Exploring the Spatially Heterogeneous Relationships Between Biodiversity Maintenance Function and Socio-Ecological Drivers in Liaoning Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
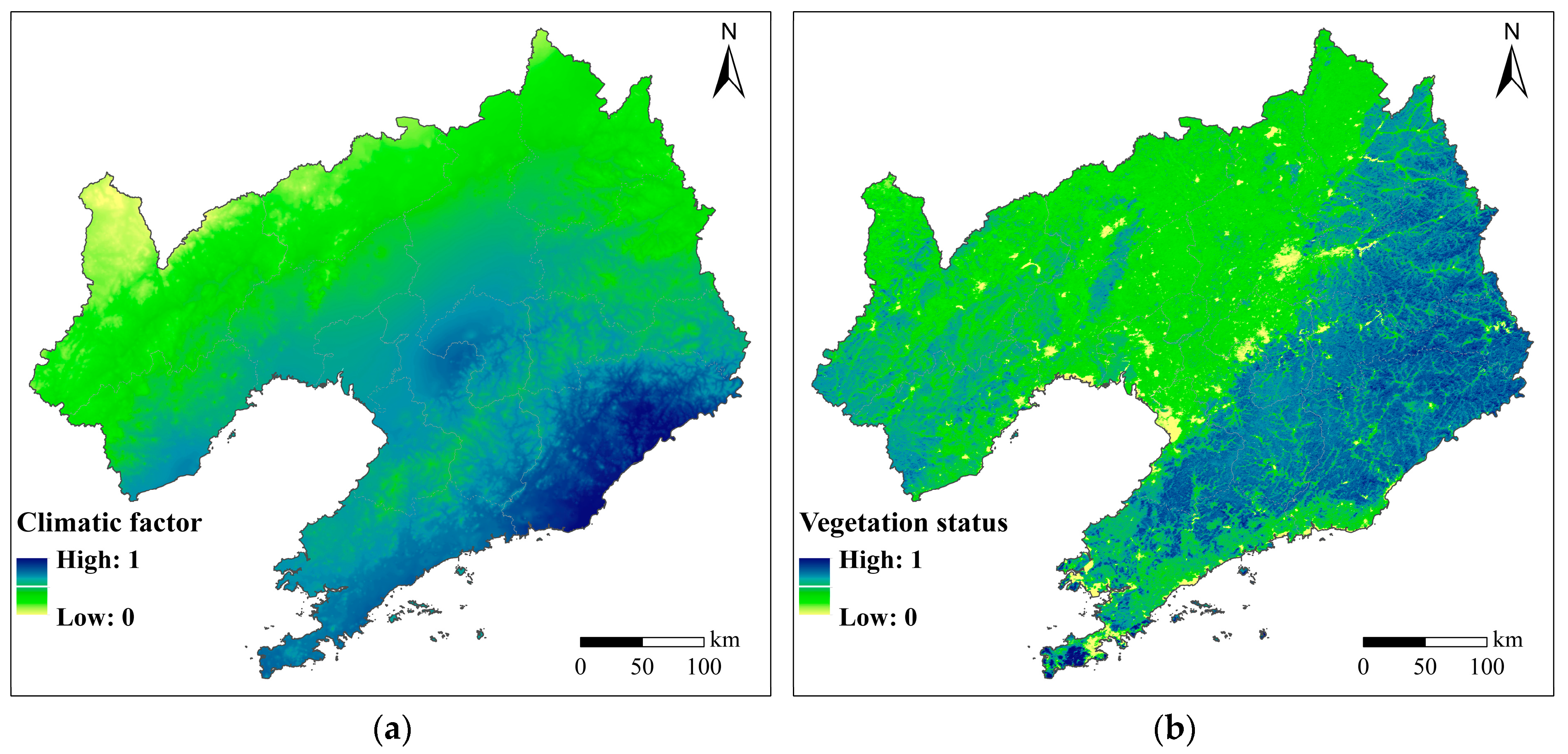
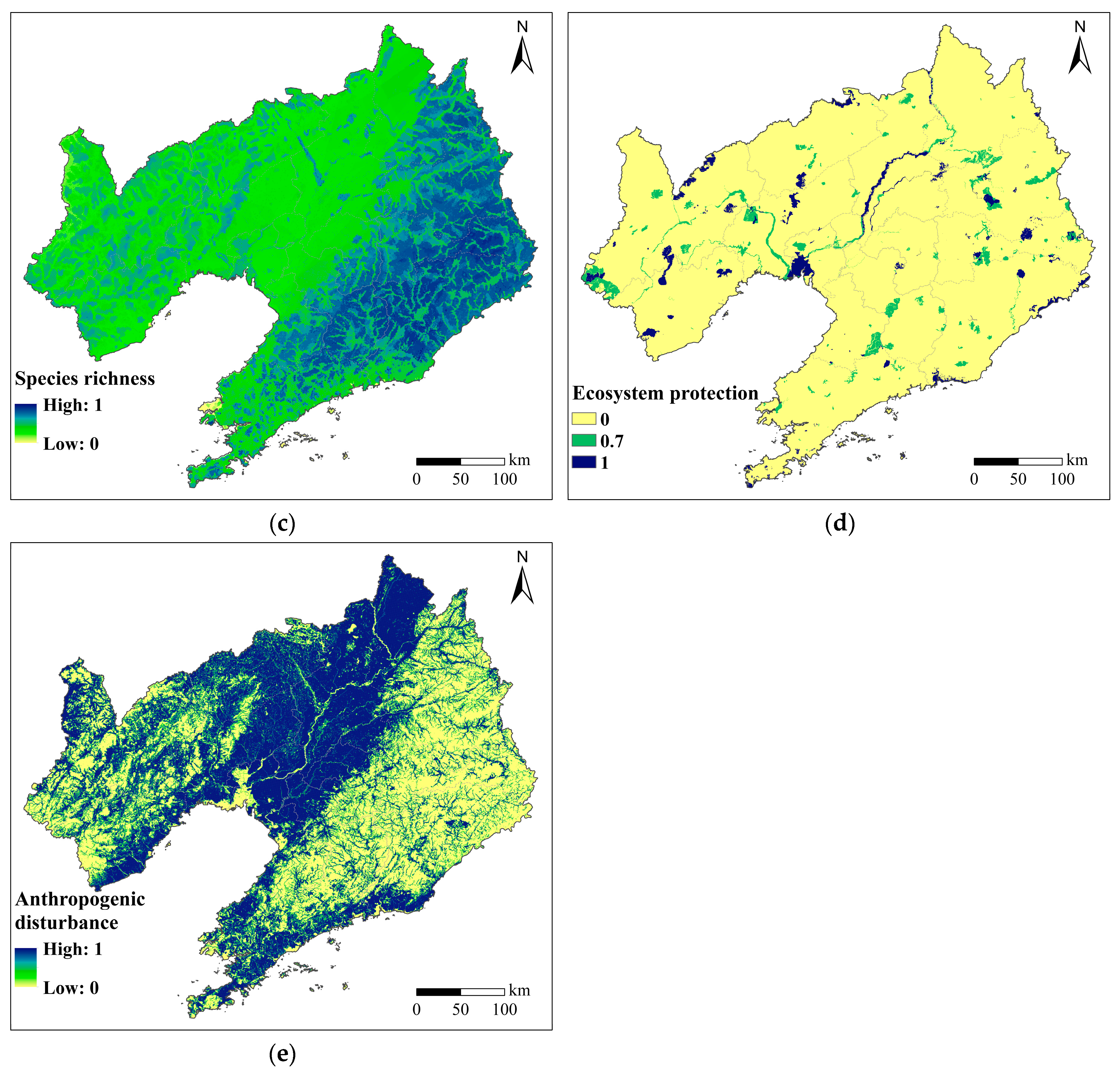
2.3. Assessment of BMF at the Regional Scale
2.3.1. Indicator System Construction
2.3.2. Calculations of Criteria Hierarchies
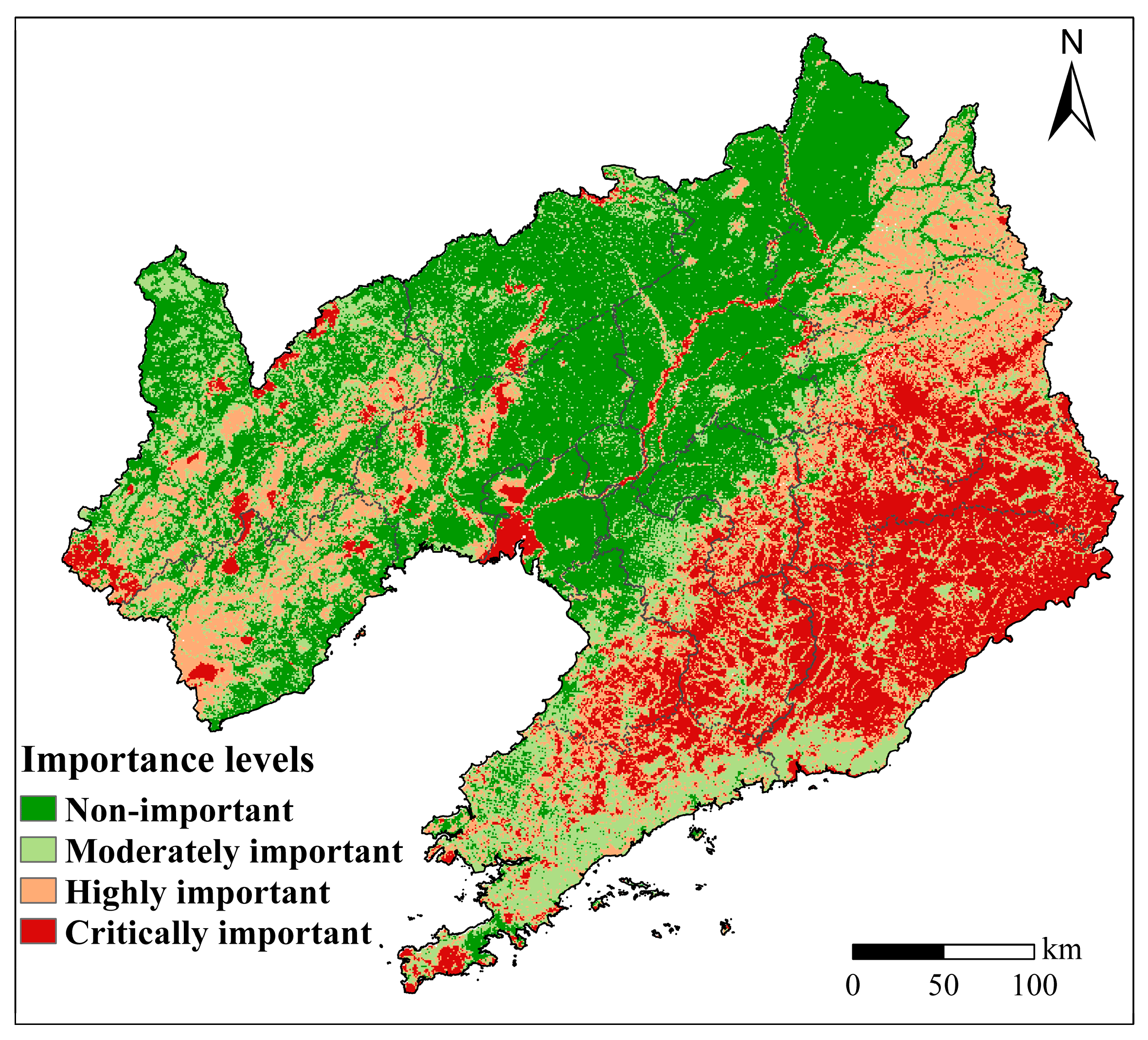
2.3.3. BMF Importance Index
2.4. Exploration of the Main Factors Influencing BMF
2.4.1. Selection of Influencing Factors
2.4.2. Geographical Detector
2.4.3. Multi-Scale Geographically Weighted Regression
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Characteristics of BMF in Liaoning Province
3.2. Effects of Socio-Ecological Factors on BMF
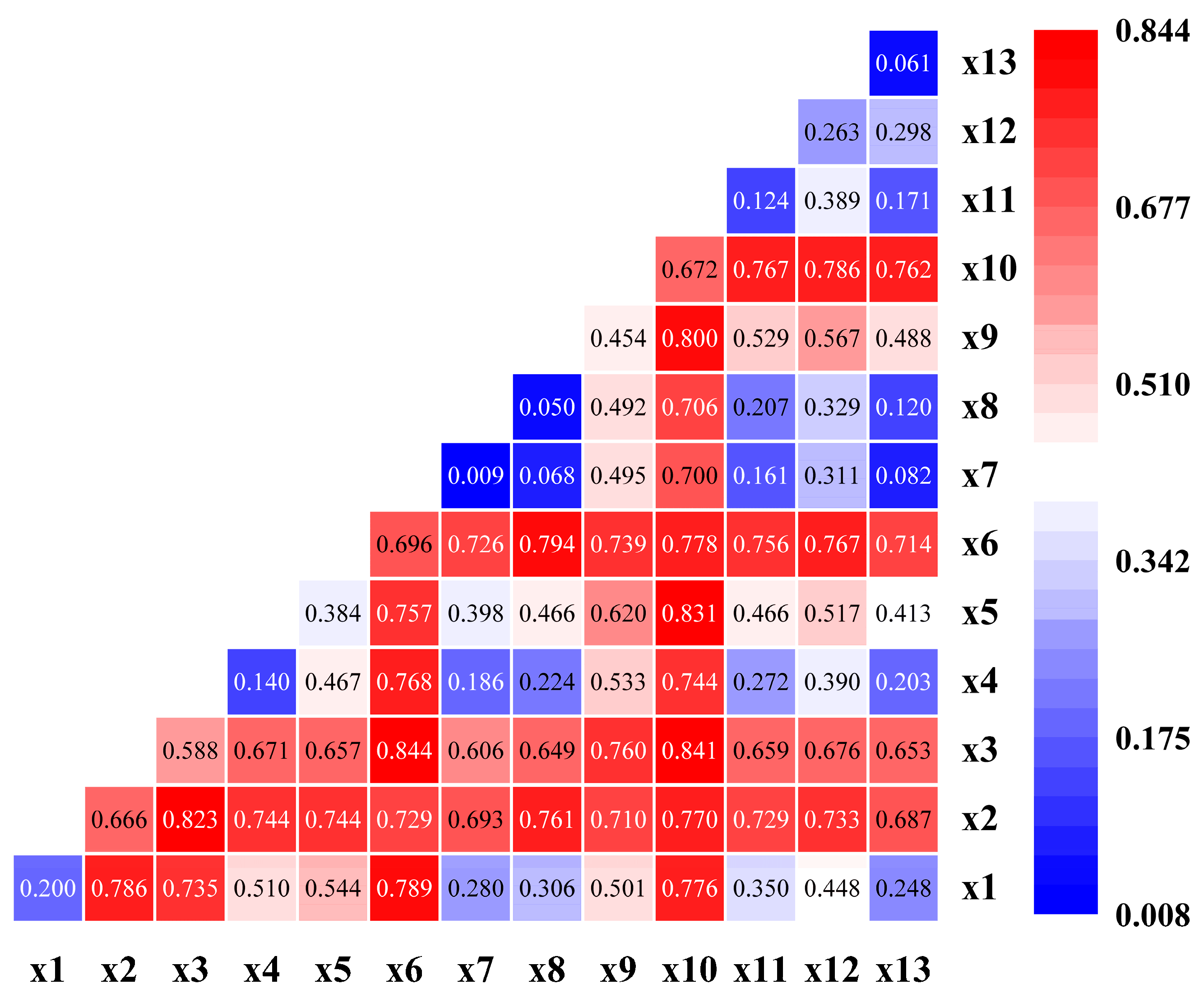
3.2.1. Spatial Autocorrelation Test
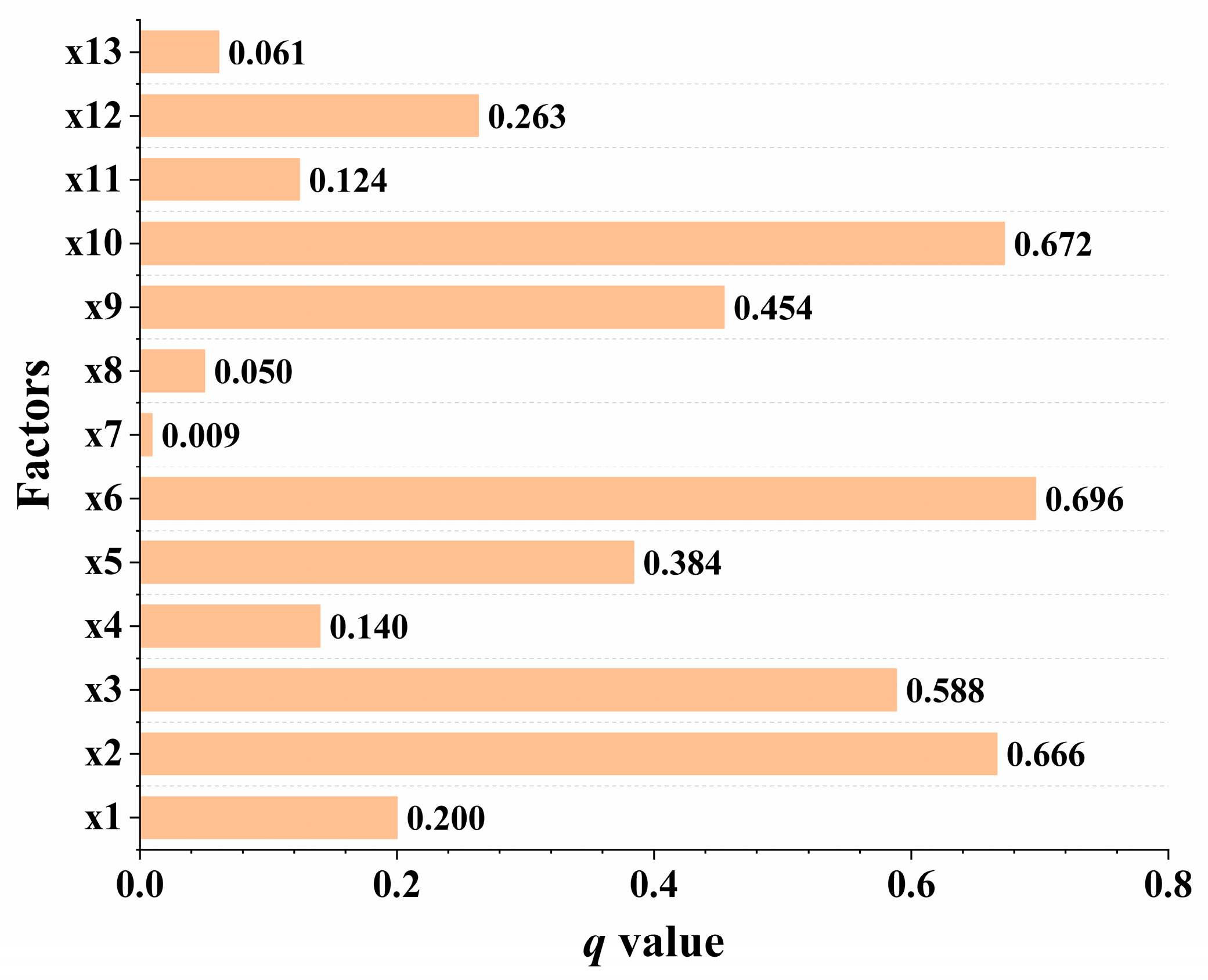
3.2.2. Single-Factor Effect on the Spatial Heterogeneity
3.2.3. Interactive Effects Among Drivers
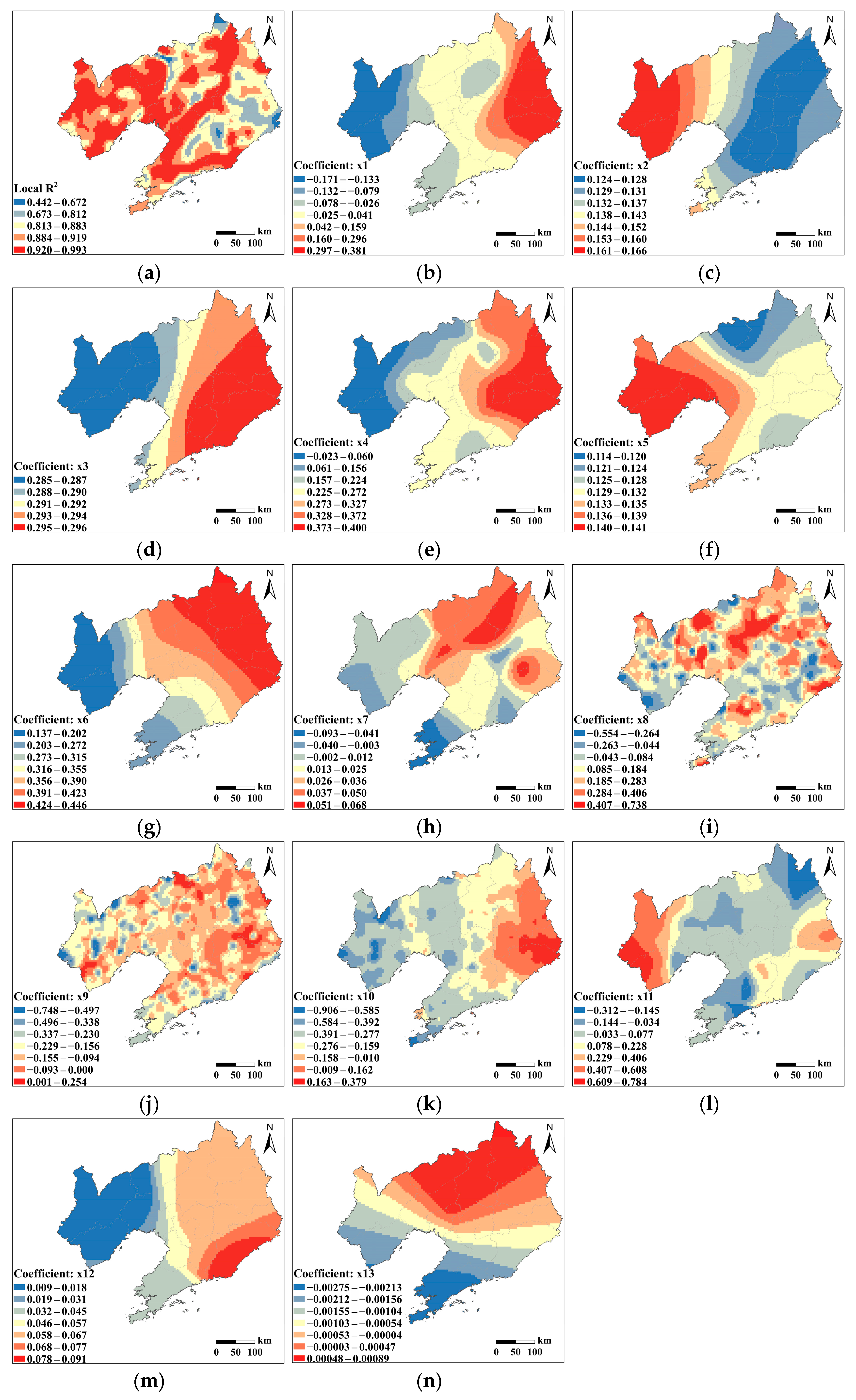
3.2.4. Spatial Heterogeneity Captured by MGWR
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of BMF in Liaoning Province
4.2. Driving Mechanism of Socio-Ecological Factors on the BMF Spatial Pattern
4.3. Management Implications and Recommendations
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMF | Biodiversity maintenance function |
| NPP | net primary productivity |
| NDVI | Normalized difference vegetation index |
| FVC | vegetation fraction cover |
| AGB | aboveground biomass |
| DEM | Digital elevation model |
| GDP | gross domestic product |
| GWR | geographically weighted regression |
| MGWR | multiscale geographically weighted regression |
References
- Keck, F.; Peller, T.; Alther, R.; Barouillet, C.; Blackman, R.; Capo, E.; Chonova, T.; Couton, M.; Fehlinger, L.; Kirschner, D.; et al. The global human impact on biodiversity. Nature 2025, 641, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Yang, L.; Ma, J.; Qiu, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Spatial and temporal variations in the relationship between the topological structure of eco-spatial network and biodiversity maintenance function in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zou, C.; Ding, J.; Lv, T.; Zhang, Y. Comprehensive evaluation method and empirical study of biodiversity maintenance function at regional scale. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2021, 37, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Jaureguiberry, P.; Titeux, N.; Wiemers, M.; Bowler, D.E.; Coscieme, L.; Golden, A.S.; Guerra, C.A.; Jacob, U.; Takahashi, Y.; Settele, J. The direct drivers of recent global anthropogenic biodiversity loss. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, J. Habitat degradation changes and disturbance factors in the Tibetan plateau in the 21st century. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Luo, Q.; Mo, Y. Response of habitat quality to urban spatial morphological structure in multi-mountainous city. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Yu, D.; Gong, Z. Recognition of priority area of biodiversity conservation in Liaoning Province, Northeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Wu, W.; Zhou, J.; Wu, R. Identifying optimized on-the-ground priority areas for species conservation in a global biodiversity hotspot. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J. Identifying priority areas for biodiversity conservation based on Marxan and InVEST model. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 3043–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; Antunes, P.; Blumentrath, S.; Brouwer, R.; Clemente, P.; Santos, R. Spatial modelling of biodiversity conservation priorities in Portugal’s Montado ecosystem using Marxan with Zones. Environ. Conserv. 2019, 46, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Zhao, Z.; Li, G.; Gao, X.; Ji, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Biodiversity survey and assessment methods in biodiversity conservation priority areas in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, P. Technological advances in biodiversity monitoring: Applicability, opportunities and challenges. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 45, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pan, Q.; Tu, C. Spatial scale effect analysis and evaluation of biodiversity maintenance function: Case study of Shaanxi province. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effects of Hubei Province based on the InVEST model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 6419–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Meng, J. Quantifying the spatial pattern for the importance of natural resource ecosystem services in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, J. Spatio-temporal variation of biodiversity maintenance function and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2020. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Interactive response and spatial heterogeneity of alpine grassland biodiversity to soil, topography, climate, and human factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4488–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Human and natural factors affect habitat quality in ecologically fragile areas: Evidence from Songnen Plain, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1444163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.; An, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Effects of the interaction among climate, terrain and human activities on biodiversity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Uncovering the determinants of biodiversity hotspots in China: Evidence from the drivers of multiple diversity metrics on insect assemblages and implications for conservation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Ou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Evaluation of biodiversity maintenance capacity in forest landscapes: A case study in Beijing, China. Land 2023, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, F.; Callois, J.-M. On the time lag between human activity and biodiversity in Europe at the national scale. Anthropocene 2021, 35, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, X. Spatio-temporal variations of habitat quality and its driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta region of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 52, e02978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xiong, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Lin, B. Direct and indirect effects of environmental factors, spatial constraints, and functional traits on shaping the plant diversity of montane forests. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Fu, B. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wei, W. Changes in soil conservation service supply-demand coordinations and their influencing factors: Evidence from the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Yao, W.; Tu, Y. Exploring the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and influencing factors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, S.; Cao, Z.; Tian, P.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y. Quantifying the driving forces of water conservation using geodetector with optimized parameters: A case study of the Yiluo River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H. Monitoring spatiotemporal characteristics of land-use carbon emissions and their driving mechanisms in the Yellow River Delta: A grid-scale analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Luo, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Shang, X.; Wang, Z. Multi-scale spatio-temporal analysis of soil conservation service based on MGWR model: A case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pearson, D.; Palmer, A.; Lowry, J.; Gray, D.; Dominati, E.J. Quantifying spatial non-stationarity in the relationship between landscape structure and the provision of ecosystem services: An example in the New Zealand hill country. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Kao, C.; Yu, H.; Bardin, S.; Oshan, T.; Li, Z.; Sachdeva, M.; Luo, W. Exploring spatial context: A comprehensive bibliography of GWR and MGWR. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Qiu, A.; Cao, A.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M. Spatial responses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies to impact factors in Liaoning Province. Environ. Manag. 2025, 75, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Bian, Z. Ecological security patterns based on ecosystem service assessment and circuit theory: A case study of Liaoning Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Han, H.; Wan, D. Summer bird diversity and annual dynamic changes in Liaoning Province from 2012 to 2019. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2020, 36, 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Huan, C.; Yang, J.; Gu, H. Temporal and spatial distribution changes, driving force analysis and simulation prediction of ecological vulnerability in Liaoning Province, China. Land 2022, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. China National Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2011–2030); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Meadows, M.; Yin, H.; He, H.S.; Su, J.; Zhou, K. Identifying priority conservation areas for threatened amphibian habitats in the Yangtze river Delta region to maintain regional biodiversity. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mu, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Z. Impacts of climate change on forest biodiversity changes in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ji, R.; Han, X.; Chen, L.; Feng, R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the biodiversity conservation function in Liaohe Delta Wetland, Northeastern China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Ju, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D. Different methods comparison of delineating the ecological protection red line for biodiversity conservation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 6959–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S. Stepwise construction and integration of ecological network in resource-based regions: A case study on Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, X.