Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
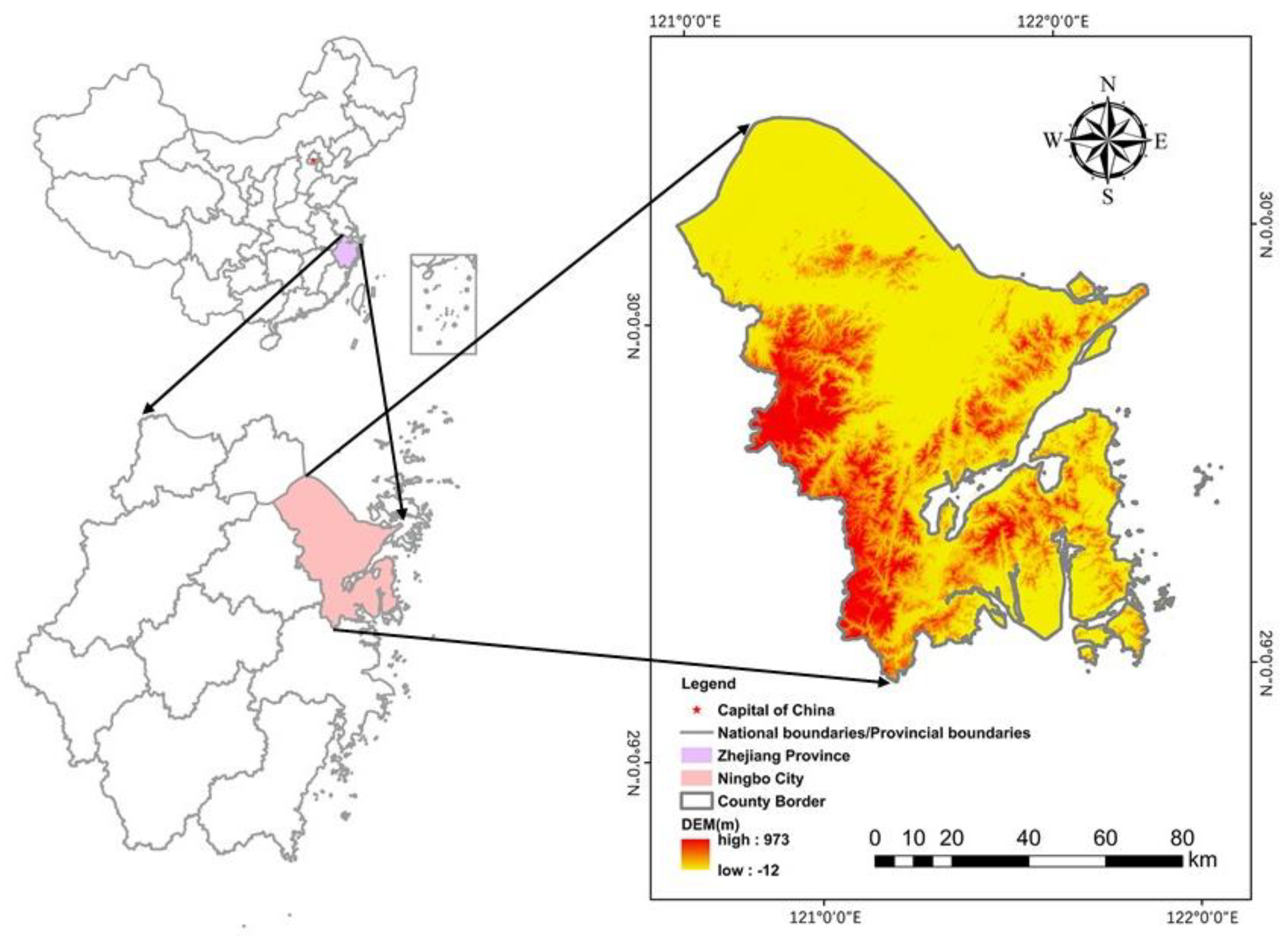
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Source
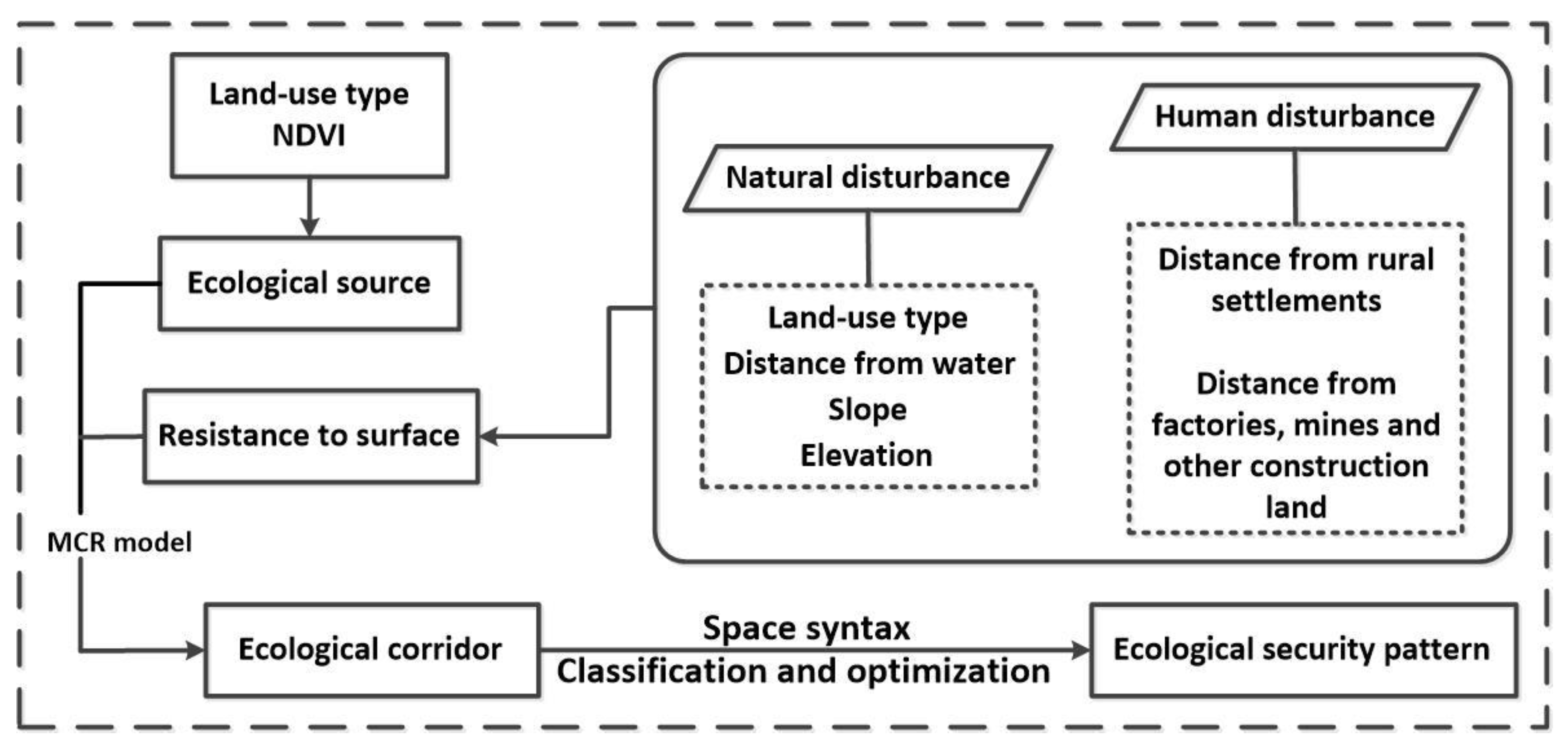
3. Method
3.1. Determination of the Source
3.2. Resistance Surface Construction
3.3. Preliminary Determination of the Corridor
3.4. Corridor Classification Based on the Space Syntax
3.5. Buffers Construction
4. Results
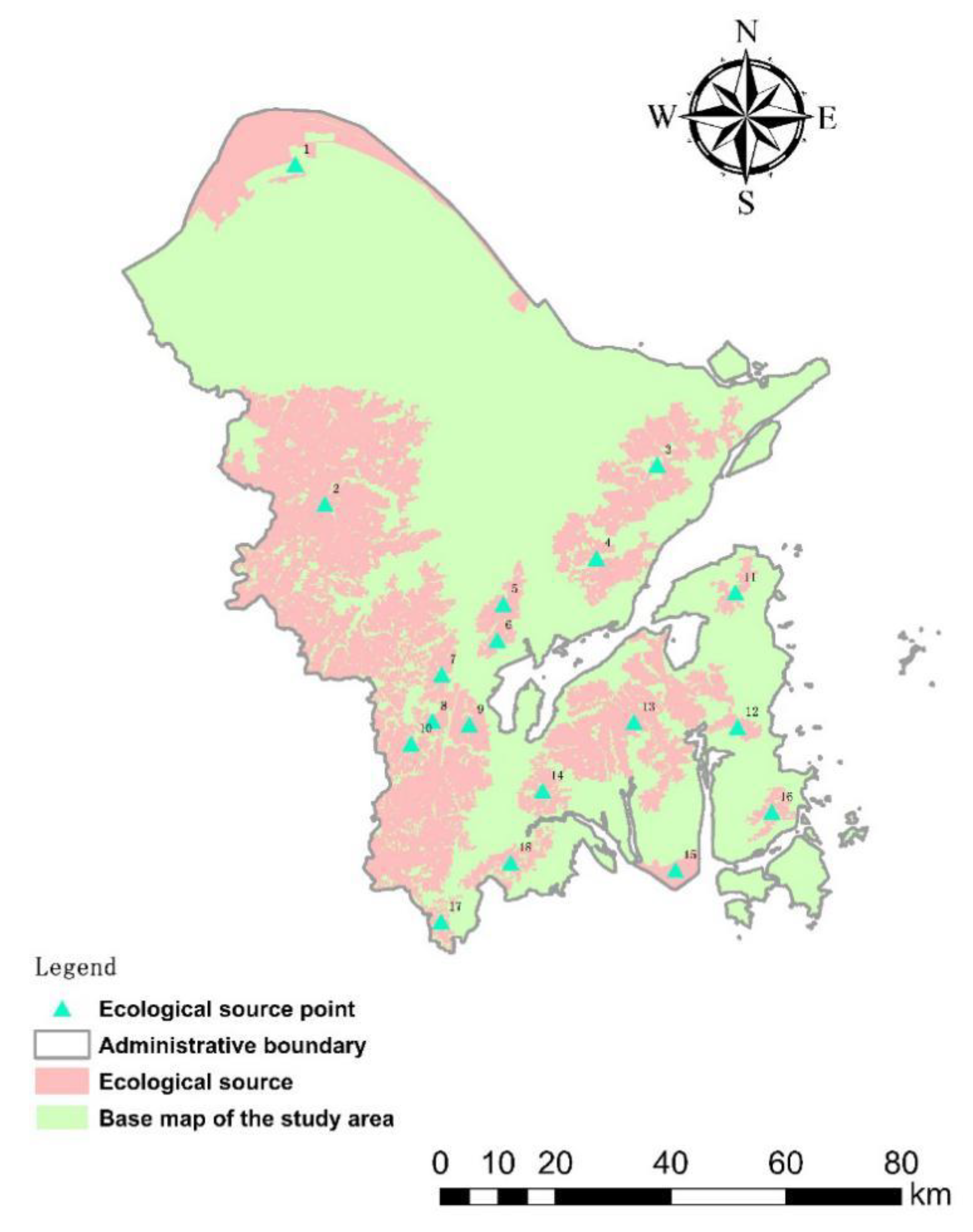
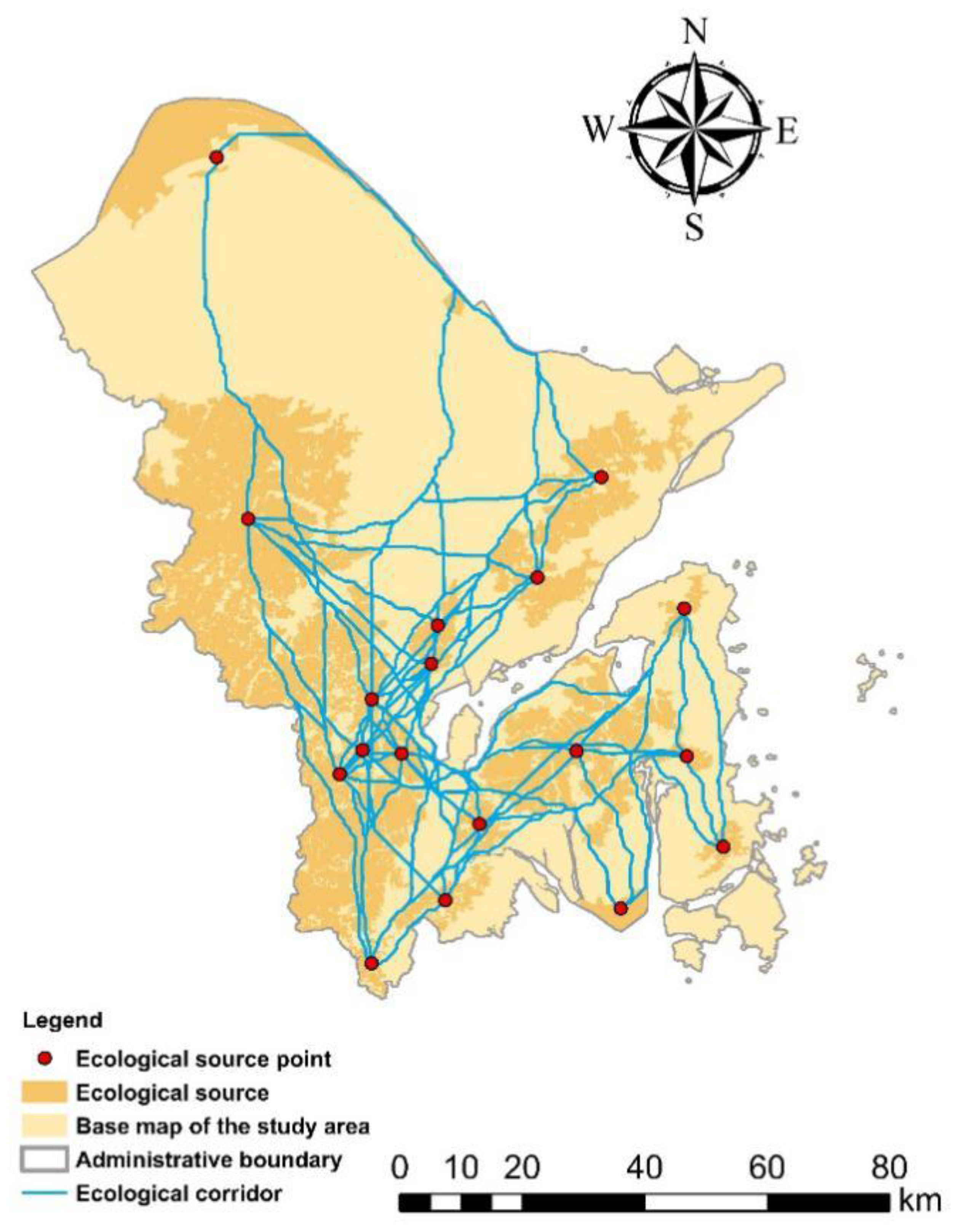
4.1. Determination of the Source
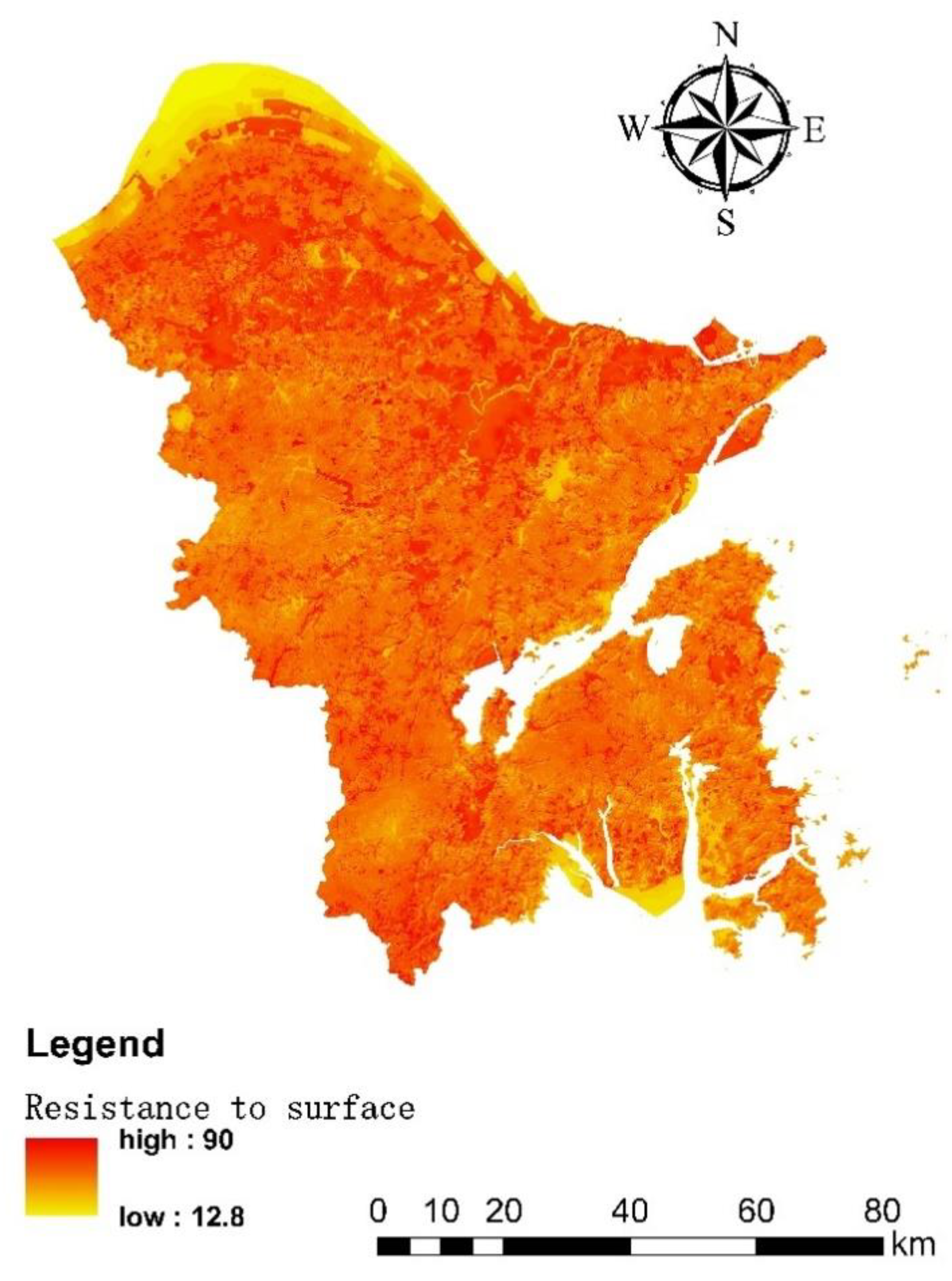
4.2. Resistance Surface
4.3. Preliminary Determination of the Corridor
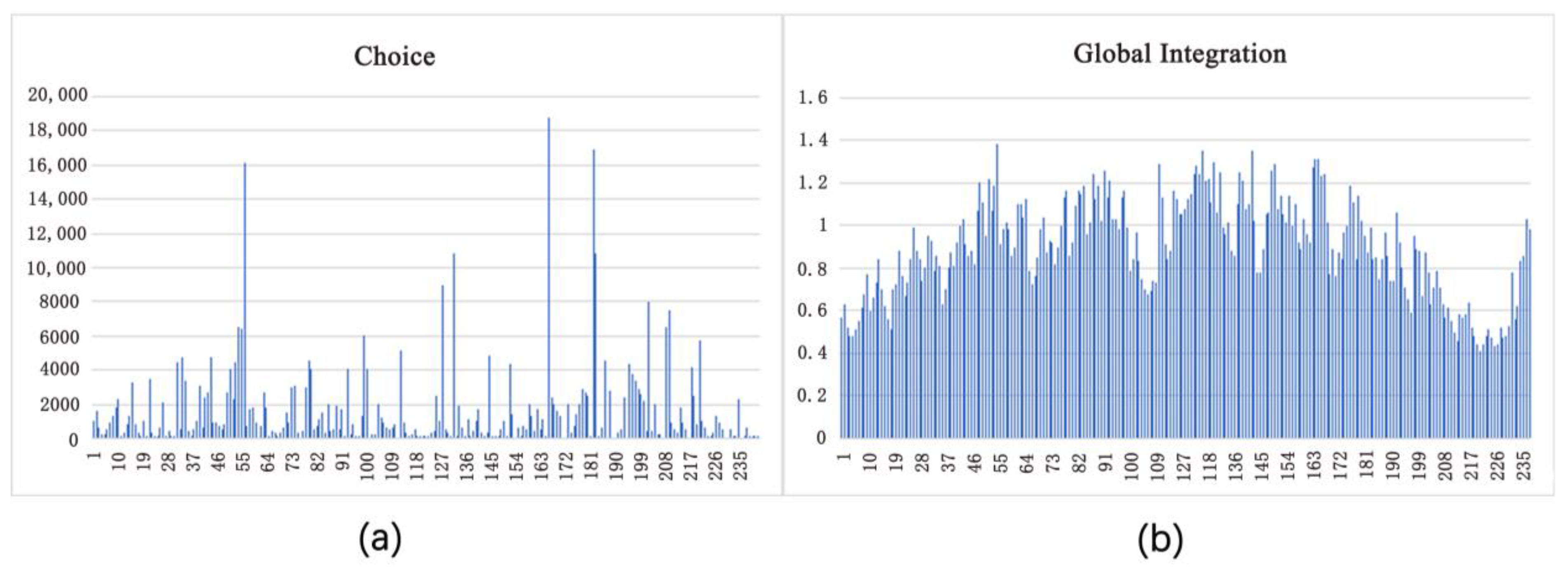
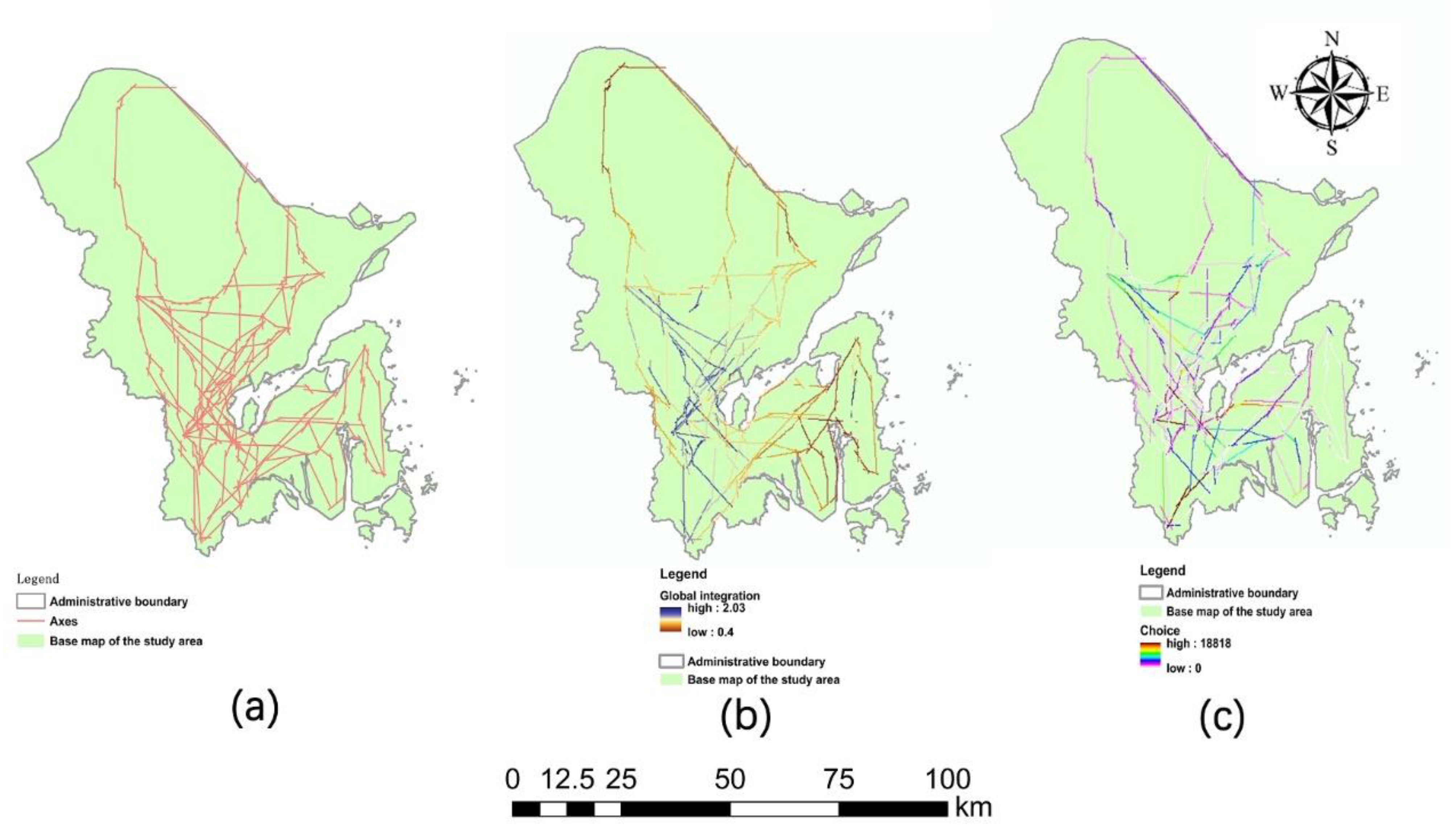
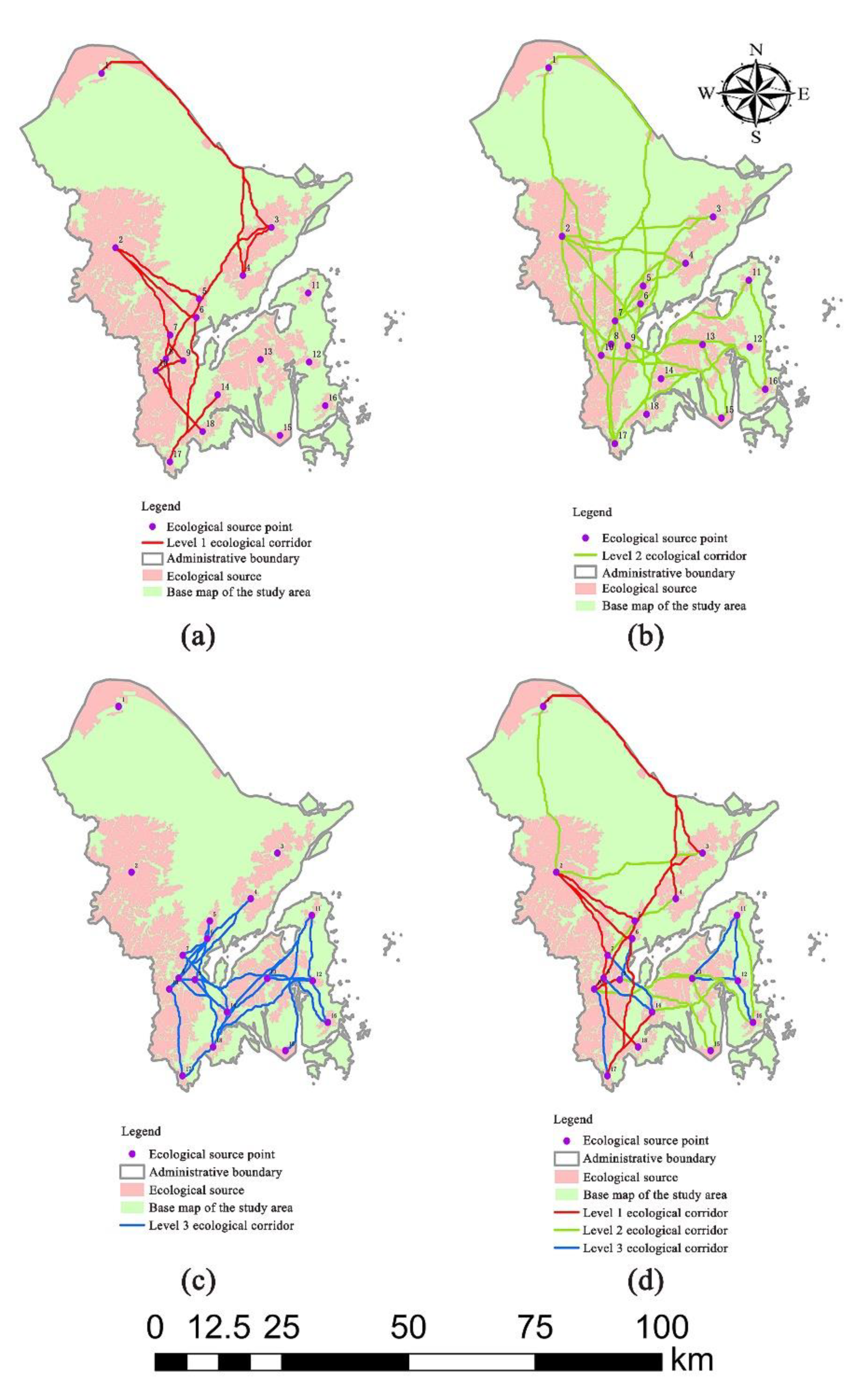
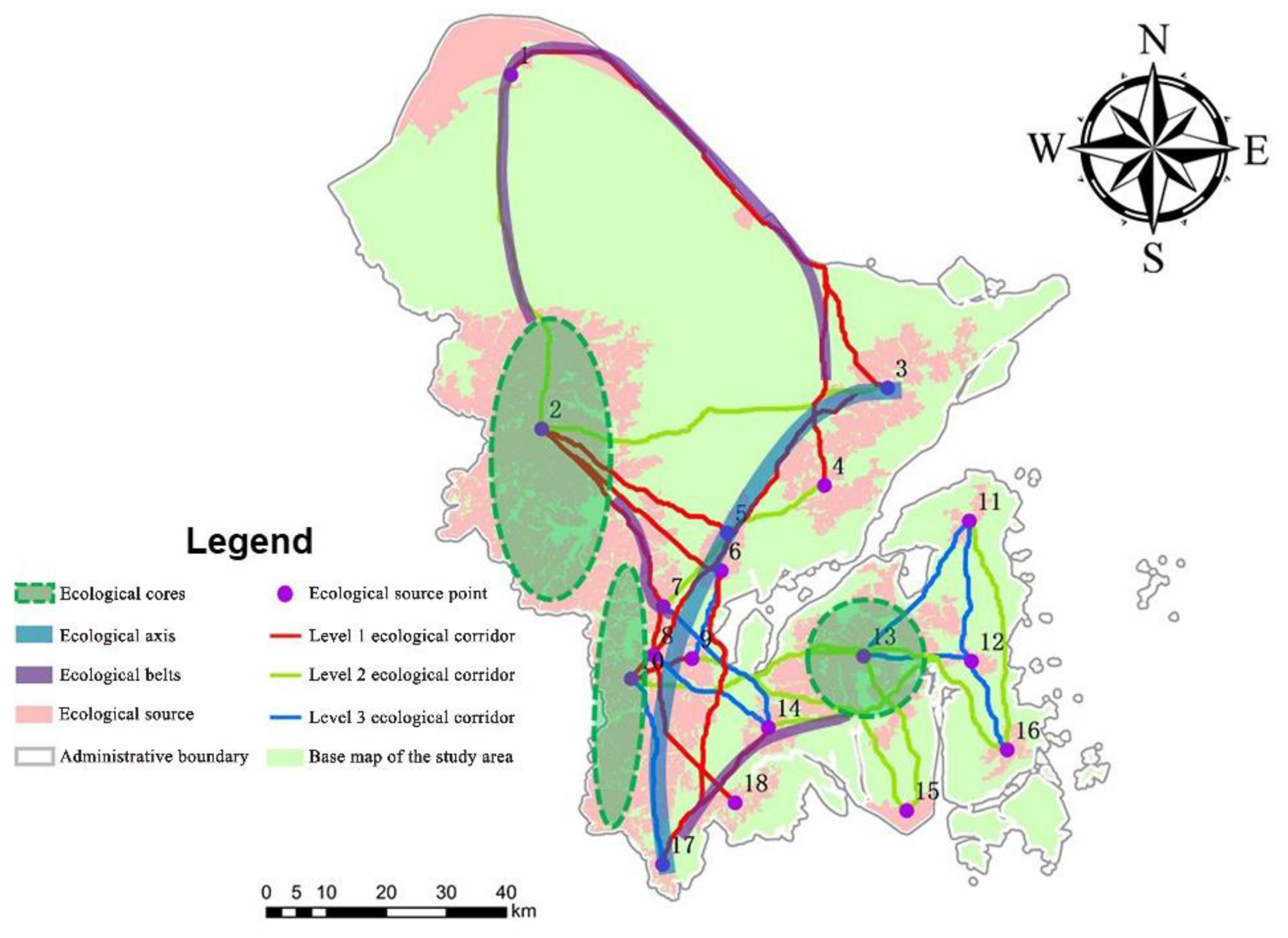
4.4. Corridor Classification Based on the Space Syntax
5. Discussion
5.1. Advantages of the Method
5.2. Layout Optimization
5.3. Research Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caprotti, F.; Cowley, R.; Datta, A.; Broto, V.C.; Gao, E.; Georgeson, L.; Herrick, C.; Odendaal, N.; Joss, S. The New Urban Agenda: Key opportunities and challenges for policy and practice. Urban Res. Pract. 2017, 10, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, S. Comparing the spatial and temporal dynamics of urban expansion in Guangzhou and Shenzhen from 1975 to 2015: A case study of pioneer cities in China’s rapid urbanization. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, R. Evaluation of urban suitable ecological land based on the minimum cumulative resistance model: A case study from Changzhou, China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.; Marvin, S. ‘Urban Ecological Security’: A New Urban Paradigm? Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2009, 33, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdorf, E.V.; Nootenboom, C.; Janke, B.; Horgan, B.P. Assessing urban ecosystem services provided by green infrastructure: Golf courses in the Minneapolis-St. Paul metro area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 208, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaensen, F.; Chardon, J.P.; De Blust, G.; Swinnen, E.; Villalba, S.; Gulinck, H.; Matthysen, E. The application of ‘least-cost’ modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliwoda, J.; Banzhaf, E.; Priess, J.A. How do the green components of urban green infrastructure influence the use of ecosystem services? Examples from Leipzig, Germany. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Wolch, J.R.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J.P. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Biest, K.; Meire, P.; Schellekens, T.; D’hondt, B.; Bonte, D.; Vanagt, T.; Ysebaert, T. Aligning biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services in spatial planning: Focus on ecosystem processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wei, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y. Construction of ecological security pattern based on the importance of ecosystem service functions and ecological sensitivity assessment: A case study in Fengxian County of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 563–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yu, L.; Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Xu, B. How does urban expansion interact with cropland loss? A comparison of 14 Chinese cities from 1980 to 2015. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesshöver, C.; Assmuth, T.; Irvine, K.N.; Rusch, G.M.; Waylen, K.A.; Delbaere, B.; Haase, D.; Jones-Walters, L.; Keune, H.; Kovacs, E.; et al. The science, policy and practice of nature-based solutions: An interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.K.; Daily, G.C. The Ecosystem Services Framework and Natural Capital Conservation. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2008, 39, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Shacham, E.; Walters, G.; Janzen, C.; Maginnis, S. Nature-Based Solutions to Address Global Societal Challenges; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, S.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Applying ant colony algorithm to identify ecological security patterns in megacities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 117, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, M.; Petit, E.J.; Croci, S.; Nabucet, J.; Georges, R.; Madec, L.; Ernoult, A. Ecological relevance of least cost path analysis: An easy implementation method for landscape urban planning. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J. Theoretical innovation in optimization of protection and development of China’s territorial space and coping strategy of 13th Five-Year Plan. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2016, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, F. Research on recognition and protection of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory: A case study of Jinan City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12414–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X. Incorporating ecological risk index in the multi-process MCRE model to optimize the ecological security pattern in a semi-arid area with intensive coal mining: A case study in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J. Building ecological security patterns based on ecosystem services value reconstruction in an arid inland basin: A case study in Ganzhou District, NW China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; He, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhong, M.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Feng, C.; Xing, W.; et al. Integrating priority areas and ecological corridors into national network for conservation planning in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, X.; He, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, L. Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneć, R. Ecological Security of Communities in Polish Cities. J. Hum. Secur. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovjova, N.V. Synthesis of ecosystemic and ecoscreening modelling in solving problems of ecological safety. Ecol. Model. 1999, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Z.; Liu, Y.S.; Xia, B.C.; Zhao, G.W. Urban ecological security assessment and forecasting, based on a cellular automata model: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3612–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chang, Q. Ecological security research progress in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y. The theories and methods for systematically understanding land resource. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh, B.; Khansefid, M. A case study of urban ecological networks and a sustainable city: Tehran’s metropolitan area. Urban Ecosyst. 2010, 13, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wu, T.; Liu, M.; Huang, M.; Stendardo, L.; Zhang, Y. The construction and optimization of ecological security pattern in the Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Xu, X.H. Research on landscape ecological security pattern in a Eucalyptus introduced region based on biodiversity conservation. Russ. J. Ecol. 2015, 46, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, J. Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Du, F.; Zuo, L.; Jiang, Y. Integrating ecosystem services and rocky desertification into identification of karst ecological security pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, V.; Pomarico, S. An integrated approach for studying the land suitability for ecological corridors through spatial multicriteria evaluations. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2013, 15, 859–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Construction of landscape ecological network based on landscape ecological risk assessment in a large-scale opencast coal mine area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P.; Noss, R.F. Do habitat corridors provide connectivity? Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K. Security patterns and surface model in landscape ecological planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1996, 36, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Beier, P. Circuit theory predicts gene flow in plant and animal populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Han, Y. Integrating spatial continuous wavelet transform and kernel density estimation to identify ecological corridors in megacities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 199, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Nakagoshi, N.; Zong, Y. Urban green space network development for biodiversity conservation: Identification based on graph theory and gravity modeling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 95, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.M.; Ma, Y.F.; Wang, J.L.; You, X.Y. Landscape pattern analysis and ecological network planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 46, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Ou, M.; Pueppke, S.G.; Ou, W.; Tao, Y. An evaluation framework for designing ecological security patterns and prioritizing ecological corridors: Application in Jiangsu Province, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 2517–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanghe, K.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, H.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, T.U.; Xiao, Y.; Luan, X.; Li, K. Gravity model toolbox: An automated and open-source ArcGIS tool to build and prioritize ecological corridors in urban landscapes. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, B. Spatial sustainability in cities: Organic patterns and sustainable forms. In Proceedings of the 7th International Space Syntax Symposium, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–11 June 2009; Royal Institute of Technology (KTH): Stockholm, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.H.; Omar, R.H. Planting design for urban parks: Space syntax as a landscape design assessment tool. Front. Archit. Res. 2015, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, M.; Song, K.; Lee, J. Planning a Green Infrastructure Network to Integrate Potential Evacuation Routes and the Urban Green Space in a Coastal City: The Case Study of Haeundae District, Busan, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A new habitat availability index to integrate connectivity in landscape conservation planning: Comparison with existing indices and application to a case study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Lv, C. Construction and optimization of green space ecological networks in urban fringe areas: A case study with the urban fringe area of Tongzhou district in Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.-L.; Shi, P.-J. Using ecosystem service supply and ecosystem sensitivity to identify landscape ecology security patterns in the Lanzhou-Xining urban agglomeration, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, C.; Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, K. Can the establishment of ecological security patterns improve ecological protection? An example of Nanchang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebendiger, Y.; Lerman, Y. Applying space syntax for surface rapid transit planning. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 128, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, H.O.; Major, M.D.; Furlan, R. Accessibility of green spaces in a metropolitan network using space syntax to objectively evaluate the spatial locations of parks and promenades in Doha, State of Qatar. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skogen, K.; Helland, H.; Kaltenborn, B. Concern about climate change, biodiversity loss, habitat degradation and landscape change: Embedded in different packages of environmental concern? J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, X.; Wu, C.; Xing, X.; Fang, M.; Garang, Z.; Wu, Y. Coupling intensive land use and landscape ecological security for urban sustainability: An integrated socioeconomic data and spatial metrics analysis in Hangzhou city. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1459–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkala, A.S.; Moilanen, A. Ecosystem services and connectivity in spatial conservation prioritization. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesús Arce-Mojica, T.; Nehren, U.; Sudmeier-Rieux, K.; Miranda, P.J.; Anhuf, D. Nature-based solutions (NbS) for reducing the risk of shallow landslides: Where do we stand? Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 41, 101293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Santé, I.; Loureiro, X.; Miranda, D. Green infrastructure spatial planning considering ecosystem services assessment and trade-off analysis. Application at landscape scale in Galicia region (NW Spain). Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzas, M.; Hermoso, V.; de-Miguel, S.; Bota, G.; Brotons, L. Designing a network of green infrastructure to enhance the conservation value of protected areas and maintain ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoui, Y.; Leski, C.D.G.; Benot, M.L.; Revers, F.; Salles, D.; van Halder, I.; Barneix, M.; Carassou, L. Integrating ecological networks modelling in a participatory approach for assessing impacts of planning scenarios on landscape connectivity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 209, 104039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, B.D.; Scharler, U.M.; Ulanowicz, R.E.; Hannon, B. Ecological network analysis: Network construction. Ecol. Model. 