Abstract
Land resources are essential natural resources and strategic economic resources for human survival and development. However, human improper use has brought unprecedented pressure and challenges to the ecosystem. Therefore, the assessment and analysis of land ecological security status and the identification and diagnosis of obstacles affecting land ecological security are helpful to avoid land ecological security problems caused by improper land use at the source and provide a theoretical basis for the sustainable use of land resources and the construction of ecological civilization in China. Based on the data from 2006 to 2020, this study constructed the land ecological risk-evaluation index system and land ecological health-evaluation index system. AHP, entropy method, combination weighting method, TOPSIS model, Boston matrix and obstacle degree model were used to assess the land ecological security situation in Nanyang City and to analyze the obstacle factors. The results show the following: (1) during the study period, the land ecological risk value of Nanyang City exhibited a Kuznets inverted “U” curve change, while the land ecological health value showed a “U” curve change; (2) the overall level of land ecological security in Nanyang City has gradually improved, with a security level pattern of “relatively safe (2006–2020)–unsafe (2011–2016)–relatively safe (2017–2019)–safe (2020)”; (3) the main obstacle factors of land ecosystem were the following: erosion area, sewage discharge, area of waterlogging control, grain sown area, coverage of urban green built-up area and farmland effective irrigated area.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Land resources are one of the important basic elements of ecological civilization construction [1], and ecological security is an important content of ecological civilization construction [2]. Therefore, assessment of land resource ecological security is the premise and foundation of ecological civilization construction [3]. Identifying and diagnosing obstacles through land ecological security assessment is of great significance to the construction of ecological civilization. The construction of ecological civilization is closely related to the well-being of the people and the sustainable development of the Chinese nation [4]. Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (CPC), the construction of ecological civilization has been promoted in an unprecedented way [4], and the concept “Lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets” [5] has gradually gained popularity. The construction of ecological civilization involves not only an urgent need to improve the ecological environment, but is also a necessary condition to ensure the sustainable development of the economy and society [6]. At present, China is in a critical period of transition from a large developing country to a socialist modernization power [7]. However, the deterioration of ecological environments restricts the development of the social economy. According to data released by the Ministry of Natural Resources, a comparison of data from the Third National Land Survey and the Second National Land Survey shows that during the 10-year period, the area of cultivated land in the country decreased by 7.53 million hectares, while the amount of construction land increased by 26.5% [8,9]. The main reason is that the relevant systems of cultivated land protection, ecological construction, economical and intensive land use and cultivated land requisition-compensation balance are not perfect, and “non-agricultural” and “non-grain” cultivated land continue to emerge [8]. Facing the severe situation of tight resource constraints and fragile state environment, China has recognized the importance of building an ecological civilization; the General Office of the State Council has issued more comprehensive and systematic ecological environment governance systems, such as “Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on preventing ‘non-grain’ cultivated land and stabilizing grain production” [10], “The Rural Revitalization Promotion Law of the People ‘s Republic of China” [11], “Regulations on the Implementation of the Land Administration Law of the People ‘s Republic of China” [12].
China, as a large agricultural country as well as a major country with great demand for grain [13], must vigorously develop agriculture to improve the quality of agricultural products to meet the growing material needs of the people [14]. As a result, the extensive use of production factors such as pesticides, fertilizers and plastic films, along with the long-term extensive development of China’s agriculture, has led to excessive land reclamation, posing unprecedented challenges to the global ecosystem [15]. Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, we have embarked on a resource-saving and environment-friendly path of agricultural modernization guided by green development [16]. In the report of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, it was pointed out that the green development of agriculture should be promoted as a national strategy, and the role of green development of agriculture in ensuring ecological security should be clarified [17]. Therefore, agricultural green development is an important way to ensure ecological security. How to ensure land ecological security under the background of agricultural green development has become an urgent problem to be solved.
In view of this, this research was based on data from 2006 to 2020 and constructed the land ecological risk-evaluation index system of Nanyang City from three dimensions: “risk source–risk receptor–risk effect” [18]. The evaluation index system of land ecological health was established from four dimensions: “land ecological elasticity–land ecological vitality–land ecological structure–land surface pollution source” [19]. The entropy method [20], the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) [21] and the combination weighting method (CWM) [22] were used to calculate the land ecological risk value and index weight. The entropy method and TOPSIS model [23] were employed to calculate the index weight, land ecological health value and annual health score. The Boston matrix [24] was used to couple the land ecological risk value and land ecological health value. Finally, the obstacle degree model [25] was used to identify the obstacle factors. The purpose of this study is to assess and analyze the land ecological security situation in Nanyang City from 2006 to 2020, identify and diagnose the obstacle factors affecting ecological security, avoid land ecological security problems caused by improper land use at the source and provide a theoretical basis for the sustainable use of land resources and the construction of ecological civilization in China.
1.2. Literature Review
Land resources are fundamental natural resources and strategic economic resources that are essential for human production and livelihood [26]. Unfortunately, with the aggravation of natural disasters, the acceleration of urbanization and the extensive management of agriculture [15], the use of land by human beings has exceeded the carrying capacity of land. This situation causes irreparable losses of biodiversity and soil erosion [27], further exacerbating the tension between humans and the environment. Therefore, issues related to land ecological security have gradually become the research object of scholars all over the world.
In 1989, the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) first introduced the concept of ecology security, which has since attracted extensive attention [28]. Land ecological security refers to a state in which the land ecosystem is able to sustainably meet the structural, quantitative and qualitative needs of both the environment and human survival and development [29]. This state results from the combined influence of the ecosystem’s own health and the risks posed to it by the external environment [30]. The core of the research into it is the assessment of ecological security status [31]. Therefore, land ecological security assessment takes ecological risk and ecological health assessment as the center, identifying and analyzing the integrity of the ecosystem and its sustainable ability to maintain health under various risks [32]. The assessment of ecological security by international scholars mainly focuses on industrial mining and agricultural pollution [33], such as soil health [34] and agricultural production. Okosa et al. analyzed the contents of heavy metals (Cr, Pb, Cd, Ni, Cu and Zn) in the soils of urban and suburban landfills in Umuahia, Abia state, and assessed the human health hazards and ecological risks of heavy metals from waste sites in the residential vicinity [35]. San et al. detected and quantified pesticide residues in the sediment of rural streams in the Pampas region and conducted acute and chronic risk assessment in these aquatic ecosystems [36]. In China, most Chinese scholars use the entropy method and analytic hierarchy process to assess forest and land ecological security [37]. Fang et al. used the entropy method and analytic hierarchy process to determine the weight of the index-evaluation system and carried out the practice and an evaluation of the saline-alkali land ecological management method in Shanxi Province [38]. Chen et al. used the entropy method to determine the weight of the forest ecological security-evaluation index system and evaluated the forest ecological security dynamics in Gansu Province [39].
In 1992, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) first defined ecological risk assessment as a process of assessing the probability of ecological insecurity that occurs or is occurring due to one or more factors [40]. Therefore, land ecological risk assessment can be regarded as an evaluation process of the impact of external environmental factors on land structure and quantity and quality and human life [41]. In recent years, the research on ecological risk assessment has been extended from the risk assessment of a single risk source and a single receptor to the ecological risk assessment of multiple risk sources at the basin and landscape scales [42]. The investigation of land ecological security in China began relatively recently and so regional application research is mainly based on international ecological risk assessment theories and methods [43]. At present, international scholars mainly use the landscape ecological risk-assessment model to analyze the ecological risk, and try to use multiple indicators to evaluate the landscape ecological risk [44]. Scott et al. combined landscape fragmentation score and land use and land cover vulnerability score, and also assessed the link between risk areas and economic activities; the environment and infrastructure are considered to be the main drivers of Delhi ‘s urban expansion [45]. Dimri et al. took the south-western foothills of Central Himalaya as a case study; this study assessed the spatiotemporal variations in landscape structure and landscape ecological risk (LER) influenced by the road network and topography, and results indicated that high-risk LER zones were closer to the road network [46]. Chinese scholars’ assessment of ecological risks mainly use land use as an incentive to explore the causes of ecological risk changes [44]. The research has mainly concentrated on basins, grasslands, cities and so on. Yu et al., based on the idea of landscape ecology, constructed an ecological risk assessment system to evaluate the ecological risk of land use in Nanchang City from 2005 to 2017 [47]. Liu et al. calculated the landscape pattern index of the Yellow River Basin and constructed an ecological risk-assessment model to reveal the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and spatial correlation of ecological risks from the grid scale and county scale [48].
