Temporal Patterns of Structural Sagebrush Connectivity from 1985 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
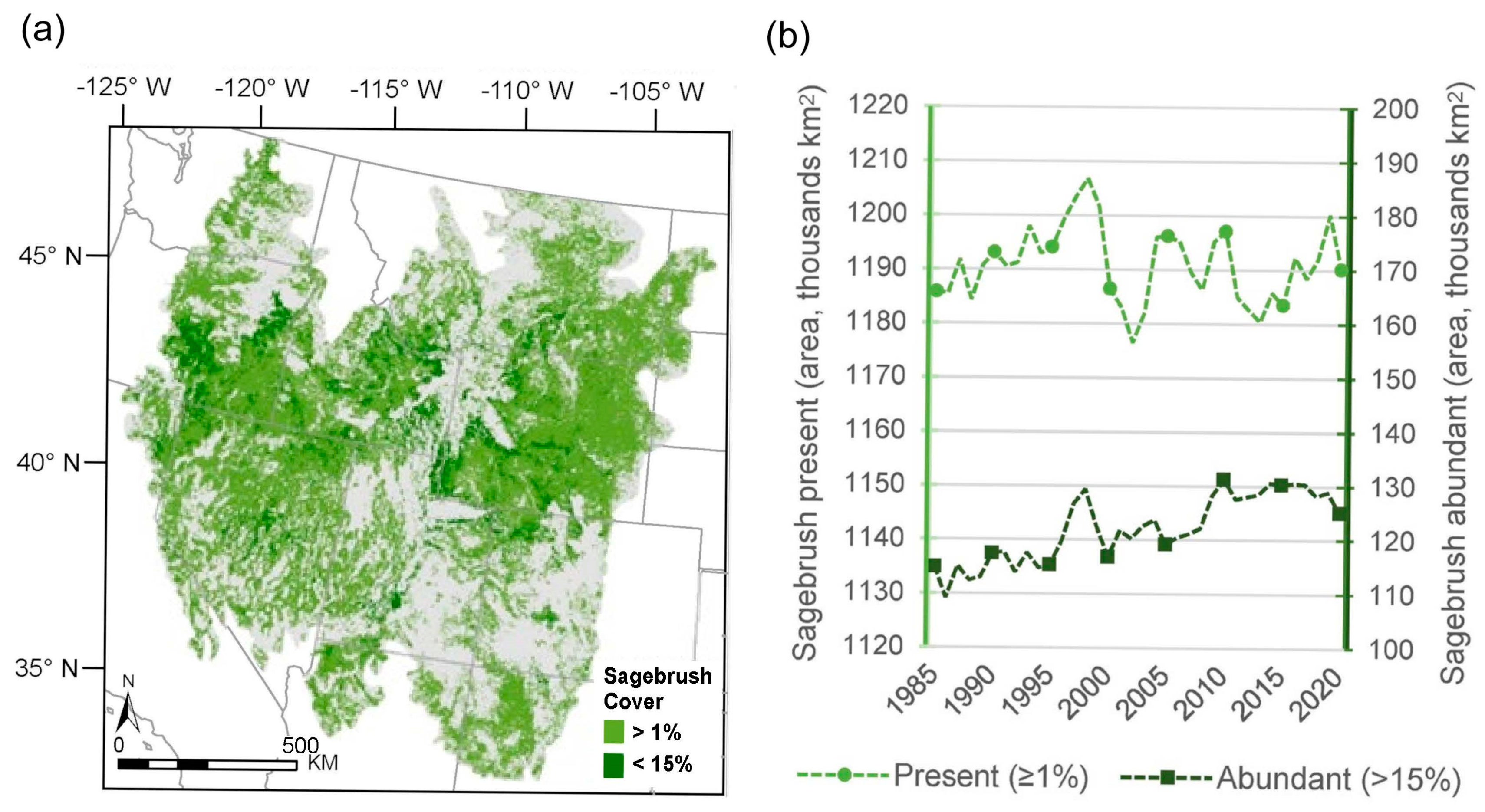
2.1. Study System
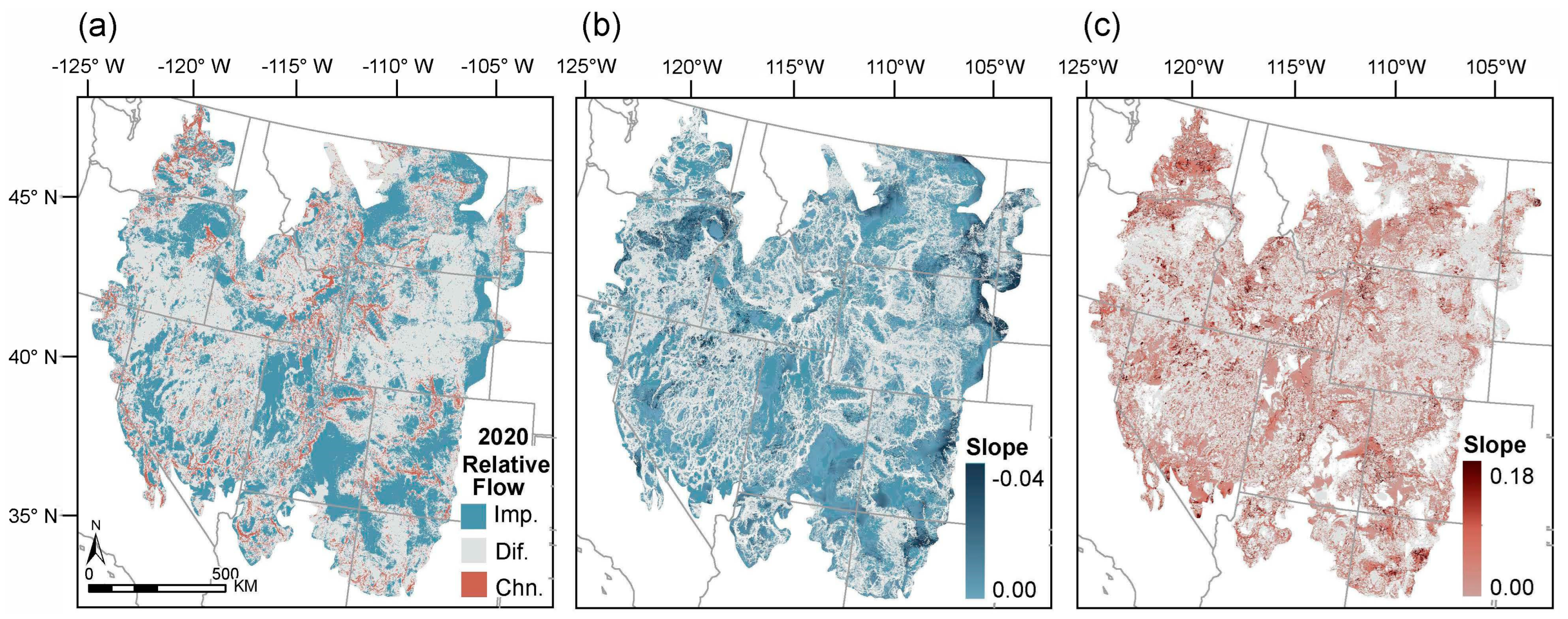
2.2. Circuit-Based Connectivity Model
2.3. Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Biome-Wide Analyses of Temporal Connectivity
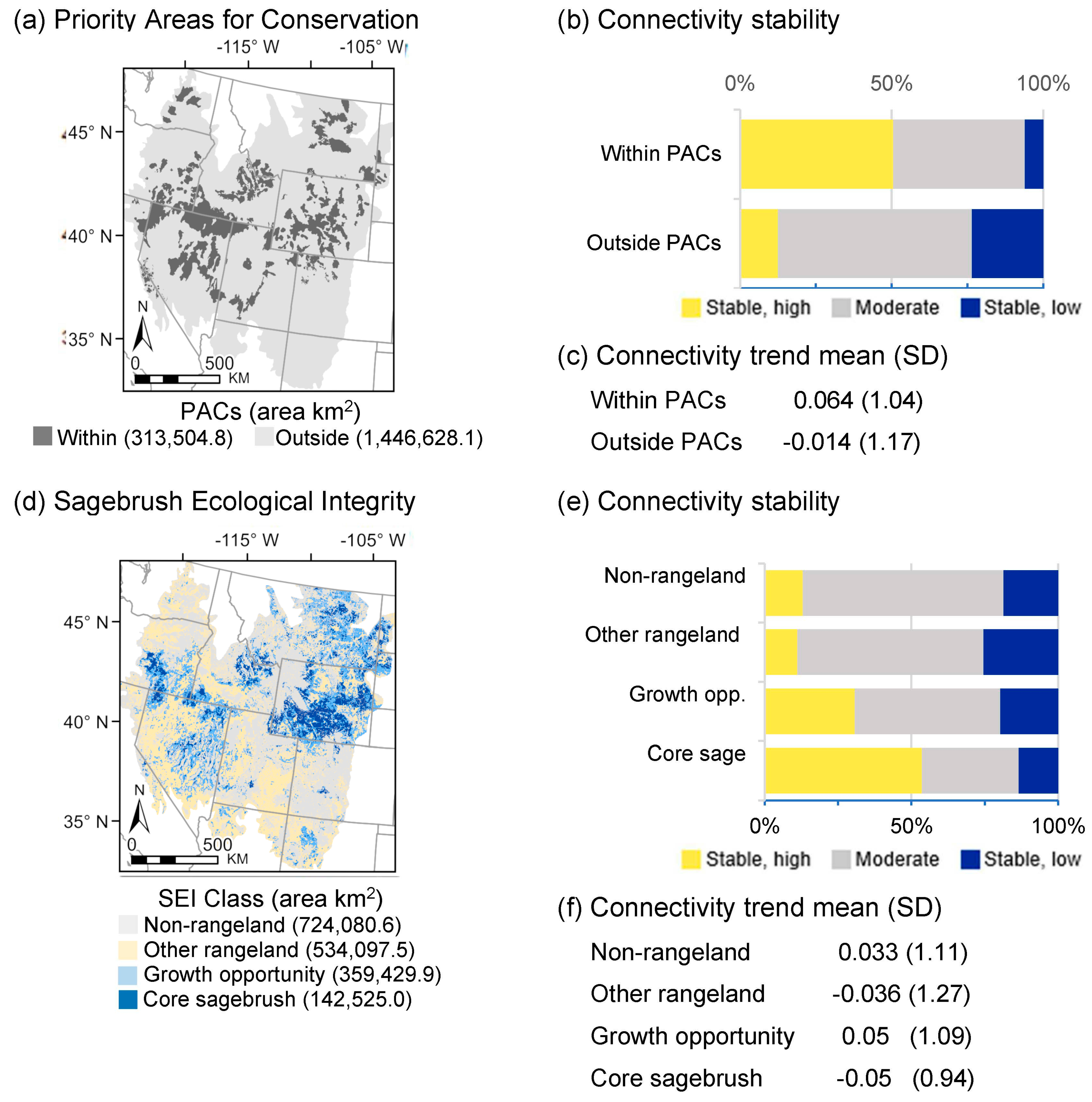
3.2. Temporal Connectivity Patterns within Conservation Areas
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grimm, N.B.; Chapin, F.S., III; Bierwagen, B.; Gonzalez, P.; Groffman, P.M.; Luo, Y.; Melton, F.; Nadelhoffer, K.; Pairis, A.; Raymond, P.A.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Ecosystem Structure and Function. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, S.R.; Rubenstein, M.A.; Crozier, L.G.; Gaichas, S.; Griffis, R.; Halofsky, J.E.; Hyde, K.J.W.; Morelli, T.L.; Morisette, J.T.; Muñoz, R.C.; et al. Climate Change Effects on Biodiversity, Ecosystems, Ecosystem Services, and Natural Resource Management in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Samie, A. Impact of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services: A Review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, S.H.; Paulukonis, E.; Simmons, C.; Russell, M.; Fulford, R.; Harwell, L.; Smith, L.M. Projecting Effects of Land Use Change on Human Well-Being through Changes in Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, J.M.; Fagan, W.F. A Comparison-Shopper’s Guide to Connectivity Metrics. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.A.; Lewison, R.; Fletcher, R.J.; Tulbure, M.G.; Jennings, M.K. Understanding the Importance of Dynamic Landscape Connectivity. Land 2020, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoros, C.; Bornette, G. Connectivity and Biocomplexity in Waterbodies of Riverine Floodplains. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffret, A.G.; Plue, J. Scale-Dependent Diversity Effects of Seed Dispersal by a Wild Herbivore in Fragmented Grasslands. Oecologia 2014, 175, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.S.; Marra, P.P.; Haig, S.M.; Bensch, S.; Holmes, R.T. Links between Worlds: Unraveling Migratory Connectivity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrec, R.; Abdel Moniem, H.E.; Iravani, M.; Hricko, B.; Kariyeva, J.; Wagner, H.H. Conceptual Framework and Uncertainty Analysis for Large-Scale, Species-Agnostic Modelling of Landscape Connectivity across Alberta, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, D.; Filotas, E.; Angers, V.A.; Messier, C. Evaluating Resilience of Tree Communities in Fragmented Landscapes: Linking Functional Response Diversity with Landscape Connectivity. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelsparre, A.H.; Shahid, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.J. Habitat Connectivity Is Determined by the Scale of Habitat Loss and Dispersal Strategy. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 5508–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Saastamoinen, M. Frontiers in Metapopulation Biology: The Legacy of Ilkka Hanski. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, T.A.; Saastamoinen, M.; Schulz, T.; Ovaskainen, O. The Relative Importance of Local and Regional Processes to Metapopulation Dynamics. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-L.; Andrello, M.; Martensen, A.C.; Saura, S.; Liu, D.-F.; He, J.-H.; Fortin, M.-J. Importance of Spatio–Temporal Connectivity to Maintain Species Experiencing Range Shifts. Ecography 2020, 43, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.J.; Beier, P. Response Variables for Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Conservation Corridors. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M. Evaluating Static and Dynamic Landscape Connectivity Modelling Using a 25-Year Remote Sensing Time Series. Landsc. Ecol 2018, 33, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, T.L.; Maher, S.P.; Lim, M.C.W.; Kastely, C.; Eastman, L.M.; Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L.; Beissinger, S.R.; Moritz, C. Climate Change Refugia and Habitat Connectivity Promote Species Persistence. Clim. Chang. Responses 2017, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, Z.; Ptacnik, R.; Vad, C.F.; Chase, J.M. Habitat Loss over Six Decades Accelerates Regional and Local Biodiversity Loss via Changing Landscape Connectance. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.G.E.; Suarez-Castro, A.F.; Martinez-Harms, M.; Maron, M.; McAlpine, C.; Gaston, K.J.; Johansen, K.; Rhodes, J.R. Reframing Landscape Fragmentation’s Effects on Ecosystem Services. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remington, T.E.; Deibert, P.A.; Hanser, S.E.; Davis, D.M.; Robb, L.A.; Welty, J.L. Sagebrush Conservation Strategy—Challenges to Sagebrush Conservation; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; Volume 2020-1125.
- Shi, H.; Rigge, M.; Homer, C.G.; Xian, G.; Meyer, D.K.; Bunde, B. Historical Cover Trends in a Sagebrush Steppe Ecosystem from 1985 to 2013: Links with Climate, Disturbance, and Management. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Row, J.R.; Doherty, K.E.; Cross, T.B.; Schwartz, M.K.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Naugle, D.E.; Knick, S.T.; Fedy, B.C. Quantifying Functional Connectivity: The Role of Breeding Habitat, Abundance, and Landscape Features on Range-Wide Gene Flow in Sage-Grouse. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.A.; Schroeder, C.A.; Wan, H.Y.; Collins, G.; Denryter, K.; Jakes, A.F.; Cushman, S.A. Forecasting Habitat and Connectivity for Pronghorn across the Great Basin Ecoregion. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 2315–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigge, M.; Homer, C.; Cleeves, L.; Meyer, D.K.; Bunde, B.; Shi, H.; Xian, G.; Schell, S.; Bobo, M. Quantifying Western U.S. Rangelands as Fractional Components with Multi-Resolution Remote Sensing and In Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, K.; Theobald, D.M.; Bradford, J.B.; Wiechman, L.A.; Bedrosian, G.; Boyd, C.S.; Cahill, M.; Coates, P.S.; Creutzburg, M.K.; Crist, M.R.; et al. A Sagebrush Conservation Design to Proactively Restore America’s Sagebrush Biome; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; Volume 2022-1081.
- Crist, M.R.; Knick, S.T.; Hanser, S.E. Range-Wide Connectivity of Priority Areas for Greater Sage-Grouse: Implications for Long-Term Conservation from Graph Theory. Condor 2017, 119, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using Circuit Theory to Model Connectivity in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Beier, P. Circuit Theory Predicts Gene Flow in Plant and Animal Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, B.G.; Albano, C.M.; Anantharaman, R.; Beier, P.; Fargione, J.; Graves, T.A.; Gray, M.E.; Hall, K.R.; Lawler, J.J.; Leonard, P.B.; et al. Circuit-Theory Applications to Connectivity Science and Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Popper, K.; Jones, A.; Schindel, M.; Buttrick, S.; Hall, K.R.; Unnasch, B.; Platt, J.R. Conserving Nature’s Stage: Mapping Omnidirectional Connectivity for Resilient Terrestrial Landscapes in the Pacific Northwest; The Nature Conservancy: Portland, ON, USA, 2016; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Rigge, M.; Bunde, B.; Meyer, D.K.; Shi, H.; Postma, K. Rangeland Condition Monitoring Assessment and Projection (RCMAP) Fractional Component Time-Series Across the Western U.S. 1985-2020. U.S. Geol. Surv. Data Release 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, A.P.; Aldridge, C.L.; O’Donnell, M.S.; Manier, D.J.; Homer, C.G.; Anderson, P.J. Using Remote Sensing Products to Predict Recovery of Vegetation across Space and Time Following Energy Development. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Greater Sage-Grouse (Centrocercus Urophasianus) Conservation Objectives: Final Report; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; p. 38.
