The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Model
3.2. Variable Descriptions
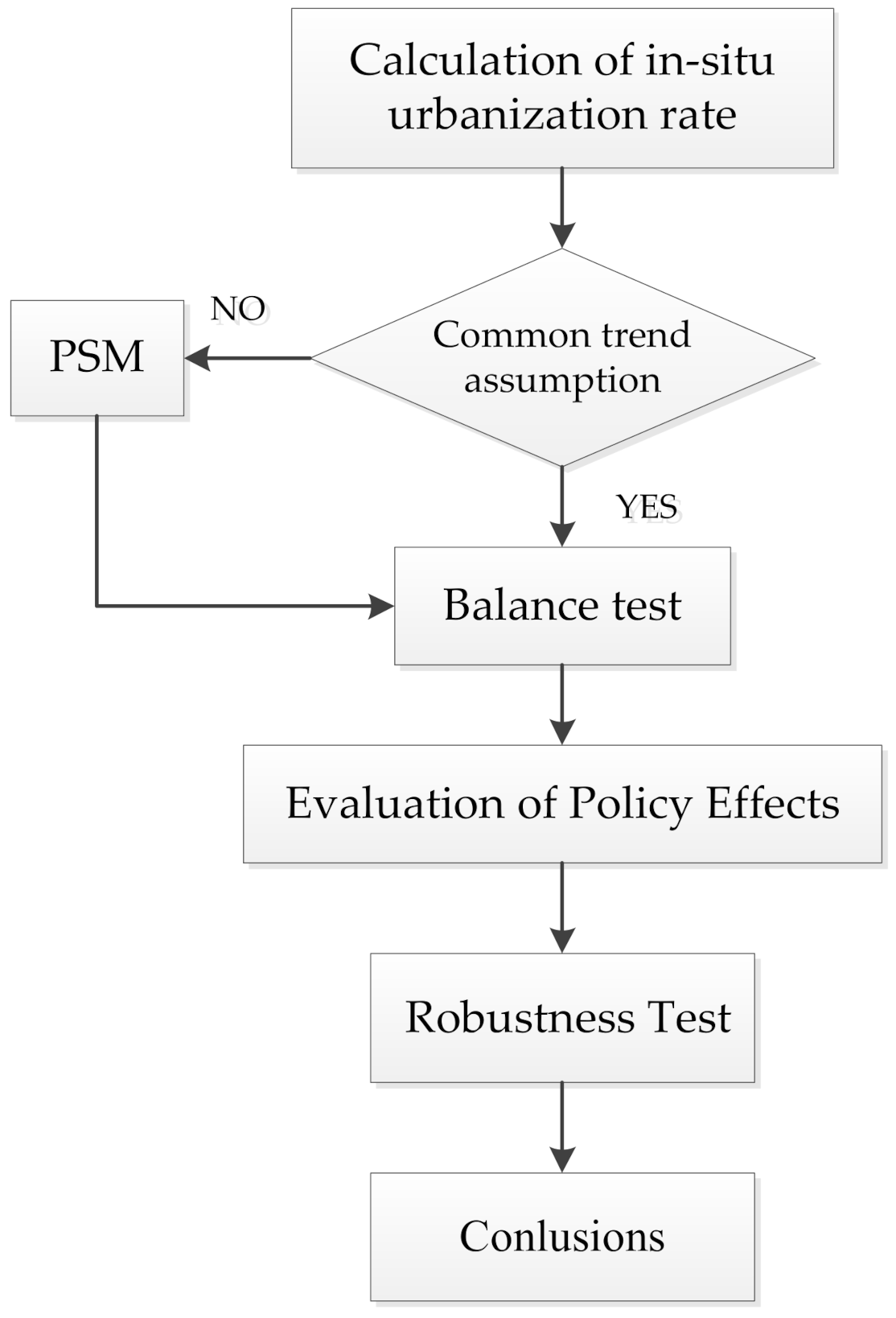
3.3. Steps
4. Analysis of In Situ Urbanization Level
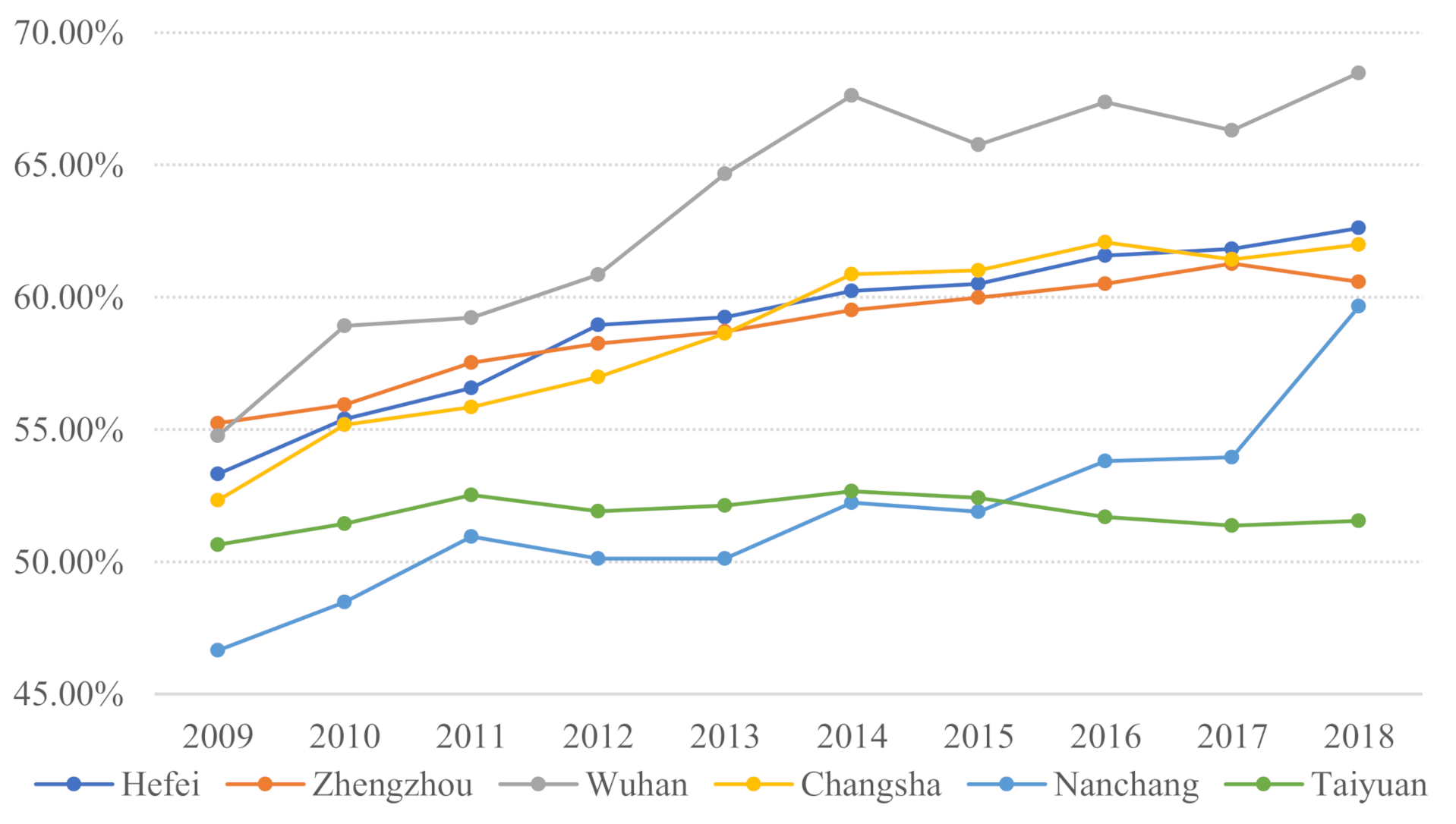
4.1. Calculation of In Situ Urbanization Rate in Central China
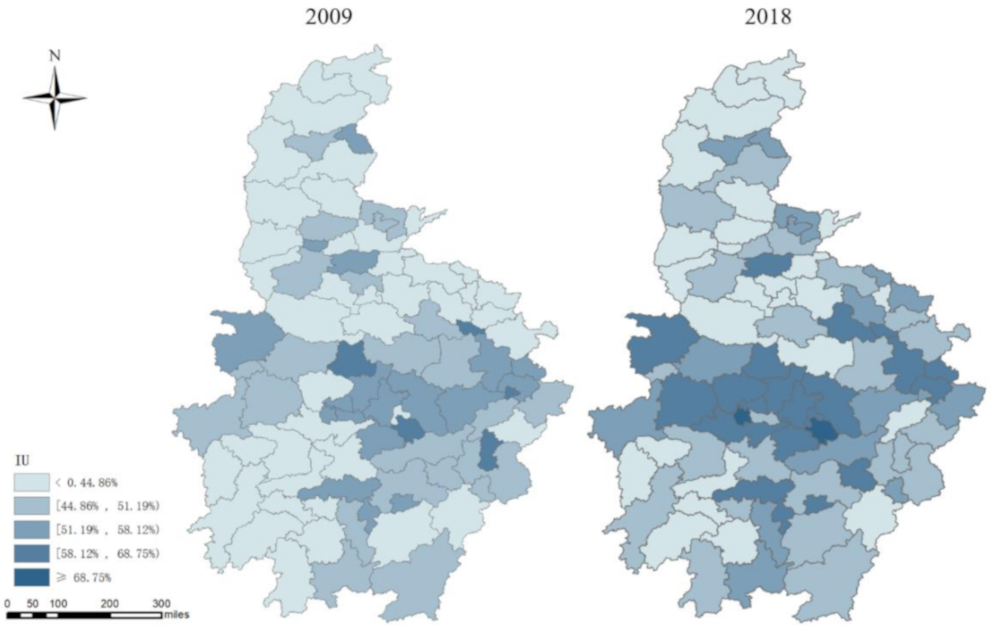
4.2. Spatial Pattern of Local Urbanization in Central China
5. Empirical Test
5.1. Influence of New Urbanization Pilot Areas on In Situ Urbanization
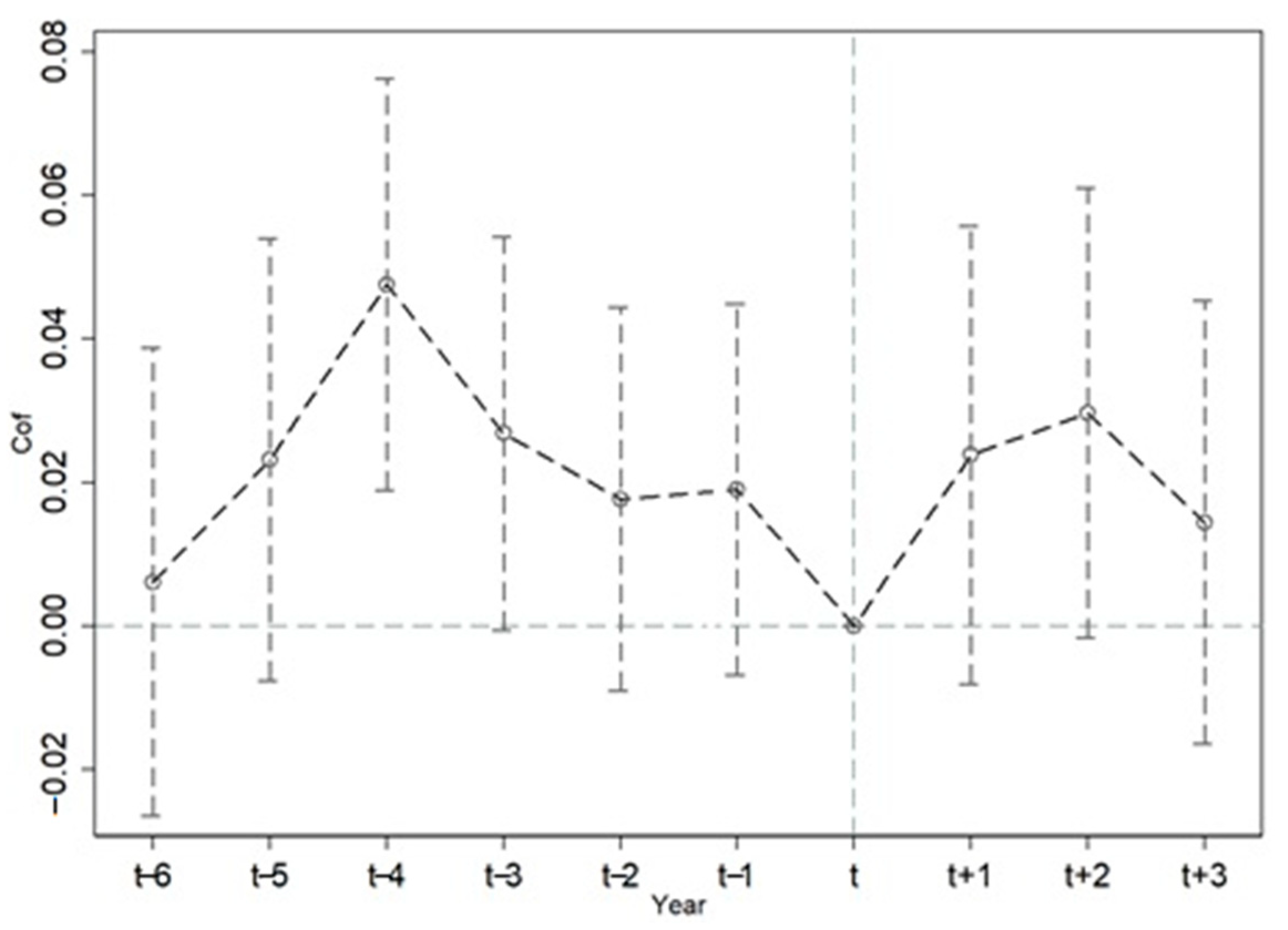
5.2. Robustness Test
6. Conclusions, Limitations, and Implications
6.1. Conclusions and Limitations
6.2. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, V. The urbanization process and economic growth: The so-what question. J. Econ. Growth 2003, 8, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, M. The effects of urbanization and industrialization on decoupling economic growth from carbon emission–A case study of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2014-03/16/content_2640075.htm (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Tang, S.; Hao, P.; Huang, X. Land conversion and urban settlement intentions of the rural population in China: A case study of suburban Nanjing. Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Wu, W.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y. Urbanization for rural sustainability–Rethinking China’s urbanization strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, A.L. Weaving the Chinese dream on the ground? Local government approaches to “new-typed” rural urbanization. J. Chin. Political Sci. 2015, 20, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Hui, E.C.M.; Choguill, C.; Jia, S.H. The new urbanization policy in China: Which way forward. Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Fan, J.; Fu, L. Exploration of smart city construction under new urbanization: A case study of Jinzhou-Huludao Coastal Area. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst 2020, 27, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Challenges and the way forward in China’s new-type urbanization. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, M. Urbanization, economic growth and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; LeGates, R.; Zhao, M.; Fang, C. The changing rural-urban divide in China’s megacities. Cities 2018, 81, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Introduction to land use and rural sustainability