Assessing the Land Use-Carbon Storage Nexus Along G318: A Coupled SD-PLUS-InVEST Model Approach for Spatiotemporal Coordination Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
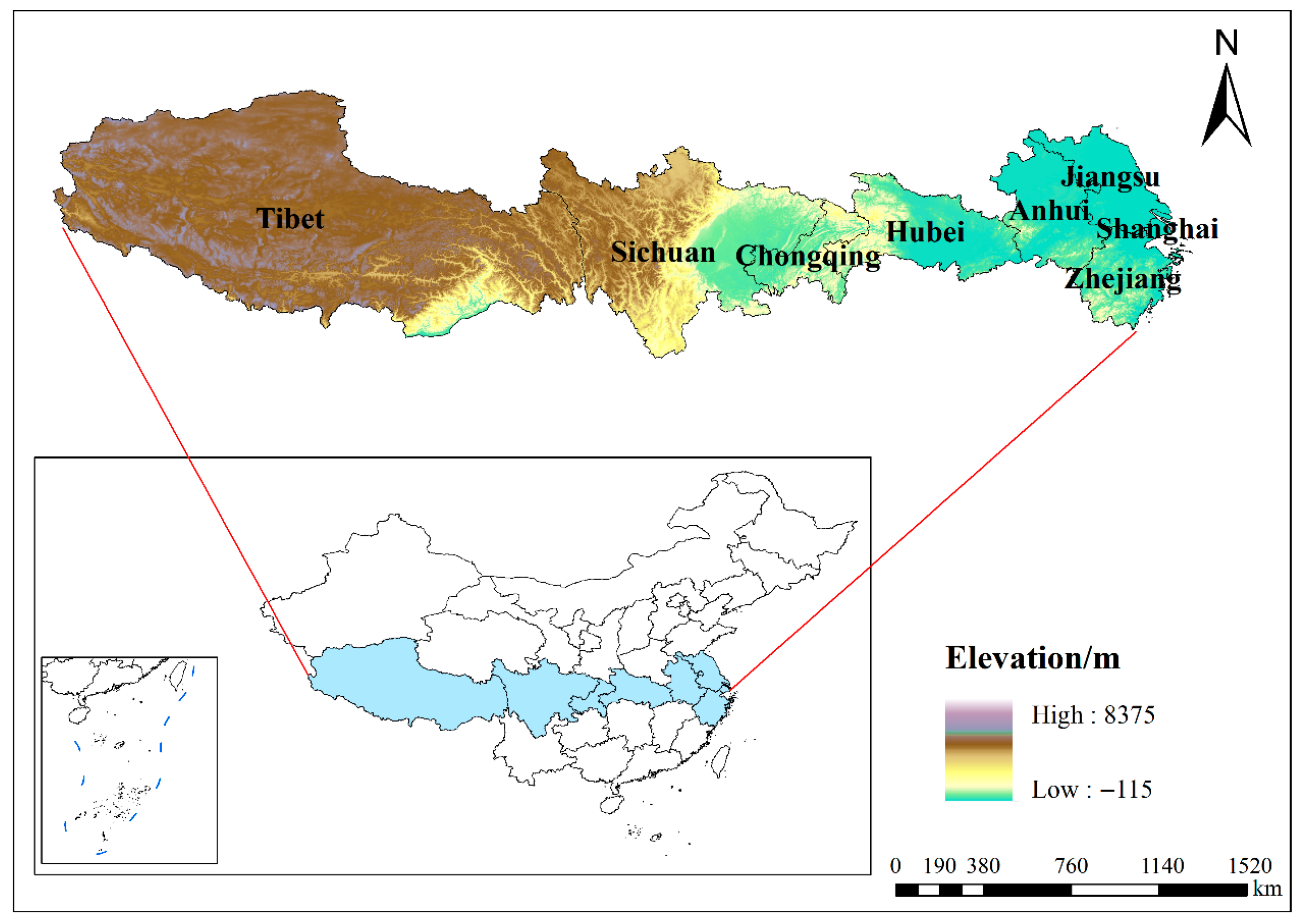
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
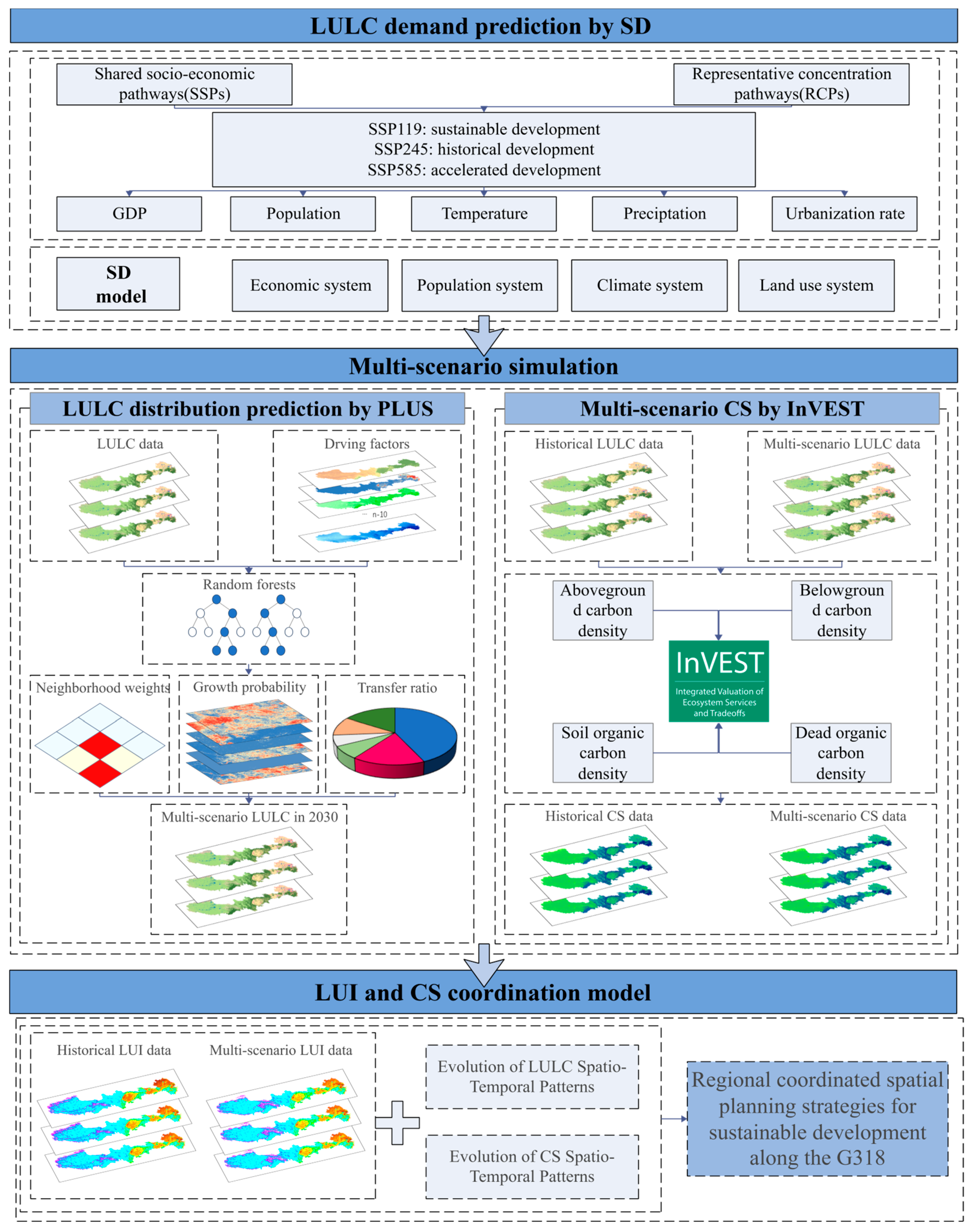
2.2.1. Modeling Framework
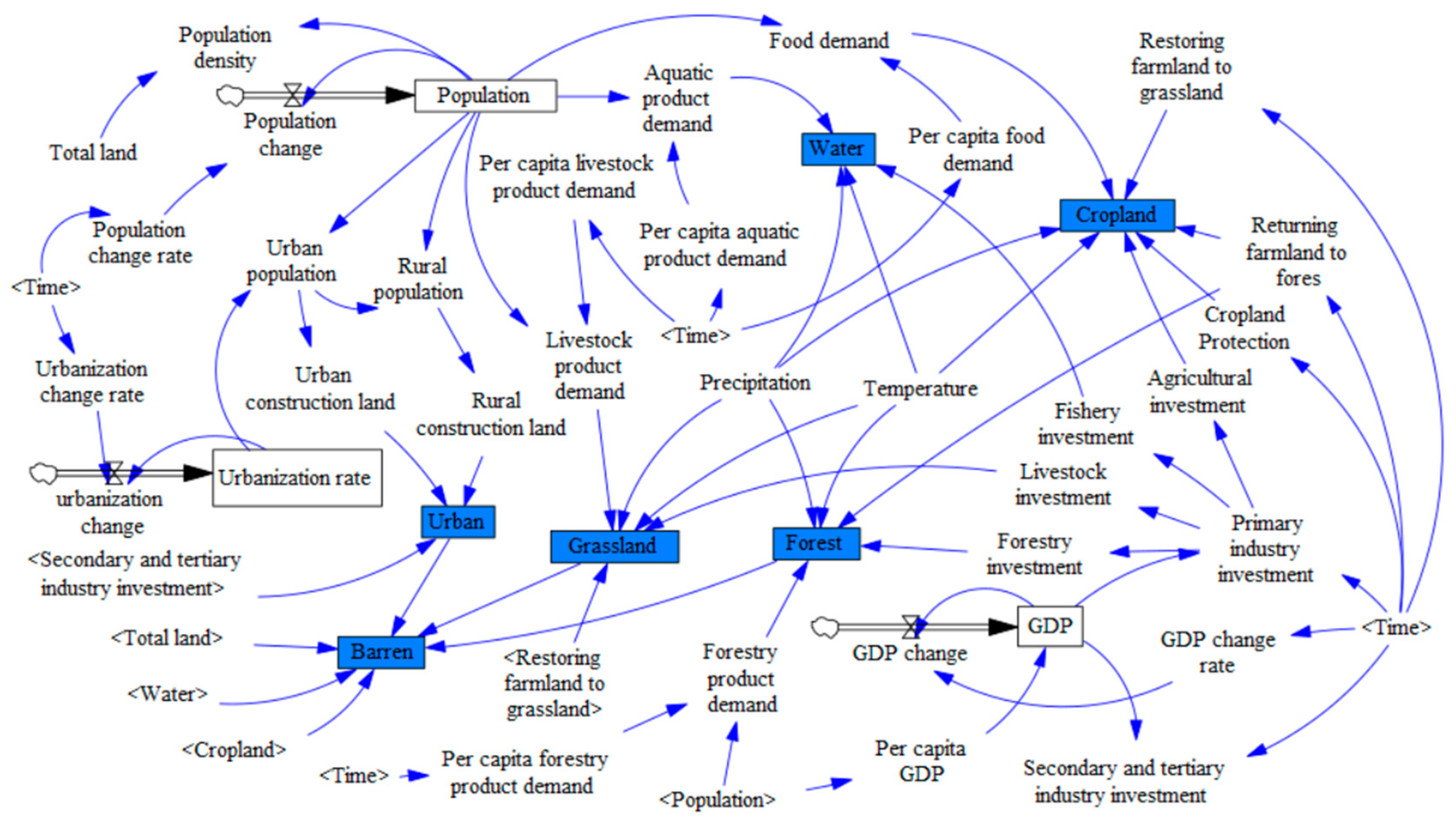
2.2.2. SD Model
2.2.3. PLUS Model
2.2.4. InVEST Model
2.2.5. LUI and Coordination Model
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Evolution of LULC
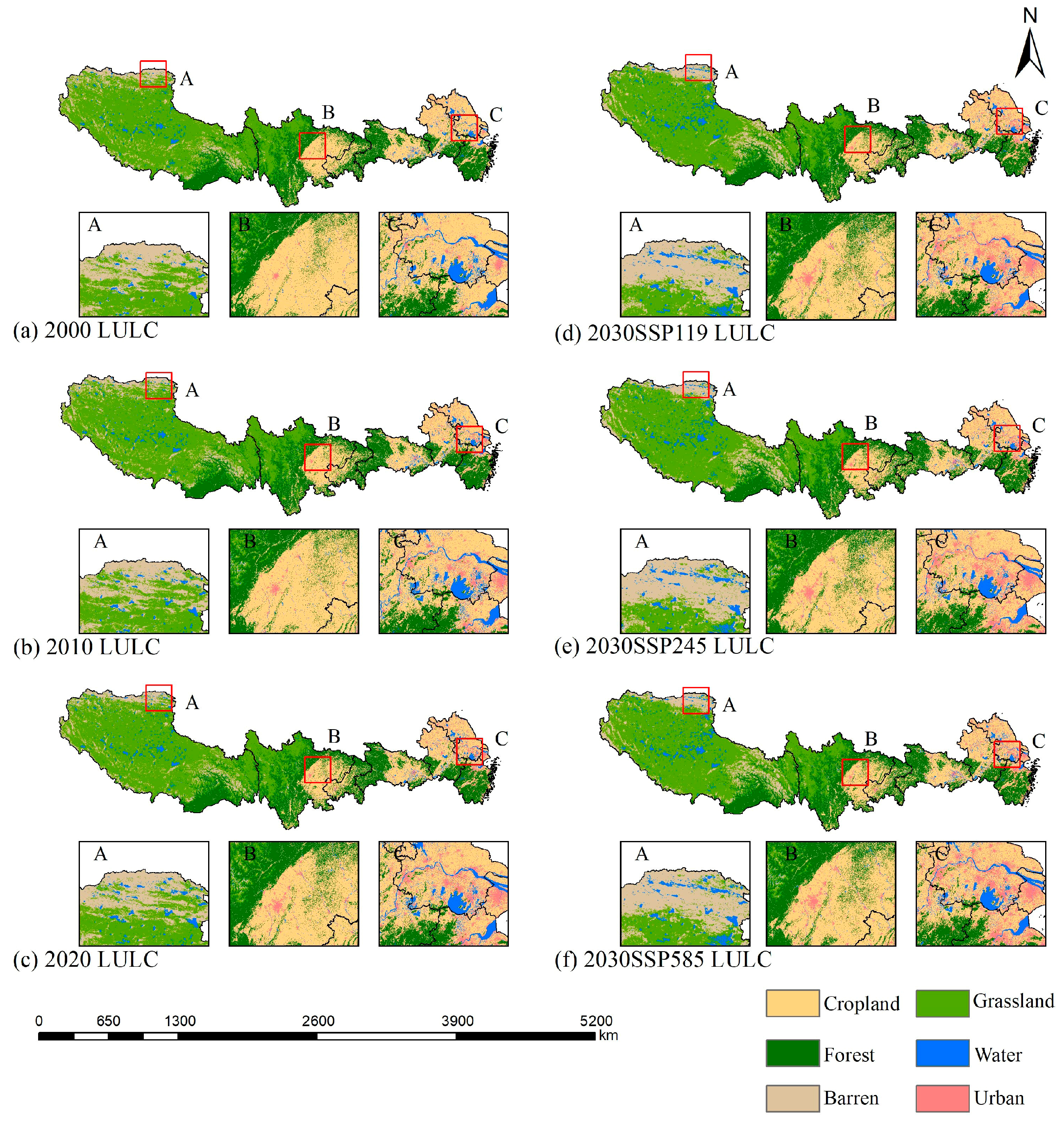
3.1.1. Analysis of Spatial Patterns of LULC Under Multiple Scenarios
3.1.2. Analysis of LULC Transfer Change Under Multiple Scenarios
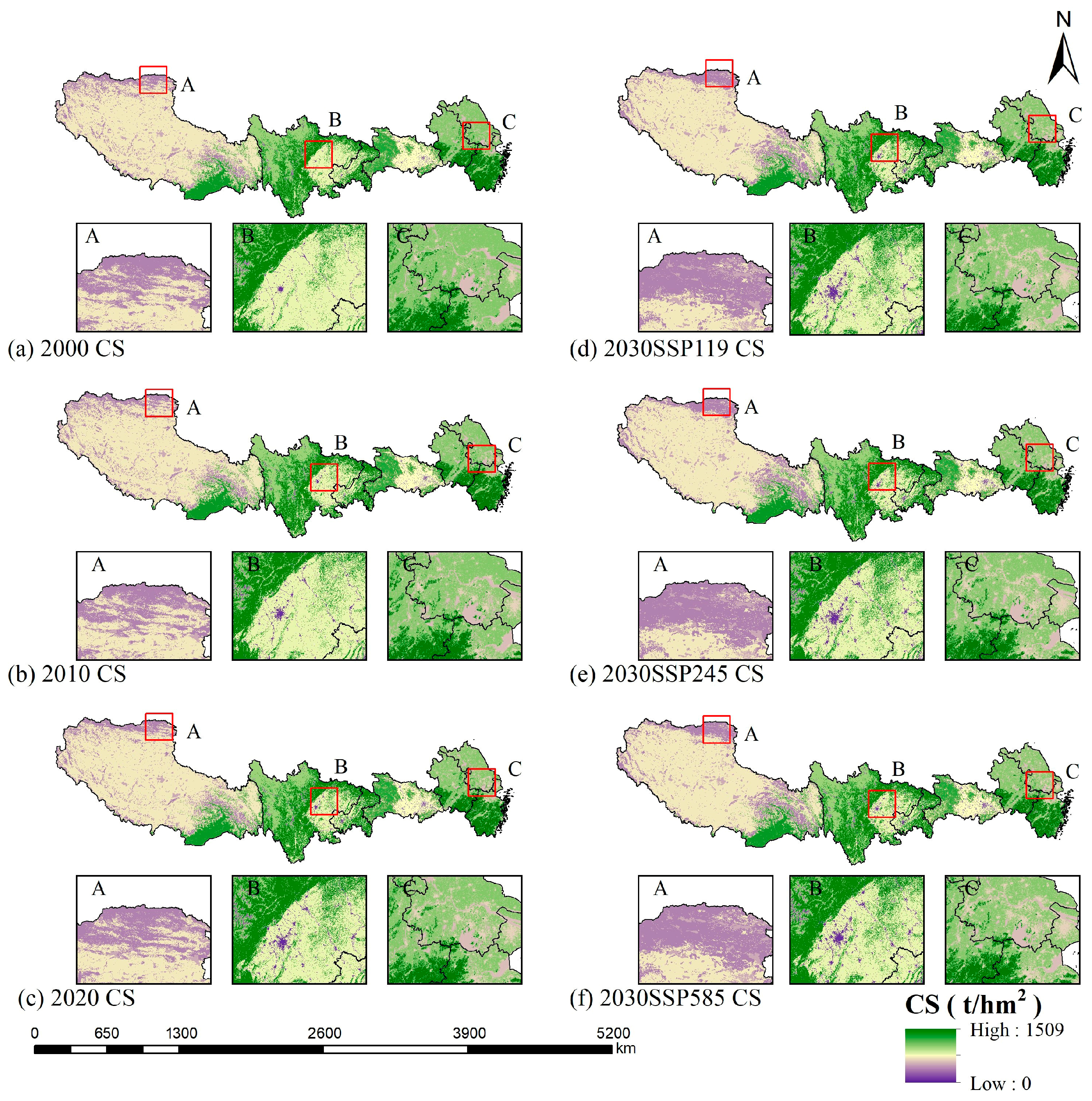
3.2. Evolutionary Assessment of CS Under Multiple Scenarios
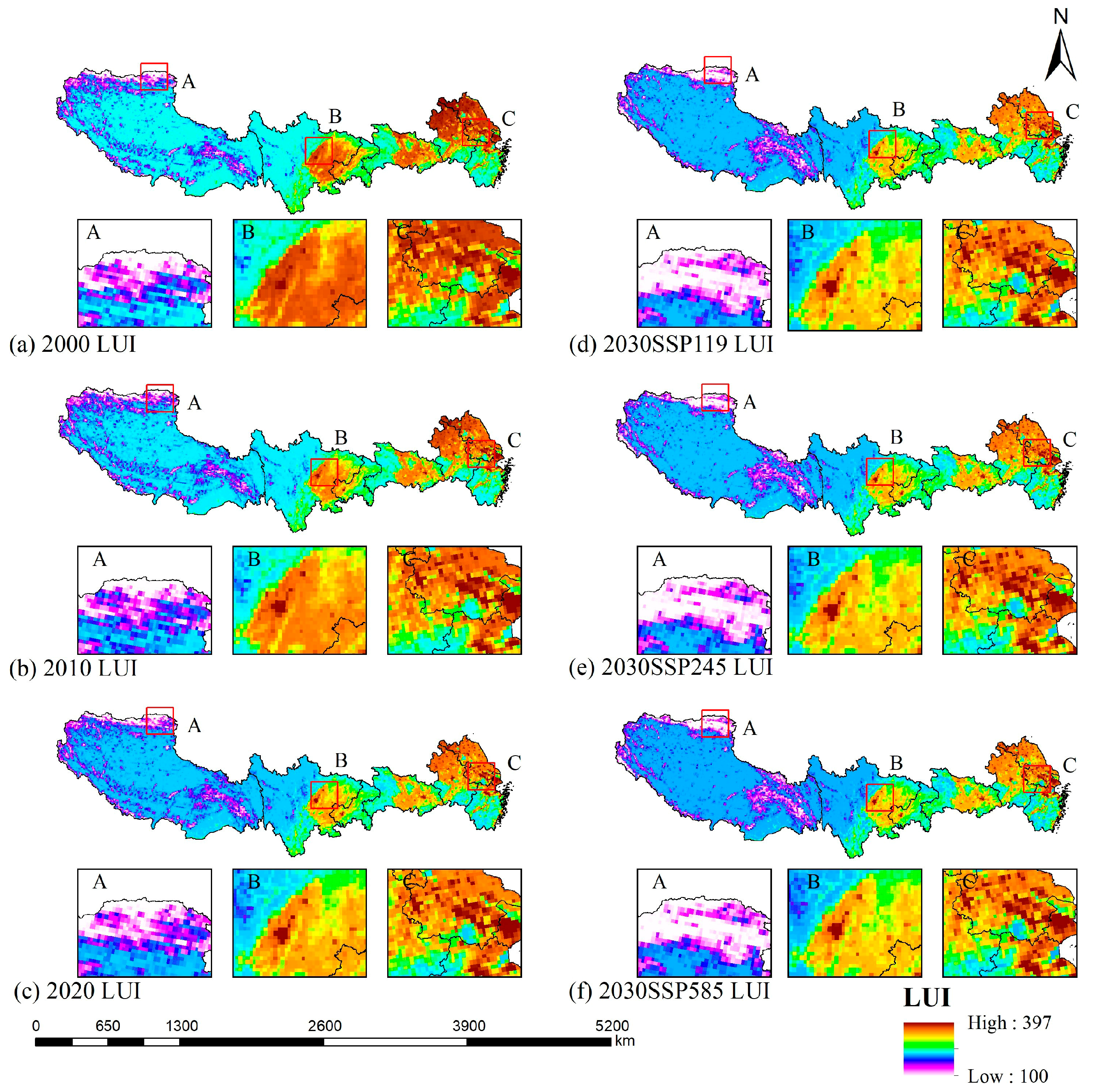
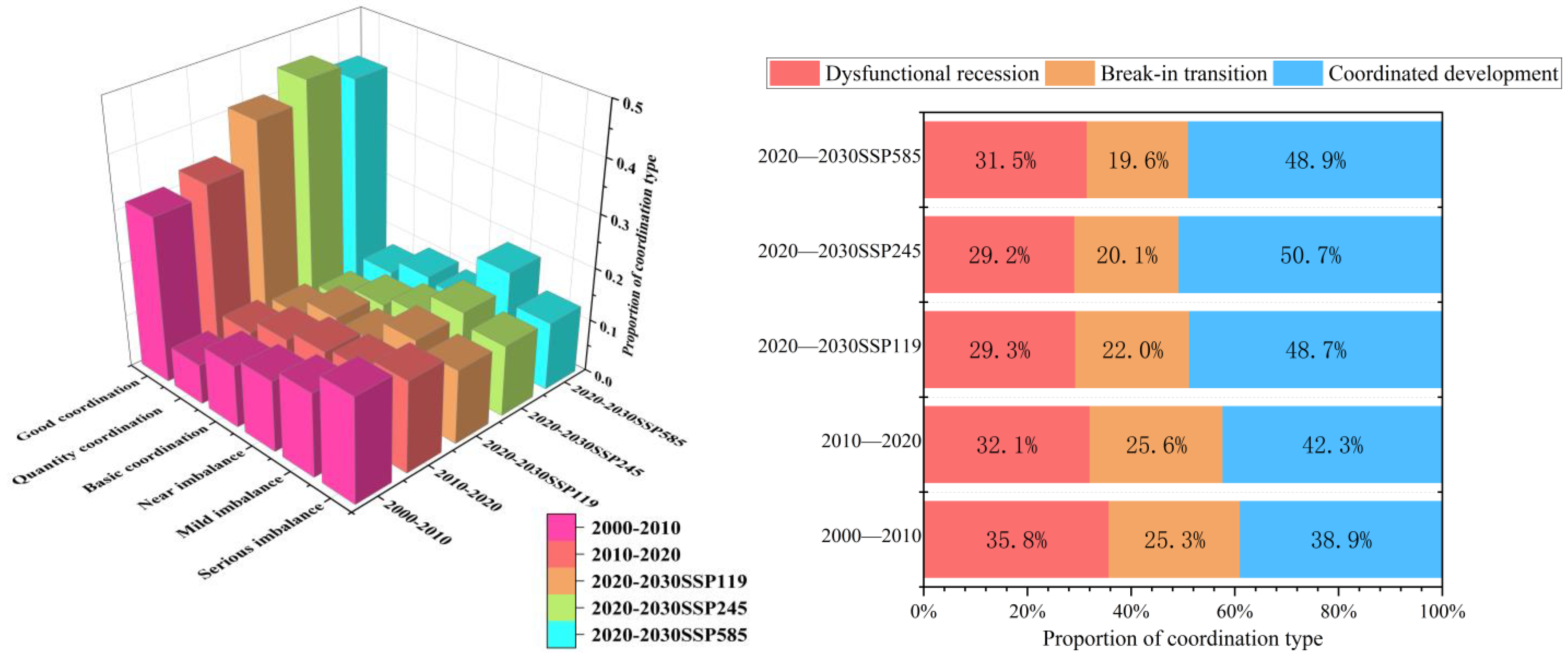
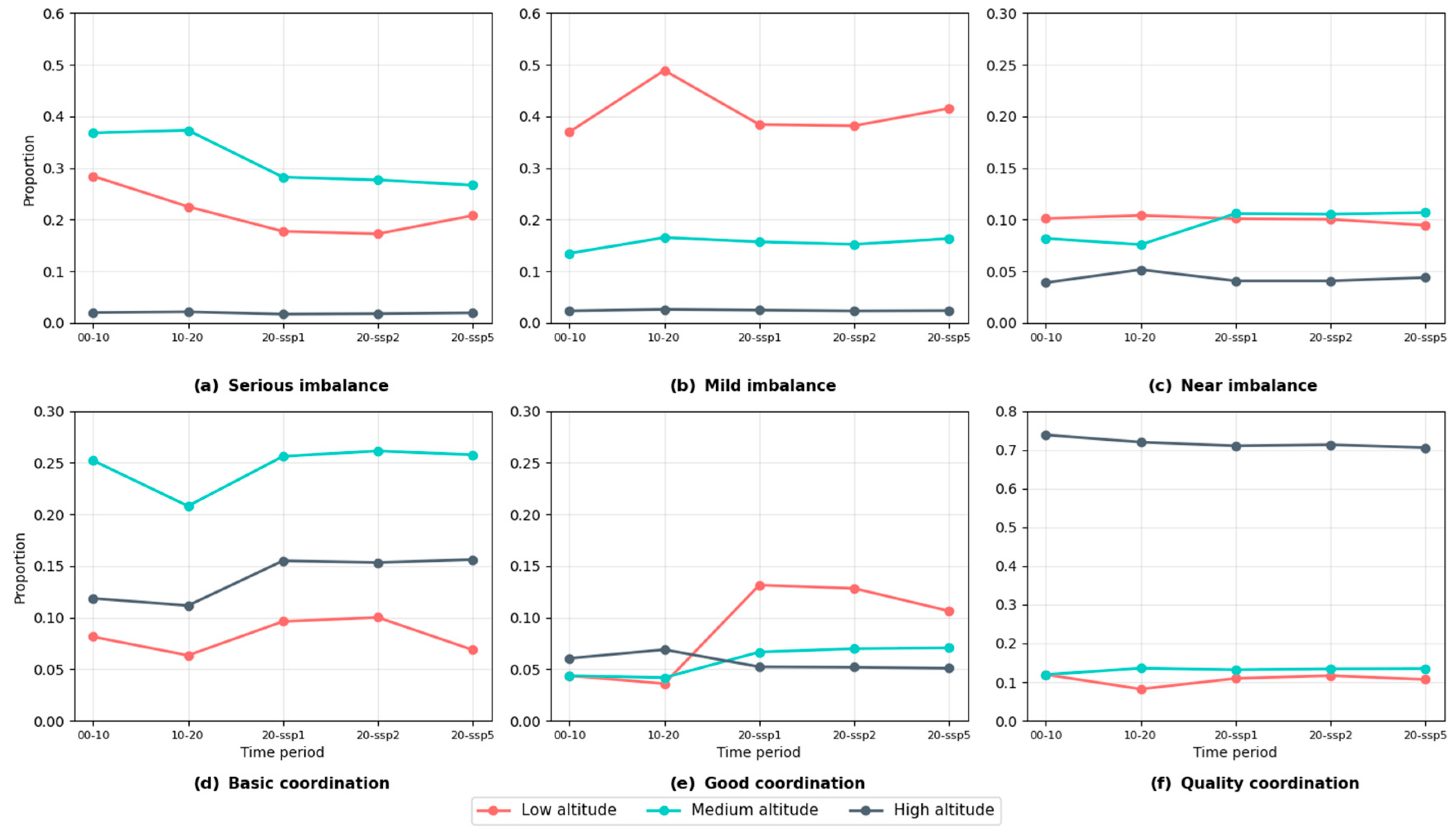
3.3. Analysis of Coordination Between LUI and CS
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variations of LUCC and CS in the G318 Region
4.2. Development Proposal
4.3. Uncertainty and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, S.I.; Conradi, T.; Muhoko, E. Shifts in vegetation activity of terrestrial ecosystems attributable to climate trends. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang, R.; Thiaw, I.; Alverson, K.; Liu, J.; Han, Z. The role of ecosystem services in climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Tong, X.; Lei, Z.; Gao, C.; Wang, J. Modeling changes in China’s 2000–2030 carbon stock caused by land use change. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, F.; Degefa, S.; Soromessa, T. Carbon stock dynamics in a changing land use land cover of the Upper Awash River Basin: Implications for climate change management. Sustain. Environ. 