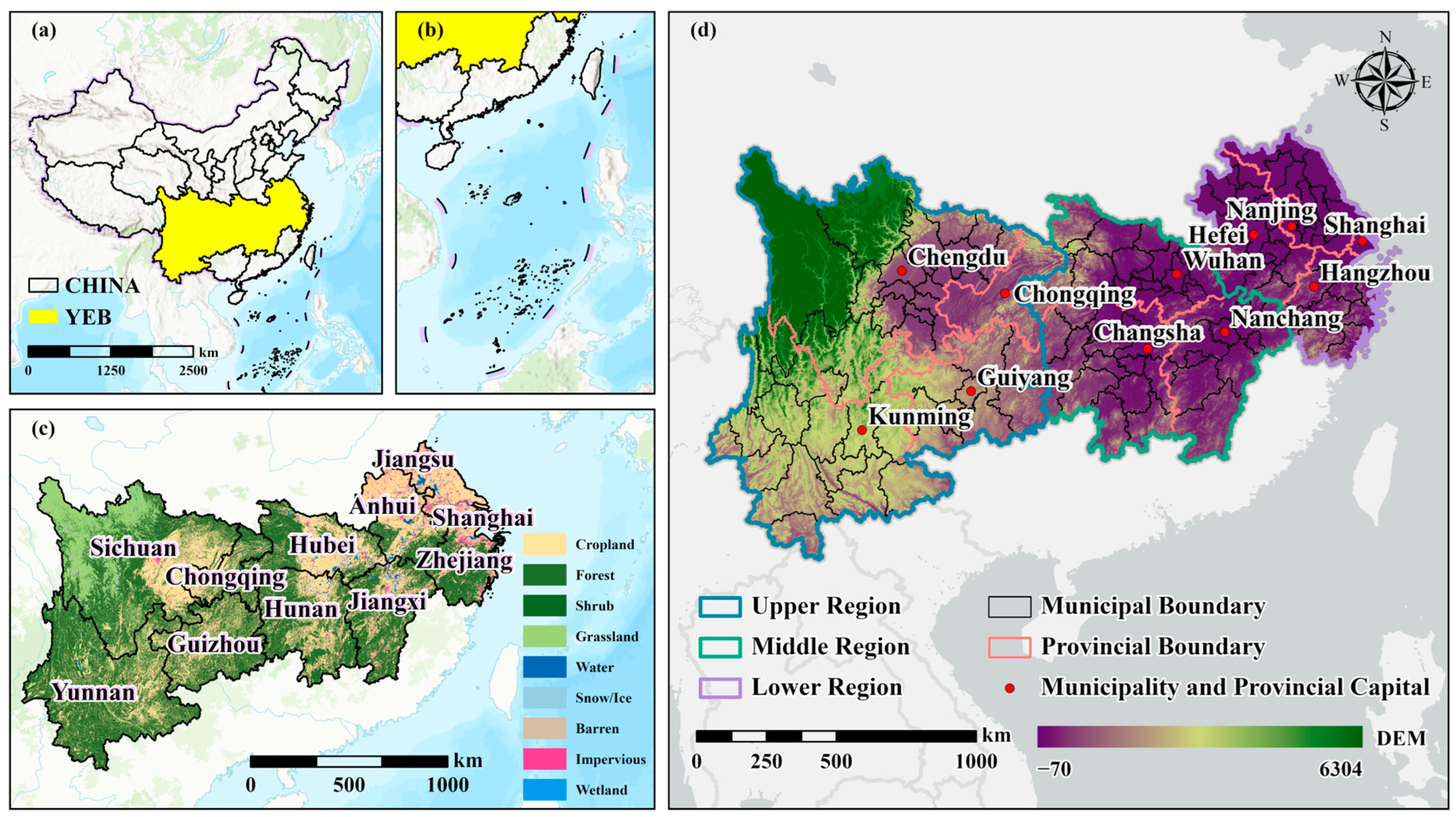
2.1. Study Area
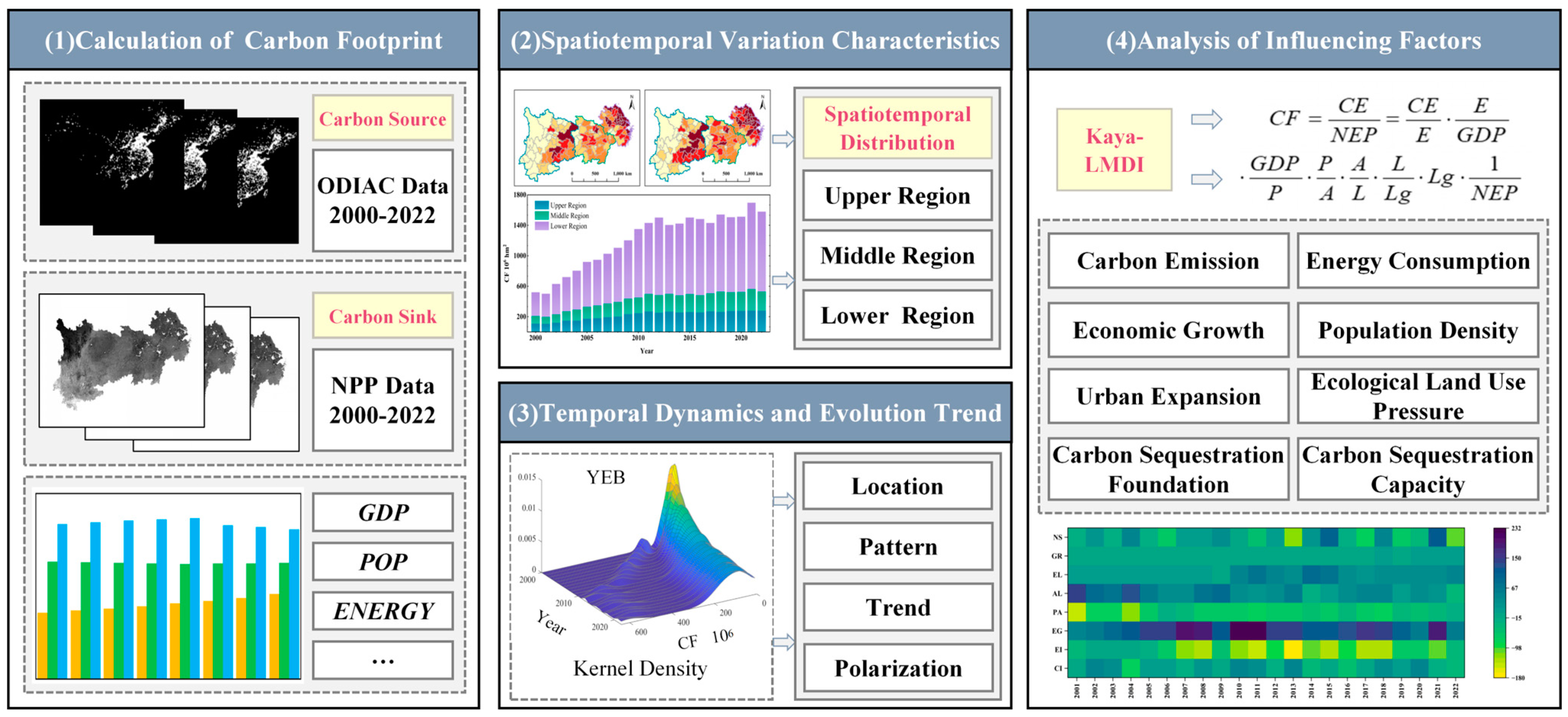
2.2. Conceptual Relationships and Research Framework
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Carbon Emission Estimation
2.3.2. Carbon Sink Estimation
- (1)
- NEP calculation of different land use types
- (2)
- Carbon Sequestration Estimation.
