Spatial and Temporal Changes in Temperature, Precipitation, and Streamflow in the Miyun Reservoir Basin of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Trend Detection and Slope Estimator
2.3.2. Serial Correlation Effect
- If the slope is nearly equal to zero, it is not necessary to calculate for trend. Otherwise, the data are detrended by the slope using Sen’s estimator of slope.
- The lag-1 serial coefficient (r1) of the detrended series is calculated and subtracted from it. After applying this subtraction, the residuals should represent an independent series. A new series was reconstructed based on the linear trend and residuals. This new series can keep the true trend and is no longer affected by the effects of autocorrelation.
3. Results
3.1. Serial Correlation of the Hydroclimatic Data
3.2. Temperature
3.3. Precipitation
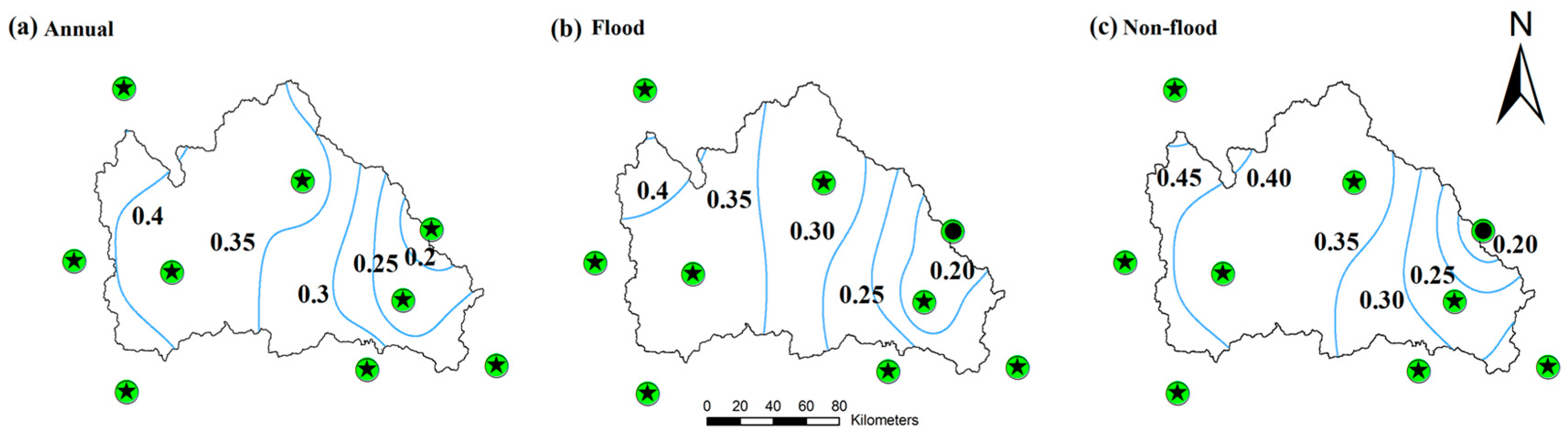
3.3.1. Spatial and Temporal Precipitation Changes
3.3.2. Changes in Precipitation Indices
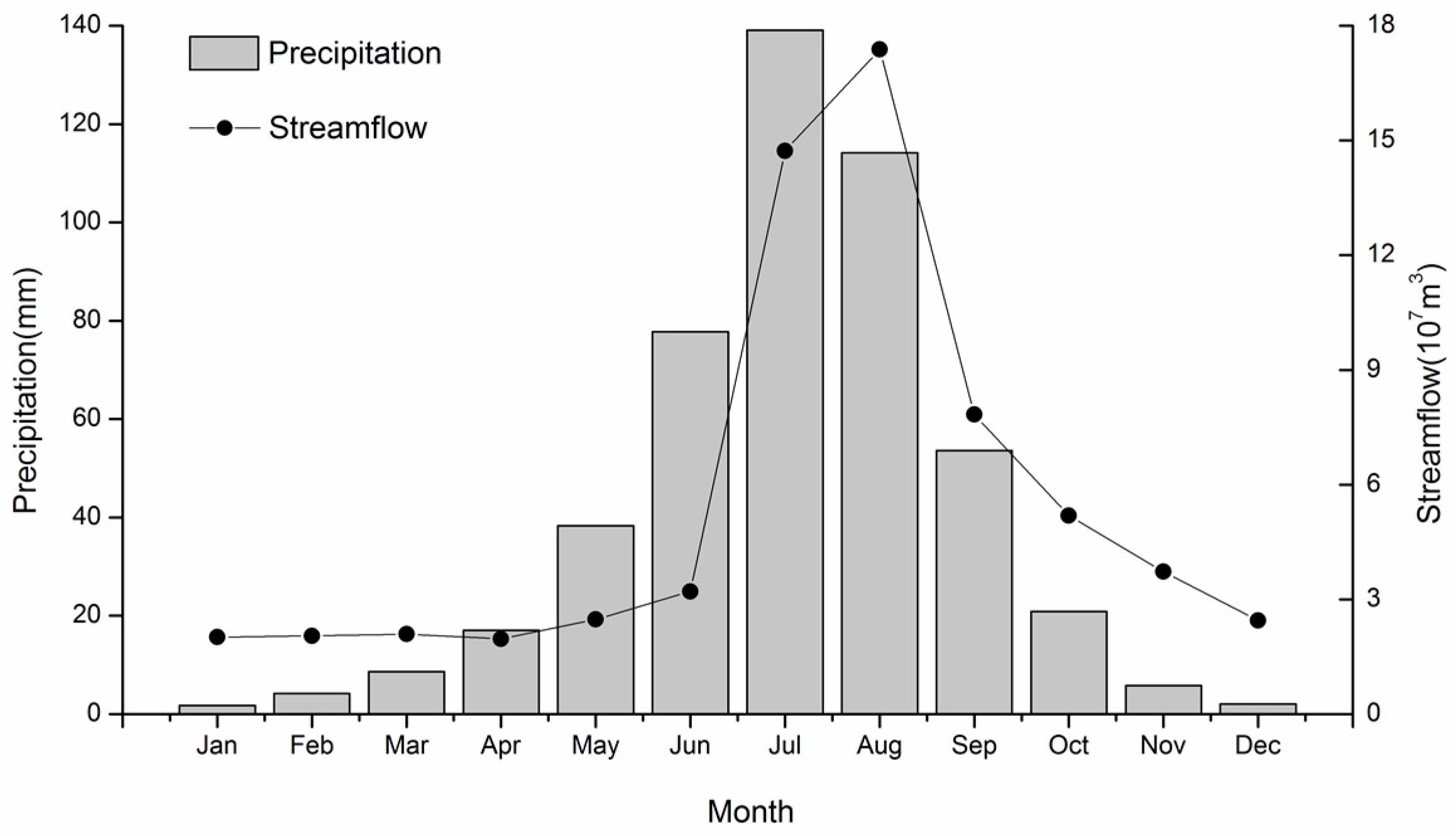
3.4. Streamflow
4. Discussion
4.1. Attribution Analysis
4.2. Implications for Watershed Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meinshausen, M.; Meinshausen, N.; Hare, W.; Raper, S.C.B.; Frieler, K.; Knutti, R.; Frame, D.J.; Allen, M.R. Greenhouse-gas emission targets for limiting global warming to 2 °C. Nature 2009, 458, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Grimm, N.B. Modelling potential impacts of climate change on water and nitrate export from a mid-sized, semiarid watershed in the US Southwest. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Gassman, P.W.; Panagopoulos, Y. Regional changes in nitrate loadings in the Upper Mississippi River Basin under predicted mid-century climate. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Charron, C.; Kumar, K.N.; Marpu, P.R.; Ghedira, H.; Molini, A.; Kayal, I. Evolution of the rainfall regime in the United Arab Emirates. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbungu, W.; Ntegeka, V.; Kahimba, F.C.; Taye, M.; Willems, P. Temporal and spatial variations in hydro-climatic extremes in the Lake Victoria basin. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 50–52, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.B.; Chen, S.L.; Liu, C.M.; Shepard, D. Hydro-climatic trends of the Yellow River Basin for the last 50 years. Clim. Chang. 2004, 65, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Finlayson, B.L.; Webber, M.; Wei, T.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. Variability and trend in the hydrology of the Yangtze River, China: Annual precipitation and runoff. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G.; Billmire, M. Trends in precipitation, runoff, and evapotranspiration for rivers draining to the gulf of maine in the United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 726–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Sensitivity of hydrological variables to climate change in the Haihe River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2294–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Liu, Z.F.; Fu, G.B.; Chen, Y.N. Trends of major hydroclimatic variables in the Tarim River Basin during the past 50 years. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guan, Y.; Shao, G.; Zhang, D. Investigating trends in streamflow and precipitation in Huangfuchuan Basin with wavelet analysis and the Mann-Kendall test. Water 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-F.; Wang, J.; Yeh, H.-F.; Lee, C.-H. Spatial and temporal streamflow trends in Northern Taiwan. Water 2015, 7, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Maugeri, M.; Nanni, T. Changes in total precipitation, rainy days and extreme events in Northeastern Italy. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chen, C.-A.; Tan, P.-H.; Chen, K.T. Mechanisms for global warming impacts on precipitation frequency and intensity. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3291–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Peng, J.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, J. Spatial-temporal changes of precipitation structure across the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 440–441, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.A.; Yang, D.W.; Tan, S.K.; Gao, B.; Hu, Q.F. Impact of climate variability and human activity on streamflow decrease in the Miyun Reservoir Catchment. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, F. Abrupt change of runoff and its major driving factors in Haihe River Catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.X.; Fu, G.B.; Wang, G.Q.; Jin, J.L.; He, R.M.; Yan, X.L.; Liu, C.S. Hydrological projection for the Miyun Reservoir Basin with the impact of climate change and human activity. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.K.; Sun, G.; Li, W.H.; Yu, X.X.; Zhang, C.; Gong, Y.B.; Tu, L.H. Impacts of land use change and climate variations on annual inflow into the Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yang, D.; Hu, H.; Gao, B. Detecting the effect of land-use change on streamflow, sediment and nutrient losses by distributed hydrological simulation. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Yang, Z.; Liang, P.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Zhu, J. Variation analysis of streamflow and ecological flow for the twin rivers of the Miyun Reservoir Basin in Northern China from 1963 to 2011. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cong, Z. Trends of precipitation intensity and frequency in hydrological regions of China from 1956 to 2005. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Leng, G. Spatio-temporal changes in precipitation, temperature and their possibly changing relationship: A case study in the Wei River Basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Xu, M.; Henderson, M.; Qi, Y. Observed trends of precipitation amount, frequency, and intensity in China, 1960–2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xing, W.; Yang, T.; Shao, Q.; Peng, S.; Yu, Z.; Yong, B. Characterizing the changing behaviours of precipitation concentration in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3375–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Somee, B.S.; Zadeh, M.R. Testing for long-term trends in climatic variables in Iran. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Edwards, D.R. Long-term trend analysis of precipitation and air temperature for Kentucky, United States. Climate 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Zhang, M.S.; Zhu, H.; Dang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.; Yin, L.H. Hydro-climatic trends in the last 50 years in the lower reach of the Shiyang River Basin, NW China. Catena 2012, 95, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Solomon, S.; Dai, A.; Portmann, R.W. How often will it rain? J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4801–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Dan, L. Trends in the different grades of precipitation over South China during 1960–2010 and the possible link with anthropogenic aerosols. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Yin, X. Hydrological responses to climate change in Nenjiang River Basin, Northeastern China. Water. Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P. A comparison of the power of the t test, Mann-Kendall and bootstrap tests for trend detection. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water-quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B.; Cavadias, G. The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Storch, H. Misuses of statistical analysis in climate research. In Analysis of Climate Variability: Applications of Statistical Techniques; von Storch, H., Navarra, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sayemuzzaman, M.; Jha, M.K. Seasonal and annual precipitation time series trend analysis in North Carolina, United States. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Climate change characteristics of Haihe River Basin in recent 51 years. J. Tianjin Norm. Univ. 2014, 34, 58–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Kuang, W.; Tao, F. Impact of urban expansion on meteorological observation data and overestimation to regional air temperature in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Inthe Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Qin, N.X.; Chen, X.; Fu, G.B.; Zhai, J.Q.; Xue, X.W. Precipitation and temperature trends for the Southwest China: 1960–2007. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3733–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.L.; Ren, G.Y. Reanalysis of surface air temperature change of the last 100 years over China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 791–798. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Yi, X.S.; Liu, W.D. Spatiotemporal variation and abrupt change analysis of temperature from 1960 to 2012 in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Levine, X.J. Water vapor and the dynamics of climate changes. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, E.J.; Rowell, D.P.; Jones, R.G. Mechanisms and reliability of future projected changes in daily precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, E.; Lenderink, G.; Hutjes, R.; Holtslag, A. Relative impacts of land use and climate change on summer precipitation in the Netherlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4129–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Mao, J. Influence of aerosol on regional precipitation in North China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Detection, causes and projection of climate change over China: An overview of recent progress. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 24, 954–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gong, D.; Li, J.; Li, B. Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the east Asian summer monsoon—Recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorol. Z. 2009, 18, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.L.; Wang, M.R.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, W. Impacts of human activity on river runoff in the northern area of China. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Wu, B.F.; Wei, Y.P.; Yan, N.N.; Wang, H.; Guo, S.Y. Quantifying impacts of climate variability and human activities on the hydrological system of the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ou, Y.; Yu, Y. Phosphorus loss from soil-runoff-sediment at slope plots. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.-Y.; Singh, V.P. Historical temporal trends of hydro-climatic variables and runoff response to climate variability and their relevance in water resource management in the Hanjiang Basin. J. Hydrol. 2007, 344, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Du, P.F.; Lang, C. Nutrient concentrations and fluxes in the upper catchment of the Miyun Reservoir, China, and potential nutrient reduction strategies. Environ. Monit. Acess. 2015, 2015, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Xu, Q.; He, W. Study of the distribution of non-point source pollution in the watershed of the Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouraoui, F.; Grizzetti, B.; Granlund, K.; Rekolainen, S.; Bidoglio, G. Impact of climate change on the water cycle and nutrient losses in a Finnish catchment. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| No. | Station Name | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Elevation (m) | Category 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anchunmengou | 40.87 | 117.20 | 450 | R |