Ecological risk and ecological health are two systems that blend and depend on each other [32]. Land ecological health refers to the state in which the land maintains its own normal metabolism, which is a manifestation of the mutually beneficial relationship between humans and the land [49]. Therefore, the evaluation of land ecological health aims to assess the health and quality of the land itself, as well as the state of each element in the land ecosystem and the interrelationships between them [29]. The concept of land health was first proposed by Aldo Leopold in 1941 and was used to evaluate the status of land function [50]. The research objects of international scholars on land ecological health mainly involve cities, agriculture and grasslands [51]. Zaredar et al. emphasized the risk of climate change on the health of agricultural land when discussing the impact of climate change on land suitability for agricultural development in Karkheh River Basin and Iran [52]. Herrick et al. provided a review of conditions for meeting management and policy objectives, summarized current approaches to defining the reference for land health and degradation assessments, and presented a protocol, “Describing Indicators of Rangeland Health” (DIRH), for collecting and organizing data that can be used to define a historic reference [53]. Chinese scholars’ research on land health mainly focuses on river basins, coastal zones and land ecological security. Li et al. constructed an ecosystem health-assessment model to analyze the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of ecosystem health in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region in 2000, 2010 and 2020 [54]. Liu et al., based on the modified vitality-organization-elasticity-service model of neighborhood variability and human disturbance, evaluated the ecosystem health status of the East China Sea coast from 1990 to 2015 [55].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
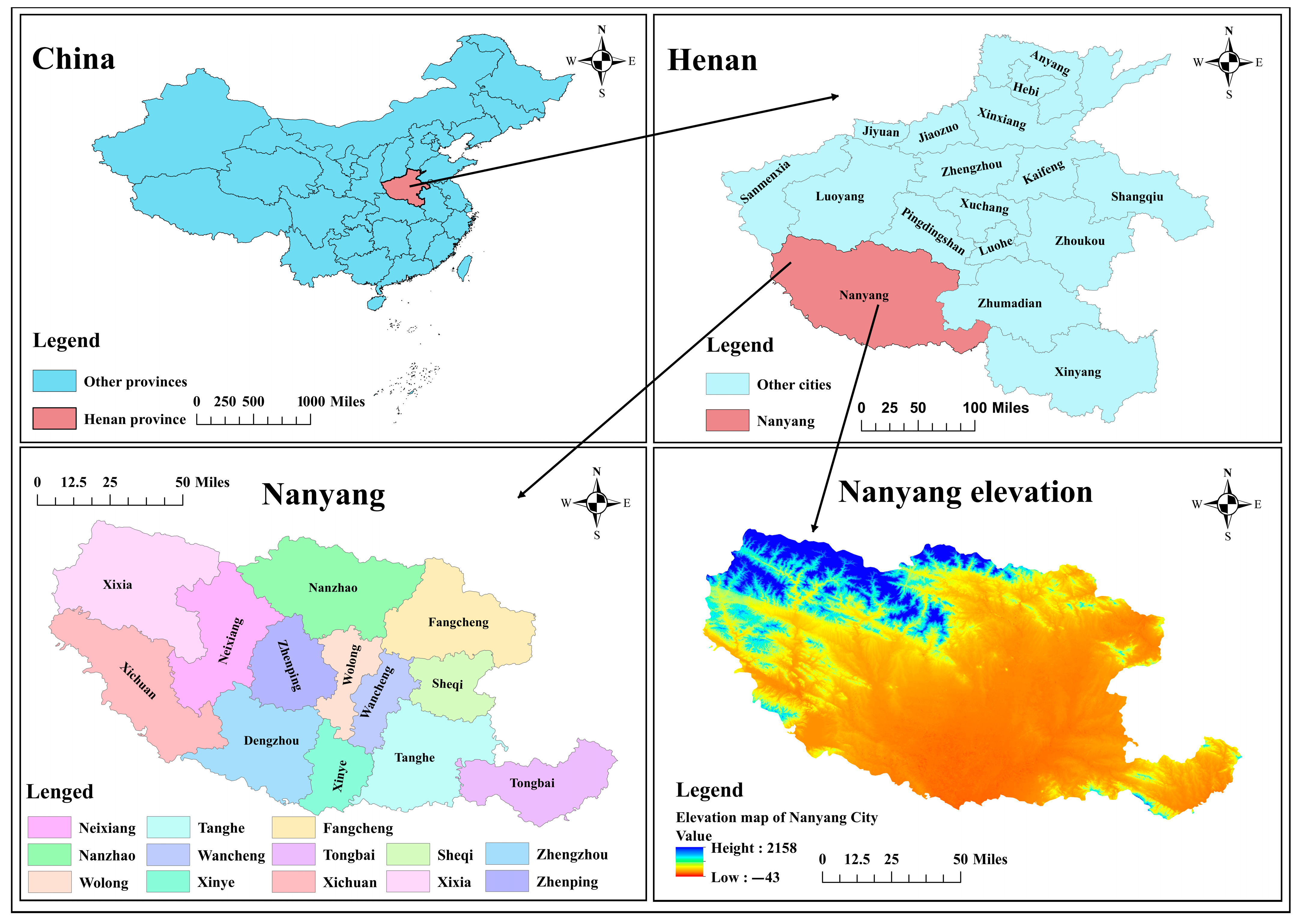
Henan Province (110°21′–116°39′ E, 31°23′–36°22′ N) is located in central and eastern China, the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River; Nanyang City (110°58′–113°49′ E, 32°17′–33°48′ N) is located in the intersection of Henan, Hubei and Shaanxi (Figure 1). According to the main data bulletin of the third land survey in Nanyang City, the cultivated land area of Nanyang City is 984,313.72 hm2, accounting for 13.11% of the cultivated land area of Henan Province (7,514,100 hm2). Nanyang City is also the water source of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, which greatly improves the efficiency of resource allocation.
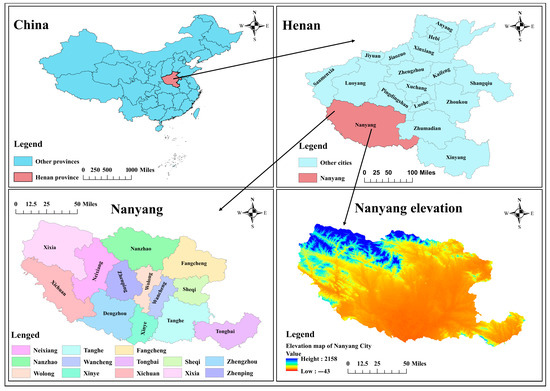
Figure 1.
The geographical location of the study area.
Nanyang City is not only an important grain-production base in China and the core area of grain production in Henan Province within the national food security strategy project, known as the “Zhongzhou granary”, but also the sub-center city of Henan Province. According to the statistics of Nanyang Municipal Bureau of Statistics in 2022, the grain output of Nanyang City is as high as 71,555 billion kilograms, accounting for 10.5% of the total grain output of the province. Nanyang city‘s annual GDP reached 455.54 billion yuan at comparable prices, an increase of 4.8% over the previous year, and 1.7 percentage points higher than the province. Therefore, it is of great typical and representative value to select this area for land ecological security evaluation.
2.2. Data Sources
The data of the study area include land use data, agricultural production factor input data, natural disaster data and socio-economic development data. The above data are derived from the Henan Statistical Yearbook 2007–2021, the Nanyang Statistical Yearbook 2007–2021, the Nanyang Water Resources Bulletin 2006–2020 and the Nanyang National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin 2006–2020. The Chinese provincial division vector map, Henan municipal division vector map and Nanyang digital elevation vector map data used in this study are all from the geospatial information cloud. The non-computational data and related information involved in the conclusion of the study are derived from the “Nanyang City National Economic and Social Development Eleventh Five-Year Plan”, the “Nanyang City National Economic and Social Development Twelfth Five-Year Plan” and the “Nanyang City National Economic and Social Development Thirteenth Five-Year Plan”. In addition, the software used for data processing in this study are IBM SPSS Statistics 27 and ArcMap 10.8.
2.3. Construction of Index System
2.3.1. Construction of Land Ecological Risk Index System
Based on the characteristics of the research area, a three-dimensional land ecological risk assessment index system was established for Nanyang City, which includes the dimensions of “risk source (A1)–risk receptor (A2)–risk effect (A3)” [17]. Risk source refers to the possible ecological risk stress factors faced by the study area, risk receptor refers to the acceptor or carrier of ecological risk and risk effect refers to the characterization of the effect of different risk receptors on risk source based on the evaluation purpose and evaluation endpoint [56]. In summary, a total of 14 indicators were selected to construct the land ecological risk index system for Nanyang City, including the amount of fertilizer use (B1), pesticide use (B2), and plastic film use in agriculture (B3). The land ecological risk index system for Nanyang City is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Nanyang City’s land ecological risk index system.
