The Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Energy Crops in Acid Soil by Sewage Sludge Fertilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- to focus on the status of heavy metals in soil after application with different sewage sludge contamination levels;
- (2)
- to determine the potential risks to the environment that heavy metal pollution could pose;
- (3)
- to evaluate the effects of two energy crops on the changes in the selected heavy metal concentrations in soil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment Design
2.2. Quality of Sewage Sludge
2.3. Soil Chemical Analysis
2.4. Study of Potential Ecological Risk
2.5. Bioconcentration Factor
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Upper Soil Layer of Both Plants under Fertilization with Sewage Sludge
3.2. Relationship between the Heavy Metals in Soil
3.3. Determination of Contamination Risk Posed by Heavy Metals in Soil
3.4. Heavy Metals Concentration in Plant Aboveground Biomass and Bioconcentration Factor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saxena, G.; Bharagava, R.N. Organic and inorganic pollutants in industrial wastes, their ecotoxicological effects, health hazards and bioremediation approaches. In Environmental Pollutants and Their Bioremediation Approaches, 1st ed.; Bharagava, R.N., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Xiao, R.; Wahid, F.; Azeem, M.; Sohail, K.; Zhang, T.; Alvarenga, P.; et al. Sewage sludge, compost, and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: Benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manag. 2020, 40, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Lu, J. Identifying quantitative sources and spatial distributions of potentially toxic elements in soil by using three receptormodels and sequential indicator simulation. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.; Fan, W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Huang, S.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, S. Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zou, B.; Feng, H.; Tang, J.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, X. Spatial distribution mapping of Hg contamination in subclass agricultural soils using GIS enhanced multiple linear regression. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 196, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payá Pérez, A.; Rodríguez Eugenio, N. Status of Local Soil Contamination in Europe: Revision of the Indicator “Progress in the Management Contaminated Sites in Europe"; EUR 29124 EN.; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 9789279800726. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Saxena, G.; Kumar, V. Phytoremediation of Environmental Pollutants: An Eco-Sustainable Green Technology to Environmental Management. In Advances in Biodegradation and Bioremediation of Industrial Waste; Chandra, R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Ali, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusaravanan, S.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Vivek, J.S.; Paramasivan, T.; Naushad, M.; Prakashmaran, J.; Gayathri, V.; Al-Duaij, O.K. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Mechanisms, methods and enhancements. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1339–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijalkowski, K.; Rosikon, K.; Grobelak, A.; Hutchison, D.; Kacprzak, M.J. Modification of properties of energy crops under Polish condition as an effect of sewage sludge application onto degraded soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcauskiene, D.; Repsiene, R.; Ambrazaitiene, D.; Skuodiene, R.; Jokubauskaite, I. Soil pH control, ecological and agro-nomic assessment in agroecosystem. In Soil pH for Nutrient Availability and Crop Performance; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Wu, D.; Liang, L.L.; Zhong, F.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; Lai, C.; Zeng, S. Municipal sewage sludge compost promotes Mangifera persiciforma tree growth with no risk of heavy metal contamination of soil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonkiewicz, J.; Kołodziej, B.; Bielińska, E.J. The use of reed canary grass and giant miscanthus in the phytoremediation of municipal sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9505–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwicka, A.; Urbaniak, M. The biochemical response of willow plants (Salix viminalis L.) to the use of sewage sludge from various sizes of wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobelak, A.; Placek, A.; Grosser, A.; Singh, B.R.; Almås, R.; Napora, A.; Kacprzak, M. Effects of single sewage sludge application on soil phytoremediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 155, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Lungu, M.; Hübner, R.; Cerbari, V. Remediation of degraded arable steppe soils in Moldova using vetch as green manure. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Jordan, F.; Waugh, W.J. Phytoremediation of a Nitrogen-Contaminated Desert Soil by Native Shrubs and Microbial Processes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, M.; Wyrwicka, A.; Tołoczko, W.; Serwecińska, L.; Zieliński, M. The effect of sewage sludge application on soil properties and willow (Salix sp.) cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Cossel, M.; Amarysti, C.; Wilhelm, H.; Priya, N.; Winkler, B.; Hoerner, L. The replacement of maize ( Zea mays L.) by cup plant ( Silphium perfoliatum L.) as biogas substrate and its implications for the energy and material flows of a large biogas plant. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2019, 14, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalan, R.L.; Muntean, C.; Kostov, A.; Kržanović, D.; Jucsor, L.; Ciulca, S.I.; Cernicova-Buca, M. The cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.)—A viable solution for bioremediating soils polluted with heavy metals. Not Bot. Horti. Agrobot. Cluj Napoca 2020, 48, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sediment logical approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.; Deng, R. Evaluating health risk indicators for PTE exposure in the food chain: Evidence from a thallium mine area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23686–23694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Tong, H.; Shen, C.; Sun, L.; Yuan, P.; He, M.; Shi, J. Bioavailability and translocation of metal oxide nanoparticles in the soil-rice plant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zang, C.; Gu, M.; Gu, C.; Shao, H.