Distribution Patterns of Sediment Organic Carbon Stocks in Shallow Lakes and the Significance for Sustainable Lake Management: Chaohu Lake in Eastern China as a Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Sample Processing Methods
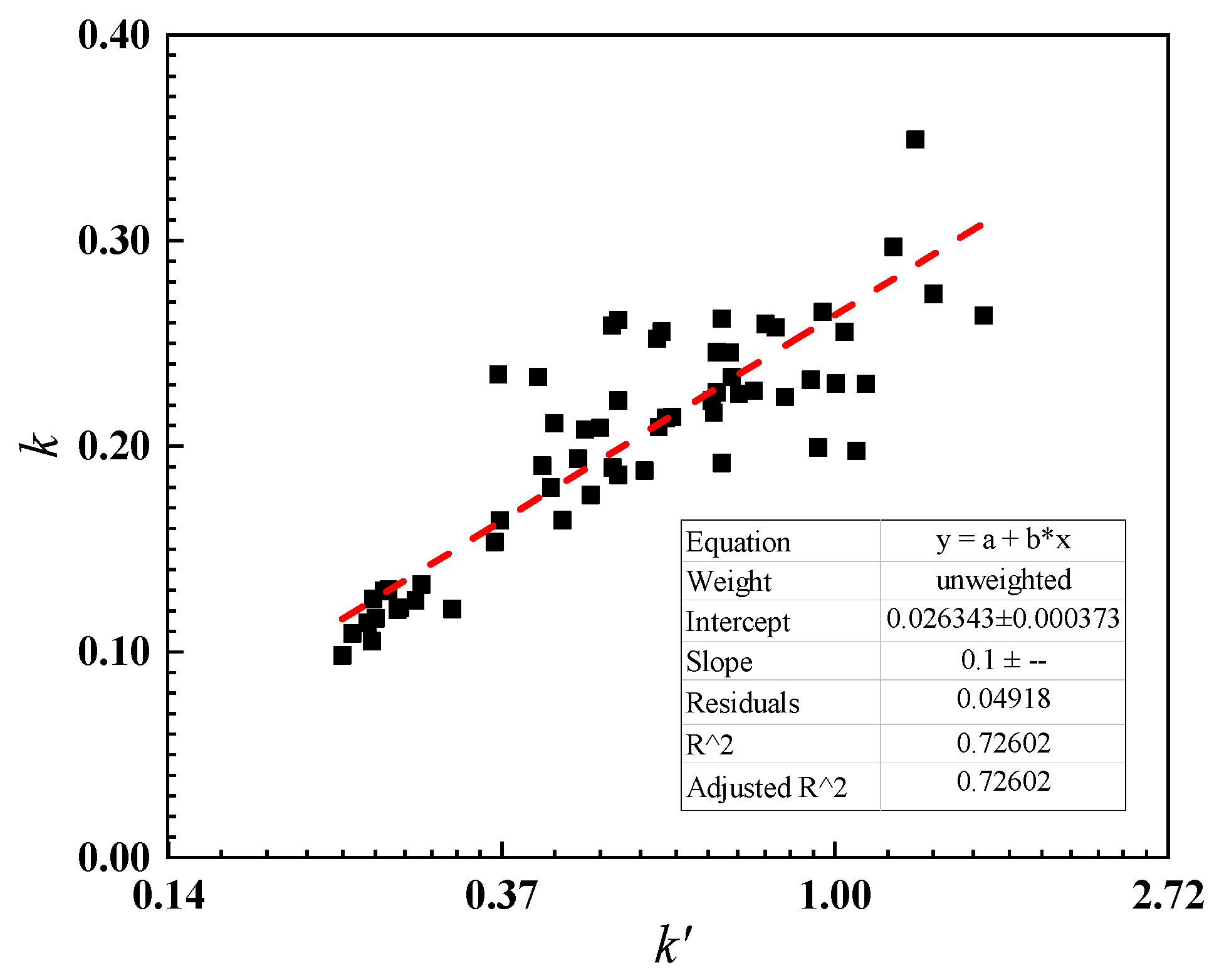
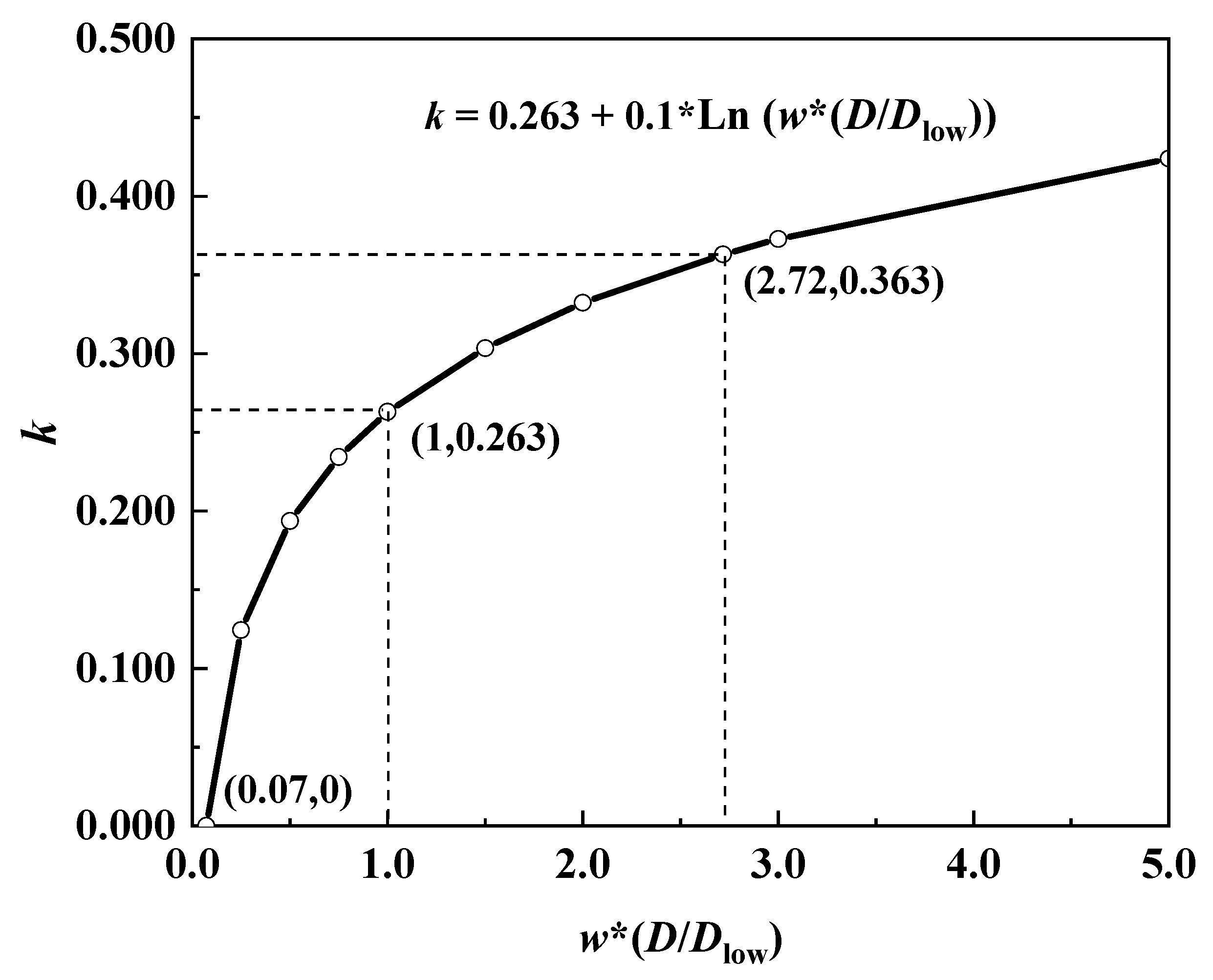
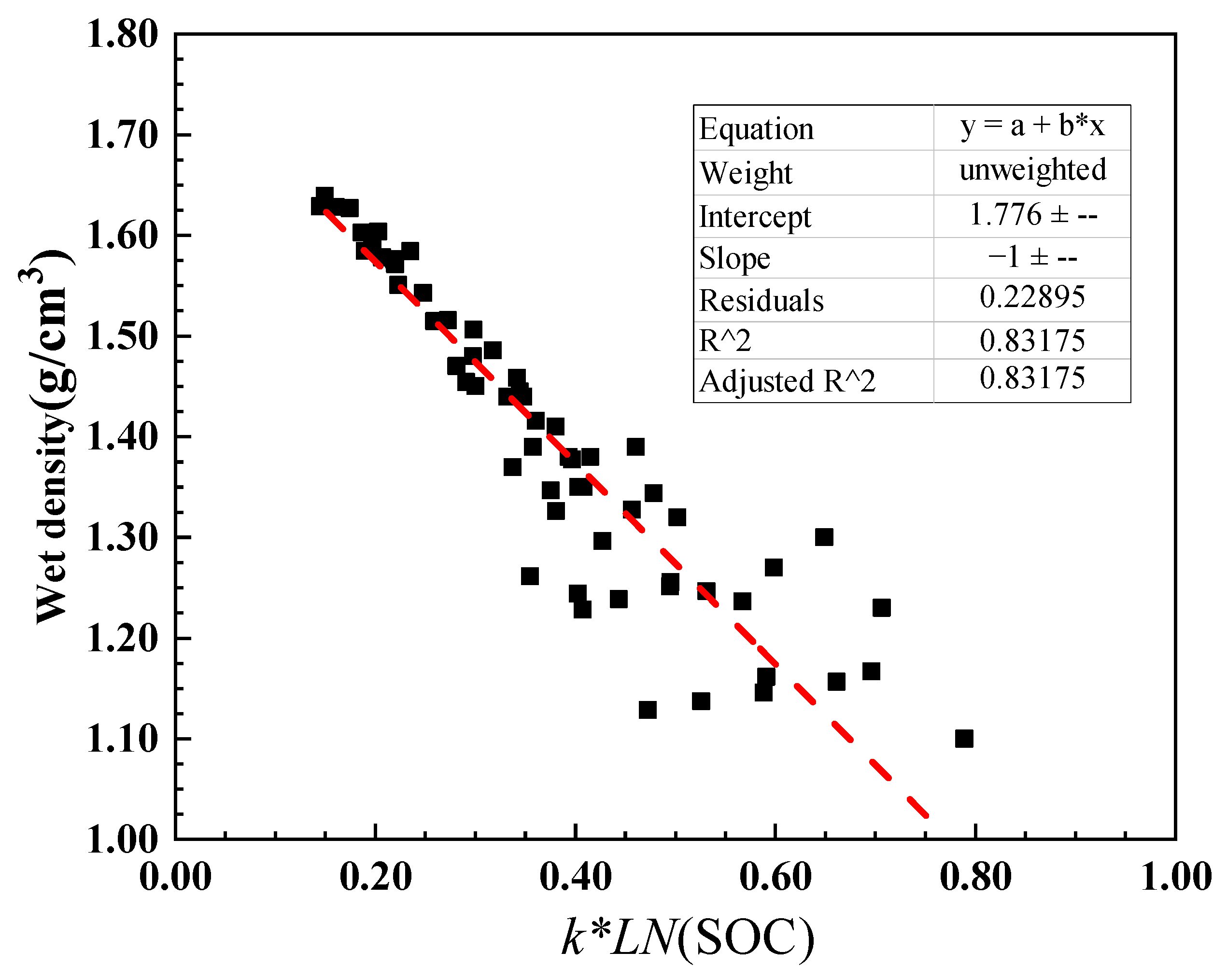
2.4. Mathematical Fitting of SOC Content
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Depth Distribution
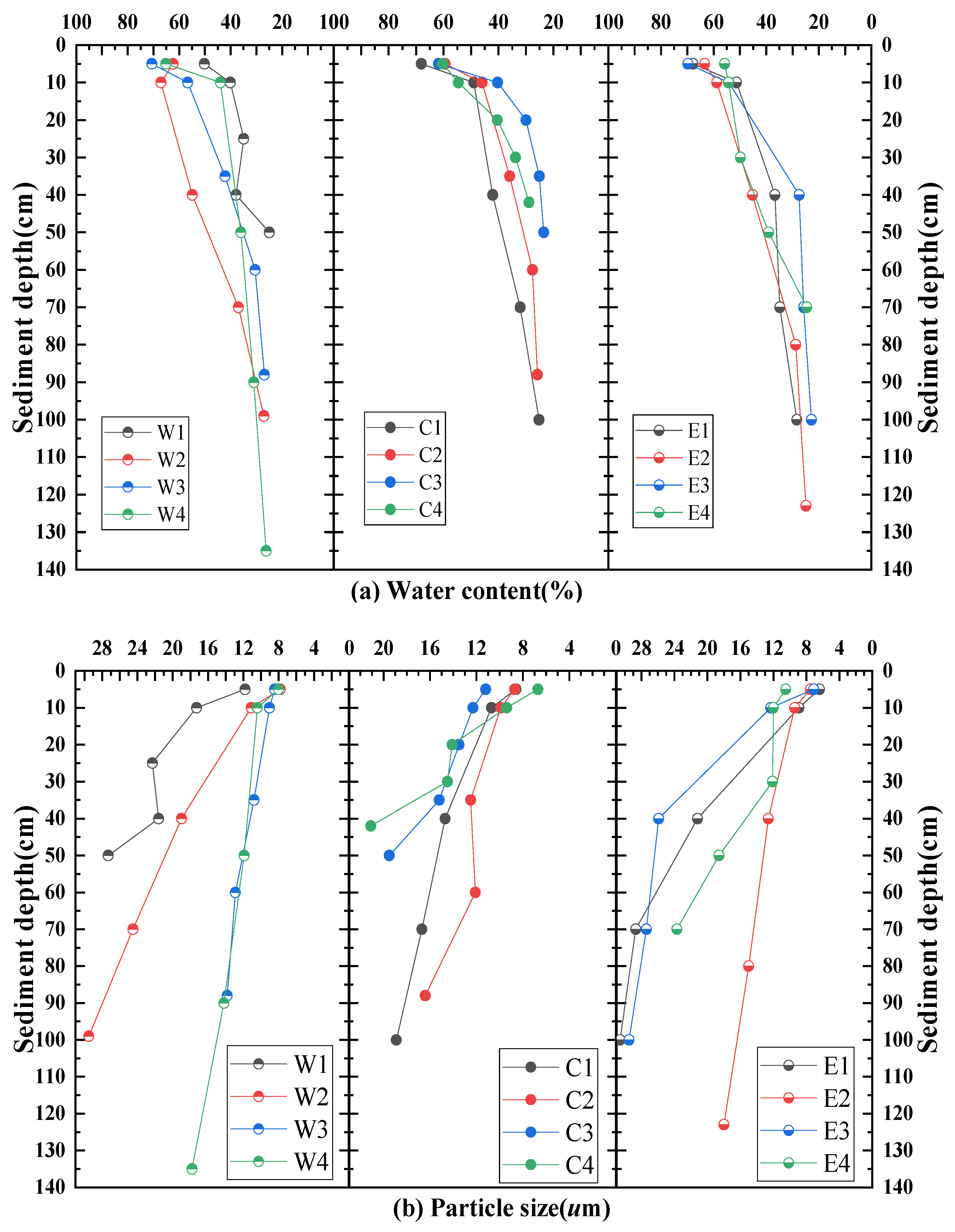
3.2. Wet Density, Water Content, and Particle Size Distribution
3.2.1. Vertical Distribution Pattern of Sediment Wet Density
3.2.2. Distribution Pattern of Water Content and Particle Size
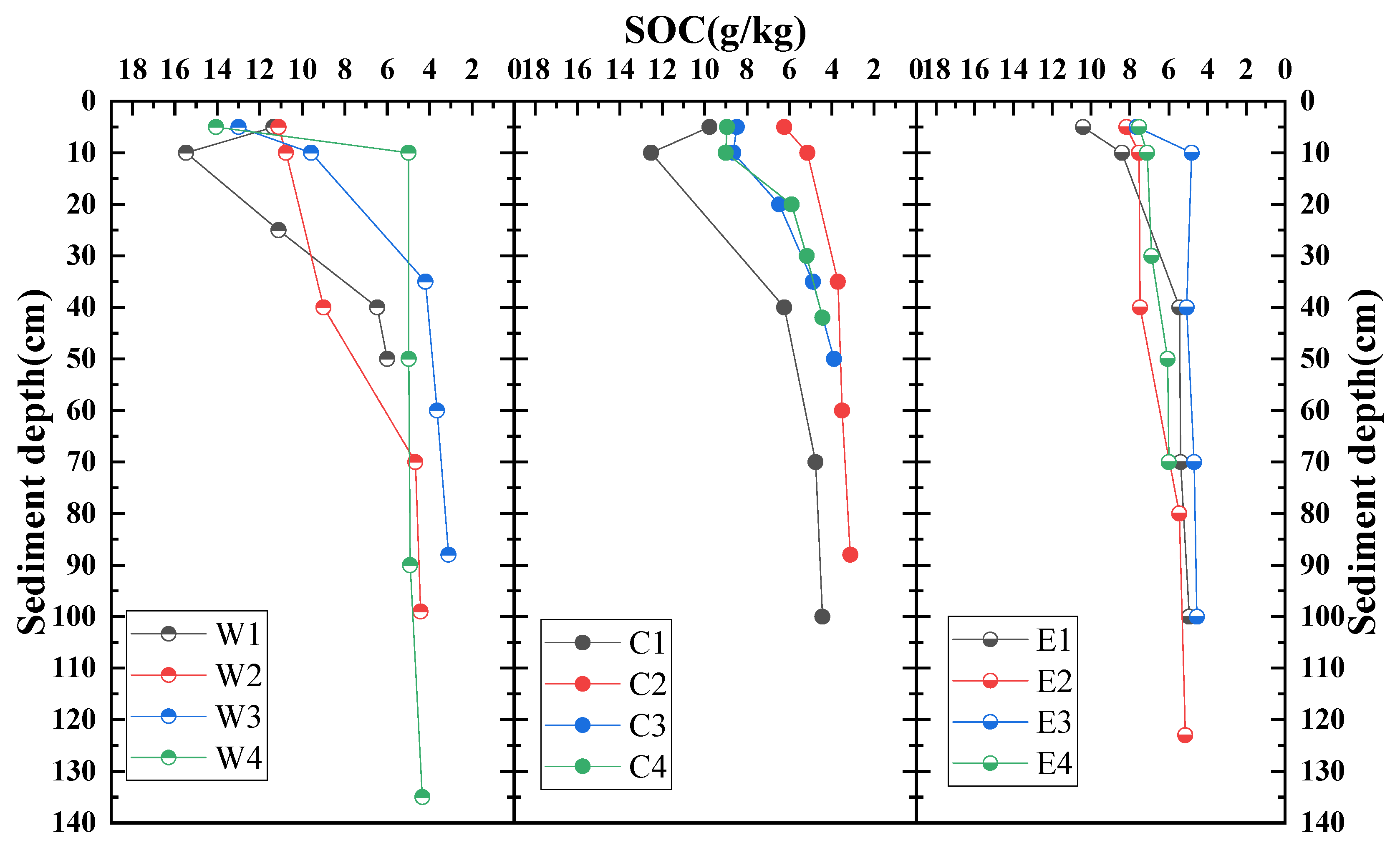
3.3. Distribution of Sediment Organic Carbon Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences from Existing Studies
4.2. Prediction of Release Potential of Sediments Organic Carbon
4.3. Implication for Sustainable Management of Lakes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastviken, D.; Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Crill, P.M.; Enrich-Prast, A. Freshwater methane emissions offset the continental carbon sink. Science 2011, 331, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, S.; Isidorova, A.; Sobek, S. Enhanced carbon loss from anoxic lake sediment through diffusion of dissolved organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeo. 2016, 121, 1959–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: Integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, M.; del Giorgio, P.; Gelinas, Y.; Lehmann, M. Benthic fluxes of dissolved organic nitrogen in the lower St. Lawrence estuary and implications for selective organic matter degradation. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7609–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhu, S.; Wu, S.; Dai, J. Comparing artificial intelligence techniques for chlorophyll-a prediction in US lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30524–30532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, T.S.; Cui, X.; Blair, N.E.; Burdige, D.J.; Eglinton, T.I.; Galy, V. Centers of organic carbon burial and oxidation at the land-ocean interface. Org. Geochem. 2018, 115, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Eglinton, T.I.; Zhang, J.; Montlucon, D.B. Spatiotemporal variation of the quality, origin, and age of particulate organic matter transported by the Yangtze River (Changjiang). J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeo. 2018, 123, 2908–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Malanson, G.P. Modeling impacts of erosion and deposition on soil organic carbon in the Big Creek Basin of southern Illinois. Geomorphology 2009, 106, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, M.; Xie, H.; Xia, N.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Mou, X.; Wen, J.; Bao, Y. Effect of water-sediment regulation of the Xiaolangdi reservoir on the concentrations, characteristics, and fluxes of suspended sediment and organic carbon in the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Deng, B.; Zhu, Z. Impact of extreme drought and the Three Gorges Dam on transport of particulate terrestrial organic carbon in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth 2011, 116, F04029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, B.A.; Ryan, J.N.; Aiken, G.R. Effects of iron on optical properties of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10098–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagai, R.; Mayer, L.M. Sorptive stabilization of organic matter in soils by hydrous iron oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.; Zak, D.; Biester, H.; Dittmar, T. Iron traps terrestrially derived dissolved organic matter at redox interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10101–10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Choi, J.H.; Hur, J. Benthic flux of dissolved organic matter from lake sediment at different redox conditions and the possible effects of biogeochemical processes. Water Res. 2014, 61, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, S.P.; Babiarz, C.L.; Hurley, J.P.; Armstrong, D.E. Influences of iron, manganese, and dissolved organic carbon on the hypolimnetic cycling of amended mercury. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadi, T.; Völkner, C.; Koschorreck, M. A sediment core incubation method to measure the flux of dissolved organic carbon between sediment and water. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr, K.H. DOC-dynamics in a small headwater catchment as driven by redox fluctuations and hydrological flow paths are DOC exports mediated by iron reduction/oxidation cycles? Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, A.C.; Arias-Esquivel, V.A. The effect of induced anoxia and reoxygenation on benthic fluxes of organic carbon, phosphate, iron, and manganese. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Yue, Y.; Lu, J.; Pang, L.; Zhu, S. Sediment phosphate release flux under hydraulic disturbances in the shallow lake of Chaohu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 60843–60851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplev, A.; Wakiyama, Y.; Wada, T.; Ivanov, M.; Komissarov, M.; Nanba, K. Reconstruction of time changes in radiocesium concentrations in the river of the Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP contaminated area based on its depth distribution in dam reservoir’s bottom sediments. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Yang, C.H.; Yin, H.B. Dynamics of phosphorus composition in suspended particulate matter from a turbid eutrophic shallow lake (Lake Chaohu, China): Implications for phosphorus cycling and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, L.; Thibodeaux, L.J. Kinetics of peat soil dissolved organic carbon release from bed sediment to water. Part 1. Laboratory simulation. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Bao, J.; Shan, M.; Qin, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. Dynamic changes of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) degradation and adsorption to biochar as affected by soil organic carbon content. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Lu, J.; Zhu, S.; Yue, Y.; Xiao, L. Investigation of the impact of hydrodynamic conditions on sediment resuspension in shallow lakes. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1676–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, K.; Shin-ichiro, O. Siltation and radiocesium pollution of small lakes in different catchment types far from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident site. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.Y.; Cui, L.P. Remote sensing monitoring and driving factor analysis of land use change in the Chaohu Lake Basin from 1962 to 2019. China Flood Drought Manag. 2024, 34, 55–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khim, B.K.; Jung, H.M.; Cheong, D. Recent variations in sediment organic carbon content in Lake Soyang(Korea). Limnology 2005, 6, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.L.; He, J. Organic carbon fractions and estimation of organic carbon storage in the lake sediments in Inner Mongolia Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Prevo, L. Production of dissolved organic carbon in aquatic sediment suspensions. Water Res. 2013, 37, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Feng, J.M.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Wang, X.Z. Composition, distribution, and source of organic carbon in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Ritvo, G.; Leon, E. Meijer, M.K. Water content, organic carbon and dry bulk density in flooded sediments. Aquacult. Eng. 2001, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Ma, T.; Chen, S.X. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of organic carbon in sediments of Tongshun River riparian zone. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Fang, H.W.; Huang, L.; Cui, Z.H. Particulate organic carbon dynamics with sediment transport in the upper Yangtze River. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.Q. On the horizontal distribution of algal-bloom in Chaohu Lake and its formation process. Acta Mech. Sin. 2014, 30, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.X. Advances and prospect in sediment-water interface of lakes: A review. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1191–1218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.F.; Kong, F.X. Diversity and Dynamics of Picocyanobacteria and the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria in a Large Shallow Eutrophic Lake (lake Chaohu, China). Limnology 2013, 72, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, B. Mechanisms of dissolved organic carbon adsorption on different typical soils in China. Soils 2017, 49, 314–320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- May, L.; Aura, C.M.; Becker, V.; Briddon, C.L.; Carvalho, L.R.; Dobel, A.J.; Jamwal, P.; Kamphuis, B.; Marinho, M.M.; McGowan, S.; et al. Getting into hot water: Water quality in tropical lakes in relation to their utilization. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 789, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Boithias, L.; Sauvage, S.; Merlina, G.; Jean, S.; Probst, J.; Perez, J.M.S. New insight into pesticide partition coefficient K-d for modelling pesticide fluvial transport: Application to an agricultural catchment in south-western France. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudasz, C.; Ruppenthal, M.; Kalbitz, K.; Cerli, C.; Fiedler, S.; Oelmann, Y.; Andersson, A.; Karlsson, J. Contributions of terrestrial organic carbon to northern lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2017, 2, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, A.M.; MacKenzie, R.A.; Giardina, C.P.; Bruland, G.L. Influence of declining mean annual rainfall on the behavior and yield of sediment and particulate organic carbon from tropical watersheds. Geomorphology 2018, 306, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Labzovskii, L. Challenging the land degradation in China’s Loess Plateau: Benefits, limitations, sustainability, and adaptive strategies of soil and water conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Lu, J. Inhibition of in situ coating of sediment ceramsite on sediment nutrient release of eutrophic lakes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 4, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
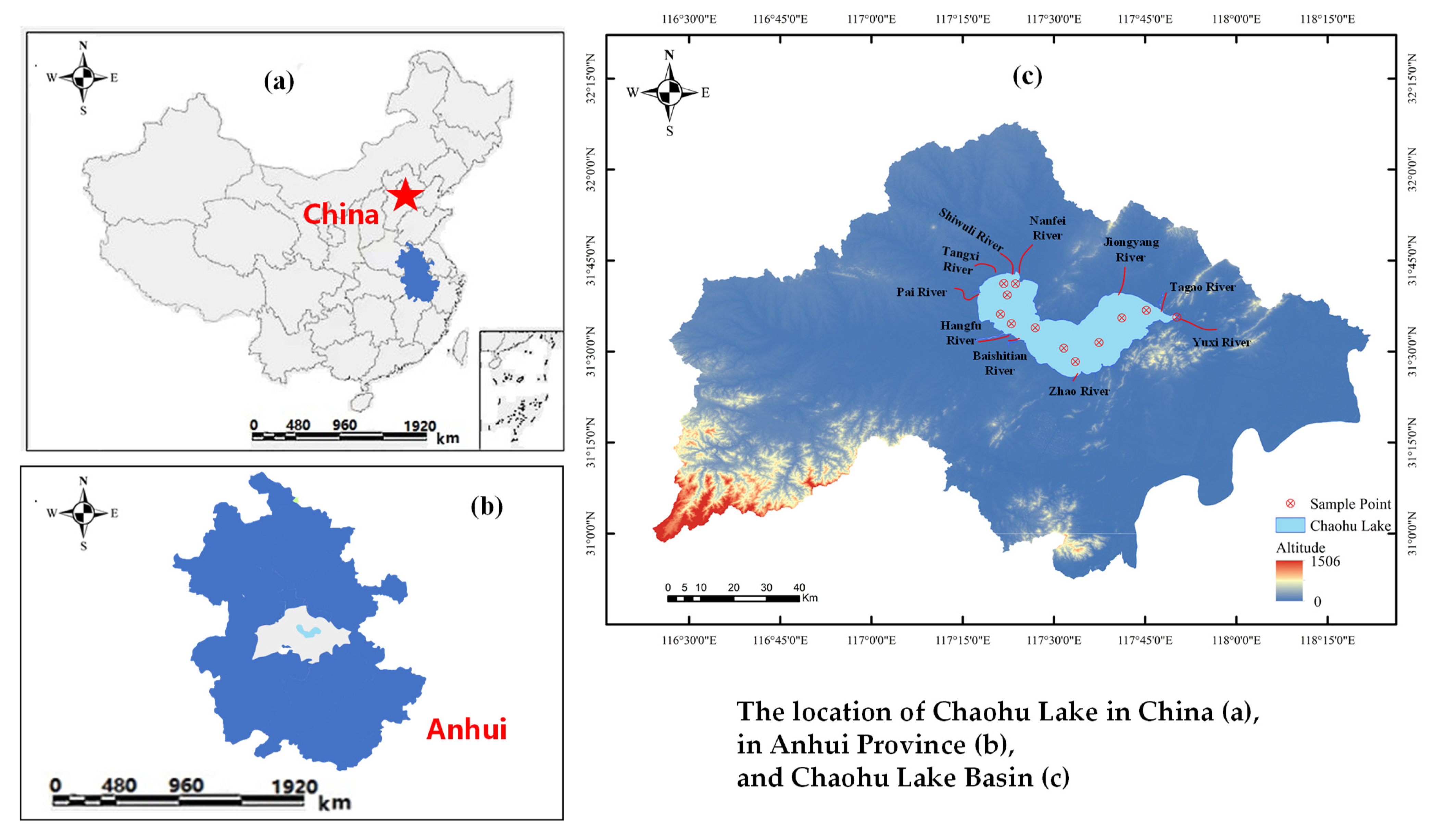
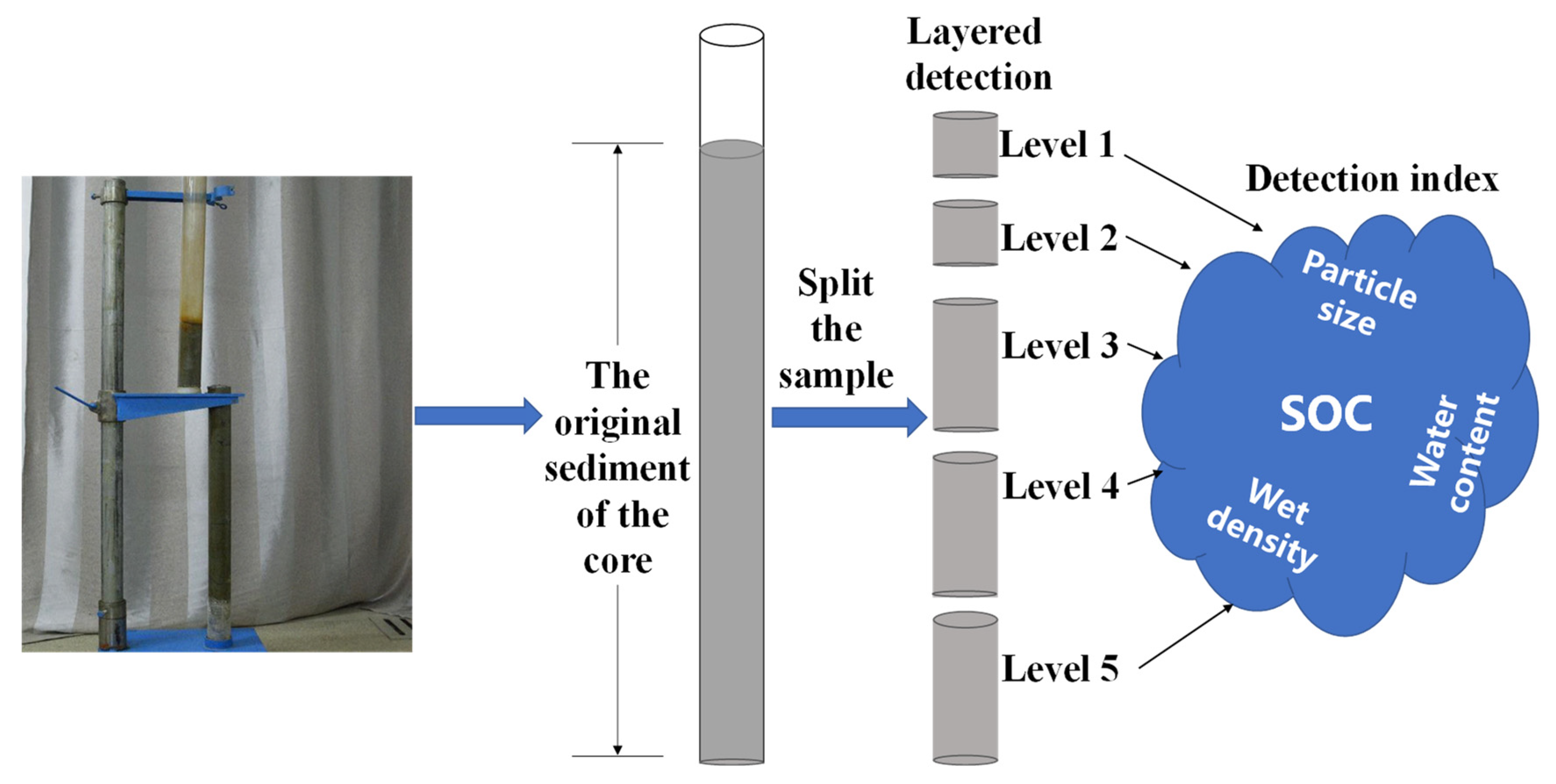
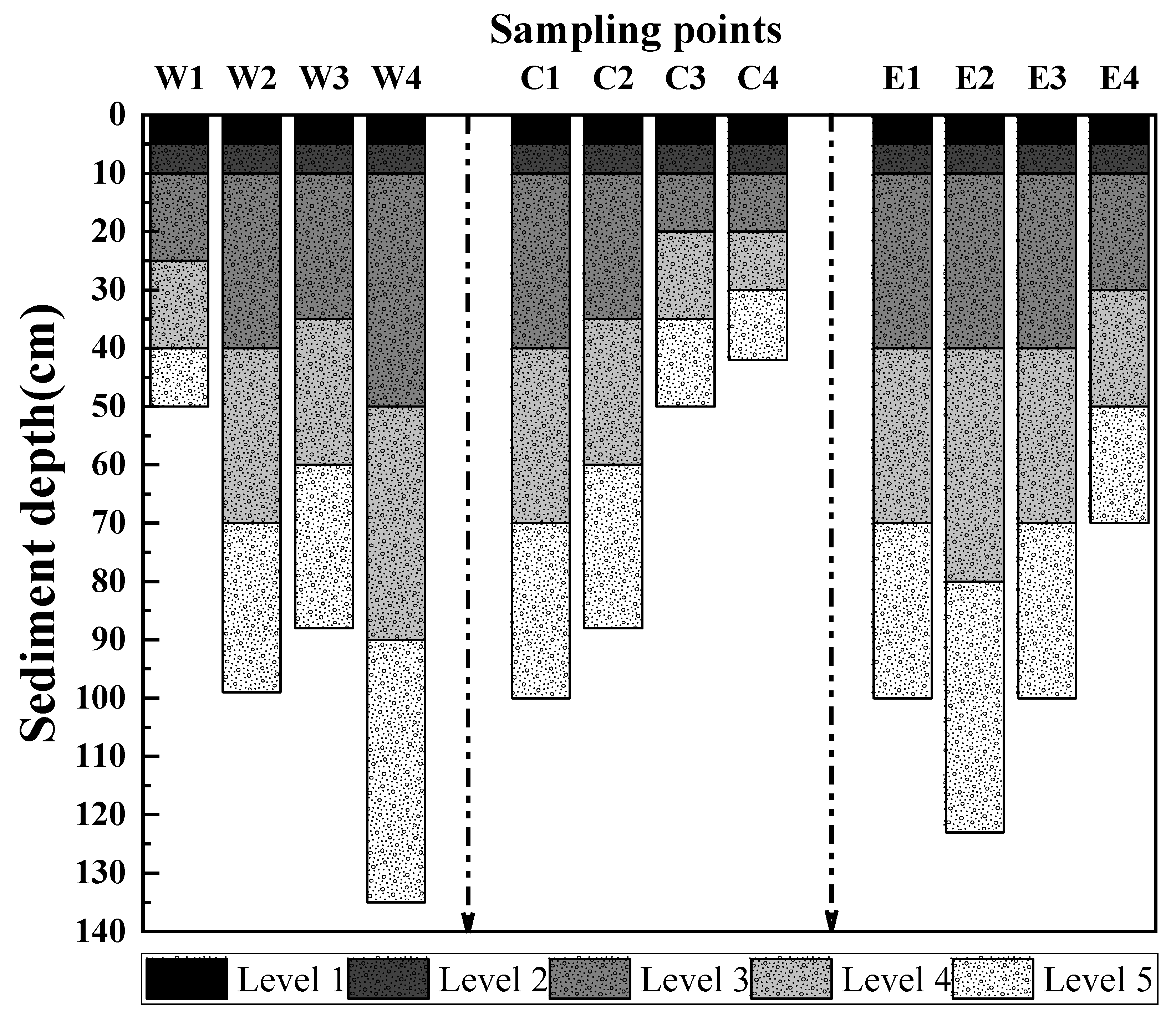
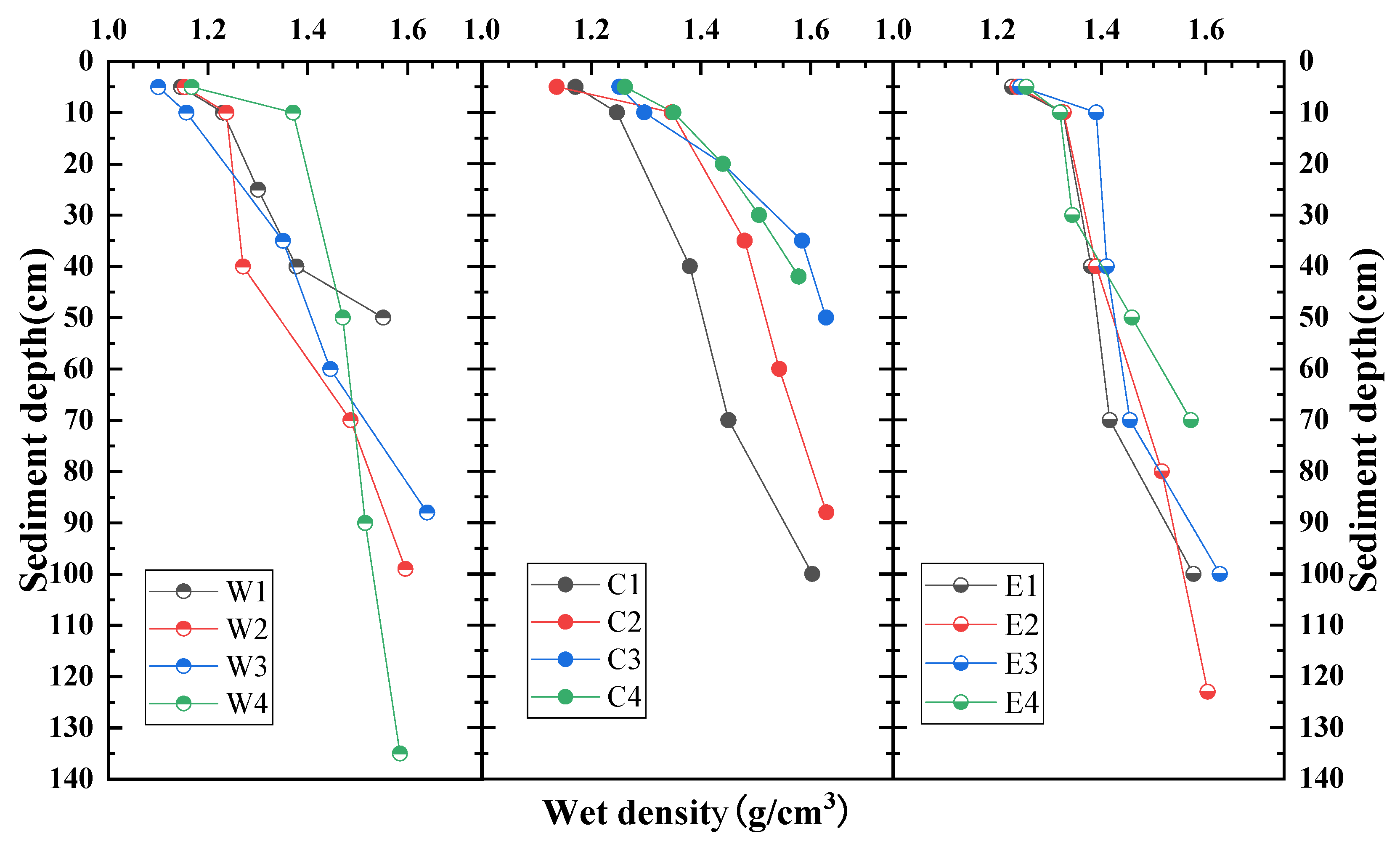
| Serial Number | Area | Sample Number | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Sediment Thickness (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Western | W1 | 31.7292 | 117.4065 | 50 |
| 2 | W2 | 31.7289 | 117.3795 | 99 | |
| 3 | W3 | 31.7083 | 117.3868 | 88 | |
| 4 | W4 | 31.6729 | 117.3700 | 135 | |
| 5 | Central | C1 | 31.6548 | 117.3955 | 100 |
| 6 | C2 | 31.6473 | 117.4524 | 88 | |
| 7 | C3 | 31.6078 | 117.5196 | 50 | |
| 8 | C4 | 31.5842 | 117.5466 | 42 | |
| 9 | Eastern | E1 | 31.6188 | 117.6038 | 100 |
| 10 | E2 | 31.6644 | 117.6615 | 123 | |
| 11 | E3 | 31.6798 | 117.7191 | 100 | |
| 12 | E4 | 31.6661 | 117.7881 | 70 |