2024, 10, 2361565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachoo, Y.H.; Cutugno, M.; Robustelli, U.; Pugliano, G. Impact of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Changes on Carbon Stocks and Economic Implications in Calabria Using Google Earth Engine (GEE). Sensors 2024, 24, 5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, C.; Cheng, Y. Spatial influence of ecological networks on land use intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, R.; Shoaib, M.; Men, C.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Impacts of landscape change on net primary productivity by integrating remote sensing data and ecosystem model in a rapidly urbanizing region in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Spatial optimization of land use and carbon storage prediction in urban agglomerations under climate change: Different scenarios and multiscale perspectives of CMIP6. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Bai, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, H.; Xie, Z.; Shi, X.; Wu, B.; et al. Carbon pools in China’s terrestrial ecosystems: New estimates based on an intensive field survey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, Z.; Zubair, M.; Zha, Y.; Mehmood, M.S.; Rehman, A.; Fahd, S.; Nadeem, A.A. Predictive modeling of regional carbon storage dynamics in response to land use/land cover changes: An InVEST-based analysis. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Nkwae, B.; Odirile, P.; Moalafhi, D.B.; Anderson, G.; Parida, B.; Qi, J. Land-Use Change Prediction in Dam Catchment Using Logistic Regression-CA, ANN-CA and Random Forest Regression and Implications for Sustainable Land–Water Nexus. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Rahman, M.F.; Jashimuddin, M. Modeling land use change using Cellular Automata and Artificial Neural Network: The case of Chunati Wildlife Sanctuary, Bangladesh. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Zheng, X.; Fu, M. Scenario analysis of sustainable intensive land use based on SD model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, M.R. Forecasting land-use changes in Mashhad Metropolitan area using Cellular Automata and Markov chain model for 2016–2030. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.J. Deriving suitability factors for CA-Markov land use simulation model based on local historical data. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Jia, K.; Wu, Y. Simulating urban land use change by incorporating an autologistic regression model into a CLUE-S model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, F.E.; Podestá, G.P.; Rovere, S.L.; Menéndez, Á.N.; North, M.; Tatara, E.; Laciana, C.E.; Weber, E.; Toranzo, F.R. An agent based model to simulate structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the argentine pampas. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3486–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Land use/land cover prediction and analysis of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under different scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Nie, J.; Zhou, L.; Chang, Q.; Cao, J. How to Simulate Carbon Sequestration Potential of Forest Vegetation? A Forest Carbon Sequestration Model across a Typical Mountain City in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S. Modeling terrestrial ecosystem productivity of an estuarine ecosystem in the Sundarban Biosphere Region, India using seven ecosystem models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 356, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; He, H.; Peng, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Gu, F.; Zhu, G.; Peng, C.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; et al. A Process-Based Model Integrating Remote Sensing Data for Evaluating Ecosystem Services. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2020MS002451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A new approach to modeling the sediment retention service (InVEST 3.0): Case study of the Cape Fear catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, L.; Boeni, A.F.; Prohászka, V.J.; Szilágyi, A.; Tormáné Kovács, E.; Pásztor, L.; Centeri, C. InVEST Soil Carbon Stock Modelling of Agricultural Landscapes as an Ecosystem Service Indicator. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, C.; Zang, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Carbon storage simulation and analysis in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on CA-plus model under dual-carbon background. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2173661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Assessing the potential impacts of urban expansion on regional carbon storage by linking the LUSD-urban and InVEST models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, Z.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, P.; Fang, S. Assessing the effects of ecological engineering on carbon storage by linking the CA-Markov and InVEST models. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, T.; Guo, X.; Xia, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, C. Plus-InVEST Study of the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration’s Land-Use Change and Carbon Storage. Land 2022, 11, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Prediction of Carbon Storage in Guilin Based on FLUS and InVEST Models. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, A.; Wei, E.; Hu, C. Carbon Storage Simulation and Land Use Optimization for High-Water-Table Resource-Based Cities Based on the Coupled GMOP-PLUS-InVEST Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Wei, F.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Z.; Lv, S.