2.3.2. Construction of Land Ecological Health Index System
Land health is an important guarantee for the green development of agriculture [57]. The ecological vitality of land refers to the ability of the ecosystem to respond to external disturbances and its overall state. The ecological resilience of land refers to the capacity of an ecosystem to recover to its original state after being exposed to external disturbances [58]. The ecological structure of land refers to the ability of an ecosystem to anticipate and prepare for external disturbances before they occur. Therefore, this study establishes the land ecological health-evaluation index system in four dimensions of “ecological resilience (C1)–ecological vitality (C2)–ecological structure (C3)–land surface pollution (C4)” [19], which includes 16 indicators such as the cultivated land pressure index (D1), forest coverage rate (D2) and surface water resources (D3). The land ecological health index system for Nanyang City is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Nanyang City’s land ecological health index system.
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Analytic Hierarchy Process
The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) was first introduced in the 1970s [21]. The AHP is a technique used to analyze problems related to decision-making that involve multiple criteria [59]. The AHP method has the capability to involve multiple participants, make interdisciplinary evaluations and ensure transparency in the decision-making process. The basic principle of the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is to break down a problem into its various constituent elements based on the nature of the problem and the overarching goal that needs to be achieved [21]. AHP forms other hierarchical sets based on the interaction and appropriate relationships between the elements, including the formation of a multi-level analytical structure model [60]. The calculation steps of the AHP in detail are as follows [60]:
Step 1: Constructing judgment matrix.
Assuming that there are solutions in the project, and each solution has indicators, represents the th indicator of the th solution. The judgment matrix is constructed by comparing the importance of each indicator among all solutions.
As the matrix shows, if = 1, it means that and are equally important. If = 5, it means that is more important than . The larger the value of , the more important is compared to .
Step 2: Calculate the Weight Vector.
In the formula, is the maximum eigenvalue (unique value) of the judgment matrix; is the weight vector, which can be used after normalization. is the weight vector of the th index and is the normalized weight after normalization.
Step 3: Consistency Check.
is the order of matrix; is the consistency indicator and is the consistency ratio. refers to Random Index. The smaller the value, the greater the consistency of the matrix. When < 0.1, it is considered that the judgment matrix has satisfactory consistency. If the consistency ratio > 0.1, it is necessary to adjust the scaling of the judgment matrix.
2.4.2. The Entropy Method
The entropy method is a widely recognized objective weighting method in decision-making [20] that determines the weight value of each index by analyzing the information entropy of the index [61]. This method assigns a higher weight to the index with a greater degree of relative change; thus, it is considered more significant in the decision-making process [61]. The detailed calculation steps of the entropy method are as follows [61]:
Step 1: Index Standardization.
Calculate the weight of the th year index value under the th index.
represents the index value of the th year under the th index, and represents the number of years.
Step 2: Calculate the weight of the th index.
Step 3: Calculate the difference coefficient of the th index.
Step 4: Define the weight of the th index.
2.4.3. Combinatorial Weighting Method
The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is used to determine the subjective weight of each indicator [62], whose value depends on the experience and knowledge of the decision maker [63]. As a method of objective weighting, the entropy method cannot reflect the relationship between relevant indicators better [64], which may violate the objective law [63]. Therefore, the combination of the AHP method and the entropy method is used for comprehensive evaluation, which not only makes full use of objective information for data analysis through the entropy method, but also satisfies the subjective desire of decision makers as much as possible through the AHP method [62,65]. Specific calculation steps are as follows:
Step 1: Using the multiplicative normalization method, the weight values obtained by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy method were coupled to obtain the comprehensive weight values of land ecological risk index factors.
where is the weight value of land ecological risk weighted by combination, is the index item and is the total amount with respect to the index. is the index weight calculated via the entropy method, and is the index weight calculated via the analytic hierarchy process.
Step 2: After the standardization of all data, the combination weighting method is used to weight all indicators, make a comprehensive evaluation and calculate the ecological risk index.
where is the ecological risk index of Nanyang City, is the year, is the total number of years and represents the value of the th index in year .
2.4.4. TOPSIS Model
The Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) [23] is a multi-criteria decision-analysis method [66]. The fundamental principle is to rank and evaluate objects by measuring the distance between the evaluated object and both the positive ideal solution and negative ideal solution [67]. The optimal solution is achieved when the evaluated object is in proximity to the positive ideal solution and far away from the negative ideal solution, while the worst solution is the opposite [66]. Thus, the TOPSIS model was employed in this study to calculate the land ecological health value of Nanyang City from 2013 to 2020 and assign a corresponding grade. The calculation steps of the TOPSIS model in detail are as follows [23,66]:
Step 1: Weight the land ecological health index calculated via the entropy method to obtain the weighting matrix:
where is the weighted matrix, is the index weight calculated via the entropy method and is the normalized vector matrix.
Step 2: Determine positive ideal solutions and negative ideal solutions.
where is the optimal solution and is the negative solution; denotes the normalized value of the th indicator in the th year.
Step 3: Determine the distance between the index and the positive ideal solution and the negative ideal solution.
where is the distance from the assessment object to the positive solution, and is the distance to the worst solution.
Step 4: Calculate the ideal solution closeness.
where the proximity index is the ecosystem health value, which generally ranges from 0 to 1; when the value of is closer to 1, it indicates that the land ecological health in the area is closer to the healthiest state. Conversely, when is closer to 0, it indicates that the land ecological health in the area is closer to an unhealthy state.
2.4.5. Boston Matrix Analysis
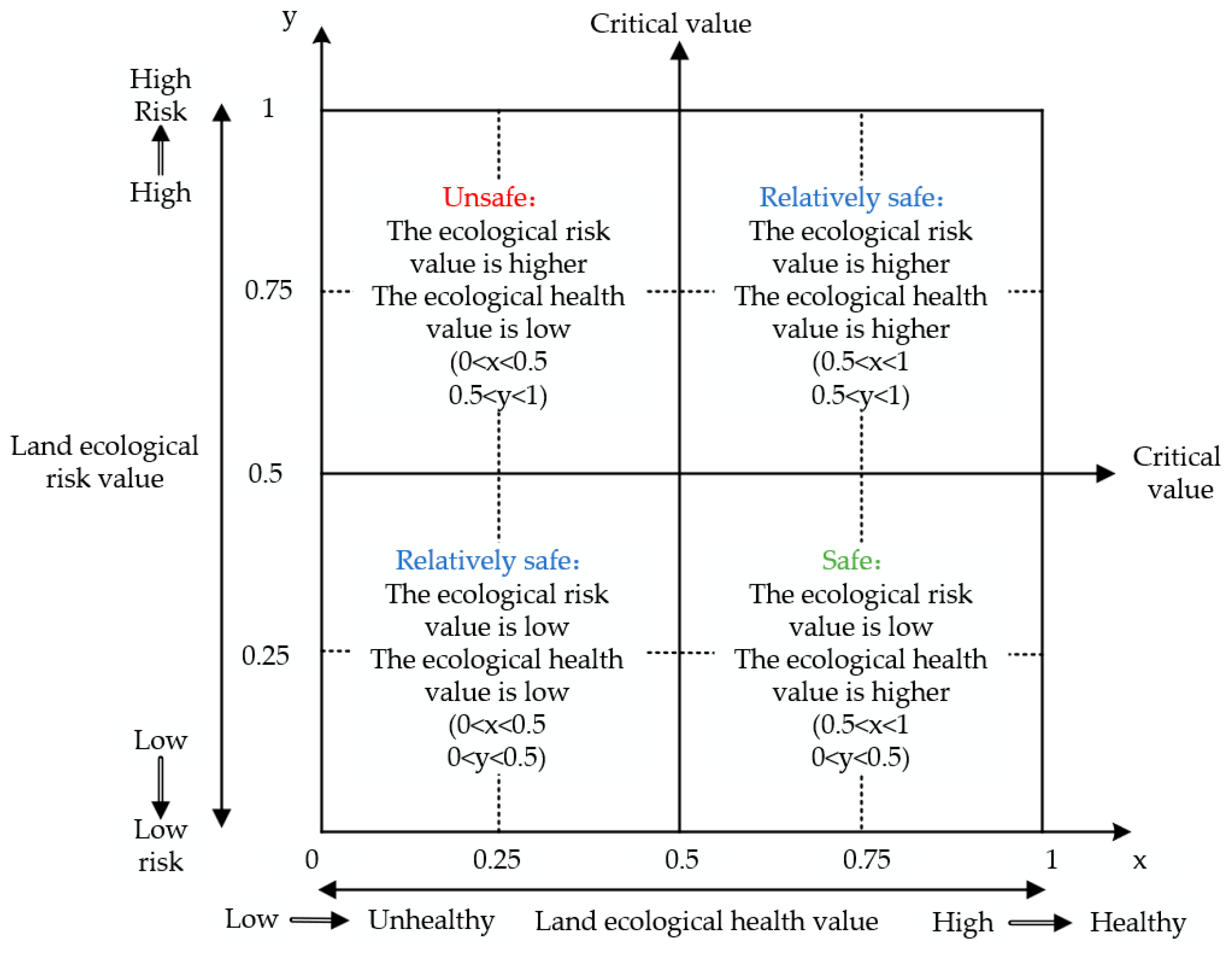
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix is a quantitative analysis method that emphasizes objectivity and accuracy [68]. It is straightforward and easy to comprehend, allowing for easy evaluation [68]. In addition, the basic principle of the Boston matrix analysis method has obvious rationality and simplicity of application [68]. Hence, this study couples the ecological risk assessment and ecological health assessment using the Boston matrix. Ecological security can be classified into three states: secure, relatively secure and insecure. “Secure” refers to a state in which the land health value is high and the risk value is low. “Relatively secure” refers to a state where both the land health value and the land risk value are either high or low. “Insecure” refers to a state where the land health value is relatively low and the land risk value is relatively high.
