Industrial Park Role as a Catalyst for Regional Development: Zooming on Middle East Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Aims and Questions
2. Relevant Literature
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Steps
3.2. Study Area
3.3. Data Source
3.4. Model Specification
- Random effects model:
4. Results
- Estimation of the model with fixed effects:
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y. The effects of National High-tech Industrial Development Zones on economic development and environmental pollution in China during 2003–2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, D.; Fu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, P. Spatial relationships between ecosystem services and socioecological drivers across a large-scale region: A case study in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhihao, Y.; Li, T. From Informal Renewal to Formal Renewal: Governance of Collectively Owned Industrial Land Renewal Based on a Case Study of Guangzhou. China City Plan. Rev. 2020, 29, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Moberg, L. The political economy of special economic zones. J. Inst. Econ. 2015, 11, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.Z. The past, present, and future of special economic zones and their impact. J. Int. Econ. Law 2021, 24, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Barbieri, E.; Di Tommaso, M.R.; Zhang, L. Development zones and local economic growth: Zooming in on the Chinese case. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 38, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.K. Special economic zones and growth in China and India: An empirical investigation. Int. Econ. Econ. Policy 2013, 10, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannecchini, P.; Taylor, I. The eastern industrial zone in Ethiopia: Catalyst for development? Geoforum 2018, 88, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, B.T.M. SEZ Development in Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam and the regional value chains. EEC Dev. Transp. Facil. Meas. Thailand Dev. Strateg. Neighboring Ctries. BRC Res. Rep. 2019, 24, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Carey, R. Exploring China’s Impacts on Development Thinking and Policies. IDS Bull. 2021, 52, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C. Chinese urbanism in question: State, society, and the reproduction of urban spaces. Urban Geogr. 2007, 28, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, F. Special economic zones: Methodological issues and definition. Transnatl. Corp. J. 2019, 26, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Pan, R.; Yuan, Q. Exploring location factors of logistics facilities from a spatiotemporal perspective: A case study from Shanghai. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 100, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdeenurit, P. Special Economic Zone: Facts, roles, and opportunities of investment. In Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2014, Hong Kong, China, 12–14 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dirksmeier, P. Extensive legal exceptionalism, an administrative export-processing zone and urbanization in Mauritius. Area Dev. Policy 2018, 3, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, G. Free zone arbitration in the United Arab Emirates: DIFC v. ADGM:(Part I). J. Int. Arbitr. 