- Doherty, K.; Theobald, D.M.; Bradford, J.B.; Wiechman, L.A. Biome-Wide Sagebrush Core Habitat and Growth Areas Estimated from a Threat-Based Conservation Design. In A Sagebrush Conservation Design to Proactively Restore America’s Sagebrush Biome 2022–1081; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, V.; Shah, V.; Anantharaman, R.; Hall, K. Omniscape.Jl: Software to Compute Omnidirectional Landscape Connectivity. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholtz, E.K.; O’Donnell, M.S.; Heinrichs, J.A.; Aldridge, C.L. Sagebrush Structural Connectivity Yearly and Temporal Trends Based on RCMAP Sagebrush Products, Biome-Wide from 1985 to 2020. U.S. Geol. Surv. Data Release 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanson, J.; Edelman, A.; Karpinski, S.; Shah, V.B. Julia: A Fresh Approach to Numerical Computing. SIAM Rev. 2017, 59, 65–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Anantharaman, R.; Landau, V.A.; Clark, M.; Dickson, B.G.; Jones, A.; Platt, J.; Edelman, A.; Shah, V.B. Circuitscape in Julia: Empowering Dynamic Approaches to Connectivity Assessment. Land 2021, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belote, R.T.; Barnett, K.; Zeller, K.; Brennan, A.; Gage, J. Examining Local and Regional Ecological Connectivity throughout North America. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 2977–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falgout, J.T.; Gordon, J.; Williams, B.; Davis, M.J. USGS Advanced Research Computing, USGS Denali Supercomputer; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022.
- Knick, S.T.; Connelly, J.W. Greater Sage-Grouse Ecology and Conservation of a Landscape Species and Its Habitats; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-520-26711-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ricca, M.A.; Coates, P.S. Integrating Ecosystem Resilience and Resistance Into Decision Support Tools for Multi-Scale Population Management of a Sagebrush Indicator Species. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 7, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Mouquet, N.; Gonzalez, A. Biodiversity as Spatial Insurance in Heterogeneous Landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12765–12770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didham, R.K. Ecological Consequences of Habitat Fragmentation. In eLS; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-470-01590-2. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; et al. Habitat Fragmentation and Its Lasting Impact on Earth’s Ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damschen, E.I.; Brudvig, L.A.; Burt, M.A.; Fletcher, R.J.; Haddad, N.M.; Levey, D.J.; Orrock, J.L.; Resasco, J.; Tewksbury, J.J. Ongoing Accumulation of Plant Diversity through Habitat Connectivity in an 18-Year Experiment. Science 2019, 365, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.L.; Lawler, J.J.; McRae, B.H.; Nuñez, T.A.; Theobald, D.M. Achieving Climate Connectivity in a Fragmented Landscape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7195–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.R.; Schloss, C.A.; Theobald, D.M.; Morrison, S.A. A Framework to Select Strategies for Conserving and Restoring Habitat Connectivity in Complex Landscapes. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, T.B.; Schwartz, M.K.; Naugle, D.E.; Fedy, B.C.; Row, J.R.; Oyler-McCance, S.J. The Genetic Network of Greater Sage-Grouse: Range-Wide Identification of Keystone Hubs of Connectivity. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 5394–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, S.J.; Aldridge, C.L.; Hooten, M.B.; Oyler-McCance, S.J. Scale-Dependent Influence of the Sagebrush Community on Genetic Connectivity of the Sagebrush Obligate Gunnison Sage-Grouse. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buchholtz, E.K.; O’Donnell, M.S.; Heinrichs, J.A.; Aldridge, C.L. Temporal Patterns of Structural Sagebrush Connectivity from 1985 to 2020. Land 2023, 12, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061176
Buchholtz EK, O’Donnell MS, Heinrichs JA, Aldridge CL. Temporal Patterns of Structural Sagebrush Connectivity from 1985 to 2020. Land. 2023; 12(6):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061176
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuchholtz, Erin K., Michael S. O’Donnell, Julie A. Heinrichs, and Cameron L. Aldridge. 2023. "Temporal Patterns of Structural Sagebrush Connectivity from 1985 to 2020" Land 12, no. 6: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061176
APA StyleBuchholtz, E. K., O’Donnell, M. S., Heinrichs, J. A., & Aldridge, C. L. (2023). Temporal Patterns of Structural Sagebrush Connectivity from 1985 to 2020. Land, 12(6), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061176