2007, 208, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Can policy maintain habitat connectivity under landscape fragmentation? A case study of Shenzhen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Interference Factor | Resistance Factor | Resistance Value | Weights | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 30 | 50 | 70 | 90 | |||
| Natural disturbance factors | Land use type | Woodl-and, water, ocean | Grassla-nd | Cultivated land | Unused land | Constructio-n land | 0.35 |
| Distance to water | <1 km | 1–3 km | 3–5 km | 5–10 km | ≥10 km | 0.12 | |
| slope | ≤3° | 3–5° | 5–10° | 10–15° | >15° | 0.14 | |
| Elevation | ≤0 m | 0–50 m | 50–100 m | 100–150 m | >150 m | 0.12 | |
| Human interference factors | Distance from rural settlements | ≥5 km | 3–5 km | 1–3 km | 0.5–1 km | <0.5 km | 0.13 |
| Distance to other built-up land, such as factories and mines | ≥15 km | 10–15 km | 5–10 km | 1–5 km | <1 km | 0.14 | |
| Choice | Global Integration | |
|---|---|---|
| ≥0.6 | <0.6 | |
| <300 | Level 3 | Level 3 |
| 300–1000 | Level 2 | Level 1 |
| >1000 | Level 1 | Level 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Yu, C.; Feng, Z.; Du, H.; Huang, C.; Wu, K. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example. Land 2021, 10, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040380
Han Y, Yu C, Feng Z, Du H, Huang C, Wu K. Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example. Land. 2021; 10(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yu, Chaoyue Yu, Zhe Feng, Hanchu Du, Caisi Huang, and Kening Wu. 2021. "Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example" Land 10, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040380
APA StyleHan, Y., Yu, C., Feng, Z., Du, H., Huang, C., & Wu, K. (2021). Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example. Land, 10(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040380