| 2 | Baicao | 41.12 | 116.08 | 990 | R |
| 3 | Dage | 41.18 | 116.68 | 620 | R |
| 4 | Heidaziying | 40.92 | 116.18 | 740 | R |
| 5 | Heilongshan | 41.25 | 116.08 | 1180 | R |
| 6 | Hushenha | 40.88 | 116.97 | 350 | R |
| 7 | Longguan | 40.78 | 115.57 | 1070 | R |
| 8 | Maying | 41.15 | 115.65 | 1130 | R |
| 9 | Sandaohe | 41.13 | 116.45 | 730 | R |
| 10 | Sandaoying | 40.78 | 116.38 | 540 | R |
| 11 | Shanghuangqi | 41.45 | 116.67 | 870 | R |
| 12 | Shipozi | 40.90 | 116.82 | 460 | R |
| 13 | Shirengou | 41.07 | 117.02 | 480 | R |
| 14 | Tuchengzi | 41.30 | 116.60 | 740 | R |
| 15 | Xiaobazi | 41.45 | 116.37 | 1045 | R |
| 16 | Yunzhou Reservoir | 41.03 | 115.77 | 980 | R |
| 17 | Zhenanbao | 41.12 | 115.88 | 1150 | R |
| 18 | Chicheng | 40.88 | 115.83 | 867 | W 1 |
| 19 | Chongli | 40.97 | 115.28 | 1248 | W |
| 20 | Fengning | 41.22 | 116.63 | 661 | W |
| 21 | Guyuan | 41.67 | 115.67 | 1412 | W |
| 22 | Huailai | 40.40 | 115.50 | 536 | W |
| 23 | Luanping | 40.93 | 117.33 | 529 | W |
| 24 | Miyun | 40.38 | 116.87 | 71 | W |
| 25 | Shangdianzi | 40.65 | 117.12 | 293 | W |
| 26 | Xinglong | 40.40 | 117.47 | 633 | W |
| 27 | Xiahui | 40.62 | 117.17 | 198 | H 1 |
| 28 | Zhangjiafen | 40.62 | 116.78 | 193 | H |
| Variables | Trend Magnitude 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Flood | Non-Flood | |
| Precipitation | −11.00 | −18.50 * | 6.91 * |
| Temperature | 0.36 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.38 ** |
| Total runoff | −1.60 ** | −1.12 ** | −0.42 ** |
| Variables | Trend Magnitude 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Flood | Non-Flood | |
| Precipitation intensity | −0.12 | −0.23 | 0.14 |
| Precipitation frequency | −0.88 | −1.50 * | 0.43 |
| Variables | Trend Magnitude 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Flood | Non-Flood | |||||||
| PA | PF | PI | PA | PF | PI | PA | PF | PI | |
| Light | −0.20 | −0.19 | 0.02 | −2.80 | −0.70 | 0.00 | 1.59 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Medium | −3.67 | −0.18 | 0.00 | −6.70 | −0.40 | 0.00 | 3.37 * | 0.21 | 0.10 |
| Large | −4.11 | −0.13 | 0.15 | −6.50 | −0.20 | 0.40 * | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.60 |
| Heavy | −4.28 | −0.06 | −0.97 | −3.80 | 0.00 | −1.00 | |||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Bai, Z.S.a.J. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Temperature, Precipitation, and Streamflow in the Miyun Reservoir Basin of China. Water 2017, 9, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020078
Yan T, Bai ZSaJ. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Temperature, Precipitation, and Streamflow in the Miyun Reservoir Basin of China. Water. 2017; 9(2):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020078
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tiezhu, and Zhenyao Shen and Jianwen Bai. 2017. "Spatial and Temporal Changes in Temperature, Precipitation, and Streamflow in the Miyun Reservoir Basin of China" Water 9, no. 2: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020078
APA StyleYan, T., & Bai, Z. S. a. J. (2017). Spatial and Temporal Changes in Temperature, Precipitation, and Streamflow in the Miyun Reservoir Basin of China. Water, 9(2), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020078







