Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage Based on Regional Ecological Security Pattern along the Straight Road (Zhidao) of the Qin Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
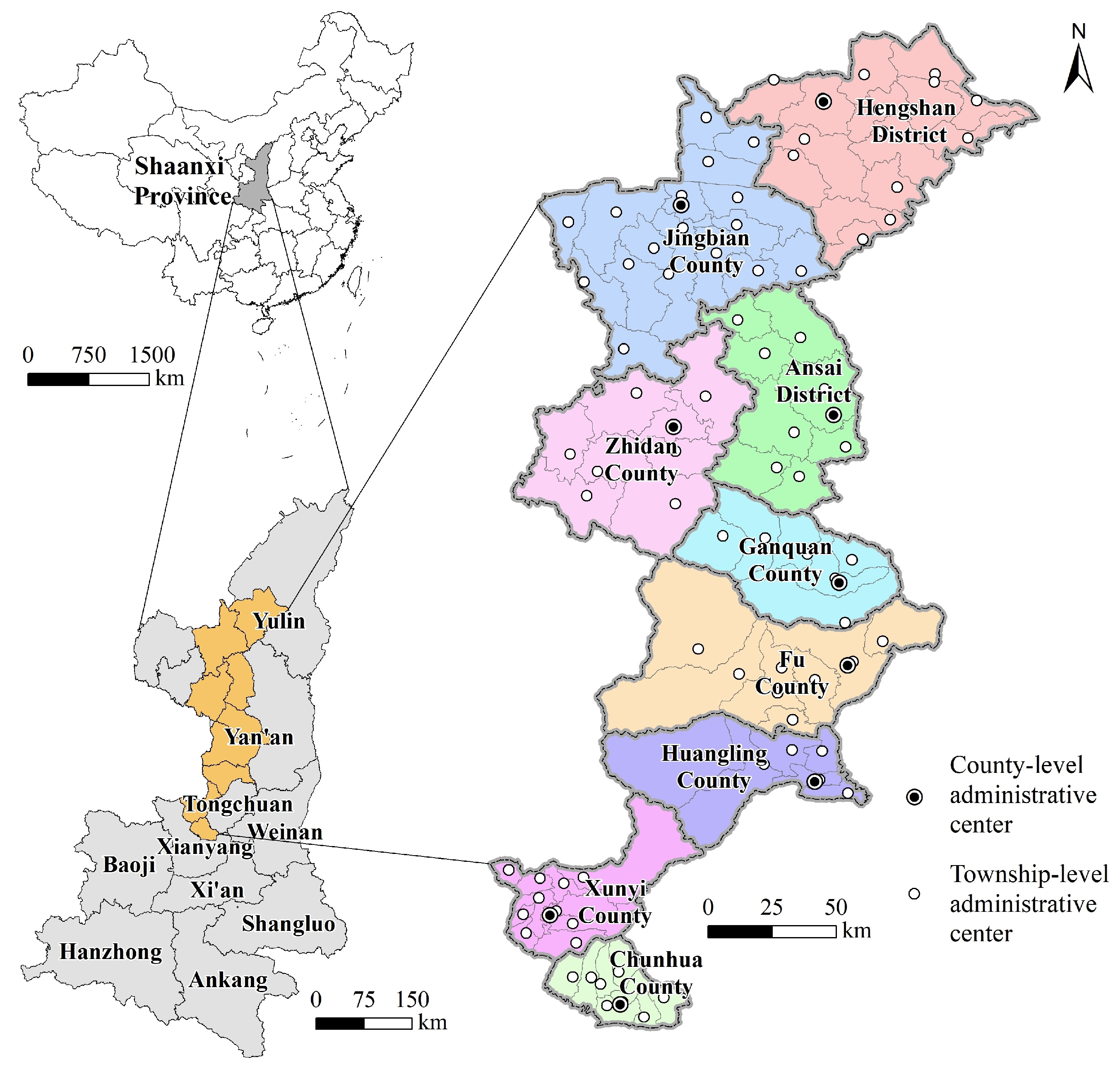
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Ecological Source Identification
2.4. Ecological Resistance Surface Construction
2.5. Ecological Network Establishment
2.6. Technology Flow and Required Indicators of Natural and Cultural Assets
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Patterns of Ecological Sources
3.2. Distribution of Ecological Resistance Surface
3.3. Characteristics of Ecological Security Pattern
3.3.1. Ecological Network and Ecological Security Pattern
3.3.2. Spatial Imbalance of Key Elements in Ecological Security Pattern
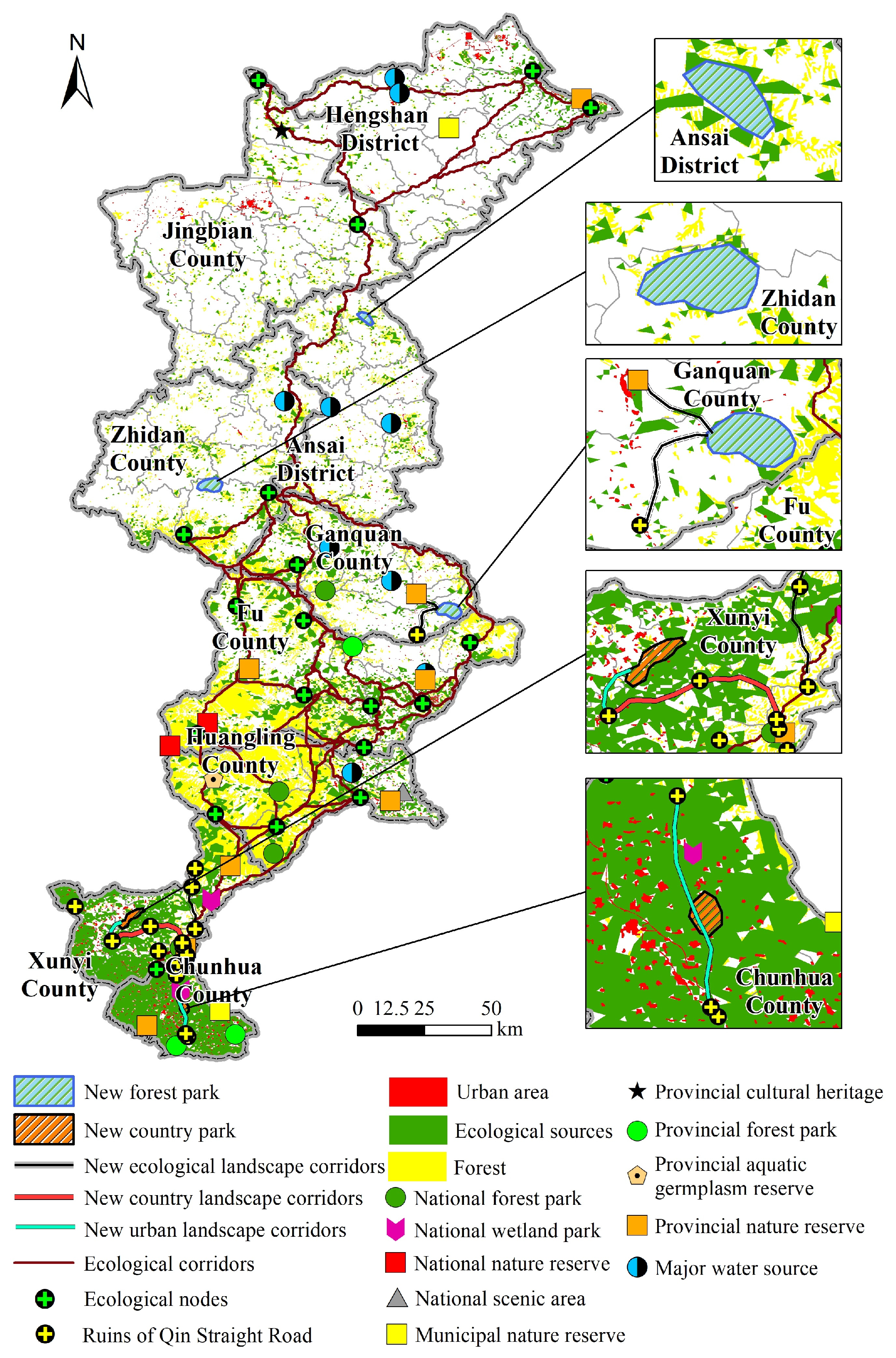
3.4. Conflicts between Key Landscape Spaces and Ecological Security Pattern
3.4.1. Spatial Conflicts of Landscape Corridors
3.4.2. Spatial Contrast of Prohibited-Development Areas and Ecological Security Pattern
4. Discussion
4.1. Solutions to the Conflicts between Human Activities and Ecological Landscapes
4.2. Direction of Ecological Conservation and Cultural-Landscape Construction
4.3. Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage
4.3.1. Objectives and Principles
4.3.2. Planning and Development Suggestions for Key Construction Projects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial reconstruction and cultural practice of linear cultural heritage: A case study of Meiguan Historical Trail, Guangdong, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Pei, T.; Chan, C.S.; Wang, M.D.; Meng, B. Tourism value assessment of linear cultural heritage: The case of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal in China. Curr. Issues Tour. 2023, 26, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q. On the protection of large-scale linear cultural heritage: Breakthrough and pressure. Cult. Relics South China 2006, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K. China faces the challenge of world heritage concept: Thoughts after the 28th World Heritage Convention. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2004, 11, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.L. On value evaluation of tourism resource of cross-regional linear cultural heritage: Taking the routes network of Chang’an-Tianshan corridor in China as an example. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Study on spatial structure evolution of linear cultural heritage: On the role of tourism. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 35, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, P.; Maselli, G.; Nesticò, A.; Ribera, F. An evaluation model for adaptive reuse of cultural heritage in accordance with 2030 SDGs and European Quality Principles. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 59, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lian, Z. On protection of intangible cultural heritage in China from the intellectual property rights perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flink, C.A.; Searns, R.M. Greenways: A Guide to Planning, Design, and Development; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Lian, H. Research on progress and developmental tendency of the linear space. Huazhong Archit. 2007, 7, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J.; Xi, X.S.; Li, D.H.; Li, H.L.; Liu, K. On the construction of the national linear culture heritage network in China. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 24, 11–16+116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.X. Cultural heritage protection shows six major trends. Xinhua Daily, 13 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Value of the ancient Yunnan-Tibet Tea-Horse Road in the perspective of the heritage corridor. J. Yunnan Natl. Univ. 2012, 29, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, R.; Xi, T.D. The protection research on lineal cultural heritages of Chinese Canal from cultural routes: A Case of Anhui Section of Chinese Canal of Sui and Tang Dynasty. Hum. Geogr. 