2018, 35, 541–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biryukov, E. About the Futuristic City of Neom in Saudi Arabia. 2017, pp. 39–43. Available online: https://vestnik.guu.ru/jour/article/view/878 (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Dursun, M.; Goker, N.; Tulek, B.D. Efficiency analysis of organized industrial zones in Eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2019, 68, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, C.C.; Cummings, J.T.; Cotter, J.V. Middle East Patterns: Places, Peoples, and Politics; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, Y. The process of peak CO2 emissions in developed economies: A perspective of industrialization and urbanization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Qu, P.; Rahmoun, T. Research on the Planning and Development of Industrial Cities in the Middle East Arab Countries Under the Belt and Road Initiative. China City Plan. Rev. 2020, 29, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, D.; Liang, X. New perspective on regional inequality: Theory and evidence from Guangdong, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 04018002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Ye, X.; Wei, Y.D.; Ning, Y.; Dai, S. Geography, ethnicity and regional inequality in Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region, China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2018, 11, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Understanding regional inequality in per capita CO2 emissions in China during 1997–2016: Sources and driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32100–32115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Li, S.; Zhuang, L.; Zhu, X. A comparison and case analysis between domestic and overseas industrial parks of China since the Belt and Road Initiative. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, G.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, L.; Yan, Y.; Yu, N. Analysis on geo-effects of China’s overseas industrial parks: A case study of Cambodia Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 712–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Kuik, C.C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, K. Policy transfer and scale reconstruction of China’s overseas industrial parks: A case study of the Malaysia-China Kuantan Industrial Park. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ma, L. Expansion of industrial parks in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration: A spatial analysis. Land 2021, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Li, J. Eco-efficiency assessment for the eco-industrial park based on the emergy analysis. In Modeling Risk Management in Sustainable Construction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Lei, H. Cluster Analysis for Study Ecological Landscape Sustainability: An Empirical Study in Xi’an of China. In LTLGB 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1041–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Fang, L. Network analysis of industrial metabolism in industrial park–A case study of Huai’an economic and technological development area. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. China in transition towards a circular economy: From policy to practice. J. Prop. Plan. Environ. Law 2020, 12, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, M. A case study in China of the influence mechanism of industrial park efficiency using DEA. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, X. Can the establishment of eco-industrial parks promote urban green innovation? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hao, G.; Cheng, Z. Investigating operations of industrial parks in Beijing: Efficiency at different stages. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2018, 31, 755–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Wang, D.; Huang, X.; Zhao, X.; Hsieh, J.C.; Tzeng, G.H.; Li, J.H.; Chen, J.T. A multi-attribute decision-making model for improving inefficient industrial parks. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 887–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, J.; Zang, N.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L. The role of industrial parks in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7754–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, R. Assessment of greenhouse gas emissions reduction potential in an industrial park in China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, S.; Xue, R.; Liu, D.; Ren, H.; Zhang, R. Uncovering the characteristics of air pollutants emission in industrial parks and analyzing emission reduction potential: Case studies in Henan, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Cai, Q.; Gao, S. Evaluating the energy-environment efficiency and its determinants in Guangdong using a slack-based measure with environmental undesirable outputs and panel data model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Shan, Y. Driving forces of CO2 emissions and mitigation strategies of China’s National low carbon pilot industrial parks. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsson, L. A Review of the Evolution of the Japanese Oil Industry, Oil Policy and Its Relationship with the Middle East; The Oxford Institute for Energy Studies: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.L. The oil curse. In The Oil Curse; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, N.S.C.; Al Abbar, S.D. Sustainability in the Middle East: Achievements and challenges. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban Dev. 2015, 6, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregenna, F. Deindustrialization and premature deindustrialization. In Handbook of Alternative Theories of Economic Development; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.R.; Engelke, P. The Great Acceleration: An Environmental History of the Anthropocene Since 1945; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Azmeh, S. Trade regimes and global production networks: The case of the qualifying industrial zones (QIZs) in Egypt and Jordan. Geoforum 2014, 57, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.; Abu El Ella, E.S.M. Integration of Remote Sensing & GIS to Manage the Sustainable Development in the Nile Valley desert fringes of assiut-sohag governorates, upper Egypt. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 759–774. [Google Scholar]
- Akyelken, N. Mobility-related economic exclusion: Accessibility and commuting patterns in industrial zones in Turkey. Soc. Incl. 2017, 5, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çal, M.; Kandemir, A.; Saygili, C.; Bayraktar, C. Efficiency Analysis of Free Zones and Strategy Policies. In New Challenges in Leadership and Technology Management; Future Academy: Hong Kong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro-Courtland, C. National report for the united arab emirates and its free zones. In Executory Contracts in Insolvency Law; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, P.; Iovino, F. Special Economic Zones: A Brief Comparative Excursus. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Teichmann, F.M.J.; Wittmann, C. Money laundering in the United Arab Emirates: The risks and the reality. J. Money Laund. Control 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Oraimi, S. Diversity and social cohesion in the United Arab Emirates. Вестник Рoссийскoгo университета дружбы нарoдoв. Серия: Сoциoлoгия. RUDN J. Sociol. 2020, 20, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell QC, D. Trusts and foundations move onshore in the Gulf. Trust. Trust. 2021, 27, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnoori, P.; Jenkins, G.P. The value of online banking to small and medium-sized enterprises: Evidence from firms operating in the uae free trade zones. Appl. Econ. 2019, 51, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, P.; Ricci, P.; Iovino, F. The urban free zones (UFZ). between disapproval, misunderstanding and recognition. as a special development tool for local finance. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference of the EuroMed Academy of Business, Rome, Italy, 13–15 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Basyoni, M.H.; Aref, M.A. Composition and origin of the sabkha brines, and their environmental impact on infrastructure in Jizan area, Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharbatoghlie, A. Urbanization and Regional Disparities in Post-Revolutionary Iran; Routledge: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hakimian, H. Iran’s Free Trade Zones: Back Doors to the International Economy? Iran. Stud. 2011, 44, 851–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, M.; Ma, M.T.; Wu, H.Z.; Yu, Z.J.; Guan, S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, D.D.; Jin, F.; et al. [Corrigendum] MicroRNA-148a inhibits breast cancer migration and invasion by directly targeting WNT-1. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guan, Y.; Xu, K.; Ding, X.; Pang, Y. Review on bioinspired planetary regolith-burrowing robots. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Baltagi, B.H. Panel Data Econometrics: Theoretical Contributions and Empirical Applications; Emerald Group Publishing: Bingley, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Latourte, A.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Luxembourger, C.; Pane, I.; Claudepierre, P.; Richette, P.; Lafforgue, P.; Combe, B.; Cantagrel, A.; Sibilia, J.; et al. Safety of surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated by abatacept: Data from the French Orencia in Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, L.; Zhou, X. Does the green industry policy reduce industrial pollution emissions?—Evidence from China’s national eco-industrial park. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L. China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Teo, T.S.; Zhou, F.; Lim, M.K.; Chen, H. Does industrial green transformation successfully facilitate a decrease in carbon intensity in China? An environmental regulation perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, E.; D’Uva, M. Social support, industrial parks and FDI location choice across Hungarian counties. Soc. Indic. Res. 2017, 133, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Wang, J. From obligated embeddedness to supplier chain park investment: A new mode of FDI. China Soft Sci 2010, 3, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, W. Planning and designing of distributed PV of Suzhou Industrial Park. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 42nd Photovoltaic Specialist Conference (PVSC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14–19 June 2015; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.; Wu, W. Green GDP accounting: Further research and discussion in the context of low-carbon development. China Popu. Resour. Environ. 2010, 20, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Ge, B.; Li, Y. Impacts of state-led and bottom-up urbanization on land use change in the peri-urban areas of Shanghai: Planned growth or uncontrolled sprawl? Cities 2017, 60, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Ghezzi, A.; Colombelli, A.; Casali, G.L. Agglomeration dynamics of innovative start-ups in Italy beyond the industrial district era. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2020, 16, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Golden, H.H. Urbanization and the development of pre-industrial areas. In Kingsley Davis; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 295–317. [Google Scholar]
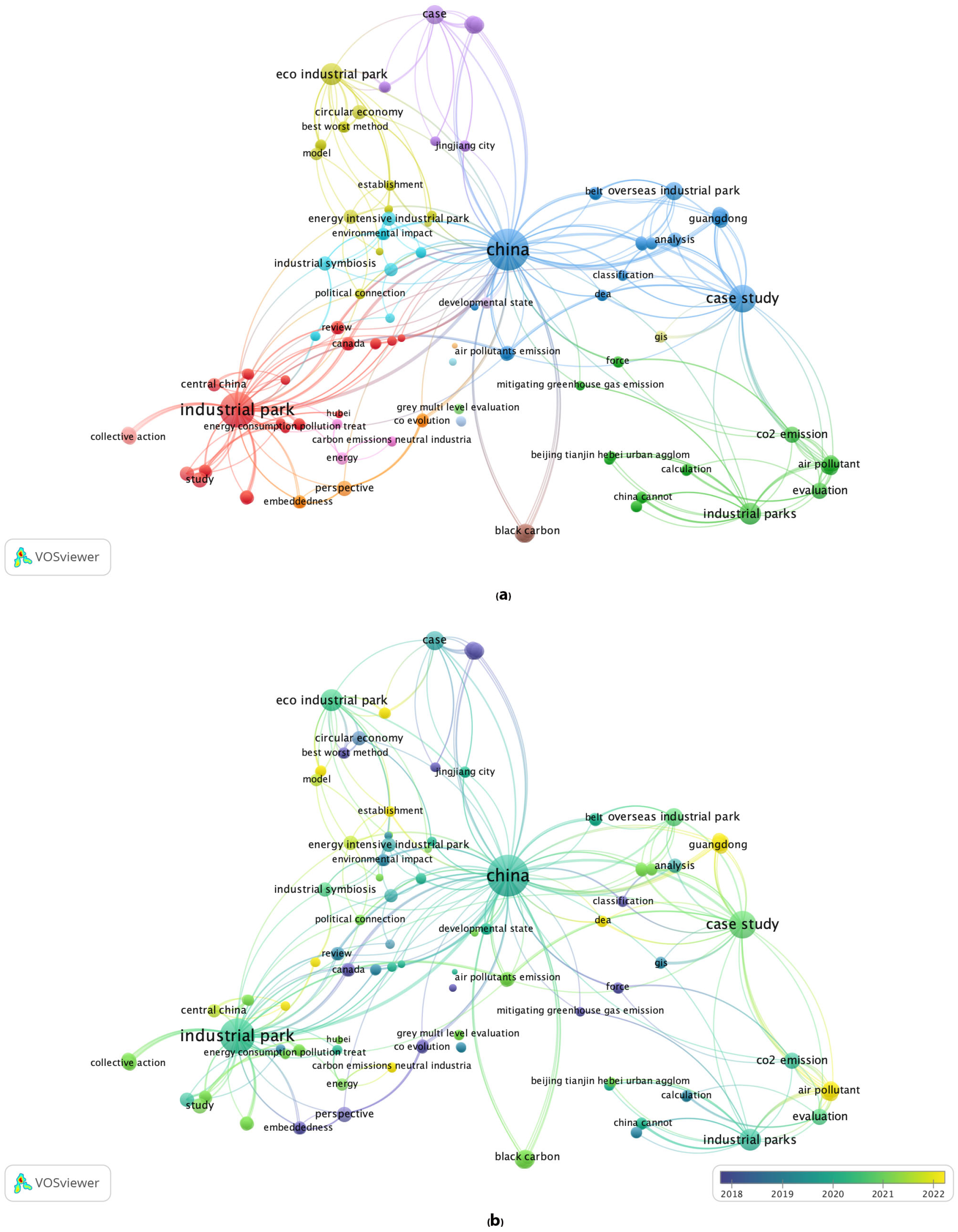

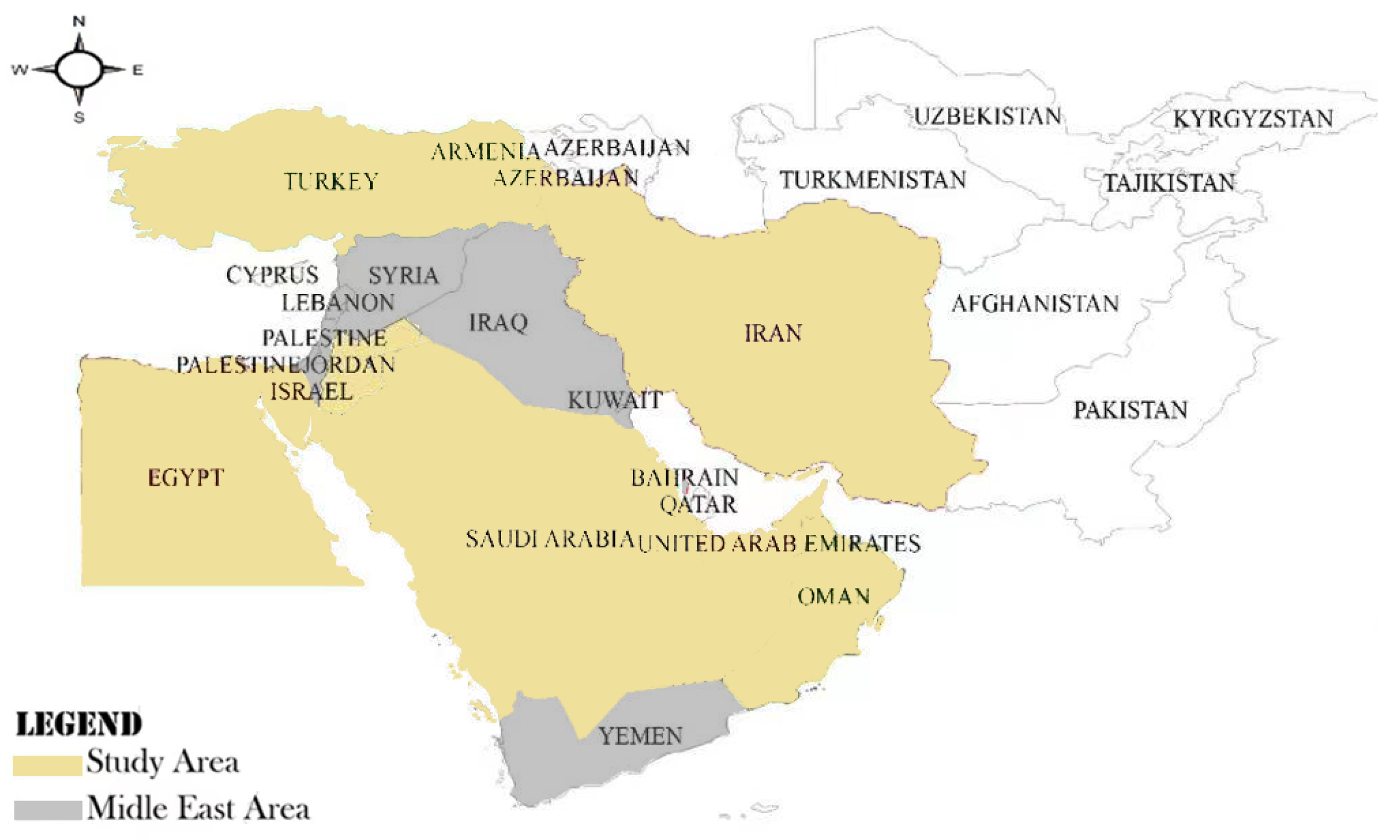
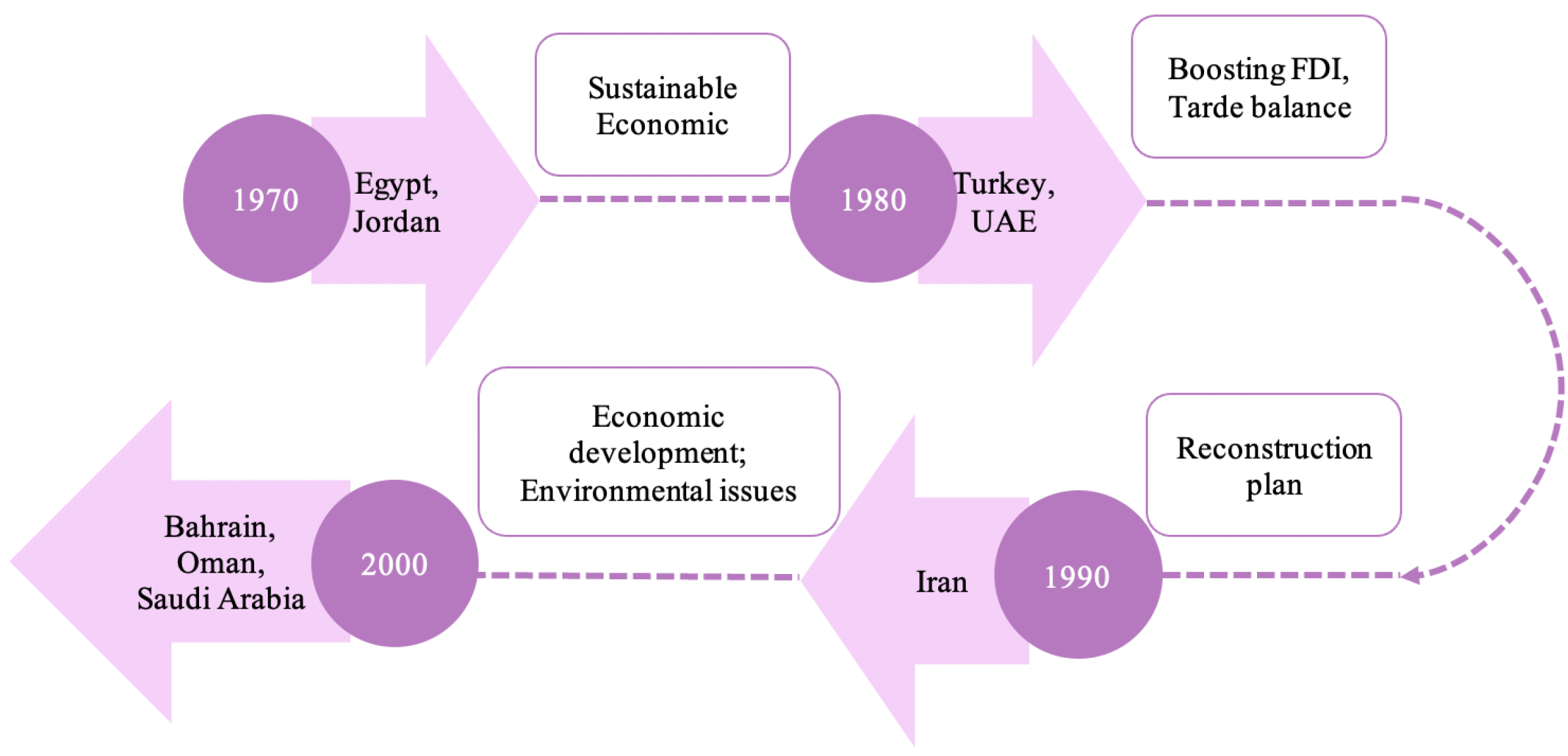


| Source | Research Fields | Dimensions | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ye et al., 2021 [25] | Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China (Thai-Chinese Rayong Industrial Zone and Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area) | economic development mode | spatiotemporal evolution |
