Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Ecological Quality in the Tengger Desert (2001–2021)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
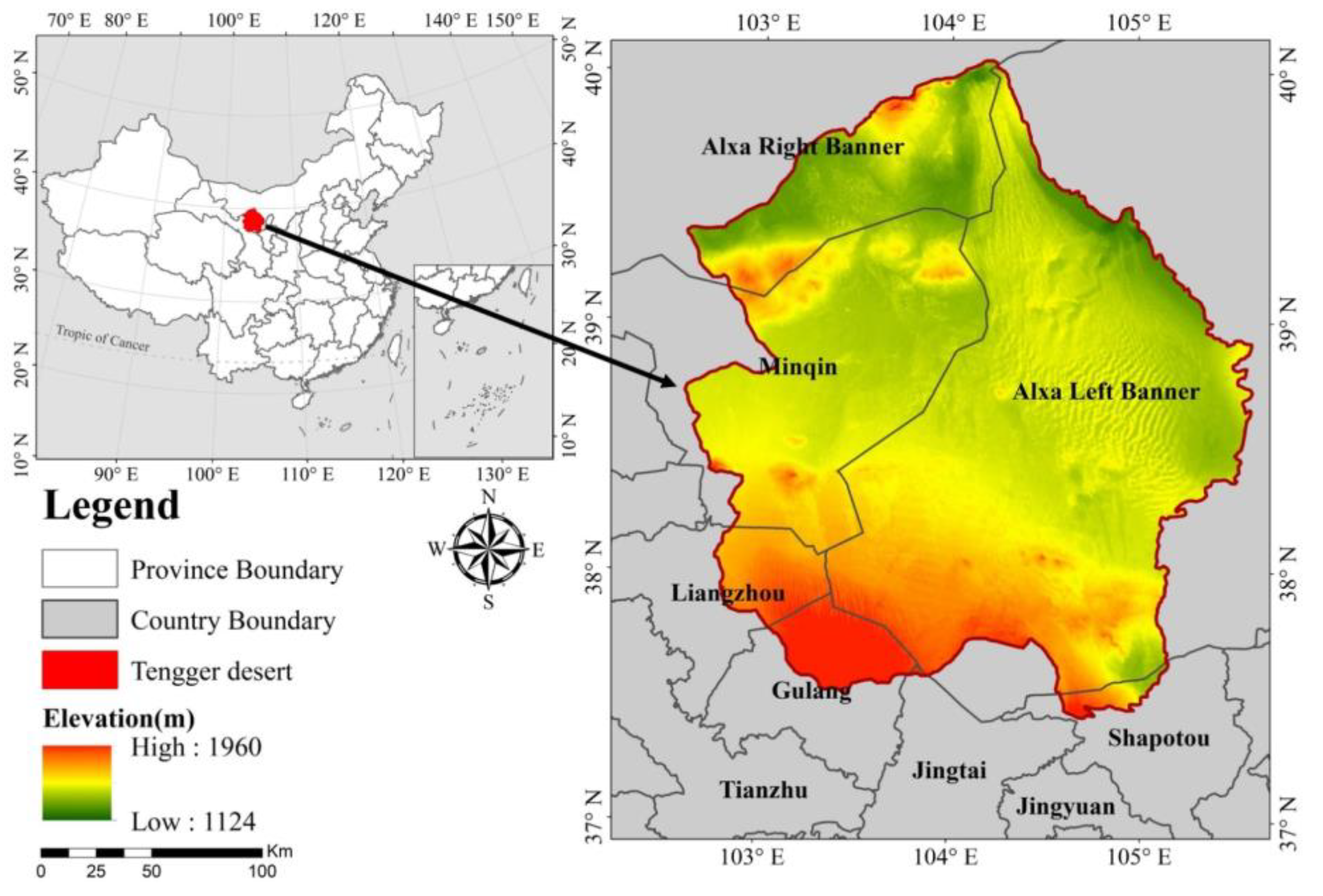
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Ecological Quality Data
2.2.2. Climate Data
