Investigation of the Influence of Urban Compactness on Transportation: A Comparative Analysis of Average Commuting Duration and Velocity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Compact Cities
2.2. The Influence of Urban Density on Transportation and Commute Patterns
2.3. The Intermediary Function of Commuting Efficiency in the Relationship Between Urban Compactness and Travel Behavior
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Urban Compactness
3.1.2. Traffic Commuting Index
3.1.3. Data from China City Statistical Yearbook
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
3.2.2. Regression Equation Model
4. Results and Analysis
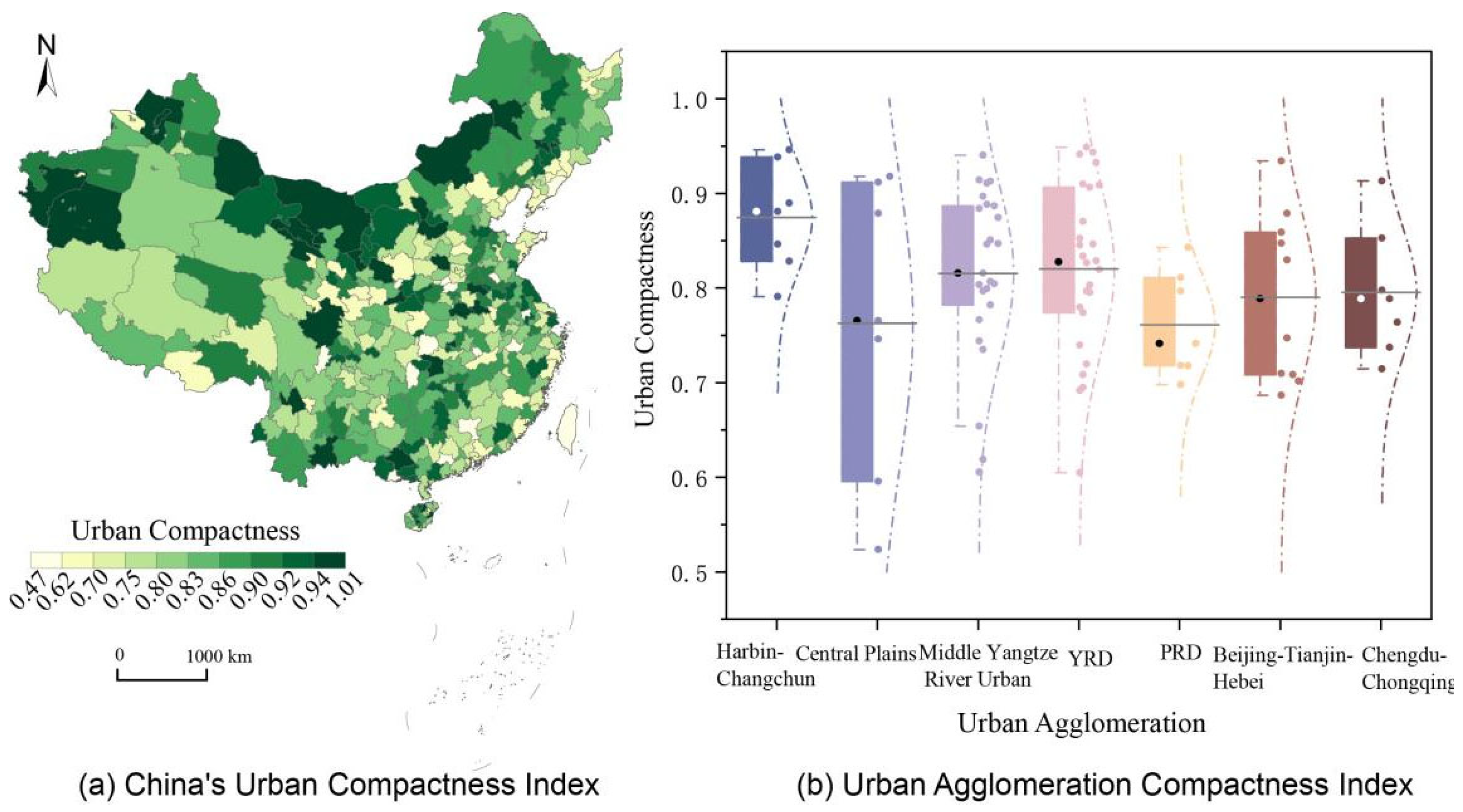
4.1. Analysis of Urban Compactness in China
4.2. Analysis of Commuting Speed and Time in Chinese Cities
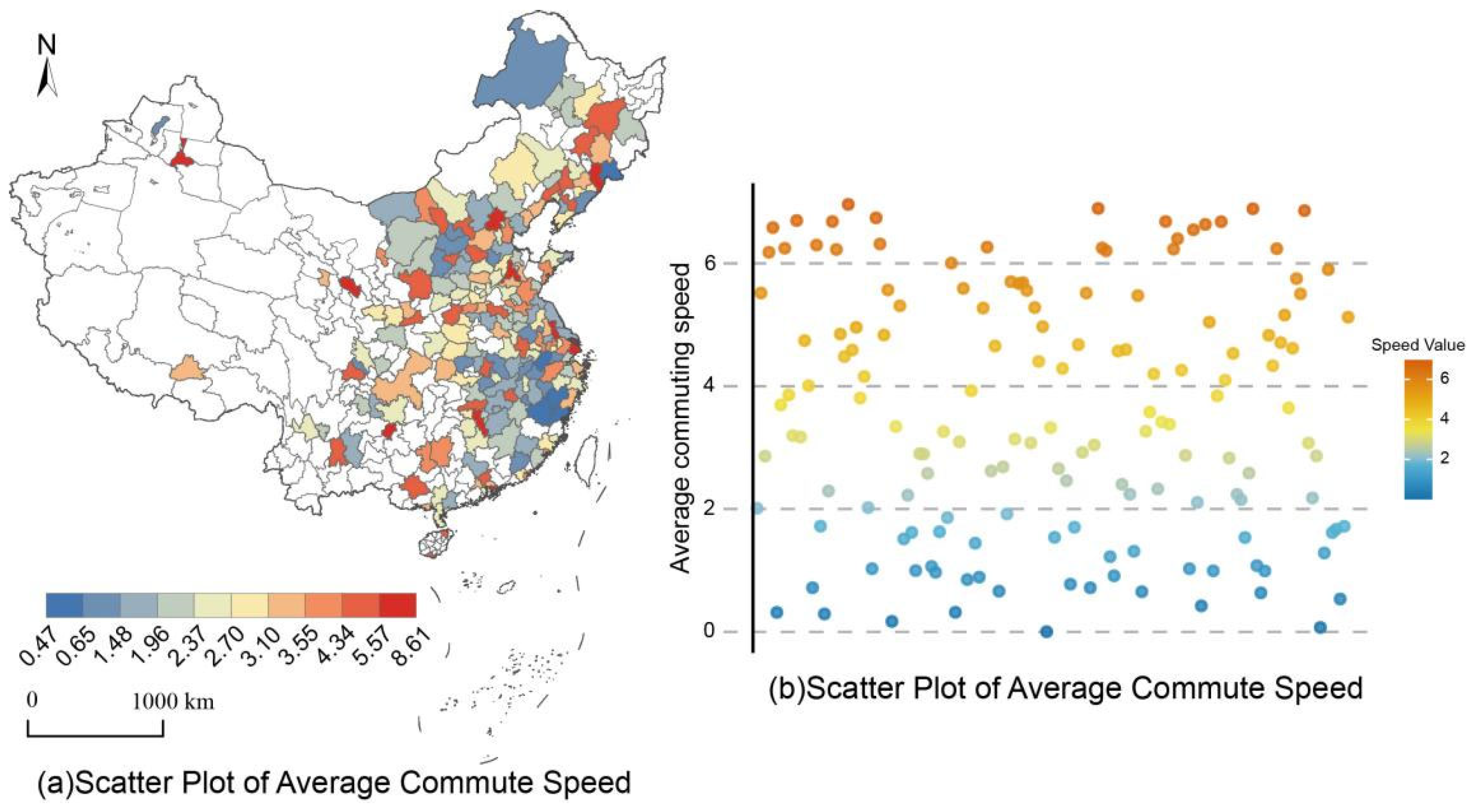
4.2.1. Analysis of Spatial Characteristics of Commuting Speed
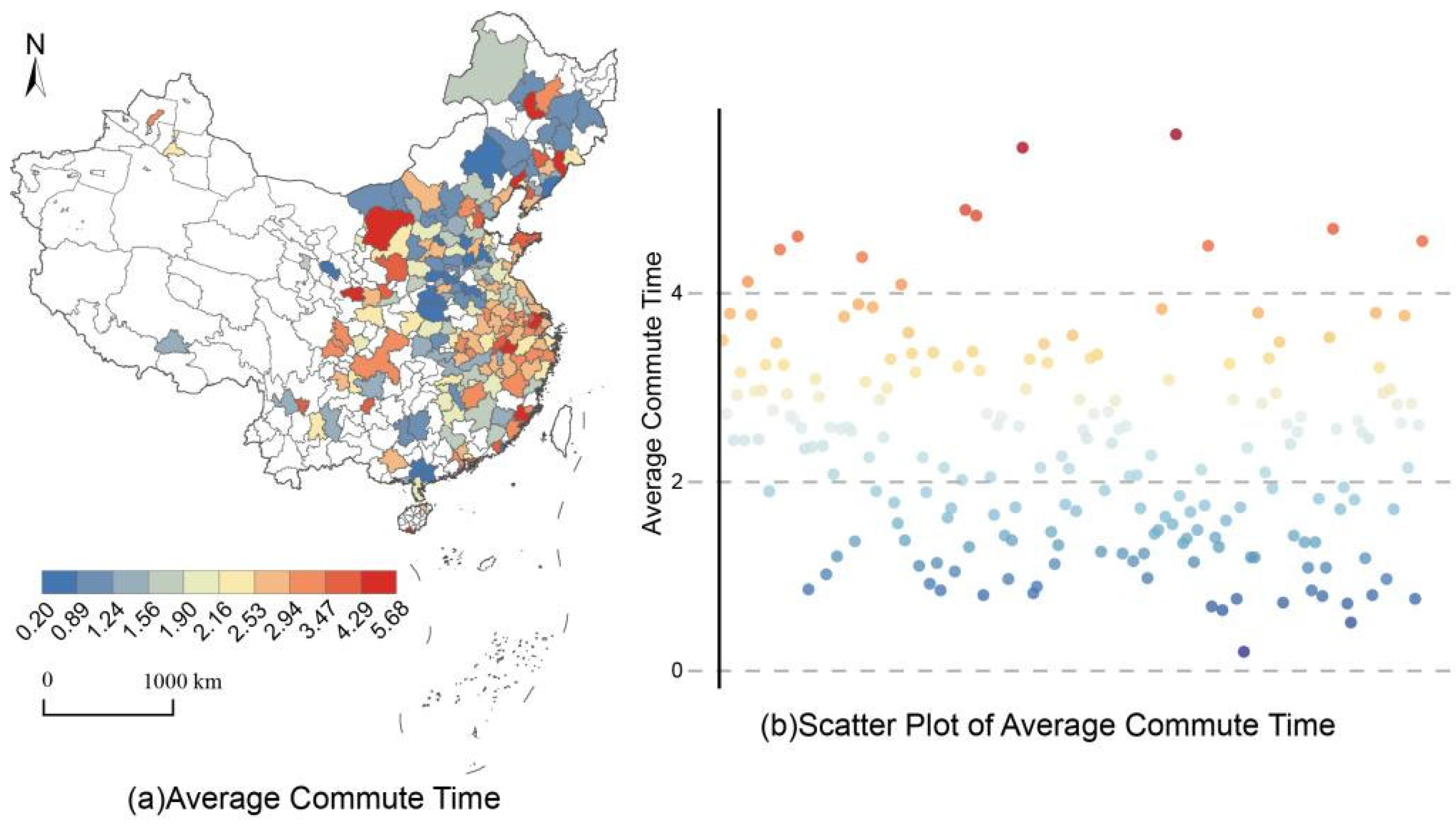
4.2.2. Analysis of Spatial Characteristics of Commuting Time
4.3. Regression Analysis
4.3.1. Variable Selection
4.3.2. Model Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, T.; Shao, G.; Xu, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, L. Measuring urban compactness based on functional characterization and human activity intensity by integrating multiple geospatial data sources. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xiao, L.; Tang, L.; Shi, L.; Su, X.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Shao, G. Effects of spatial form on urban commute for major cities in China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2014, 21, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L. The Fragmentation of Urban Footprints: Global Evidence of Sprawl, 1990–2000; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nechyba, T.J.; Walsh, R.P. Urban sprawl. J. Econ. Perspect. 2002, 18, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jia, B.; Lau, S. Sustainable urban form for Chinese compact cities: Challenges of a rapid urbanized economy. Habitat Int. 2008, 32, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditjandra, P.T. The impact of urban development patterns on travel behaviour: Lessons learned from a British metropolitan region using macro-analysis and micro-analysis in addressing the sustainability agenda. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2013, 7, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. Compact Urbanism and the Synergic Potential of its Integration with Data-Driven Smart urbanism: An Extensive Interdisciplinary Literature Review. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.; Tian, G.; Lyons, T. Does compact development increase or reduce traffic congestion? Cities 2018, 72, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Shi, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Towards a more compact urban form: A spatial-temporal study on the multi-dimensional compactness index of urban form in China. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 171, 103368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J.; Kärrholm, M. Compact City Planning and Development: Emerging Practices and Strategies for Achieving the Goals of Sustainability. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 4, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Kong, S.; Yu, Y. Tight spaces, strong cities: The resilience payoff of urban compactness. Land Use Policy 2025, 156, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.; Luan, B.; Chen, Y. On the urban compactness to ecosystem services in a rapidly urbanising metropolitan area: Highlighting scale effects and spatial non–stationary. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E. Measuring urban compactness in UK towns and cities. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2002, 29, 219–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabareen, Y.R. Sustainable Urban Forms Their Typologies, Models, and Concepts. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2016, 26, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.; Cervero, R. Travel and the built environment: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2010, 76, 265–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.; Boarnet, M.; Ewing, R.; Killingsworth, R.E. How the built environment affects physical activity: Views from urban planning. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2002, 23 (Suppl. 1), 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, G.; Lan, T.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiao, L.; Small, C. Global consistency of urban scaling evidenced by remote sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2025, 4, pgaf037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Malekzadeh, N. Driving factors of formation, development, and change of spatial structure in metropolitan areas: A systematic review. J. Urban Manag. 2020, 9, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Pan, J.; Xie, L.; Zhou, T.; Bai, H.; Zhu, Y. Spatial–temporal evolution and regional differentiation features of urbanization in China from 2003 to 2013. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qu, S.; Peng, K.; Feng, Y. Quantifying Urban Sprawl and Its Driving Forces in China. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Qin, M.; Li, S.L. Urban spatial structure and labour income. World Econ. 2019, 4, 123–148. [Google Scholar]
