Assessing Variations in River Networks Under Urbanization Across Metropolitan Plains Using a Multi-Metric Approach
Abstract
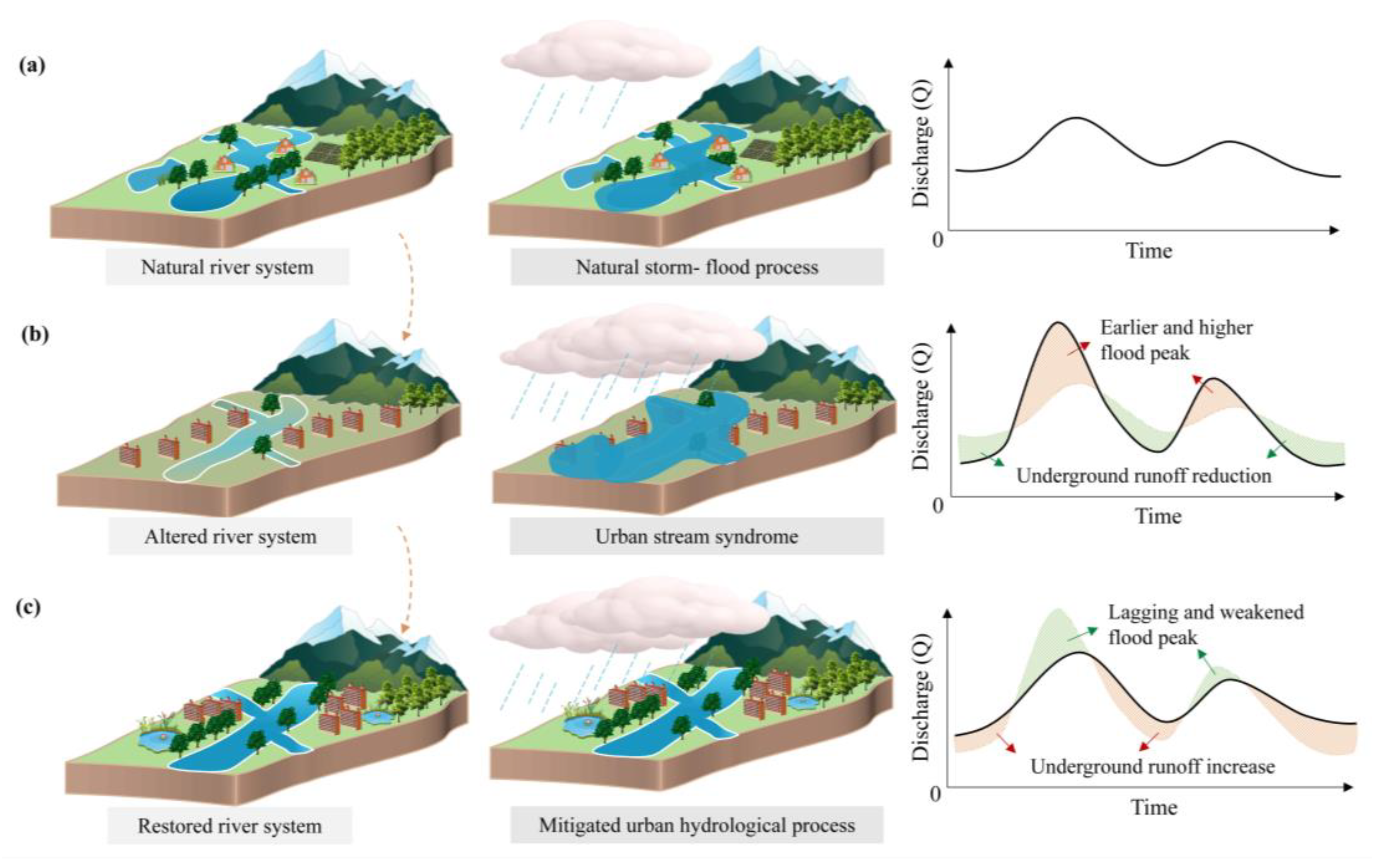
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
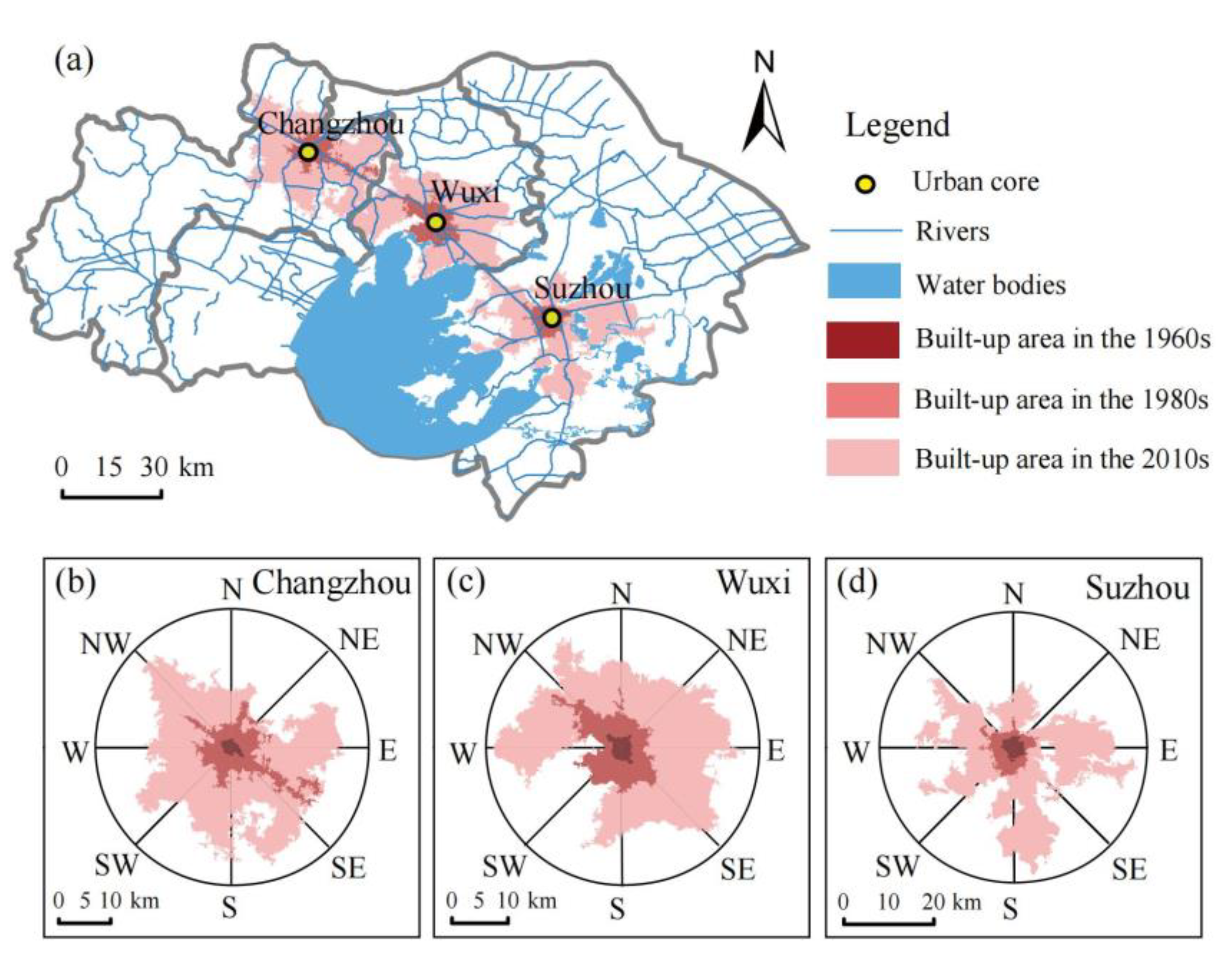
2.1. Study Area
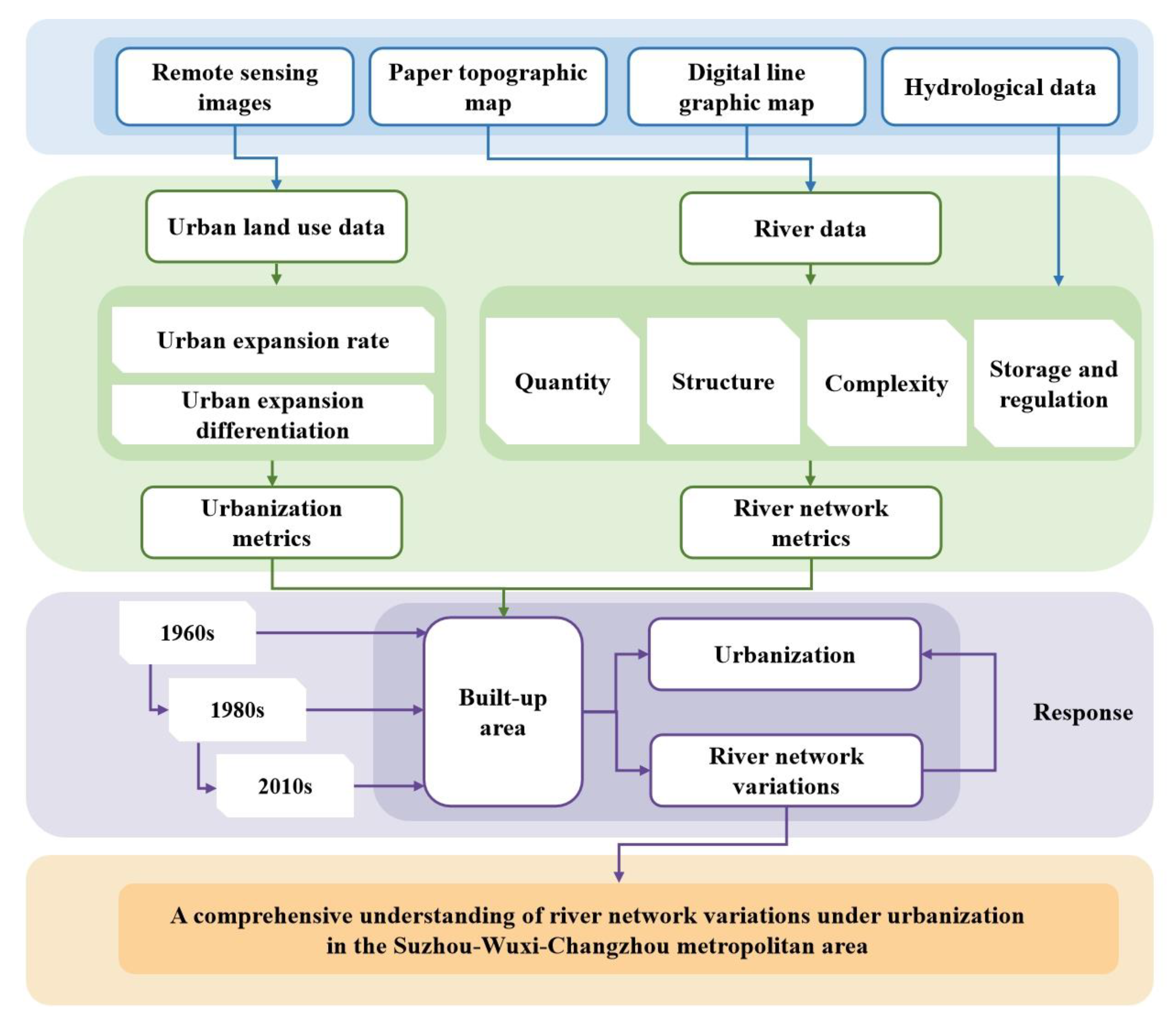
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Data Acquisition and Preparation
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Measuring Urbanization
- (1)
- Urban expansion rate (UER)
- (2)
- Urban expansion differentiation (UED)
2.4.2. Assessing Variations in the River Network
Quantity Characteristics
- (1)
- River density (Rd)
- (2)
- Proportion of water surface (Wp)
Structure Characteristics
- (1)
- Area-length ratio of main rivers (RAL)
- (2)
- Tributary development coefficient (K)
Complexity Characteristics
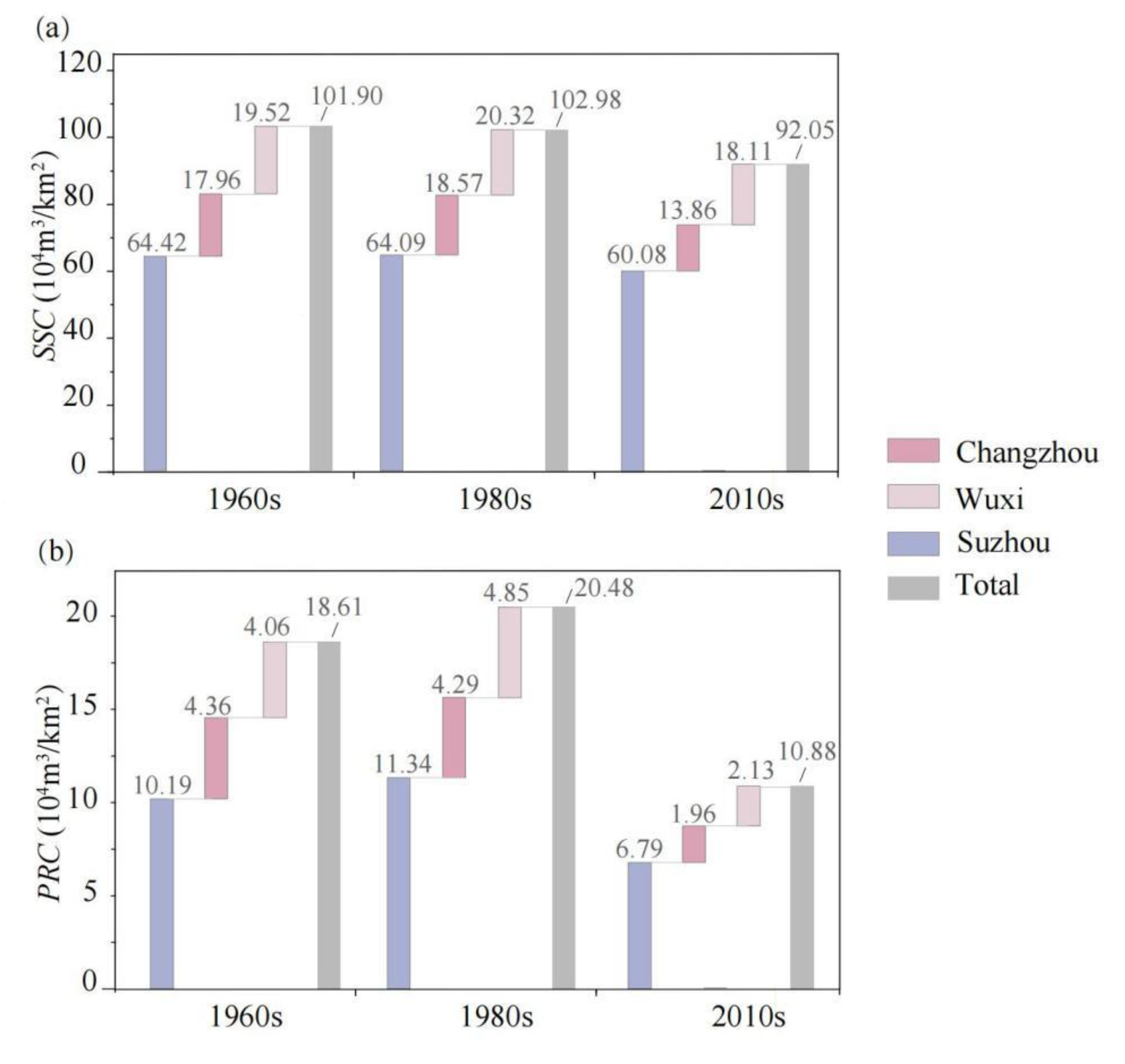
Storage and Regulation Characteristics
- (1)
- Static Storage Capacity (SSC)
- (2)
- Potential regulation capacity (PRC)
3. Results
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Urban Expansion
3.2. Multi-Dimensional Variations in River Networks
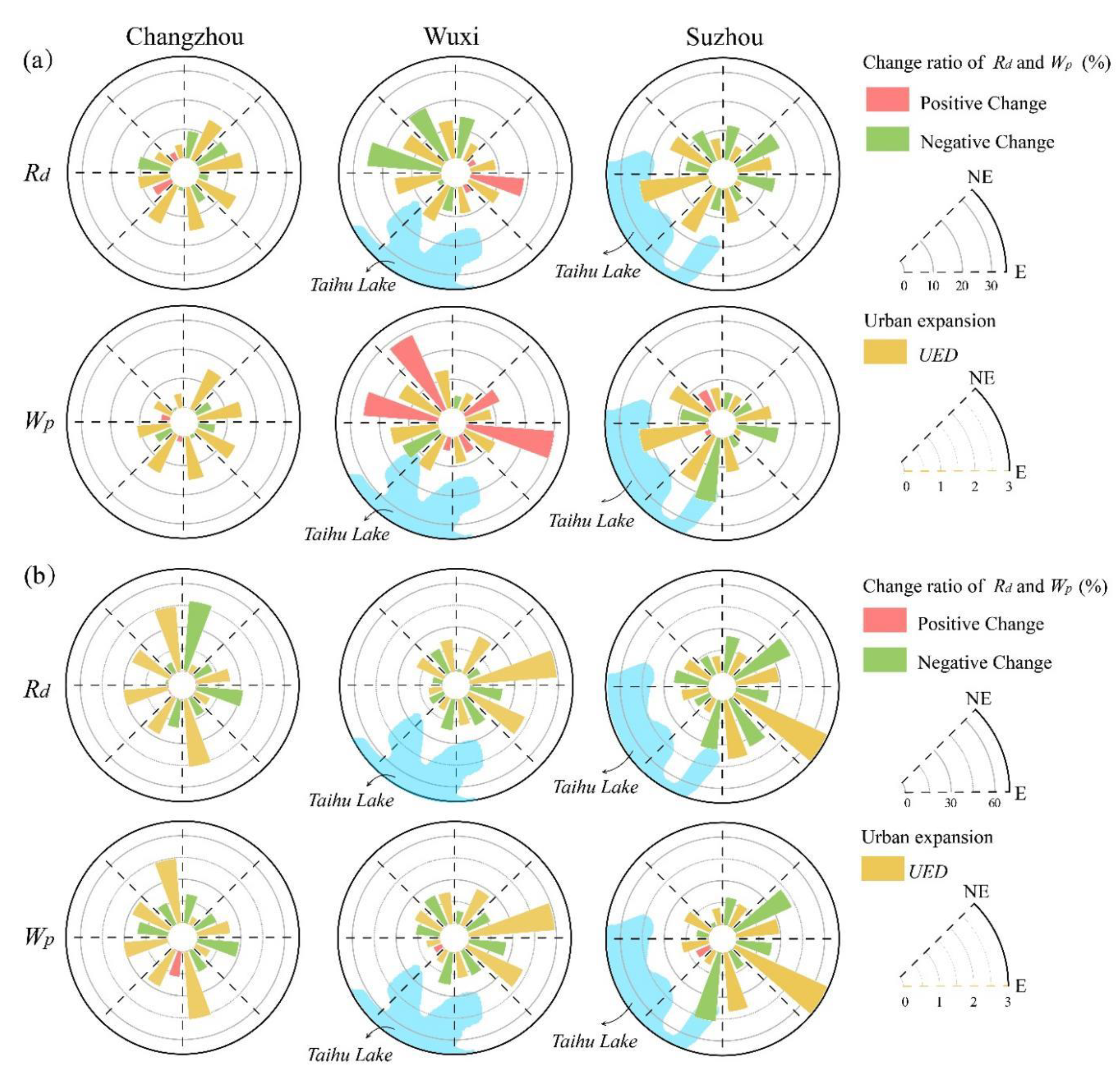
3.3. Responses of River Networks to Urbanization
4. Discussion
4.1. Common Simplification in River Networks Across Metropolitan Areas
4.2. Impacts of Local Urbanization on River Network Variations
4.3. Implications for Sustainable Urban-River System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, G.; Garbutt, R.; Kijas, J.; Pelizzon, A.; Page, J.; Wessell, A.; Parker, F.B.; Reichelt-Brushett, A. Speaking with the river: Confluence and interdisciplinarity in rivers and river systems. Environ. Plan. Nat. Space 2023, 11, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1952, 63, 1117–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.H.; Xu, J.; Fan, C.Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Wang, S.D.; Chen, X.B.; Song, L.J.; Song, C.Q. Remote sensing reconstruction of long-term water level and storage variations of a poorly-gauged river in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 40, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A. Urban transformation of river landscapes in a global context. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 460–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P. Towards a sociogeomorphology of rivers. Geomorphology 2015, 251, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.W.; Park, Y.; Park, S.R. Enhancing Stream Ecosystems Through Riparian Vegetation Management. Land 2025, 14, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J.; Xu, Y.P.; Han, L.F.; Song, S.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.F. Impacts of urbanization on river systems in the Taihu Region, China. Water 2015, 7, 1340–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.P.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xiang, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y. Impact of rapid urbanization on river system in a river network plain. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, T.; Hauer, C.; Schmid, M.; Stöglehner, G.; Stumpp, C.; Ertl, T.; Graf, W.; Habersack, H.; Haidvogl, G.; Hood-Novotny, R.; et al. The coupled socio-ecohydrological evolution of river systems: Towards an integrative perspective of river systems in the 21st century. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, J.P.; Wilgruber, N.A.; de Beurs, K.M.; Mayer, P.M.; Jawarneh, R.N. Long-term impacts of land cover changes on stream channel loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 537, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzoli, I.; Montanari, A.; Ceola, S. Influence of urban areas on surface water loss in the contiguous United States. AGU Adv. 2022, 3, e2021AV000519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottero, E.; Larcher, F.; Cassatella, C. Defining