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Assessing spatio-temporal characteristics and their driving factors of ecological vulnerability in the northwestern region of Liaoning Province (China). Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y. Identification of ecological restoration spaces based on ecological network construction and ecological resilience in mega city: A case of Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 4626–4637. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Yang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yao, X.; Xiao, L. The impact of human activity expansion on habitat quality in the Yangtze River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Kang, F.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z. Exploring drivers of ecosystem services variation from a geospatial perspective: Insights from China’s Shanxi Province. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, Q.; Li, Z. Analysis of spatial characteristics and influence mechanism of human settlement suitability in traditional villages based on multi-scale geographically weighted regression model: A case study of Hunan province. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chen, X.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, D. Modeling the spatially heterogeneous relationships between tradeoffs and synergies among ecosystem services and potential drivers considering geographic scale in Bairin Left Banner, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fotheringham, A.S. Computational improvements to multi-scale geographically weighted regression. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 1378–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. mgwr: A python implementation of multiscale geographically weighted regression for investigating process spatial heterogeneity and scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Plant community differentiation of desertification region in northwest Liaoning Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Cong, P.; Qu, L.; Liang, S.; Sun, Z.; Han, J. Biological connectivity and its driving mechanisms in the Liaohe Delta wetland, China. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 76, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, S.; Hui, C.; Verburg, P.H.; Van Teeffelen, A.J.A. Quantifying spatiotemporal drivers of environmental heterogeneity in Kruger National Park, South Africa. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2013–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Webb, A.A.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.; Han, Z.; Wang, S.; Yu, P. Influence of climatic and geographic factors on the spatial distribution of Qinghai spruce forests in the dryland Qilian Mountains of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Kang, J.; Lei, W.; Zhang, D. Spatiotemporal distribution and habitat characteristics of shorebirds in the coastal wetlands of Dalian, Liaoning, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Hu, N.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Ye, H. Study on eco-environmental effects of land-use transitions and their influencing factors in the central and southern Liaoning urban agglomeration: A production–living–ecological perspective. Land 2022, 11, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Shen, Z.; Yu, H. Drought risk assessment in China: Evaluation framework and influencing factors. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.-F.; Cao, A.-H.; Wang, F.-Y. Response and multi-scenario prediction of carbon storage and habitat quality to land use in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshana, T.S.; Martin, E.A.; Sirami, C.; Woodcock, B.A.; Goodale, E.; Martínez-Núñez, C.; Lee, M.-B.; Pagani-Núñez, E.; Raderschall, C.A.; Brotons, L.; et al. Crop and landscape heterogeneity increase biodiversity in agricultural landscapes: A global review and meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2024, 27, e14412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbell, F.; Balvanera, P.; Mori, A.S.; He, J.; Bullock, J.M.; Regmi, G.R.; Seabloom, E.W.; Ferrier, S.; Sala, O.E.; Guerrero-Ramírez, N.R.; et al. Expert perspectives on global biodiversity loss and its drivers and impacts on people. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 21, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Niu, B.; Si, G.; Wang, J.; Yeh, C.-F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions: Interplay between geology and contemporary environments. ISME J. 2020, 14, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafitte, A.; Sordello, R.; Ouédraogo, D.