Dynamics of the Interaction between Freeze–Thaw Process and Surface Energy Budget on the Permafrost Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Model
2.2.1. Model Description
2.2.2. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. The Influence of the Freeze–Thaw Process on the Surface Energy Flux
3.2. The Effect of Surface Energy Accumulation on Freeze–Thaw Processes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobiński, W. Permafrost active layer. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Permafrost and groundwater on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in northeast China. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ding, Y.; Han, T.; Chang, Y.P.; Shi, F.; You, Y. The hydrothermal changes of permafrost active layer and their impact on summer rainfall-runoff processes in an alpine meadow watershed, northwest china. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2022, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Fitzhugh, L.; Whiting, G.; Frolking, S.; Harrison, M.; Dimova, N.; Burnett, W.; Chanton, J.P. Greenhouse gas balance over thaw-freeze cycles in discontinuous zone permafrost. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreves, K.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Si, B.; Clough, T. Nitrous oxide emissions and biogeochemical responses to soil freezing-thawing and drying-wetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yang, M.; Wang, H. Characteristics of land surface heat and water exchange under different soil freeze/thaw conditions over the central Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y. Weakening sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau revisited: Effects of the land–atmosphere thermal coupling. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, F.; Ma, Z.; Lei, B. Thermal–moisture dynamics and thermal stability of active layer in response to wet/dry conditions in the central region of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2023, 15, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, T.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Du, Y.; Yang, S. The surface energy budget and its impact on the freeze-thaw processes of active layer in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Zhang, F. Impacts of soil freeze–thaw process and snow melting over Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer monsoon system: A review and perspective. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. The freeze/thaw process and the surface energy budget of the seasonally frozen ground in the source region of the Yellow River. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 138, 1631–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Luo, S.; Lü, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D. Effects of the soil freeze-thaw process on the regional climate of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Clim. Res. 2014, 59, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jin, R.; Pan, X.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J. Changes in the near-surface soil freeze–thaw cycle on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Xue, X.; Peng, F.; Dong, S.; Gao, Y. Surface water and heat exchange comparison between alpine meadow and bare land in a permafrost region of the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Van der Velde, R.; Su, Z.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, K. Evaluation of Noah frozen soil parameterization for application to a Tibetan meadow ecosystem. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Jiao, Y. Evaluation of CLM5. 