2013, 28, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.S.; Feng, B.; Zhai, H.M. A preliminary discussion about the new approach of protecting and planning Guilin heritages. Tour. Trib. 2007, 22, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, D.T.; Zhu, T.X. The “harmony with distinctiveness” in tourism development based on the case of the Silk Road. Hum. Geogr. 2011, 26, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the tourism value of linear heritage corridor in the Silk Road on the northwestern China. Arid. Land Geogr. 2011, 34, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, K.J.; Li, D.H. The theoretical framework of heritage corridor and the Grand Canal. Urban Probl. 2004, 26, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.J.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.H. A study on the spatial distribution characteristics of towns along the Silk Road. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 20, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Tao, L.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, J. Study on cultural corridor extent calculation and the construction of its tourism spatial structure—A case study of the southwestern Silk Road. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 128, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Shen, X.W.; Gao, J. Spatial structure of the leisure zone in urban waterfront: A case study of the Grand Canal in Downtown Hangzhou. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, A. “Chinese don’t walk?”—The emergence of domestic walking tourism on China’s Ancient Tea Horse Road. J. Leis. Res. 2020, 52, 424–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Chon, J.; Ahn, C. Planning landscape corridors in ecological infrastructure using least-cost path methods based on the value of ecosystem services. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7564–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, D.; Prescott, M.F.; Padawangi, R.; Girot, C.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Understanding the value of urban riparian corridors: Considerations in planning for cultural services along an Indonesian river. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishmanova, M.V. Cultural tourism in cultural corridors, itineraries, areas and cores networked. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 188, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N. The exploration of the relics of the Qin Shihuang’s Straight Road. Cult. Relics 1975, 10, 44–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Presumption about Wang Zhaojun’s Northbound Route. J. Northwest Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. Edit. 2014, 44, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jian, Z.; Sun, Y.; Pan, F.; Han, H.F.; Liu, Q.H.; Mei, Y. Ecological sustainability and high-quality development of the Yellow River Delta in China based on the improved ecological footprint model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Hu, S. Intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin: Its spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and differentiation causes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henareh Khalyani, A.; Mayer, A.L.; Webster, C.R.; Falkowski, M.J. Ecological indicators for protection impact assessment at two scales in the Bozin and Marakhil protected area, Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. A worldwide country-based assessment of social-ecological status (c. 2010) using the social-ecological status index. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquete, C.; Kleeschulte, S.; Dige, G.; Maes, J.; Grizzetti, B.; Olah, B.; Zulian, G. Mapping green infrastructure based on ecosystem services and ecological networks: A Pan-European case study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, K.; Buor, D.; Afriyie, K.; Dumedah, G.; Segbefifi, A.Y.; Guodaar, L.; Garsonu, E.K.; Adu-Gyamfifi, S.; Forkuor, D.; Ofosu, A.; et al. Urban sprawl and green space depletion: Implications for flood incidence in Kumasi, Ghana. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.R.; Kuang, W.H.; Liu, W.D.; Liu, A.L.; Pan, T. Optimizing the layout of eco-spatial structure in Guanzhong urban agglomeration based on the ecological security pattern. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Pan, Y.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, Y.L. Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Psomiadis, E. Inherent relationship of the USLE, RUSLE topographic factor algorithms and its impact on soil erosion modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.X. Estimating the ecological effect of soil conservation by vegetation in northwest China. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 610–617. [Google Scholar]
- Kouli, M.; Soupios, P.; Vallianatos, F. Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Yang, Y. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.W.; Zhen, J.H.; Ma, C.Y. Evaluation of ecological carrying capacity and optimization of ecological security pattern in Inner Mongolia. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J.; Wang, S.S.; Li, D.H. The function of ecological security patterns as an urban growth framework in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, Z.Y. Study on distribution characteristics of landscape elements along the terrain gradient. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2001, 21, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.W.; Zhen, J.H.; Feng, Y.; Tao, Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Han, S. Method and demonstration of urban growth boundary delimitation in arid regions: A case study of Hohhot city, Inner Mongolia. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Liu, C.X.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, H.; Min, J.; Wang, Y. Assessment and spatial differentiation of sensitivity of soil erosion in Three Gorges Reservoir area of Chongqing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 788–796. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, H.; Li, W.B.; Wu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.L. The ecological security pattern and its constraint on urban expansion of a black soil farming area in northeast China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.P.; Xu, X.L. Ecological corridors analysis based on MSPA and MCR model-a case study of the Tomur World Natural Heritage region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilty, J.L.; Lidicker, W.M.; Merenlender, A.M. Corridor Ecology: The Science and Practice of Linking Landscapes for Biodiversity Conservation; Island Press, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, G. Linkages in Practice: A Review of their Conservation Value; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2004.