2.3.3. Carbon Footprint
2.3.4. Kernel Density Estimation
2.3.5. Kaya-LMDI Model
3. Results
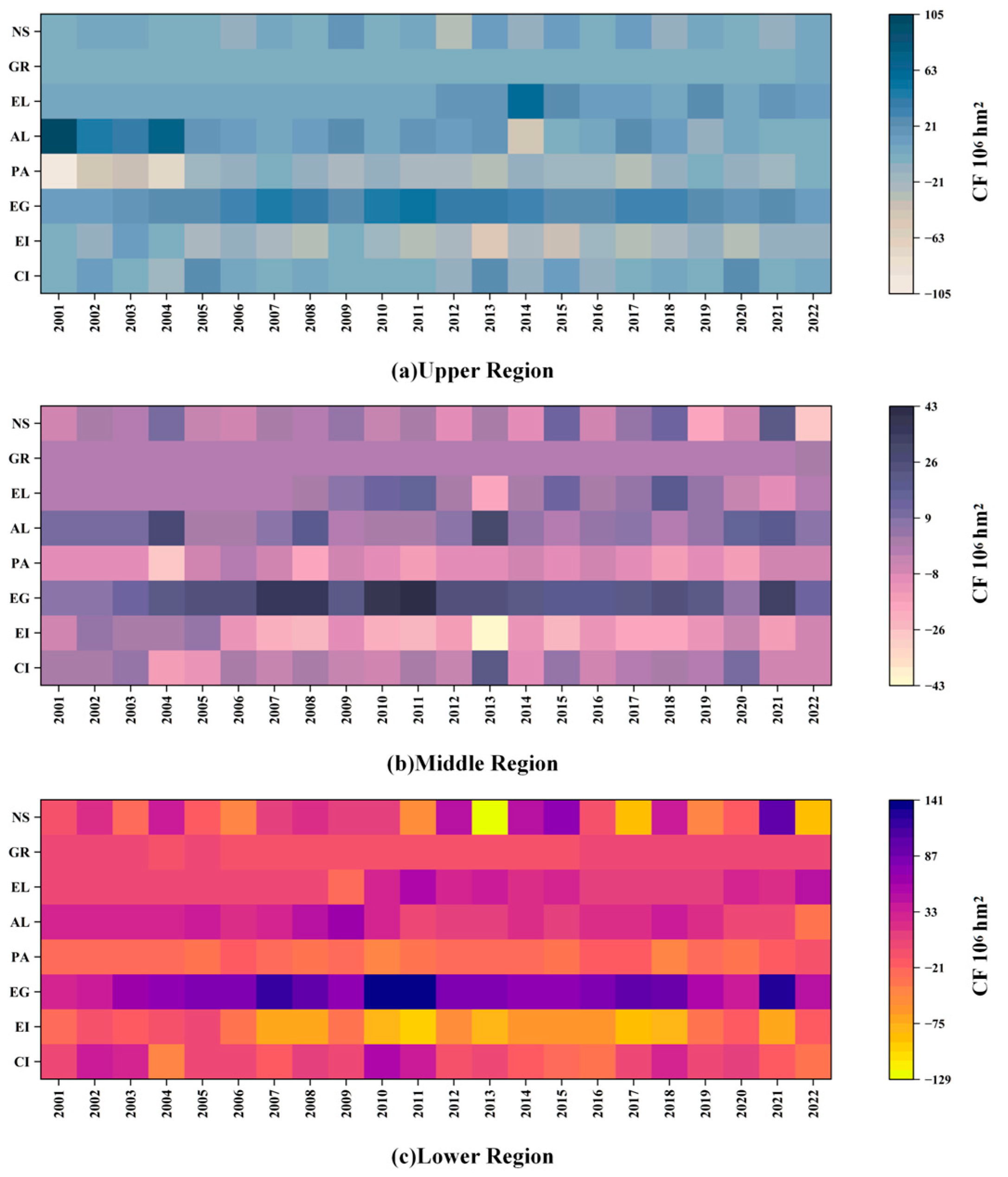
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics
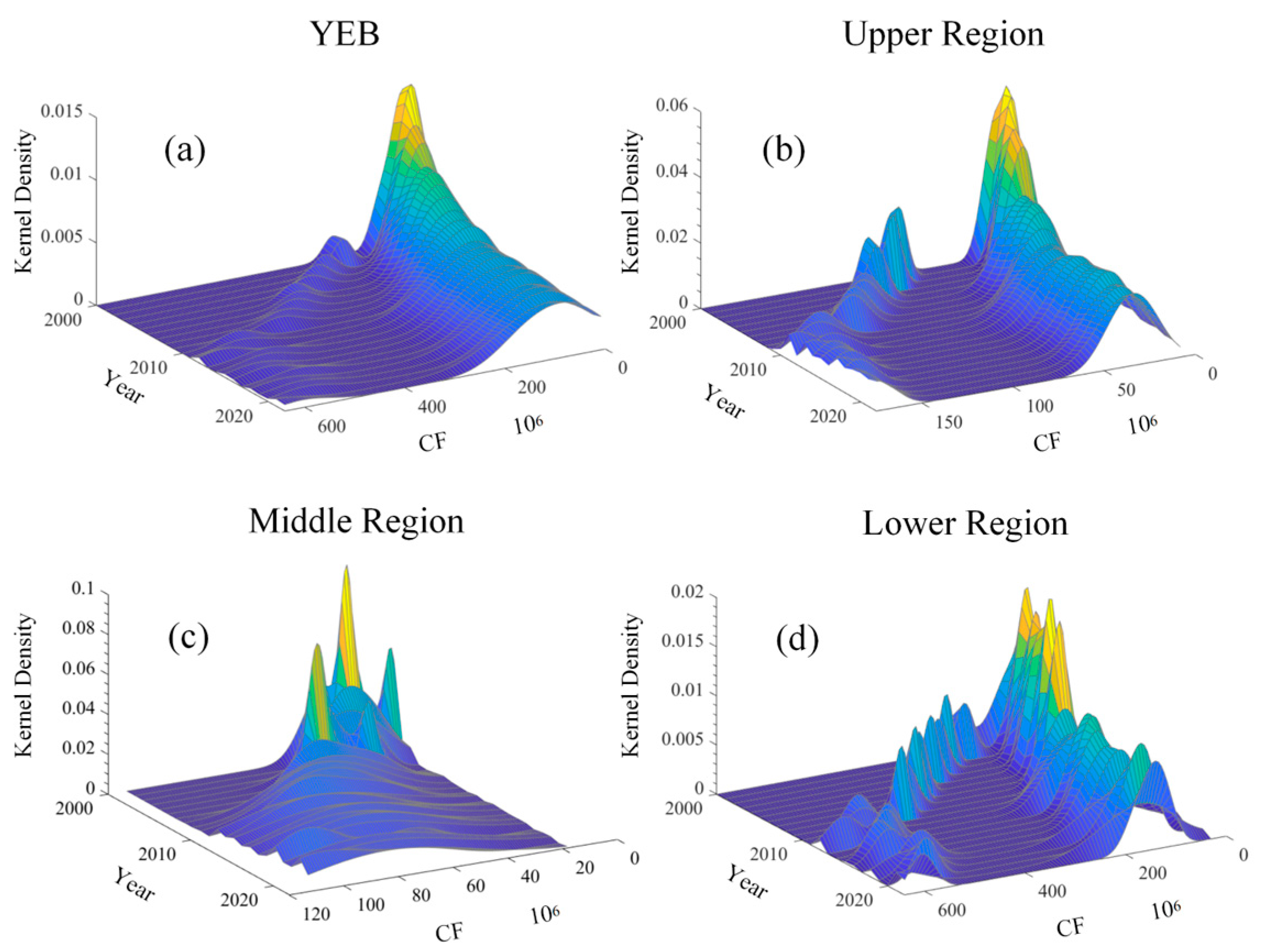
3.2. Temporal Dynamics and Evolution Trend
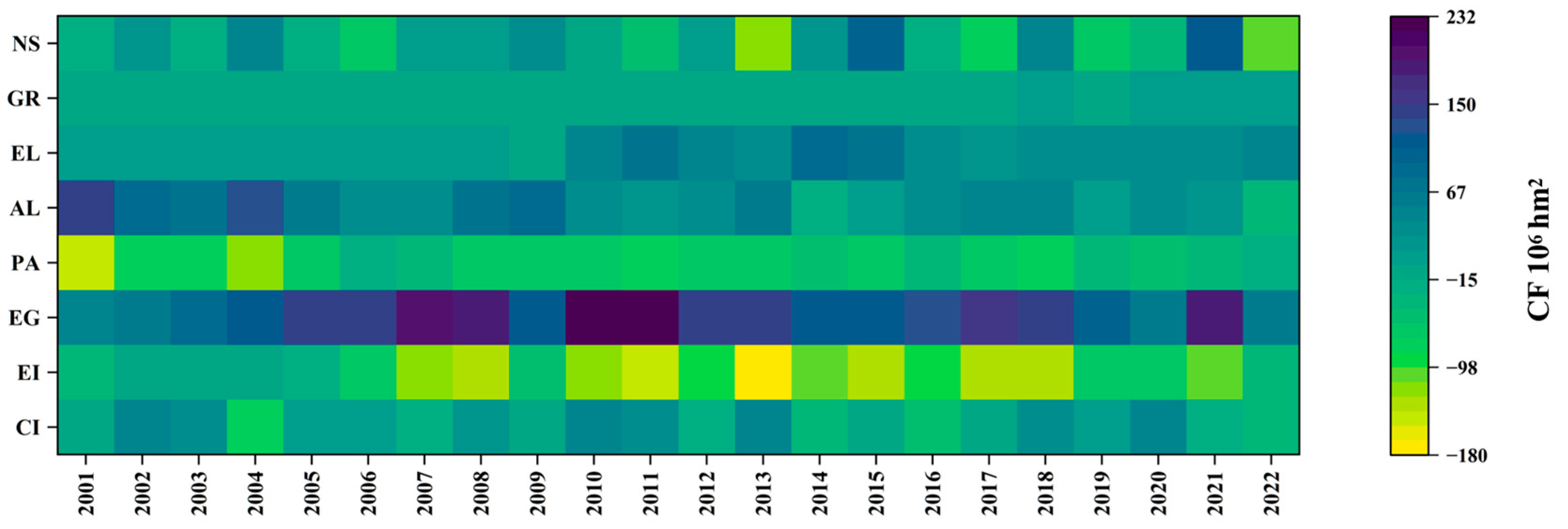
3.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Different Regions
4.2. Policy Recommendation
4.3. Contributions, Limitations, and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3269–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; He, Y.; Chen, F. Estimation of China’s Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Sink: Methods, Progress and Prospects. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 52, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zohner, C.M.; Reich, P.B.; Liang, J.; de Miguel, S.; Nabuurs, G.-J.; Renner, S.S.; van den Hoogen, J.; Araza, A.; Herold, M.; et al. Integrated Global Assessment of the Natural Forest Carbon Potential. Nature 2023, 624, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Jiang, Z. Environmental Kuznets Curve Prediction and Influencing Factors Analysis of Carbon Dioxide in China. Manag. World 2009, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.; Tulloch, A.I.T.; Radford, J.Q.; Williams, B.A.; Reside, A.E.; Macdonald, S.L.; Mayfield, H.J.; Maron, M.; Possingham, H.P.; Vine, S.J.; et al. Impact of 2019–2020 Mega-Fires on Australian Fauna Habitat. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, D.S.; Broadman, E. Revisiting the Holocene Global Temperature Conundrum. Nature 2023, 614, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswami, A.; Tong, K.; Fang, A.; Lal, R.M.; Nagpure, A.S.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, D.; Russell, A.G.; Shi, L.; et al. Urban Cross-Sector Actions for Carbon Mitigation with Local Health Co-Benefits in China. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, J.; Ottelin, J.; Ala-Mantila, S.; Wiedmann, T.; Clarke, J.; Junnila, S. Spatial Consumption-Based Carbon Footprint Assessments—A Review of Recent Developments in the Field. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, S. Inter-Provincial Flow and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Carbon Footprint in China and Its Policy Implication. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.; Minx, J. A Definition of Carbon Footprint. Ecol. Econ. Res. Trends 2008, 2, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Heijungs, R.; de Snoo, G. The Footprint Family: Comparison and Interaction of the Ecological, Energy, Carbon and Water Footprints. Rev. Metall.