| District | Area (km2) | Present | Saturation | Release Potential (104 t) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd (kg/m2) | TC (104 t) | Cd (kg/m2) | TC (104 t) | |||
| W | 190.79 | 1.34 | 25.61 | 0.99 | 18.98 | −6.63 |
| C | 293.80 | 1.08 | 31.66 | 1.13 | 33.26 | 1.59 |
| E | 284.96 | 0.99 | 28.31 | 1.05 | 30.04 | 1.73 |
| All | 769.55 | 1.14 | 85.58 | 1.06 | 82.28 | −3.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Pan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, S. Distribution Patterns of Sediment Organic Carbon Stocks in Shallow Lakes and the Significance for Sustainable Lake Management: Chaohu Lake in Eastern China as a Case Study. Land 2024, 13, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040507
Luo W, Pan Y, Fan Y, Lu J, Zhu S. Distribution Patterns of Sediment Organic Carbon Stocks in Shallow Lakes and the Significance for Sustainable Lake Management: Chaohu Lake in Eastern China as a Case Study. Land. 2024; 13(4):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wenguang, Yan Pan, Yangzhen Fan, Jing Lu, and Senlin Zhu. 2024. "Distribution Patterns of Sediment Organic Carbon Stocks in Shallow Lakes and the Significance for Sustainable Lake Management: Chaohu Lake in Eastern China as a Case Study" Land 13, no. 4: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040507
APA StyleLuo, W., Pan, Y., Fan, Y., Lu, J., & Zhu, S. (2024). Distribution Patterns of Sediment Organic Carbon Stocks in Shallow Lakes and the Significance for Sustainable Lake Management: Chaohu Lake in Eastern China as a Case Study. Land, 13(4), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040507








