Abstract
Decreases in pan evaporation (Epan) over the last decades have been reported in many regions of the world. In this study, changes of Epan in the Zoige Plateau alpine wetland (hereinafter referred to as “Zoige wetland”) and its peripheral regions from 1969 to 2014 were investigated using the PenPan model based on the long-term meteorological data. The contribution of climate factors to Epan change were quantified by using partial derivatives of the PenPan model. Results indicated that Epan in Zoige wetland exhibited an obvious decreasing trend before 1989, but rapidly increased after 1990. The increase in Epan in the Zoige wetland is more significant than that in its peripheral regions and the entire Tibetan Plateau, which contributed to the more significant warming in the Zoige wetland. The pan evaporation in Zoige wetland after 1990 could be mostly attributed to changes in the aerodynamic component, and the decreasing radiation and wind speed is the primary contributor to the decline of pan evaporation during 1969–1989, while increasing air temperature and vapor pressure deficit were the major contributors to the increase of pan evaporation after 1990.
1. Introduction
Wetlands in many parts of the world have undergone severe deterioration and drastic shrinkage under the influence of climate change in the past few decades [1,2,3,4,5]. For instance, in China the water level of Qinghai lake in Northwest China showed an overall decreasing trend (−0.07 m/year) with an increasing temperature (+0.03 °C/year) from 1956 to 2009 [6]. The significant climate warming was also the major cause of considerable shrinkage of Baiyangdian Lake in North China Plain since the 1980s [7]. Climate change has a pronounced effect on wetlands through alterations in hydrological regimes. The increased temperature and altered evapotranspiration and other climate variables may play important roles in determining regional and local impacts [8]. As an important factor of hydrological processes, evapotranspiration has significant effects on the water level, area, ecological process, and functions of wetlands [9]. Increasing evapotranspiration may be one of the important factors that cause wetland reduction. However, it is hard to obtain accurate measured wetland evapotranspiration; the observed pan evaporation data are usually used to estimate crop water requirements and lake evaporation to detect the amount of and changes in actual evapotranspiration [10,11]. As a diagnostic of the state of the global hydrological cycle, the dominant factors for pan evaporation change are very significant for wetland preservation, water resource management, irrigation control, and water supply. Therefore, analyzing the changes in pan evaporation and their contributions is important for the studies of the deterioration mechanism of wetlands.
The decreases in pan evaporation since the 1950s have been reported in the United States [12], India [13], Australian [14], New Zealand [15], China [16,17]. The pan evaporation decrease usually accompanied by climate warming, that is the “pan evaporation paradox” [18]. Air temperature is not the only factor that affects pan evaporation. The influence of other meteorological factors, such as solar radiation, wind speed, and vapor pressure, should be seriously considered [19,20,21]. Roderick et al. [20] used the PenPan model [21] to attribute changes in pan evaporation to changes in the underlying physical variables. The evaporation rate is divided into radiative (EpR) and aerodynamic component [22], derivation dEpA/dt is expressed as the sum of wind speed, vapor pressure, and air temperature, and the derivation coefficients are the contribution of climate factors to evaporation changes. This approach has been successfully used in quantifying the contributions of climate factors and the dominant factors [20,21,23]. According to PenPan model, Yang and Yang [24] developed a model (PenPan-20 model) suitable for China’s D20 mini-type evaporation pan (with a diameter of 20 cm), which is widely used in the study of pan evaporation [16,23,25].
The Tibetan Plateau plays an important role in climate change because it shows critical impacts on climate in Asia and elsewhere in the Northern Hemisphere [26]. Wetlands or lakes in this region are highly sensitive to climate change, especially the hydrological processes, such as evaporation, runoff, are more susceptible to climate warming. The decrease in Nam Co Lake evaporation in the Tibetan Plateau is responsible for approximately four percent of the rapid water level increase and areal expansion of Nam Co Lake [27]. By contrast, the increase in evaporation has induced lake shrinking and wetland degradation in the headwater regions in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [28]. The Zoige Plateau alpine wetland (hereinafter referred to as “Zoige wetland”), as the largest distributed plateau peat bog in the world, is located in the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. This unique inland wetland is known as the “kidney of the plateau” because it is the most important water conservation ecological function region in the Upper Yellow River and an important protected area of biodiversity in China [29,30]. Significant shrinkage and deterioration have occurred in the Zoige wetland since the 1960s [29], and increasing evaporation was considered an important factor that contributes to the degradation [31,32,33]. Generally, pan evaporation in the Tibetan Plateau exhibited a downward trend for the past few decades [16,23], indicating the increase in actual evapotranspiration [11,17]. However, the changes in pan evaporation and their contributions to the Zoige wetland remain elusive, which limits the study of the influence of climate factors on the deterioration of the Zoige wetland.