-Cah. Inf. Tech. 2013, 110, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J.B.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P.; Buonamici, R.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Life Cycle Assessment: Past, Present, and Future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E.G.; Peters, G.P. Carbon Footprint of Nations: A Global, Trade-Linked Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontief, W.W. Input-Output Economics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; ISBN 978-0-19-503525-4. [Google Scholar]
- Caglar, A.E.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Akin, C.S. Analysing the Ecological Footprint in EU-5 Countries under a Scenario of Carbon Neutrality: Evidence from Newly Developed Sharp and Smooth Structural Breaks in Unit Root Testing. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Lin, L.; Hao, Z.; Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Schlautman, M.A.; Post, G.C. Contribution of Land Cover Conversions to Connecticut (USA) Carbon Footprint. Geographies 2022, 2, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; He, N.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Ma, F.; Pan, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Plant Height as an Indicator for Alpine Carbon Sequestration and Ecosystem Response to Warming. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhao, C.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Chen, F.; Li, C.; Ran, C.; et al. Spring Photosynthetic Phenology of Chinese Vegetation in Response to Climate Change and Its Impact on Net Primary Productivity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A. Analyzing Three Zeros (Zero Poverty, Unemployment, and Carbon Emissions) in Asia and the Pacific Region: Assessment of Sustainable Development Goals through the STIRPAT Model. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 4782–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: Analytic Tools for Unpacking the Driving Forces of Environmental Impacts. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, J.A.; Shahbaz, M. Decomposition and Decoupling: A Case Study of Colombia’s Energy Consumption and Economic Growth. Energy 2024, 312, 133523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansino, J.M.; Sanchez-Braza, A.; Rodriguez-Arevalo, M.L. Driving Forces of Spain’s CO2 Emissions: A LMDI Decomposition Approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Y. County-Level CO2 Emissions and Sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Cheng, H. Exploring the Temporal and Spatial Effects of City Size on Regional Economic