Spatial Heterogeneity of the Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics and Vitality Realization of Suburban Areas in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Chinese Cities and the Division of Suburban
2.2. Indicators of the Natural and Socio-Economic Characteristics
2.3. Quantitative Assessment of Vitality of Suburban
2.4. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis
2.5. Correlation and Regression Analysis
2.6. Normalization and Visualization
2.7. Data Sources and Preprocessing
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics of Suburban Areas
3.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vitality in Suburban
3.3. Impacts of Natural and Socio-Economic Characteristics on Suburban Vitality
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Heterogeneity of Suburban Vitality
4.2. Pathways to Enhance Suburban Vitality
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, D.; Lin, T.; Tang, L. Rapid urbanisation, ecological effects and sustainable city construction in xiamen. Int. J. Sust. Dev. World 2010, 17, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Gueneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, K. Clean energy, population density, urbanization and environmental pollution nexus: Evidence from bangladesh. Renew. Energ. 2021, 172, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chakraborty, T.C.; Li, J.; Li, D.; He, C.; Sarangi, C.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Leung, L.R. Urbanization impact on regional climate and extreme weather: Current understanding, uncertainties, and future research directions (vol 39, pg 819, 2022). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueneralp, B.; Seto, K.C.; Ramachandran, M. Evidence of urban land teleconnections and impacts on hinterlands. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2013, 5, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, K. Sustainable regions: Governance, innovation and scale. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2004, 12, 871–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.; Habersetzer, A.; Meili, R. Rural-urban linkages and sustainable regional development: The role of entrepreneurs in linking peripheries and centers. Sustainability 2016, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Reid, B.J.; Meharg, A.A.; Banwart, S.A.; Fu, B. Optimizing peri-urban ecosystems ( pure ) to re-couple urban-rural symbiosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Gibson, V.; Cui, S.; Yu, C.; Chen, S.