0 for simulating surface energy budget and soil hydrothermal regime in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 332, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V. Recent third pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: Multidisciplinary approach with observations, modeling, and analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, K. A new scheme for considering soil water-heat transport coupling based on Community Land Model: Model description and preliminary validation. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, R.; Huang, Z.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Du, Y. Evaluation and spatio-temporal analysis of surface energy flux in permafrost regions over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Arctic using CMIP6 models. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 1947–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhao, L.; Gu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Jiao, K. The surface energy budget in the permafrost region of the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Gu, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Qiao, Y. Estimation of surface energy fluxes in the permafrost region of the Tibetan Plateau based on in situ measurements and the surface energy balance system model. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 5783–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, L.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Wu, T.; Zou, D.; Zhu, X.; Jie, C.; Su, Y.; Hao, J. Dynamics of the freeze–thaw front of active layer on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, M.R.I.E.W. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; An-Min, D.; Qing-Long, Y.; Die, H. Research progress on climate change and its impact on water resources over the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 20, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Sheng, Y.; Hu, G.; Cheng, G.; Zhao, L.; Jin, H.; Zou, D.; Wu, X. Characteristic, changes and impacts of permafrost on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, L.; Fang, Y. Seasonal spatial heterogeneity of warming rates on the Tibetan Plateau over the past 30 years. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Nan, Z.; Wu, X.; Ji, H.; Zhao, S. The role of winter warming in permafrost change over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 11261–11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, G.; Liu, W.; Jiao, Y. The spatiotemporal variations of freezing index and its relationship with permafrost degradation over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1977 to 2016. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guojie, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhe, S.; Defu, Z.; Yao, X.; Guangyue, L.; Erji, D.; Chong, W.; Yuanwei, W.; Xiaodong, W. Spatiotemporal characteristics and variability in the thermal state of permafrost on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2024, 35, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Wen, Z.; Yin, Z.; Tang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, Q. Degraded frozen soil and reduced frost heave in China due to climate warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskaborn, B.K.; Smith, S.L.; Noetzli, J.; Matthes, H.; Vieira, G.; Streletskiy, D.A.; Schoeneich, P.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Lewkowicz, A.G.; Abramov, A. Permafrost is warming at a global scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrenko, I.A.; Kirillov, S.A.; Tremblay, L.B.; Kassens, H.; Anisimov, O.A.; Lavrov, S.A.; Razumov, S.O.; Grigoriev, M.N. Recent changes in shelf hydrography in the Siberian Arctic: Potential for subsea permafrost instability. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Abbott, B.W.; Norris, A.J.; Mu, M.; Fan, C.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Yang, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K. The status and stability of permafrost carbon on the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 211, 103433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.; McGuire, A.D.; Schädel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J.W.; Hayes, D.J.; Hugelius, G.; Koven, C.D.; Kuhry, P.; Lawrence, D.M. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature 2015, 520, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Nan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, G. Qinghai-Tibet Plateau wetting reduces permafrost thermal responses to climate warming. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 562, 116858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhou, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, R.; Chen, S. Assessing the dynamics of human activity intensity and its natural and socioeconomic determinants in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2023, 4, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Zhu, X.; Zou, D.; Hao, J.; Li, W. Long-term soil temperature dynamics of the Kunlun Pass permafrost region on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 149, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, G.; Zou, D.; Wu, X.; Ma, L.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, S. Permafrost Changes and Its Effects on Hydrological Processes on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. China Acad. J. 2019, 34, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Zou, D.; Hu, G.; Wu, T.; Du, E.; Liu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Li, R.; Pang, Q.; Qiao, Y. A synthesis dataset of permafrost thermal state for the Qinghai–Tibet (Xizang) Plateau, China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4207–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yao, J.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Du, Y. Soil thermal conductivity and its influencing factors at the Tanggula permafrost region on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.; Wu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Du, E.; Liu, G.; Qiao, Y. Temporal and spatial variations of the active layer along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway in a permafrost region. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 4609–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Fisher, R.A.; Koven, C.D.; Oleson, K.W.; Swenson, S.C.; Bonan, G.; Collier, N.; Ghimire, B.; van Kampenhout, L.; Kennedy, D. The Community Land Model version 5: Description of new features, benchmarking, and impact of forcing uncertainty. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 4245–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Lawrence, D. Assessing a dry surface layer-based soil resistance parameterization for the Community Land Model using GRACE and FLUXNET-MTE data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10, 210–299, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Fisher, R.; Koven, C.; Oleson, K.; Swenson, S.; Vertenstein, M.; Andre, B.; Bonan, G.; Ghimire, B.; van Kampenhout, L. Technical description of version 5.0 of the Community Land Model (CLM). NCAR Tech. Note 2018, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Slater, A.G. Incorporating organic soil into a global climate model. Clim. Dyn. 2008, 30, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Meng, X.; Lyv, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jing, H. Comparison of soil water and heat transfer modeling over the Tibetan Plateau using two Community Land Surface Model (CLM) versions. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wen, J.; Hu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X. Parameter sensitivities of the Community Land Model at two alpine sites in the three-river source region. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domine, F.; Barrere, M.; Sarrazin, D. Seasonal evolution of the effective thermal conductivity of the snow and the soil in high Arctic herb tundra at Bylot Island, Canada. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2573–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S.; Ni, J. Evaluation of 11 soil thermal conductivity schemes for the permafrost region of the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2020, 193, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Hu, G.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of soil thermal conductivity schemes incorporated into CLM5. 0 in permafrost regions on the Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Ding, Y.; Xin, Y.; Zou, D.; Xiao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Sun, L. Temporal and spatial variations of global solar radiation over the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau during the past 40 years. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 113, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, G.; Zou, D.; Li, W.; Yu, W.; Jiao, Y. The impact of surface energy exchange on the thawing process of active layer over the northern Qinghai–Xizang Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Pei, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, S. Permafrost Degradation Risk Evaluation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Under Climate Change Based on Machine Learning Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD039611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, H. Simulation of permafrost and seasonally frozen ground conditions on the Tibetan Plateau, 1981–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5216–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, G. Climate warming over the past half century has led to thermal degradation of permafrost on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, M.; Von Deimling, T.S.; Westermann, S.; Rolph, R.; Rutte, R.; Antonova, S.; Rachold, V.; Schultz, M.; Oehme, A.; Grosse, G. Thawing permafrost poses environmental threat to thousands of sites with legacy industrial contamination. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, B.; Yu, G.; Li, W. Study on the water-heat coupled phenomena in thawing frozen soil around a buried oil pipeline. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 73, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Kang, H. Soil respiration of alpine meadow is controlled by freeze–thaw processes of active layer in the permafrost region of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2835–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, T.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Yao, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Jiao, Y. Evaluating the Impact of Soil Enthalpy upon the Thawing Process of the Active Layer in Permafrost Regions of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Using CLM5. 0. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, U.; Jin, S.; Duan, W.; Bilal, M.; Ali, M.A.; Farooq, H. Spatio-temporal trends of surface energy budget in Tibet from satellite remote sensing observations and reanalysis data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