Therefore, in order to explore the trends in pan evaporation and its attribution in the Zoige wetland, distinct from the changes of wetland hydrological regimes under climate changes, the PenPan-20 model was adopted to simulate Epan from 1969 to 2014, and examine the changes in Epan and the contributions of climate factors in the Zoige wetland in this study. The dominant impact factors of pan evaporation were also analyzed and discussed. These findings would support future studies of the mechanisms of shrinkage and deterioration of the Zoige wetland.
2. Study Area, Data, and Method
2.1. Study Area and Data
The Zoige wetland located at the eastern region of the Tibetan Plateau, with the average altitude of more than 3400 m. It is one of the four major swamp areas in China. The Black River and White River are the main rivers of the Zoige wetland (Figure 1). The Zoige wetland is known as the kidney of the plateau because of its important ecological function of retaining water in the upstream area of the Yellow River. This region contributes approximately 30% of the observed annual runoff of Marchu hydrological station in the Yellow River (approximately 4.6 billion m3) [34]. The climate of the study area is typical alpine humid and semi-humid continental monsoon with considerable variation in diurnal temperature; the area has a long frozen season, an annual mean temperature of approximately 0.6 °C to 1.2 °C, and mean annual precipitation ranges from 600 mm to 800 mm [29].
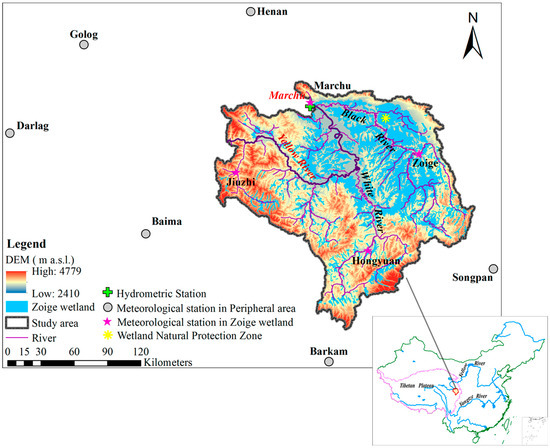
Figure 1.
Location of the Zoige wetland in the Tibet Plateau and the distribution of meteorological stations.
The daily meteorological data of stations in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas (Table 1) were provided by the China Meteorological Data Service Center (CMDC) (http://data.cma.cn/), which is responsible for the data quality control and management of the Climate Data Center. The data include daily precipitation, air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, radiation and pan evaporation data. The pan evaporation data before 2001 are observed with the Chinese D20 micropan, which is widely used to measure evaporation in China. The pan is 20 cm in diameter, 10 cm high, and installed 70 cm above the ground on a wooden platform. In this study, in order to ensure data integrity and accuracy, the average daily missing data of these selected stations is around 0.3%, and therefore, a simple linear interpolation according to data before and after three days was used to interpolate the daily missing data at one station. Then the climate data were adjusted to become homogeneous by using RHtestsV4 software, with a two-phase regression technique for the detection and adjustment of inhomogeneity of data [35]. Consequently, ten selected meteorological data from 1969 to 2014 (Table 1) were used to explore the changes of pan evaporation and contributions of meteorological variables in the Zoige wetland. Six stations in the peripheral areas of the Zoige wetland are used for comparison.

Table 1.
List of meteorological stations in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas with WMO number, station name, longitude, latitude, and elevation.
The monthly averages from daily data were first calculated and then proceeded with calculating annual averages to analyze the trends of annual climatic factors. The arithmetic average of annual climate variables of four stations (Jiuzhi, Hongyuan, Zoige and Marchu) were used to describe the climate change in the Zoige wetland, as well as the other six stations for the peripheral area. The annual mean temperature (Ta) in the study area from 1969 to 2014 was 1.41 °C, which is significantly lower than that of its peripheral areas (2.89 °C). The mean water vapor pressure deficit (D) (2.26 hPa) in the Zoige wetland is also lower than that of its peripheral areas (2.96 hPa). The mean annual precipitation (P) (685.2 mm) in the Zoige wetland is slightly higher than that of its peripheral areas (633.95 mm) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Statistical values of the annual average temperature (Ta), net radiation (Rn), wind speed (u2), vapor pressure deficit (D), precipitation (P) and pan evaporation (Epan_o) in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas between 1969 and 2014.