2.2.3. Human, Topographic and Vector Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Theil–Sen Slope Estimation
2.3.2. Mann–Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.4. The Hurst Index
2.3.5. Geodetector
3. Results
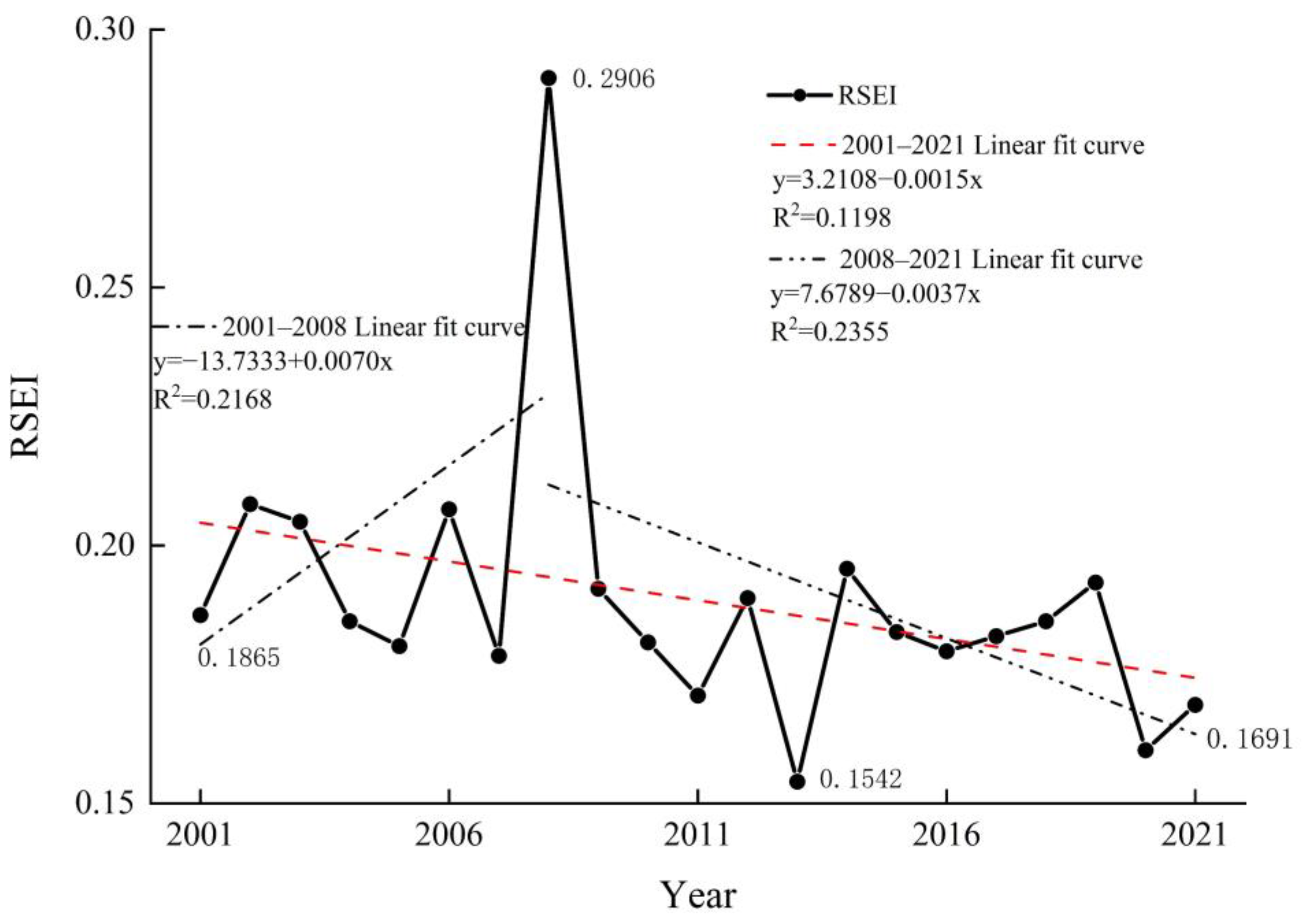
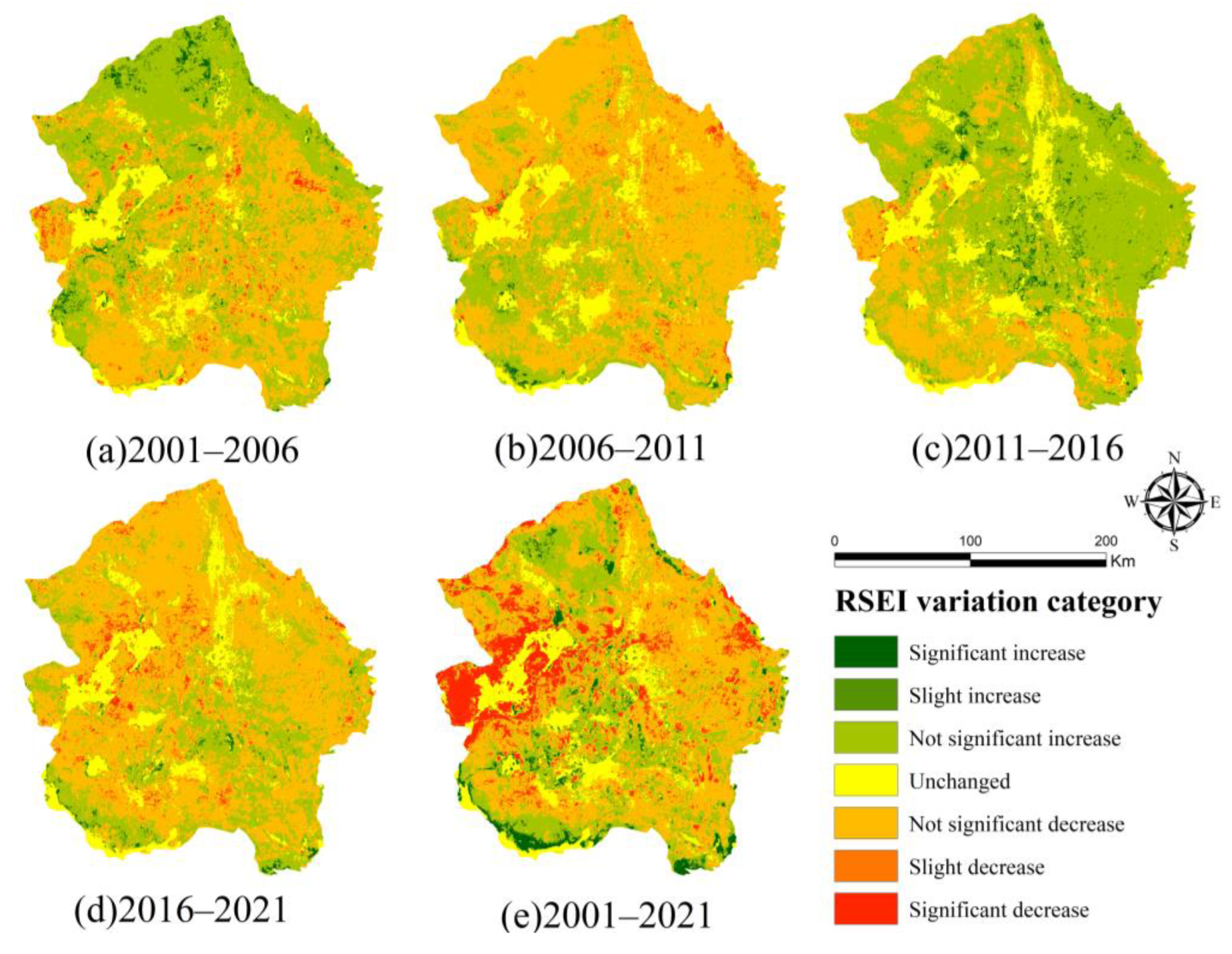
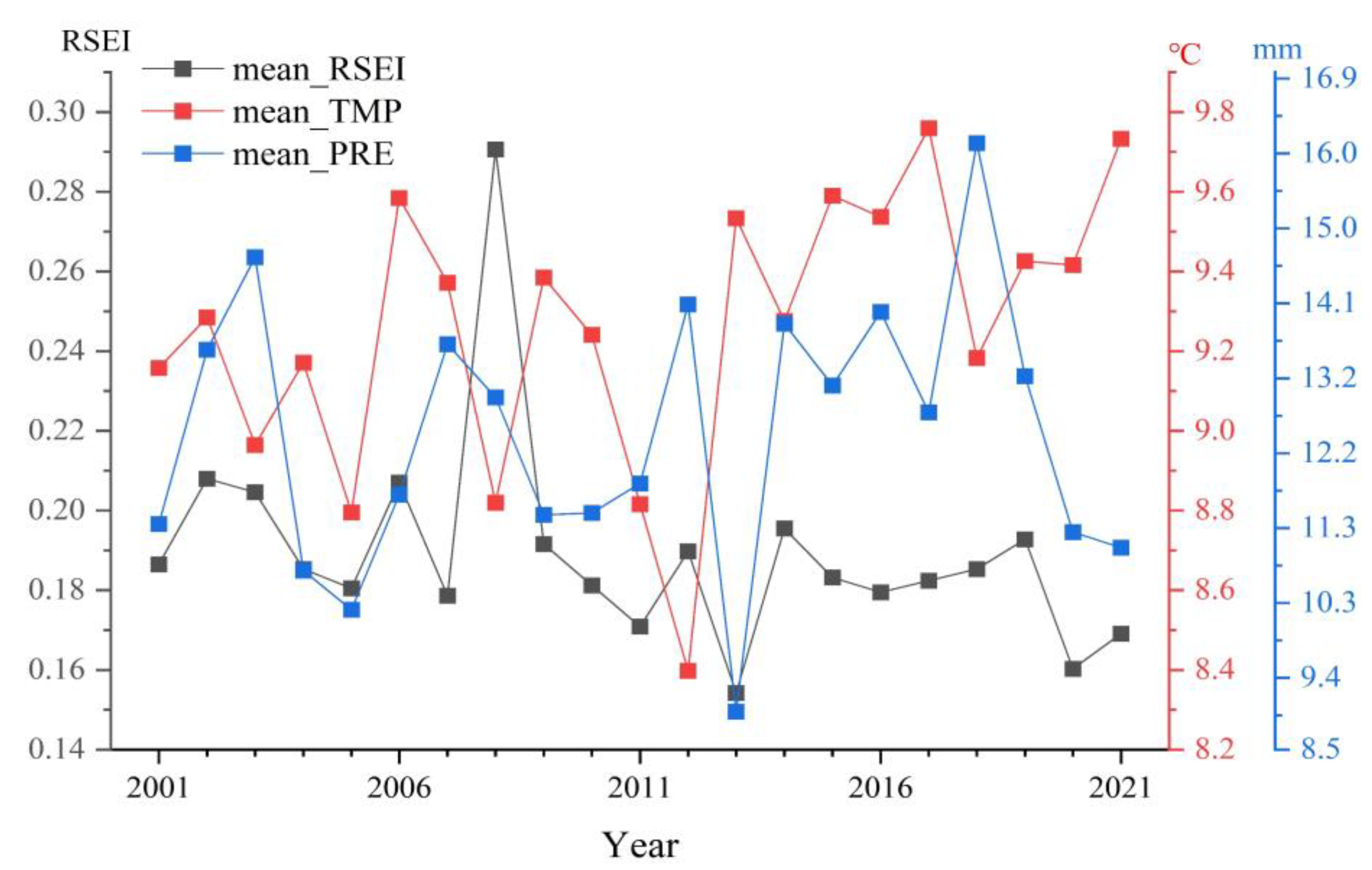
3.1. Dynamic Change of RSEI