and regulating peri-urban areas through a landscape planning approach: The case study of Turin Metropolitan Area (Italy). Land 2023, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsukushima, R.; Ohtsuki, K. A century of stream burial due to urbanization in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y. Evolution of river network due to urbanization in the Southeast Yinzhou Plain of Yongjiang River Basin, China. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 379, 134718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M.; Moggridge, H.L. Rediscovering the value of urban rivers. Urban Ecosyst. 2012, 15, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreve, R.L. Variation of mainstream length with basin area in river networks. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Q.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, J.; Qian, G.R. Changes in reticular river network under rapid urbanization: A case of Pudong New Area, Shanghai. Water 2022, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Li, F.W.; Zhao, Y. Structural characteristics of the river network and its functional responses in the Haihe River basin based on small-world networks. Adv. Water Sci. 2023, 34, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Lan, G.; Ou, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.P.; Xia, J. Impact of urbanization on the spatial and temporal evolution of the water system pattern: A study of the Wuhan metropolitan area in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Deng, X.J. The response of river network structure to urbanization: A multifractal perspective. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 221, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedd, R.; Anandhi, A. Land use changes in the southeastern United States: Quantitative changes, drivers, and expected environmental impacts. Land 2022, 11, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.J.; Chin, A. Evaluation of the imprint of urban channel variation and enlargement. Geogr. J. 2018, 184, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, H. An integrated approach to investigate the coupling coordination between urbanization and flood disasters in China. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 375, 134191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.H.; Quan, Q.; Yang, S.M.; Dong, Y.X. A social-ecological coupling model for evaluating the human-water relationship in basins within the Budyko framework. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Lane, S.N.; Wilcox, A.C. The science and practice of river restoration. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5974–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.M. Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Ma, R.Q.; Cui, L.B.; Tang, G.; Ma, Z.J. Exploring the impacts of energy and environmental constraints on China’s urbanization process. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.X.; Zhang, K.R.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, W.Y. Spatial and temporal differentiation and influencing factors of environmental governance performance in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Threshold and resilience management of coupled urbanization and water environmental system in the rapidly changing coastal region. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.S.; Guan, X.L.; He, C.; Zhang, J.L. Spatio-temporal patterns and policy implications of urban land expansion in metropolitan areas: A case study of Wuhan urban agglomeration, central China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 4723–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, K.; Tang, M.; Xu, Q.X. Stream structure characteristics and their impact on storage and flood control capacity in the urbanized plain river network. Geogr. Res. 2005, 24, 717–724. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.H.; Zhao, H. The fractal dimension of river network and its interpretation. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1996, 16, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.J.; Xu, Y.P. Degrading flood regulation function of river systems in the urbanization process. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Dallaire, C.O.; Chouinard, E.F.; Sindorf, N.; Lehner, B. Development of new indicators to evaluate river fragmentation and flow regulation at large scales: A case study for the Mekong River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Wu, L. Changes in river networks and their storage and regulation capacities in the rapidly urbanized Taihu Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Xue, D. The morphological evolution of river and water body in urban area of Guangzhou City in 1990–2010. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Xue, L.F.; Yu, H.X.; Meng, Y.Y. Change of steam structure in the Nansi Lake Basin during the urbanization process since 1980s. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napieralski, J.A.; Welsh, E.S. A century of stream burial in Michigan (USA) cities. J. Maps 2016, 12, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.K.; Heffernan, J.B. Morphological characteristics of urban water bodies: Mechanisms of change and implications for ecosystem function. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napieralski, J.A.; Carvalhaes, T. Urban stream deserts: Mapping a legacy of urbanization in the United States. Appl Geogr. 2016, 67, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sear, D.A.; Newson, M.D. Environmental change in river channels: A neglected element. Towards geomorphological typologies, standards and monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 310, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, U.; Maheshwari, B.L. River health assessment in peri-urban landscapes: An application of multivariate analysis to identify the key variables. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3915–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, S.J.; Taylor, M.P. Why rehabilitate urban river systems? Area 2006, 38, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.A.; Marcus, W.A. The human role in changing fluvial systems: Retrospect, inventory and prospect. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, C.; Wang, S.; Yao, Y. Analysis of streamflow variations in the Heihe River Basin, northwest China: Trends, abrupt changes, driving factors and ecological influences. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 3, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullos, D.; Baker, D.W.; Crowe Curran, J.; Schwar, M.; Schwartz, J. Enhancing resilience of river restoration design in systems undergoing change. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 147, 03121001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zheng, B.H. The relationship between the change of water system and the urban land expansion in Changsha. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1429–14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.P.; Lin, Z.X.; Yu, Z.H. Identifying changes in flood characteristics and their causes from an event-based perspective in the Central Taihu Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranmer, A.W.; Caamaño, D.; Arteaga, A.E. Urban stream syndrome: Quantifying topographic variation along an urban-rural gradient. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G.; Lespez, L.; Sear, D.A.; Macaire, J.J.; Houben, P.; Klimek, K.; Brazier, R.E.; Van-Oost, K.; Pears, B. Natural vs anthropogenic streams in Europe: History, ecology and implications for restoration, river-rewilding and riverine ecosystem services. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 180, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.; Hall, J.W. Designing green infrastructure and sustainable drainage systems in urban development to achieve multiple ecosystem benefits. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Tan, L. Blue-green infrastructure for flood and water quality management in Southeast Asia: Evidence and knowledge gaps. Environ. Manag. 2022, 69, 699–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Stead, D. Governing resilience planning: Organizational structures, institutional rules, and fiscal incentives in Guangzhou. Land 2023, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Direction | Period 1 (1960s–1980s) | Period 2 (1980s–2010s) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UER (km2/a) | UED | UER (km2/a) | UED | |||||||||
| CZ | WX | SZ | CZ | WX | SZ | CZ | WX | SZ | CZ | WX | SZ | |
| N-NE | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.21 | 1.31 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.94 | 2.77 | 1.69 | 0.28 | 1.19 | 0.73 |
| NE-E | 0.78 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 1.32 | 0.75 | 1.05 | 3.37 | 5.01 | 4.25 | 1.00 | 2.55 | 1.26 |
| E-SE | 1.92 | 0.72 | 0.10 | 1.26 | 0.98 | 0.22 | 4.11 | 4.83 | 4.93 | 0.50 | 1.81 | 2.97 |
| SE-S | 0.59 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 5.09 | 3.03 | 6.19 | 1.99 | 0.77 | 1.73 |
| S-SW | 0.79 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 1.26 | 1.16 | 1.49 | 4.04 | 1.51 | 2.58 | 1.18 | 0.42 | 0.45 |
| SW-W | 0.72 | 0.89 | 0.54 | 0.97 | 1.42 | 2.04 | 4.17 | 1.34 | 3.35 | 1.32 | 0.42 | 0.80 |
| W-NW | 0.72 | 1.36 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 1.34 | 1.31 | 4.02 | 4.29 | 4.81 | 1.22 | 0.88 | 0.84 |
| NW-N | 0.39 | 1.08 | 0.25 | 0.44 | 1.15 | 0.65 | 3.54 | 3.75 | 1.29 | 1.91 | 0.95 | 0.51 |
| Average | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.41 | 1.05 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 3.66 | 3.32 | 3.64 | 1.18 | 1.12 | 1.16 |