| Wang et al., 2021 [26] | Cambodia Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone (BRI) | Geo political, economic social and cultural | interviews and a case study |
| Liang et al., 2021 [27] | Malaysia-China Kuantan Industrial Park | policy transfer theory | Interview as data collection |
| Kang, 2021 [28] | Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei | urban agglomeration and supplements | Critical analysis |
| Shang and Li, 2021 [29] | an industrial Park | economic performance and the environmental performance | Eco- efficiency |
| Liu and Lei, 2013 [30] | An Empirical Study in Xi’an of China industrial parks (environment, economic criteria) | the concept of ecological landscape | DEARA (Data Envelopment-Regression Analysis) model, |
| Fan et al., 2017 [31] | Huai’an economic and technological development area | Economic agglomerations | ecological network analysis |
| Zhao et al., 2020 [32] | Suzhou New District and Shanghai city in the building CE-oriented industrial park and CE city, | circular economy | a top-down approach |
| He et al., 2020 [33] | 36 industrial parks Jiangxi Province of china | economic efficiency | DEA |
| Wu and Gao, 2022 [34] | 264 prefecture-level cities in China | achieving green and sustainable development | difference-in-difference (DID) model and panel data |
| Yang et al., 2018 [35] | Beijing China | Economic returns | multi-stage operational process |
| Lin et al., 2019 [36] | China’s case study | Policy and economic inefficacy of industrial parks | multi-attribute decision- making model interview |
| Guo et al., 2018 [37] | greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of 213 Chinese national-level industrial parks | Low carbon industrial park development | investigation and questionnaires;analysis by ArcGIS software |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [38] | Yongcheng Economic Technological Development Zone | Boosting economic and reducing carbon emissions | scenario, Math analysis, IPCC guidelines as the main method |
| Gao et al., 2021 [39] | 11 industrial parks located in Henan Province | CO, PM10, PM2.5, VOCs and NH3emissions from (which industry, and what kind of energy use) and economic ouput | bottom-up emission factor method and material balance method |
| Wang et al., 2019 [40] | Summary on China’s industrial park project | green growth and sustainable development | Review theory |
| Yu et al., 2017 [41] | 20 pilot industrial parks adopted by National Low Carbon Industrial Parks Pilot Programme (LCIPPP) | CO emissions | STIRPAT (Stochastic Impacts by Regression on Population, Affluence and Technology) model |
| Variables | Unit | Min | Max | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Industrial parks | - | 0 | 4 | 0.447 | 0.796 |
| labor force | person | 305,457 | 32,833,549 | 11,738,565 | 10,968,542 |
| Urbanization rate | percent | 42.704 | 90.979 | 74.701 | 13.960 |
| CO | kt | 15,880 | 629,290 | 204993.289 | 183430.365 |
| GDP | US | 15,447,922,938 | 988,642,300,212 | 272,997,718,273 | 232,898,089,116 |
| FDI | US | 2,172,431,730 | 39,455,863,929 | 5,301,513,483 | 6,816,401,775 |