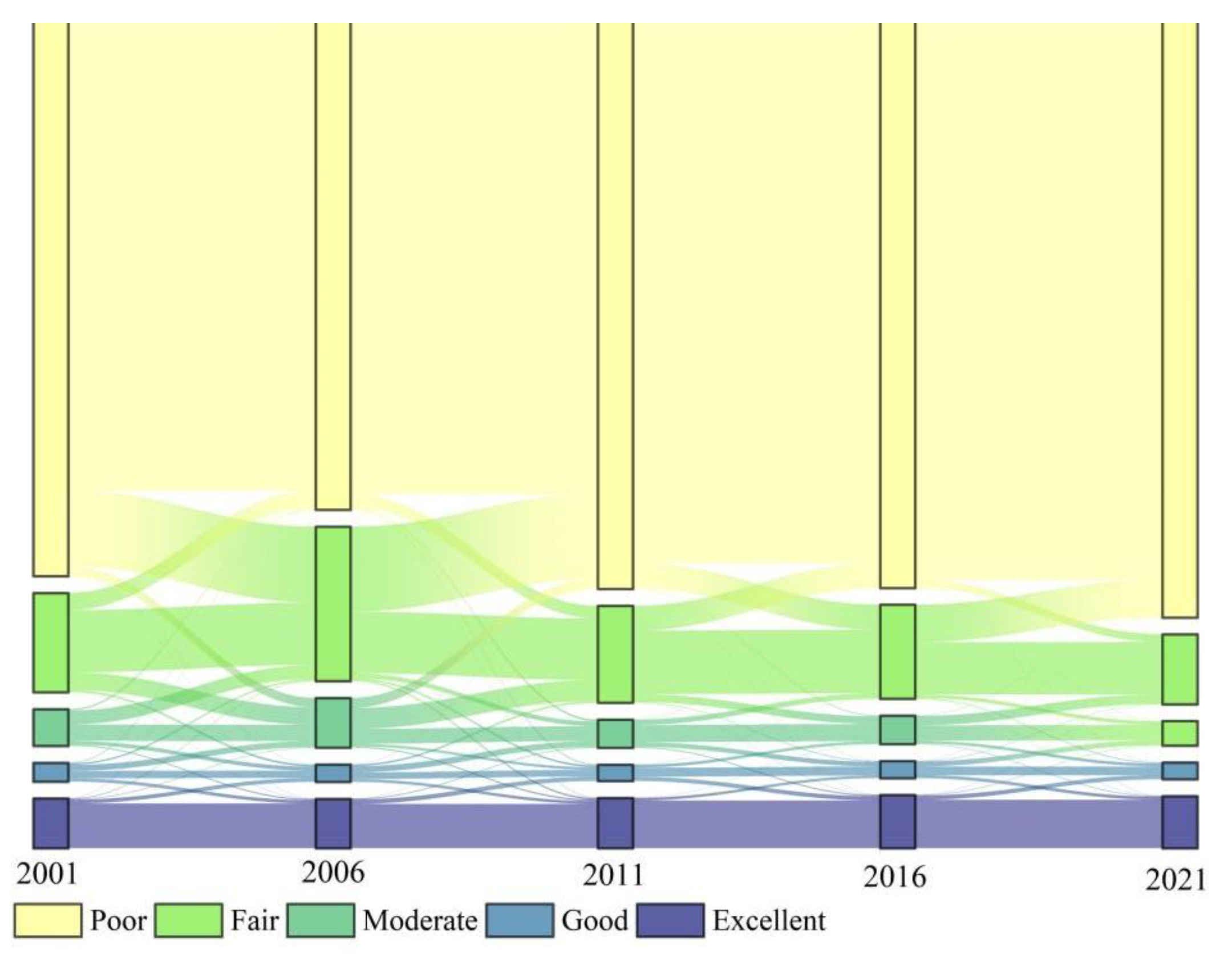
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Ecological Quality
3.2.1. Temporal Characteristics
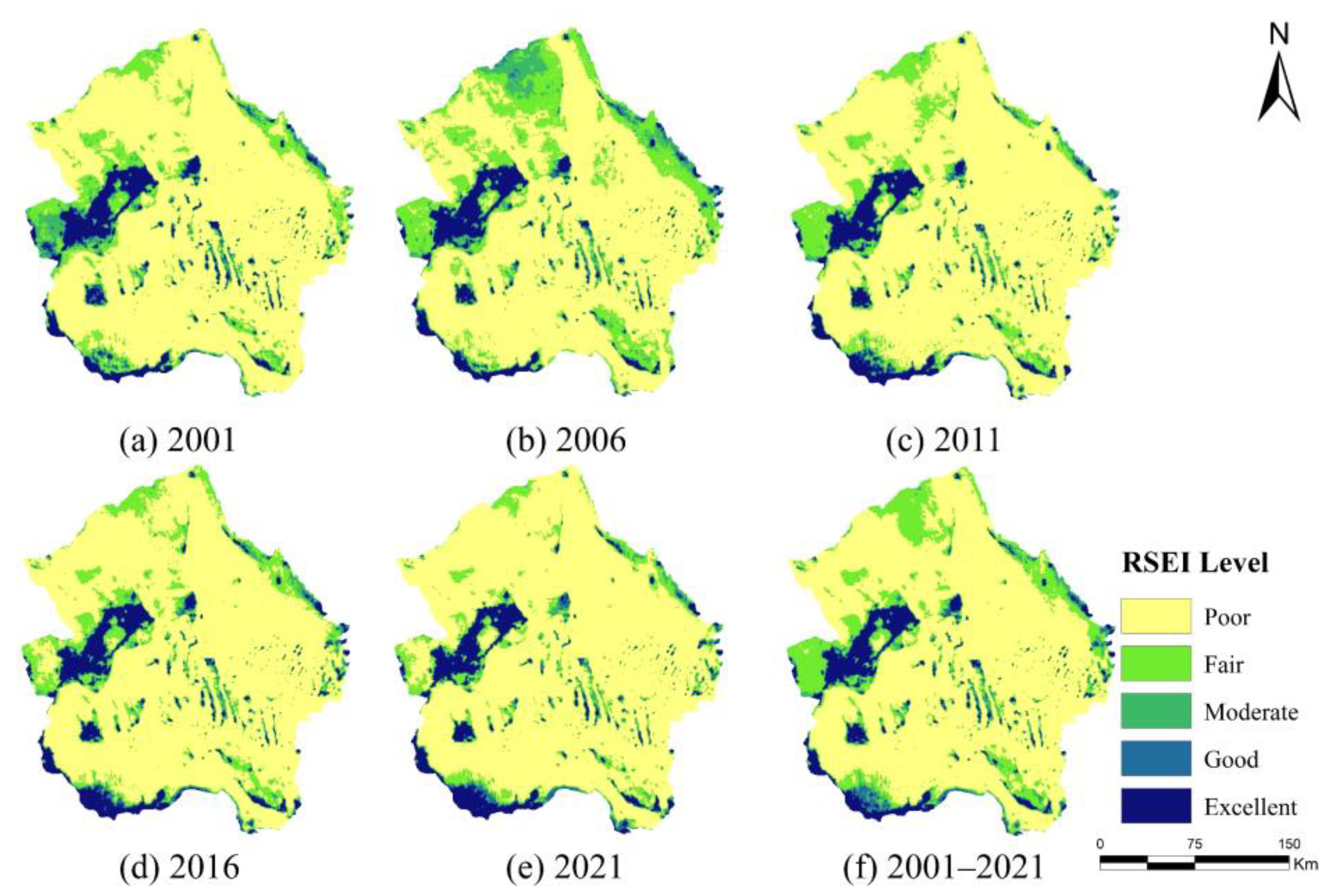
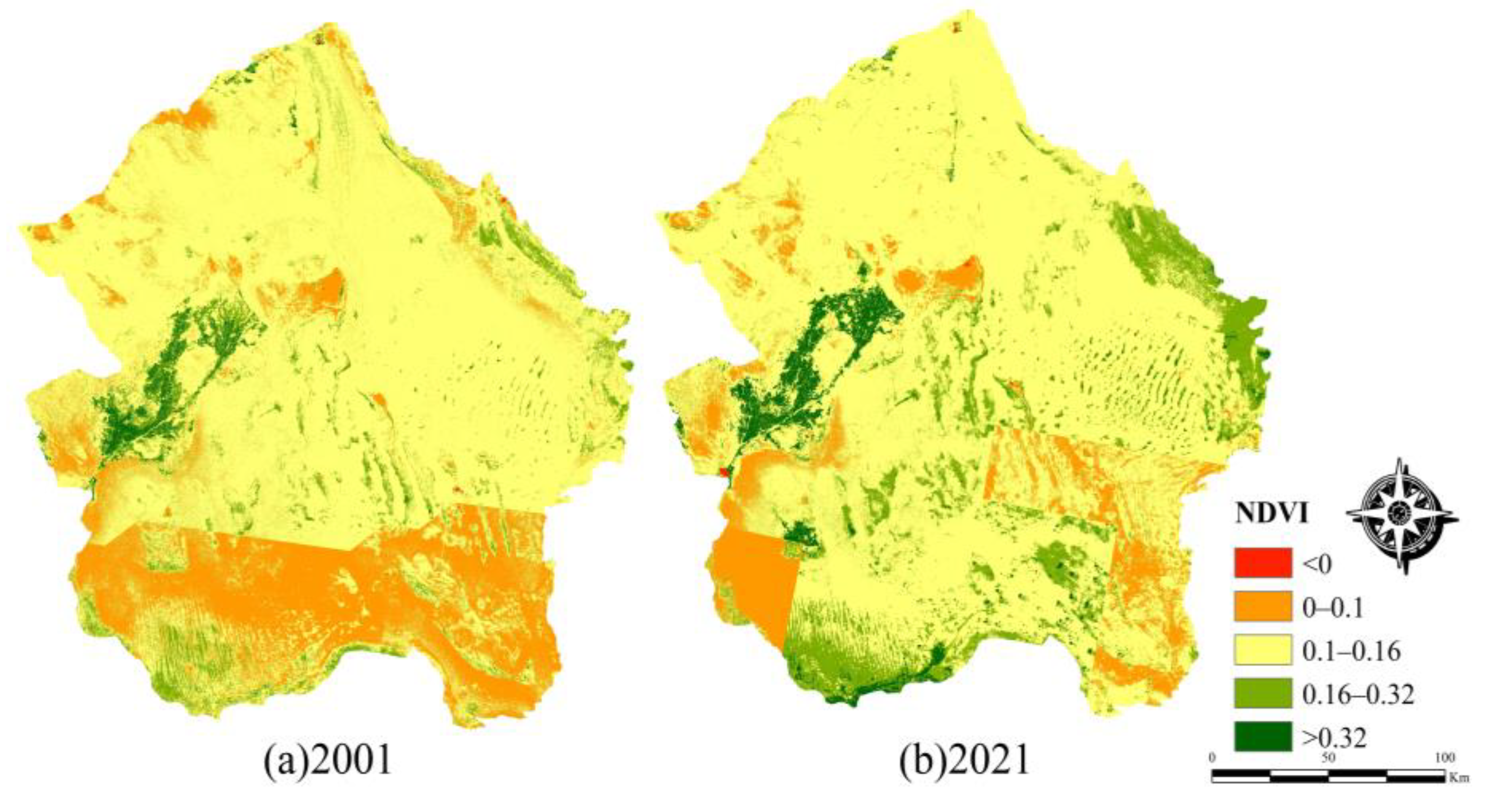
3.2.2. Spatial Characteristics
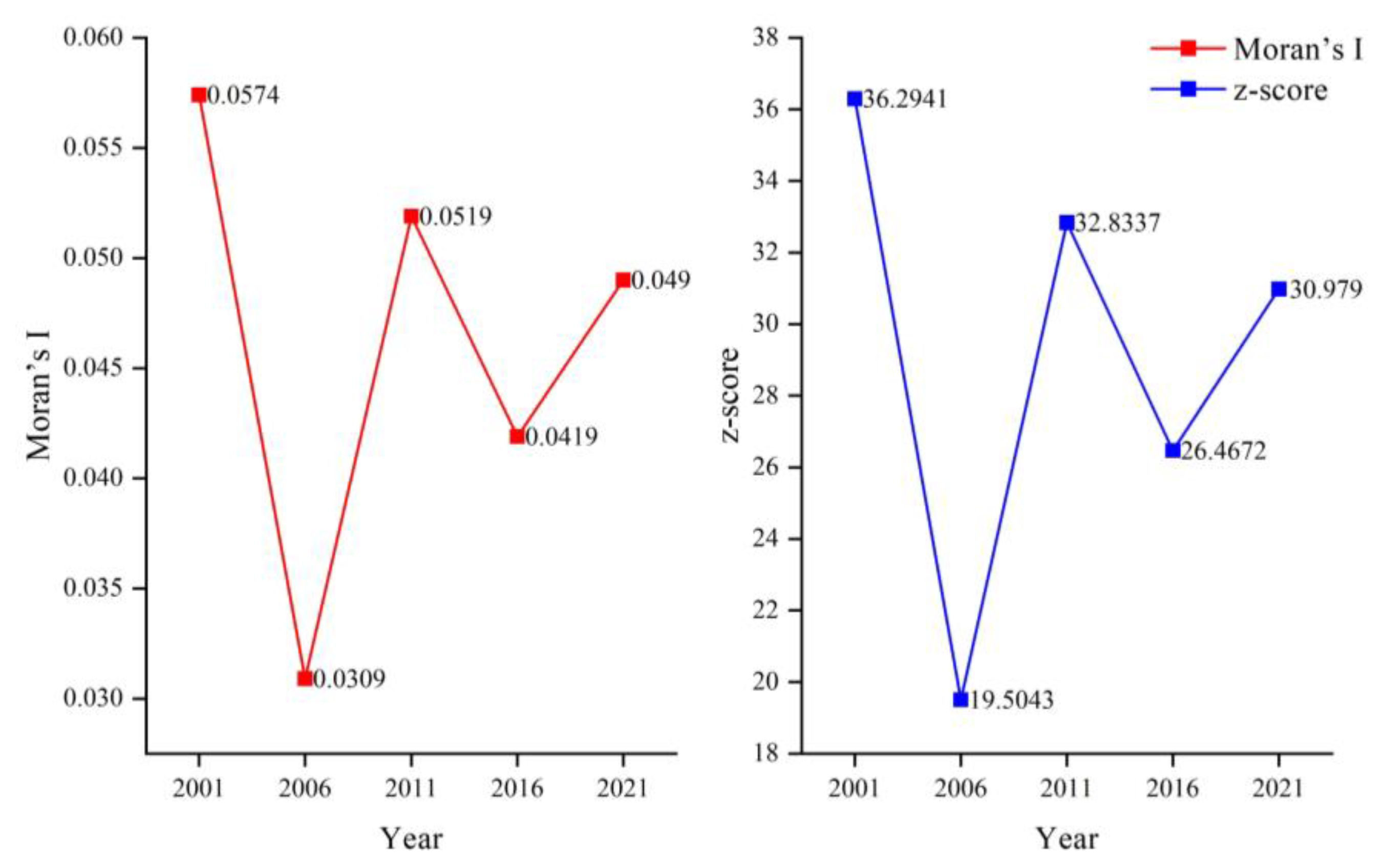