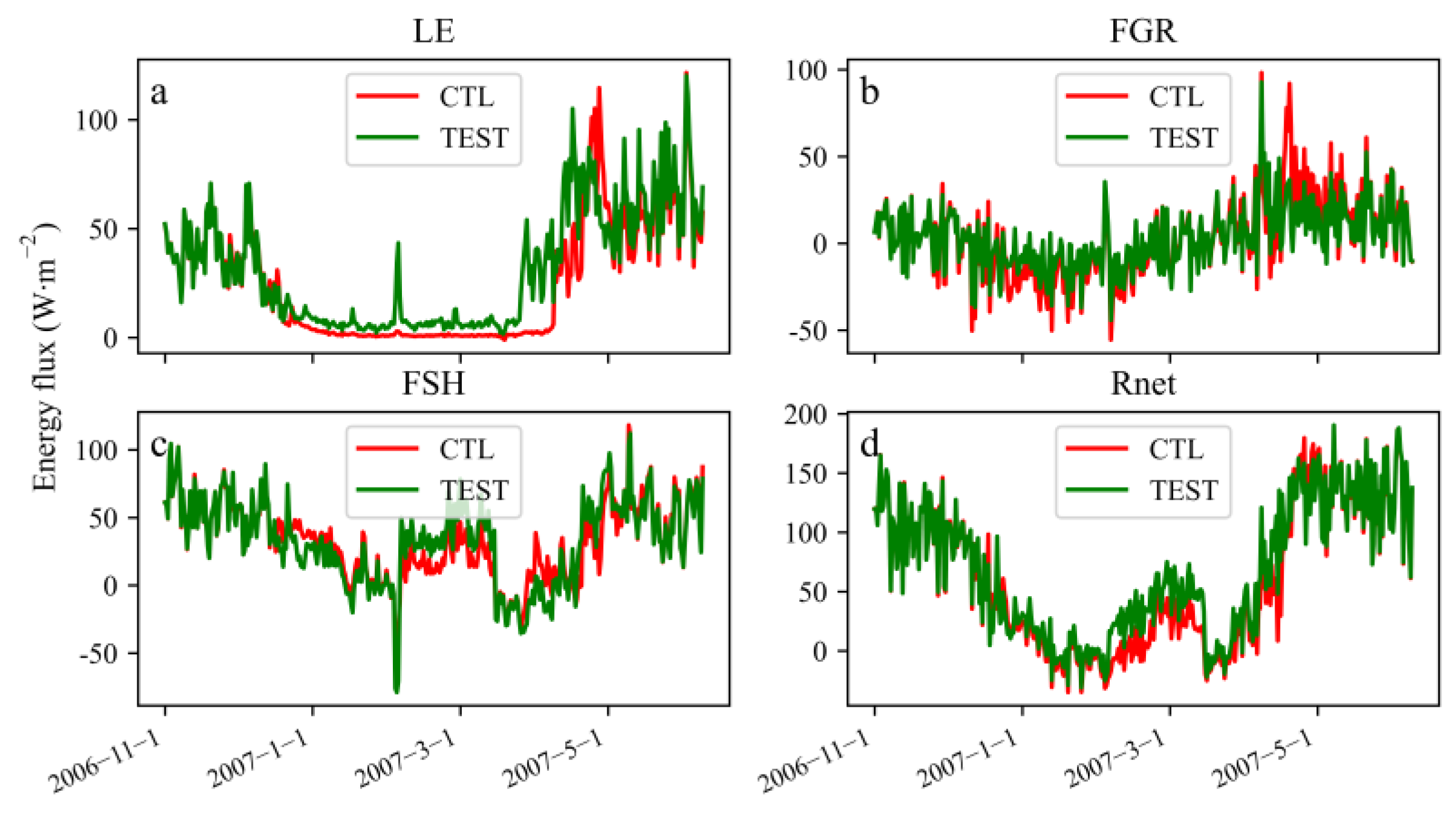

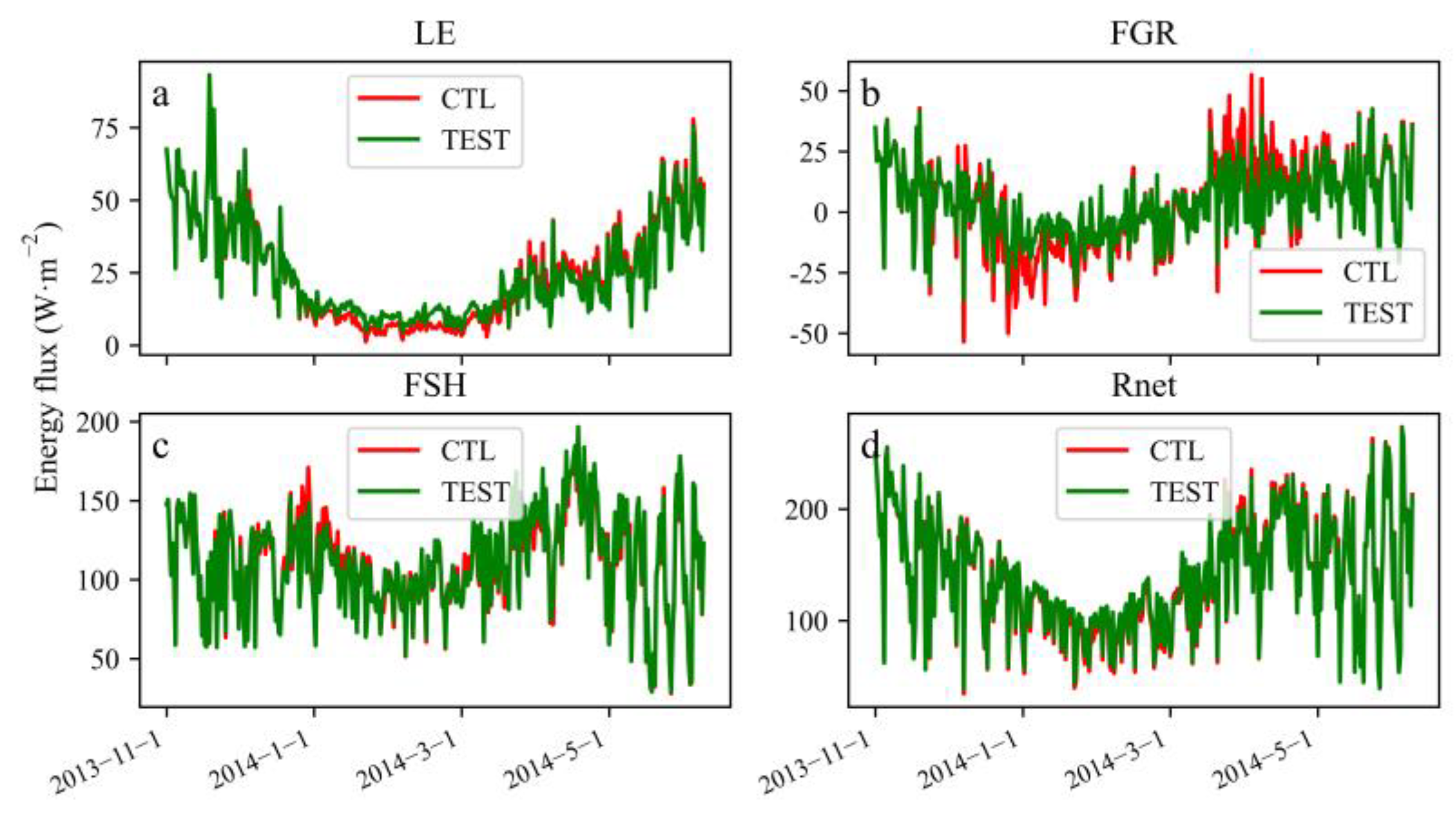


| Study Site | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Altitude (m) | Vegetation Type | Study Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGL | 91°01′ | 32°58′ | 5100 | Alpine meadow | 2006.1.1–2007.12.31 |
| XDT | 94°08′ | 35°43′ | 4538 | Alpine meadow | 2011.1.1–2013.12.31 |
| BLH | 92°55′ | 34°49′ | 4656 | Alpine meadow | 2009.1.1–2010.12.31 |
| LDH | 91°44′ | 31°49′ | 4808 | Alpine wet meadow | 2017.1.1–2017.12.31 |
| TSH | 79°33′ | 35°22′ | 4844 | Alpine dessert | 2016.1.1–2017.12.31 |
| Observation Items | Instrumentation and Equipment | Monitoring Frequency | Error Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature | HMP45C, Vaisala | 30 min | ±0.5 °C |
| Air humidity | HMP45C, Finland | 30 min | ±3% RH |
| Wind | 05103_L/RM, Campbell, USA | 30 min | ±0.3 m/s |
| Precipitation | T-200B Precipitation Gauge | 30 min | ±0.1 mm |
| Upward longwave/shortwave radiation flux | CM3, Kipp & Zonen, The Netherlands | 30 min | ±10% |
| Downward longwave/shortwave radiation flux | CM3, Kipp & Zonen, The Netherlands | 30 min | ±10% |
| Soil temperature | 105T/109 | 30 min | ±0.1 °C |
| Soil moisture | CS616 | 30 min | ±2.5% |
| Energy Flux | Test Name | 8.01–8.23 | 8.24–10.7 | 10.8–12.6 | 12.7–4.9 | 4.10–7.31 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thawing Stage (W·m−2) | Complete Thawing Stage (W·m−2) | Freezing Stage (W·m−2) | Complete Freezing Stage (W·m−2) | Thawing Stage (W·m−2) | ||
| Rn * | CTL | 113.63 | 99.4 | 24.31 | 5.85 | 113.66 |
| TEST | 113.59 | 99.29 | 26.35 | 21.47 | 118.22 | |
| G0 * | CTL | 8.67 | 4.04 | −15.53 | −5.03 | 20.56 |
| TEST | 8.62 | 4.79 | −9.38 | −3.5 | 16.16 | |
| H * | CTL | 65.59 | 54.7 | 32.79 | 17.45 | 41.64 |
| TEST | 65.5 | 54.42 | 25.25 | 15.6 | 83.36 | |
| LE * | CTL | 39.37 | 40.4 | 7.06 | 1.1 | 51.94 |
| TEST | 39.46 | 40.12 | 10.46 | 9.37 | 60.5 |
| Depth (cm) | TGL | XDT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (%) | Clay (%) | Gravel (%) | Sand (%) | Clay (%) | Gravel (%) | |
| 9 | 75 | 7 | 26 | 82 | 1 | 2 |
| 16 | 70 | 12 | 12 | 80 | 1 | 6 |
| 26 | 65 | 13 | 11 | 82 | 1 | 3 |
| 40 | 85 | 5 | 27 | 76 | 2 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Li, R.; Wu, T.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, S.; et al. Dynamics of the Interaction between Freeze–Thaw Process and Surface Energy Budget on the Permafrost Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land 2024, 13, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101609
Ma J, Li R, Wu T, Liu H, Wu X, Hu G, Liu W, Wang S, Xiao Y, Tang S, et al. Dynamics of the Interaction between Freeze–Thaw Process and Surface Energy Budget on the Permafrost Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land. 2024; 13(10):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101609
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Junjie, Ren Li, Tonghua Wu, Hongchao Liu, Xiaodong Wu, Guojie Hu, Wenhao Liu, Shenning Wang, Yao Xiao, Shengfeng Tang, and et al. 2024. "Dynamics of the Interaction between Freeze–Thaw Process and Surface Energy Budget on the Permafrost Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Land 13, no. 10: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101609
APA StyleMa, J., Li, R., Wu, T., Liu, H., Wu, X., Hu, G., Liu, W., Wang, S., Xiao, Y., Tang, S., Shi, J., & Qiao, Y. (2024). Dynamics of the Interaction between Freeze–Thaw Process and Surface Energy Budget on the Permafrost Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land, 13(10), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101609