in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yuan, H.; Tian, X. Sustainable development in China: Trends, patterns, and determinants of the “Five Modernizations” in Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Sustainable urbanization in China: A comprehensive literature review. Cities 2016, 55, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y. Addressing the rural in situ urbanization (RISU) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region: Spatio-temporal pattern and driving mechanism. Cities 2018, 75, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. New Paths to Urbanization in China: Seeking More Balanced Patterns; Nova Publishers: Harpark, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. In situ urbanization in rural China: Case studies from Fujian Province. Dev. Change 2000, 31, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.P.; Zhao, Q.Y. The Inspiring and Thinking for In-Situ Urbanization of South Jiangsu. Urban Dev. Stud. 2013, 20, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, X.; Bin, L.; Tianzuo, W. New Patterns of County In-Situ Urbanization and Rural Development Based on E-Commerce. Urban Plan. Int. 2015, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Lo, K. Urbanization in remote areas: A case study of the Heilongjiang Reclamation Area, Northeast China. Habitat Int. 2014, 42, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. In situ urbanization in China: Processes, contributing factors, and policy implications. China Popul. Dev. Stud. 2017, 1, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.P. Adouble-pull model of rural labor migration and its in situ urbanizationeffect: Cases studies of three coastal areas in southeast China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zou, J. Study and Enlightenment of the In-Situ Urbanization of Rural Areas in China in the Background of New Pattern Urbanization—Taking Zhanqi Village, Pi County for Instance. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2015, 3, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Impact of urbanization on cultivated land changes in China. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wong, C. Master planning under urban–rural integration: The case of Nanjing, China. Urban Policy Res. 2012, 30, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Chen, T.; Li, X. A new style of urbanization in China: Transformation of urban rural communities. Habitat Int. 2016, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, M.; Che, X.; Fang, F. Farmers’ Rural-To-Urban Migration, Influencing Factors and Development Framework: A Case Study of Sihe Village of Gansu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Zhao, M.Q.; Liwu, D.S. Joint migration decisions of married couples in rural China. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 38, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Liao, T.F. Labor out-migration and agricultural change in rural China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, L. An analysis of push and pull factors in the migration of rural workers in china. Soc. Sci. China 2003, 1, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X. Exploring the relationship between rural village characteristics and Chinese return migrants’ participation in farming: Path dependence in rural employment. Cities 2019, 88, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, W. Factors influencing rural households’ willingness of centralized residence: Comparing pure and nonpure farming areas in China. Habitat Int. 2018, 73, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Y. Research on the Path of In-situ Urbanization and the Sustainable Development—A Case Study of You Yang County in Chongqing. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, S1, 549–552. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, W. A comprehensive quantitative evaluation of new sustainable urbanization level in 20 Chinese urban agglomerations. Sustainability 2016, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.W. China’s new urbanization plan: Progress and structural constraints. Cities 2020, 103, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, G. Characteristics of state-owned construction land supply in Chinese cities by development stage and industry. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Bo, Y. The Coupling Analysis of Agricultural Surplus Labor Transfer and New Urbanization Construction. Sci. Econ. Soc. 2020, 38, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M. Uneven growth of urban clusters in megaregions and its policy implications for new urbanization in China. Land Use Policy 2017, 66, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenfelter, O.; Card, D. Using the longitudinal structure of earnings to estimate the effect of training programs. Natl. Bur. Econ. Res. 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, X. An analysis of education inequality in China. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2014, 37, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, C.S. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Bureau: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C. China’s Economic Development: Growth and Structural Change; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council Issue the 13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Modern Comprehensive Transport System. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-02/28/content_5171345.htm (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Ranking of the Urbanization Rate of Permanent Resident Population of All Provinces and Cities in 2019. Available online: https://s.askci.com/news/hongguan/20200422/1346571159528.shtml (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Heckman, J.J.; Ichimura, H.; Todd, P.E. Matching as an econometric evaluation estimator: Evidence from evaluating a job training programme. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1997, 64, 605–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, W. Relations of Balanced Development of Urban-Rural Education and Urban-Rural Income Gap with the New Urbanization. Financ. Econ. 2014, 8, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Yang, M. Impact of Urbanization on the Health of Chinese Residents: An Empirical Study Based on Provincial Panel Data. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2015, 7, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X. Analysis on the Key Influence Factors of Urbanization and Its Effects in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 12, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, G. Research on Determinants of Infrastructure Investment: Based on Analysis of a Multinational Panel Data. J. World Econ. 2009, 3, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Hu, A. Test on the Externality of Infrastructure in China: 1988–2007. Econ. Res. J. 2010, 3, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Xia, E. Research on the Influence of Human Capital on China Economy Growth Based on Extended Solow Model. China. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 23, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ziying, F.; Binbin, T. Tax competition, Tax enforcement and tax avoidance. Econ. Res. J. 2013, 9, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Smith, R.P. Counterfactual analysis in macroeconometrics: An empirical investigation into the effects of quantitative easing. Res. Econ. 2016, 70, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Experimental Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Max | Min | Mean | SE | Max | Min | |