2.2. PenPan-20 Model and Its Contributions
The PenPan-20 model developed by Yang and Yang [24] is used to simulate evaporation from the D20 pan (Epan) and expressed as:
where is the radiation term; is the aerodynamic term; is the slope of the saturated vapor pressure–temperature curve (kPa K−1); Rn is the net solar radiation (MJ m−2 day−1); is the latent heat of vaporization of water (MJ kg−1); is the hygrometer constant (kPa K−1); is the ratio of the effective surface areas for heat and water vapor transfer, which can be derived in theory according to the shape and size of the pan ( = 5 for the D20 pan); D is vapor pressure deficit (kPa); is the mean wind speed at 2 m (m/s); is the transfer function of wind speed (kg m−2 day−1 kPa); and , where a and b are the calibrated parameters.
Rn is calculated as:
where is the outgoing longwave radiation of pan evaporation (MJ m−2 day−1); is the incoming longwave radiation (MJ m−2 day−1); is the net longwave radiation (MJ m−2 day−1); is the pan albedo, which is generally set as 0.14 [20,21]; and is the incoming shortwave radiation of a pan (MJ m−2 day−1), which can be estimated as:
where is the solar radiation (MJ m−2 day−1), which can be calculated using the formula in FAO-56 [36]; is the pan evaporation factor, which refers to the additional direct radiation intercepted by the pan wall; is the proportion of direct radiation in the global radiation; is the surface albedo (=0.23) of the meteorological station; and is calculated using the following equation (MJ m−2 day−1):
where is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant (4.903 10−9 MJ m−2 day−1 K−4); is the actual vapor pressure; is the zenithal radiation (MJ M−2 day−1), which can be calculated using the formula in FAO-56 [36]; and is the altitude of the meteorological station (m).
D is calculated using the following equation:
where is the saturated vapor pressure, which can be estimated as follows:
where Ta is the mean temperature (°C) and RH is the relative humidity (%).
The method proposed by Roderick et al. [20] was adopted to derive the first-order partial differential form of the radiation and aerodynamic terms of Epan:
In Equation (8), the change in EpR is mainly caused by changes in and net radiation Rn. is only related to Ta. Therefore,
where and are the contributions of the climate factors ( and ) to EpR, with and . Changes in with respect to time is calculated using the following equation:
where , , and are the contributions of , u, and D to .
Mean temperature Ta can also alter the net radiation Rn and vapor pressure deficit D and affect Epan indirectly. Therefore, this effect should be considered in the analysis of Ta contribution and model sensitivity:
where is the contribution of to via Rn and is the contribution of to via D.
2.3. Trend Analysis
The Mann-Kendall (M-K) test is a nonparametric test for detecting trends in a time series and is widely used in the fields of meteorology and hydrology because it does not require independent and normally distributed sample data, nor is it affected by abnormal values. However, the significance of series trends is likely to be magnified by using the M-K test due to the serial correlation between climatic and hydrologic series. To eliminate the influence of a serial autocorrelation on the M-K test, Kulkarni and von Storch [37] proposed to pre-whiten a series prior to applying the M-K test. Yue and Wang [38] modified the pre-whiten procedure and proposed a trend-free pre-whitening method (TFPW).
In this study, the TFPW method was applied to eliminate the influence of serial correlation, and then the trends in climatic factors. The significance of each climate factor at p-level was also tested. The slope of the trend can be estimated as follows [39,40]:
where Xi and Xj are the time series data of the ith and jth years, respectively, and β is the slope of each station. A negative β value indicates a downward (decreasing) trend, whereas a positive β value indicates an upward (increasing) trend.
3. Results
3.1. Change in the Main Climate Factors
The four stations in the Zoige wetland show significant warming trends (p = 0.05) from 1969 to 2014 (Figure 2). However, the three stations located in the south beyond the Zoige wetland exhibit weak warming trends. The three stations located in the northwest beyond the Zoige wetland exhibit decreasing trends (Golog and Darlag stations) or no trend (Henan station). Comparatively, the average temperature Ta of the four stations in the Zoige wetland increased more significantly (with a trend slope of 0.41 °C decade−1, p < 0.01) (Figure 3) than that of the six stations in the peripheral areas (with a trend slope of 0.20 °C decade−1, p < 0.01) (Table 3).