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, Y. Managing urban nutrient biogeochemistry for sustainable urbanization. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Cai, J.; Geng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zheng, Y. Incorporating suburban cropland into urban green infrastructure: A perspective of nature-based solutions in china. Nat.-Based Solut. 2024, 5, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, L.; Mcphearson, T. Nature—based solutions for global climate adaptation. Nature 2022, 606, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, R. Urban ecological infrastructure: An integrated network for ecosystem services and sustainable urban systems. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 163, S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, Z.J.; Mcphearson, T.; Matsler, A.M.; Groffman, P.; Pickett, S.T. A What is green infrastructure? A study of definitions in us city planning. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, M.O.; Rau, G.C.; Ekstrom, M.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Bates, A.J. Global climate-driven trade-offs between the water retention and cooling benefits of urban greening. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, A.; Mudu, P. How can vegetation protect us from air pollution? A critical review on green spaces‘ mitigation abilities for air-borne particles from a public health perspective-with implications for urban planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bux, Q.; Anderson, P.; O’Farrell, P.J. Understanding the local biodiversity and open space strategies in two south african cities. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lin, T.; Hamm NA, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, T.; Geng, H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Quantitative evaluation of urban green exposure and its impact on human health: A case study on the 3-30-300 green space rule. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ye, X.; Ren, F.; Du, Q. Check-in behaviour and spatio-temporal vibrancy: An exploratory analysis in shenzhen, china. Cities 2018, 77, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z. Deep exploration of street view features for identifying urban vitality: A case study of qingdao city. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2023, 123, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Lin, T.; Han, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, M.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y. Urban green vitalization and its impact on green exposure equity: A case study of shanghai city, china. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Wu, Q.; Yan, S.; Bilal, K.; Junaid, M.B.; Hatamleh, W.A. Multifunctional Role of Land-Use Planning in Peri-Urban and Urban Agricultural Drylands: The Mediating Effect of Urbanization Level. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2025, 151, 04024067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Assessing accessibility to peri-urban parks considering supply, demand, and traffic conditions. Landsc. Urban Plan 2025, 257, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ye, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Kuang, L. Multifunctional Evolution Response Mechanisms to Urbanization Processes on Peri-Urban Cultivated Land, Nanchang City, China. Land 2025, 14, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M. The Transformation of Peri-Urban Agriculture and Its Implications for Urban–Rural Integration Under the Influence of Digital Technology. Land 2025, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Dai, Q.; Su, H. Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: Achievements, challenges and reflections. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Realizing china’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Le Yu Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Peng, D.; Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Gong, P. China’s ongoing rural to urban transformation benefits the population but is not evenly spread. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, R. Socio-economic-natural complex ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1984, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, Z. Association between Land Use and Urban Vitality in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area: A Multiscale Study. Land 2024, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Long, Y. Urban vitality area identification and pattern analysis from the perspective of time and space fusion. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ma, S.; Xiang, W.; Kan, C.; Wu, K.; Long, Y. Classification of shrinking cities in China using Baidu big data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Shen, R.; Chen, Q.; Duan, M.; Zhao, X. Site Selection for Elderly Care Facilities in the Context of Big Data: A Case Study of Xi’an, China. Sustianability 2025, 17, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, M.; Lin, T.; Zhang, J.; Jones, L.; Yao, X.; Geng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cao, X.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity of vegetation phenology caused by urbanization in china based on remote sensing. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liwenjun Li, P.; Xiao, C. Relief degree of land surface and its geographical meanings in the qinghai-tibet plateau, china. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar]


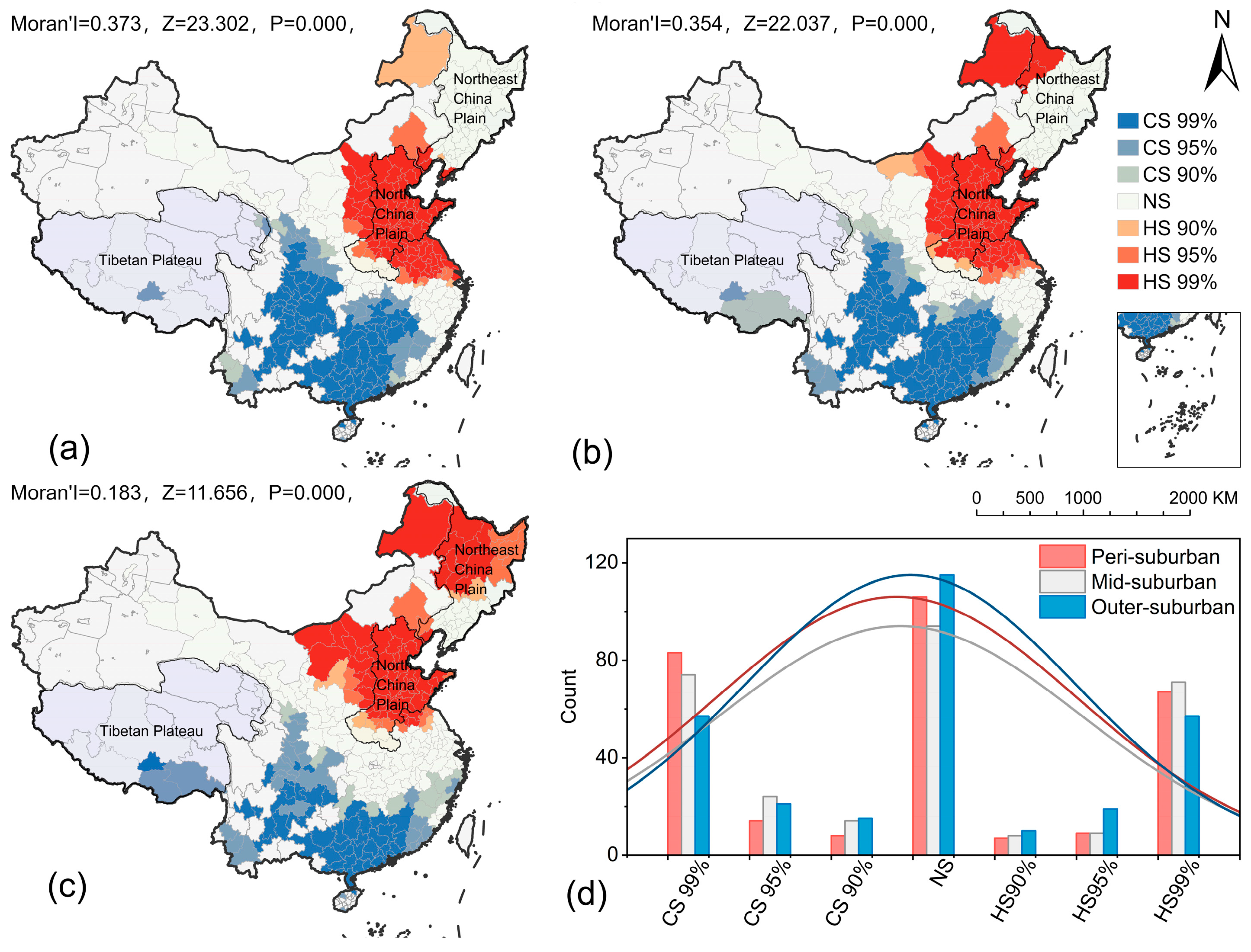
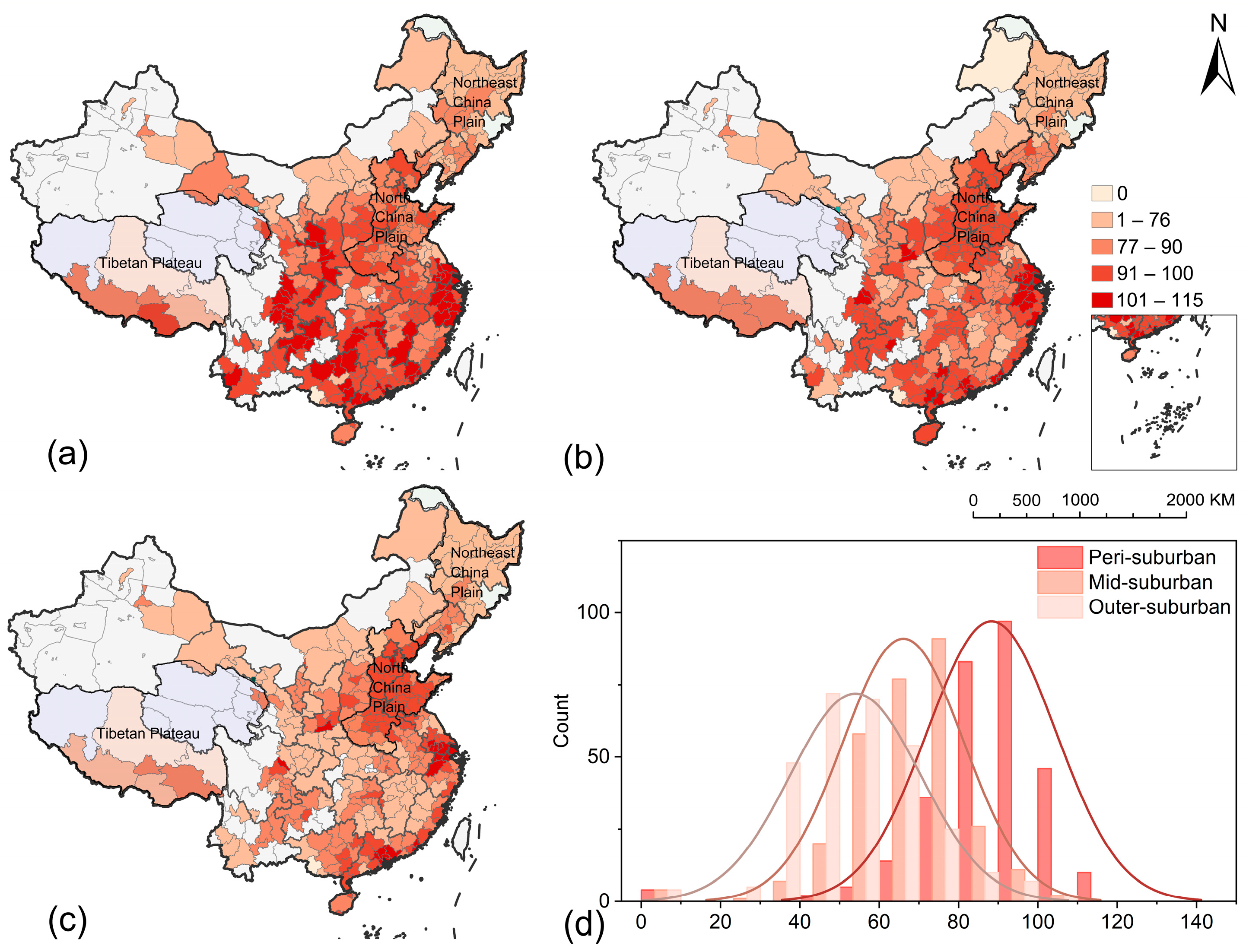
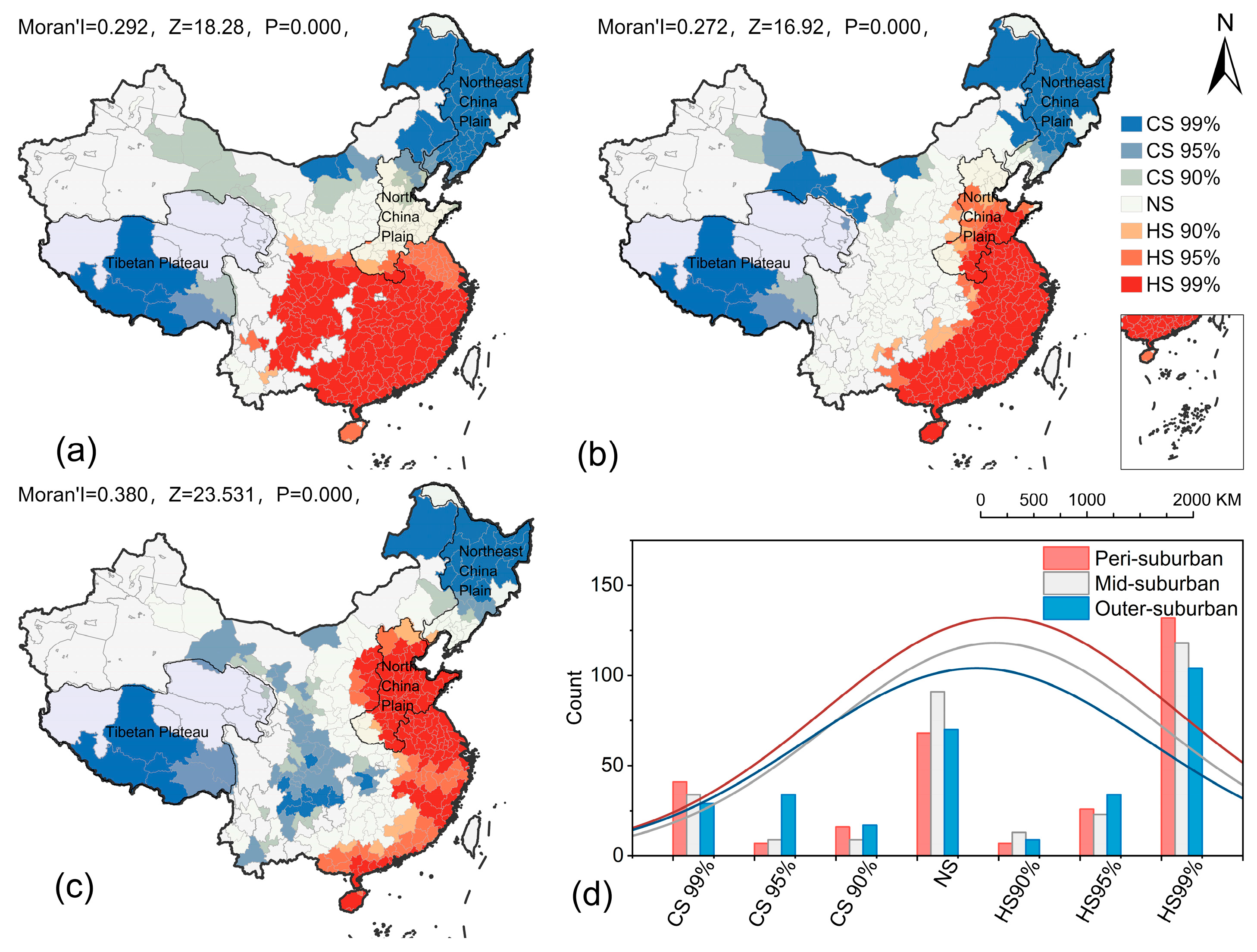

| ID | Natural Characteristics | Units | ID | Socio-Economic Characteristics | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suburban Area | km2 | 1 | Total GDP | Million Yuan |
| 2 | Cropland Area | km2 | 2 | GDP per square kilometer | Million Yuan per square kilometer |
| 3 | Greenland Area | km2 | 3 | Total population | Person |
| 4 | Water Area | km2 | 4 | Population per square kilometer | Person per square kilometer |
| 5 | Built-up Area | km2 | 5 | Road length | km |
| 6 | Other Land Use Area | km2 | 6 | Road density | km/km2 |
| 7 | Cropland Rate | % | 7 | Number of POIs | Points |
| 8 | Greenland Rate | % | 8 | POI density | Points per square kilometer |
| 9 | Water Rate | % | -- | ||
| 10 | Built-up Rate | % | -- | ||
| 11 | Other Land Use Rate | % | -- | ||
| 12 | Mean Elevation | m | -- | ||
| 13 | Relief Amplitude | ° | -- |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workday | 10 January 2024; 11 January 2024; 12 January 2024; 15 January 2024; 16 January 2024 | 10 April 2023; 11 April 2023; 12 April 2023; 15 April 2023; 16 April 2023 | 10 July 2023; 11 July 2023; 12 July 2023; 15 July 2023; 16 July 2023 | 10 October 2023; 11 October 2023; 12 October 2023; 15 October 2023; 16 October 2023 |
| Weekend | 13 January 2024; 14 January 2024 | 13 April 2023; 14 April 2023 | 13 July 2023 14 July 2023 | 13 October 2023; 14 October 2023 |
| Data Name | Data Type | Time | Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| City Boundaries | Vector | 2020 | -- | https://www.webmap.cn (accessed on 10 January 2024, below) |