| IU | 0.5126 | 0.0866 | 0.7755 | 0.3004 | 0.4637 | 0.0973 | 0.7155 | 0.2795 |
| GAP | 0.4171 | 0.0723 | 0.5906 | 0.2483 | 0.3988 | 0.0809 | 0.6237 | 0.2239 |
| EDU | 7.7850 | 1.2499 | 10.9731 | 5.2933 | 7.0634 | 1.5912 | 9.3271 | 0 |
| GOV | 0.1712 | 0.0629 | 0.4235 | 0.0461 | 0.1084 | 0.0758 | 0.0714 | 0.5016 |
| TRA | 5.6374 | 0.7173 | 6.8942 | 3.6378 | 5.5309 | 0.9726 | 7.2928 | 1.9459 |
| MED | 10.3697 | 0.5570 | 11.7845 | 8.7759 | 10.2190 | 0.5153 | 11.3913 | 8.7828 |
| Covariant | Status | Mean | SD (%) | t-Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Group | Control Group | t Value | p Value | |||
| GAP | Before matching | 0.4171 | 0.3988 | 23.8 | 3.47 | 0.001 *** |
| After matching | 0.4090 | 0.4003 | 7.3 | 1.45 | 0.138 | |
| EDU | Before matching | 7.7850 | 7.0634 | 50.4 | 7.47 | 0.000 *** |
| After matching | 7.4619 | 7.5045 | −5.9 | −1.57 | 0.117 | |
| GOV | Before matching | 0.1712 | 0.2084 | −33.3 | −5.17 | 0.000 *** |
| After matching | 0.1787 | 0.1824 | −3.3 | −0.75 | 0.452 | |
| TRA | Before matching | 5.6374 | 5.5309 | 12.5 | 1.86 | 0.064 * |
| After matching | 5.6331 | 5.7022 | −8.1 | −1.34 | 0.182 | |
| MED | Before matching | 10.37 | 10.219 | 28.1 | 4.03 | 0000 *** |
| After matching | 10.26 | 10.224 | 6.8 | 1.10 | 0.271 | |
| Matching Method | Status | Ps R2 | LR chi2 | p > chi2 | Mean of SD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest neighbor matching | Before matching | 0.063 | 73.83 | 0.000 | 29.6 |
| After matching | 0.005 | 5.90 | 0.316 | 6.3 |
| Variables | Whole Central Area | Yangtze River Economic Belt | Non-Yangtze River Economic Belt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| DID | 0.0040 (0.0114) | 0.0083 (0.0099) | 0.0119 (0.0203) | 0.0090 *** (0.0022) | 0.0061 *** (0.0018) | 0.0274 (0.0688) | 0.0114 (0.0169) | 0.0129 (0.0150) | 0.0058 (0.0279) |
| lnGAP | −0.3858 *** (0.0958) | −0.4187 *** (0.0875) | −0.4560 *** (0.1312) | −0.6071 *** (0.1029) | −0.3983 *** (0.1055) | −0.5112 *** (0.0084) | |||
| lnEDU | 0.0027 (0.0129) | 0.0064 (0.0339) | 0.0040 (0.0230) | 0.0081 (0.0709) | 0.0079 (0.0166) | 0.0833 * (0.0502) | |||
| lnGOV | 0.4260 *** (0.0964) | 0.5805 *** (0.0188) | 0.3978 *** (0.1170) | 0.4436 *** (0.0892) | 0.7725 *** (0.2301) | 0.4961 *** (0.1897) | |||
| lnTRA | 0.0271 *** (0.0090) | −0.0169 (0.1134) | 0.0264 ** (0.0108) | 0.0067 (0.0091) | 0.0035 (0.0181) | −0.0226 (0.0973) | |||
