The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
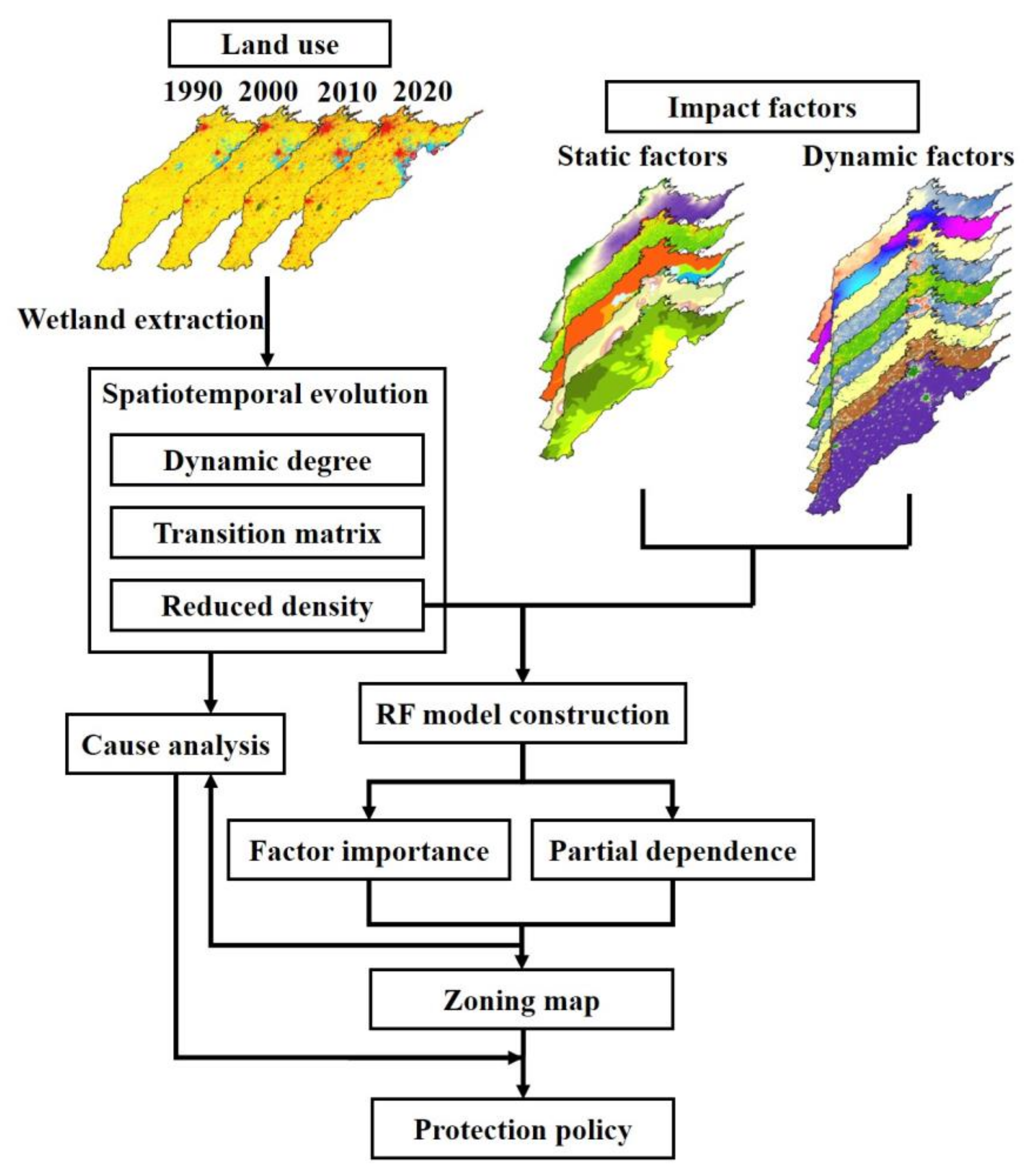
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
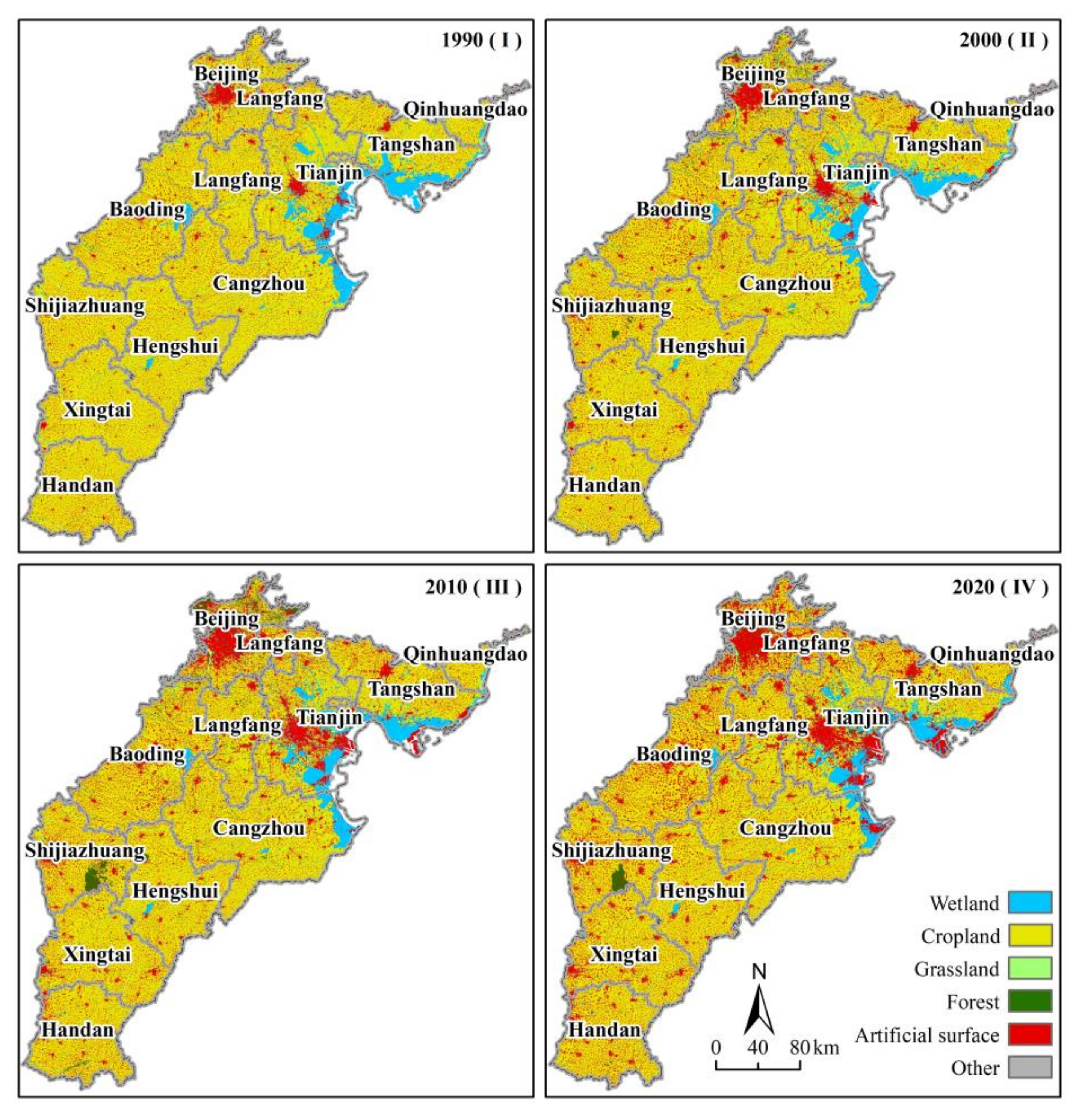
2.2.1. Wetland Data
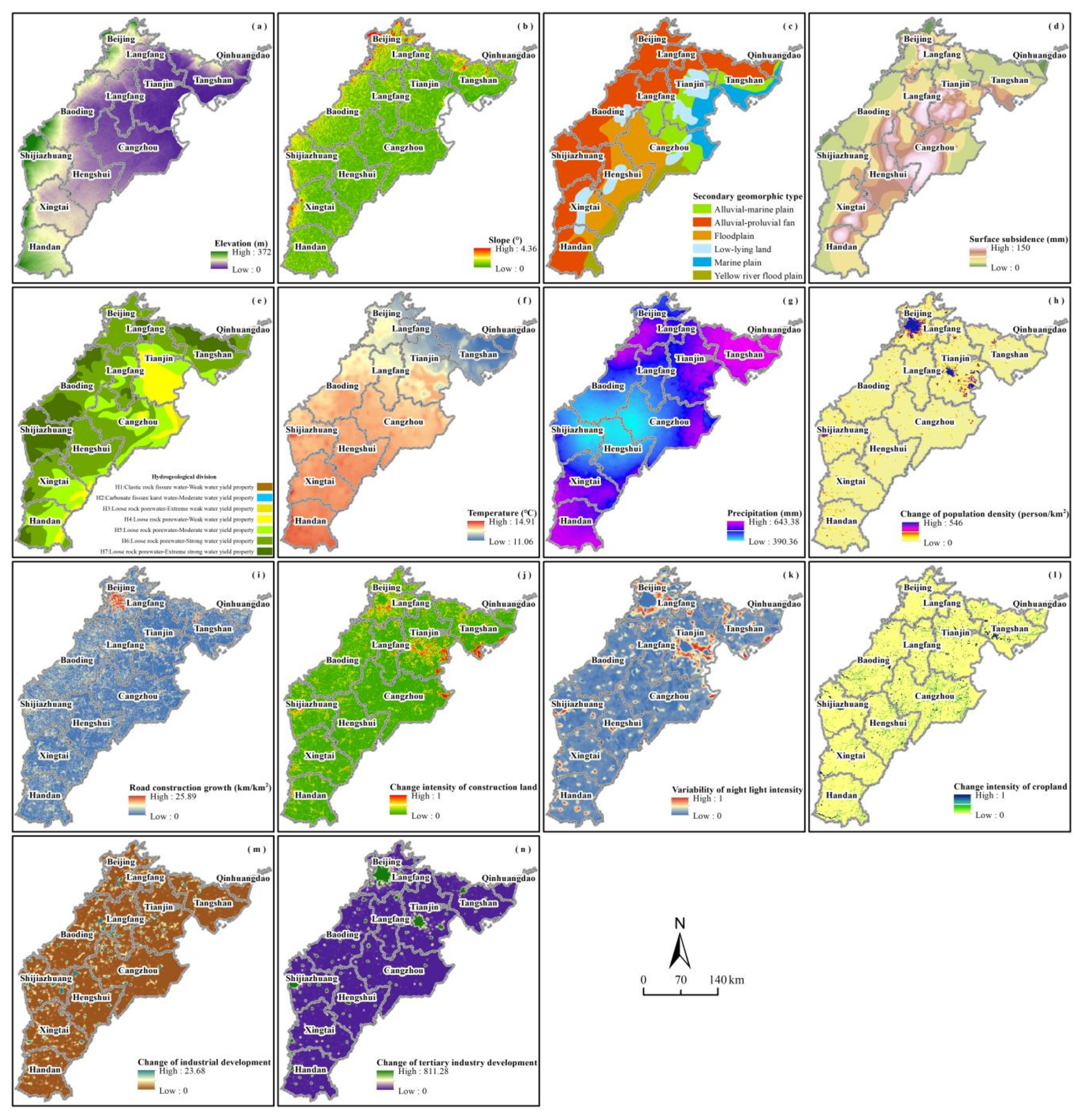
2.2.2. Impact Factor of Wetland Change
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Statistical Method
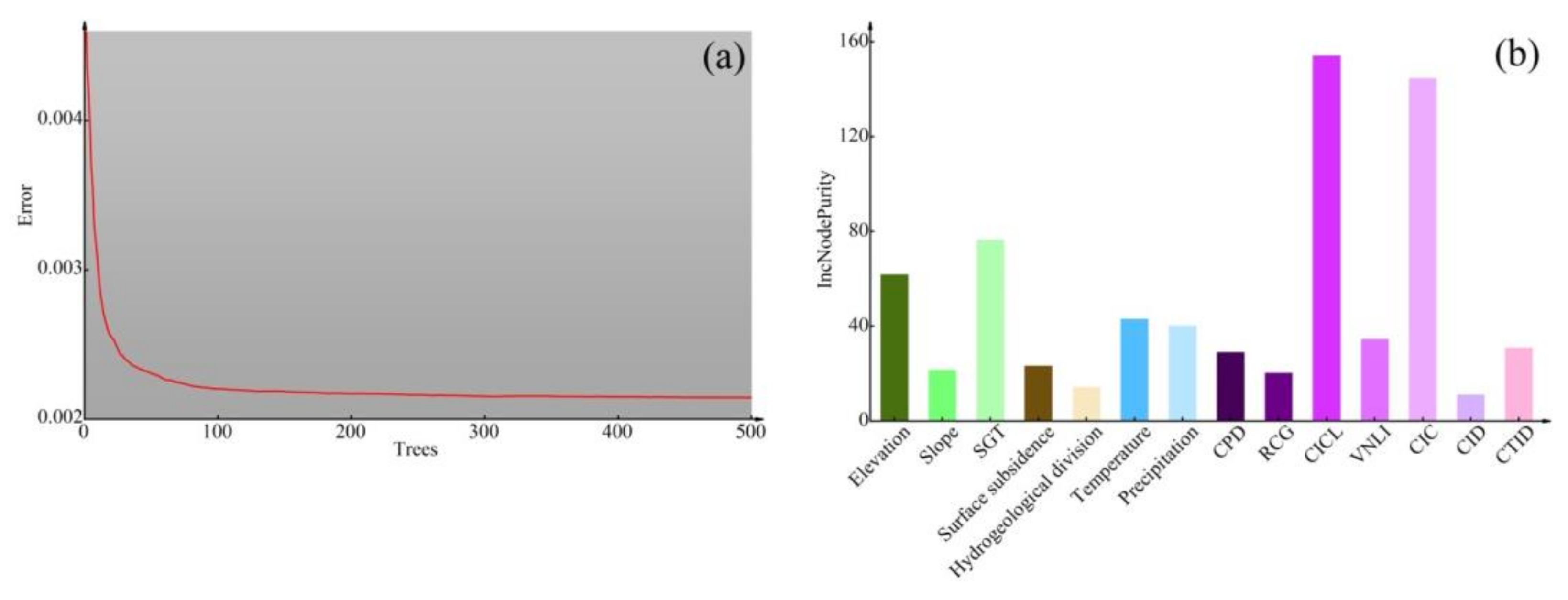
2.3.2. Random Forest (RF)
2.3.3. Partial Dependence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Change Characteristics of Wetlands
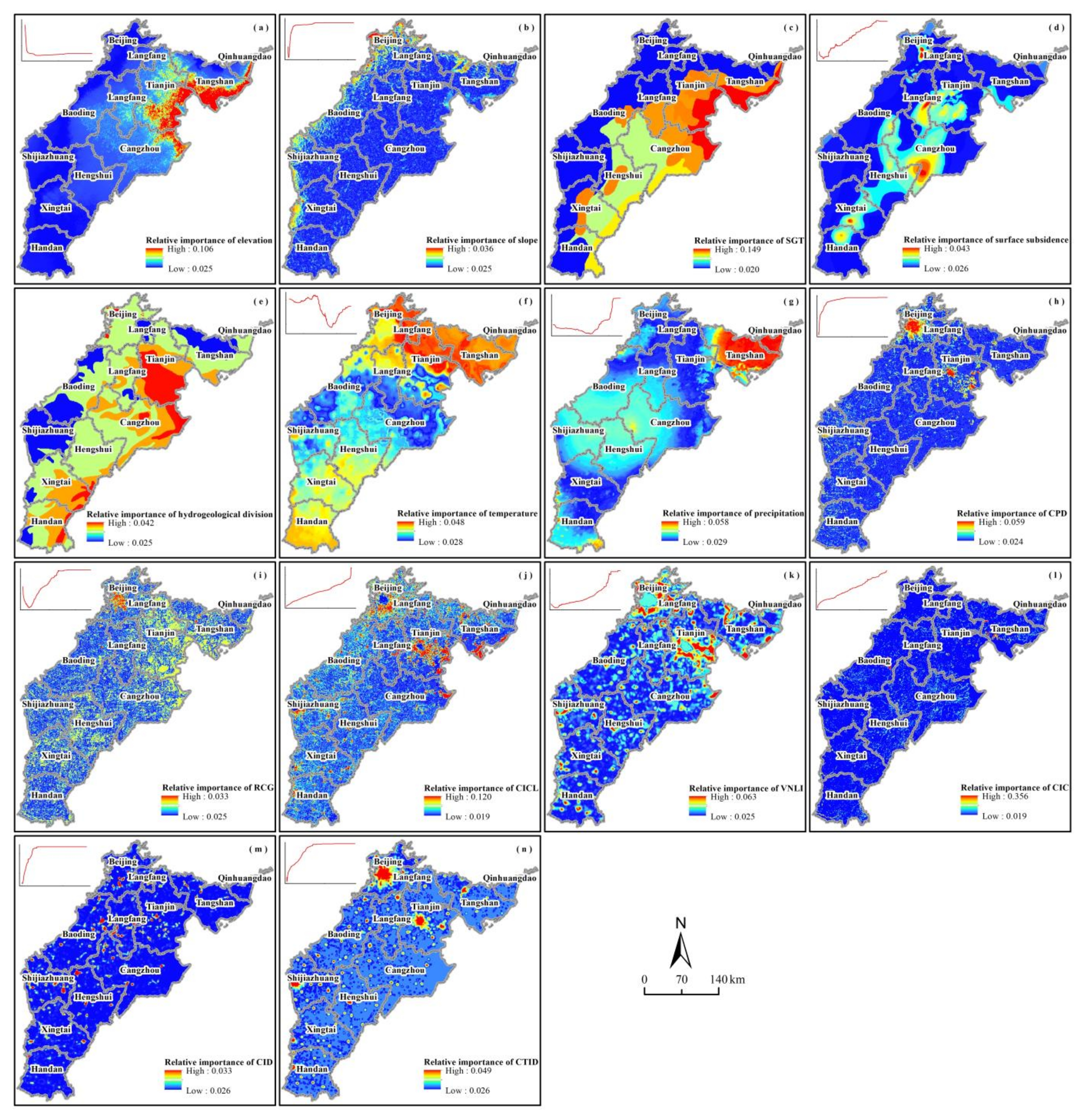
3.2. Factor Importance and Partial Dependence
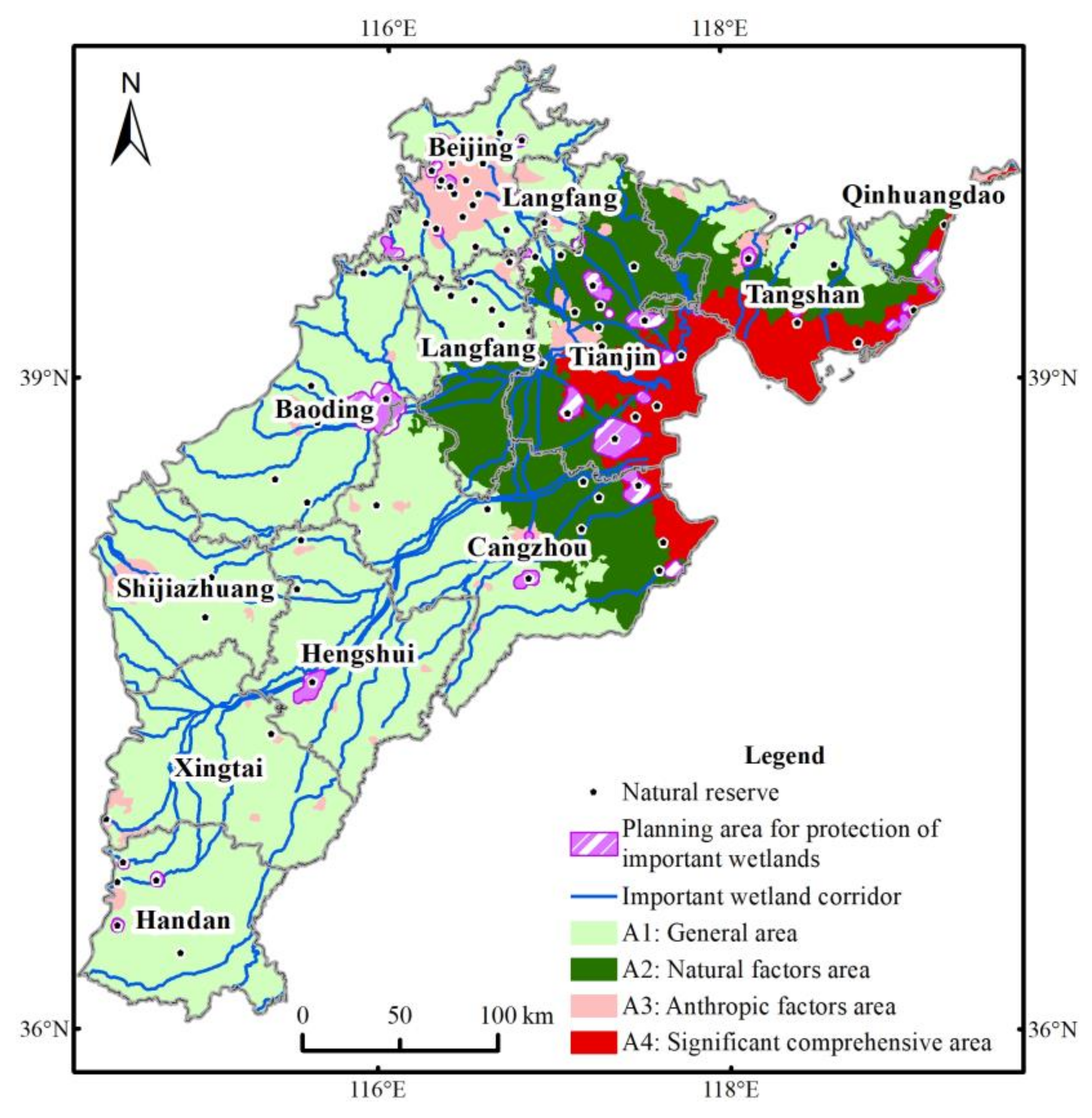
3.3. Planning Map
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Spatial–Temporal Change Characteristics of Wetlands
4.2. Cause Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Variation of Wetlands
4.2.1. Topographic Factors
4.2.2. Geological Factors
4.2.3. Meteorological Factors
4.2.4. Anthropic Factors
4.3. Cause-Based Policy Advice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Musyimi, Z.; Jiang, Q. Spatio–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Landscape Patterns Based on Remote Sensing in Yellow River Delta, China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Deng, L.; Kim, D.-G.; Huang, C.; Tian, K. Carbon budgets of wetland ecosystems in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. WETLAND RESOURCES: Status, Trends, Ecosystem Services, and Restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Shen, H.; Hu, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Q. Rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q. Four Decades of Estuarine Wetland Changes in the Yellow River Delta Based on Landsat Observations Between 1973 and 2013. Water 2018, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.J.; Sun, P.; Zhu, W.H.; Xu, Z.; Fu, J.; Man, W.D.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Qin, L. Landscape dynamics and driving forces of wetlands in the Tumen River Basin of China over the past 50 years. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 13, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Huang, C.; Lang, M.W.; Yeo, I.-Y.; Stehman, S.V. Monitoring of wetland inundation dynamics in the Delmarva Peninsula using Landsat time-series imagery from 1985 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, Y.V.; Quintana, R.D.; Radeloff, V.C.; Gavier-Pizarro, G.I. Wetland loss due to land use change in the Lower Parana River Delta, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, R.; Ghosh, S. Wetland spatial dynamics and mitigation study: An integrated remote sensing and GIS approach. Nat. Hazards 2015, 80, 975–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingi, J.K.; Marsh, S.E. Assessment of environmental impacts of river basin development on the riverine forests of eastern Kenya using multi-temporal satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 22, 2701–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Nie, N. Climate Change and Anthropogenic Impacts on Wetland and Agriculture in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Land use change and effect analysis of tideland reclamation in Hangzhou Bay. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, R. Changes in wetland landscape patterns on Yinchuan Plain, China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2010, 17, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Bu, K.; Chang, L. Monitoring spatiotemporal changes of marshes in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Zribi, M.; Oyoshi, K.; Dassas, K.; Huc, M.; Sobue, S.; Toan, T.L. Quality Control of CyGNSS Reflectivity for Robust Spatiotemporal Detection of Tropical Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, X.; Qin, F.; Zhou, H.; Dan, D.; Xia, Y.; Ulambadrakh, K. Effects of climate variability and land use/land cover change on the Daihai wetland of central Inner Mongolia over the past decades. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 3070–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Gong, H.; Wang, Y.; Khan, S.; Zhao, K. Driving Forces for the Marsh Wetland Degradation in the Honghe National Nature Reserve in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environ. Model. Assess. 2008, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Regional Ecological Risk Assessment with Respect to Human Disturbance in the Poyang Lake Region (PYLR) Using Production–Living–Ecology Analysis. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 49, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, H.; Long, X.; Cai, Y. Analyzing the spatiotemporal pattern and driving factors of wetland vegetation changes using 2000-2019 time-series Landsat data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerakis, A.; Kiriaki, K. Agricultural Activities Affecting the Functions and Values of Ramsar Wetland Sites of Greece. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 70, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Domon, G.r.; Blois, S.d.; Bouchard, A. Temporal (1958–1993) and Spatial Patterns of Land Use Changes in Haut-Saint-Laurent (Quebec, Canada) and Their Relation to Landscape Physical Attributes. Landsc. Ecol. 1999, 14, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Tan, Z. Dynamic landscapes and the driving forces in the Yellow River Delta wetland region in the past four decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhan, Q.; Zhan, D.; Zhao, H.; Yang, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Lakes under Rapid Urbanization: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Water 2021, 13, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ayllon, S.; Radke, J. Diffuse Anthropization Impacts in Vulnerable Protected Areas: Comparative Analysis of the Spatial Correlation between Land Transformation and Ecological Deterioration of Three Wetlands in Spain. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Lianhua County (China): A comparison between a random forest data mining technique and bivariate and multivariate statistical models. Geomorphology 2016, 259, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Kerle, N. Random forests and evidential belief function-based landslide susceptibility assessment in Western Mazandaran Province, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Application of Random Forests Algorithm in Researches on Wetlands (in Chinese). Wetl. Sci. 2019, 17, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bu, R.; Liu, J.; Leng, W.