-Y.; Thierry, C.; Marx, G.; Froidevaux, J.; Schatz, B.; Kerbiriou, C.; Gourdain, P.; Reyjol, Y. Existing evidence on the effects of photovoltaic panels on biodiversity: A systematic map with critical appraisal of study validity. Environ. Evid. 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Data | Sources | Type | Spatial Resolution | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average annual precipitation | National Earth System Science Data Sharing Platform (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 1 km | 2000–2020 |
| Average annual temperature | National Earth System Science Data Sharing Platform (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 1 km | 2000–2020 |
| Digital elevation model (DEM) | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM; http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/, accessed on 2 December 2023) | Raster | 90 m | — |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | SPOT/VEGETATION products (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 500 m | 2020 |
| Net primary productivity (NPP) | SPOT/VEGETATION products (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 500 m | 2020 |
| Fractional vegetation cover (FVC) | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 500 m | 2020 |
| Aboveground biomass (AGB) | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn, accessed on 10 November 2024) | Raster | 500 m | 2020 |
| Amphibian, mammal, and bird species richness | IUCN (https://iucn.org/, accessed on 14 September 2024) | Raster | 1 km | 2015 |
| GDP Density | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 10 August 2024) | Raster | 1 km | 2020 |
| Population Density | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 10 August 2024) | Raster | 1 km | 2020 |
| Road | Peking University’s Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure (http://geodata.pku.edu.cn, accessed on 10 August 2024) | Vector | — | 2015 |
| Land use and land cover (LULC) | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 10 August 2024) | Raster | 30 m | 2020 |
| Criteria Hierarchy | Indicator Hierarchy |
|---|---|
| Climatic factors | Long-term average precipitation |
| Long-term average temperature | |
| Vegetation status | Net primary productivity (NPP) |
| Vegetation fraction cover (FVC) | |
| Aboveground biomass (AGB) | |
| Species richness | Avian richness |
| Mammalian richness Amphibian richness | |
| Floral richness | |
| Ecosystem protection | National or provincial nature reserve |
| Anthropogenic disturbance | Anthropogenic disturbance index |