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Shan, Y.; Feng, K. Sewage sludge as an initial fertility driver for rapid improvement of mudflat salt-soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzel, H.; Krüger, O.; Hermann, L.; Adam, C. Sewage sludge ash—A promising secondary phosphorus source for fertilizer production. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, H.; Clarke, B.O.; Pritchard, D.L.; Meehan, B.; Beshah, F.; Smith, S.R.; Porter, N.A. A critical review of nitrogen mineralization in biosolids-amended soil, the associated fertilizer value for crop production and potential for emissions to the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1310–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.; de Souza, A.J.; Oliveira, F.C.; Coscione, A.R.; Viana, D.G.; Regitano, J.B. Chemical attributes of sewage sludges: Relationships to sources and treatments, and implications for sludge usage in agriculture. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, V.; Gardner, M.; Ellor, B. Concentrations of trace substances in sewage sludge from 28 wastewater treatment works in the UK. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M. Influence of metals on essential oil content and composition of lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus (DC) Stapf.) grown under different levels of red mud in sewage sludge amended soil. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.; Mounia, K.; Aziz, A.; Ahmed, H.; Rachid, B.; Lotfi, A. Sewage sludge used as organic manure in Moroccan sun-flower culture: Effects on certain soil properties, growth, and yield components. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jama, A.; Nowak, W. Willow (Salix viminalis L.) in purifying sewage sludge treated soils. Pol. J. Agron 2012, 9, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.H.; Han, S.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Ike, I.A.; Ok, Y.S.; Hur, J. Enhancing copper binding property of compost-derived humic sub-stances by biochar amendment: Further insight from two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Yang, X.; Gielen, G.; Bolan, N.; Ok, Y.S.; Niazi, N.K.; Xu, S.; Yuan, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, T.; Tsang, D.C.; Zhao, N.; Wei, H.; Feng, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, R. Effects of Zn in sludge-derived biochar on Cd immobilization and biological uptake by lettuce. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Jia, Y.; Rees, F.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Qiu, R.; Wang, H. Metal immobilization by sludge-derived biochar: Roles of mineral oxides and carbonized organic compartment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 39, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyka, M. Polish agriculture and crop production for energy purposes. In Studies and Reports IUNG—PIB; Monogr. Rozpr. Nauk; IUNG—PIB: Puławy, Poland, 2009; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Oleszczuk, P. Phytotoxicity of municipal sewage sludges compost related to physico-chemical properties, PAHs and heavy metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourioug, M.; Gimbert, F.; Alaoui-Sehmer, L.; Benbrahim, M.; Aleya, L.; Alaoui-Sossem, B. Sewage sludge application in a plan-tation: Effects on trace metal transfer in soil-plant-snail continuum. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiora, S.C.; Chukwu, A.; Chibuike, G.; Nwegbu, A.N. Potentially harmful elements and their health implications in cultivable soils and food crops around lead-zinc mines in Ishiagu, Southeastern Nigeria. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 204, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, S.; Laird, D.A.; Wang, X.; Meng, Z. Adsorption behavior and mechanisms of cadmium and nickel on rice straw biochar’s in single- and binary-metal systems. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Ramasamy, V.; Meenakshisundaram, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Ponnusamy, V. Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, W. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and food crops in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration of China. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, M.; Haddioui, A.E.M. Assessment of metals contamination and ecological risk in ait Ammar abandoned iron mine soil, Morocco. Ekologia 2016, 35, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkunas, I.; Woźniak, A.; Mai, V.C.; Rucińska-Sobkowiak, R.; Jeandet, P. The Role of Heavy Metals in Plant Response to Biotic Stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebielec, G.; Stuczyński, T. Trace metals in municipal sewage sludge produced in Poland. Proc. ECOpole 2008, 2, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazaryan, K.A.; Movsesyan, H.S.; Minkina, T.M.; Nevidomskaya, D.G.; Rajput, V.D. Phytoremediation of cop-per-contaminated soil by Artemisia absinthium: Comparative effect of chelating agents. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Delgado, M.; de Imperial, R.M.; González, I.; Lobo, C.; Plaza, A.; Martínez, S.; Martín, J.V. Phytoremediation potential of thistle (Cynara Cardunculus L.) and its ability to remove heavy metals from polluted soils with high rates of sewage sludge. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pam, A.A.; Sha’Ato, R.; Offem, J.O. Evaluation of heavy metals in soils around auto mechanic workshop clusters in Gboko and Makurdi, Central Nigeria. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2013, 5, 298–306. [Google Scholar]

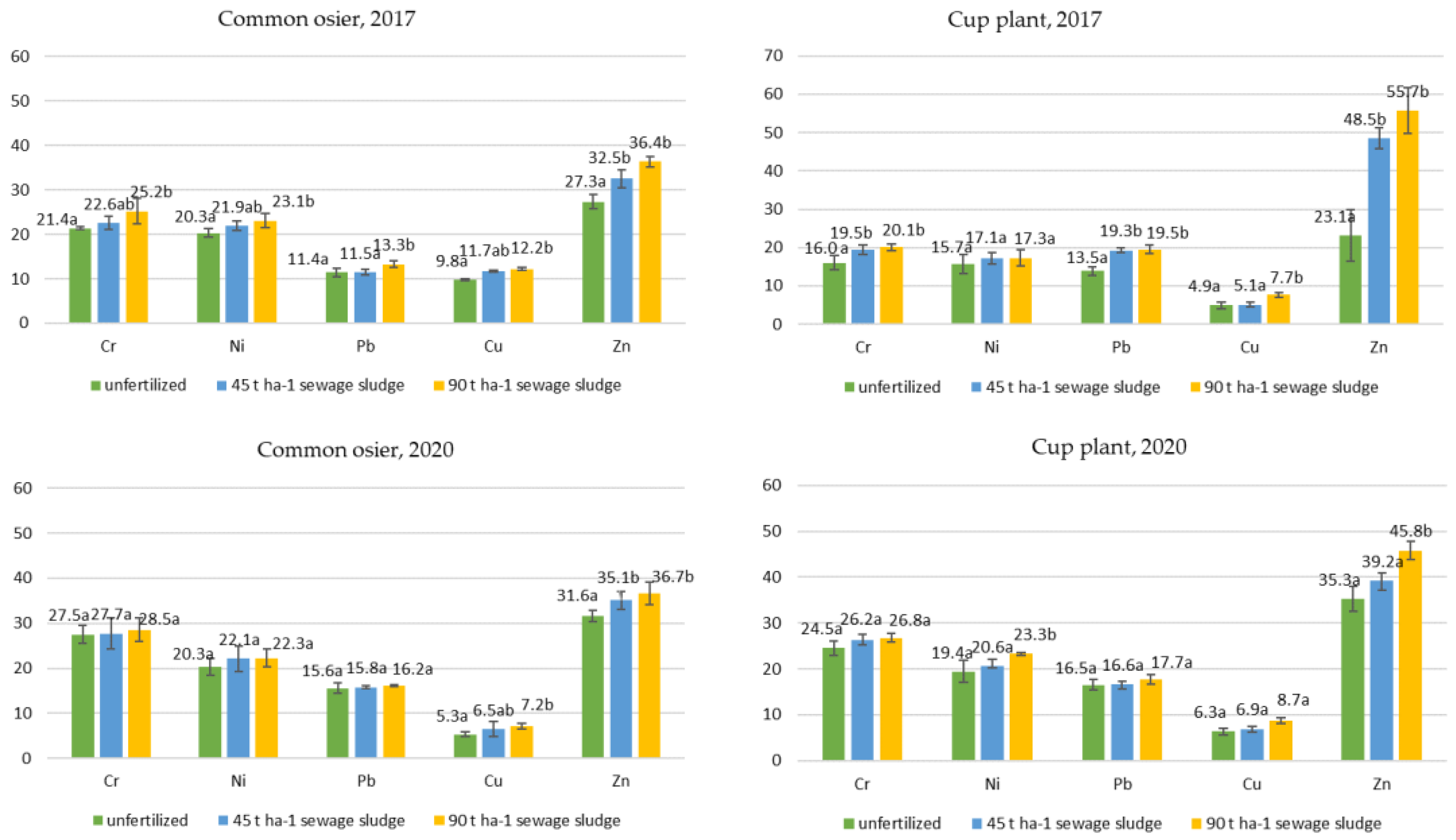
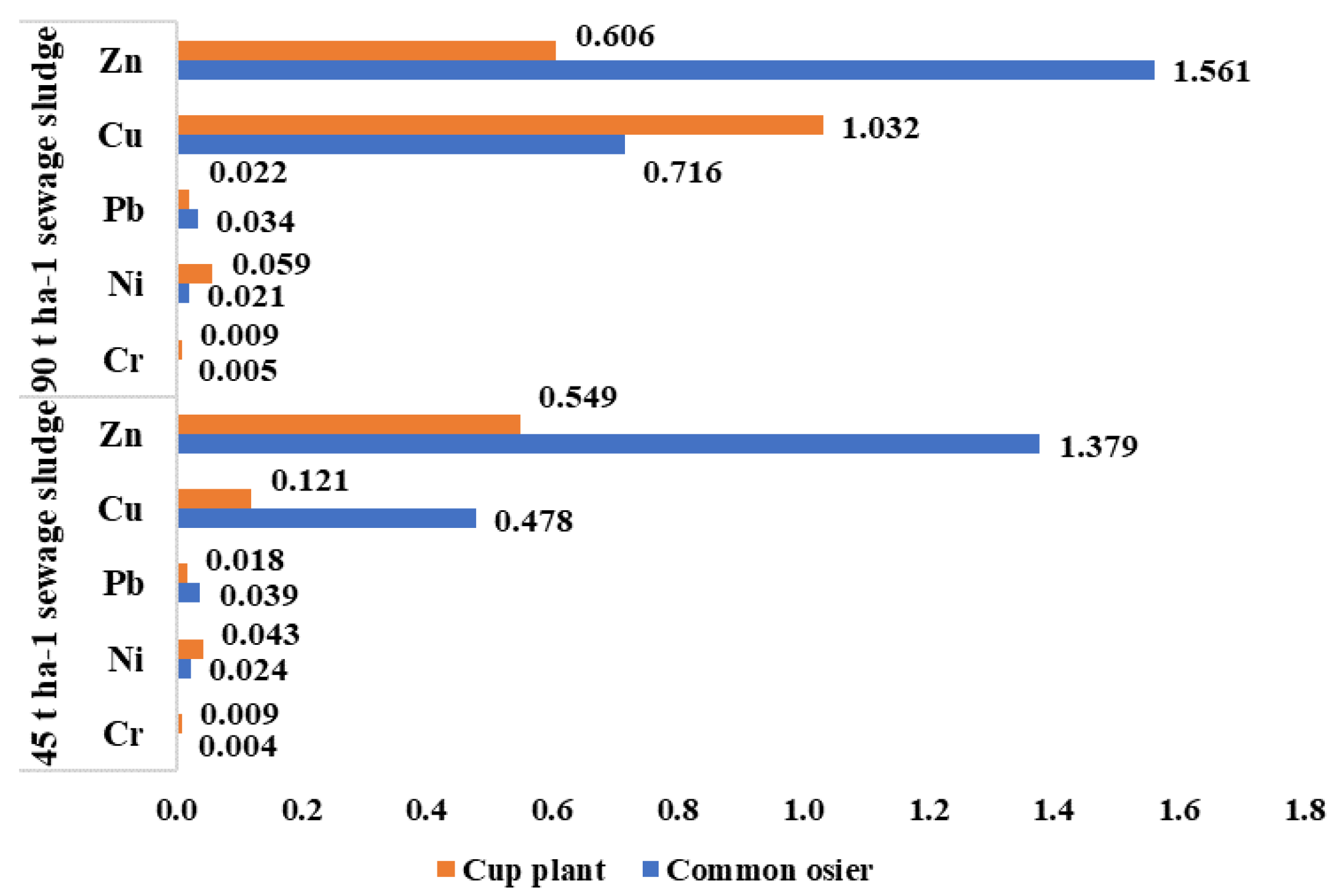
| Parameter | Extraction Method | Average Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Osier | Cup Plant | ||
| pHKCl | ISO 10390:2021 | 4.59 | 4.30 |
| mobile P2O5 | LVP D-07:2016 Egner–Rhiem–Domingo method | 88 mg kg−1 | 85 mg kg−1 |
| mobile K2O | 191 mg kg−1 | 185 mg kg−1 | |
| mobile Al | ISO 14254:2018 | 33.89 mg kg−1 | 34.28 mg kg−1 |
| total N | ISO 11261-1995 | 1.26 mg kg−1 | 1.57 mg kg−1 |
| total C C/N ratio | ISO 10694:1995 | 12.5g kg−1 9.92 | 13.9 g kg−1 8.85 |
| Cr | LST EN13650:2006 LST EN11885:2009 LST EN13650:2006 | 30.24 mg kg −1 | 49.57 mg kg−1 |
| Ni | 26.24 mg kg −1 | 19.93 mg kg−1 | |
| Pb | 12.82 mg kg−1 | 17.58 mg kg−1 | |
| Cu | LST EN13650:2006 LST ISO 8288:2002 | 8.89 mg kg−1 | 6.93 mg kg−1 |
| Zn | 27.55 mg kg−1 | 31.06 mg kg−1 | |
| Soil Granulometric Composition | Concentration of Heavy Metals, mg/kg | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cr | Zn | Cu | Ni | |
| Sand | 50 | 50 | 160 | 50 | 50 |
| Loams, clays | 80 | 80 | 300 | 75 | 75 |