- Nielsen, A.; Bascompte, J. Ecological networks, nestedness and sampling effort. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, M.; Song, K.; Lee, J. Planning a green infrastructure network to integrate potential evacuation routes and the urban green space in a coastal city: The case study of Haeundae District, Busan, south Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, H.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Wu, J.S. Research progress and prospect on regional ecological security pattern construction. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; Wit, P. IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria; Information Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Samways, M.J.; Pryke, J.S. Large-scale ecological networks do work in an ecologically complex biodiversity hotspot. Ambio 2015, 45, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Lindquist, M. Enhancing landscape connectivity through multi-functional green infrastructure corridor modeling and design. Urban For. Urban Green 2018, 38, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, V. Protecting the natural and cultural heritage of local landscapes: Finding substance in law and legal decision making. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.; Lennon, J. Cultural landscapes: A bridge between culture and nature? Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2011, 17, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, L.J.; Gordon-Nesbitt, R.; Elsden, E.; Chatterjee, H.J. The role of cultural, community and natural assets in addressing societal and structural health inequalities in the UK: Future research priorities. Int. J. Equity Health 2021, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.B.; Shi, Y.H.; Siaw, M.J.; Yang, F.; Wu, R.W.; Wu, X.K.; Zheng, X.Y.; Bao, Z.Y. Constructing and optimizing ecological network at county and town scale: The case of Anji County, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Song, W. Identifying ecological corridors and networks in mountainous Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Cao, Y.R.; Wu, J.Y.; Xiong, Y.M. Ecological network construction and optimization in Guangzhou from the perspective of biodiversity conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, É.G.; Brigatti, E.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Vieira, M.V. Dispersal movement through fragmented landscapes: The role of stepping stones and perceptual range. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 3249–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshany, M.; Shapira, A.; Nir-Goldenberg, S.; Paola, P.D. Progression of greenway corridors through conflict: Cellular automata simulation and AHP evaluation. Environ. Model Assess 2023, 28, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhao, G.H.; Fagerholm, N.; Primdahl, J.; Plieninger, T. Participatory mapping of cultural ecosystem services for landscape corridor planning: A case study of the Silk Roads corridor in Zhangye, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Asset Types | Indicators | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Natural assets | Land use and land cover types | Forest, grassland, cropland, wetland, water bodies, construction land, transportation land, bare area, snow/ice |
| Typical ecosystem services | Carbon sequestration and oxygen release, water conservation, habitat maintenance, soil retention | |
| Ecological sources | Concentrated contiguous high-quality ecological landscapes with high ecosystem services | |
| Ecological nodes | The center of ecological sources and the junctions of adjacent ecological corridors | |
| Ecological corridors | The linkages of ecological sources and nodes | |
| Cultural assets | Key sites of cultural heritage on the Qin Straight Road | Name, era, longitude and latitude, photos of heritages, conservation and construction situation, grade of cultural relics protection, protection range and construction control, value assessment |
| Routes and directions of Qin Straight Road | Location, length, width, conservation and construction situation, grade of cultural relics protection, protection range and construction control, value assessment | |
| Social and economic development of the counties | Economic development, population, urban and rural construction, traffic network | |