| Metrics | Phase | CZ | WX | SZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | River density (Rd)/(km·km−2) | 1960s | 2.55 | 2.38 | 3.17 |
| 1980s | 2.44 | 2.21 | 3.02 | ||
| 2010s | 1.58 | 1.64 | 2.63 | ||
| Proportion of water surface (Wp)/% | 1960s | 5.61 | 4.62 | 12.21 | |
| 1980s | 5.35 | 5.72 | 11.53 | ||
| 2010s | 3.91 | 3.88 | 9.60 | ||
| Structure | Area-length ratio of main rivers (RAL) | 1960s | 40.58 | 41.80 | 45.57 |
| 1980s | 38.53 | 44.22 | 47.43 | ||
| 2010s | 38.74 | 48.68 | 49.89 | ||
| Tributary development coefficient (K) | 1960s | 1.65 | 3.33 | 3.20 | |
| 1980s | 1.56 | 2.54 | 2.53 | ||
| 2010s | 0.99 | 2.09 | 2.06 | ||
| Complexity | Fractal dimension (D) | 1960s | 1.44 | 1.42 | 1.52 |
| 1980s | 1.43 | 1.44 | 1.50 | ||
| 2010s | 1.31 | 1.41 | 1.50 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Z.; Luo, S.; Lu, M.; Dai, S.; Xu, Y. Assessing Variations in River Networks Under Urbanization Across Metropolitan Plains Using a Multi-Metric Approach. Land 2025, 14, 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101994
Lin Z, Luo S, Lu M, Dai S, Xu Y. Assessing Variations in River Networks Under Urbanization Across Metropolitan Plains Using a Multi-Metric Approach. Land. 2025; 14(10):1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101994
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Zhixin, Shuang Luo, Miao Lu, Shaoqing Dai, and Youpeng Xu. 2025. "Assessing Variations in River Networks Under Urbanization Across Metropolitan Plains Using a Multi-Metric Approach" Land 14, no. 10: 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101994
APA StyleLin, Z., Luo, S., Lu, M., Dai, S., & Xu, Y. (2025). Assessing Variations in River Networks Under Urbanization Across Metropolitan Plains Using a Multi-Metric Approach. Land, 14(10), 1994. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101994