In summary, this study utilizes the Boston matrix model and applies it to research on land ecological security. The land ecological risk value and land ecological health value of Nanyang City are both presented separately in this matrix model. In the matrix, the horizontal axis represents the index of land ecological health assessment, while the vertical axis represents the index of land ecological risk assessment. The Boston matrix is constructed by combining the two variables, land ecological health evaluation and land ecological risk evaluation. The closer the ecological risk index is to 0, the smaller the land ecological risk. The closer the ecological health index is to 1, the healthier the land ecology. The Boston matrix distribution diagram for land ecological security assessment is shown in Figure 2 below:
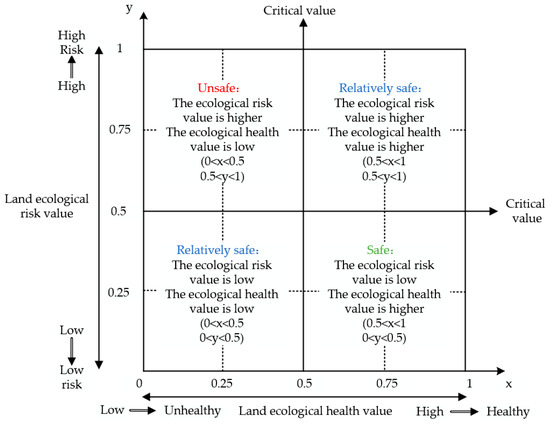
Figure 2.
Boston matrix distribution diagram for land ecological security assessment.
2.4.6. Obstacle Degree-Analysis Model
The obstacle-analysis model analyzes and diagnoses various indicators by mining the trends and degrees of their impact on the development of things, and identifies key factors that have a significant impact on the results of land ecological security assessment [25]. The evaluation of land ecological security is not only intended to judge the regional land ecological status, but also to clarify the obstacle factors affecting land ecological security [69]. Therefore, introducing factor contribution (the factor contribution degree represents the contribution degree of indicators to the target, which can be expressed by the weight of indicators [69]), indicator deviation (index deviation degree represents the difference between index and ideal value [69]) and obstacle degree (the influence degree of the single index and the index layer on land ecological risk or ecological health or ecological security is expressed, respectively), a model for obstacle analysis can be developed to analyze the obstacle factors that affect ecological security. The calculation steps of the obstacle degree-analysis model in detail are as follows [69]:
Step 1: Determine index deviation degree.
where is the deviation degree of indicators, and is the standardized value of each indicator.
Step 2: Calculate the obstacle degree of a single indicator.
In the formula, and , respectively, represent the obstacle degree of single index and index layer to land ecological risk or land ecological health. is the factor contribution degree, namely the index weight, and 15 is the research interval.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Assessment Results and Discussion
3.1.1. Land Ecological Risk Assessment
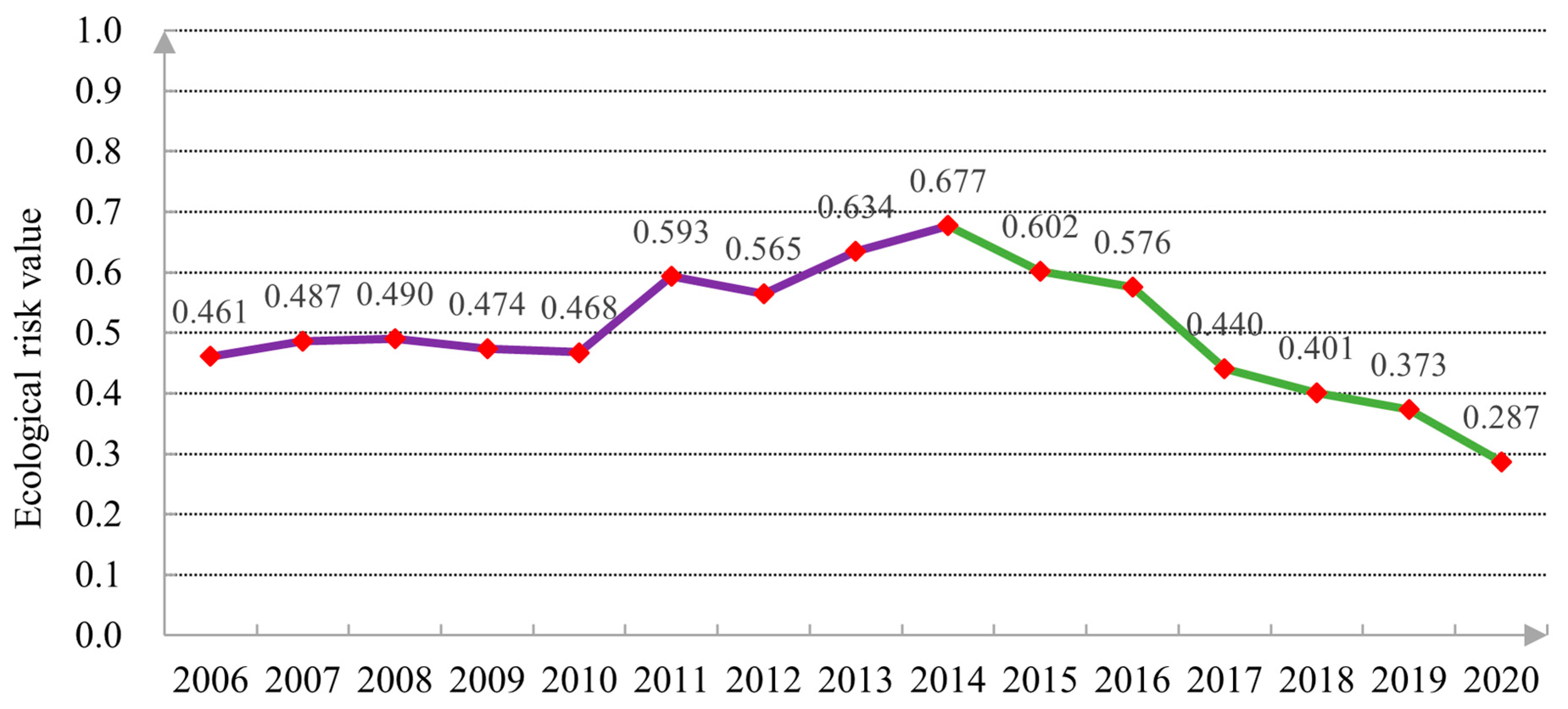
Formulas (1)–(10) were used to calculate the value of land ecological risk in Nanyang City, and in order to accurately and intuitively analyze the results of land ecological risk in Nanyang City, a trend chart was drawn as shown in Figure 3. As can be seen from the figure, the land ecological risk value of Nanyang City presents the change of a Kuznets curve [70], with the risk value first rising and then declining. The colors of the two sections in the broken line chart respectively represent the two trends of the change of land ecological risk value. During the period of 2006 to 2014, the broken line color was purple, and the risk value continued to rise from 0.461 in 2006 to 0.677 in 2014. During this period, there was no significant change in the ecological risk value from 2006 to 2010, and during 2010 to 2014, ecological risk value increased significantly. Between 2015 to 2020, the broken line color is green, and the risk value decreases year by year from 0.602 in 2015 to 0.287 in 2020.