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, H. Predicting the wetland distributions under climate warming in the Great Xing’an Mountains, northeastern China. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Su, S.; Weng, M.; Cai, Z. Biophysical and socioeconomic determinants of tea expansion: Apportioning their relative importance for sustainable land use policy. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, G.; Shen, Y. Changes and Driving Forces of Land Use/Cover and Landscape Patterns in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region (in Chinese). Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tao, S.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. Lake Area Changes in Jing-Jin-Ji Region in Recent 30 Years (in Chinese). Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2020, 56, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, W.; Gong, H. Driving Forces Analysis of Reservoir Wetland Evolution in Beijing Based on Logistic Regression Model (in Chinese). Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 357–367. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhen, Q.; Cheng, M.; Ouyang, Z. The Main Drivers of Wetland Changes in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Shen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, D. Evaluating water conservation effects due to cropping system optimization on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei plain, China. Agric. Syst. 2018, 159, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; He, Y.; Xie, X. Exploring the factors influencing ecological land change for China’s Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region using big data. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Land Use Transition and Its Eco-Environmental Effects in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration: A Production–Living–Ecological Perspective. Land 2020, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Urban growth and environmental impacts in Jing-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze, River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, L.; Ke, H.; Zheng, Y. Environmental Protection, Industrial Structure and Urbanization: Spatiotemporal Evidence from Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J. Coastal flooding and wetland loss in the 21st century: Changes under the SRES climate and socio-economic scenarios. Glob. Environ. Change 2004, 14, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creed, I.F.; Sanford, S.E.; Beall, F.D.; Molot, L.A.; Dillon, P.J. Cryptic wetlands: Integrating hidden wetlands in regression models of the export of dissolved organic carbon from forested landscapes. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 3629–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z. Wetland Landscape Pattern Change and its Driving Forces in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in Recent 30 Years (In Chinese). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4492–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Identification of Urban Functional Regions Based on POI Data and Place2vec Model (In Chinese). Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 36, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Liao, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Body Changes and Their Influencing Factors in the Seasonal Lakes of the Poyang Lake Region (in Chinese). Water 2021, 13, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Ni, Z.; Pu, M.; Zhou, G.; Luo, Y. Regionalization of Environmental Geological Sensitivity in Beijing⁃Tianjin⁃Hebei Region Based on Resource Utilization and Disaster Risk (In Chinese). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2251–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, L. Quantitative Study on the Driving Factors of Marsh Change based in Geographical Detector (in Chinese). J. Northeast Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 49, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Wan, Y.; Sheng, S.; Wen, T.; Xu, C.; An, S. Characteristics, Hotspots and Influencing Factors of Wetland Change in Huaihe River Basin (in Chinese). J. Nat. Resour. 2013, 28, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q. Landform System of the Great Plain of North China and its Tendency of Environmental Evolution (in Chinese). Geogr. Res. 1989, 8, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Cao, Q.; Cao, J.; Duan, L.; Zuo, J.; Shi, M. Land Subsidence Response to Different Land Use Types and Water Resource Utilization in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, P.; Stubbe, H.; Weinert, M.; Zimmermann, J.; Fach, S.; Dierkes, C.; Kories, H.; Messer, J.; Mertsch, V.; Geiger, W.F.; et al. Near-natural stormwater management and its effects on the water budget and groundwater surface in urban areas taking account of the hydrogeological conditions. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Xiao, H.; Peng, X.; Song, X. Hydroclimate-driven changes in the landscape structure of the terminal lakes and wetlands of the China’s Heihe River Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irdemez, S.; Eymirli, E.B. Determination of spatiotemporal changes in Erzurum plain wetland system using remote sensing techniques. Env. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Analysis on Wetland Shrinking Characteristics and Its Cause in Heilongjiang Province for the Last 50 Years (in Chinese). J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, B.; Dolui, G.; Pramanik, M.; Maity, S.; Biswas, S.S.; Pal, R. Urban expansion and wetland shrinkage estimation using a GIS-based model in the East Kolkata Wetland, India. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, J. Analysis on Wetland Use Change in Zhangdu Watershed Hubei Province (in Chinese). Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2005, 14, 600–604. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Ren, W. A POI Data-Based Study on Urban Functional Areas of the Resources-Based City: A Case Study of Benxi, Liaoning (in Chinese). Hum. Geogr. 2020, 11, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, K. Boundary Identification and Spatial Pattern Optimization of Central Urban Areas Based on POI Data: Taking Gaotang County for Example (in Chinese). Urban Dev. Stud. 2021, 28, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Ma, T. Dynamics and changes in spatial patterns of land use in Yellow River Basin, China. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.G.; Kim, R.S.; Aloe, A.M.; Becker, B.J. Extracting the Variance Inflation Factor and Other Multicollinearity Diagnostics from Typical Regression Results. Basic Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2017, 39, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tsangaratos, P.; Ilia, I.; Liu, J.; Zhu, A.; Chen, W. Application of fuzzy weight of evidence and data mining techniques in construction of flood susceptibility map of Poyang County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, A.; Pradhan, B.; Rezaei, K. Gully erosion zonation mapping using integrated geographically weighted regression with certainty factor and random forest models in GIS. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudby, A.; Brenning, A.; LeDrew, E. New approaches to modelling fish–habitat relationships. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, J.N.; Brenning, A.; Petschko, H.; Leopold, P. Evaluating machine learning and statistical prediction techniques for landslide susceptibility modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xie, B. A Review of Technologies on Random Forests (in Chinese). Stat. Inf. Forum 2011, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, D.; Cai, X.; Cao, Y. Predict Seasonal Low Flows in the Upper Yangtze River Using Random Forests Model (in Chinese). J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2012, 31, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ni, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, W.; Long, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhou, G.; Luo, Y.; Geng, C. Susceptibility Analysis of Geohazards in the Longmen Mountain Region after the Wenchuan Earthquake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J. Development and Optimization of the Ecological Network in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolitan region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4383–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Haider, F.; Ishtiaque, A.; Mahmud, M.S.; Masrur, A. Remote Sensing & GIS Based Spatio-Temporal Change Analysis of Wetland in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Mei, J. Analysis of changes of Baiyangdian wetland from 1975 to 2018 based on remote sensing (in Chinese). J. Remote Sens. 2019, 23, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Z. Analysis on Variation Characteristics of Tianjin Wetland Area and Its Main Controlling Factors During 1976-2009 (in Chinese). J. Tianjin Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2013, 33, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Qi, T.; Liu, Y.; Fu, T.; Yu, S.; Zhao, L. Spatiotemporal characteristics of human activity on coastal landscape of Laizhou Bay. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 29, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Yin, K.; Li, X.; Kia, K.; Zhu, L. Impacts of human activities on the evolution of estuarine wetland in the Yangtze Delta from 2000 to 2010. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Munizaga, J.; Rojas, O.; Martínez, C.; Pino, J. Urban development versus wetland loss in a coastal Latin American city: Lessons for sustainable land use planning. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneff, M.D.; Royle, J.A. Modeling wetland change along the United States Atlantic Coast. Ecol. Model. 2004, 177, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Dong, C. Regional Differentiation and Factors Influencing Changes in Swamps in the Sanjiang Plain from 1954 to 2015 (in Chinese). Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4821–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Niu, Z.; Qi, W.; Zhang, H. Driving Forces of Wetland Change in China (in Chinese). J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, C.; Lin, N.; Feng, Y. Characteristics of Wetland Dynamic Variations in Western Liaohe River Basin and Their Influenced Factors (in Chinese). Glob. Geol. 2016, 35, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Cheng, X.; He, X. Wetland Changes and Their Relation to Climate Change in the Pumqu Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Tedesco, L.; Li, F.; Jin, C.; Du, J. Wetlands shrinkage, fragmentation and their links to agriculture in the Muleng-Xingkai Plain, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cui, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, C. A View on Geomorphologic Zonalization of North China Plain (in Chinese). Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 25, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.; Zeng, F.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, B. Driving Factors of Coastal Wetland Degradation in Binhai New Area of Tianjin (in Chinese). Acta Sci. Circumst. 2012, 32, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, B. Analysis of Cause of Sharp Decrease of Wetlands in Hebei Plain (in Chinese). Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 26, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, H.; Li, W.; Tian, X. Relationship Between Land Subsidence and Deep Groundwater Yield in the North China Plain (in Chinese). South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, R. Direct observation of complex Tóthian groundwater flow systems in the laboratory. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3568–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, G.; Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Shao, J.; Song, X. Evolution Mechanism and Control of Groundwater in the North China Plain (in Chinese). Acta Geosci. Sin. 2014, 35, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zheng, C.; Scanlon, B.R.; Liu, J.; Li, W. Use of flow modeling to assess sustainability of groundwater resources in the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Garduno, H.; Evans, R.; Olson, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, Z. Quaternary Aquifer of the North China Plain?assessing and achieving groundwater resource sustainability. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Huang, H.; Li, C.; et al. Mapping wetland changes in China between 1978 and 2008. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poiani, K.A.; Johnson, W.C. Potential Effects of Climate Change on a Semi-Permanent Prairie Wetland. Clim. Chang. 1993, 24, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, B.; Sheng, L.; Tian, X. Dynamic Patterns of Change in Marshes in the Sanjiang Plain and Their Influential Factors (in Chinese). Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Peng, K. Identification of Wetland Damage Degree and Analysis of Its Driving Forces in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration (in Chinese). J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, N.K.; Donmez, N.Y. Effects of Urbanisation and human activities on Basin ecosystem: Sapanca Lake Basin. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2019, 20, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, D.; Ning, K.; Du, C.; Wang, S. Effects of Roads on Natural Landscape Connectivity of the Estuary Wetland in the Yellow River Delta (in Chinese). J. Ludong Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 38, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, M.; Hu, H.; Ma, D.; Zhang, F. Effects of Expressway Construction and Operation On the Soil Properties of Adjacent Wetland (in Chinese). J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2009, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. Human negative, positive, and net influences on an estuarine area with intensive human activity based on land covers and ecological indices: An empirical study in Chongming Island, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Mo, X.; Li, H.; He, M. An Analysis on Multivariate Corelations Betwen Wetland Degradation Characteristics and Its Driving Factors in Tianjin City (in Chinese). Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 26, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z.; Wilson, M.C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. Conversions between natural wetlands and farmland in China: A multiscale geospatial analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Hu, S.; Lin, Z.; Liu, S.; Xia, J. Impacts of climate change on agricultural water resources and adaptation on the North China Plain. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, M. Impacts of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on the Ecological Restoration of Wetlands in the Arid Regions of China. Energies 2016, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Delinking indicators on regional industry development and carbon emissions: Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei economic band case. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, L.; Cao, Y.; Yang, L. Industrial land supply at different technological intensities and its contribution to economic growth in China: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Climate Change Effects of Industrial Structure Adjustments and Technical Improvements (in Chinese). J. Cap. Univ. Econ. Bus. 2016, 18, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Comparative study on the influence of final use structure on carbon emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the factors influencing urbanization and ecological environment synergistic effects within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cao, C.; Liu, D.; Tian, R.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ma, G.; Bao, D. An evaluating system for wetland ecological health: Case study on nineteen major wetlands in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type | Data Name | Data Sources | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topographic factor | Elevation | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/; accessed on 1 May 2022) | 90 m × 90 m |