Integration: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, F.; Hu, Y. Carbon Emission Efficiency of Land Use in Urban Agglomerations of Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Based on Three-Stage SBM-DEA Model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chang, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Huang, M.; Yu, Y.; Guo, K.; Gu, F.; et al. Estimation of National and Provincial Carbon Emissions, Terrestrial Carbon Sinks and Their Relative Contribution to Emission Reductions during 1980~2020. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2024, 54, 2459–2478. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Yun, H.; Xu, W.; Hu, B.; He, M.; Mo, X.; Zhang, L. Is Urban Green Space a Carbon Sink or Source?—A Case Study of China Based on LCA Method. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 94, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Pappas, C.; Zscheischler, J.; Leuzinger, S. Modelling Carbon Sources and Sinks in Terrestrial Vegetation. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jia, P.; Feng, T.; Li, H.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, J. Uncovering the Spatiotemporal Impacts of Built Environment on Traffic Carbon Emissions Using Multi-Source Big Data. Land Use Policy 2023, 129, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Chevallier, F.; Ciais, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Rödenbeck, C.; Sardans, J.; Vicca, S.; Yang, H.; Sitch, S.; et al. Diagnosing Destabilization Risk in Global Land Carbon Sinks. Nature 2023, 615, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Han, X. Unfolding the Effectiveness of Ecological Restoration Programs in Enhancing Vegetation Carbon Sinks across Different Climate Zones in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S.; Andres, R.J. The Open-Source Data Inventory for Anthropogenic CO2, Version 2016 (ODIAC2016): A Global Monthly Fossil Fuel CO2 Gridded Emissions Data Product for Tracer Transport Simulations and Surface Flux Inversions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A Very High-Resolution (1 km × 1 km) Global Fossil Fuel CO2 Emission Inventory Derived Using a Point Source Database and Satellite Observations of Nighttime Lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Xue, Y.; Yuan, T.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, X. Retrieval Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions from OCO-2 and Comparison with Gridded Emission Inventories. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligent Urban Ecosystem Management System. Available online: https://www.iuems.com/eco/index.html (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning; Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences. The Technical Guideline on Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) (1.0 Version). Available online: http://www.caep.org.cn/zclm/sthjyjjhszx/zxdt_21932/202101/W020210122402035975103.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Song, M.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, E. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influence Mechanism of the Carbon Footprint of Energy Consumption at County Level in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, W.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Song, M. Driving Factors of Global Carbon Footprint Pressure: Based on Vegetation Carbon Sequestration. Appl. Energy 2020, 267, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P. A Study on the Spatio-Temporal Disparities and Evolution of Distribution of Chinese-Style Modernization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Shen, Z.; Song, M.; Vardanyan, M. The Role of Green Financing in Facilitating Renewable Energy Transition in China: Perspectives from Energy Governance, Environmental Regulation, and Market Reforms. Energy Econ. 2023, 120, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Cheng, J.; Dong, H. How Has China’s Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy Influenced Its CO2 Abatement Costs? Analysis from the Perspective of the Shadow Price. Energy Econ. 2022, 115, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y. Impact of Carbon Dioxide Emission Control on GNP Growth: Interpretation of Proposed Scenarios. In Proceedings of the Response Strategies Working Group, Paris, France, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Jiao, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, W. The impact mechanism of spatial agglomeration of construction land resources on the synergistic reduction of pollutants and CO2. ACTA Geogr. Sin. 2024, 79, 688–711. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Mo, J.; Sun, Y.; Yan, H. Study on the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of forest NEP in Southwest China. ACTA Ecol. Sin. 2025, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Meng, J. Quantifying the spatial pattern for the importance of natural resource ecosystem services in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P. Research on the Spatio-temporal Patterns and Interactive Effects of Manufacturing Carbon Emissions and IFDI in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2025, 34, 252–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ru, S.; Xue, F. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Dynamic Evolution of Ecological Resilience in The Yellow River Basin: Based on the Analysis of Emergy Ecological Footprint Model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Jian, Z.; Sun, Y.; Pan, F.; Han, H.; Liu, Q.; Mei, Y. Ecological Sustainability and High-Quality Development of the Yellow River Delta in China Based on the Improved Ecological Footprint Model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S. Research on the Factors Influencing CO2 Emission Reduction in High-Energy-Consumption Industries under Carbon Peak. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Geographical Regions | Area | Cropland | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | Wetland |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | SH | 0.116 | 0.149 | 0.116 | 0.015 | 0.059 |
| JS | 0.082 | 0.14 | 0.082 | 0.094 | 0.069 | |
| ZJ | 0.151 | 0.158 | 0.151 | 0.112 | 0.052 | |
| AH | 0.112 | 0.163 | 0.112 | 0.129 | 0.045 | |
| JX | 0.085 | 0.112 | 0.085 | 0.118 | 0.065 | |
| Central and South | HB | 0.13 | 0.162 | 0.13 | 0.113 | 0.038 |
| HN | 0.07 | 0.097 | 0.07 | 0.084 | 0.084 | |
| Southwest | CQ | 0.183 | 0.176 | 0.183 | 0.17 | 0.082 |
| SC | 0.203 | 0.255 | 0.203 | 0.287 | 0.146 | |
| YN | 0.163 | 0.226 | 0.163 | 0.136 | 0.08 | |
| GZ | 0.008 | 0.049 | 0.008 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Period | CI | EI | EG | PA | AL | EL | GR | NS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2005 | −188.22% | 198.97% | 380.47% | −132.22% | 102.33% | −1.76% | 1.76% | 138.67% |
| 2005–2010 | −95.35% | −793.51% | 1436.46% | −369.27% | 227.75% | 193.52% | −7.05% | −92.53% |
| 2010–2015 | 615.81% | −202.79% | −620.76% | 177.05% | 45.81% | −224.77% | −7.01% | 716.66% |
| 2015–2022 | 1761.52% | −873.07% | 820.10% | −2547.38% | 2995.14% | −834.53% | −38.81% | −582.97% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Land 2025, 14, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030641
Shao Z, Li X, Chen J, Geng Y, Zhai X, Zhang K, Zhang J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Land. 2025; 14(3):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030641
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Zhehan, Xiaoshun Li, Jiangquan Chen, Yiwei Geng, Xuanyu Zhai, Ke Zhang, and Jie Zhang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt" Land 14, no. 3: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030641
APA StyleShao, Z., Li, X., Chen, J., Geng, Y., Zhai, X., Zhang, K., & Zhang, J. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Land, 14(3), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030641