| Change in Heavy Metals Concentrations in Soil between 2017 (=100%) and 2020 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Osier | Cup Plant | |||||||||
| Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | |
| 45 t ha−1 sewage sludge | +22.5 | +0.9 | +37.4 | −44.4 | +8.0 | +34.3 | +20.4 | −13.9 | +35.3 | −19.2 |
| 90 t ha−1 sewage sludge | +13.1 | −3.5 | +21.8 | −40.9 | +0.82 | +33.3 | +34.6 | −9.2 | +12.8 | −17.7 |
| Growing Common Osier | Growing Cup Plant | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | ||
| Cr | 1 | 0.377 | 0.69 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.48 * | Cr | 1 | 0.72 ** | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.17 |
| Ni | 1 | −0.08 | 0.01 | 0.08 | Ni | 1 | 0.18 | 0.38 | −0.03 | ||
| Pb | 1 | −0.69 ** | 0.39 | Pb | 1 | 0.11 | 0.79 ** | ||||
| Cu | 1 | −0.03 | Cu | 1 | −0.25 | ||||||
| Zn | 1 | Zn | 1 | ||||||||
| Growing Common Osier | Growing Cup Plant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 t ha−1 Sewage Sludge | 90 t ha−1 Sewage Sludge | 45 t ha−1 Sewage Sludge | 90 t ha−1 Sewage Sludge | ||
| Cf | Chromium | 1.03 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| Ei | 2.06 | 2.20 | 2.10 | 2.08 | |
| Cf | Nickel | 1.09 | 1.11 | 1.04 | 1.03 |
| Ei | 5.44 | 5.54 | 5.19 | 5.16 | |
| Cf | Lead | 1.00 | 1.08 | 1.19 | 1.02 |
| Ei | 5.00 | 5.40 | 5.95 | 5.11 | |
| Cf | Copper | 1.07 | 1.16 | 1.17 | 1.06 |
| Ei | 42.2 | 44.7 | 45.17 | 41.76 | |
| Cf | Zinc | 1.15 | 1.24 | 1.44 | 1.16 |
| Ei | 1.15 | 1.24 | 1.44 | 1.16 | |
| RI | 55.84 | 59.14 | 59.86 | 55.27 | |
| Heavy Metals Concentration (mg kg−1) in Plant Aboveground Biomass, 2020 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Osier | Cup Plant | |||||||||
| Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | |
| 45 t ha−1 sewage sludge | 0.11 ± 0.003 | 0.53 ± 0.126 | 0.45 ± 0.091 | 3.11 ± 0.267 | 48.40 ± 2.781 | 0.23 ± 0.113 | 0.88 ± 0.384 | 0.29 ± 0.093 | 5.76 ± 0.877 | 21.52 ± 1.574 |
| 90 t ha−1 sewage sludge | 0.14 ± 0.012 | 0.46 ± 0.221 | 0.55 ± 0.0104 | 5.15 ± 1.063 | 57.28 ± 3.890 | 0.24 ± 0.074 | 1.37 ± 0.260 | 0.38 ± 0.001 | 8.97 ± 1.256 | 27.75 ± 3.219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mockevičienė, I.; Šiaudinis, G.; Karčauskienė, D.; Repšienė, R.; Barčauskaitė, K.; Anne, O. The Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Energy Crops in Acid Soil by Sewage Sludge Fertilization. Land 2023, 12, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040866
Mockevičienė I, Šiaudinis G, Karčauskienė D, Repšienė R, Barčauskaitė K, Anne O. The Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Energy Crops in Acid Soil by Sewage Sludge Fertilization. Land. 2023; 12(4):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040866
Chicago/Turabian StyleMockevičienė, Ieva, Gintaras Šiaudinis, Danutė Karčauskienė, Regina Repšienė, Karolina Barčauskaitė, and Olga Anne. 2023. "The Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Energy Crops in Acid Soil by Sewage Sludge Fertilization" Land 12, no. 4: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040866
APA StyleMockevičienė, I., Šiaudinis, G., Karčauskienė, D., Repšienė, R., Barčauskaitė, K., & Anne, O. (2023). The Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of the Energy Crops in Acid Soil by Sewage Sludge Fertilization. Land, 12(4), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040866