Figure 2.
Annual trends in (a) Ta, (b) Rn, (c) u2, and (d) D in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas from 1969 to 2014, where −1 represents a significant downward trend (p = 0.05), 1 represents a significant upward trend (p = 0.05), and 0 indicates the lack of a significant trend (p = 0.05).

Figure 3.
Arithmetic average of (a) annual air temperature (Ta), (b) annual net radiation (Rn), (c) annual wind speed two meters above ground (u2), and (d) annual water vapor pressure deficit (D) from the four stations in the Zoige wetland.

Table 3.
The annual trends of the main meteorological factors in Zoige wetland and its peripheral area.
In the Zoige wetland, Zoige and Hongyuan stations show significantly decreasing trends (p = 0.05) in net radiation Rn, whereas Marchu and Jiuzhi stations show no obvious trends in net radiation Rn. Similarly, in the peripheral areas, the four stations exhibit significantly decreasing trends in net radiation Rn (p = 0.05), whereas the other two stations (Darlag and Henan stations) show no trends at p = 0.05. The average net radiation Rn of the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas show similar decreasing trends (with a trend slope of −0.16 and −0.18 W m−2 decade−1, respectively).
All of the stations in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas exhibited significant downward trends in wind speed u2 (p = 0.05), except for the Hongyuan station (no trend at p = 0.05). The average wind speed u2 of the Zoige wetland declined slower (−0.07 m/s decade−1) than that of its peripheral areas (−0.12 m/s decade−1). All of the stations in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas exhibited significant upward trends in D, except for the Barkam station (no trend at p = 0.05). Comparably, the average vapor pressure deficit D of the Zoige wetland shows more significant increasing trends (0.11 hPa decade−1) than its peripheral areas (0.08 hPa decade−1).
3.2. Changes in the Observed Epan
The observed pan evaporation (Epan_o) of three stations in the Zoige wetland exhibit increasing trends during 1969–2001, whereas Marchu exhibits decreasing trends (Table 4). By contrast, four of the six stations in the peripheral areas exhibit decreasing trends in Epan_o. Comparatively, the average Epan_o of the four stations in the Zoige wetland increased during 1969–2001 (with a trend slope of 0.7 mm decade−1, p < 0.05), whereas that of the six stations in the peripheral areas decreased (with a trend slope of −20.3 mm decade−1, p < 0.05).

Table 4.
The annual trends in the observed Epan in Zoige wetland and its peripheral area at different stages (unit: mm decade−1).
A change point is observed in the time series of the average Epan_o of the four stations in the Zoige wetland (Figure 4). Epan_o in the Zoige wetland decreased significantly (−66.5 mm decade−1, p < 0.05) during 1969–1989, but increased significantly during 1990–2001 (with a trend slope of 140.8 mm decade−1, p < 0.05). Similarly, Epan_o in the peripheral areas decreased significantly (−73.1 mm decade−1, p < 0.05) during 1969–1989, but increased significantly during 1990–2001 (with a trend slope of 107.0 mm decade−1, p < 0.05).

Figure 4.
Comparison between the observed pan evaporation (Epan_o) and the PenPan model-calculated pan evaporation (Epan_c): (a) variations of the annual Epan_o and Epan_c (including the EpA and EpR) in the Zoige wetland, and (b) linear fit regression of monthly pan evaporation in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral area.
3.3. Contributions of the Main Climate Factors on the Changes in Epan
The PenPan-20 model was used to simulate the pan evaporation (Epan_c) from 1969 to 2014. The parameters a and b in the wind speed conversion function (a = 0.62; b = 0.75) were calibrated by a trial-and-error method, with Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) as the objective function. First, the daily simulated pan evaporation Epan_c was calculated using the climate factors (Rn, Ta, u2, and D). Then, the monthly Epan_c was calculated and compared with the observed values (Epan_o). As shown in Figure 4, a strong correlation (with R2 > 0.87, NSE > 0.82, MAE < 14 mm, RMSE < 17.8 mm) exists between the calculated and observed pan evaporation in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas. It indicates that the PenPan-20 model could accurately simulate the pan evaporation Epan and effect of climate factors on Epan.