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Tang, Y. Prediction of Land Use Change and Carbon Storage in Lijiang River Basin Based on InVEST-PLUS Model and SSP-RCP Scenario. Land 2025, 14, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, T.; Song, J.; Halik, Ü.; Betz, F.; Yusup, A. Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales. Land 2024, 13, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. Sustainable management of land use patterns and water allocation for coordinated multidimensional development. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 457, 142412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Fan, K.; Shen, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J. Dynamic vulnerability of ecological systems to climate changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, P.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Yang, L. Mapping Chinese land system types from the perspectives of land use and management, biodiversity conservation and cultural landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Duan, H.; Liao, J.; Song, X.; Xue, X. Land use in the Gan-Lin-Gao region of middle reaches of Heihe River Basin based on a PLUS-SD coupling model. Arid. Zone Res. 2022, 39, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, D.A.; Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Romero, G.Q.; Sobral-Souza, T.; Cardinale, B.J.; Kratina, P.; Perkins, D.M.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Jeppesen, E.; Heino, J.; et al. Human pressure drives biodiversity–multifunctionality relationships in large Neotropical wetlands. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Luo, Y. Gridded datasets for population and economy under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways for 2020–2100. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 18, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, K. Provincial and gridded population projection for China under shared socioeconomic pathways from 2010 to 2100. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Yamaji, K.; Fujino, J. Evaluation of bioenergy resources with a global land use and energy model formulated with SD technique. Appl. Energy 1999, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebs, T.; Brandenburg, M.; Seuring, S. System dynamics modeling for sustainable supply chain management: A literature review and systems thinking approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Long, Y. Projecting 1 km-grid population distributions from 2020 to 2100 globally under shared socioeconomic pathways. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutale, B.; Qiang, F. Modeling future land use and land cover under different scenarios using patch-generating land use simulation model. A case study of Ndola district. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1362666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, K.; Sharifi, A. Balancing priorities for a sustainable future in cities: Land use change and urban ecosystem service dynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 382, 125460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, G.H.; Xu, Z.R. The Ecosystem Carbon Storage Dataset in Tibet (2001–2010). J. Glob. Change Data Discov. 2018, 2, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, Z.; Feng, W.; Yuxin, C.; Keyu, Q. Coupling coordination degree spatial analysis and driving factor between socio-economic and eco-environment in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Dong, B.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X. The spatiotemporal evolution and scenario prediction of carbon storage in typical wetlands in the Poyang Lake region. Water Soil Conserv. Bull. 2023, 43, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Response and multi-scenario prediction of carbon storage to land use/cover change in the main urban area of Chongqing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, B.; Han, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, W.; Liu, X.; Benson, D. Dynamic Simulation of Land Use and Habitat Quality Assessment in Baiyangdian Basin Using the SD-PLUS Coupled Model. Water 2024, 16, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Ji, G.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, M. Spatial and Temporal Variability Characteristics of Future Carbon Stocks in Anhui Province under Different SSP Scenarios Based on PLUS and InVEST Models. Land 2023, 12, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xia, J.; Ou, D.; Tian, Z.; Gao, X. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes and Carbon Storage Prediction Coupled with the SD-PLUS-InVEST Model: A Case Study of the Tuojiang River Basin, China. Land 2024, 13, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; He, J.; Tian, X.; Hou, P.; Wu, L.; Guan, D.; Wang, T.; Huang, S. Analysis of Evolving Carbon Stock Trends and Influencing Factors in Chongqing under Future Scenarios. Land 2024, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
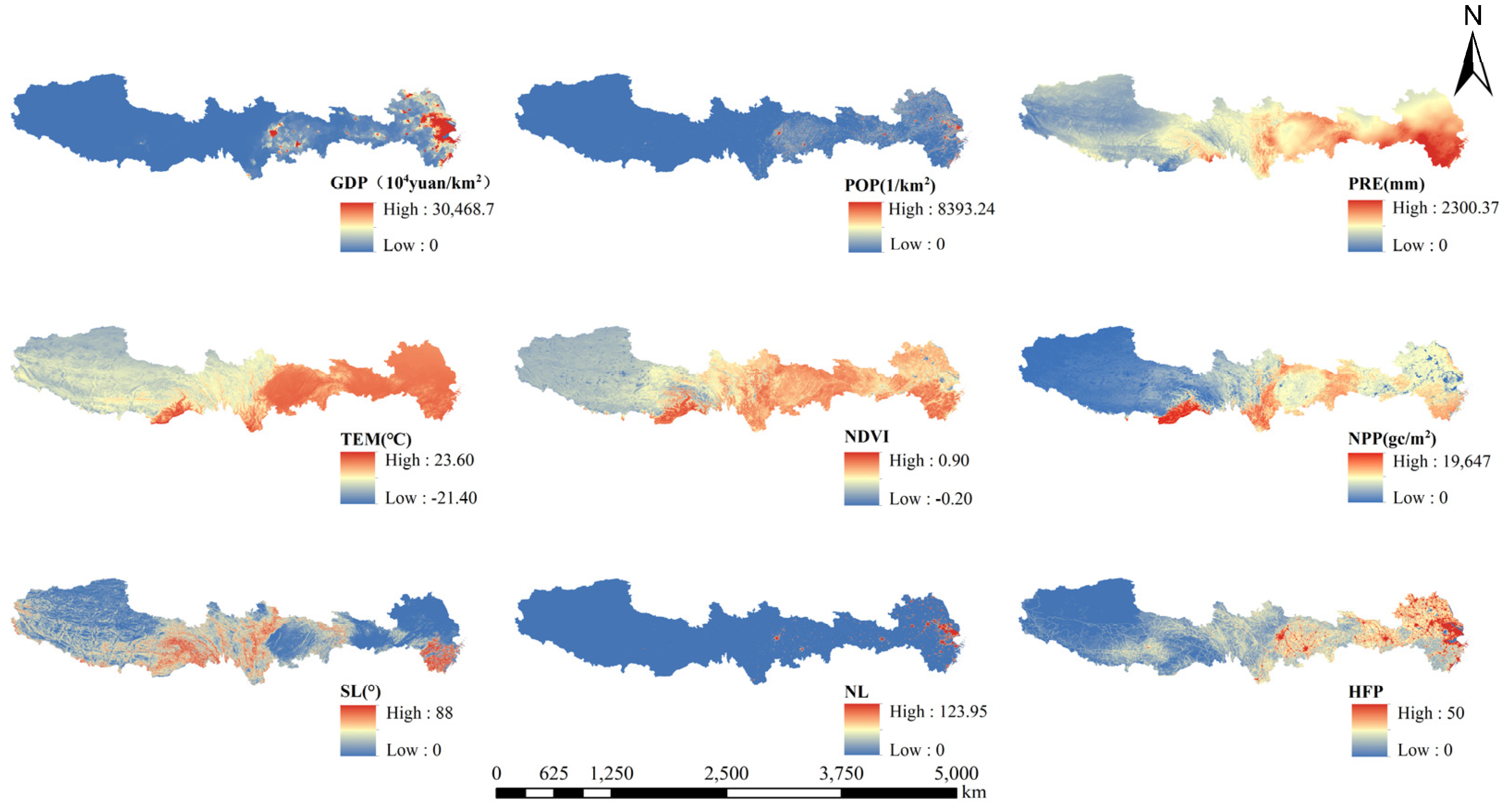

| Data Category | Temporal Coverage | Resolution | Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLCD | 2000, 2010, 2020 | 30 m | Zenodo Platform (https://zenodo.org/record/8176941) (accessed on 24 September 2024) |
| GDP distribution Population (POP) Temperature (TEM) Precipitation (PRE) Net Primary Productivity (NPP) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | 2010 | 1 km | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/) (accessed on 8 March 2025) |
| Nighttime light (NL) | 2010 | 500 m | AI Earth (https://engine-aiearth.aliyun.com/) (accessed on 7 March 2025) |
| Elevation Slope (SL) | 2020 | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) (accessed on 7 March 2025) |
| Human Footprint maps (HFP) | 2009 | 1 km | [38] |