3.2.3. RSEI Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
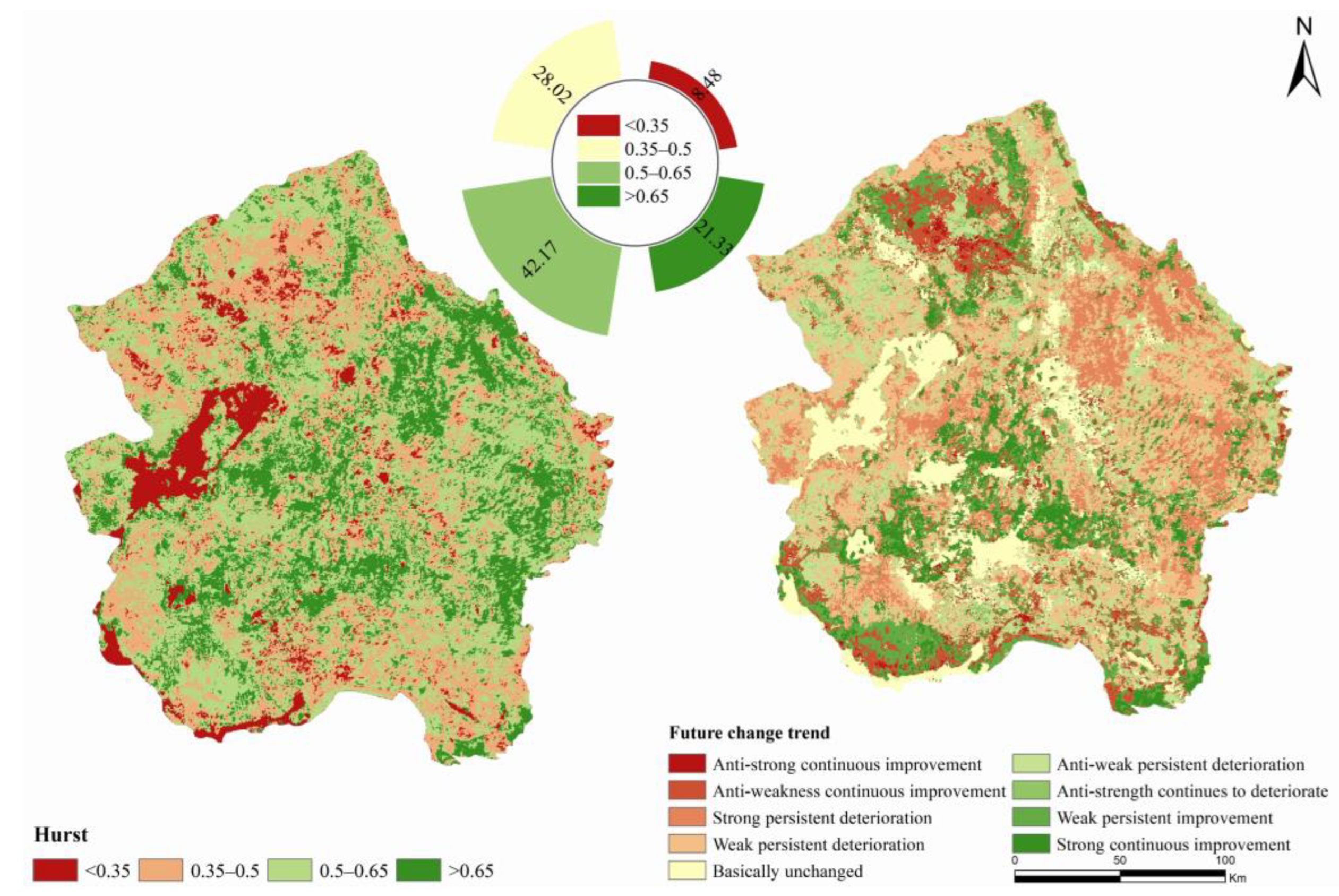
3.3. RSEI Trend Persistence Analysis
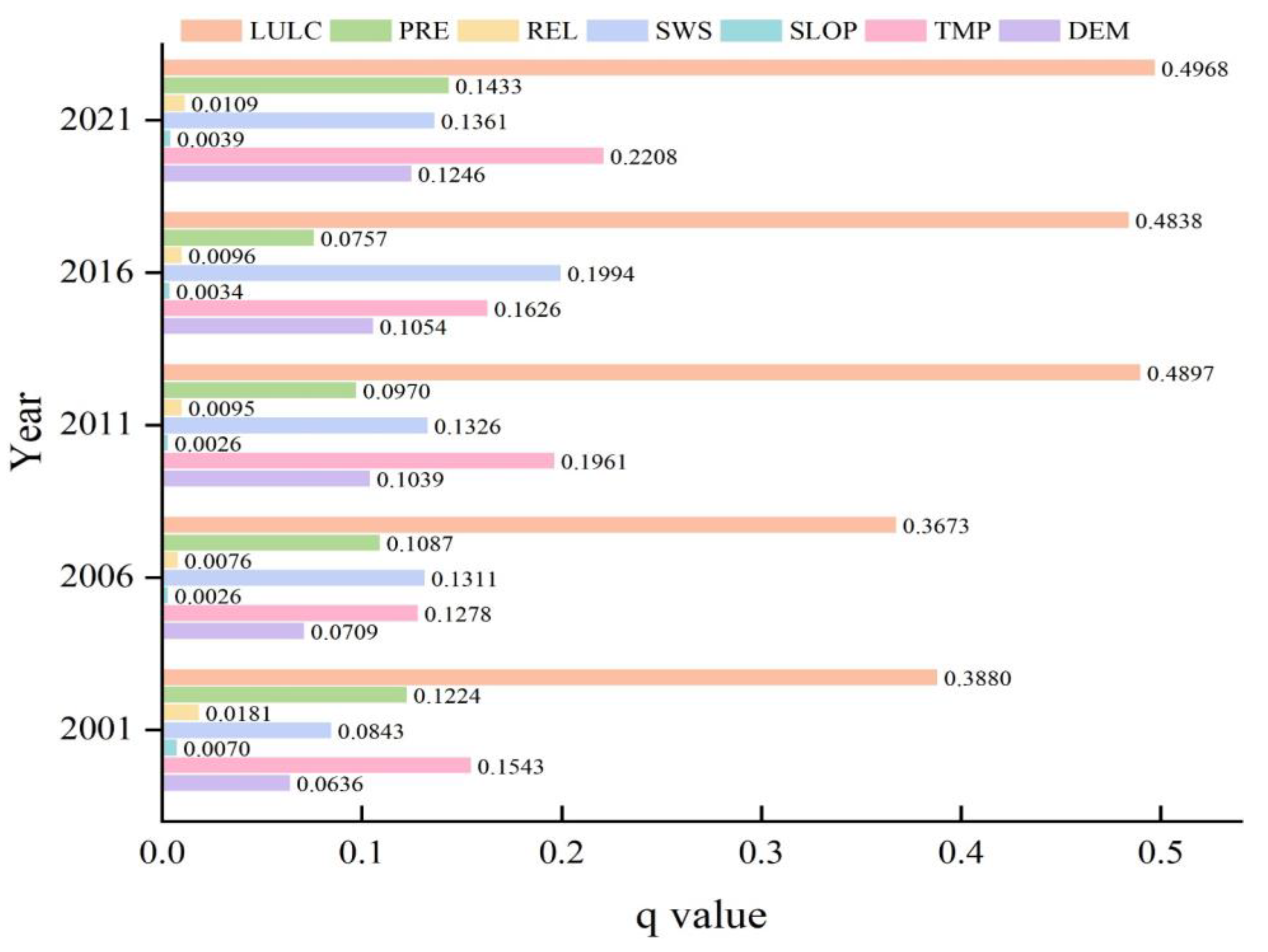
3.4. Factors Driving RSEI
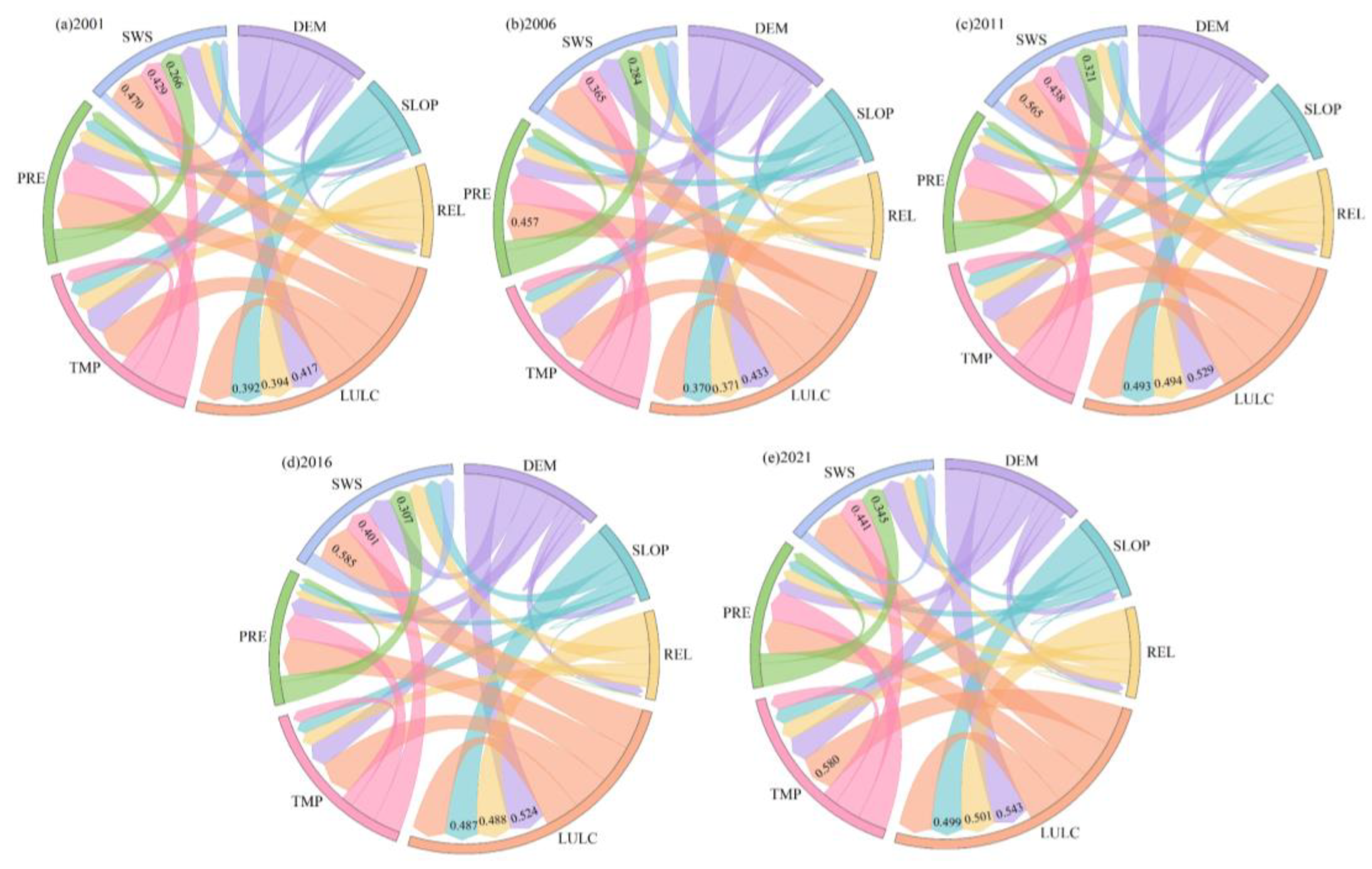
3.4.1. Single-Factor Detection
3.4.2. Factor Interaction Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. RSEI Spatial and Temporal Characteristics
4.2. Factors Driving RSEI
4.3. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- From 2001 to 2021, the average RSEI value in the Tengger Desert decreased by 9.33%, reflecting an overall decline in ecological quality. There are periodic changes in the ecological quality in the study area: 2001–2006 is the improvement stage, 2006–2011 is the accelerated deterioration stage, 2011–2016 is the improvement stage, and 2016–2021 is the deterioration stage. Through the analysis of a spatial transfer matrix, it is concluded that the ecological positions of different levels have migrated, mainly between two adjacent levels.