| Population | NO | 664,611 | 98,423,598 | 34,122,892 | 33,672,860 |
| Variables | T-Statistic | Prob | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. Industrial parks | −5.40679 | 0.0000 | I(0) |
| labor force | −7.11154 | 0.0000 | I(0) |
| Urbanization rate | −1.82847 | 0.0337 | I(0) |
| CO emission | −2.46149 | 0.0069 | |
| FDI | −2.39850 | 0.0082 | I(0) |
| Population | −1.99382 | 0.0231 | I(0) |
| GDP | −0.98403 | 0.1626 | I(1) |
| Equation: EQ01 | |||
| Test cross-section fixed effects | |||
| Effects Test | Statistic | d.f. | Prob |
| Cross-section F | 362.673267 | (7.130) | 0.0000 |
| Variables | Coefficient | Std.Error | t-Statistic | Prob |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | − 9.14 | 6.14 | −14.89862 | 0.0000 |
| Co2Kt | 434439.9 | 33209.84 | 13.08166 | 0.0000 |
| FDI | 0.753961 | 0.153564 | 4.909754 | 0.0000 |
| URrate | 3.79 | 1.85 | 2.051503 | 0.0422 |
| Labor | 28072.47 | 1468.923 | 19.11091 | 0.0000 |
| Population | −2892.254 | 680.5519 | −4.249866 | 0.0000 |
| Industrial park | 2.27 | 8.07 | 2.809662 | 0.0057 |
| Weighted Statistics | |||
| R-squared | 0.997091 | Mean dependent var | 11.27881 |
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.996800 | S.D. dependent var | 23.58215 |
| R-squared | 0.997091 | Mean dependent var | 11.27881 |
| S.E. of regression | 0.890959 | Sum squared resid | 0.999807 |
| F-statistic | 3427.734 | Durbin-Watson stat | 103.1950 |
| Prob(F-statistic) | 0.000000 | ||
| Unweighted Statistics | |||
| R-squared | 0.983306 | Mean dependent var | 2.67 |
| Sum squared resid | 1.22 | Durbin-Watson stat | 0.313567 |
| Equation: EQ01 | |||
| Test cross-section random effects | |||
| Test Summary | Chi-Sq Statistic | Chi-Sq.d.f. | Prob |
| Cross-section random | 313.897100 | 6 | 0.0000 |
| Ranks | Countries | Average Value of GDP at Constant Price (Intercept) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saudi Arabia | 172,000,000,000 |
| 2 | UAE | 146,000,000,000 |
| 3 | Oman | 59,700,000,000 |
| 4 | Bahrain | 55,500,000,000 |
| 5 | Jordan | 47,300,000,000 |
| 6 | Turkey | 42,500,000,000 |
| 7 | Egypt | − 245,000,000,000 |
| 8 | Iran | −277,000,000,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falahatdoost, S.; Wang, X. Industrial Park Role as a Catalyst for Regional Development: Zooming on Middle East Countries. Land 2022, 11, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081357
Falahatdoost S, Wang X. Industrial Park Role as a Catalyst for Regional Development: Zooming on Middle East Countries. Land. 2022; 11(8):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081357
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalahatdoost, Soniya, and Xingping Wang. 2022. "Industrial Park Role as a Catalyst for Regional Development: Zooming on Middle East Countries" Land 11, no. 8: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081357
APA StyleFalahatdoost, S., & Wang, X. (2022). Industrial Park Role as a Catalyst for Regional Development: Zooming on Middle East Countries. Land, 11(8), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081357