| Future Population Future GDP | 2021–2030 | — 1 | [39] |
| Future urbanization rate | 2021–2030 | — | [40] |
| Future Temperature Future Precipitation | 2021–2030 | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Science Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/) (accessed on 20 January 2025) |
| Type of Coordination | Dysfunctional Recession | Break-in Transition | Coordinated Development | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordination index interval | [0, 0.2) | [0.2, 0.4) | [0.4, 0.6) | [0.6, 0.8) | [0.8, 0.9) | [0.9, 1] |
| Classification | Serious imbalance | Mild imbalance | Near imbalance | Basic coordination | Good coordination | Quality coordination |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, X.; Wang, Q.; Meng, F.; Liu, P.; Huang, L.; Zhuo, W. Assessing the Land Use-Carbon Storage Nexus Along G318: A Coupled SD-PLUS-InVEST Model Approach for Spatiotemporal Coordination Optimization. Land 2025, 14, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102067
Xing X, Wang Q, Meng F, Liu P, Huang L, Zhuo W. Assessing the Land Use-Carbon Storage Nexus Along G318: A Coupled SD-PLUS-InVEST Model Approach for Spatiotemporal Coordination Optimization. Land. 2025; 14(10):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102067
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Xiaotian, Qi Wang, Fei Meng, Pudong Liu, Li Huang, and Wei Zhuo. 2025. "Assessing the Land Use-Carbon Storage Nexus Along G318: A Coupled SD-PLUS-InVEST Model Approach for Spatiotemporal Coordination Optimization" Land 14, no. 10: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102067
APA StyleXing, X., Wang, Q., Meng, F., Liu, P., Huang, L., & Zhuo, W. (2025). Assessing the Land Use-Carbon Storage Nexus Along G318: A Coupled SD-PLUS-InVEST Model Approach for Spatiotemporal Coordination Optimization. Land, 14(10), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102067