| Slope | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/; accessed on 1 May 2022) | 90 m × 90 m | |
| Secondary geomorphic type | China Geological Survey (https://www.cgs.gov.cn/; accessed on 1 May 2022) | Vector Data | |
| Geological factor | Surface subsidence | China Geological Survey (https://www.cgs.gov.cn/; accessed on 1 May 2022) | Vector Data |
| Hydrogeological division | China Geological Survey (https://www.cgs.gov.cn/; accessed on 1 May 2022) | Vector Data | |
| Meteorological factor | Temperature | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/; accessed on 2 May 2022) | 1000 m × 1000 m |
| Precipitation | |||
| Anthropic factor | Population density | WorldPop (https://www.worldpop.org/; accessed on 5 May 2022) | 1000 m × 1000 m |
| Road | NAVINFO (https://www.navinfo.com/; accessed on 5 May 2022); OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/; accessed on 5 May 2022) | Vector Data | |
| Night light | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/; accessed on 10 May 2022) | 1000 m × 1000 m | |
| POI | Gaode Open Platform (https://lbs.amap.com/ accessed on 11 May 2022) | Vector Data |
| Type | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 1990–2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area Change (km2) | Si (%) | Area Change (km2) | Si (%) | Area Change (km2) | Si(%) | Area Change (km2) | Si(%) | |
| River | −286.22 | −2.56 | −14.88 | −0.19 | +342.99 | 4.37 | +41.89 | +0.133 |
| Marshland | −102.30 | −1.22 | −10.50 | −0.15 | −58.29 | −0.82 | −171.09 | −0.73 |
| Lake | −2.15 | −2.94 | −1.00 | −2.02 | +1.70 | 4.42 | −1.45 | −0.70 |
| Reservoir | −286.40 | −0.67 | −214.59 | −0.54 | −109.39 | −0.29 | −610.38 | −0.51 |
| Overall | −677.07 | −1.09 | −240.97 | −0.44 | +177.01 | 0.34 | −741.03 | −0.42 |
| Sy (%) | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.77 | ||||
| Factor Name | Tolerance | VIF | Factor Name | Tolerance | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation | 0.356 | 2.811 | CPD | 0.613 | 1.631 |
| Slope | 0.746 | 1.341 | RCG | 0.707 | 1.415 |
| SGT | 0.537 | 1.861 | CICL | 0. 712 | 1.405 |
| Surface subsidence | 0.751 | 1.331 | VNLI | 0.763 | 1.311 |
| Hydrogeological division | 0.576 | 1.736 | CIC | 0.972 | 1.029 |
| Temperature | 0.397 | 2.520 | CID | 0.894 | 1.119 |
| Precipitation | 0.562 | 1.781 | CTID | 0.536 | 1.864 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Ma, H.; Yang, D.; Hu, W.; Li, H. The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Land 2023, 12, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020480
Li S, Ma H, Yang D, Hu W, Li H. The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Land. 2023; 12(2):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuai, Haiyu Ma, Di Yang, Wei Hu, and Hao Li. 2023. "The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain" Land 12, no. 2: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020480
APA StyleLi, S., Ma, H., Yang, D., Hu, W., & Li, H. (2023). The Main Drivers of Wetland Evolution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Land, 12(2), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020480