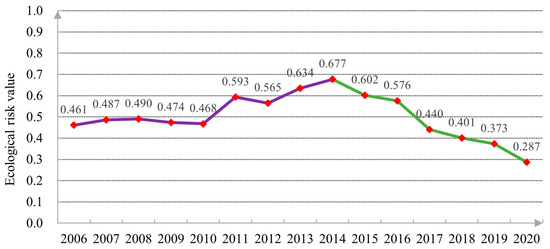
Figure 3.
Nanyang City’s trend chart of land ecological risk value.
3.1.2. Land Ecological Health Assessment Results
As shown in Table 3, the land ecological health score and ranking of Nanyang City from 2006 to 2020 were calculated via Formulas (5)–(8) and Formulas (11)–(16). It can be seen from the table that the score of land ecological health in 2020 is the highest in the study area, the score in 2019 is the second highest and the land ecological health in 2015 is ranked 15, which is the worst year in the study area. From 2006 to 2015, the score of land ecological health in Nanyang City gradually decreased, and the score of ecological health gradually increased from 2016 to 2020, and the ranking also gradually increased.

Table 3.
Calculation results of TOPSIS model of land ecological health in Nanyang City from 2006 to 2020.
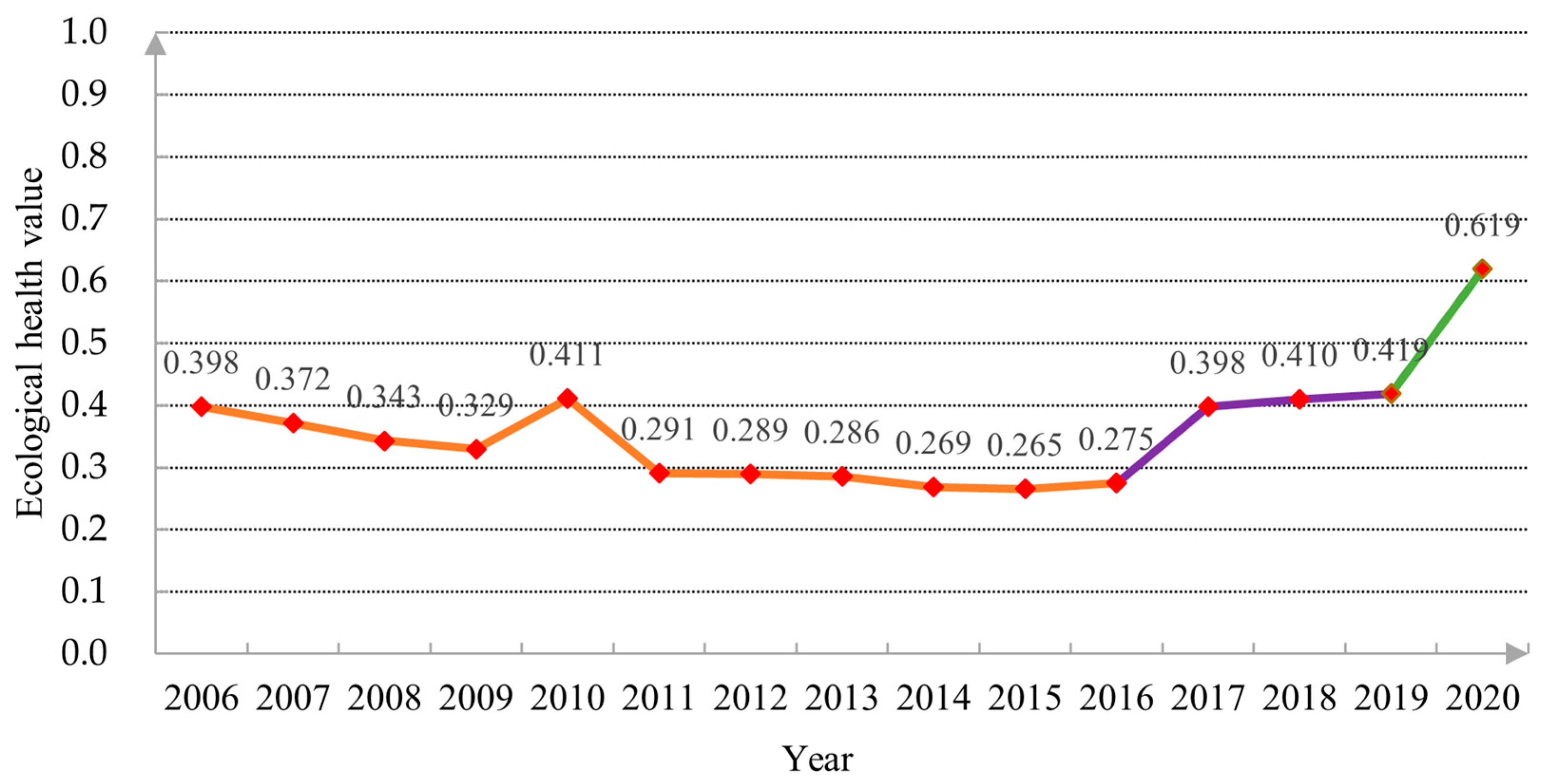
As shown in Figure 4, this is the trend map of land ecological health evaluation in Nanyang City, showing a U-shaped curve change. The three colors in the trend map represent the three health states of land ecology in Nanyang City. During 2006–2016, the line chart was orange yellow, and the ecological health value decreased from 0.398 to 0.275 year by year. During 2017–2020, the line chart was purple and green, and the ecological health value steadily increased from 0.398 to 0.619 during the green period. By comparing the land ecosystem health assessment criteria (Table 4), the orange-yellow area (2006–2016) in the trend map is in a relatively unhealthy state, 2017–2019 (purple area) is in a critical health state and 2020 (green area) is in a relatively healthy state.
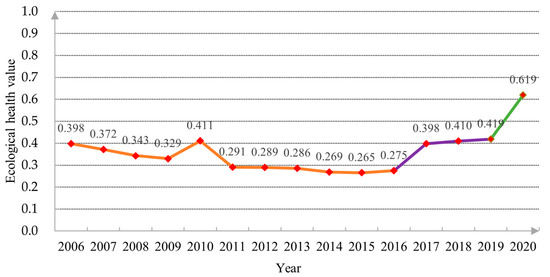
Figure 4.
Nanyang City’s trend chart of land ecological health value.

Table 4.
Land ecosystem health-evaluation criteria.
3.1.3. Land Ecological Security-Assessment Results Based on Boston Model
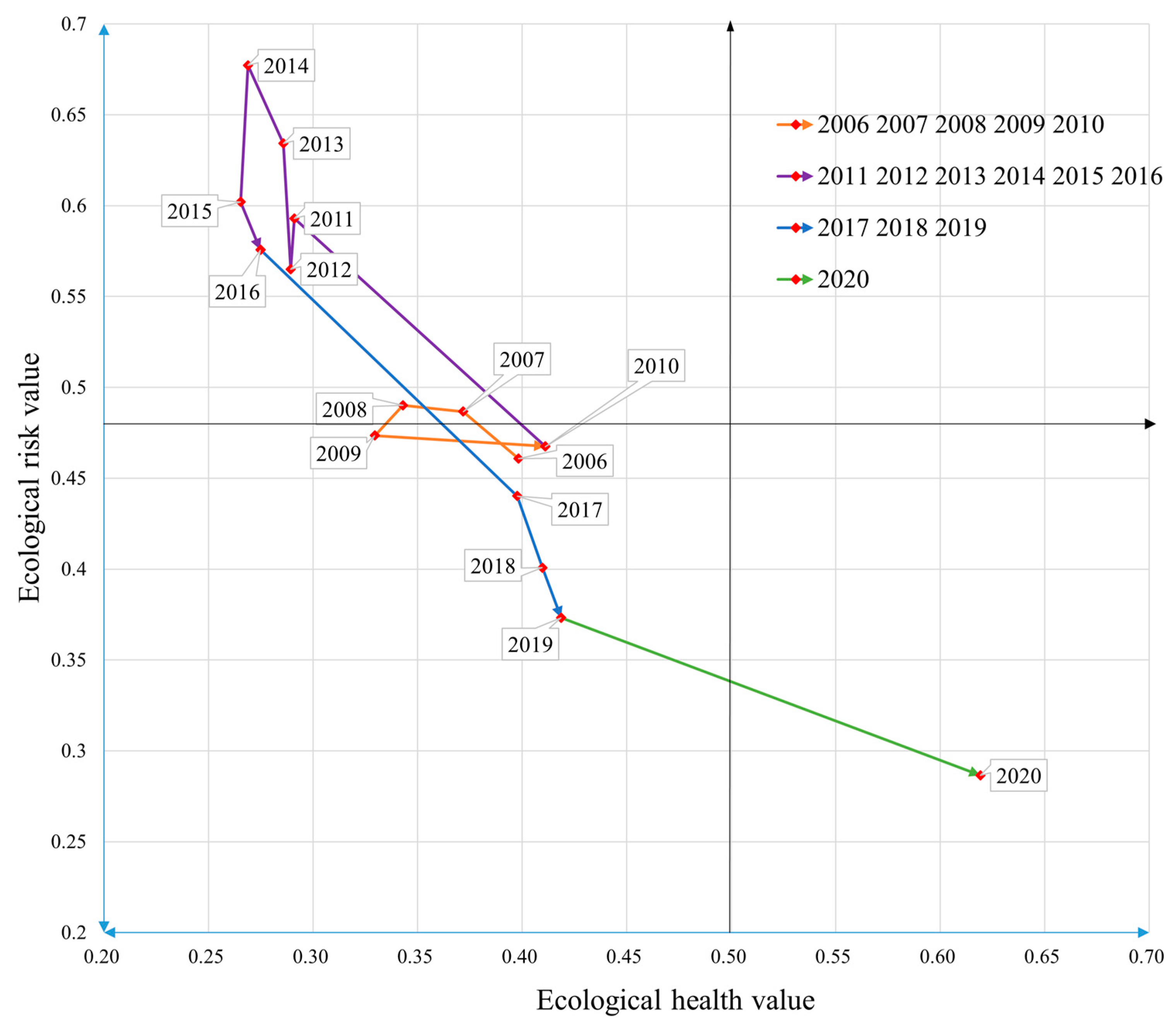
In the past, assessment and research methods often relied on a relatively narrow range of assessment indexes to conduct research and assessments. This study utilizes the Boston matrix model to assess the safety status of the land ecological system by integrating both the land ecological risk value and the land ecological health value. The coupling results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 5.