| Built-up area Boundary | Vector | 2020 | -- | Chen et al., 2023 [35] |
| Land Use Cover | Raster | 2020 | 10 m | https://viewer.esa-worldcover.org/worldcover/ |
| Elevation | Raster | 2020 | 500 m | https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=123 |
| Relief Amplitude | Raster | 2020 | 500 m | Feng et al., 2020 [36] |
| GDP | Raster | 2020 | 1 km | http://geodata.nnu.edu.cn |
| Population | Raster | 2020 | 1 km | https://www.worldpop.org/ |
| Road Network | Vector | 2020 | -- | https://www.openstreetmap.org/ |
| Point of Interest | Vector | 2020 | -- | https://www.amap.com |
| Mobile Population Location | Vector | 2023 | 500 m | https://huiyan.baidu.com/products/platform |
| Natural and Socio-Economic Characteristics | Peri-Suburban | Mid-Suburban | Outer-Suburban | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’I | Z | p | Moran’I | Z | p | Moran’I | Z | p | |
| Cropland Area | 0.550 | 34.486 | 0.000 | 0.588 | 36.506 | 0.000 | 0.495 | 30.685 | 0.000 |
| Greenland Area | 0.068 | 4.614 | 0.000 | 0.088 | 5.992 | 0.000 | 0.114 | 7.831 | 0.000 |
| Water Area | 0.259 | 16.383 | 0.000 | 0.306 | 19.988 | 0.000 | 0.438 | 27.614 | 0.000 |
| Built-up Area | 0.379 | 23.792 | 0.000 | 0.434 | 27.158 | 0.000 | 0.506 | 31.422 | 0.000 |
| Other Land Use Area | 0.175 | 11.101 | 0.000 | 0.172 | 11.088 | 0.000 | 0.124 | 8.386 | 0.000 |
| Cropland Rate | 0.716 | 44.086 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 41.048 | 0.000 | 0.674 | 41.503 | 0.000 |
| Greenspace Rate | 0.517 | 31.883 | 0.000 | 0.540 | 33.278 | 0.000 | 0.574 | 35.394 | 0.000 |
| Water Rate | 0.410 | 25.435 | 0.000 | 0.450 | 27.973 | 0.000 | 0.540 | 33.951 | 0.000 |
| Built-up Rate | 0.215 | 13.443 | 0.000 | 0.382 | 23.721 | 0.000 | 0.487 | 30.320 | 0.000 |
| Other Land Use Rate | 0.228 | 14.486 | 0.000 | 0.180 | 11.617 | 0.000 | 0.176 | 11.354 | 0.000 |
| Mean Elevation | 0.357 | 22.735 | 0.000 | 0.358 | 22.815 | 0.000 | 0.362 | 23.040 | 0.000 |
| Relief Amplitude | 0.283 | 17.971 | 0.000 | 0.303 | 19.175 | 0.000 | 0.343 | 21.576 | 0.000 |
| Total GDP | 0.249 | 16.030 | 0.000 | 0.341 | 22.244 | 0.000 | 0.334 | 22.134 | 0.000 |
| GDP per square kilometer | 0.362 | 22.982 | 0.000 | 0.385 | 26.519 | 0.000 | 0.410 | 28.116 | 0.000 |
| Total Population | 0.178 | 11.399 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 15.216 | 0.000 | 0.300 | 19.001 | 0.000 |