The dominant factors contributing to the change in Epan in the Zoige wetland were explored based on the PenPan model. The increases in Epan during 1969–2014 were mainly caused by changes in vapor pressure deficit (D) at Marchu, Jiuzhi, and Zoige stations, with contributions of 18.7, 24.2, and 16.9 mm decade−1, respectively, and by changes in temperature (Ta) at Hongyuan station (13.7 mm decade−1) (Figure 5). The increase in vapor pressure deficit (D) was the dominant factor of changes in Epan at the three stations (Golog, Darlag, and Songpan) in peripheral areas, with a mean contribution of 16 mm decade−1. The increase in temperature (Ta) was the dominant factor of changes in Epan at Baima (28.8 mm decade−1). The decrease in wind speed (u2) was responsible for the reduction in Epan at Henan and Barkam stations, with contributions of −20 and −13 mm decade−1, respectively. The decrease in wind speed (u2) was the dominant factor leading to the decrease in Epan before 1989 for the four stations in the Zoige wetland, whereas the increase in water vapor pressure deficit (D) was the most important factor driving the increase in Epan after 1990 (except for Marchu, with the increase in temperature (Ta) as the first driver).
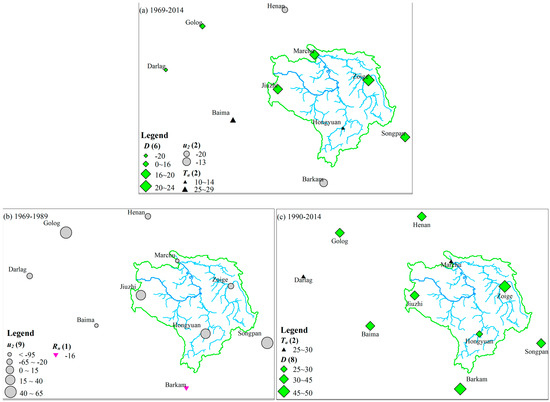
Figure 5.
Dominant factors controlling pan evaporation change in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas, (a) 1969–2014, (b) 1969–1989, and (c) 1990–2014. The numbers in brackets denote the frequency that each factor is the most important governing Epan trend, and the numbers behand each symbol refer to the contribution rate (unit: mm decade−1) of climate factors.
The contributions of Rn, u2, Ta, and D to the change in Epan in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas were evaluated according to the arithmetic average values of the corresponding stations (Table 5). Increasing temperature (Ta) and vapor pressure deficit (D) were the dominant factors leading to the change in Epan in the Zoige wetland from 1969 to 2014 (19.0 and 16.0 mm decade−1, respectively). Although the decreasing Rn and u2 offset the increase in Epan (−4.1 and −8.6 mm decade−1, respectively), the simulated Epan in the Zoige wetland shows increasing trends. The effects of the increasing temperature (Ta) and vapor pressure deficit (D) on Epan are significant after 1990, with contributions of 24.4 and 32.4 mm decade−1, respectively. Comparatively, the effects of the increasing temperature (Ta) and vapor pressure deficit (D) on Epan from 1969 to 2014 in the peripheral areas are weaker than those of the decreasing wind speed (u2) and net radiation (Rn). As a result, the peripheral areas exhibited a weak decline in Epan during 1969–2014.

Table 5.
Contributions of climate factors to changes in annual pan evaporation for the Zoige wetland and its peripheral area as a whole, respectively (unit: mm decade−1).
Considering the contributions of temperature (Ta) on via net radiation (Rn) and on via water vapor pressure deficit (D), the total contribution of increasing temperature (Ta) on the trends in Epan in the Zoige wetland is 26.61 mm decade−1 during 1969–2014 and is more significant during 1990–2014 (40.88 mm decade−1) (Table 6). The effects of temperature (Ta) in the Zoige wetland are more significant than those in the peripheral regions.

Table 6.
Contributions of temperature (Ta) on annual Epan via changes in net radiation (Rn) and water vapor pressure deficit (D) in the Zoige wetland and its peripheral areas (unit: mm decade−1).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
The observed Epan in the Zoige wetland decreased (−63 mm decade−1, p = 0.01) during 1969–1989, but significantly increased since 1990 (167.7 mm decade−1 during 1990–2001, p = 0.01). This two-stage pattern of the changes in Epan in the Zoige wetland is similar to that in its peripheral regions and other regions in China [25,41]. The trends in Epan in the Zoige wetland during the 1969–1989 period are similar to that in the peripheral regions (−57.1 mm decade−1) and the entire Tibetan Plateau, but are more significant in the 1990–2001 period (116.7 mm decade−1 in the peripheral regions). Meanwhile, the Zoige wetland exhibited significant warming during 1969–2014, which is also consistent with that in the entire Tibetan Plateau [16,23,42,43,44]. However, the warming trend in the Zoige wetland after 1990 (0.63 °C decade−1, p = 0.01) is more significant than those in the peripheral regions (0.20 °C decade−1, p = 0.01) and the entire Tibetan Plateau (0.27 °C decade−1) [45].