Table 5.
Ecological risk value and ecological health value of land in Nanyang City from 2013 to 2020.
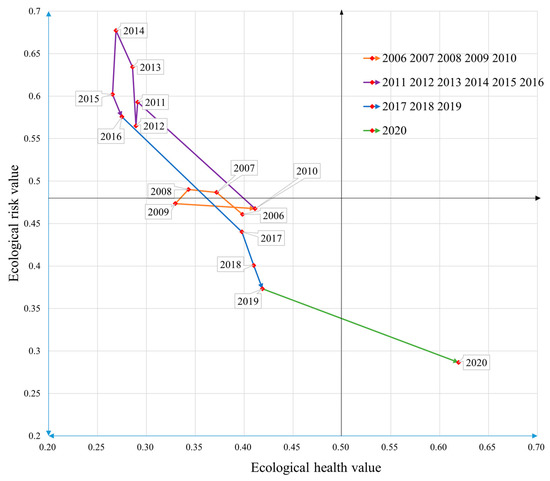
Figure 5.
Coupling results of land ecological security in Nanyang City.
As shown in Figure 5, the four-color curves represent the four stages of land ecological security in Nanyang City. The orange-yellow color in the diagram is the ecological security change trend from 2006 to 2010. Nanyang City maintained a relatively safe condition with stable ecological risk and ecological health values (0.46, 0.40) and (0.47, 0.41), respectively. The purple line segment is the change trend of 2011–2016, the land ecology of Nanyang City in an unsafe state with an overall increase in ecological risk value (0.59 to 0.60) and a decrease in ecological health value (0.29 to 0.27). The blue line segment represents the change of land ecological security from 2017 to 2019. During this period, the land ecological risk value decreased from 0.440 in 2017 to 0.373 in 2019, and the ecological health value increased from 0.398 in 2017 to 0.419 in 2019. The land ecology is in a relatively safe state. The green line segment represents the change in land ecological security from a relatively secure state to a secure state from 2019 to 2020. The ecological risk value decreased from 0.373 in 2019 to 0.287 in 2020, and the ecological health value increased from 0.419 in 2019 to 0.619 in 2020.
3.2. Obstacle Factor Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of the Risk Obstacle Factors for Land Ecology
Table 6 displays the obstacle degree of the indicator layer for land ecological risk assessment in Nanyang City, sorted by subsystems of risk source, risk receptor and risk effect. Overall, from 2006 to 2014, the obstruction degree of risk effect (A3) was found to be higher than that of risk source (A1), which was in turn higher than the obstruction degree of risk receptor (A2). During the period from 2015 to 2020, the obstruction degree of risk receptor (A2) was found to be higher than that of risk source (A1), which was in turn higher than the obstruction degree of risk effect (A3). Overall, the degree of obstruction of risk effect (A3) gradually changes to the obstructive degree of risk receptor (A2), indicating a reduction in the threat of ecological risk in Nanyang City.

Table 6.
Table of obstruction degree ranking of criterion layer for land ecological risk assessment.
To further determine the obstacle factors affecting the land ecological risk in Nanyang City, Table 7 shows the ranking of obstacle degree for individual indicators, in which the top five obstacle factors are selected as the main obstacle factors.

Table 7.
Table of obstruction degree ranking of index layer for land ecological risk assessment.
From the ranking results, it can be seen that during the period from 2006 to 2014, indicators such as B4 (amount of sewage discharge) (9 times), B6 (area affected by soil erosion) (8 times), B7 (area of land used for planting crops) (7 times) and B9 (area covered by urban greenery) (6 times) appeared with high frequency in the ranking of main obstacle factors. Among them, B4 (amount of sewage discharge) and B7 (area of land used for planting crops) mainly occupy the top positions of the main obstacle factors. During the period from 2015 to 2020, four indicators, namely B6 (area affected by soil erosion) (6 times), B8 (effective irrigation area of farmland) (6 times), B5 (area prone to flooding) (6 times) and B14 (area of land used for flood control) (6 times) were the factors with high frequency in the ranking of obstacle factors. During the 6-year period, B6 (area affected by soil erosion) occupied the first place in the obstacle factors.
During the “11th Five-Year” and “12th Five-Year” periods, accelerating the industrialization process of Nanyang City was placed in a prominent position of economic and social development, taking the deep processing industry of agricultural products, the textile industry, the petroleum alkalization industry and the metallurgical building materials industry as the pillar industries. In addition, the “12th Five-Year Plan” emphasized the need to build Nanyang City into a regional central city and a comprehensive transportation hub between Henan, Hubei and Shaanxi provinces. There is no doubt that the policy has accelerated population aggregation, so that industrial water and domestic water use have increased dramatically, and the amount of sewage discharge in 2020 doubled compared with 2006. In addition, Nanyang City strengthened the forestry ecological construction, established the green ecological barrier of Funiu Mountain and Tongbai Mountain, the green ecological barrier of Danjiangkou Reservoir area and the ecological corridor of the main channel of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, instead of building the regional ecological construction pattern of “three belts and three belts”, and consolidated and expanded the achievements of converting farmland to forest. The forest coverage rate of Nanyang City increased by 20.81 percent during the period. An increase in forest coverage directly leads to a decrease in soil-erosion area.
3.2.2. Analysis of the Health Obstacle Factors for Land Ecology
Table 8 presents the ranking of obstruction degrees for the criterion layer of land ecological health in Nanyang City. As observed in the table, the obstruction degree of land ecological vitality (C2) was dominant during the period 2006 to 2020. However, it consistently decreased after reaching its peak at 53.46% in 2014. During the study period, the obstruction degree of land ecological resilience (C1) mainly ranked second, and it showed an overall upward trend, increasing from 19.57% to 23.65%. The obstruction degrees of land ecological structure (C3) and surface pollution sources (C4) in Nanyang City were interrelated, with changes in one affecting the other. Despite reaching its lowest value of 3.39% in 2014, the obstruction degree of surface pollution sources (C4) continued to rise and even ranked first in the list of obstruction degrees for land ecological health in 2020. It can be seen from Table 2 that the land ecological vitality (C2) index layer includes four indicators: effective irrigation area of farmland, coverage area of urban green built-up area, per capita park green area and harmless treatment of domestic waste. Therefore, Nanyang has made remarkable progress in the construction of ecological civilization and new urbanization.

Table 8.
Table of obstruction degree ranking of criterion layer for land ecological health assessment.