| Variable Category | Variable | Code | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topographic factors | DEM | x1 | Digital elevation model | m |
| Slope | x2 | Slope gradient | ◦ | |
| Climatic factors | Pre | x3 | Long-term average precipitation | mm |
| Tem | x4 | Long-term average temperature | °C | |
| NDVI | x5 | Normalized difference vegetation index | – | |
| Habitat factors | Forest | x6 | Forestland proportion | % |
| Grass | x7 | Grassland proportion | % | |
| Wetland | x8 | Wetland proportion | % | |
| Anthropogenic factors | Urban | x9 | Urban proportion | % |
| Farmland | x10 | Farmland proportion | % | |
| GDP | x11 | GDP density | 10,000 yuan/km2 | |
| Population | x12 | Population density | People/km2 | |
| Road | x13 | Road density | km/km2 |
| Variable | Moran’s I | Z-Scores | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMF | 0.859 | 131.583 | 0.000 |
| x1 | 0.916 | 140.367 | 0.000 |
| x2 | 0.869 | 133.147 | 0.000 |
| x3 | 0.994 | 152.281 | 0.000 |
| x4 | 0.931 | 142.706 | 0.000 |
| x5 | 0.653 | 100.179 | 0.000 |
| x6 | 0.840 | 128.778 | 0.000 |
| x7 | 0.510 | 79.164 | 0.000 |
| x8 | 0.525 | 80.714 | 0.000 |
| x9 | 0.665 | 102.035 | 0.000 |
| x10 | 0.785 | 120.270 | 0.000 |
| x11 | 0.609 | 96.956 | 0.000 |
| x12 | 0.706 | 109.711 | 0.000 |
| x13 | 0.619 | 95.316 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Xu, W. Exploring the Spatially Heterogeneous Relationships Between Biodiversity Maintenance Function and Socio-Ecological Drivers in Liaoning Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112276
Qiao Y, Wang Z, Zhang H, Liu K, Xu W. Exploring the Spatially Heterogeneous Relationships Between Biodiversity Maintenance Function and Socio-Ecological Drivers in Liaoning Province, China. Land. 2025; 14(11):2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112276
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Yajun, Zhi Wang, Haonan Zhang, Kun Liu, and Wanggu Xu. 2025. "Exploring the Spatially Heterogeneous Relationships Between Biodiversity Maintenance Function and Socio-Ecological Drivers in Liaoning Province, China" Land 14, no. 11: 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112276
APA StyleQiao, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, K., & Xu, W. (2025). Exploring the Spatially Heterogeneous Relationships Between Biodiversity Maintenance Function and Socio-Ecological Drivers in Liaoning Province, China. Land, 14(11), 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112276