| lnMED | −0.0647 *** (0.0124) | −0.0172 (0.0454) | −0.0564 ** (0.0272) | −0.0288 ** (0.0131) | −0.1084 *** (0.0273) | −0.0132 (0.0560) | |||
| Time Effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Area Effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Cons | −0.7475 *** (0.0031) | −1.7963 *** (0.1189) | −1.4368 *** (0.0985) | −0.7117 *** (0.0034) | −1.7038 *** (0.1863) | −2.169 *** (0.3338) | −0.8175 *** (0.0045) | −1.9706 *** (0.2154) | −1.5524 *** (0.0783) |
| Observation | 783 | 783 | 783 | 519 | 519 | 519 | 264 | 264 | 264 |
| Variables | Counterfactual Test | Single Difference Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| L2_DID | 0.0045 (0.0101) | 0.0162 (0.0138) | ||||
| L3_DID | 0.0126 (0.0094) | 0.0227 (0.0153) | ||||
| DID | 0.0470 *** (0.0091) | 0.0206 *** (0.0048) | ||||
| lnGAP | −0.5266 *** (0.1128) | −0.4649 *** (0.1049) | −0.4153 *** (0.1299) | |||
| lnEDU | 0.0072 (0.0192) | 0.0086 (0.0191) | 0.0041 (0.0228) | |||
| lnGOV | 0.4056 *** (0.1110) | 0.4511 *** (0.1139) | 0.3583 *** (0.1207) | |||
| lnTRA | 0.0253 ** (0.0109) | 0.0301 *** (0.0110) | 0.0265 (0.0184) | |||
| lnMED | −0.0644 *** (0.0153) | −0.0759 *** (0.0167) | −0.0515 * (0.0271) | |||
| Time Effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO |
| Area Effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Cons | −0.7273 *** (0.0045) | −1.8253 *** (0.1702) | −0.7354 *** (0.0049) | −1.9551 *** (0.1890) | −0.7065 *** (0.0038) | −1.6345 *** (0.1796) |
| Observation | 519 | 519 | 519 | 519 | 519 | 519 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tu, G.; Huang, X. The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model. Land 2021, 10, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020178
Peng J, Liu Y, Wang Q, Tu G, Huang X. The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model. Land. 2021; 10(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020178
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jing, Yanhong Liu, Qi Wang, Guoping Tu, and Xinjian Huang. 2021. "The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model" Land 10, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020178
APA StylePeng, J., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Tu, G., & Huang, X. (2021). The Impact of New Urbanization Policy on In Situ Urbanization—Policy Test Based on Difference-in-Differences Model. Land, 10(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020178