Table 9 presents the ranking of the obstacle degree of various indicators of land ecological health in Nanyang City. During the period from 2006 to 2016, the main obstacle factors were D6 (area covered by urban greenery in built-up areas) (11 times), D8 (rate of harmless treatment of domestic waste) (9 times), D3 (surface water resources) (9 times) and D2 (forest coverage rate) (8 times). Among them, D6 (area covered by urban greenery in built-up areas) ranked first in obstacle degree ranking, and the obstacle degree showed an overall trend of first rising and then falling. From 2017 to 2020, the main obstacles affecting land ecological health were D5 (effective irrigated area of farmland) (4 times), D14 (amount of phosphate fertilizer applied) (4 times), D6 (area covered by urban greenery in built-up areas) (3 times), D9 (proportion of primary industry) (3 times) and C3 (surface water resources) (3 times), among the five indicators. Among them, D6 (area covered by urban greenery in built-up areas) continued to occupy the first place in the obstacle degree of land ecological health index system.

Table 9.
Table of obstruction degree ranking of index layer for land ecological health assessment.
During the “12th Five-Year Plan” period, Nanyang City actively promoted the construction of various ecological spaces, promoted the construction of ecological spaces such as theme parks in central urban areas, green belts around the city, urban greenways and public green spaces, and achieved full coverage of comprehensive parks in county-level cities. It also accelerated the construction of urban green space, scenic forest land and urban ecological forest belts along the South-to-North Water Diversion. In addition, Nanyang City promoted the development of the “four-city linkage” during the “13th Five-Year Plan” period, and promoted the construction of county parks and street green spaces. Therefore, the coverage area of the urban-greening built-up area in Nanyang City reached 17,448.58 hm2, an increase of 7 times compared with 2006.
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
By constructing the land ecological risk-evaluation index system and land ecological health-evaluation index system, this study uses the Boston matrix to couple the land ecological risk value and land ecological health value in order to obtain land security-evaluation results of Nanyang City and analyze them. Finally, the obstacle degree model is used to identify and diagnose the obstacle factors affecting ecological security. This provides a theoretical basis for the sustainable utilization of land resources and the construction of ecological civilization in China. Based on the above analysis and identification, the following conclusions can be drawn.
(1) In general, the land ecological risk of Nanyang City showed an inverted “U” curve change of Kuznets [70], with an upward trend from 2006 to 2014 and a downward trend from 2015 to 2020. The ecological health of the land in Nanyang City demonstrated a “U”-shaped trend, with its value continuously declining from 2006 to 2016, experiencing a slight fluctuation in 2010, and then significantly increasing from 2017 to 2020. From 2006 to 2016, the land in Nanyang City was in a relatively unhealthy state. However, it improved significantly and reached a critical healthy state from 2017 to 2019, and continued to improve to a relatively healthy state in 2020.
(2) Using the Boston matrix model, the coupling of the risk-evaluation results and health-evaluation results can be obtained: From 2006 to 2010, Nanyang City was in a relatively safe condition. However, it became unsafe from 2011 to 2016. From 2017 to 2019, it returned to a relatively safe condition, and in 2020 it was in a safe condition. The construction of ecological civilization in the land of Nanyang City has achieved remarkable results, including the optimization of land resource allocation and the efficient and intensive use of land.
(3) In the criteria layer of the land ecological risk subsystem, the risk effect and risk receptor have a relatively high number of obstacles, and the risk effect obstacles gradually transfer to the risk receptor. The main obstacle factors are transferred from an area removed from waterlogging, an urban green coverage area and a harmless treatment rate of domestic waste to a soil-erosion area, a grain-planting area and an effective irrigation area of farmland. Ecological vitality has the most significant impact on obstacles in the criteria layer of the land ecological health subsystem, and the obstacles of land ecological structure and surface pollution sources are transferred to each other. The main obstacle factors have shifted from the proportion of the primary industry, grain-sowing area, etc., to the use of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer and agricultural diesel in the land ecological health subsystem. Based on comprehensive risk and health obstacle degree findings, the main obstacle factors of the entire land ecological security system are the following: area of land used for planting crops, amount of sewage discharge, area affected by soil erosion and area covered by urban greenery in built-up areas.
4.2. Policy Suggestion
Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, China has had remarkable achievements in the rational utilization of land resources and the construction of ecological civilization [71]. However, China still faces historical problems such as “high input, high consumption, low output and low efficiency” in land and agricultural production [72]. Therefore, China’s ecological civilization construction still has a long way to go. Based on the above research conclusions, the following policy suggestions are put forward:
(1) The government continues to increase investment in “agriculture, rural areas and farmers”. First, preferential subsidies for production factors such as seeds, fertilizers and pesticides are provided to farmers who carry out grain production. Secondly, the relevant departments carry out macro-control without violating the laws of the market, increase the purchase price of grain and increase the income of farmers. Furthermore, improve the treatment of grain farmers, increase pensions, insurance quotas and medical reimbursement ratios, create a glorious atmosphere for growing grain and continue to increase farmers enthusiasm for growing grain, and then increase the grain-sown area.
(2) Taking advantage of the fact that roses are the city flower of Nanyang, actively carry out the planting of roses in public places such as city streets, parks, communities, units and riverbanks. Continue to carry out corridor-greening projects along the South-to-North Water Diversion route, accelerate the construction of urban ecosystems and increase the coverage area of urban greening.
(3) Continuing to implement the forest rights system and the policy of returning farmland to forest and grassland, vigorously planting trees, increasing the forest coverage rate, implementing crop rotation and intercropping, and increasing the construction of agricultural water-conservation facilities such as terraces and dams. These measures can not only prevent soil erosion, but also increase the effective irrigated area of farmland.
4.3. Research Prospect
The scope of this study is the whole of Nanyang City in terms of research scale. However, during the evaluation process, there is a risk of overlooking specific land ecological risks, ecological health and ecological safety of the counties. Hence, in the future, a more precise and comprehensive evaluation of the land ecological safety of Nanyang City will be carried out on a larger scale, covering all thirteen districts and counties, including but not limited to Wolong District, Wancheng District and Dengzhou City. In addition, the index system of land ecological risk and land ecological health will be comprehensively optimized, and the impact of urbanization, the proportion of agricultural land and construction land on ecological risk will be fully considered and included, as well as a series of land ecological spatial structure indicators related to the spatial tolerance of risk receptors, such as landscape diversity index, dominance index, fragmentation index and ecosystem service value.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Y.L.; methodology, Z.L.; writing—review and editing, T.Z. and X.X.; data curation, Y.W. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (Grant No. 222300420465) and by the philosophy and social science planning project of Henan Province (Grant No. 2020BJJ037).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yun, W.J.; Sang, L.L. Research on Environmental Risk Control in Land Use in China. Environ. Prot. 2018, 46, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Tang, C.C.; Zeng, R. Review of Tourism Ecological Security from the Perspective of Ecological Civilization Construction. J. Resour. Ecol. 2022, 13, 734–745. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Luo, C. Ecological Security Condition of Cultivated Land Resources and Spatial Agglomeration Pattern in Jianghan Plain. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2015, 119, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.Z.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhou, H. Ecological Civilization Construction: Scientific Connotation and Basic Paths. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, W. The Value Connotation and Global Significance of Chinese Modernization and the New Form of Human Civilization. J. Soc. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2023, 52, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B. Discussion on the sustainable development of regional ecological civilization. J. Commer. Econ. 2011, 544, 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.R. The Evolution of the Neo-Liberal World Order and the Realization of China’s National Interest in the New Era. Forum World Econ. Politics 2022, 350, 126–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.mnr.gov.cn/dt/ywbb/202108/t202108262678340.html (accessed on 13 May 2023).
- Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.mnr.gov.cn/zt/hd/dqr/47dqr/zygq/201312/t201312302060254.html (accessed on 13 May 2023).
- Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2020-11/17/content_5562088.htm (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-04/30/content_5604050.htm (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-07/30/content_5628461.htm (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Shi, Q.L.; Lin, Y.Z.; Zhang, E.P.; Yan, H.M.; Zhan, J.Y. Impacts of Cultivated Land Reclamation on the Climate and Grain Production in Northeast China in the Future 30 Years. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 853098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.J.; Zhang, J.H. An Evaluation of the Development of Multifunctional Agriculture Based on the Grey Multi-level Model—A Case Study of Harbin. J. Liaoning Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2014, 42, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.W. Study on the Eco-Compensation Policies for the Green Transformation Development of Agriculture in China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 14–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/xy19d/lsfz/201705/t20170511_5603586.htm (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Yin, C.B.; Li, F.D.; Wang, S.; Hao, A.B. The concept, connotation and principle of agricultural green development in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.B.; Yang, G.S.; Zhu, T.M.; Su, W.Z.; Wan, R.R. Assessment of Land Use Ecological Risks in Rapidly Developing Regions: A Case Study on Kunshan City. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Jiang, G.H.; Zhang, R.J.; Ma, Q.W.; Zhou, T. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Ecosystem Health Based on the Pressure-State-Response Model: A Case Study of Pinggu District, Beijing. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.H.; Deng, B.; Deng, B.; Liu, S.Y.; Xiang, Y.F. A Case Study of Grassroots Water Conservancy Services Evaluation and Obstacle Factors Diagnosis Based on Gray Correlation-TOPSIS Model in Hunan Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Guo, X. Research on Multi-target Selection and Sequencing Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2221, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, W.L.; Chen, M.J.; Hu, Q.F.; Song, Z.Y. Operation Safety Risk Assessment of Water Distribution Networks Based on the Combined Weighting Method (CWM). KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.W.; Zhu, B.W.; Cui, C.S. The Evaluation of Urban Ecological Civilization Construction in Pearl River Delta Based on Entropy Weight TOPSIS Method. Math. Pract. Theory 2020, 50, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.Z. Of the Limitation of BCG Matrix Approach. Commer. Res. 2005, 16, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Chen, J.F.; Ding, T.H.; Gu, Y. Security assessment and obstacle factors diagnosis of water-energy-food nexus based on pressure-state-response framework in Northwest China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 37, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Z.S. New Progress and Its Prospects of Land Resources Sciences Research in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Borger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.; et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, M.Y. Spatiotemporal evaluation and analysis of cultivated land ecological security based on the DPSIR model in Enshi autonomous prefecture, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F. On land ecological safety in China. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2006, 6, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, D.H.; Cao, Y.H.; He, C.G.; Gao, K. Conceptual Distinction of Ecological Health, Ecological Risk and Ecological Security. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2016, 42, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.F.; Hou, K. Research on the progress of regional ecological security evaluation and optimization of its common limitations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Cheng, G.D.; Qian, J. Several problems in ecological security assessment research. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L.; Xie, Y.L.; Jia, W.Y.; Shi, P.J. Ecological Security Assessment and Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Shanxi Province. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Elbehiry, F.; Elbasiouny, H.; El-Ramady, H.; Brevik, E.C. Mobility, distribution, and potential risk assessment of selected trace elements in soils of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okosa, I.; Paul, T.; Ikechukwu-Edeh, C.E.; Ehiomogue, P.; Emeka-Chris, C.C.; Okereke, A.C. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals: A case study of residential waste sites in Umuahia, South-East Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, M.R.F.; Lavarias, S.M.L.; Aparicio, V.; Larsen, K.E.; Lerner, J.E.C.; Cortelezzi, A. Ecological risk assessment of pesticides in sediments of Pampean streams, Argentina. Chemosphere 2022, 313, 137598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H. Progress and prospect of ecological security research at home and abroad: Based on the overall national security concept and the background of ecological civilization construction. J. Fujian Prov. Comm. Party Sch. CPC Fujian Acad. Gov. 2015, 418, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Lou, L.T. Constructing the Evaluation System of Urban Land Ecosystem Based on Entropy Method and Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Shaanxi Province as an Example. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 295, 012072. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.J.; Qu, W.L.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, X.Z.; Gou, S.P. Study on forest ecological dynamic security in Gansu Province. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2016, 25, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.H.; ZhuFu, H.Y. An Assessment on Regional Financial Ecological Risk. J. Financ. Dev. Res. 2010, 339, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xing, Y.G.; Li, J.C. Theoretical Basis and Model Development for Land Ecological Risk Assessment. China Land Sci. 2012, 26, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.M.; Hu, Q.W.; Li, H.D.; Wang, S.H. Ecological Risk Assessment of Mount Emei Based on RS and GIS. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 2745–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.L.; Ni, J.R. Recent Progress of Ecological Risk Assessment. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2005, 41, 646–654. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Liu, S.K.; Lu, R.C.; Lin, S.G.; Liang, Q.X.; Bao, B.J. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment and Terrain Gradient Analysis of Guangxi’s Border Areas in the Past 40 Years from the “Production-Living-Ecological” Space. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2021, 37, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, H.; Biswajit, M.; Pragya, S.; Debolina, K.; Sarita, B. Spatio-temporal Assessment of Landscape Ecological Risk and Associated Drivers: A Case Study of Delhi. Environ. Urban. Asia 2021, 12, 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Dimri, D.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D.K.; Sharma, A. Spatio-temporal variation of trace elements distributed over surface water of Upper Ganga River Basin in Western Himalayan Region. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 20, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Liang, Z.B.; Xiao, Z.J.; Sun, C.K.; Zheng, Y.Y. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Land Ecological Risk in Nanchang City Based on Landscape Ecology. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Z.; Li, X.S.; Jiang, D.M. Landscape pattern identification and ecological risk assessment using land-use change in the Yellow River Basin. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Q.; Liu, T.J. On land health and land sustainable use. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2003, 13, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.M.; Zhao, J.Z.; Ma, K.M.; Zhang, P.; Ji, L.Z.; Deng, H.B.; Lu, Z.H. Assessment method of ecosystem health. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 486–490. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Tian, D.X.; Liu, Y.H. The Contrary Reseaches on the Chinese and Foreign Ecological Security Assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 199, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zaredar, N.; Jozi, S.A.; Khorssani, N.; Shariat, S.M. Climate-induced land health risk in farmland systems: A case study of Qarasou sub-basin in Karkheh River Basin. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, J.E.; Shaver, P.; Pyke, D.A.; Pellant, M.; Toledo, D.; Lepak, N. A strategy for defining the reference for land health and degradation assessments. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, L.L. Spatial-temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Health and Its Influencing Factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Environ. Sci. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M.; Xu, N.Y.; Zeng, H. Ecosystem health assessment and its scale dependence in the coastal region of the East China Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 9913–9926. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.J.; Zhou, G.H.; Tang, C.L.; He, Y.H. The Analysis of Spatial Conflict Measurement in Fast Urbanization Region Based on Ecological Security—A Case Study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Shen, J.B.; Tian, J.; Jin, K.M.; Zhang, F.S. Soil Health and Agriculture Green Development: Opportunities and Challenges. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 783–796. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wen, J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.C. Review on grassland ecosystem health. Pratacultural Sci. 2011, 28, 549–560. [Google Scholar]
- Meherul, A.N.; Chayna, J.; Debashis, M.; Kumari, M.S.; Shekhar, S.S.; Uday, M.; Sabyasachi, M.; Gouranga, K. Applying Analytic Hierarchy Process for Identifying Best Management Practices in Erosion Risk Areas of Northwestern Himalayas. Land 2022, 11, 832. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Mei, Q.; Lu, Y.M.; Ji, M. Analysis and Study on AHP-Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. China Saf. Sci. J. 2004, 14, 89–92+3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Qin, S.Z.; Wu, N.N. The Measurement and Spatial-Temporal Evolution Features of Touristization Levels in China. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.M.; Wang, X.Z.; Chang, X.K.; Qiao, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Xing, D.Q. A safety assessment model of filling mining based on comprehensive weighting-set pair analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 60746–60759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; He, B.W.; Qu, N.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, Y.W.; Chen, C.L. Benefits Evaluation Method of an Integrated Energy System Based on a Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method. Symmetry 2022, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.J.; Ran, B.P. The Fluctuation and Regional Difference of Quality of Economic Growth in China. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Yin, G.F.; Xie, Q.S.; Niu, M.Q. Manufacturing resource combination evaluation method oriented to networked manufacturing. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2008, 14, 955–961. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, J.; Duan, Y.C.; Qu, Y.K.; Sun, F.H.; Li, Z.Y. Study on the Relationship between Different Wastewater Treatment Technologies and Effluent Standards in Jilin Liaohe River Basin Based on the Coupled Model of AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS Method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ye, X.W.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Comprehensive Land Use Efficiency Based on TOPSIS. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 32, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Wang, Q.H. Limitation, correction and application of Boston matrix analysis. Sci. Technol. Innov. Her. 2009, 141, 199+201. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Wen, F.; Yang, Q.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Zong, H.M. An Evaluation of Urban Land Use Performance Based on the Improved TOPSIS Method and Diagnosis of Its Obstacle Indicators: A Case Study of Chongqing. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.T.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, X.; Ji, X.X.; Zhu, D.L. Whether ecological measures have influenced the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC)? An analysis using land footprint in the Weihe River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Gao, L.N.; Jiang, R.K. Historical Logic and Basic Experience in a Century of the Institutional Construction of Land Rule of Law in China. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Y.P.; Yi, M.D. Precision agriculture promoting the development of modern agriculture: Theoretical mechanism and practical evidence. Res. Agric. Mod. 2018, 39, 551–558. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).