| Population per square kilometer | 0.501 | 31.015 | 0.000 | 0.479 | 30.081 | 0.000 | 0.498 | 31.833 | 0.000 |
| Road Length | 0.295 | 18.673 | 0.000 | 0.332 | 20.914 | 0.000 | 0.355 | 22.362 | 0.000 |
| Road Density | 0.313 | 19.503 | 0.000 | 0.361 | 22.613 | 0.000 | 0.475 | 30.072 | 0.000 |
| Number of POI | 0.275 | 17.550 | 0.000 | 0.365 | 23.671 | 0.000 | 0.354 | 23.087 | 0.000 |
| POI Density | 0.407 | 25.429 | 0.000 | 0.460 | 30.945 | 0.000 | 0.491 | 32.161 | 0.000 |
| Peri-Suburb | Mid-Suburb | Outer-Suburb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | Coef. | Coef. | |||
| Intercept | 68.168 | Intercept | 47.297 | Intercept | 39.397 |
| Built-up rate | 0.831 *** | Built-up rate | 1.8 *** | Built-up rate | 1.8 *** |
| Population per square kilometer | 0.089 *** | Population per square kilometer | 0.214 *** | -- | -- |
| POI density | 0.129 *** | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| R-square | 0.347 | R-square | 0.589 | R-square | 0.726 |
| Adj. R-square | 0.34 | Adj. R-square | 0.587 | Adj. R-square | 0.725 |
| RMSE | 11.07 | RMSE | 8.868 | RMSE | 8.204 |
| F | 51.401 | F | 208.841 | F | 772.574 |
| p | <0.001 | p | <0.001 | p | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.; Zeng, Z.; Geng, H.; Huang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Zheng, Y. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics and Vitality Realization of Suburban Areas in China. Land 2025, 14, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030593
Lin T, Zeng Z, Geng H, Huang Y, Cai J, Wang X, Cao X, Zheng Y. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics and Vitality Realization of Suburban Areas in China. Land. 2025; 14(3):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030593
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Tao, Zhiwei Zeng, Hongkai Geng, Yiyi Huang, Jiayu Cai, Xiaotong Wang, Xin Cao, and Yicheng Zheng. 2025. "Spatial Heterogeneity of the Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics and Vitality Realization of Suburban Areas in China" Land 14, no. 3: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030593
APA StyleLin, T., Zeng, Z., Geng, H., Huang, Y., Cai, J., Wang, X., Cao, X., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Spatial Heterogeneity of the Natural, Socio-Economic Characteristics and Vitality Realization of Suburban Areas in China. Land, 14(3), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030593