- Boussauw, K.; Neutens, T.; Witlox, F. Relationship between spatial proximity and travel-to-work distance: The effect of the compact city. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 687–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, X. Does polycentric and compact development alleviate urban traffic congestion? A case study of 98 Chinese cities. Cities 2019, 88, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiao, L.; Lan, T.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, H.; Li, C.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y. Mapping hierarchical urban boundaries for global urban settlements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R. Urban spatial structure and commute duration: An empirical study of China. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-R.; Banister, D. Urban spatial change and excess commuting. Environ. Plan. A 2007, 39, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.J. The effects of polycentric evolution on commute times in a polycentric compact city: A case of the Seoul Metropolitan Area. Cities 2020, 98, 102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.R. Does Compact Development Make People Drive Less? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2016, 83, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirilli, A.; Veneri, P. Spatial Structure and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions Due to Commuting: An Analysis of Italian Urban Areas. Reg. Stud. 2013, 48, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, A.; Alidadi, M.; Sharifi, A. Compact development policy and urban resilience: A critical review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Yang, J.; Dai, D.; Wu, K.; He, Q. Urban growth pattern and commuting efficiency: Empirical evidence from 100 Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zuo, M.; Chen, S.; Tang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, J. Impact of Urban Spatial Compactness on Carbon Emissions: Heterogeneity at the County Level in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Area, China. Land 2024, 13, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Allan, A.; Cui, J. The impact of polycentric urban development on commuting behaviour in urban China: Evidence from four sub-centres of Beijing. Habitat Int. 2015, 50, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Antipova, A. Structural equation model in exploring urban sprawl and its impact on commuting time in 162 US urbanized areas. Cities 2024, 148, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Investigating the impacts of three-dimensional spatial structures on CO2 emissions at the urban scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 762, 143096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.F.; Hui, E.C.M.; Lin, Y.Y. Relationship between urban spatial structure and carbon emissions: A literature review. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Cao, Y. Commuting inequity and its determinants in Shanghai: New findings from big-data analytics. Transp. Policy 2020, 92, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Saphores, J.D.M. An L.A. story: The impact of housing costs on commuting. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 98, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Debbage, N. Urban morphology and traffic congestion: Longitudinal evidence from US cities. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 89, 101676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shu, X.; Luo, J. The formation of a polycentric city in transitional China in a three-level analysis framework: The case study of Hangzhou. Land 2022, 11, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Han, Z.; Xin, J.; Luo, X.; Su, S.; Weng, M. Transit oriented development among metro station areas in Shanghai, China: Variations, typology, optimization and implications for land use planning. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, W.; Huang, J. Extending TOD through the interrelationship between transport and land use: A case study of Beijing. Land Use Policy 2024, 144, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Xia, Q. Urban Development Boundary Setting Versus Ecological Security and Internal Urban Demand: Evidence from Haikou, China. Land 2023, 12, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Variable Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Average Commute Time | dependent variable | The average duration of all express train orders in the city |
| Average commuting speed | dependent variable | The ratio of the order mileage to the order duration of all express trains in the city |
| Urban compactness | core independent variable | The degree of spatial intensification in urban form |
| Registered residence population at the end of the year | independent variable | It refers to the statistics of registered residence of the city at 24:00 on December 31 every year |
| Administrative area land area | independent variable | All land and water areas within the jurisdiction |
| Regional Gross Domestic Product | independent variable | The final result of production activities of all resident units in a region during a certain period of time |
| Actual urban road area at the end of the year | independent variable | Actual pavement area of the road |
| Total passenger volume of public transportation | independent variable | The total number of passengers transported |
| Average travel distance | independent variable | The average mileage of all express train orders in various cities on the Didi platform |
| Job–housing balance | independent variable | The extent of spatial correspondence between employment and residence |
| Variable | Min. | Max. | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Commute Time | 0.465 | 8.608 | 2.883 | 1.367 |
| Average commuting speed | 0.203 | 5.676 | 2.279 | 1.065 |
| Urban compactness | 1.017 | 2.128 | 1.255 | 0.176 |