- (2)
- From 2001 to 2021, the ecological quality of the Tengger Desert was in a deteriorating state, mainly distributed in a large area, with the largest area of mild deterioration. The improvement area accounted for 28.21%, mainly distributed in the edge and centre of the study area. In addition, 49.53% of the study area may be at risk of ecological environment deterioration in the future. It is necessary to pay attention to the ecological situation in the eastern part of the study area and the edges of the towns and take ecological restoration measures to curb the ecological deterioration trend of the Tengger Desert.
- (3)
- Land use and land use cover emerged as the most significant factors influencing RSEI. The interaction of land use with wind speed had the strongest explanatory power, highlighting the role of anthropogenic factors and natural forces in shaping ecological conditions. Other climate variables, such as temperature and precipitation, also played important roles, though their influence was less pronounced than that of land use.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal change and landscape pattern variation of eco-environmental quality in Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration from 2001 to 2015. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125534–125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, C.; Song, K.; Su, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhong, L.; Gao, Y. Analysis of Coupling Coordination Variance between Urbanization Quality and Eco-Environment Pressure: A Case Study of the West Taiwan Strait Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhao, W.; Yan, J.; Xia, F.; Pereira, P. Land degradation neutrality assessment and factors influencing it in China’s arid and semiarid regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Y.W.; Shen, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W.Q. Coalbed methane system potential evaluation and favourable area prediction of Gujiao blocks, Xishan coalfield, based on multi-level fuzzy mathematical analysis. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 160, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Fan, C. Estimation of remote sensing based ecological index along the Grand Canal based on PCA-AHP-TOPSIS methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Hansson, C.; Hörstmeier, O.; Saggel, S. Ecological footprint analysis as a tool to assess tourism sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 43, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, l.; Bai, H.; Jing, Q.; Liu, T.; He, X. Urbanization-induced ecological degradation in Midwestern China: An analysis based on an improved ecological footprint model. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Li, D.; Yan, J.; Wu, Y. Study on the Correlation between Life Expectancy and the Ecological Environment around the Cities along the Belt and Road. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dang, C.; Yue, H.; Lv, C.; Qian, J.; Zhu, R. Comparison between modified remote sensing ecological index and RSEI. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting ecological changes with a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) produced time series and change vector analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Ran, W.; Du, M.; Guo, J.; Hou, G. Assessing the effect, attribution, and potential of vegetation restoration in open-pit coal mines’ dumping sites during 2003–2020 utilizing remote sensing. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.; Plummer, R.; Jollineau, M.; Dale, G. Evaluating ecological outcomes from environmental stewardship initiatives: A comparative analysis of approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbane, C.; Lang, S.; Pipkins, K.; Alleaume, S.; Deshayes, M.; Milián, V.; Strasser, T.; Vanden Borre, J.; Spanhove, T.; Foerster, M. Remote sensing for mapping natural habitats and their conservation status—New opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 37, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K. Remote sensing change detection for ecological monitoring in United States protected areas. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Xue, Z.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climate on the Loess Plateau from 1985 to 2015. Catena 2021, 203, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ma, Y. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: A case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, J.; Tong, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, P.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, P. NIRv and SIF better estimate phenology than NDVI and EVI: Effects of spring and autumn phenology on ecosystem production of planted forests. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 315, 108819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Shui, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Cong, J. A multi-scale daily SPEI dataset for drought characterization at observation stations over China’s mainland from 1961 to 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal drought analysis by the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) in Sichuan Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.; Ahmad, S.; Abbas, S.; Asharf, A.; Siddiqui, N.; ul Islam, Z. Quantifying the contribution of diminishing green spaces and urban sprawl to urban heat island effect in a rapidly urbanizing metropolitan city of Pakistan. Land Use Policy 2022, 113, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kikon, N.; Verma, P. Impact of land use change and urbanization on urban heat island in Lucknow city, Central India. A remote sensing based estimate. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Ge, R.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, N.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Ye, H.; Yin, K. A quantitative method to assess the ecological indicator system’s effectiveness: A case study of the Ecological Province Construction Indicators of China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Alavipanah, S.; Konyushkova, M.; Mijani, N.; Fathololomi, S.; Firozjaei, M.; Homaee, M.; Hamzeh, S.; Kakroodi, A. A Remotely Sensed Assessment of Surface Ecological Change over the Gomishan Wetland, Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Yang, B.; Li, M. An improved framework for assessing the impact of different urban development strategies on land cover and ecological quality changes-A case study from Nanjing Jiangbei New Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal change and driving factors of the Eco-Environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 137, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, M.; Choudhary, K.; Paringer, R.; Kupriyanov, A. Spatiotemporal ecological vulnerability analysis with statistical correlation based on satellite remote sensing in Samara, Russia. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, C.; Marinello, F. Instability of remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) and its improvement for time series analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.; Kiavarz, M.; Homaee, M.; Arsanjani, J.; Alavipanah, S. A novel method to quantify urban surface ecological poorness zone: A case study of several European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, R.; Lu, H. Response of ecological environment quality to land use transition based on dryland oasis ecological index (DOEI) in dryland: A case study of oasis concentration area in Middle Heihe River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; He, J.; Qi, Z.; Saitiniyazi, A. Evolution pattern and driving mechanism of eco-environmental quality in arid oasis belt—A case study of oasis core area in Kashgar Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Qiu, T. Response of vegetation dynamics in environmentally sensitive and fragile areas to natural and anthropogenic factors: A case study in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Anthropocene 2023, 44, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Han, Z.; Xu, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Holmgren, M.; Xu, Z. Climate, topography and anthropogenic effects on desert greening: A 40-year satellite monitoring in the Tengger desert, northern China. Catena 2022, 209, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Ren, H.; Hui, D.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J. Dominant ecological processes and plant functional strategies change during the succession of a subtropical forest. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Z. Accumulated temperature changes in desert region and surrounding area during 1960–2013: A case study in the Alxa Plateau. Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, X.; Jia, R.; Yang, H.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Fu, T. Response of biocrust nitrogenase activity to the variation of rainfall regime in the Tengger Desert, northern China. Catena 2022, 212, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Z. Effect of rainfall pulses on plant growth and transpiration of two xerophytic shrubs in a revegetated desert area: Tengger Desert, China. Catena 2016, 137, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, R.; Gao, Y.; Chim, C.H.; Liao, H. Recrystallization of Holocene calcareous root tubes in the Tengger Desert, Northwest China and its effects on the reliability of paleoenvironmental reconstruction results. Quat. Int. 2020, 562, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, X.; Tang, R.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Bai, T. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Ecological Environment Quality in China from 2002 to 2019 and Influencing Factors. Land 2024, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Bai, Z.; Zheng, B. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Ecological Environment Quality in Coastal Cities: A Remote Sensing and Land Use Perspective in Changle District, Fuzhou. Land 2024, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of climate change trends over the Loess Plateau in China from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. A Spatial Downscaling Algorithm for Satellite-Based Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau Based on NDVI, DEM, and Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, T.; Yang, H.; Li, X. Revegetation enhances soil organic carbon mineralization and its temperature sensitivity in the Tengger Desert, North China. Catena 2022, 218, 106541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. The treatment of ties in ranking problems. Biometrika 1945, 33, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Y.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.; Arikena, M. Assessment of spatial and temporal variation of ecological environment quality in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedamu, W.; Plank-Wiedenbeck, U.; Wodajo, B. A spatial autocorrelation analysis of road traffic crash by severity using Moran’s I spatial statistics: A comparative study of Addis Ababa and Berlin cities. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2024, 200, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H. Long-term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xiu, L.; Yao, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, X. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors analysis of the eco-quality in the Lanxi urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Xie, P.; He, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Khanal, R. Spatiotemporal change of ecologic environment quality and human interaction factors in three gorges ecologic economic corridor, based on RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A.; Liang, C. Historical landscape dynamics of Inner Mongolia: Patterns, drivers, and impacts. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1579–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, H. “Tengger Desert Border-Locking Ecology Project” in full swing. Inner Mongolia Daily, 13 April 2008; p. 1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.; Ye, J.; Geng, J.; Ding, Z. Long-time series ecological environment quality monitoring and cause analysis in the Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environment quality in arid areas based on the remote sensing ecological distance index: A case study of Yuyang district in Yulin city, China. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Y. Vegetation Change and Eco-Environmental Quality Evaluation in the Loess Plateau of China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, X.; Xiao, N. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Ecosystem Quality Based on Key Indicators in Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2018. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 2945–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broquet, M.; Campos, F.; Cabral, P.; David, J. Habitat quality on the edge of anthropogenic pressures: Predicting the impact of land use changes in the Brazilian Upper Paraguay river Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, B.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, L. Impacts and predictions of urban expansion on habitat quality in the densely populated areas: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Han, L.; Kang, S.; Sun, Y. Effects of human activity intensity on habitat quality based on nighttime light remote sensing: A case study of Northern Shaanxi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Ali, S. Abiotic stress and human activities reduce plant diversity in desert riparian forests. Ecological Indicators 2023, 152, 110340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. Landscape degradation in the Jazan coastal desert: Understanding the impact of human activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 14874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, N.; Singh, P. Linkages between land use changes, desertification and human development in the Thar Desert Region of India. Land Use Policy 2016, 51, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S.; Xie, Z.; Shen, W.; Zheng, Z.; Li, M.; Rong, P.; Qin, Y. Detection of spatiotemporal changes in ecological quality in the Chinese mainland: Trends and attributes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Huang, H.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, D.; Xiang, X.; et al. How do natural and socio-economic factors influence the sustainable development of the ecological environment in the World Natural Heritage Sites? Evidence from the Jiuzhaigou, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 458, 139238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Su, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.; Luo, J. Spatio-temporal Evolution Patterns and Spatial Differentiation Attribution of Ecological Quality in Guiyang from 1991 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Tao, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, S.; Shi, S.; Shang, Y. Retrieval of Chla Concentrations in Lake Xingkai Using OLCI Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, C.; Patidar, G.; Swain, D.; Chowdary, V.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Total suspended matter distribution in the hooghly river estuary and the sundarbans: A remote sensing approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9064–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Ai, X.; Qin, Y. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Total Phosphorus in the Pearl River Channels Based on the GF-1 Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Hou, J.; Lu, H. Research on the Influence of Satellite Image Resolution in Urban Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Green Technol. 2021, 23, 173–177+181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Shi, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, A. Spatial and temporal variability of ecosystem services in the Shiyang River Basin and its multi-scale influencing factors. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Basis for Judgment | Types of the Interaction |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear attenuation | |
| Unilinear attenuation | |
| Two-factor enhancement | |
| Independent | |
| nonlinear enhancement |
| RSEI Levels | 2021 (km2) | Total (km2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor | Fair | Moderate | Good | Excellent | |||
| 2001 (km2) | Poor | 2143.4875 | 1981.7252 | 1979.3879 | 1979.1584 | 1979.0736 | 10,062.8326 |
| Fair | 1993.3964 | 1990.817 | 1980.1176 | 1979.5741 | 1979.7191 | 9923.6242 | |
| Moderate | 1980.4561 | 1983.6106 | 1981.2788 | 1979.7469 | 1979.8999 | 9904.9923 | |
| Good | 1978.972 | 1979.6497 | 1980.9664 | 1979.9197 | 1980.1457 | 9899.6535 | |
| Excellent | 1978.8713 | 1979.0449 | 1979.6182 | 1980.6172 | 1990.7458 | 9908.8974 | |
| Total (km2) | 10,075.1833 | 9914.8474 | 9901.3689 | 9899.0163 | 9909.5841 | 49,700 | |
| RSEI Variation Category | 2001–2006 | 2006–2011 | 2011–2016 | 2016–2021 | 2001–2021 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | |
| Significant decrease | 511.91 | 1.03 | 298.20 | 0.6 | 109.34 | 0.22 | 745.5 | 1.50 | 5134.01 | 10.33 |
| Slight decrease | 1103.34 | 2.22 | 1804.11 | 3.63 | 278.32 | 0.56 | 1689.8 | 3.40 | 2584.4 | 5.2 |
| No significant decrease | 22,176.14 | 44.62 | 31,435.25 | 63.25 | 12,812.66 | 25.78 | 29,750.42 | 59.86 | 22,449.49 | 45.17 |
| Unchanged | 4234.44 | 8.52 | 4796.05 | 9.65 | 6192.62 | 12.46 | 5258.26 | 10.58 | 5511.73 | 11.09 |
| No significant increase | 19,914.79 | 40.07 | 10,934 | 22.00 | 27,856.85 | 56.05 | 11,639.74 | 23.42 | 11,704.35 | 23.55 |
| Slight increase | 1192.8 | 2.4 | 273.35 | 0.55 | 1868.72 | 3.76 | 367.78 | 0.74 | 839.93 | 1.69 |
| Significant increase | 566.58 | 1.14 | 159.04 | 0.32 | 581.49 | 1.17 | 248.5 | 0.50 | 1476.09 | 2.97 |
| Hurst | Change Directions | Future Change Trend | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <−5 | <0.35 | From deterioration to improvement | Anti-strength continues to deteriorate | 1153.04 | 2.32 |
| 0.35~0.5 | Anti-weak persistent deterioration | 8613.01 | 17.33 | ||
| 0.5~0.65 | Continuous degradation | Weak persistent deterioration | 13,394.15 | 26.95 | |
| >0.65 | Strong persistent deterioration | 6684.65 | 13.45 | ||
| ≥5 | <0.35 | From improvement to deterioration | Anti-strong continuous improvement | 521.85 | 1.05 |
| 0.35~0.5 | Anti-weakness continuous improvement | 4015.76 | 8.08 | ||
| 0.5~0.65 | Continuous improvement | Weak persistent improvement | 5869.57 | 11.81 | |
| >0.65 | Strong continuous improvement | 3300.08 | 6.64 | ||
| −5~5 | 0~1 | Basically unchanged | Basically unchanged | 6147.89 | 12.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, F.; Qin, F.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, L. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Ecological Quality in the Tengger Desert (2001–2021). Land 2024, 13, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13111838
Dong F, Qin F, Dong X, Wu Y, Zhao K, Zhao L. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Ecological Quality in the Tengger Desert (2001–2021). Land. 2024; 13(11):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13111838
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Feifei, Fucang Qin, Xiaoyu Dong, Yihan Wu, Kai Zhao, and Longfei Zhao. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Ecological Quality in the Tengger Desert (2001–2021)" Land 13, no. 11: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13111838
APA StyleDong, F., Qin, F., Dong, X., Wu, Y., Zhao, K., & Zhao, L. (2024). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Drivers of Ecological Quality in the Tengger Desert (2001–2021). Land, 13(11), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13111838