The Tibetan Plateau has been experiencing rapid warming and wetting [45,46], as well as wind stilling and solar dimming [47,48]. The decreasing u2 and Rn have resulted in the decline in Epan in the Tibetan Plateau in the past fifty years [16,23]. However, in the Zoige wetland, although decreasing wind speed (u2) and net radiation (Rn) resulted in negative effects on Epan, the increasing water vapor pressure deficit (D) and temperature (Ta) resulted in the increasing trend in Epan during 1969–2014. It is different from that in the peripheral areas, as well as the entire Tibetan Plateau. Considering the influences of increasing temperature (Ta) on net radiation (Rn) and water vapor pressure deficit (D), the significant warming in the Zoige wetland is the main driver of the significant increase in Epan, particularly after 1990.
During the period of 1969–1989, the radiation term EpR plays a dominant role in the decreasing trends in pan evaporation of the Zoige wetland, whereas the aerodynamic term EpA is the leading factors for the increasing Epan during 1990–2014, with a contribution of 35.4 mm decade−1. However, the aerodynamic term EpA are dominant in peripheral regions in both phases. During 1969–2014, the radiation term of Epan in the Zoige wetland increased significantly (13.6 mm decade−1) and the trend slope is larger than that of the aerodynamic term (8.6 mm decade−1). The increasing evapotranspiration would be one of the main reasons for the shrinkage and deterioration of the Zoige wetland in recent years [31,32,33]. The runoff of Black river and White river in the Zoige wetland declined by 35.4% and 28.1%, respectively during 1990–2011 compared with 1960–1989 [30,49]. However, the trends in annual precipitation in the Zoige wetland exhibited a significant increasing trend (39.8 mm decade−1, p = 0.05) during 1990–2014. The changes and attributions of pan evaporation in the Zoige wetland under climate warming are explored in this study, which are conducive to investigations of hydrological processes in the Alpine wetland. Due to the particularity and importance of the Tibetan Plateau on the climate change and hydrological cycle in the Northern Hemisphere, even slight changes in pan evaporation will be of considerable interest. The actual evaporation and relationships regarding pan evaporation and actual evaporation in this region also should be pursued and investigated in future studies, including the impact of vegetation changes and anthropogenic activities on the deterioration mechanism of Zoige Alpine wetlands.
Acknowledgments
Supported by the National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant from CAFINT (Grant No. CAFINT2015K06); the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin (China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research), Grant No. IWHR-SKL-201612p; The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51609243); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51509170).
Author Contributions
The manuscript was done by Nana Zhao and Si Gou providing review and comments. Beibei Zhang analyzed the data and Yilei Yu contributed methods. Songjun Han conceived the research idea of this study and providing review and comments. All the authors were engaged in the final manuscript preparation and agreed to the publication of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Woo, M. Impacts of climate variability and change on Canadian Wetlands. Can. Water Resour. J. 1992, 17, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poiani, K.A.; Johnson, W.C. Potential effects of climate change on a semi-permanent prairie wetland. Clim. Chang. 1993, 24, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankers, R.; Christensen, O.B. Climate change impact on snow coverage, evaporation and river discharge in the sub-arctic Tana Basin, Northern Fennoscandia. Clim. Chang. 2005, 69, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bu, R.; Liu, J.; Leng, W.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, H. Predicting the wetland distributions under climate warming in the great Xing’an mountains, Northeastern China. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.L.; Li, X.Y. The impact of climate changes on water level of Qinghai Lake in China over the past 50 years. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Duan, S.; Tian, M.; Yi, D. Water level variation of Lake Qinghai from satellite and in situ measurements under climate change. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 053532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, G.; Huang, H. Shrinking and drying up of Baiyangdian Lake wetland: A natural or human cause? Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, K.L. Wetlands and global climate change: The role of wetland restoration in a changing world. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, W.; Melesse, A. Wetland Evapotranspiration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Indications of increasing land surface evaporation during the second half of the 20th century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Use of pan evaporation to estimate terrestrial evaporation trends: The case of the Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbins, M.T.; Ramírez, J.A.; Brown, T.C. Trends in pan evaporation and actual evapotranspiration across the conterminous U.S.: Paradoxical or complementary? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, D.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Sarkar, D.; Sarkar, S. Temporal characteristics of pan evaporation trends under the humid conditions of Northeast India. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, M.L.; Farquhar, G.D. Changes in Australian pan evaporation from 1970 to 2002. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, M.L.; Farquhar, G.D. Changes in New Zealand pan evaporation since the 1970s. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, D.Y. Pan evaporation modelling and changing attribution analysis on the Tibetan Plateau (1970–2012). Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2164–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Trends in pan evaporation and reference and actual evapotranspiration across the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W.; Parlange, M.B. Hydrologic cycle explains the evaporation paradox. Nature 1998, 396, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcvicar, T.R.; Niel, T.G.V.; Roderick, M.L.; Donohue, R.J. Ecohydrology bearings—Invited commentary less bluster ahead? Ecohydrological implications of global trends of terrestrial near-surface wind speeds. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, M.L.; Rotstayn, L.D.; Farquhar, G.D.; Hobbins, M.T. On the attribution of changing pan evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotstayn, L.D.; Roderick, M.L.; Farquhar, G.D. A simple pan-evaporation model for analysis of climate simulations: Evaluation over Australia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, D.; Singh, V.P. Trends in temperature, diurnal temperature range and sunshine duration in Northeast India. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Shang, Y. Temporal and spatial characteristics of pan evaporation trends and their attribution to meteorological drivers in the three-river source region, China. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 6391–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, D. Climatic factors influencing changing pan evaporation across China from 1961 to 2001. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Analysis of changing pan evaporation in the arid region of Northwest China. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, Y.; Szilagyi, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhai, J.; Gao, H. Evaluating the complementary relationship of evapotranspiration in the alpine steppe of the Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Szilagyi, J.; Niu, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y. Evaporation variability of Nam Co Lake in the Tibetan Plateau and its role in recent rapid lake expansion. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, K. Rs based evaporation estimation of Three River sources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its response to lakes and wetlands. J. Jilin Univ. 2009, 39, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, H. Effects of alpine wetland landscapes on regional climate on the Zoige Plateau of China. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Song, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Acharya, K. Effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff in the Zoige alpine wetland in the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.-K.; Shen, Y.-P.; Ma, Z.-F.; Wang, X.-L. Climate variation and abrupt change in wetland of Zoigê Plateau during 1961–2008. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Li, G.-P. Climate change in Zoigê Plateau marsh wetland and its impact on wetland degradation. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, S.; Duoerji, S.; Dong, L.; Yao, P.; Zheng, R. Analysis on climate change characteristics of Zoige p Lateau during 1967–2014. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2016, 36, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Han, L.; Zhao, N. A study on the mechanism of wetland degradation in Ruoergai swamp. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L. Comments on “detection of undocumented changepoints: A revision of the two-phase regression model”. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements-fao irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.; Storch, H.V. Monte Carlo experiments on the effect of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test of trend. Meteorol. Z. 1995, 4, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, D.H.; Elnur, M.A.H. Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J. Hydrol. 2002, 255, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.Y. Hydroclimatic trends and possible climatic warming in the Canadian Prairies. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 3009–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C. Recent changes in pan-evaporation dynamics in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Yin, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, D. Spatial and temporal variation patterns of reference evapotranspiration across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1971–2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 4427–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Wang, H. The significant climate warming in the Northern Tibetan Plateau and its possible causes. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihui, D.; Li, Z. Intercomparison of the time for climate abrupt change between the Tibetan Plateau and other regions in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 794–805. [Google Scholar]
- You, Q.; Min, J.; Kang, S. Rapid warming in the Tibetan Plateau from observations and CMIP5 models in recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 36, 2660–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B. Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Fu, R. Observed coherent trends of surface and upper-air wind speed over China since 1960. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ding, B.; Qin, J.; Tang, W.; Ning, L.; Lin, C. Can aerosol loading explain the solar dimming over the Tibetan Plateau? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, L. Hydrologic variations and stochastic modeling of runoff in Zoige Wetland in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).