| Development of culture-related infrastructure | Monument for cultural relics protection, heritage protection fence, heritage signboard, warning signs, museum |
| County Unit | Ecological Sources | Ecological Corridors | Ecological Nodes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Proportion (%) | Length (km) | Proportion (%) | Number (Node) | Proportion (%) | |
| Hengshan District | 267.61 | 6.08 | 310.97 | 10.58 | 2 | 10.53 |
| Jingbian County | 214.20 | 4.87 | 180.11 | 6.13 | 2 | 10.53 |
| Zhidan County | 295.43 | 6.71 | 204.10 | 6.95 | 2 | 10.53 |
| Ansai District | 186.10 | 4.23 | 175.41 | 5.97 | 0 | 0 |
| Ganquan County | 302.24 | 6.87 | 347.42 | 11.82 | 1 | 5.26 |
| Fu County | 886.49 | 20.15 | 1132.15 | 38.53 | 7 | 36.84 |
| Huangling County | 450.91 | 10.25 | 340.87 | 11.60 | 3 | 15.79 |
| Xunyi County | 961.77 | 21.86 | 246.04 | 8.37 | 0 | 0 |
| Chunhua County | 835.14 | 18.98 | 1.42 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 |
| Project Type | Name | Scale | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landscape corridor | Urban Landscape Corridor of the Culture–Ecology of the Qin Straight Road (Xunyi) | 9.12 km | Chengguan Street (Xunyi County) |
| Landscape corridor | Urban Landscape Corridor of the Cultural Heritage of the Qin Straight Road (Chunhua) | 22.96 km | Tiewang Town (Chunhua County) |
| Landscape corridor | Countryside Landscape Corridor of the Cultural Heritage of the Qin Straight Road (Xunyi) | 26.49 km | Chengguan Street (Xunyi County) |
| Landscape corridor | Ecological Landscape Corridor of the Natural Scenery of the Qin Straight Road (Xunyi) | 21.07 km | Malan Town (Xunyi County) |
| Landscape corridor | Ecological Landscape Corridor of the Cultural Heritage of the Qin Straight Road (Ganquan) | 13.09 km | Dao Town (Ganquan County) |
| Landscape corridor | Ecological Landscape Corridor of the Natural Scenery of the Qin Straight Road (Ganquan) | 8.53 km | Meishui Street (Ganquan County) |
| Park | Malanhe Municipal Country Park in Xunyi County (Municipal) | 19.51 km2 | Zhitian Town (Xunyi County) |
| Park | Yeyuhe Municipal Country Park in Chunhua County (Municipal) | 8.87 km2 | Tiewang Town (Chunhua County) |
| Park | Beiluohe Provincial Forest Park in Ganquan County (Provincial) | 30.59 km2 | Dao Town (Ganquan County) |
| Park | Zhouhe Provincial Forest Park in Zhidan County (Provincial) | 27.71 km2 | Yongning Town (Zhidan County) |
| Park | Yanhe Provincial Forest Park in Ansai District (Provincial) | 11.77 km2 | Pingqiao Town (Ansai District) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Cao, X.; Yao, L. Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage Based on Regional Ecological Security Pattern along the Straight Road (Zhidao) of the Qin Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071361
Li H, Zhang T, Cao X, Yao L. Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage Based on Regional Ecological Security Pattern along the Straight Road (Zhidao) of the Qin Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China. Land. 2023; 12(7):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Han, Tian Zhang, Xiaoshu Cao, and Lingling Yao. 2023. "Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage Based on Regional Ecological Security Pattern along the Straight Road (Zhidao) of the Qin Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China" Land 12, no. 7: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071361
APA StyleLi, H., Zhang, T., Cao, X., & Yao, L. (2023). Active Utilization of Linear Cultural Heritage Based on Regional Ecological Security Pattern along the Straight Road (Zhidao) of the Qin Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China. Land, 12(7), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12071361