| Registered residence population at the end of the year | 3.434 | 8.136 | 6.031 | 0.683 |
| Administrative area land area | 7.286 | 12.474 | 9.31 | 0.812 |
| Regional Gross Domestic Product | 6.159 | 10.549 | 7.894 | 0.866 |
| Actual urban road area at the end of the year | 0.336 | 5.401 | 3.032 | 0.844 |
| Total passenger volume of public transportation | 5.529 | 12.655 | 9.446 | 1.159 |
| Average travel distance | 0.138 | 6.276 | 1.129 | 0.676 |
| Job–housing balance | 2.594 | 7.385 | 6.419 | 0.442 |
| Variable | Regression Analysis of Average Commuting Speed | Regression Analysis of Average Commuting Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | SLM | SEM | OLS | SLM | SEM | |
| Urban compactness | −0.958 *** | −0.955 *** | −0.925 *** | 1.082 *** | 1.081 *** | 1.139 *** |
| Registered residence population at the end of the year | 0.322 * | 0.325 ** | 0.291 ** | −0.660 *** | −0.594 *** | −0.558 *** |
| Administrative area land area | −0.060 | −0.060 | −0.054 | 0.005 | 0.032 | 0.027 |
| Regional Gross Domestic Product | −0.380 *** | −0.380 *** | −0.363 ** | 0.725 *** | 0.625 *** | 0.659 *** |
| Actual urban road area at the end of the year | 0.193 ** | 0.188 * | 0.187 * | −0.087 | −0.029 | −0.038 |
| Total passenger volume of public transportation | 0.327 *** | 0.329 *** | 0.340 *** | −0.400 *** | −0.414 *** | −0.449 *** |
| Average travel distance | 1.462 *** | 1.456 *** | 1.449 *** | 0.893 *** | 0.947 *** | 0.925 *** |
| Job–housing balance | 0.003 | 0.002 | −0.006 | 0.106 | 0.142 | 0.142 |
| Constant | 0.362 | 0.390 | 0.297 | 1.481 | 0.844 | 1.137 |
| R2 | 0.787 | 0.787 | 0.791 | 0.437 | 0.474 | 0.493 |
| AIC | 407.531. | 406.497 | 402.011 | 504.430 | 489.269 | 483.759 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Investigation of the Influence of Urban Compactness on Transportation: A Comparative Analysis of Average Commuting Duration and Velocity. Land 2025, 14, 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102082
Wang F, Cao Y, Wang Z, Li J, Xu H. Investigation of the Influence of Urban Compactness on Transportation: A Comparative Analysis of Average Commuting Duration and Velocity. Land. 2025; 14(10):2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102082
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fan, Yuan Cao, Zhen Wang, Junchen Li, and Hongmei Xu. 2025. "Investigation of the Influence of Urban Compactness on Transportation: A Comparative Analysis of Average Commuting Duration and Velocity" Land 14, no. 10: 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102082
APA StyleWang, F., Cao, Y., Wang, Z., Li, J., & Xu, H. (2025). Investigation of the Influence of Urban Compactness on Transportation: A Comparative Analysis of Average Commuting Duration and Velocity. Land, 14(10), 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102082






